Cellular Respiration: Pathways and Processes Section 2, 3, and 4: Glycolysis, Pyruvate Oxidation & Entry to Citric Acid Cycle, and Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
A-Level Chemistry
AQA
Organic Chemistry
Pyruvate Oxidation & Entry to Citric Acid Cycle
Section 3: Pyruvate Oxidation & Entry to Citric Acid Cycle
Cellular Respiration: P&P Section 3
Pyruvate Oxidation & Entry to Citric Acid Cycle
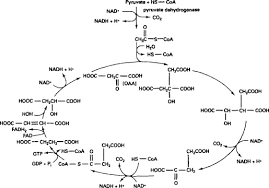
Pyruvate Oxidation
Entry to Citric Acid Cycle
Cellular Respiration: P&P Section: 2, 3, and 4
Cellular Respiration: P&P Section 2
Cellular Respiration: P&P Section: 4
Cellular Respiration: Pathways and Processes Section 4: Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
Cellular Respiration: P&P Section: 4
Section 4: Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle)
Section 4 Module: 8 Kreb cycle
Citric acid cycle Cellular respiration
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Glycolysis
First step of cellular respiration in cytoplasm, converting glucose to pyruvate and producing ATP.

NAD+
Coenzyme acting as an electron carrier in respiration.
Hydrogen Atom Transfer
Process of moving hydrogen atoms during oxidation.
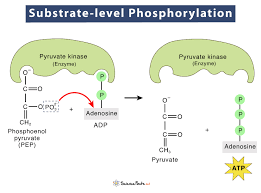
Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
Direct ATP production occurs from organic substrates without electron transport involvement.
Energy investment phase
Initial ATP usage during glycolysis.
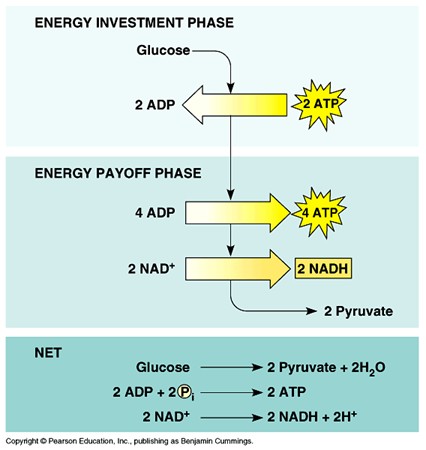
Energy payoff phase
Energy payoff phase: ATP production phase in glycolysis.
