Unit Two AP World Pt 2
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Decline/ fall of western Roman Empire
(476)
Legal fall of empire
German king took over Italy and then later Roman Empire
He took the crown/scepter and sent it to the East as away to show he was ruling FOR the East (not true)
Let Roman administrators be
Germans eventually got overthrown
Created a new civilization
Feudalism started because _______
Of Viking and Magyar (Hungarian) raiders; Vikings were vicious and eventually disappeared; Muslims and Magyars attack
Feudalism (9th-10th century)
Relying on local military commanders instead of state power
these leaders became their own leaders and did not listen to the monarch
It was a political system
Manoralism- feudal pyramid
Large estates-manors had power (political, social, economic) that was exercised by warrior class of lan owning lords (vassals swore to protect kings’s or big shot lords)
Feudal pyramid rankng
king
Nobles
Knights| vassals
Peasants
ALL NOBLE MEN WERE KNIGHTS
NOBLES GET LAND WERE SUPPOSED TO SERVE KING
Abbots
Head of monastery
Urbanization ________
Decreased after fall of Roman Empire
Church
had its own legal system where clergy could be tried and represents independent institutions
Independent institutions
Powerful people often fought so merchants took over and had their own rules| city laws in place; some became independent city states
Parliaments|estates
Were used to embody the three estates
1 - clergy
2- landowning nobility
3- Commoners
Strengthened royal authority through consulting major social groups
At first only applied to nobility
Climate
Warmer weather in summer allowed for farmers|pastoralists to move to the highlands to herd their flock
Population of EU
Grew from 35 mil to 80 mil in 340 years during High Middle Ages
High Middle Ages
1000-1300
Caused the acceleration of social and economic change; education and urbanization got better
Serfdom pt 2
