APUSH TOPICS 2.3, 2.4, 2.5 & 2.6 EUROPEAN COLONIZATION, SLAVERY, TRIANGULAR TRADE and INDIAN INTERACTION
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
Nathanael Bacon
Virginia settler and English aristocrat whose grievances with the Virginia colonial leadership led to a rebellion in 1676 that revealed the differences in eastern and western Virginia, landowners and landless free white men, and the continued encroachment of whites onto Indian land.

2
New cards
William Berkeley
Long time governor of Virginia from the 1640s-1670s whose leadership provided stability for the growing Virginia colony. However, his lack of sufficient response to continued Indian conflicts on the frontier led to major problems in his later years of governance.

3
New cards
Powhatan
The local American Indian tribes were part of a confederacy of smaller tribes under the leadership of a single chief. This confederacy faced intermittent conflict and peace with the Virginia colonists.

4
New cards
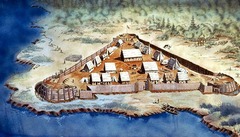
Jamestown
Funded by the Virginia Company of investors in 1607, this became the first permanent English settlement in North America.
5
New cards
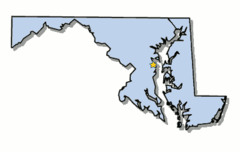
Maryland
The King of England granted proprietor George Calvert -- Lord Baltimore -- a tract of land surrounding the Chesapeake Bay as a potential real estate venture and haven for Catholics.
6
New cards
William Bradford
Early leader and governor of the Plymouth Plantation whose leadership enabled it to survive despite meager resources and difficulties.

7
New cards
Roger Williams
Puritan dissenter whose views got him exiled in 1636. He proceeded to found the colony of Rhode Island.

8
New cards
Plymouth Colony (1620)
A group of Separatist Puritans in England obtained permission from the Virginia Company to settle in British America. There they would form a colony in 1620 outside the Virginia Company's claim at this location.
9
New cards
Mayflower Compact
When the Pilgrims (Separatist Puritans) landed in 1620, they realized they had no legal basis settling where they did. As a result, they drew up this early document establishing a civil government and proclaiming their allegiance to the king.

10
New cards
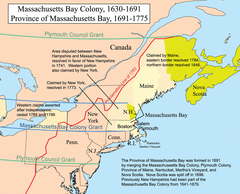
Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630)
Founded in 1630 under the leadership of John Winthrop among others, this colony became a haven for dissenting English Puritans. The first wave of settlers included 17 ships and over 1000 people --- mostly family groups --- to settle the colony.
11
New cards
headright system
In an effort to recruit new settlers to the Virginia colony, 50 acre grants of land were given to existing colonists and potential new colonists who were sponsored by colonial landholders.

12
New cards
King Philip's War
Major conflict in 1675-1676 when members of the Wampanoag tribe attacked English settlers in Massachusetts killing over 1000 colonists. The English responded with their Indian allies and eventually subdued the Wampanoag tribe and killed their chief, Metacomet.

13
New cards
Carolina Colony
After Charles II was restored to the English throne in 1660, he granted charters to eight individuals a title to land stretching from southern Virginia to the Florida peninsula. In honor of this, they named the territory after the king.
14
New cards
Anne Hutchinson
Puritan woman and dissenter whose teachings and views against church leadership and teachings had her exiled in 1637.

15
New cards
The Restoration
In 1660 the Stuart dynasty of the monarchy was put back into power in England after 2 decades of English Civil War and subsequent rule by English Protestants.

16
New cards
Barbados
Richest of the English possessions in the Caribbean, this Island was widely known for producing sugar cane.
17
New cards
Dominion of New England
In 1685, King James II attempted to seize control over the colonies of Massachusetts, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire by revoking their charters and making them all directly under the control of the crown. Stiff resistance followed and this temporary control was lifted in 1688 during the Glorious Revolution.
18
New cards
Georgia
Founded as a buffer colony against the Spanish, proprietor James Oglethorpe welcomed numerous petty criminals to this last of the original 13 colonies.
19
New cards
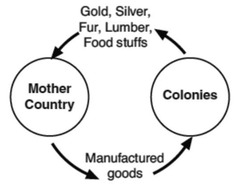
Mercantilism
The insistence of a mother country to monopolize trade with its colonies and funnel all wealth through and into the mother country. Focused on exports. Colonies were subject to the mother country and not independent in this system.
20
New cards
William Penn
As part of a debt owed to this man's father, Charles II granted him proprietorship over a huge tract of land in North America between New York and Maryland and insisted it be named after him.