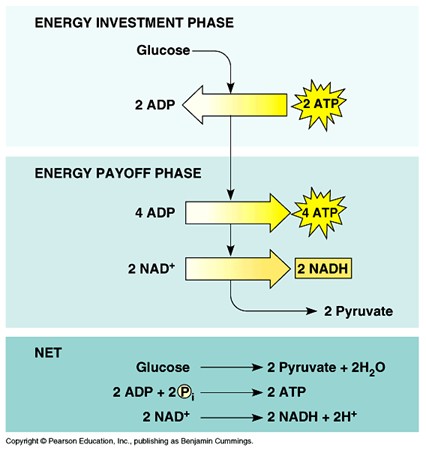
Net yield of glycolysis
2 ATP and 2 NADH per glucose.
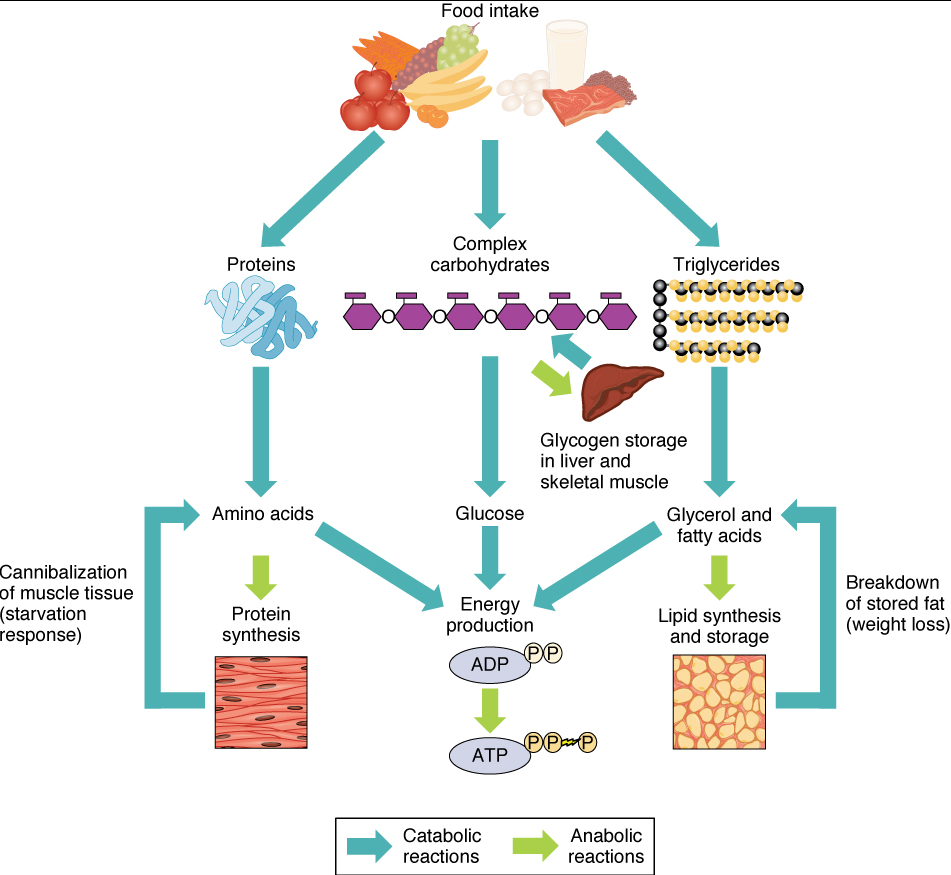
Glucose
Primary energy source oxidized during respiration.
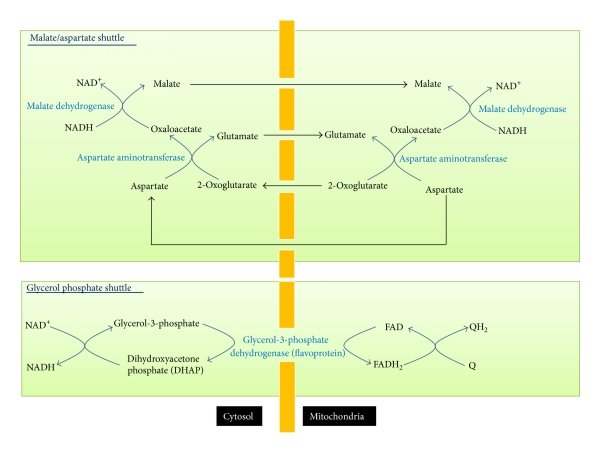
Shuttle Systems
Transport mechanisms for NADH into mitochondria.