Many peasants were able to get out of serfdom bc of a greater stability and power of states over lords —> money over labor
Black Death
Created shortages of labor —> people alive demanded lower rents, wages, and labor conditions
Agriculture
Creation of
Heavy wheeled plow
Horse drawn plows
More effective collars
Three field crop rotation
All improved agriculture to support growing population. Also new land was made
Serfdom pt1
Had rights but tied to land
People received a small and such protection which was the most protection some people could receive
Post 1000: rise of Nation-States
Economic and political recovery
End of dark ages
A system of competing states started and had royal courts, beaucracies, and professional administration.
There were city states (Italy) and principalities (Germany)
Wars
Often brought death, destruction, and disruption to communities —> made roles|status of military men and lords
Gunpowder
Canons; firearms
Borrowed from china
EU was first to use it in canons
By 14th C had the most impressive arsenal
Naval technology
Magnetic compasses were taken from china
Advances in ship building, axel rudder, different kinds of sails, and navigational techniques helped further mastery of sea
Roman church
Influence was all over Europe; had laity
Hierarchy/ Network
Popes, bishops, priest;
Had a church in almost every community
Wealth/ power
Collected large amounts of land —> made the church powerful and funded the religious, educational, and charitable initiatives
Church big men e living lavish lives
People left money to the churhc
Continued fragmentation
(100 in NS)
Never united again like Rome
“Compared to china —> lots of unity”false
Flagellants
Believed the Black Death was a punishment form God
Atoned for sons through beating themselves
Pogroms
Violent reaction where they killed Jewish people
Environment of EU
Developments caused damage such as deforestation for fields overfishing, human waste pollution
