Test #1 : History of the Modern World
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
Paleolithic Era
Old Stone Age. Way of life guided by stone tools. Humanity dispersed out of Africa.
Paleolithic Peoples
Peoples who—despite the invention of agriculture—continued to live in Old Stone Age lifestyles.
Firestick Farming
The practice of deliberately setting fires to clear underbrush and reduce the risk of forest fires.
Affluent Gathering.
Practiced by early Northwest Americans (Chinook, Tulalip, Skagit). Thrived due to their bountiful environment.
Neolithic Era
New Stone Age. Marked by the emergence of agriculture + the transition from hunter-gatherer lifestyles to settled agricultural communities.
Neolithic Revolution
Wide-scale transition from hunter-gatherer lifestyles into agricultural settlements. Begins in Mesopotamia.
Fertile Crescent
Region in the Middle East. Between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers.
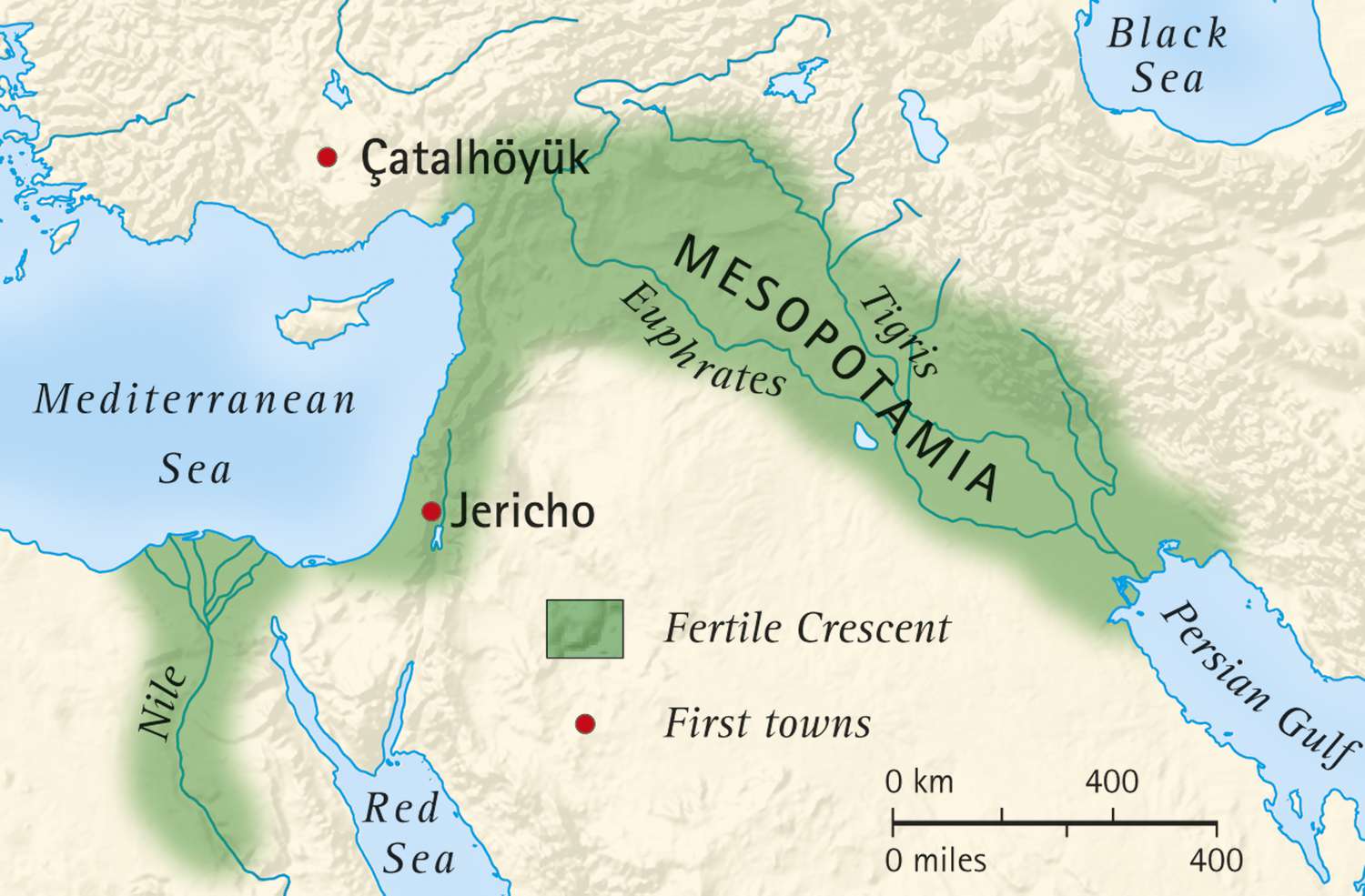
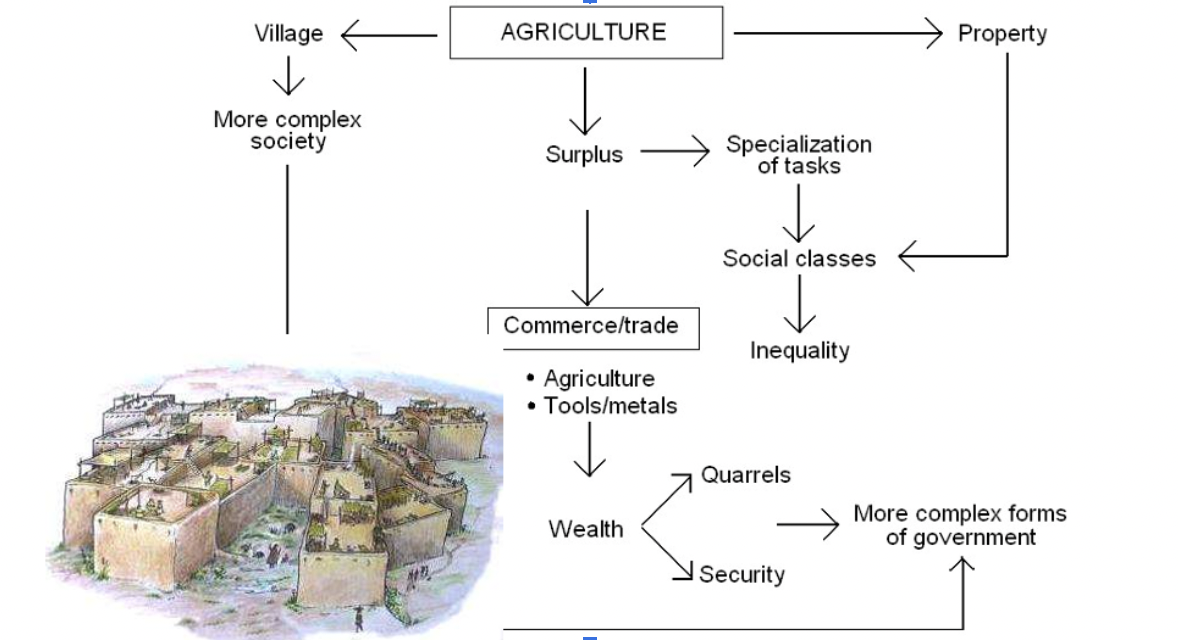
Agricultural Societies
Fully agricultural peoples organized in villages. Not yet kingdoms. Kinship-based.
Civilization
Process by which society reaches an advanced state of social and cultural development and organization
Cuneiform
The oldest known writing system, invented by the Sumerians and used on clay tablets for various purposes.
Hammurabi Law Code
Babylonian legal text codified by King Hammurabi. Introduced proportional punishment. Unequal punishment between social classes.
Epic of Gilgamesh
An epic poem from Ancient Mesopotamia that recounts the story of King Gilgamesh and his quest for immortality.
Pastoral Peoples
Nomadic peoples who relied on herding animals for their livelihood, such as the Hebrews, Mongolians, and Fulbe.
Igbo
Lived east of the Niger River. Rejected kings and ranked societies.
