Lecture 16: Microbiota Guest Lecture
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Microbiota
Community of microorganisms (includes bacteria, viruses, fungi)
• Varies between body sites
• Today we are focusing on the gut (colon) microbiota
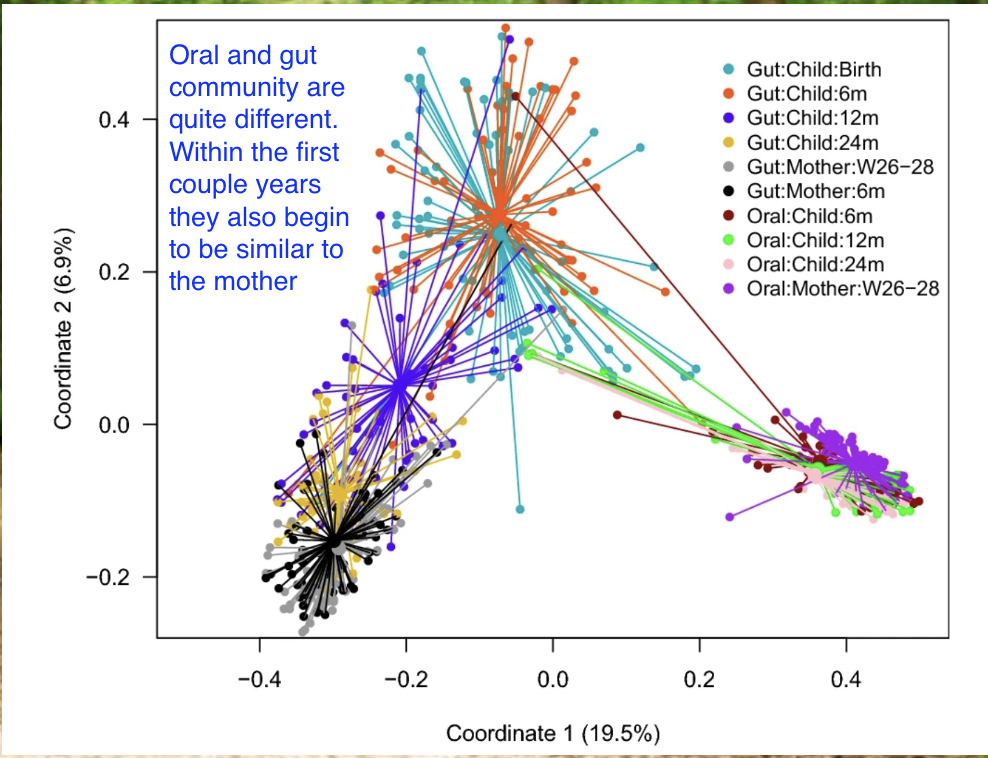
Microbiota development
Exposed to microbes from birth
• Vaginal microbes / skin microbes (C-section) →
• Rapid increases in complexity
• Community develops with facultative microbes
• Transitions to anaerobes → after they use up the oxygen
The Microbiota in the Adult colon
Dense colonization
Varies from person to person
More in composition than function
Anaerobic (during healthy state)
Dominated by Firmicutes (Bacillota) and Bacteroidetes (Bacteroidota) phyla;
small numbers of Proteobacteria (Pseudomonadota), Actinobacteria (Actinomycetota) and others
Beneficial functions
Digestion of complex carbohydrates in anaerobic fermentation à short-chain fatty acids (SCFA)
Produce diverse metabolites that influence host locally (gut) and systemically
Great Chemists/Biochemists!
Biosynthetic gene clusters
Host compounds; mucus, bile acids
Xenobiotics
Microbial products
Provide colonization resistance
An Ancient Connection between microbes and the immune system
immune system evolved in presence of microbes
used to think the microbiota was largely ignored – the immune system was only on lookout for pathogens
Now: recognize that the microbiota trigger a response
The catch → response occurs without inducing overt inflammation → homeostatic immunity
Relationship stressed by rapid changes (on an evolutionary scale) in microbiota
Increased autoimmune, inflammatory disorders
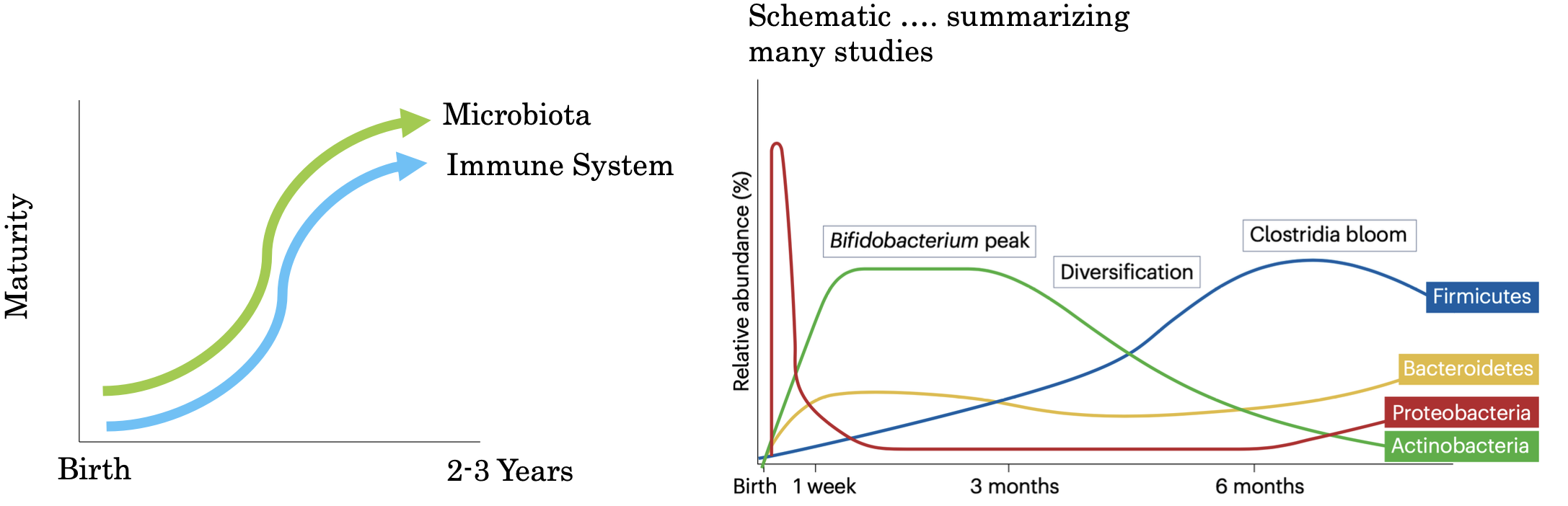
When you are born, is the immune system fully developed?
