APHG, Unit 3: Cultural Patterns and Processes Cumulative
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
Creole languages
A language that results from the mixing of the colonizer's language with the indigenous language of the people being dominated. These are romance languages spoken in some former colonies that can also be classified as separate languages because they differ substantially from the original introduced by European colonizers. Examples include French Creole in Haiti, Papiamento (creolized Spanish) in Netherlands Antilles (West Indies), and Portuguese Creole in the Cape Verde Islands off the African coast.
Basque
An isolated European language that is the only language currently spoken in Europe that survives from the period before the arrival of Indo-European speakers. It is now the first language of 666,000 people in the Pyrenees Mountains of northern Spain and southwestern France. It's lack of connection to other languages reflects the isolation of the people in these mountains. This isolation has helped them preserve their language.
extinct languages
languages that were once in use, even in the recent past, but are no longer spoken or read in daily activities by anyone in the world.
EXAMPLES:
- Native American languages (74 of them)
- Peru's indigenous languages
- Gothic (an old Eastern/Northern European language): the last speakers of this language lived in Crimea in the 16th century; many switched to speaking Latin after their conversion to Christianity
lingua franca
a language of international communication, usually used to facilitate trade/business
EX: English, Swahili, Arabic, French, Mandarin
pidgin language
a simplified form of a lingua franca, which mixes words from one's native language with the lingua franca
Two ways that expansion diffusion has occurred in English
1. English is changing through diffusion of new vocabulary, spelling and pronunciation.
2. English words are fusing with other languages.
Universalizing religions
a religion that attempts to appeal to all people, not just those living in a particular location
Ethnic religions
a religion with a relatively concentrated spatial distribution whose principles are likely to be based on the physical characteristics of the particular location in which its adherents are concentrated.
atheism