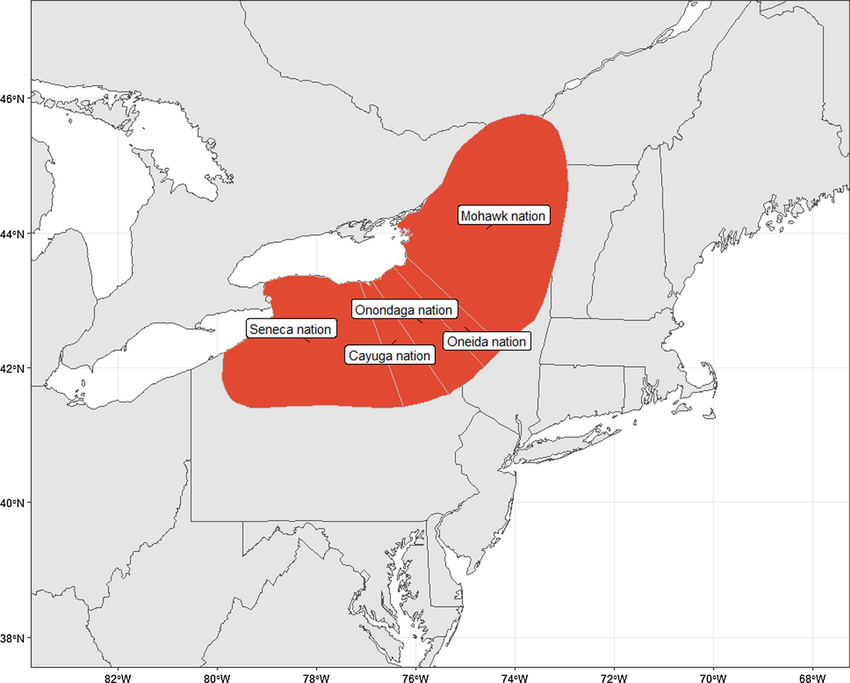
Iroquois
Matrilineal society united under the Haudenosaunee Confederacy. Adopted agriculture fully in the 1300s.
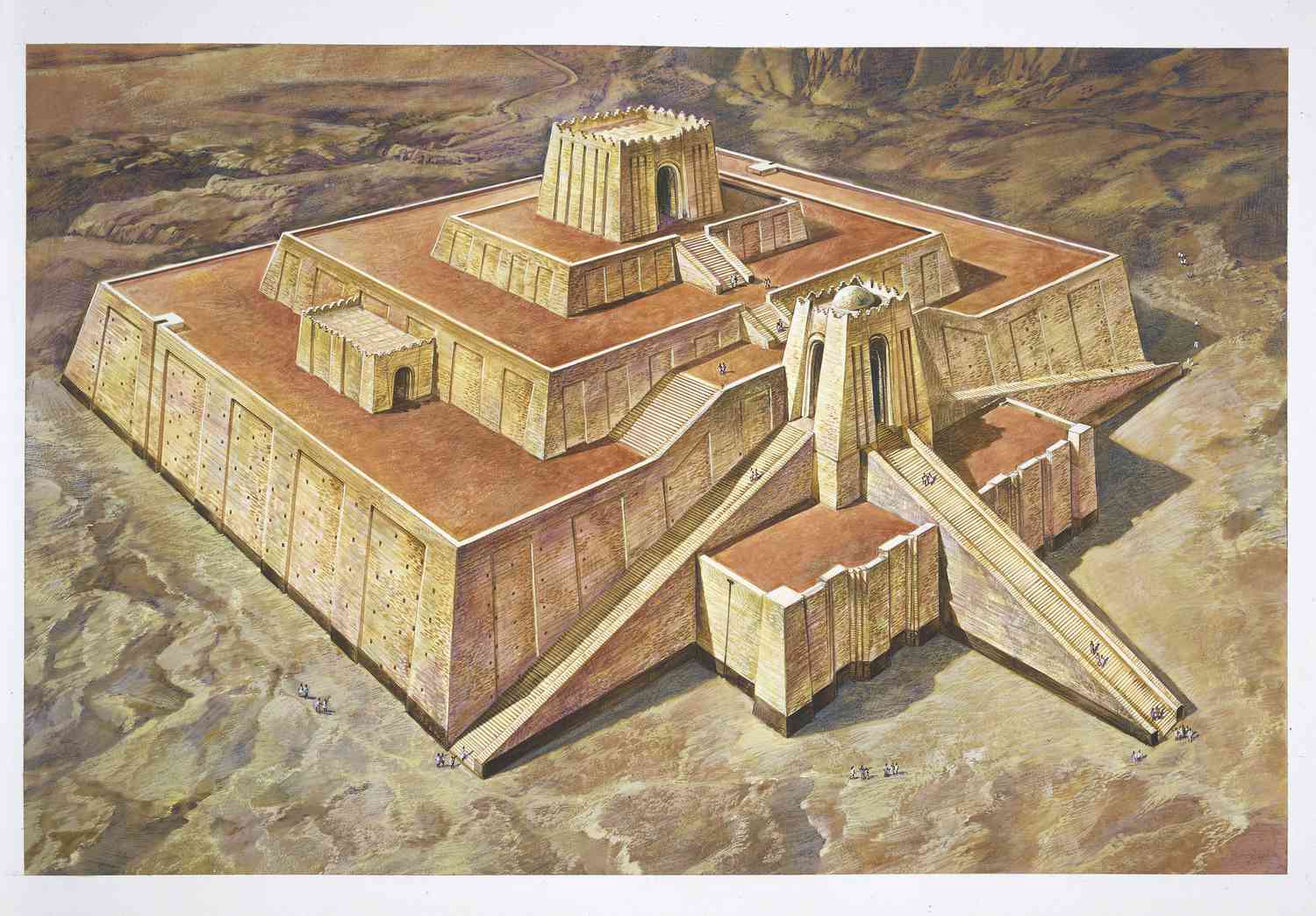
Ziggurats
Mesopotamian religious temples meant to pay homage to their Gods.