21
New cards
John Winthrop
Early leader and governor of the Massachusetts Bay colony whose leadership enabled it to survive and develop into a thriving colonial government.

22
New cards
New York
As part of the growing English and Dutch competition in North America, the English challenged New Amsterdam in 1664 and captured it. They claimed New Netherland and renamed it.
23
New cards
John Rolfe
English entrepreneur who introduced tobacco to the Virginia colony. He also ended up marrying Pocahontas, daughter of the local chief Powhatan.

24
New cards
John Smith
Captain whose decisive and firm leadership included imposing work and order on Jamestown and also included organized raids on nearby Indian villages. He is credited with saving the colony of Jamestown in its earliest stages.

25
New cards
Pequot War
First major conflict between the Indians and Puritans in 1637 in which the English settlers and their Indian allies nearly destroyed the Pequot Indians in the Connecticut River valley.

26
New cards
Proprietary Colonies
Type of English colony where and individual or small group were given land and a great amount of authority and latitude to run the colony as trustees.

27
New cards
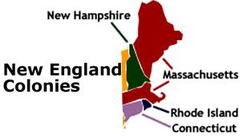
New England Colonies
Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, Connecticut, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire: Puritans, rocky soil, fishermen, tradesmen, families, community centered.
28
New cards
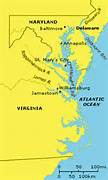
Chesapeake Colonies
Virginia and Maryland: Founded on the Chesapeake Bay along the east coast of the modern United States. Tobacco farming, plantations, Catholic haven, estates.
29
New cards
Middle Colonies
Pennsylvania, Delaware, New York, and New Jersey: Founded between New England and the Chesapeake. Agricultural, cosmopolitan [Dutch, Swedes, English, Jews, French].
![Pennsylvania, Delaware, New York, and New Jersey: Founded between New England and the Chesapeake. Agricultural, cosmopolitan [Dutch, Swedes, English, Jews, French].](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8bdca0a54c264a81898a756bafdd22ec.jpg)
30
New cards
Southern Colonies
Carolinas and Georgia, [Chesapeake - sort of], Transplants from the West Indies, haven for convicts, borderland between Spanish Florida, shipbuilding, haven for pirates [privateers], plantations, higher slave population.
![Carolinas and Georgia, [Chesapeake - sort of], Transplants from the West Indies, haven for convicts, borderland between Spanish Florida, shipbuilding, haven for pirates [privateers], plantations, higher slave population.](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/cac4716ed57c40dfbf62b36fd0d9a5ed.jpg)
31
New cards
West Indies
Barbados, Jamaica, etc. British sugar islands. Many planters from here, moved to the Carolinas importing their slave populations with them.
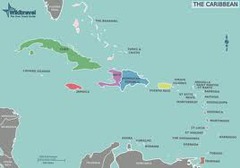
32
New cards
Royal Colonies
English colony that was under direct control of the crown.

33
New cards
Corporate Colonies
Colonies operated by joint-stock companies for the sole purpose of earning money for its investors.

34
New cards
Colonial Charter
Document given by a government (monarchy) granting the recipient(s) the right to settle a colony.

35
New cards
Restoration Colonies
Colonies that were given to supporters who helped restore Charles II to the British throne during the English Civil War. Included the Carolinas, New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware.
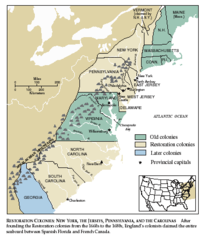
36
New cards
Act of Toleration (1649)
Passed in Maryland, it guaranteed toleration to all Christians but decreed the death penalty for those, like Jews and atheists, who denied the divinity of Jesus Christ. Ensured that Maryland would continue to attract a high proportion of Catholic migrants throughout the colonial period.