no
proteobacteria → use oxygen
Window of Opportunity
Adult like stability in gut microbiota and immune system occurs by 2-3 years
window of opportunity refers to privileged period of development where influences of the microbiota on the immune system are durable
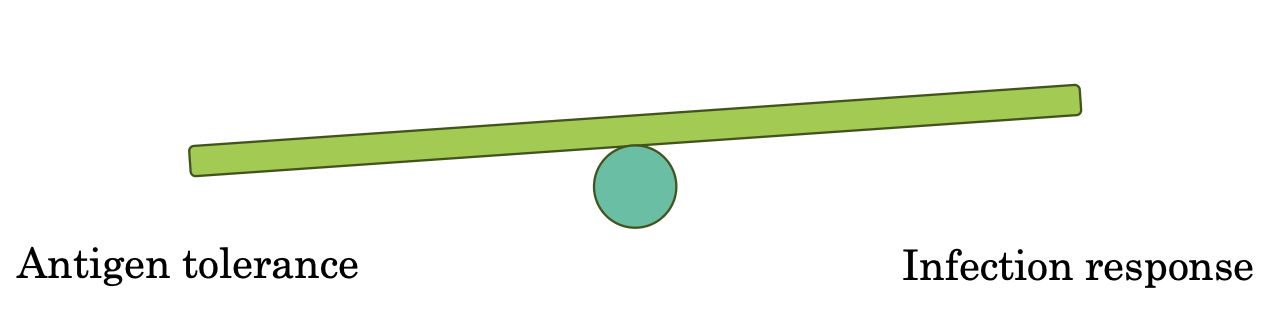
After birth; immune system goes through a developmental trajectory that balances tolerance of new antigens and ability to respond to infections
Key factors affecting this dynamic system
Route of delivery → helps determine the starting point for microbiota
Antibiotics
Environmental exposure to different microbes & antigens
Feeding: Breastmilk or formula
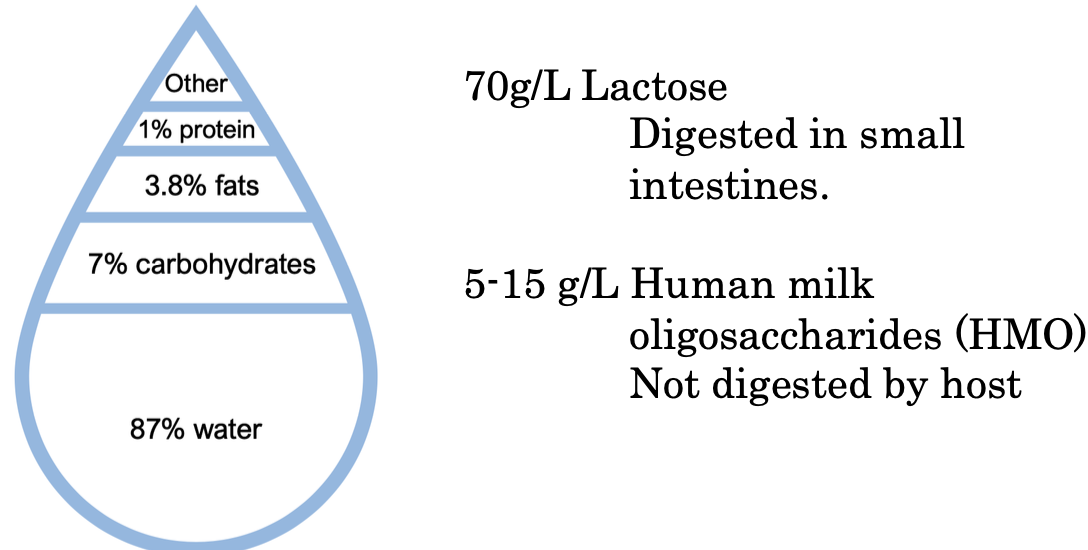
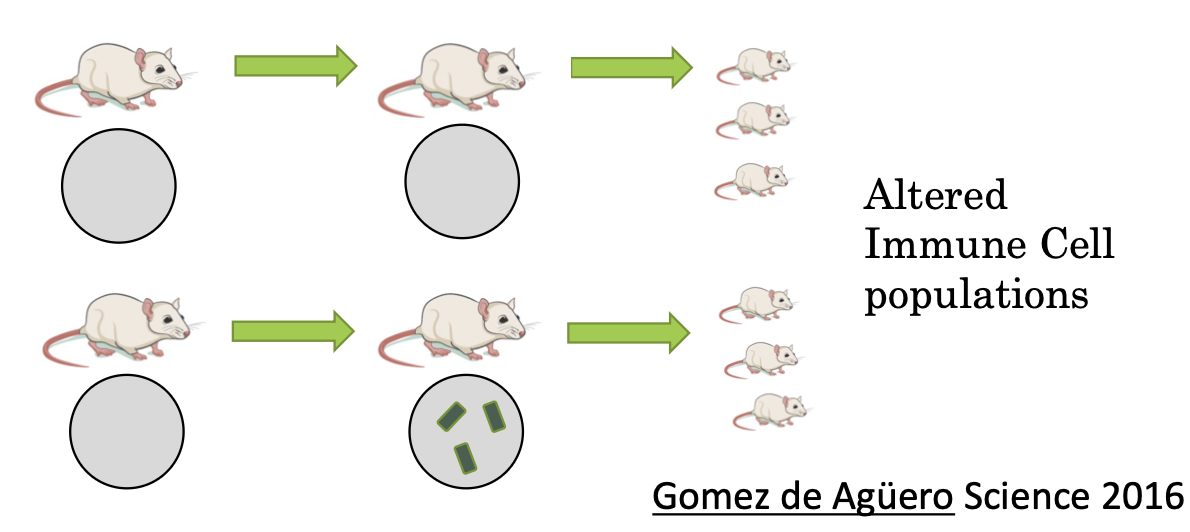
Development Crosstalk Example 1: An Early Start
A mother’s microbiota influences their offspring's immune system before birth
Small metabolites (SCFA) reach the fetus
Experiments using transient colonization of germfree mice show alterations of innate lymphoid cell populations in pups
immune cells of the developing fetus is affected by the mothers microbes
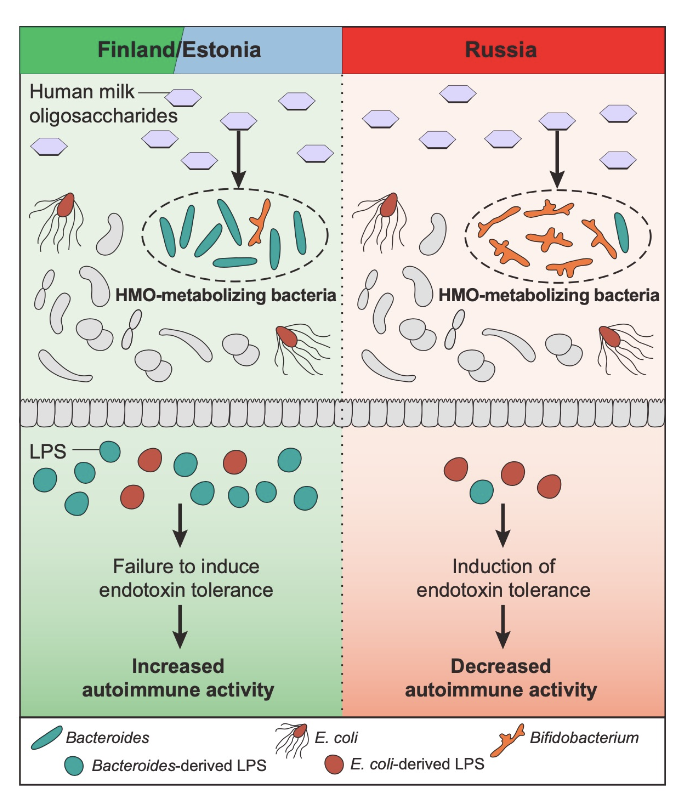
Development Crosstalk Example 2: LPS & Type 1 Diabetes
finland has more type 1 diabetes than Russia (5-6x more)
theres is a difference in HMO utilizing bacteria between the populations
Finland → higher bacteroides while other have e coli
bacteroids and e coli are both gram negative → have LPS which causes differential activation of ———- by the macrobiotic
Example 2: The Microbiota and T Cells
The microbiota controls the differentiation of T cells
Specific microbes: SFB Segmented filamentous bacteria
Microbial Metabolites:
Butyrate, or secondary bile acids
study with the microbiota and T cells?