Pastoral Peoples
Nomads who travel with herds of livestock. Include the Hebrews, the Fulbe and the Mongols.
Hebrews
Known as the “landless peoples.” Remained a nomadic, pastoral tribe even as their neighbors were settling down.
Mongols
Pastoral peoples from the Mongolian steppes. Founders of the world’s largest empire.
The Fulbe
Largest pastoral people in West Africa. Led religious uprisings that rapidly expanded Islam.
Great Law of Peace
Assembly of Five Nations (Oneida, Mohawk, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca). Created to stem increased warfare since full agricultural adoption.
Minoans
Bronze Age civilization of Crete. Known for their peaceful society, advanced infrastructure, and the invention of a writing system.
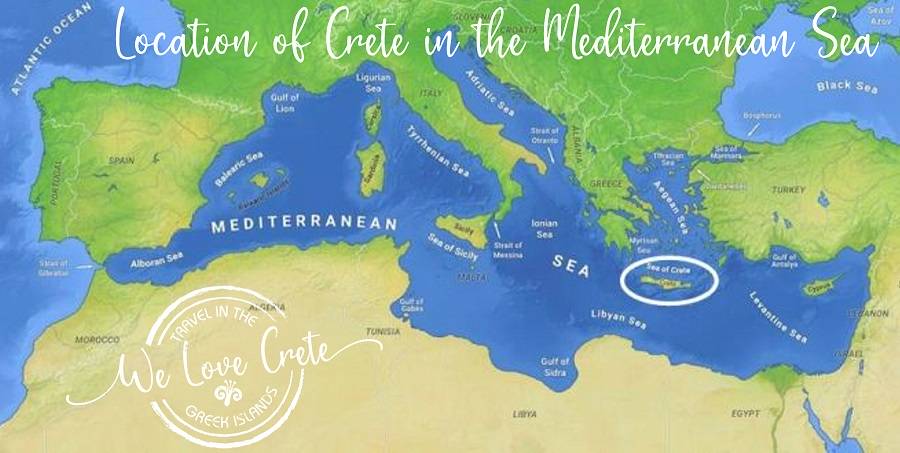
Ancient Greece
Collection of city-states with similar language, faith, and culture. Included Sparta, Athens and Thebes.
Athenian democracy.
Only adult male citizens could vote. Democratic institutions included the Archons, Boule, Ecclesia + the Helie.
Archons
Political leaders (10 men) elected by their peers. Corrupt leaders were exiled for ten years.
Citizens
Individuals granted citizenship in Ancient Athens if born to two Athenian citizen parents.
Ecclesia
The popular assembly of male citizens in Ancient Athens, where voting took place.
Boule
Council appointed to run daily affairs of the city. Group of 500 men chosen randomly.
Helie
Court of Justice in Ancient Athens.
Alexander the Great
King of Macedonia and the Greeks. Conquered the Persian Empire and spread Hellenistic influences.
Hellenistic Philosophy
Emergence of Epicureanism and Stoicism. Emphasized individual happiness and virtue.
Roman Empire
The lands and peoples subject to Ancient Rome. Evolved from a monarchy to a republic and eventually became an empire.
Struggle of the Orders
A political struggle in Ancient Rome where plebeians sought political equality with patricians. Led to expanded citizenship + the creation of tribunes.
Senate
Highest assembly of Ancient Rome. 300 senators named for life.
Patricians
Elite class in Ancient Rome. Wealthy landowners. Enfranchised.
Plebeians
Underclass of Ancient Rome. Majority of its population and its military.
