Cornea and Conjunctiva
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
into what foramen does the cornea insert
anterior scleral foramen
average refractive power of cornea
43 D (2/3 of total power of eye)
function of cornea
transmit and refract light
barrier against pathogens and edema
main refractive element of the cornea
interface between air and tear film due to it having the largest difference in index of refraction between 2 layers
gives cornea 44 D of power
tear/cornea interface gives 5 D, and cornea/aqueous interface gives -6 D
where is cornea thickest
periphery
WTR vs. ATR
WTR: steepest meridian is vertical
ATR: steepest meridian is horizontal
what happens to astigmatism with age
shifts towards ATR
probably due to loss of lid tension (cornea is not being flattened vertically)
average anterior and posterior radius of curvature and diameter
anterior ROC: 7.8 mm
posterior ROC: 6.5 mm
diameter: 11.7 mm
average thickness of cornea and individual layers
cornea: 550 microns
epithelium: 52 microns
Bowman’s: 8-14 microns
stroma: 450 microns
Descemet’s: 5-15 microns
endothelium: 5 microns
(remember 55, 15, 450, 10, 5)
4 layers of corneal epithelium
surface layer, wing cells, basal layer, stem cells
histology of corneal epithelium
non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium with 5-6 cell layers about 52 microns thick in total
what is the surface layer of the corneal epithelium composed of and how does it work
2 layers of non-keratinized squamous cells
how do the cells of the surface layer of the corneal epithelium function