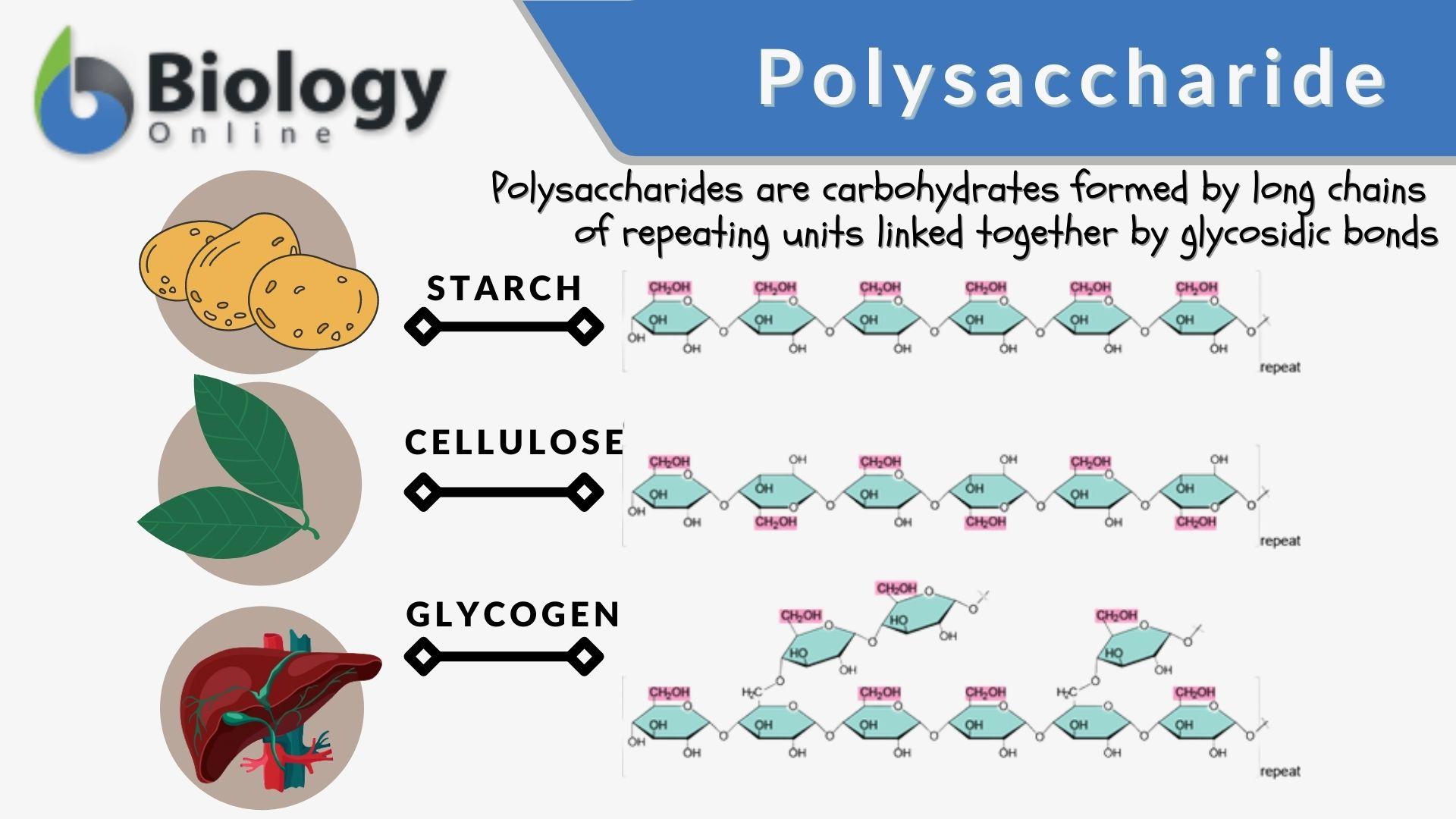
Polysaccharides
Complex carbohydrates hydrolyzed to glucose for energy.
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins, can enter respiration pathways.
Anabolic Pathways
Synthesize molecules, consuming ATP instead of generating.