the belief that God does not exist
agnosticism
the belief that nothing can be known about whether God exists
branch (of a religion)
a large and fundamental division within a religion
sect
a relatively small group that has broken away from an established denomination
Orthodox Christianity
the branch of Christianity usually practiced in Eastern Europe and the MIddle East; it includes the Russian Orthodox Church and 13 other self-governing churches
Catholicism
The original Christian church; it is headed up by the Pope in Rome, and the leaders of individual, local churches are called priests.
Protestant Christianity
A branch of Christianity with individual denominations rather than central leadership. It was initiated by Martin Luther in 1517, when he posted his 95 disagreements with the Catholic Church on the door of his church.
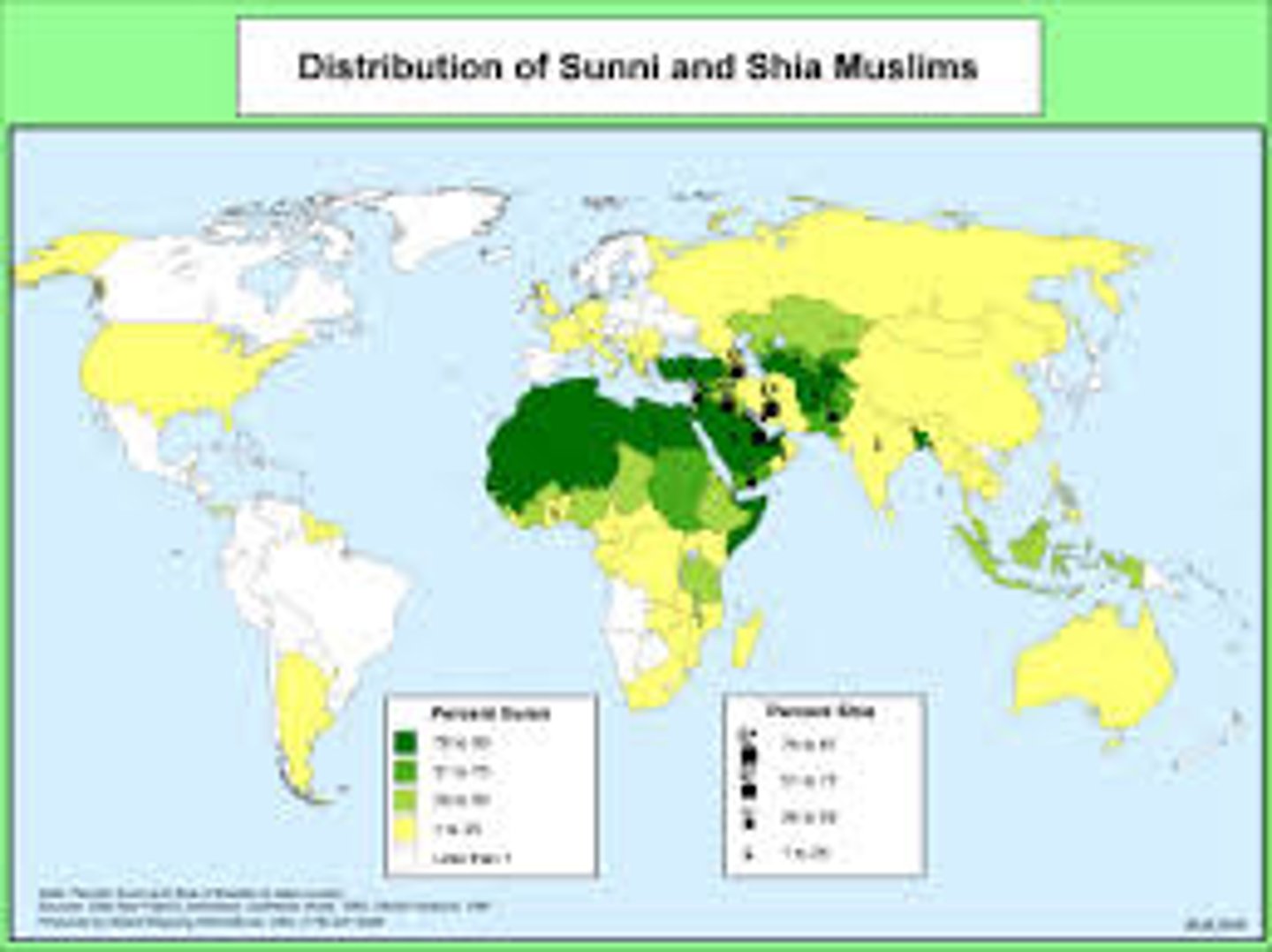
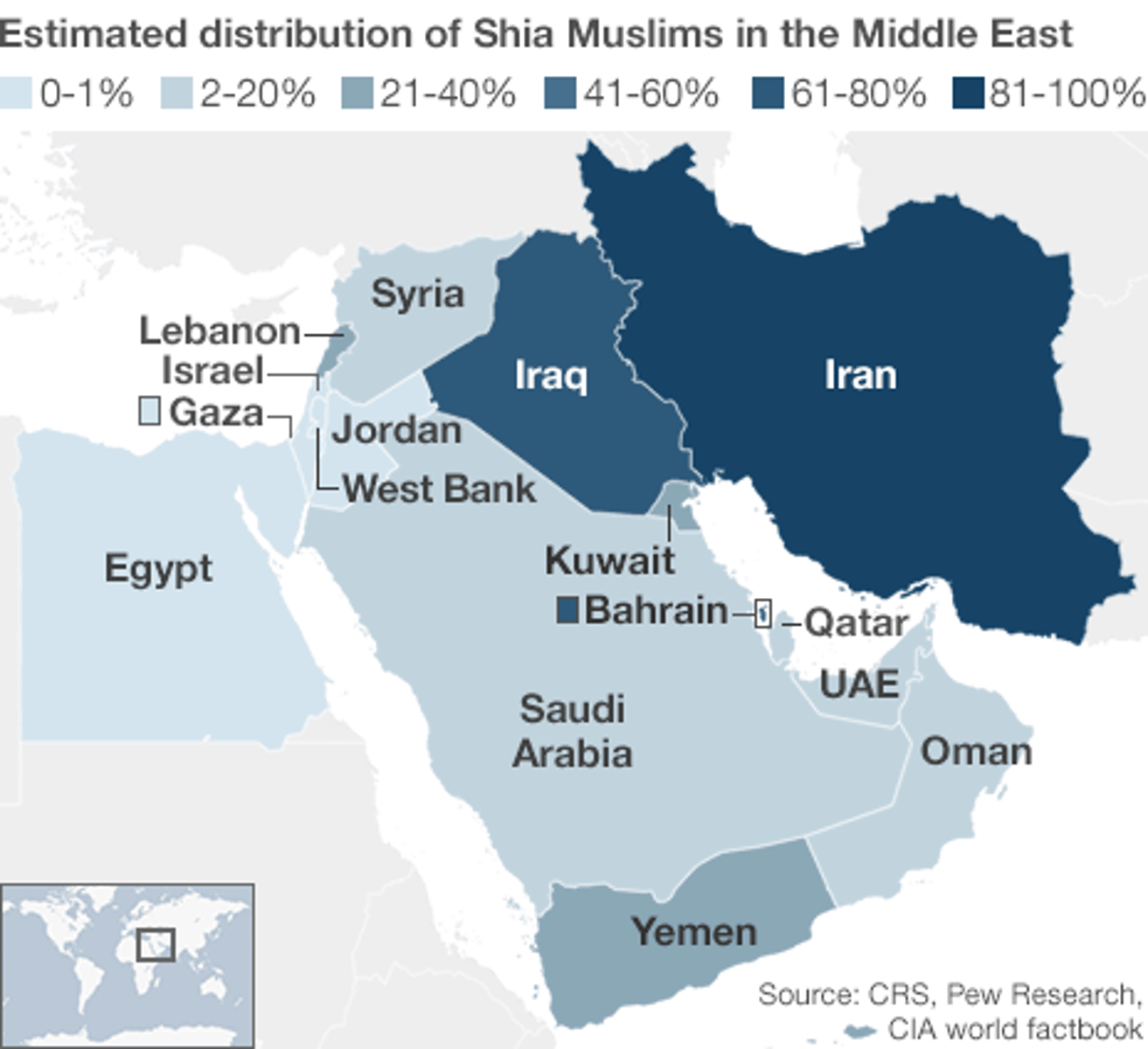
Sunni
A branch of Islam whose name comes from the Arabic for, "people following the example of Muhammad." They comprise 83 percent of Muslims and are the largest branch in most Muslim countries in Southwest Asia and North Africa.
Shiite
A branch of Islam whose name comes from the Arabic word for, "sectarian." They comprise 16 percent of Muslims, clustered in a handful of countries. Nearly 30 percent of all of this group lives in Iran, 15 percent in Pakistan, and 10 percent in Iraq. They comprise nearly 90 percent of the population in Iran and more than half the population in Azerbaijan, Iraq, and the less populous countries of Oman and Bahrain
Mahayana
A branch of Buddhism that split from Theravada Buddhism about 2,000 years ago. The name of this branch translates, "the great vehicle," and followers call Theravada by the name, "HINAYANA," which means, "the inferior vehicle." Followers of this branch claim that their approach to Buddhism can help more people because it is less demanding and all-encompassing. They emphasize Buddha's later years of teaching and helping others. They cite Buddha's compassion as his most prominent characteristic.
Theravada