contain plasma/cell membrane that secretes a glycocalyx
cells have microvilli and micro plicae that increase surface area and help stabilize tear film
what happens to the surface layer cells of the corneal epithelium as they age
slough off into the tear film
what do zonula occludens and desmosomes do
form tight barrier between cells to stop particles from moving between cells
what is the wing cell layer of the corneal epithelium composed of
2-3 cell layers with desmosomes that join cells to each other and to surrounding layers
what is the only mitotic layer in the corneal epithelium
basal layer
what is the basal layer of the corneal epithelium composed of
1 layer of columnar cells
what does the basal layer of the corneal epithelium do
secretes its own basement membrane (basal lamina)
what does the basal lamina attach to the basal layer of corneal epithelium with
hemidesmosomes
what does the basal lamina of the basal layer of the corneal epithelium attach to and how
attaches to basal layer via hemidesmosomes
attaches to Bowman’s via hemidesmosomes that penetrate Bowman’s and attach to ECM of stroma
what happens to the BM of the corneal epithelium with age
BM goes through reduplication and doubles in thickness by 60 years old
basal lamina vs reticular lamina
2 layers of a basement membrane
basal lamina: secreted by epithelial cells
reticular lamina: produced by underlying stroma cells in the corneawh
what 3 things increase the risk of recurrent corneal erosions (RCEs)
poor hemidesmosome attachments (BM)
EBMD
age-related BM thickening