Epicureanism
Disciples of Epicurus. Goal of life is pleasure; uninterested in public service.
Stoicism
Teaches the development of self-control as a means to overcome destructive emotions. Public service is noble.
Julius Caesar
Roman general and dictator who weakened the republic and paved the way for its eventual extinction under Augustus.
Magistrates
Elected officials of the Roman Republic. Headed by two consuls and (later) two tribunes.
Augustus
The first emperor of Rome. Founder of the Julio-Claudian Dynasty. Established absolute leadership and diminished the power of democratic institutions.
Antonine Dynasty
Oversaw 100 years of peace in Rome. Respected ruling class. Adopted capable men as their successors.
Appeal of Christianity
Spiritual equality. Promise of paradise. Handbook on “moral” life.
Causes of the Roman Empire’s Collapse
Christianity, Migration, Lead Poisoning, Plague, Slavery, Political Stagnancy, Barbarian Invasions.
Christianity
Religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Initially suppressed by the Romans but later adopted as the state religion.
Barbarian Invasions
Movements of Germanic peoples that contributed to the collapse of the Roman Empire. Triggered by Attila the Hun's rampage.
“Barbarian” Peoples
Ostrogoths, Visigoths, Gauls and Vandals.
Gender parallelism
Men and women operate in two different (but equal) spheres
Aztec Empire
Founded by the Mexica people. Conquered much of Central Mexico. Loosely structured and highly unstable.
Incan Empire
Largest state in the Western Hemisphere. Located in the Andes mountains. Bureaucratic empire that sought to assimilate its subjects.
Barbarian invaders
Eastern European invaders who ended the Roman Empire with the conquest of Rome by Odoacer in 476.
Byzantine Empire
Eastern half of the Roman Empire. Survived 1000 years after the West collapsed.
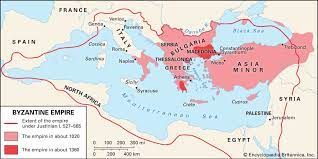
End of the Byzantine Empire.
Capture of Constantinople by the Ottomans (c. 1453).
Justinian I
Most important emperor of the Byzantines. Reformed the law code. Temporarily reconquered Italy. Heavily invested in infrastructure.
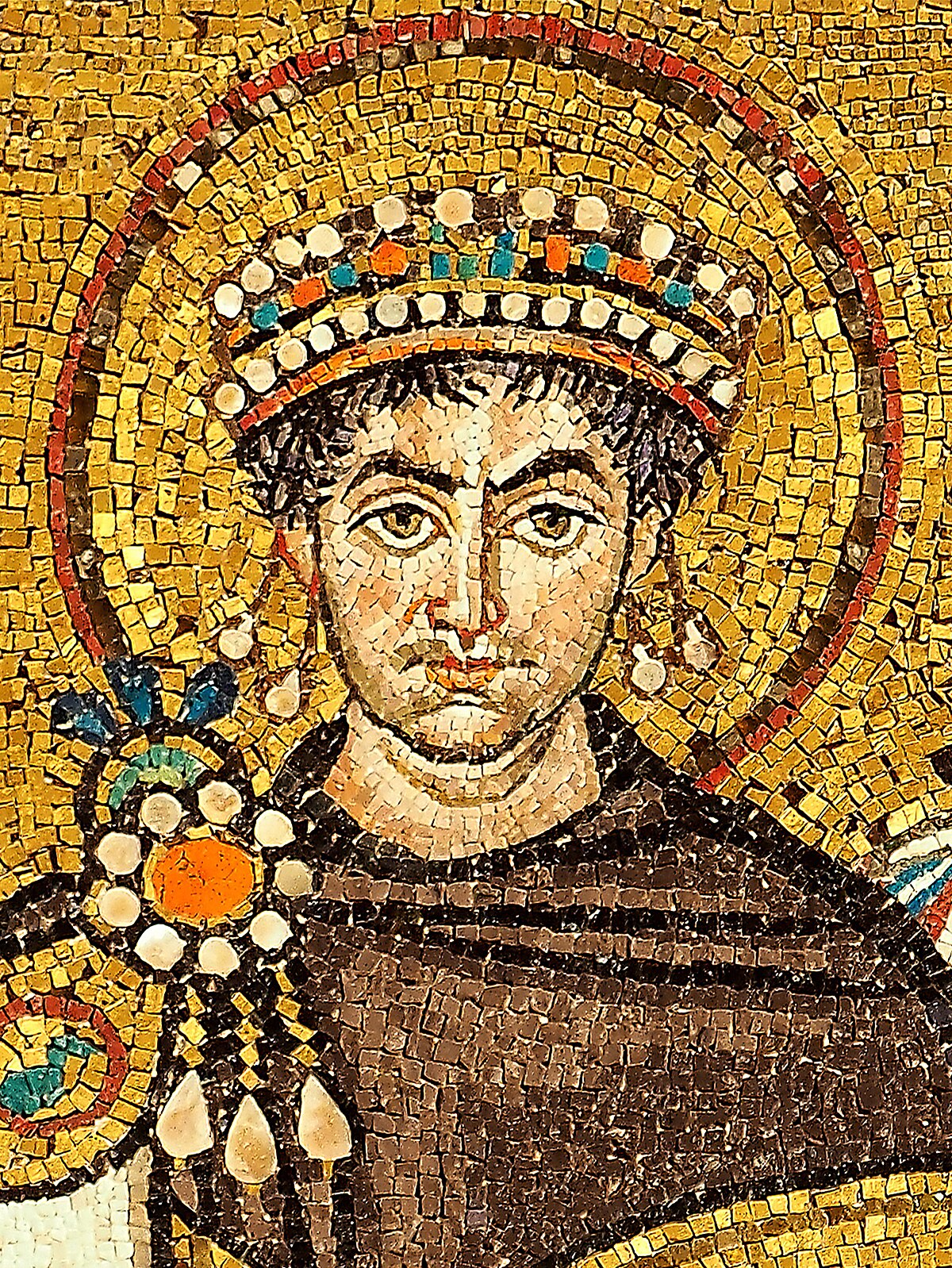

Justinian Law Code
Basis of modern civil law.
Theodoric
King of the Ostrogoths who became the absolute ruler of Rome in 493 after assassinating Odoacer.
Gauls (Franks)
Barbarian invaders from France. Established the most successful Barbarian state. Founded the Merovingian Dynasty.
Vandals
Barbarian invaders that settle in North Africa.
Visigoths