Germfree mice have low numbers of TH17 cells
Mice from different vendors had different numbers of TH17 cells
Compare microbiota between vendors:
Jackson mice lack SFB!
Mono-colonizing mice rescues TH17
Induces a major shift in immune system
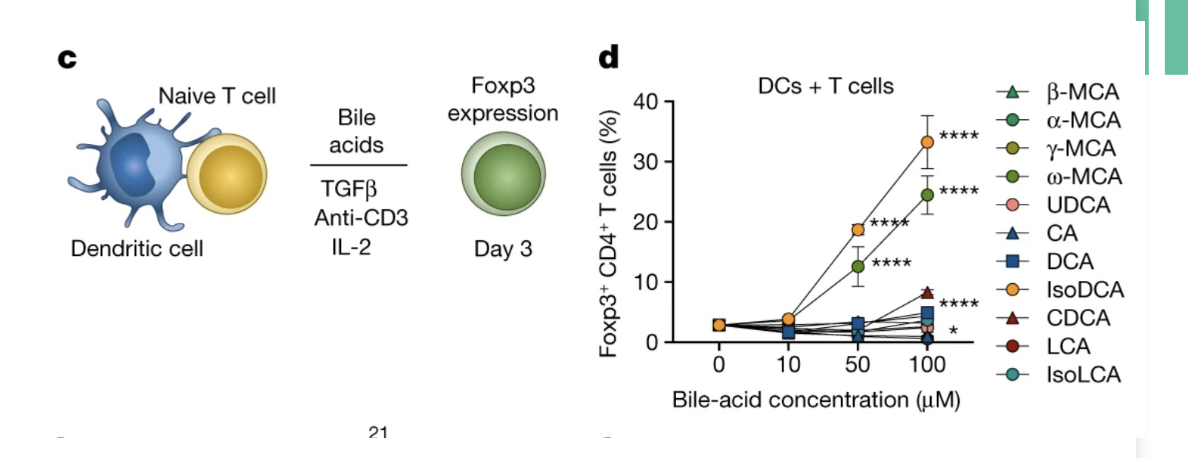
Bile acids: The Microbiota and T Cells
We secrete primary bile acids (CA, CDCA)
• Helps with digestion
• The microbiota converts these into secondary bile acids
• DCA, LCA
• That used to be the end… but now we are realizing there are many more modifications!
New modifications are being discovered
• Modified bile acids alter T cell differentiation
• Bile acid metabolism is another axis of cross talk between immune system and microbiota
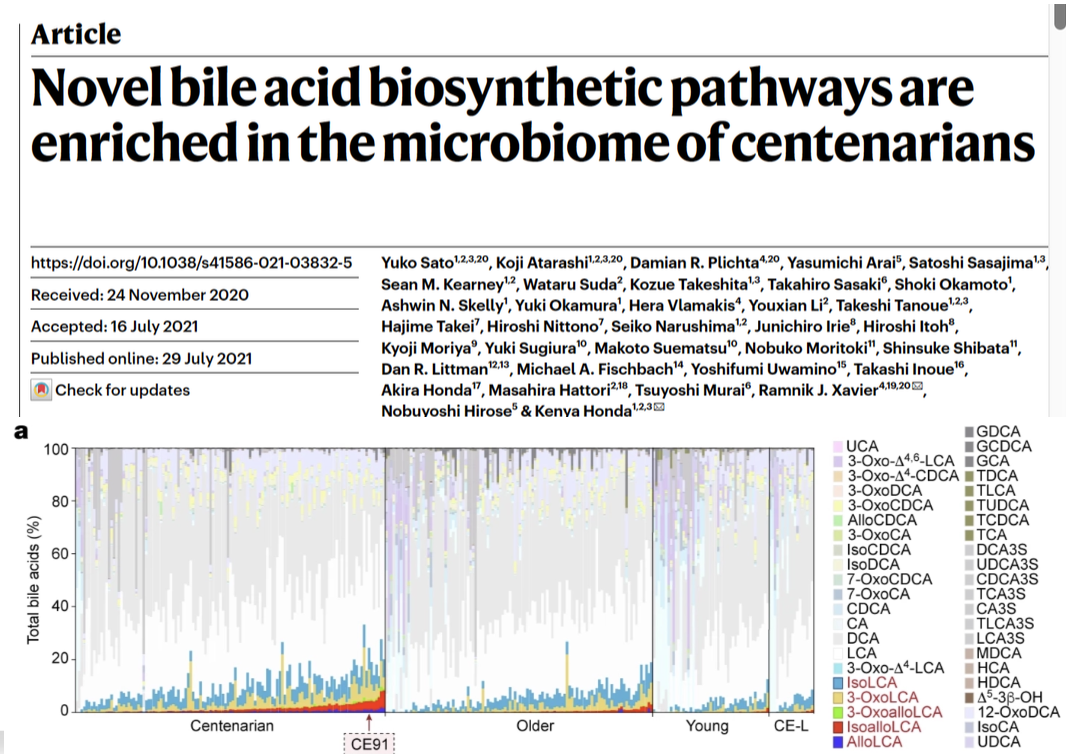
Bile acids and aging: The Microbiota and T Cells
Some secondary bile acids are further
modified
• These modified bile acids alter T cell
differentiation
• Bile acid metabolism is another axis of
cross talk between immune system and
microbiota
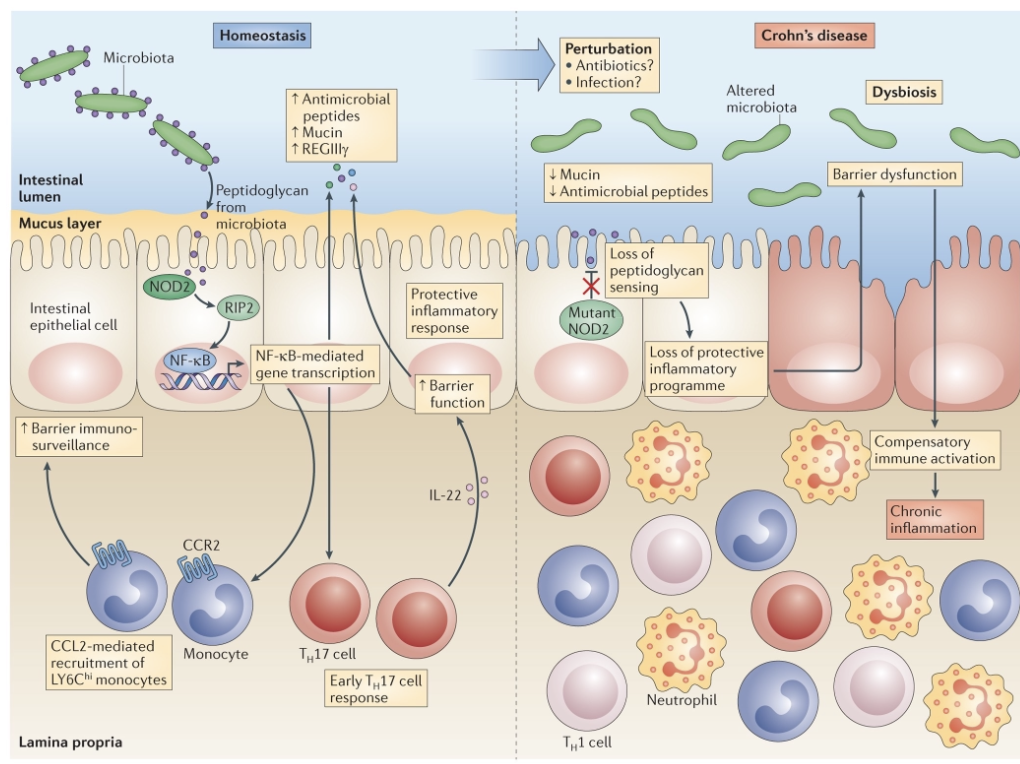