Energy
After 1000, mechanical energy was used (cranks, flagwheels, camshafts) affected trade
Trade
Increase in energy caused agricultural expansion and long distance trade within Europeans Byzantium and Islam. Commercial bonds were formed between these people
Urbanization
Population of cities and towns grew
attracted new people and started universities
Division of labor
People do diferente jobs; always existed
Guilds
Associations of people pursuing the same line of work
Women of EU
Had more substantial opportunities
Were active in many urban professions
By 15th c —> artisian roles declined
Many were attracted to religious roles and therefore men’s power tightened over them (religious roles were often used as punishment)
Crusades
“Holy Wars”
Authorized by Pope
Started from a request of aid from the Byz. Emperor
Told people the real goal was to “take back the holy land from Islam”
Crusaders received an indulgence for their vows
Showed active engagement in other countries affairs
Papacy
All the bishops and popes
Indulgence
Immunity from lawsuits and moratorium on the repayment of debts
First Crusade| Jerusalem
1099
Happened in Jerusalem to get Islamic control away from Holy Land
Most famous crusade
Christians in 1098 started to attack in waves many Mediterranean countries
Pushed Muslims
Crusader States
Started after First Crusade
Four were carved out and last recaptured in 1291 by the Muslims
Failed very quickly
Consequences of crusades
Europe —> had very significant and long term consequences (people wanted what they had over in Islamic world; Muslim scholarship entered Europe
Rift between EOC and RCC deepened
Anti-semitism was expressed and acted on —> people said “God willed” the killings
Today —> ideas of what happened during crusades shapes ideas
Legal system in west
Provided measure of independence to many institutions, especially universities; reflected ancient traditions of Rome.started in Rome