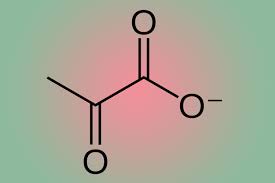
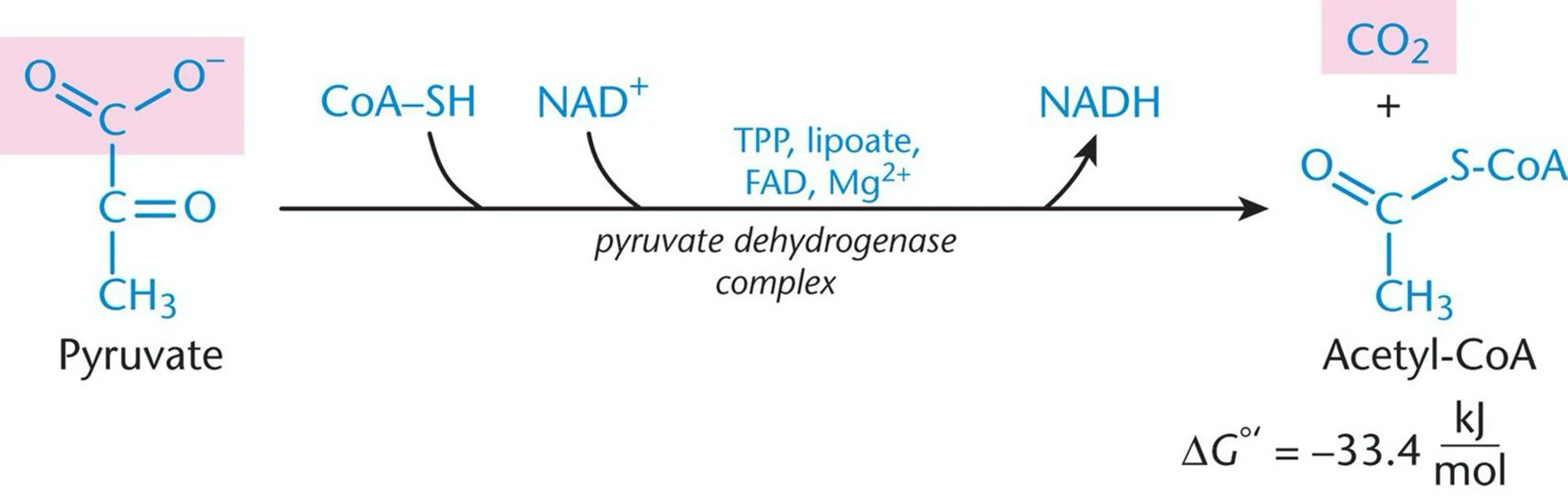
Pyruvate
End product of glycolysis, converted to acetyl CoA.
The Link & Product of Acetyl CoA
A 2-carbon molecule with a coenzyme A attached, formed from pyruvate and serving as the primary fuel that enters the citric acid cycle.
Dehydrogenase Enzymes
Enzymes that remove hydrogen atoms (and electrons) from pyruvate during its conversion to Acetyl CoA.
Mitochondrial Matrix (location):
The specific compartment within the mitochondrion where pyruvate oxidation takes place.
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
One carbon atom from pyruvate is released as carbon dioxide during this transition step
NADH (produced from pyruvate):
NAD+ is reduced to NADH, capturing energy from oxidizing pyruvate.
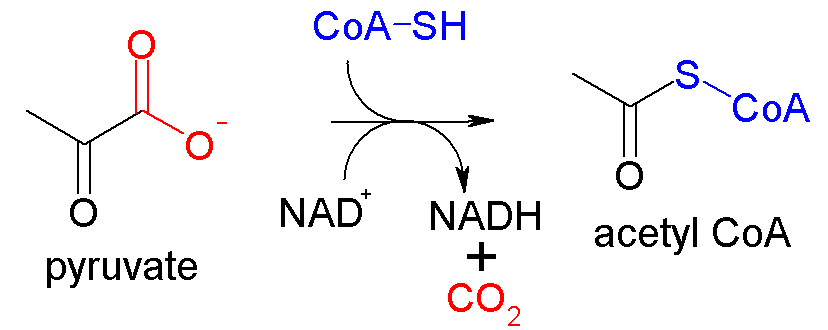
The stage of Pyruvate
The 3-carbon molecule produced by glycolysis that enters the mitochondrion for the next stage.
High energy of Acetyl CoA
This thioester bond in Acetyl CoA stores significant potential energy that will be harnessed in the subsequent steps of respiration.
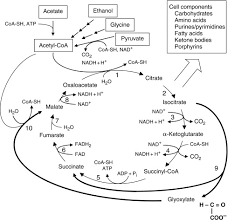
Citric Acid Cycle
Second step of cellular respiration oxidizes acetyl CoA, producing ATP and carriers.