Barbarian invaders that settle in Spain. Promoted coexistence with Romans. Maintained its legal system.
Ostrogoths
Barbarian invaders that settle in Italy. End the empire (c. 476) with the conquest of Rome by Odoacer. Maintained segregation with Romans. LEAST successful Barbarian state.
Germanic Society
New society that emerged after the collapse of the Roman Empire, where family replaced the state as the most important social bond.
Germanic Customary Law
Legal system that regulated Germanic society, including the wergeld, compurgation, and ordeal.
Wergeld ("Man Money")
Monetary value established for a person's life in Germanic law, classified according to societal usefulness.
Compurgation
Group of oath-helpers who can certify an accused person's innocence in Germanic law.
Ordeal
Test of guilt by subjecting the accused to severe pain, taken as divine proof in Germanic law.
Merovingian Dynasty
Original Frankish dynasty established by Clovis I. Known as the "do-nothing" kings who delegated administration to the Mayor of the Palace.
Mayor of the Palace
Hereditary position in the Merovingian Empire tasked with running the state.
Carolingian Dynasty
Second Frankish Dynasty that reached its summit under Charlemagne. Eventually led to the rise of feudalism.
Charlemagne
Most prominent ruler of the Carolingian dynasty who expanded his territory through conquest and marriage and reformed the administrative system.
Counts
Temporary position tasked with overseeing the management of a specific province in the Carolingian Empire.
Missi Dominici
Inspectors who supervised regional administration and reported back to the emperor in the Carolingian Empire.
Feudalism
Contract between vassals and their lords. Promised land + protection in exchange for rent and labor. Emerged in the wake of increased conflict.
Collapse of the Carolingian Empire
After the death of Charlemagne’s son, the empire is divided among his three grandsons. Massive conflict results.
Serf
Agricultural laborer bound under the feudal system to work on their lord's estate, owed labor and rent to their lord, and received protection.
Ottoman Empire
Turkish empire that dominated much of the Middle East and North Africa. Ended the Byzantine Empire.
Siege of Vienna
End of Ottoman expansion into Western Europe (1524).
Janissary Units
Elite military units in the Ottoman Empire. Formed by thousands of kidnapped Christian boys.
Safavid Empire
Shia empire that ruled over modern-day Iran. Declared the Shia branch of Islam its state religion.
Technological innovations in the Age of Exploration.