Universities
“Zones of intellectual autonomy”
Scholars could research with some freedom from Church/ politics
Famous institutions (Cambridge, Salamanca, Oxford, Bologna, Paris)
Started because of a need for literacy in workforce
Professors guild instructed started degrees
Scholasticism
Attempted to reconcile classical philosophy ESPECIALLY ARISTOTLE and reason with the Christian faith
Aristotle
Made a deep impression on scholasticism—> work dominated the thought of Western Europe; the man of scholasticism and universities
Peter Abelard
French philosopher who founded nominalism and pioneered in ethics.
Wrote “Yes and No”
“Yes and No”
Talks about how we should question EVERYTHING
Including the Bible, regardless of what Pope says
THEY DID NOT LIKE HIM FOR SAYING DOUBT THE CHURCH
This questioning style pioneered scholasticism
Thomas Aquinas
1225-1274
Analyzed Aristotle’s ideas and made them work with Church dogma.
Doctor and saint of church
Wrote Summa Theologica
TA writing style
Had questions followed by objections and then replies to objections
Argument gives reason to claim
5 ways of St Thomas Aquinas
USED TO PROVE EXISTENCE OF GOD
Ex: Argument from motion
Some things are in motion
Whatever is the motion has been put into motion by another thing
No infinite chain of movers/ movees
So there is a first unmoved mover
This everyone calls God.
Italian Renaissance
Started in northern Italy
Used past inspiration
Had many great artists
“Rebirth” of classical greco-Roman literature

Who constructed the pieta
Michelangelo (p)

Who painted Saint Jerome and Saint John the Baptist
Masaccio (s)
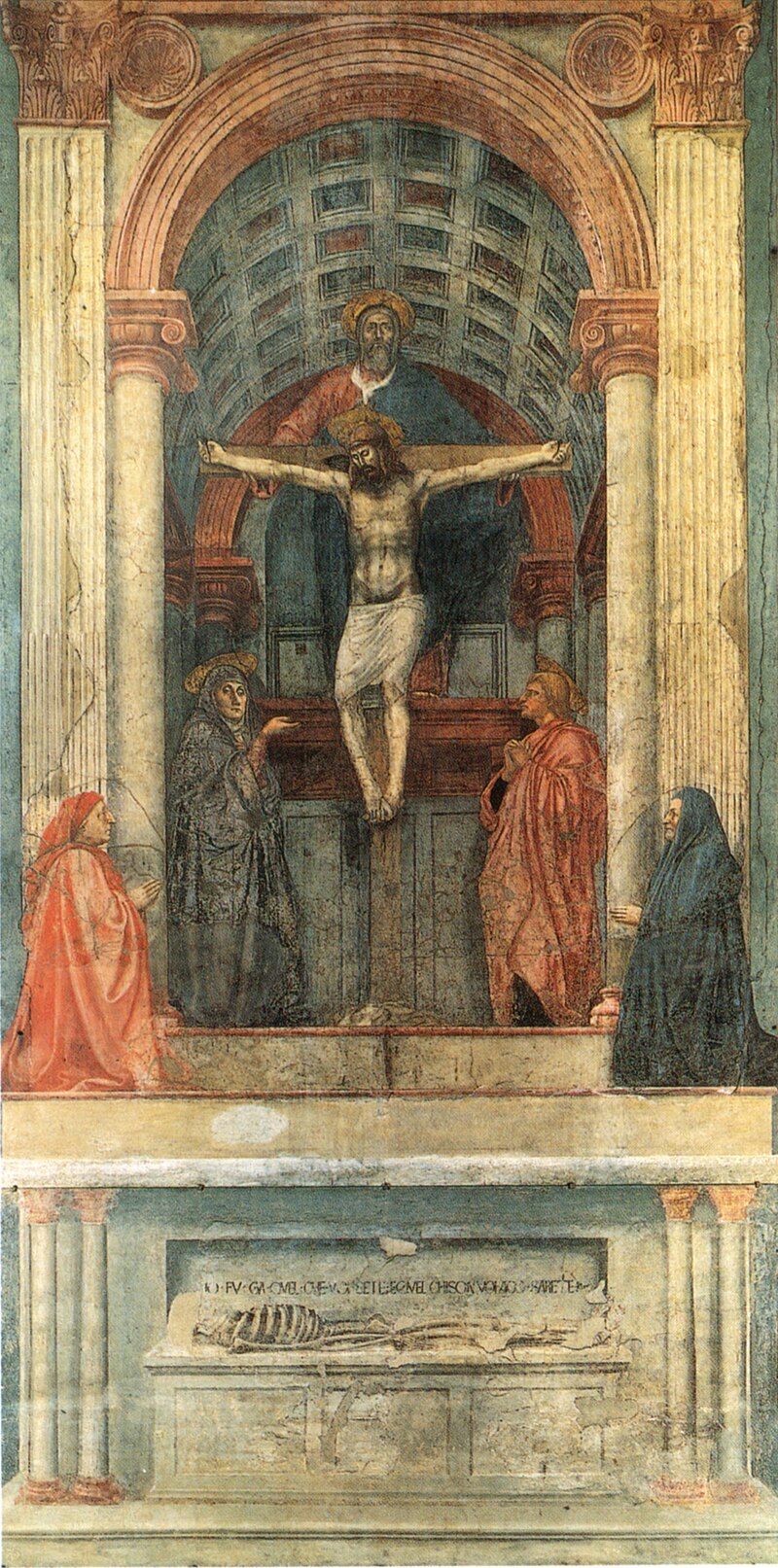
Who painted the trinity
Masaccio (T)
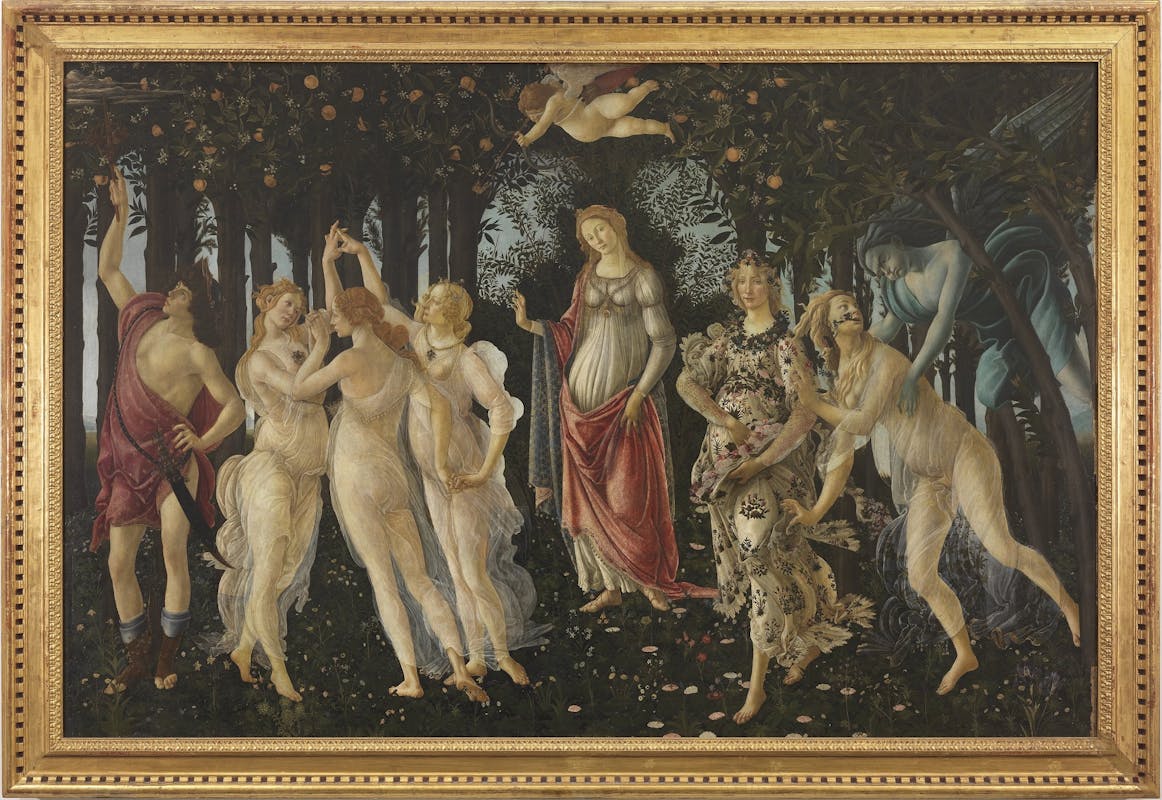

Who painted la primavera
Botticelli (p)

Who painted the birth of venus
Botticelli (v)
Who painted the last supper
Leonardo da Vinci (s)
Who painted the mona lisa
Leonardo da Vinci (m)