A branch of Buddhism that is the older of the two larger branches (the other large branch is Mahayana). The name of this branch means, "the way of the elders," indicating that those who are a part of this branch believe that they are closer to Buddha's original approach. They believe that Buddhism is a full-time occupation, so to become a good Buddhist, one must renounce worldly goods and become a monk, They also emphasize Buddha's life of self-help and years of solitary introspection. They also cite Buddha's wisdom as his most prominent characteristic.
Vajrayana
A branch of Buddhism that emphasizes the practice of rituals, known as Tantras, which have been recorded in texts. They believe that Buddha began to practice Tantras during his lifetime, although other Buddhists regard this branch as an approach to Buddhism that evolved from Mahayana Buddhism several centuries later.
Confucianism
A traditional Chinese religion centered around the teachings of Confucius, a philosopher and teacher in the Chinese province of Lu. His sayings, which were recorded by his students, emphasized the importance of the ancient Chinese tradition of li, which can be translated roughly as, "propriety" or "correct behavior." It was also concerned with the ideas of ethical, orderly conduct, following traditions, and fulfilling obligations, specifically the obligation of respect for one's elders.
Taoism
A traditional Chinese religion organized by Lao-Zi (Lao Tse). Although a government administrator by profession, Lao-Zi's writings emphasized the mystical and magical aspects of life rather than the importance of public service, which Confucius had emphasized. The meaning of this term is "The way" or "the path."
monotheism
the belief that there is only one god
polytheism
the belief that there are many gods
Buddhism's Four Noble Truths
1. All living beings must endure suffering.
2. Suffering, which is caused by a desire to live, leads to reincarnation (repeated rebirth in new bodies or forms of life).
3. The goal of all existence is to escape suffering and the endless cycle of reincarnation into Nirvana (a state of complete redemption), which is achieved through mental and moral self-purification.
4. Nirvana is attained through an Eightfold Path, which includes rightness of belief, resolve, speech, action, livelihood, effort, thought, and meditation.
Five Pillars of Islam (Faith)
1. Shahada, which means frequent recitation that there is no god worthy of worship except the one God, the source of all creation, and Muhammad is the messenger of God.