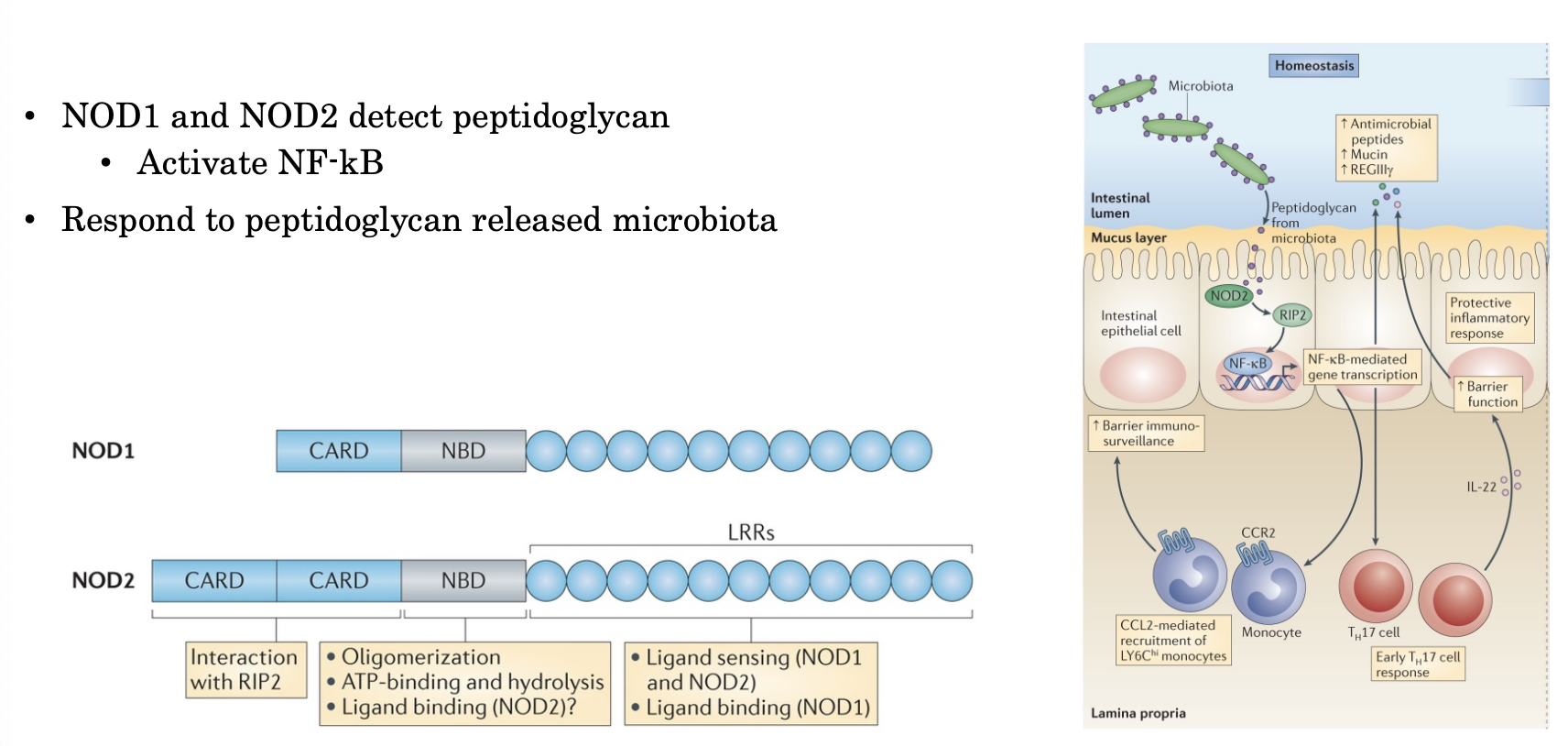
The Microbiota and Innate Immunity
NOD1 and NOD2 detect peptidoglycan
Activate NF-kB
Respond to peptidoglycan released microbiota
Is this important?
Mutations of NOD2 à strongest risk factor for Crohn’s disease
Overall model: microbiota releases PG; immunomodulatory function
Who? →
Dysbiosis
Disrupted communities have altered interactions with the immune system.
Changes in microbiota:immune interactions have been associated with many diseases:
Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis
Colorectal Cancer
many extra-intestinal conditions.
Chemotherapy/radiation
Trying to treat cancer by
targeting the tumor
Cancer immunotherapy
Broad range of approaches to
manipulate the immune
system to treat cancer
A war on cancer
Paul Ehrlich 1900s: We are constantl generating cancerous cells
• They are being eliminated by our immune system
• Recognition of cancer neo-antigens by T cells
• Altered expression of cell surface markers à killing by NK cells
• Our immune system effectively wages a constant war on cancer!