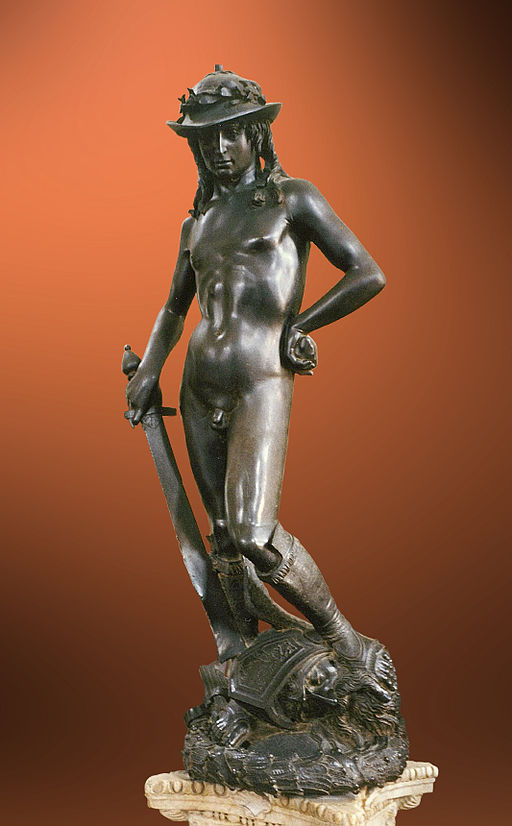

Who constructed this david
Donatello
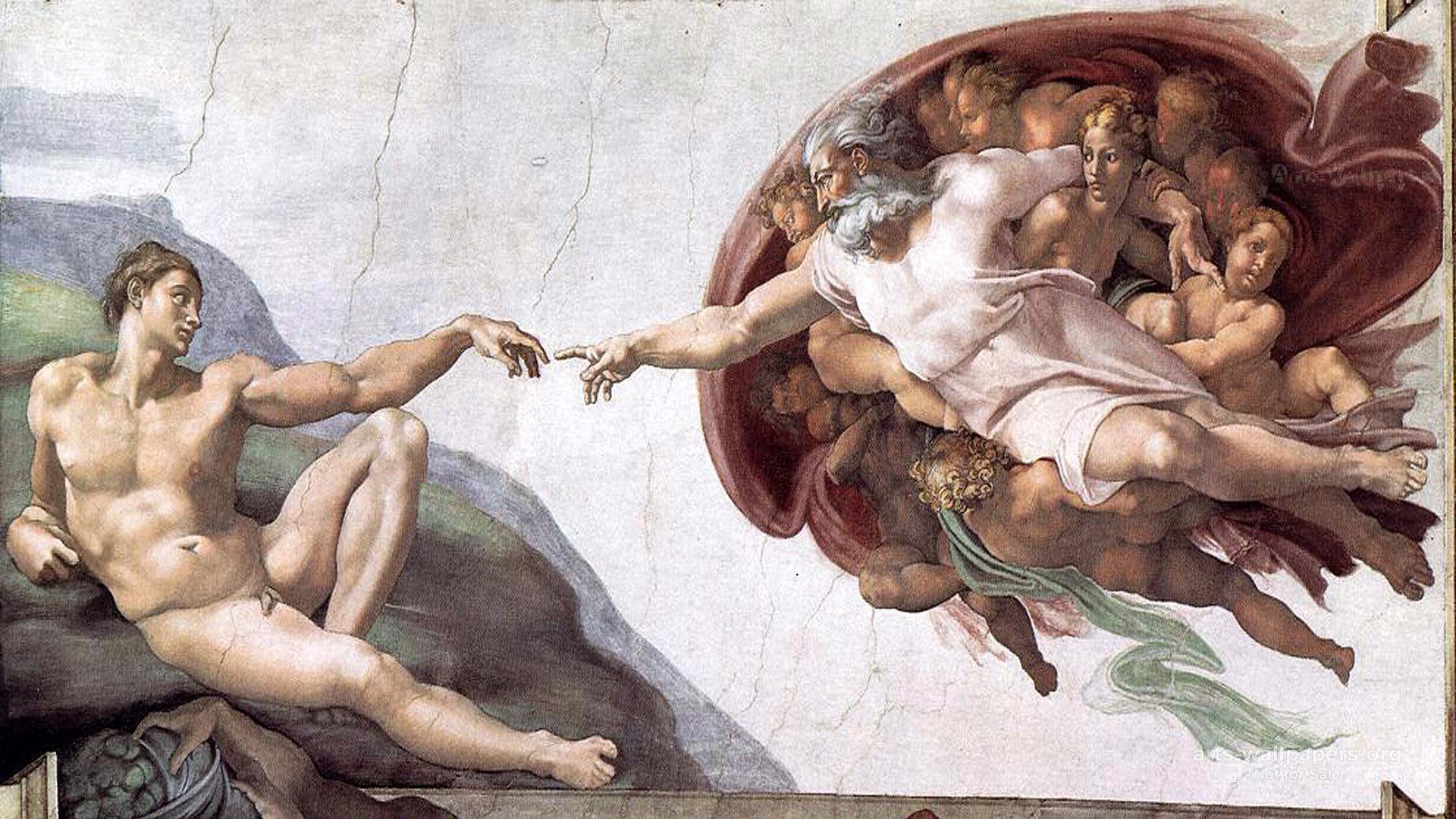
Who painted the Sistine chapel
Michelangelo (S)

Who painted the school of athens
Rafael
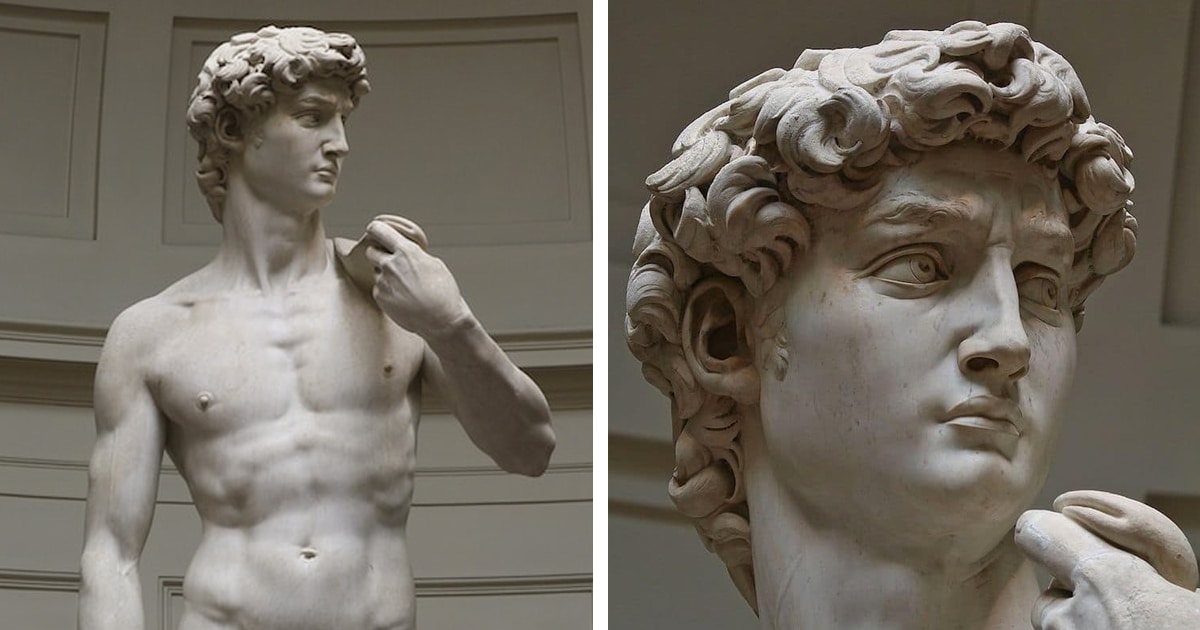

Who constructed this David
Michelangelo (D)

Who painted the dome of the cathedral of Florence
Brunelleschi
Mesoamerica / andes
The major civilizations of the Americas
Had very little contact with one another
Both witnessed the rise and decline of sophisticated states
Had intensive agricultural technology
Religions of similar deities
Human sacrifices were done for the gods
First major civilization here was the OLMEC (1200)
Maya
(250-900CE)
Found in Yucatán region of Mexico
Had an elaborate writing style and complex mathematical system
Consisted of highly fragmented political system Of city states, lords, and regional kingdoms
Mexica/ Aztec Empire
1345-1528
Last and largest of Mesoamerican states before Spanish conquest
Was this size because of mexica people
Mexica people
Semi-nomadic group who established themselves on a small island in Lake Texcoco
Tenochtitlán
Capital of Mexica empire; core population ~ 5-6 million
MESO conquests
Bought more of area within a single political framework
Government
Had around 5-6 mil people
Loosely strutted and unstable conquest state
Frequent rebellions
Had local imperial tribute collectors
Slaves/ warfare
(Usually captured during war)
Were destined typically for sacrifice which was crucial
Religion of Az
Sun was central to all life
Patron deity Huitzilopochtli
This deity lost energy and needed to be replenished through blood
Very proper for people to give their blood
Andes geography
Long, winding mountain train that sought resources through colonization, conquest, or trade.
This region also had deserts, rivers down the mountain, and a rich marine life.
The rivers made it hospitable
Inca Empire
Spoke quechua
Built empire along almost the entire spine of Andes Mountain