2. Salat, which means that five times daily, a Muslim prays, facing the city of Makkah (Mecca), as a direct link to God.
3. Zakat, which means that a Muslim gives generously to charity as an act of purification and growth.
4. Sawm of Ramadan, which means that a Muslim fasts during the month of Ramadan as an act of self-purification.
5. Hajj, which means that if physically and financially able, a Muslim makes a pilgrimage to Makkah.
Muhammad
the prophet of Islam
Missionaries
individuals who help to transmit a universalizing religion through relocation diffusion
mosque
Muslim religious building
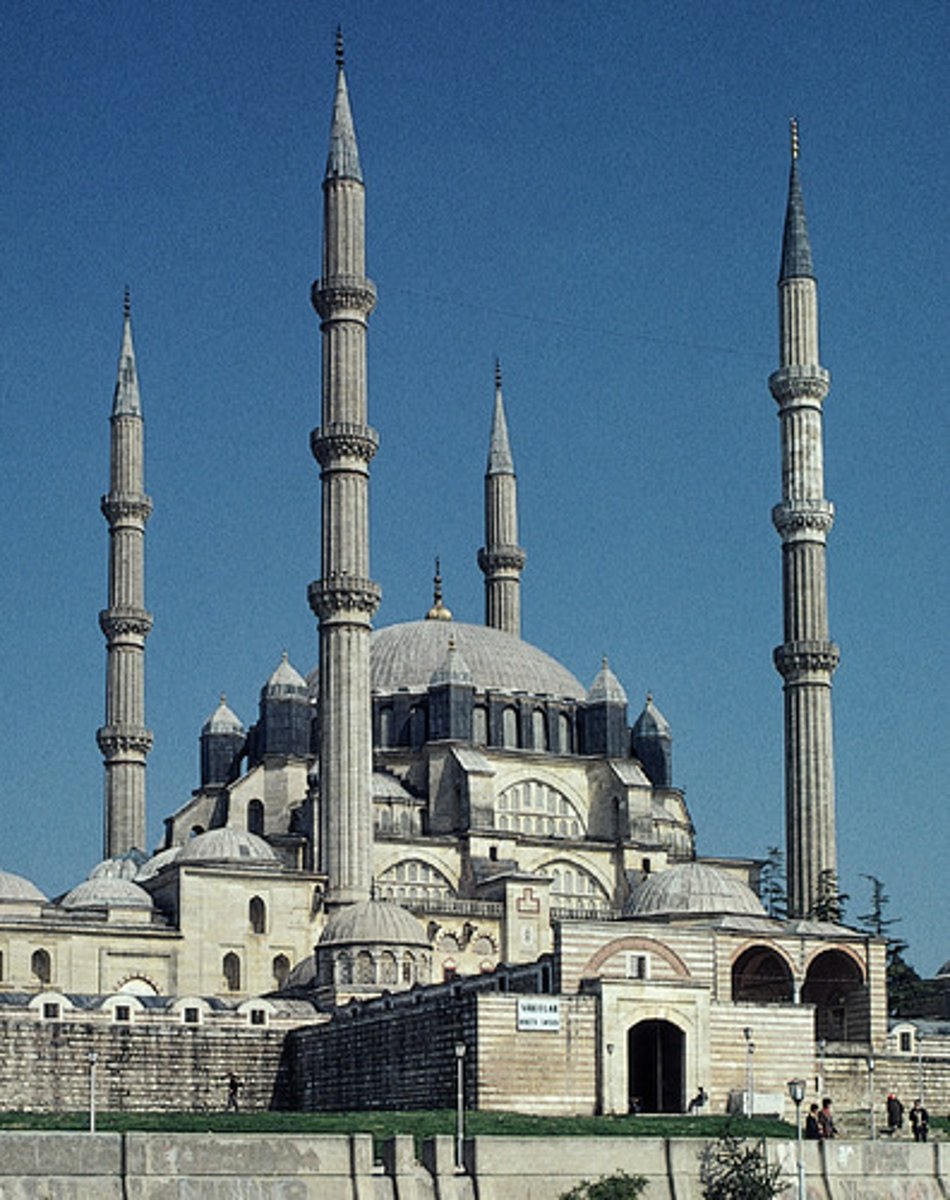

minaret
a tower where a muezzin calls people to worship

pagoda