The compass, the sextant and the sail.
European Advantage
European countries on the Atlantic (Portugal, Spain, Britain, France) were much closer to America than their Asian counterparts.
Motivations behind the Age of Exploration
Europeans were marginalized from Asian spice markets. Sought to bypass Muslim intermediaries on the Silk Road.
Great Dying
Widespread epidemics that wiped out a significant portion of the Native American population in the Americas.
Little Ice Age
Period of unusually cool temperatures that caused widespread crop failures, famines, and cold snaps.
General Crisis
Record-cold winters across the globe that sparked massive unrest and conflicts in various regions.
Cause of the Little Ice Age.
Demographic collapse in the Americas led to massive drop in CO2. Provoked significant global cooling.
Columbian Exchange
Widespread transfer of plants, animals, peoples, diseases, and cultures between Europe, Africa, and the Americas triggered by the Great Dying and the General Crisis.
Funding for the Industrial Revolution.
Natural wealth of the Americas.
Impact of Horses on Native American societies.
Dominance of bison hunting. Decrease in women’s status. Rise of the Comanche.
Mercantilism
An economic system where a country attempts to amass wealth through trade. Encourages exports over imports. Prioritizes the accumulation of precious metals.
Encomienda
A forced labor system that chained workers to haciendas
Chinese Expansion (1500-1700s).
Undertaken by the Manchu (Qing) dynasty. Did not seek to assimilate conquered peoples. Created the borders of contemporary China.
Manchu (Qing) Dynasty.
Conquered China in the wake of the General Crisis. Hailed from Manchuria, north of the Great Wall.
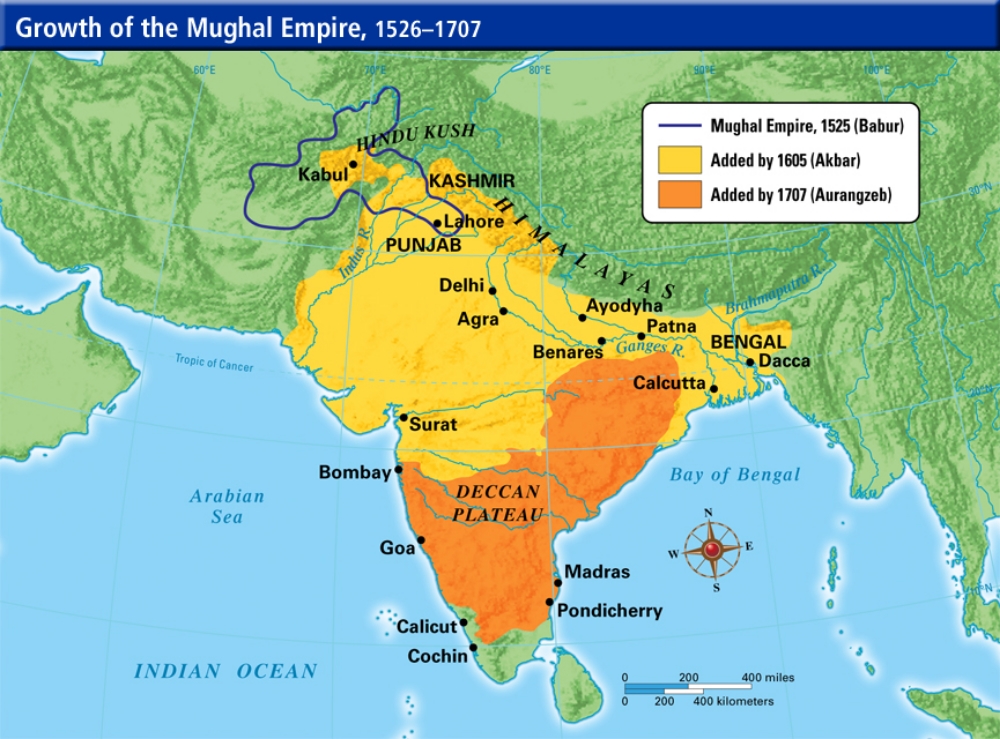
Mughal Empire
Muslim dynasty of Turkish and Mongol origin. Ruled India from the 1500s to the 1700s.
Akbhar the Great
Leader of the Mughal Empire. Sought to unite Hindu and Muslim populace peacefully.
Aurangzeb
Leader of the Mughal Empire. Reversed Akbhar’s policy of religious accommodation. Imposed sharia onto society and the court.