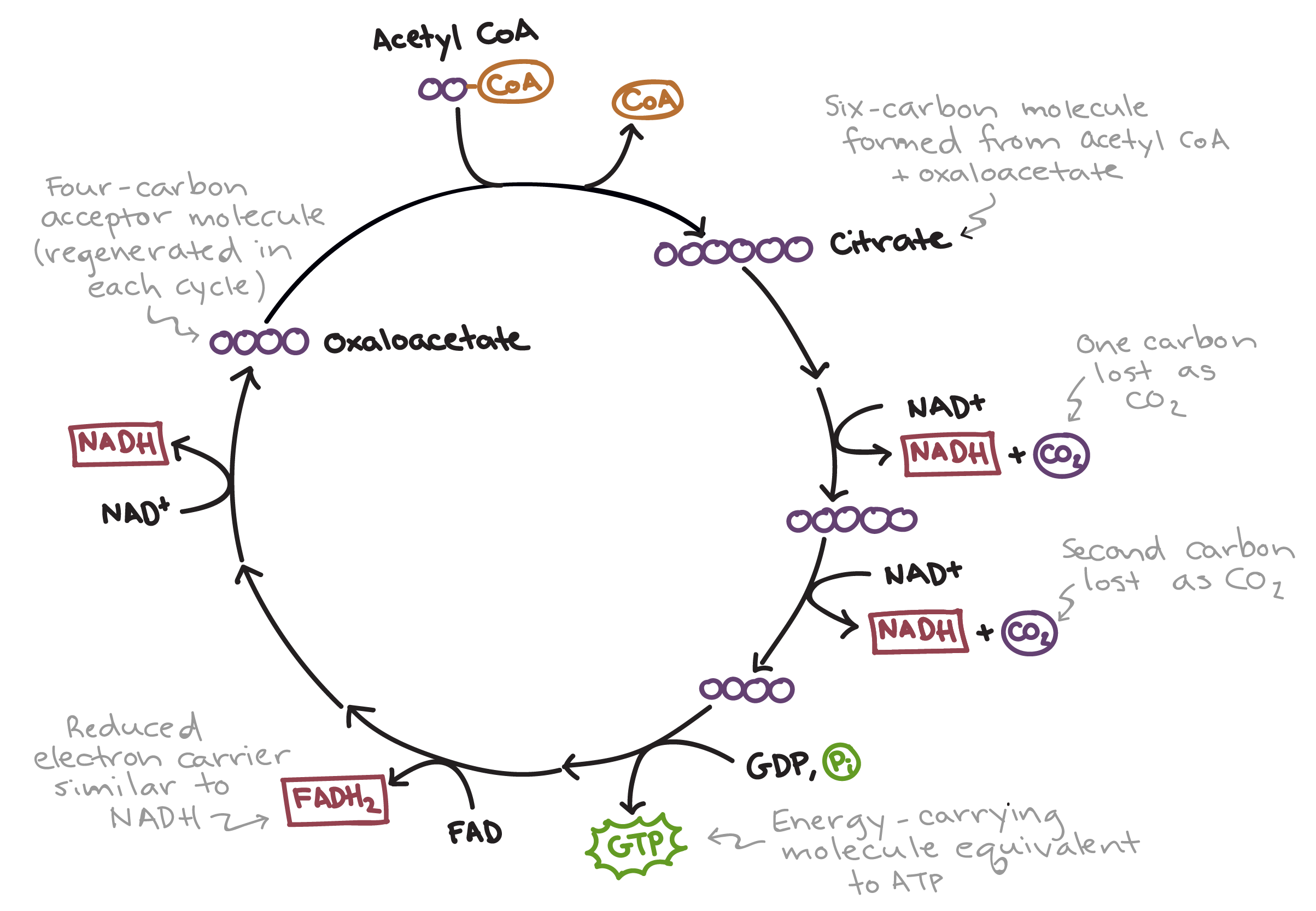
Krebs cycle
Another name for the citric acid cycle.
Oxaloacetate
Four-carbon molecule combining with acetyl CoA.
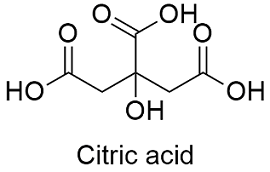
Citrate
Six-carbon compound formed in the citric acid cycle.
FADH2
Reduced FAD is an electron carrier transporting electrons.
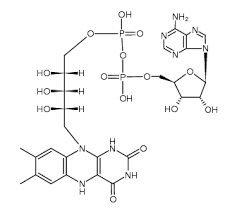
Acetyl CoA
Pyruvate oxidation produces high-energy compound for citric acid cycle.