Buddhist religious building

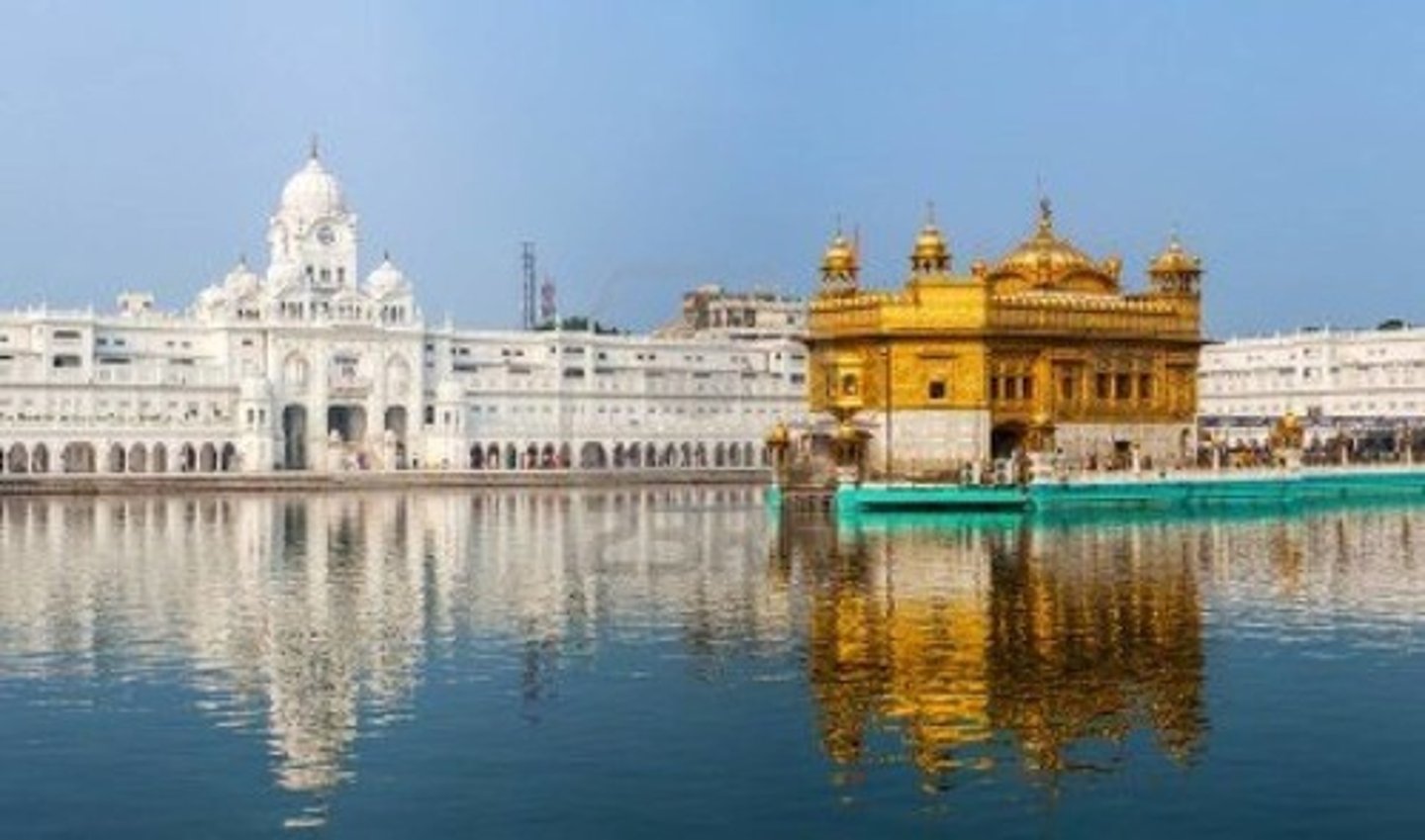
Golden Temple of Amritsar
Sikhism's most holy structure built by Arjan, the fifth guru, in the Punjab, a region in India

pilgrimage
a journey for religious purposes to a place considered sacred
hajj
a Muslim pilgrimage to mecca
Germanic Branch
-Part of Indo-European family
- Includes: West Germanic group, which is further divided into High Germanic and Low Germanic subgroups, so named because they are found in high and low elevations within present-day Germany. High German, spoken in the southern mountains of Germany, is the basis for the modern standard German language. English is classified in the Low Germanic subgroup of the West Germanic group.