• In cancer immunotherapy, we try to harness and accelerate this function
• Much focus devoted to T cells
T cell basics
TCR recognizes antigen in the context of MHC
Class II (CD4) MHC Class I (CD8)
• But need co-stimulation
• CD28 and related receptors
• Potent co stimulatory molecules
• Recognize CD80/86 (B7-1/-2) Provided by APC
• After T cell activation: Inhibitory receptors are
also induced
Checkpoint
molecules
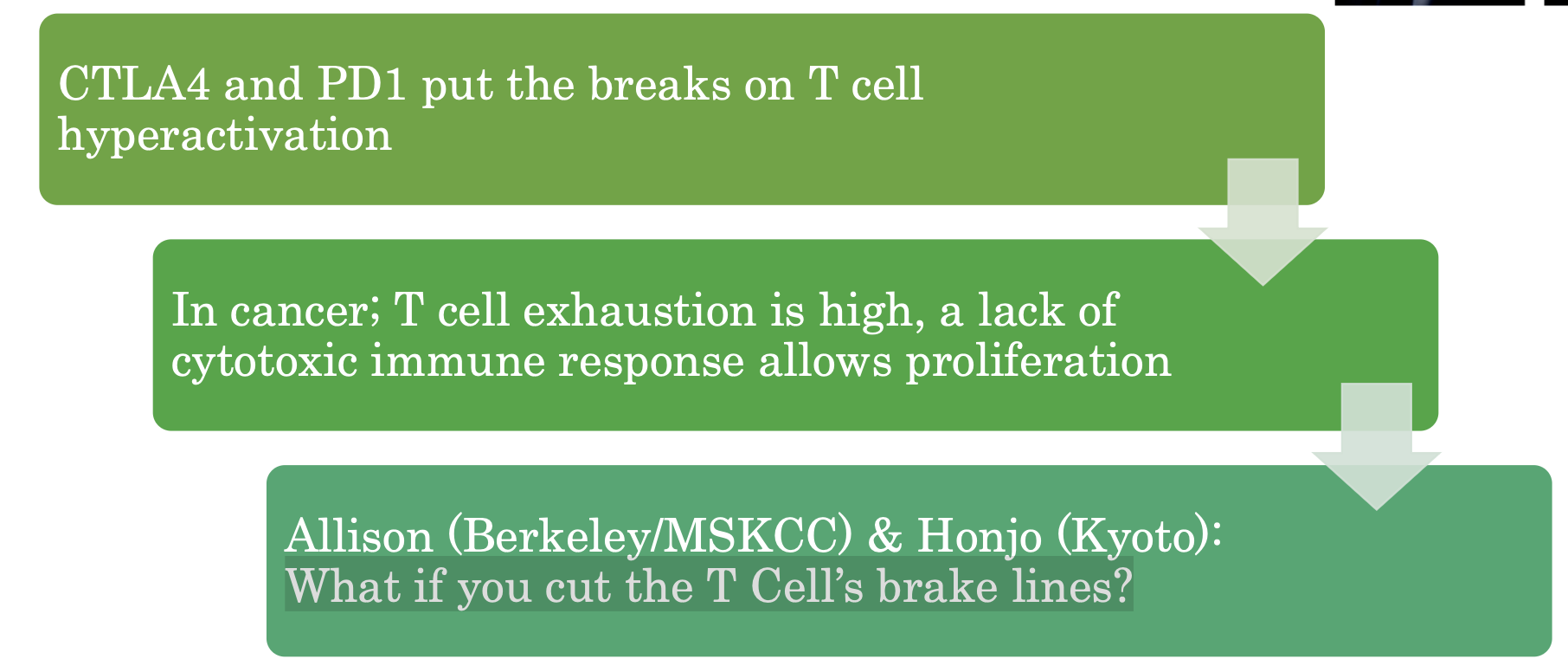
CTLA4: T. lymphocyte assoc.
protein 4
• PD1: programmed death 1
• CTLA4/PD1: Most potent T cell
immune checkpoints
• Prevent hyperactivation
What if you cut the T Cell’s brake lines?
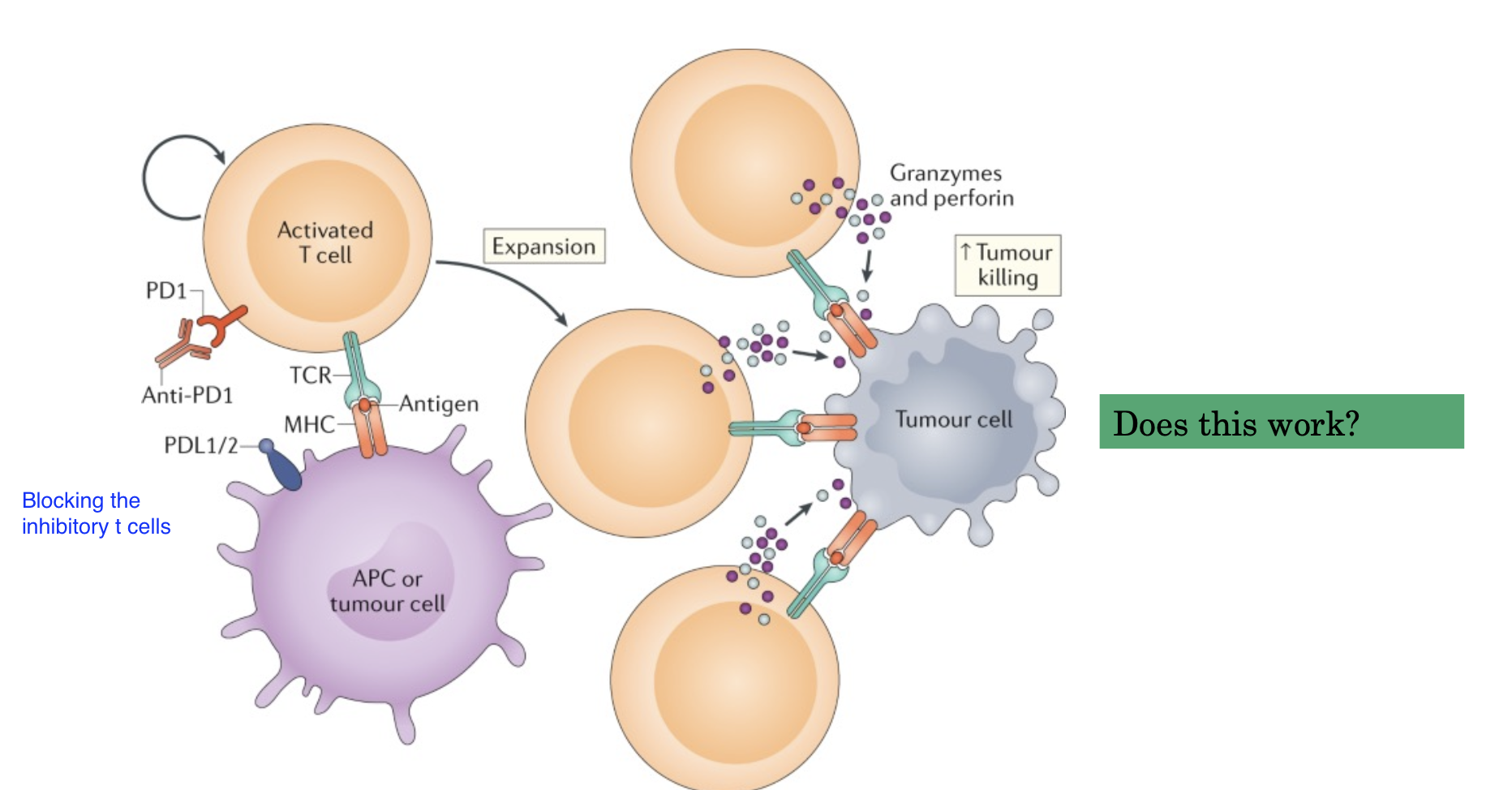