what is the Palisades of Vogt
0.5-1.0 mm band around the limbus of the cornea at the same level as the corneal basal layer, where stem cells originate and migrate circumferentially to become basal cells
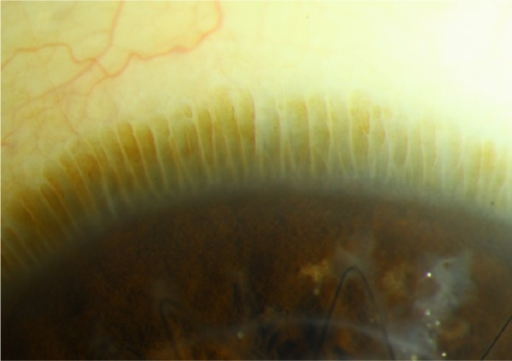
pathway of formation of the layers of the corneal epithelium
stem cells migrate circumferentially to become basal cells
basal cells produce BM and wing cells
wing cells migrate anteriorly to become epithelial surface layer
what conditions does limbal stem cell deficiency commonly affect and how
contributes to poor corneal epithelial maintenance
aniridia, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, alkali corneal burns
histology of Bowman’s layer
acellular layer made mostly of type 1 and type 5 collagen fibrils
how does Bowman’s layer respond to injury
Bowman’s is a tough layer that is resistant to injury
if injury does occur, Bowman’s cannot regenerate, resulting in a scar
Bowman’s layer (CAN/CANNOT) regenerate in response to injury
cannot
Bowman’s layer (IS/IS NOT) a basement membrane
is not
band keratopathy
calcium deposits in Bowman’s layer
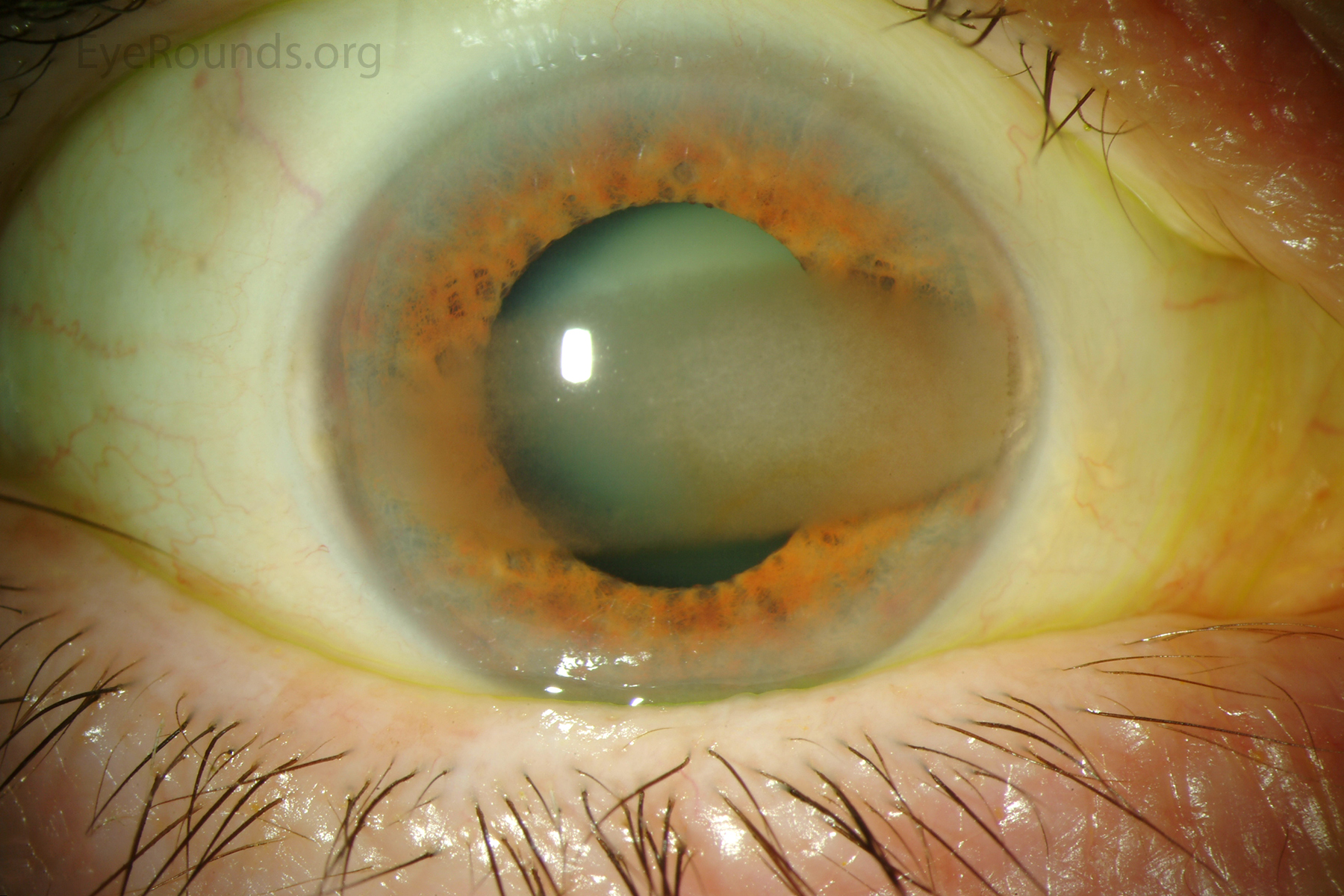
how do pterygia relate to Bowman’s layer
they destroy Bowman’s layer as they progress onto the cornea
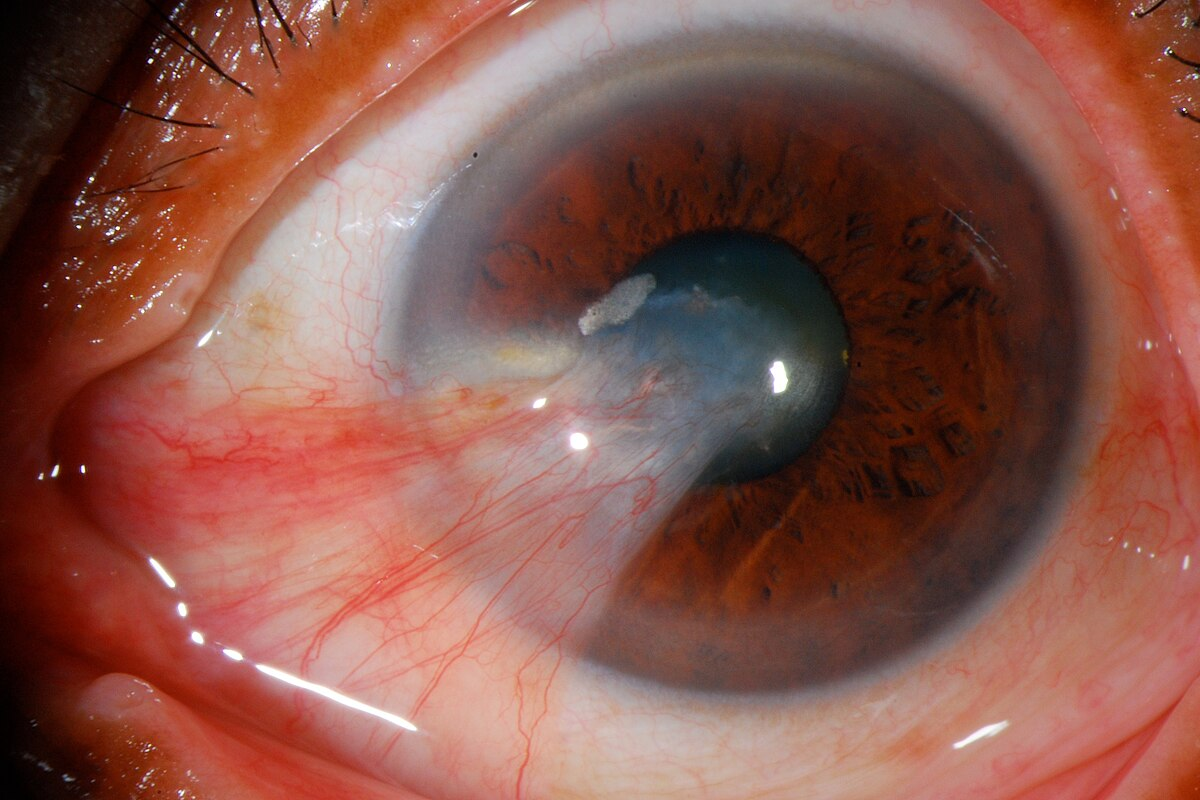
crocodile shagreen and what layers it involves
bilateral grayish white polygonal stromal opacities
involve stroma and possibly Bowman’s layer
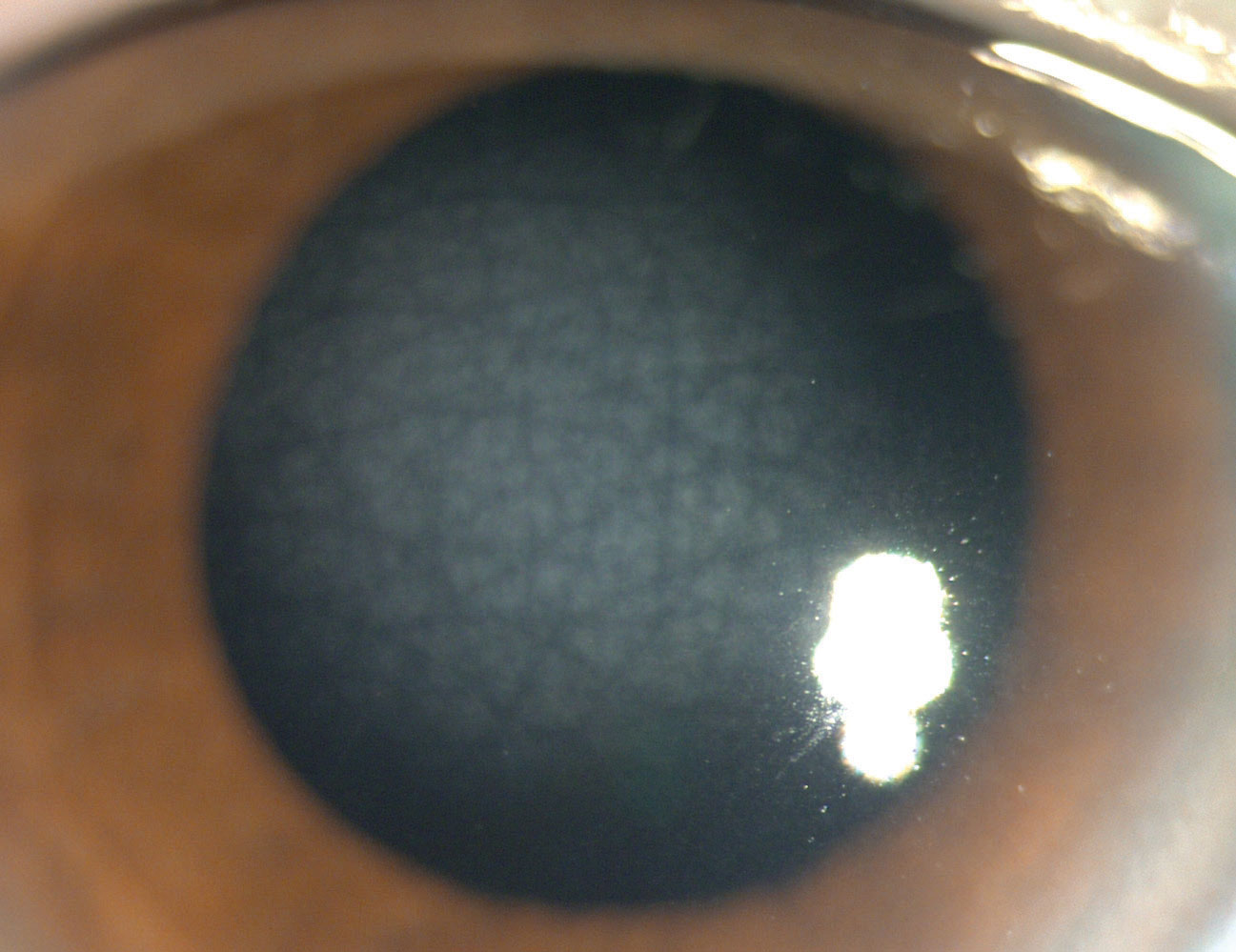
Reis-Buckler’s dystrophy
rare corneal epithelial dystrophy that appears early in life and is secondary to damage in Bowman’s layer