- Other Low Germanic languages include Dutch (Belgium) and Afrikaans (South Africa)
-Frisian (some people in Netherlands)
_ALSO North Germanic group (Scandanavian languages--Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, and Icelandic)
Romance Branch
This branch evolved from Latin language spoken by the Romans 2,000 years ago. The four most widely used languages of this branch are Spanish, Portuguese, French, and Italian
language
a system of communication through speech, a collection of sounds that a group of people understands to have the same meaning
taboo
a restriction on behavior imposed by social custom
animism
most prevalent in Africa and the Americas, doctrine in which the world is seen as being infused with spiritual and even supernatural powers
artifact
any item that represents a material aspect of culture
cultural hearth
locations on earth's surface where specific cultures first arose
cultural trait
the specific customs that are a part of everyday life a particular culture, such as language, religion, ethnicity, social institutions, and aspects of popular culture
culture
comprises the shared practices, technologies, attitudes, and behaviors transmitted by a society
acculturation
when a culture is substantially changed through interaction with another culture
relocation diffusion
the spread of a cultural trait by people who migrate and carry their cultural traits with them.
universalizing religions
A religion that attempts to appeal to all people, not just those living in a particular location.
assimilation
the process through which people lose originally differentiating traits, such as dress, speech, particularities, or mannerisms when they come into contact with another society or culture
ethnic religions
focus on one ethnic group and generally have not spread into other cultures
contagious diffusion
occurs when a cultural trait spreads continuously outward from its hearth through contact among people
cultural relativism
the idea that a person's beliefs, values, and practices should be understood based on that person's own culture, rather than be judged against the criteria of another.
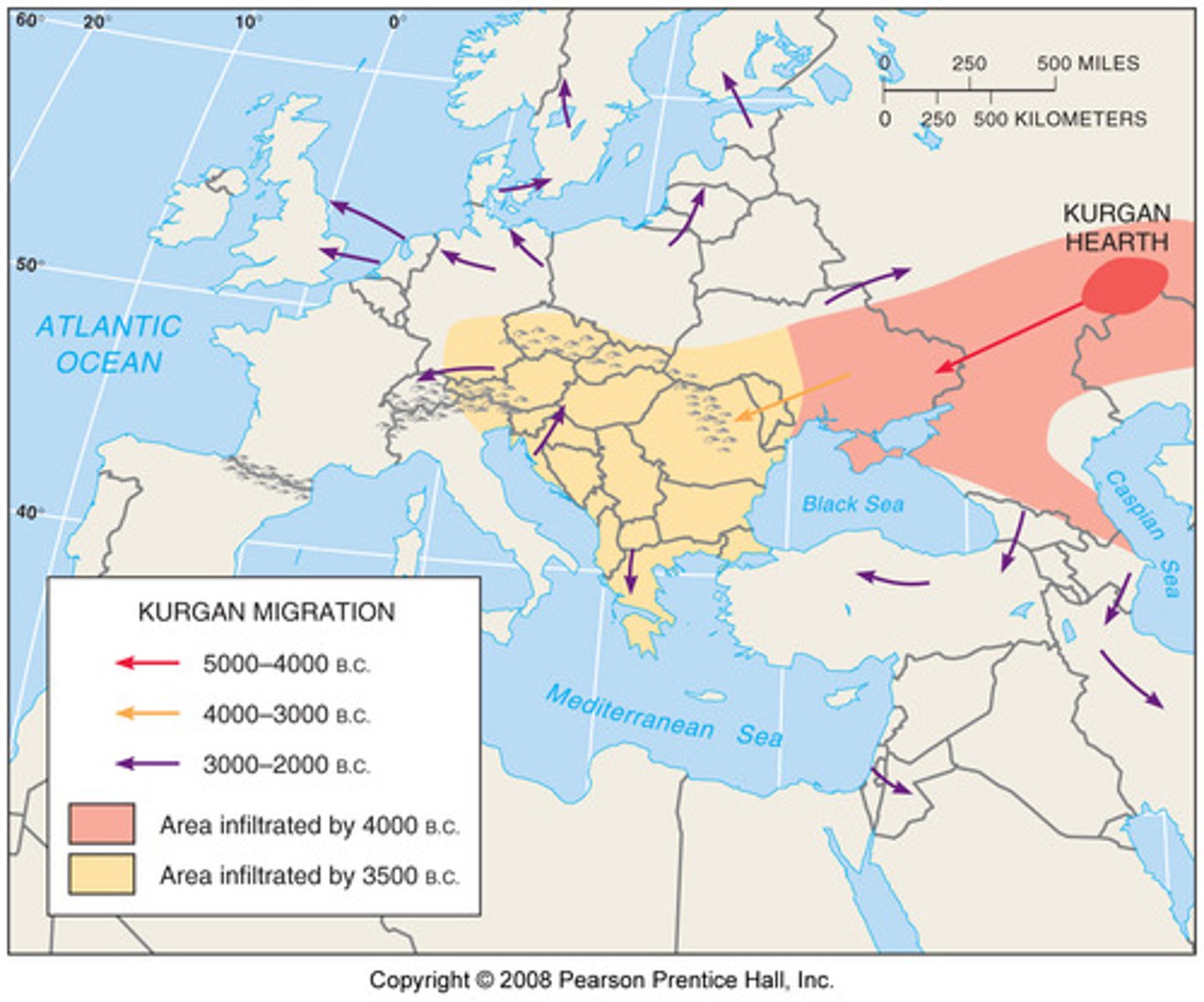
Nomadic Warrior Hypothesis
theory of the diffusion of the Proto-Indo-European language into Europe through the speakers' overpowering of earlier inhabitants through warfare and technology
expansion diffusion
The spread of a feature or trend among people from one area to another in a snowballing process.