1996 Allison lab
Inject mice with colon carcinoma cells. Inject Anti-CD28, Anti-CTLA-4 or control Antibodies
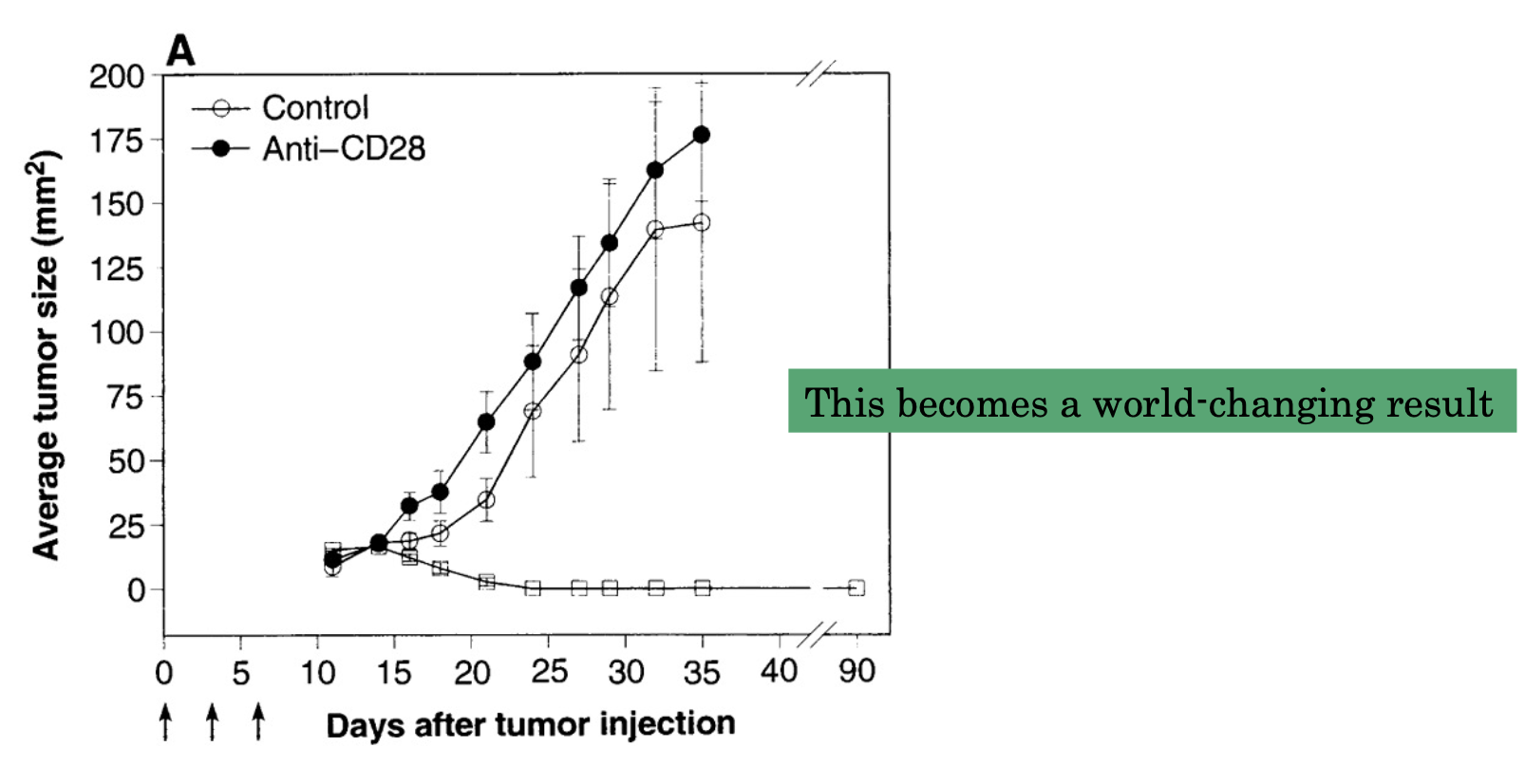
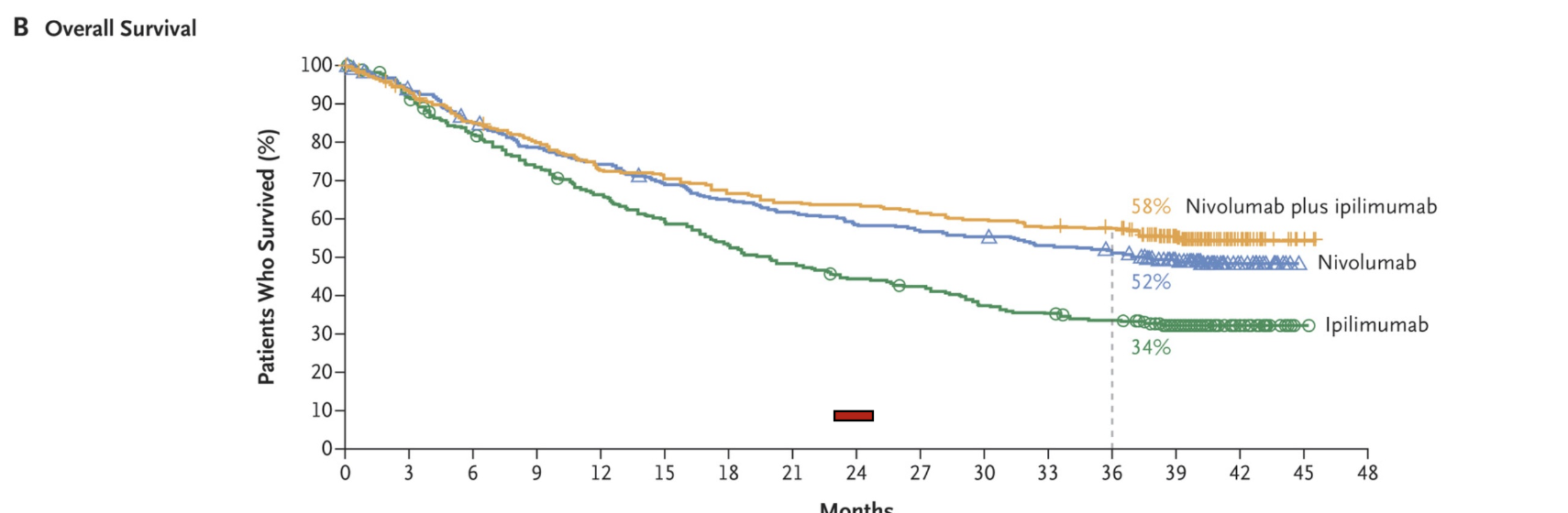
Combination immunotherapy
Previously, about 10% survival at 24 months
But not everybody responds to the checkpoint blockade. How can you ID responders and Non-responders?
Is dysbiosis during disease or antibiotic
use associated with lack of PD-1 blockade
response?
The microbiota has been implicated in response to chemotherapies
1. Disruption with antibiotics à less
response
2. Survival and response to cancer
immunotherapy is associated with
differences in the microbiome
Are these microbes causative?