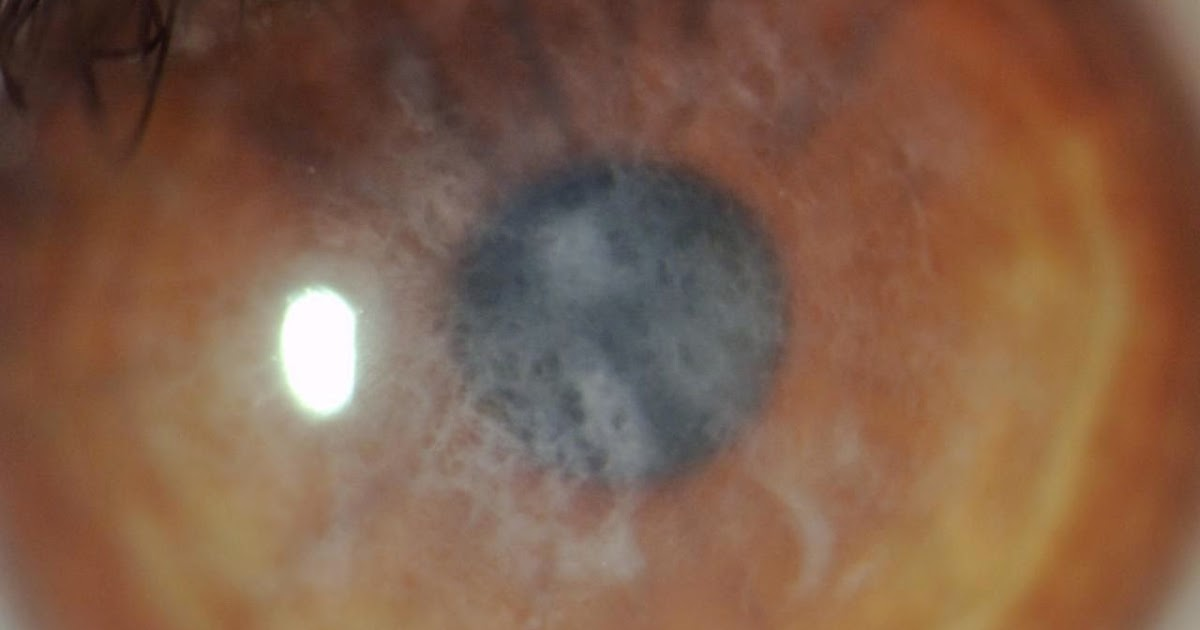
where does initial damage occur in Keratoconus
Bowman’s
damage to what epithelial layer causes hydrops in Keratoconus
ruptures in Descemet’s
why does PRK cause post-op corneal haze
laser applied goes through Bowman’s layer
what layers does the flap created in LASIK surgery impact
surface epithelium and Bowman’s layer
what is the substantia propria
another name for corneal stroma
what is the make up of corneal stroma
dense regular connective tissue
composed of keratocytes (fibroblasts), collagen fibrils, ground substance, and water
75-80% of the stroma is made up of _________
water
what are keratocytes and what do they produce
fibroblasts (cells that create CT) of the cornea
produce collagen fibrils and ECM
collagen fibril organization in the corneal stroma
200-300 layers of uniformly spaced lamellae that run parallel to corneal surface
collagen is mainly type 1
differences in anterior vs. posterior stroma
anterior 1/3: more cross linking makes it more rigid and able to maintain the corneal curvature
posterior 2/3: more organized with larger lamellae that have less cross linking results in higher incidence of corneal edema
higher incidence of corneal edema in the (anterior/posterior) stroma
posterior (more organized lamellae with less cross linking)
ground substance function in corneal stroma
filler between keratocytes and collage fibrils
has GAGs that attract water and allow collagen to maintain even spacing and transparency
what is the function of GAGs in the corneal stroma