1. contagious
2. hierarchical
3. stimulus
ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group.
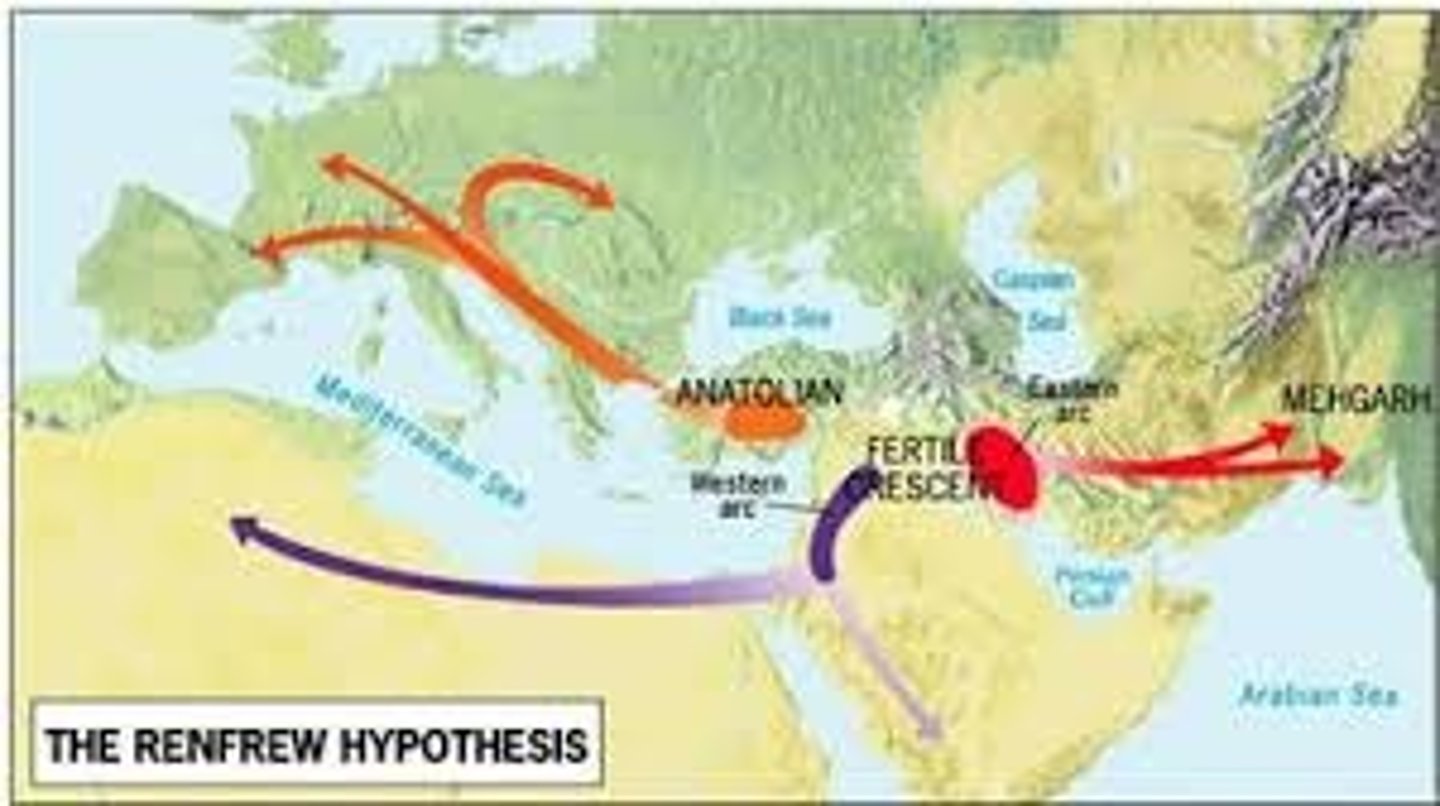
Sedentary Farmer Hypothesis
Colin Renfrew and Russell Gray; lived 2,000 yrs before Kurgans; E. Anatolia (Turkey); to Greece, then west towards italy, france, spain; diffuse by agricultural practices; isolation caused diff languages
hierarchical diffusion
the spread of a feature or trend from one key person or node of authority or power to other persons or places
multiculturalism
the idea that different cultures in a society deserve value and respect for unique differences
reverse hierarchical diffusion
diffusion up a hierarchy, such as from a small town to large cities

culture hearth
a center where cultures developed and from which ideas and traditions spread outward
multilingual states
countries in which more than one language is spoken
stimulus diffusion
The spread of an underlying principle, even though a specific characteristic is rejected.

