Simple pendulums and mass–spring systems
1/9
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
The simple pendulum
t the only factors that affect the time period of the pendulum are the length of the pendulum and the gravity (gravitational force)
Small angle approximation
Using the sin function for these small angles barely changes the value at all. sinθ≈θ. In the context of SHM, the equations only work when angles are small (smaller than about 10°).
Equation for the time period of a pendulum
T=2π√(l/g)
Factors that affect time period
mass & spring constant
Factors that do not affect time period
amplitude & gravity
Equation for the time period of a mass–spring system
T=2π√(m/k)
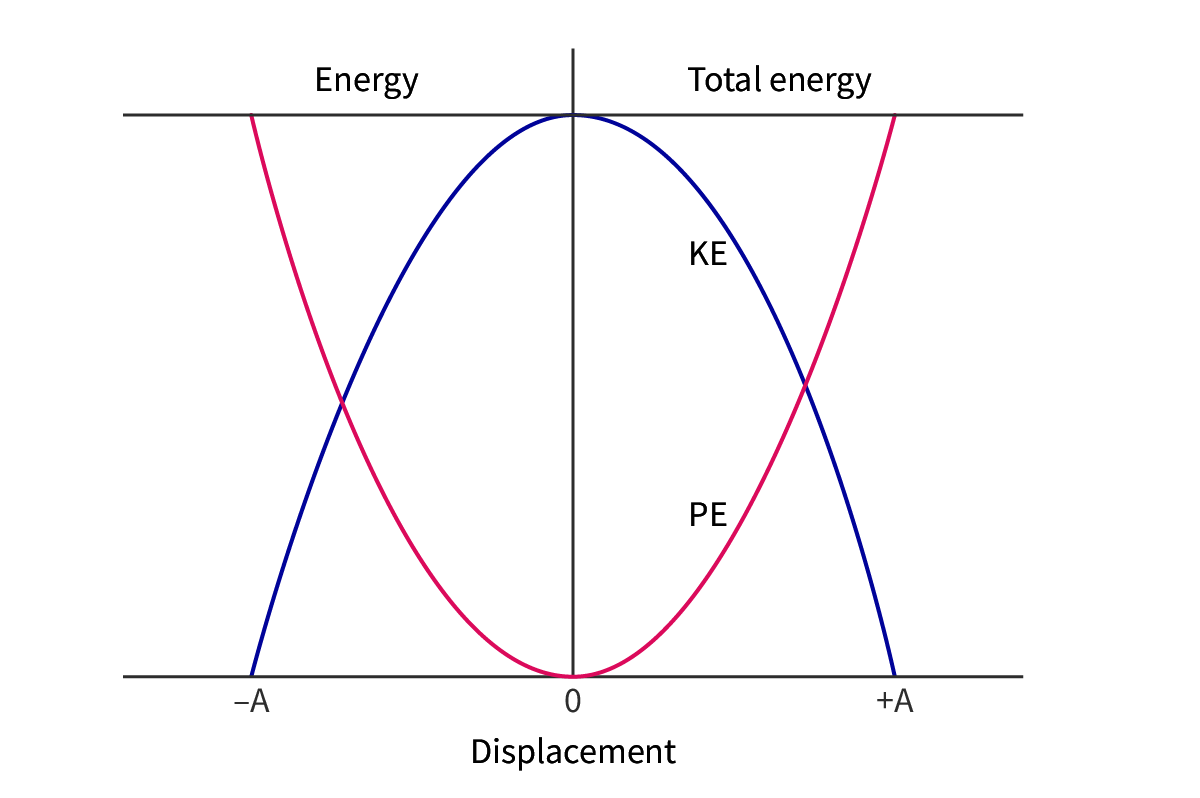
Energy of SHM
When the pendulum is at the peak of its path (maximum displacement), all of its energy is gravitational potential energy. When the pendulum is at the equilibrium position, all of this energy has been transferred to kinetic energy.
Horizontal mass-spring systems
the potential energy is elastic potential energy, but the same transfer to kinetic energy occurs.
Vertical mass-spring systems
the potential energy is gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy at the top, and elastic potential energy at the bottom. But the general principle still applies.
energy transfers in SHM