GAGs attract water that help the collagen lamellae maintain uniform spacing, allowing the cornea to be transparent
what is the main GAG in the corneal stroma
keratin sulfate
what is descemet’s membrane
basement membrane produced by the corneal endothelium that increases in thickness with age
what is descemet’s membrane composed of
type 4 collagen
descemet’s membrane (IS/IS NOT) a basement membrane
is
what is the difference between bowman’s layer and descemet’s membrane in their trauma response
both layers are very resistant to trauma
while bowman’s definitely does not regenerate in response to trauma, descemet’s may regenerate in response to trauma
where does descemet’s membrane terminate and what does it become
terminates at the limbus
becomes Schwalbe’s line
Haab’s striae
folds in descemet’s membrane in congenital glaucoma
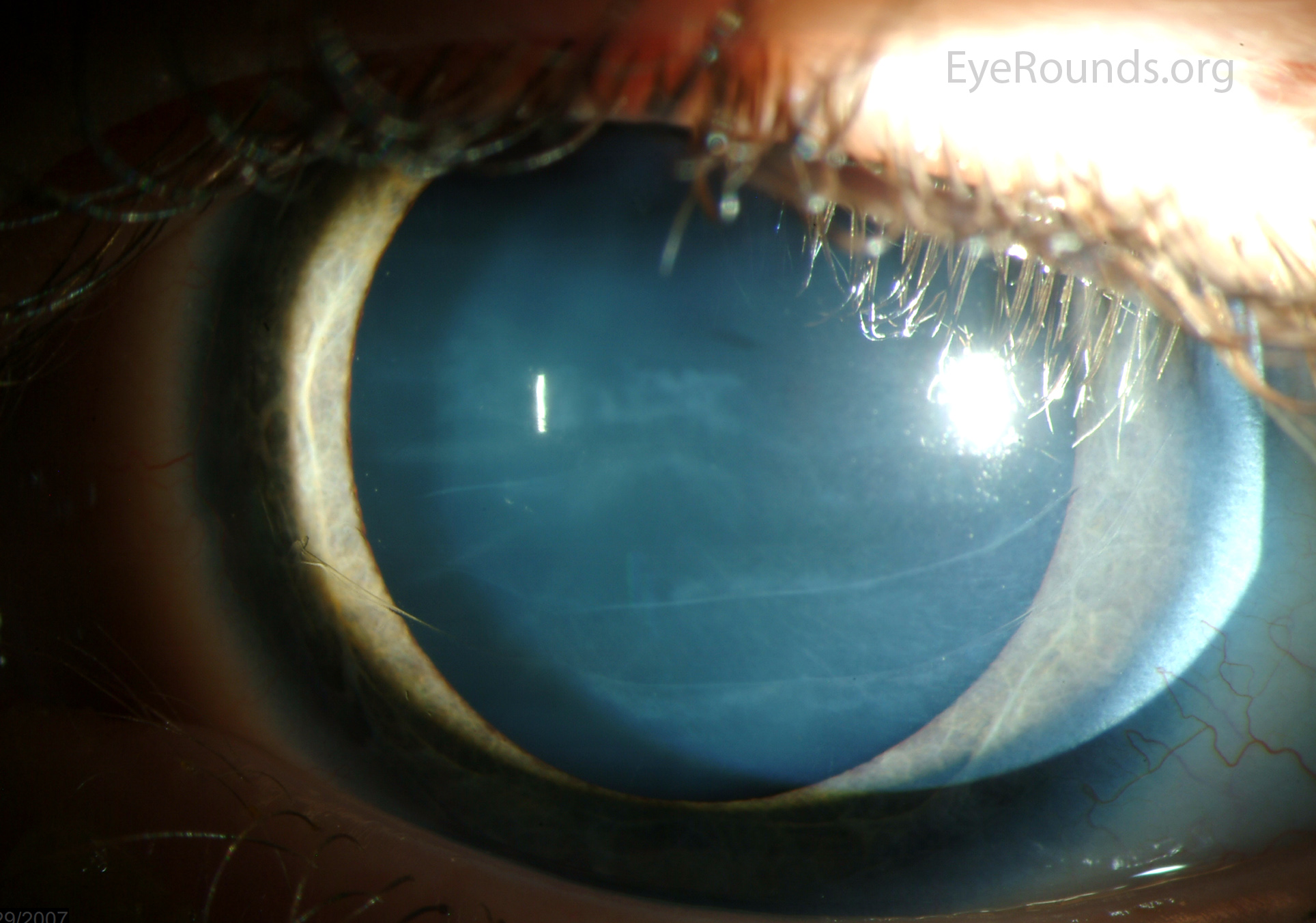
Hassall-Henle bodies
small areas of thickened descemet’s membrane in the peripheral cornea
extend into anterior chamber
called guttata when they appear centrally
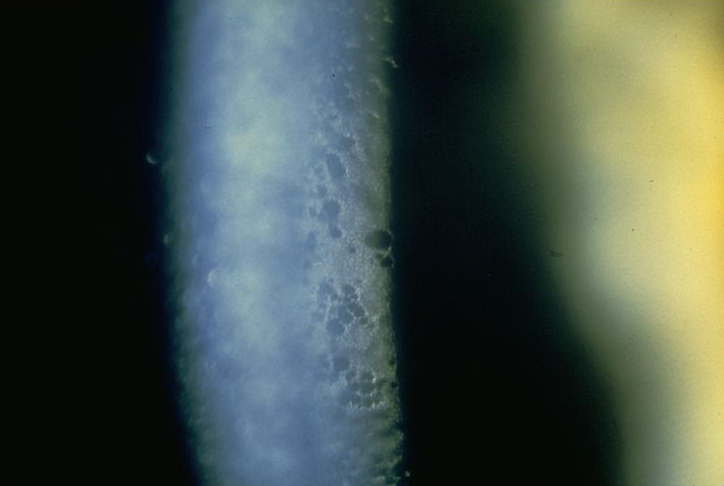
where is Dua’s layer located
between posterior stroma and descemet’s membrane
histology of corneal endothelial layer
1 layer of squamous cells about 5 microns thick
what pumps do endothelial cells have and what is their function
Na+/K+ ATP pumps
maintain corneal hydration and transparency by regulating water and ion flow between the aqueous humor and stroma
endothelial cells are rich in __________
organelles and mitochondria
endothelial cells are linked at their (apical/basal) borders by ____________ junctions