10 million people
Cared a lot about how their people lived
Bureaucratic / cultural integration
Inca had an empero at the top who was divine
Had 80 provinces w governors
State owned all the land “lands of the sun” alongside properties owned by temples, elites, and traditional communities
Cultural integration required people to learn Quechua and acknowledge Inca deities
Labor service (mita)
Had to stay on labor farms or herd
Most special were women who trained in Incan ideology and married to important men or were sacrificed
YOU HAD TO WORK OR GIVE GOODS AS TAXES
Gender parallelism
Two separate but equal spheres
This is not true
Civilization
The use of this word is believed to signify superiority and implies solidarity
Also claims that civilization brought inequality
However, egalitarianism never truly existed
Quipus
Used to record population; were string with balls of yarn
What did Machiavelli say it was better to be
He said it was better to be both, but because that was hard, try to be feared
What did Erasmus say a ruler should be
He said a ruler should be kind, and those who weren’t should prepare to go to Hell.
Machiavelli
Practical politician
Took over for Medicis
Was arrested for conspiracy to kill medicis
Was exiled and turned to writing
Erasmus
Catholic monk
Spent his days writinG
Urged reform in church
Later did not help Martin Luther with his reformation
Why did Machiavelli say a ruler should be feared
He said that humans are bad and are self-seeking and the fear inside them will always stay while love will not.
Why did Erasmus say a ruler should be loved
He said that he needs to act on the best interests of his people so he can stay in good favor with them. Probably inspired by Catholic beliefs.
Differences between medieval art and Renaissance art
Medical did not get proportions right, very pagan
Renaissance added shadows and depth, anatomically correct, and Christian