Origin of Romance Languages
Latin
folk culture
the beliefs and practices of small, homogenous groups of people, often living in rural areas that are relatively isolated and slow to change
Diffusion of English
•Migration - Spread English when they migrated to the US via. beating the French assuring English to be the main language.
•Colonizing - All of the countries colonised by the British have made English their official language.
Note: More recently the US has been responsible for spreading English, notably the Philippines (Spanish-American War)
creole
A language that results from the mixing of a colonizer's language with the indigenous language of the people being dominated.
EX: Haitian
popular culture
Culture found in a large, heterogeneous society that shares certain habits despite differences in other personal characteristics.
extinct language
A language that was once used by people in daily activities but is no longer used.
pidgin
A simplified form of speech developed from two or more languages
other words for folk culture
local, traditional
sense of place
State of mind derived through the infusion of a place with meaning and emotion by remembering important events that occurred in that place or by labeling a place with a certain character.
dialect
A regional variety of a language distinguished by vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation.
EX: Appalachian English
other words for popular culture
globalized/globalization
uniform landscape
How popular culture's landscape look the same.
sequent occupancy
the succession of groups and cultural influences throughout a place's history
isogloss
A boundary that separates regions in which different language usages predominate.
toponym
The name given to a portion of Earth's surface.
distribution
The arrangement of something across Earth's surface.
Origins of universalizing religions
precise places of origin based on events in the life of a man
colonization
One country taking over another area to be used for their benefit
Origins of ethnic religions
unknown or unclear origins, not tied to single historical individuals
imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.
Origin of Christianity
Jerusalem; founded upon the teachings of Jesus
space-time compression
The reduction in the time it takes to diffuse something to a distant place, as a result of improved communications and transportation systems
Origin of Islam
Saudi Arabia; founded by the Prophet Muhammad
globalization
Actions or processes that involve the entire world and result in making something worldwide in scope.
cultural landscape
Fashioning of a natural landscape by a cultural group.
adherents
someone who supports a particular party, person, or set of ideas
time-space convergence
The idea that distance between some places is actually shrinking as technology enables more rapid communication and increased interaction among those places
Quran
The holy book of Islam
built environment
The man-made surroundings that provide the setting for human activity, ranging in scale from personal shelter to neighborhoods to the large-scale civic surroundings.
ethnicity
Identity with a group of people that share distinct physical and mental traits as a product of common heredity and cultural traditions.
Sunni Muslims
Majority of the Muslims; believe successor of Muhammad can be an elected caliph.
Mostly in N. Africa and SW Asia
indigenous language
the native language of a people in an area
denomination
A division of a branch that unites a number of local congregations in a single legal and administrative body.
ethnic enclaves
locations with a high concentration of one specific ethnicity
placemaking
the process of creating a comfortable personal environment that reflects the values, experiences, and tastes of the couple
branch of a religion
A large and fundamental division within a religion
Shi'ite Muslims
Muslims that believe only descendants of Muhammad and his son-in-law Ali should rule
Mostly in Iran
cultural convergence
contact and interaction of one culture and another
Universalizing religion
A religion that attempts to appeal to all people, not just those living in a particular location.
cultural divergence
the restriction of a culture from outside influences