apical (face anterior chamber)
maculae occludens (also a few zonula occludens)
why do endothelial cells have maculae occludens junctions
they are weaker junctions that create a weak barrier, allowing for amino acids, glucose, and nutrients from the aqueous humor to enter the cornea
endothelial cells (DO/DO NOT) replicate
do not
what happens to endothelial cells with age
they decrease in number
change shape and change size to compensate for loss of density
change in shape of endothelial cells with age
pleomorphism
change in size of endothelial cells with age
polymegathism
why does stromal edema occur with age
loss of endothelial cells causes loss of Na+/K+ pumps
Na+/K+ regulate water and ion flow
what is the vasculature of the cornea
cornea is avascular
3 sources cornea gets its nutrients from
diffusion from aqueous humor
limbal conj and episcleral capillary networks
palpebral conj capillary networks
main source of oxygen for the cornea when the eye is open
tear film
has oxygen that has diffused from the atmosphere
main source of oxygen for the cornea when the eye is closed
palpebral conjunctival blood networks
what happens to the cornea when it is deprived from oxygen
corneal neovascularization
what factors encourage corneal neovascularization to occur
increase in cytokines and growth factors, including VEGF
where do new vessels stem from in corneal neovascularization
endothelial cells of limbal capillary network
what is corneal innervation responsible for in the cornea
proper wound healing
pain sensation