37
New cards
Holy Experiment
William Penn's term for the government of Pennsylvania, which was supposed to serve everyone and provide freedom for all.

38
New cards
Charter of Liberties (1701)
Guaranteed Pennsylvanians freedom of worship and unrestricted immigration.

39
New cards
Tobacco
Cash crop that made a profit and saved Jamestown
40
New cards
Headright System
Virginia Company's system in which settlers and the family members who came with them each received 50 acres of land. Attracted more settlers to the colony.

41
New cards
Separatists/Pilgrims
These religious dissenters of the Church of England believed it could not be reformed and thus wanted to organize a completely separate church independent of royal control that did not have Catholic influences. They fled to America and settled in Plymouth.

42
New cards
Great Puritan Migration (1630-1640)
Many Puritans migrated from England to North America during the 1620s to the 1640s due to belief that the Church of England was beyond reform. Ended in 1642 when King Charles I effectively shut off emigration to the colonies with the start of the English Civil War.
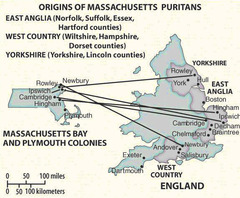
43
New cards
Thomas Hooker
A Puritan minister who led about 100 settlers out of Massachusetts Bay to Connecticut because he believed that the governor and other officials had too much power. He wanted to set up a colony in Connecticut with strict limits on government.
44
New cards
James Oglethorpe
Founder and governor of the Georgia colony. He ran a tightly-disciplined, military-like colony. Slaves, alcohol, and Catholicism were forbidden in his colony. Many colonists felt that Oglethorpe was a dictator, and that (along with the colonist's dissatisfaction over not being allowed to own slaves) caused the colony to break down and Oglethorpe to lose his position as governor.

45
New cards
Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
Set up a unified government for the towns of the Connecticut area (Windsor, Hartford, and Wethersfield). First constitution written in America.

46
New cards
Virginia House of Burgesses (1619)
First representative assembly in the American colonies. Representatives immediately began to enact laws and to safeguard the individual rights. Setting precedent in the colonies for individual rights protected by law ( British law did not provide for individual rights.)

47
New cards
rice-growing plantations
large plantations in South Carolina worked by enslaved Africans that resembled the economy and culture of the West Indies

48
New cards
Triangular Trade
A three way system of trade during 1600-1800s Africa sent slaves to America, America sent Raw Materials to Europe, and Europe sent Guns and Rum to Africa
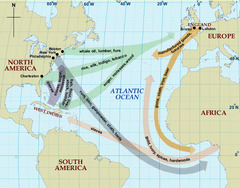
49
New cards
Middle Passage
A voyage that brought enslaved Africans across the Atlantic Ocean to North America and the West Indies

50
New cards
Navigation Acts
Acts passed in 1660 passed by British parliament to increase colonial dependence on Great Britain for trade; limited goods that were exported to colonies; caused great resentment in American colonies.
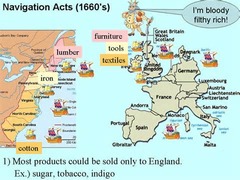
51
New cards
Salutary Neglect
British colonial policy during the reigns of George I and George II. Relaxed supervision of internal colonial affairs by royal bureaucrats contributed significantly to the rise of American self government

52
New cards
Glorious Revolution
A reference to the political events of 1688-1689, when James II abdicated his throne and was replaced by his daughter Mary and her husband, Prince William of Orange.

53
New cards
Indentured Servants
Colonists who received free passage to North America in exchange for working without pay for a certain number of years

54
New cards
Slave Laws
A set of statutes passed throughout the colonies to keep African Americans in bondage for life. Racism was soon integral to the colonies.
55
New cards
Increased demand for slaves
1. Reduced migration due to increased wages in England reduced supply of immigrants 2. Dependable work force which was a result of the scare of Bacon's Rebellion in 1676 AND possibility for indentured servants to revolt 3. Cheap labor force to grow labor-intensive rice and indigo