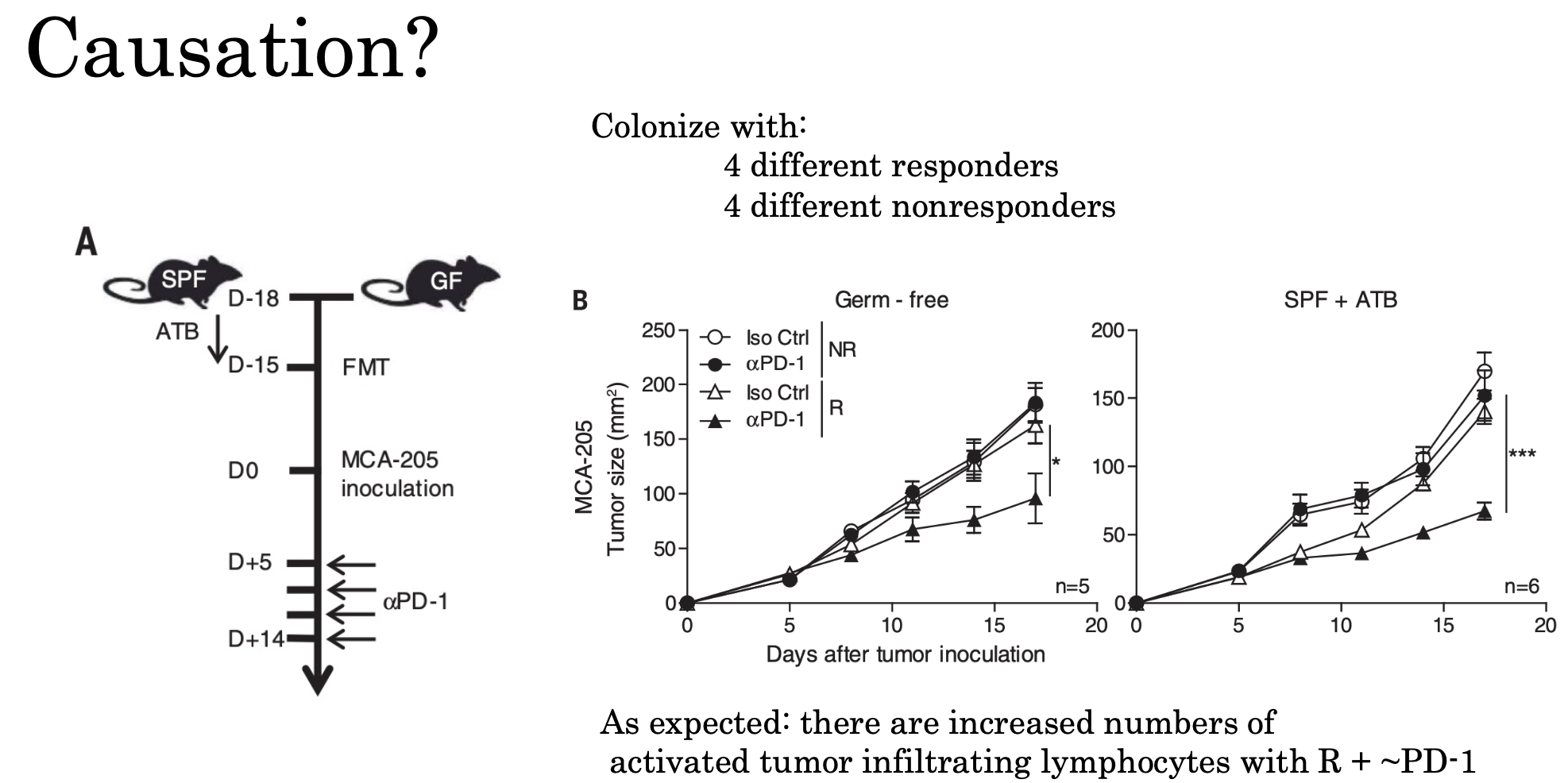
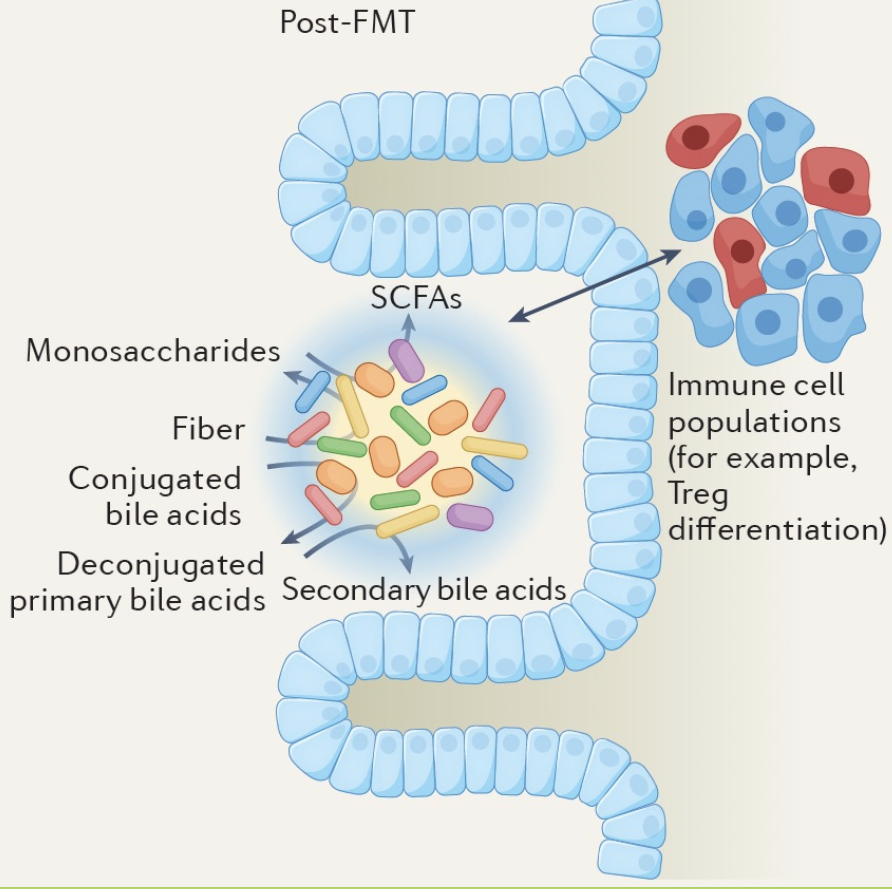
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT)
Transfer of complex, incompletely defined community of microorganisms
• Transfer from a healthy donor
• Screening for pathogens is critical
• Goal is the rapid re-establishment of community
• Actively investigated for a range of conditions;
• C. difficile
• Multidrug resistant infection Enterobacteriaceae
• Can be as high as 90% effective for treating recurrent C. difficile infections
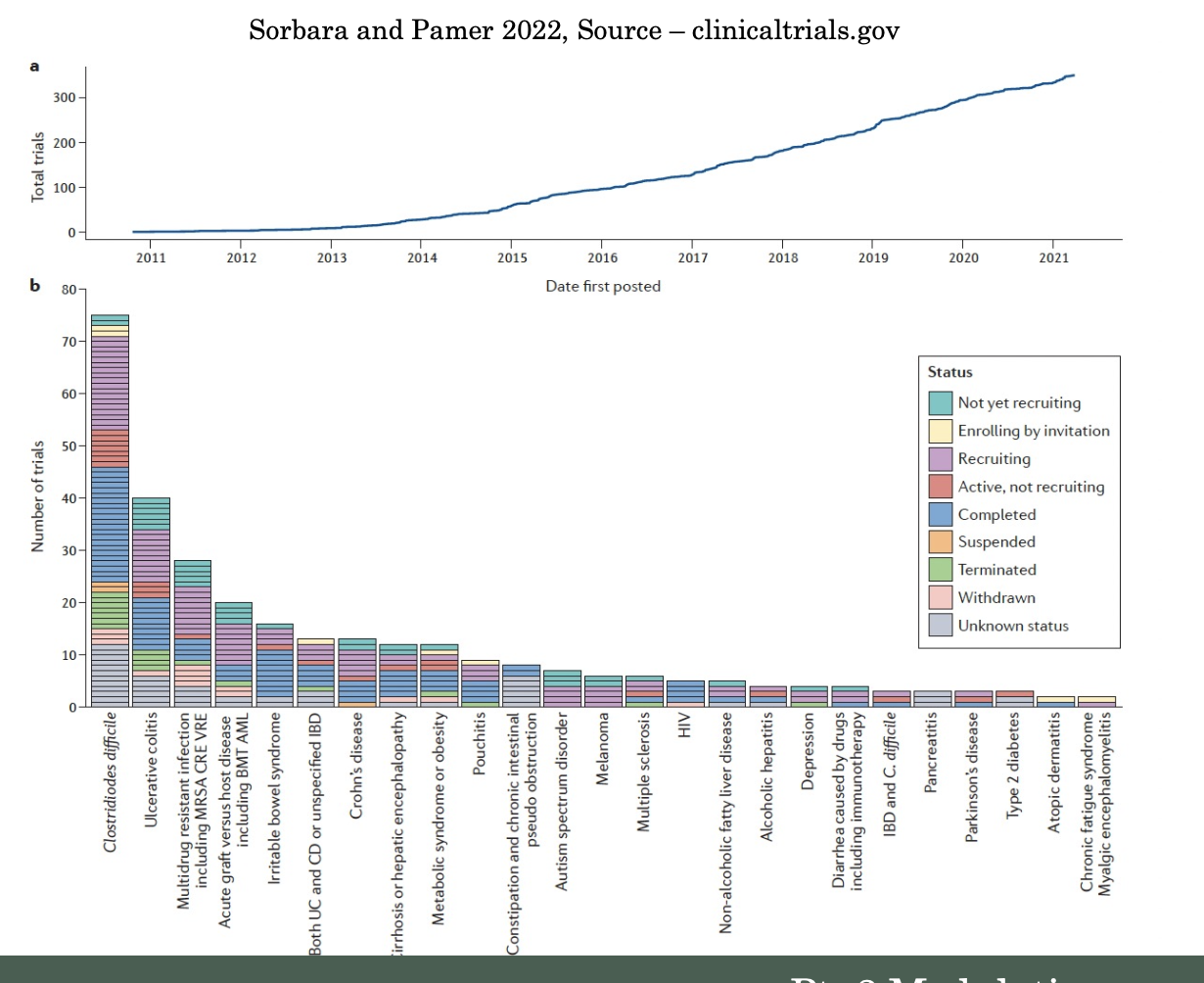
Concerns with FMT
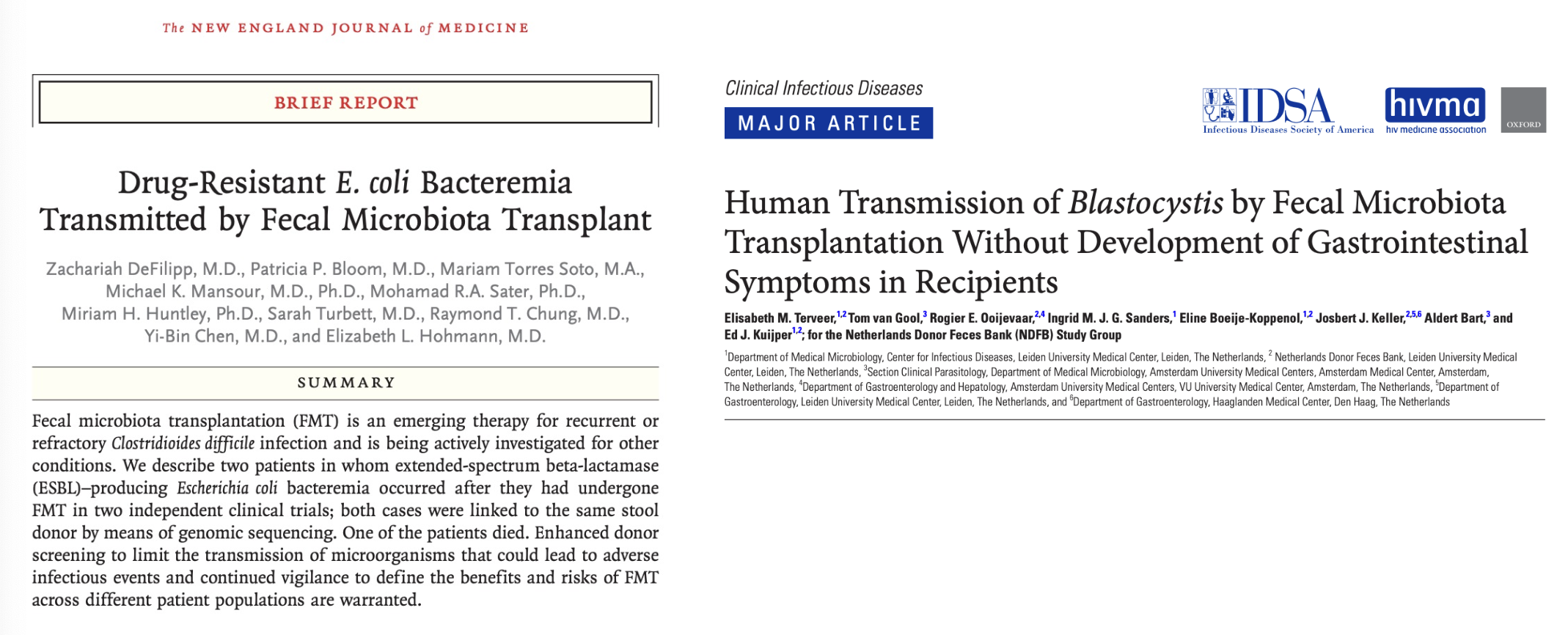
Classes of Microbiome-directed therapeutics
Supplementation of microbiota-target substrates
such as specific dietary fibers to promote a desired
compositional change in the microbiota, or
production of a desired metabolite
• Transfer of a group of isolates, selected or designed
to promote specific microbiota functions
• Transfer of bacteria that colonize the targeted site
and are engineered to have a desired function or
deliver a desired product/metabolite
• Direct supplementation with beneficial proteins or
metabolites (i.e SCFA)
Microbiome-targeted therapeutics
There is lots of excitement in developing microbiome-targeted therapeutics
• Two new first in class live biotherapeutics were FDA approved in 2023
• There is lots of work yet to do in developing microbiome-based therapeutics
• As we learn more about the interaction with the immune system, new opportunities