what cranial nerve is responsible for innervating the cornea
CN V1 (trigeminal)
what nerves provide corneal innervation
CN V1 > nasociliary nerve > long posterior ciliary nerves and short posterior ciliary nerves
LPCNs and SPCNs innervate the cornea
LPCN formation vs. SPCN formation
LPCNs branch right off of the nasociliary nerve
After the nasociliary nerve travels through the ciliary ganglion, SPCNs form
SPCNs form after the __________ nerve travels through _____________
nasociliary
ciliary ganglion
path for LPCNs and SPCNs to penetrate the cornea
SPCNs and LPCNs form a myelinated network of 60-80 nerves and enter the mid-stroma
travel 2-4 mm inside the stroma anteriorly
lose myelin sheath and penetrate Bowman’s to enter the epithelium
when do SPCNs and LPCNs lose their myelin sheath
as they penetrate Bowman’s layer to enter the corneal epithelium
where are nocireceptors found and what is their role
receptors found in corneal nerves when they penetrate corneal epithelium
mediate pain
why is the cornea so sensitive
corneal nerves lose their myelin sheath as they penetrate the corneal epithelium, leaving the nerves naked and highly sensitive
neurotrophic keratitis
damage of CN V1 causes poor corneal innervation
characterized by poor corneal wound healing and lack of corneal sensitivity (role of corneal nerves)
ulcer with no pain
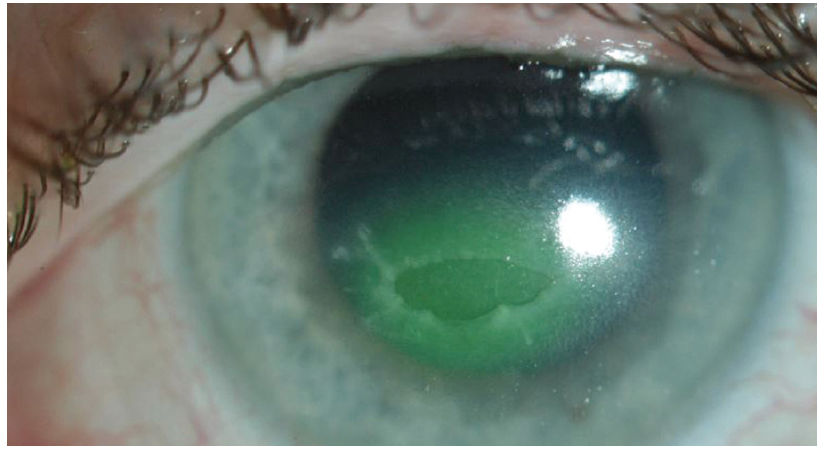
what diseases can cause neurotrophic keratitis
any diseases that damage CN V1
commonly herpes simplex, herpes zoster, CVA, diabetes
3 locations of corneal nerve networks
epithelium
