3.6 government intervention
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Explain the role of the competition and markets authority (CMA)
The CMA is the UK's primary competition and consumer authority. It is an independent department with responsibility for carrying out investigations into mergers, markets and the regulated industries and enforcing competition and consumer law
impact of merger regulation
Choice
Avoids the build up of monopolies which may reduce range of choice
Price
Regulation prevents exploitation of consumers by powerful firms (closer to allocative efficiency)
Costs
Greater competition provides a stronger incentives to keep x-inefficiencies to a minimum
Innovation
Greater competition provides a stronger incentive for firms to innovate (dynamic efficiency)
price regulation to control monopolies
Monopolies raise price and restrict output compared to competitive markets – as a result they are allocatively inefficient
Allocative efficiency can be created by setting a maximum price where P=MC
Examples:
Train fares – some routes have been regulated this way
Water
RPI - X
Allow prices to increase at the rate of RPI but subtract an amount reflecting the efficiency gains that the regulator believes can be achieved by the firm
RPI + K
Takes the RPI and allows the addition of ‘K’ which is the additional capital spending a firm has agreed with the regulator is necessary
Water industry is regulated using RPI – X + K
price cap
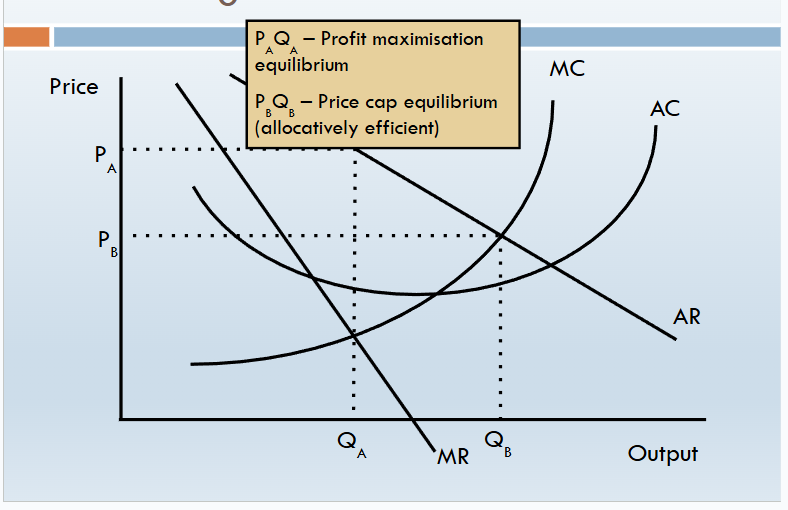
arguments for price capping
Prevents powerful monopolies from exploiting consumers via high prices
Cuts in price of necessity items increases affordability for consumers (particularly poorer households)
i.e. it increases allocative efficiency
Price caps create an incentive for firms to lower costs in order to increase profits (especially RPI-X)
arguments against price capping
Price capping distorts the price mechanism – could create supply issues in the long run
Regulators may lack accurate information for setting price caps
Capping prices reduces profits which could lead to reduced investment (dynamic inefficiency)
Under-investment could harm long run infrastructure
profit regulation
Set a maximum level of profit that can be earned
Typically this is done by taking the operating costs and adding a rate of return on capital employed
Used extensively in the US to control electricity and water companies
evaluate profit regulation
Regulators need to have a good understanding of costs and rates of return in the industry
The monopolist has more information than the regulator (asymmetric information) – it may attempt to present to regulators that costs are higher than they are
It creates little incentive to minimise costs
If they cover costs and earn a profit on capital employed it creates no gain to the monopolist to reduce costs as they are covered by the consumer
profit cap
quality standards
Where quality is an issue government can set quality standards to be met
In the UK the Post Office has a legal obligation to provide a daily letter delivery service to rural areas, despite the fact that it is a loss making activity
A company making decisions purely on profit maximising grounds would not provide the service
Electricity companies may be required to have enough capacity to prevent blackouts occurring
quality standards
Monopolies will try to resist or water down any quality requirements
Regulators need to ensure that standards are not set so high as to be too restrictive to businesses
Regulators need to have understanding of the industry to impose meaningful quality standards
performance targets
Similar in principle to quality standards
Governments may set targets for price, product quality or choice
Used in the UK for rail travel
Train companies given targets for the percentage of trains that arrive on time
problems with performance targets
Monopolists may find ways round meeting performance targets without actually making improvements
E.g. train companies could change timetables to appear that journeys are completed on time, even if journey times have not changed
explain the term regulatory capture and why may it undermine the governments efforts to control dominant firms in an industry
Regulatory capture is a form of government failure. It happens when a government agency operates in favour of producers rather than consumers.
how regulatory capture undermines government efforts to control dominant firms in an industry
Regulatory capture undermines government efforts to manage dominant firms by turning regulatory bodies into protectors rather than monitors. This results in the following issues:
Creation of Entry Barriers: Captured agencies often create strict licensing, permits, and compliance standards that protect incumbent firms from competition. These regulations raise the costs for new competitors, allowing dominant firms to maintain their market power.
deregulation to promote contestability
Removing government controls in order to promote competition and improve efficiency through lower costs
Fewer constraints on business should allow more flexibility and remove costly bureaucracy
Can lead to problem of private firms focussing only on profitable sections of the industry
E.g. rural bus routes disappearing after deregulation in 1980s