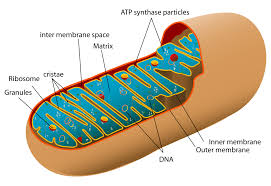
Mitochondrion
Organelle where aerobic respiration occurs (site of the citric acid cycle in eukaryotes).
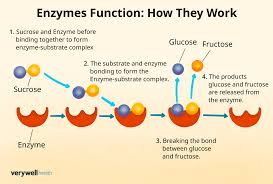
Enzyme
Catalyst speeding up biochemical reactions (many enzymes involved in the cycle).
Chemical energy
Energy stored in molecular bonds (transformed during the cycle).
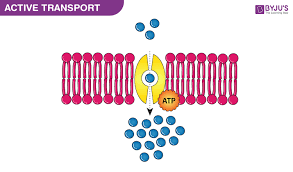
Active transport
Energy-dependent movement of molecules across membranes (relevant for moving molecules in/out of mitochondria for the cycle).
High potential energy
Energy-rich state of acetyl CoA (entering the cycle).
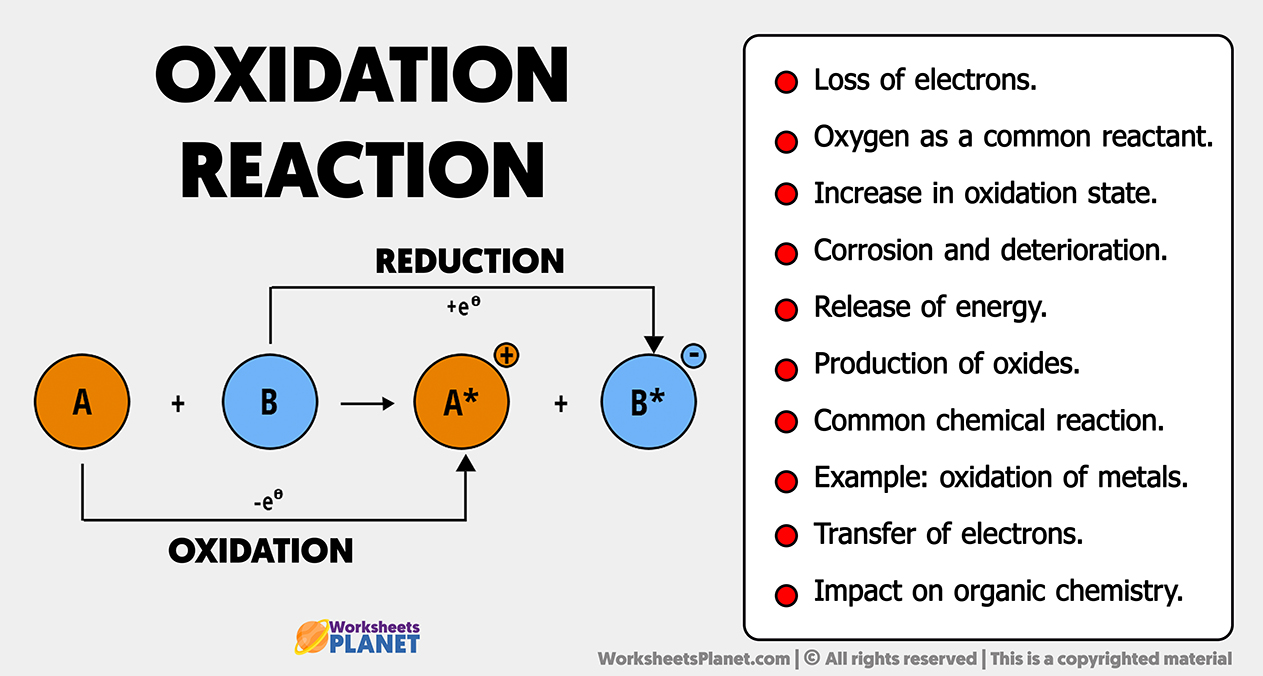
Oxidation
Loss of electrons from a substance.