anterior stroma/Bowman’s
mid stroma
nerve network in corneal epithelium
intraepithelial plexus
nerve network in anterior stroma/bowman’s
subepithelial plexus
nerve network in mid stroma
stromal plexus
where in the cornea are there no corneal nerves and why
posterior stroma, descemet’s, or endothelium
corneal nerves enter at the level of the mid stroma and travel anteriorly
where do corneal nerves enter the cornea
mid-stroma
4 main functions of the conjunctiva
protects the tissues of the lids and orbit
allows for lots of eye movement without damaging the soft tissues
antimicrobial
produces the mucin layer of the tears
what layer of the tear film does the conjunctiva produce
mucin layer
2 layers of the conj
stratified non-keratinized epithelial layer
submucosa
how does the histology of the conj epithelium change between the palpebral and bulbar conj
epithelial cells are cuboidal/columnar in the palpebral conj, and become squamous in the bulbar conj
conjunctival epithelial cells (increase/decrease) as you get closer to the limbus
decrease
what does does the stratified non-keratinized epithelial layer of the conj consist of
superficial cells containing melanin, microvilli, and goblet cells
what is the conjunctival submucosa
deeper layer of the conj made of loose CT and separated into 2 layers
2 layers of conjunctival submucosa
outer lymphoid layer
deep fibrous layer
contents and role of outer lymphoid layer of conjunctival submucosa
IgA, macrophages, mast cells, lymphocytes, PMN leukocytes, eosinophils, Langerhans cells
defends the eye against pathogens