Psychology Biopsychology | Neurones
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Neurone structure
.
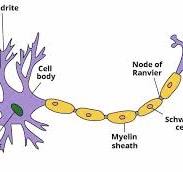
Dendrites
A short branched extension of a nerve cell, along which impulses received from other cells at synapses are transmitted to the cell body
Myelin Sheath
Cover the axon and work like insulation to help keep electrical signals inside the cell, which allows them to move more quickly
Axon terminal
The ending of one neuron, this is separated from the next neuron by a small gap called a synapse
Nucleus
Contrains the cell’s DNA
Axon
A long thread-like part of a nerve cell along which impulses are conducted from the cell body to other cells
Schwann cell
The cells which produce the myelin sheath
Node of ranvier
These speed up the transmission of the impulse by forcing it to jump across gaps in the axon
Cell body [soma]
The main part of the neuron in which the dendrites branch off from
Motor Neurons
Connect CNS to effectors such as muscles and glands. When stimulated, they release neurotransmitters that bind to receptors on muscles which trigger movement.
Sensory neurons
Carry messages from PNS [Receptors such as eyes, skin, ears, tongue] to CNS [Brain and Spinal cord]. Leading to sensations such as vision, touch, hearing, taste
Relay neurons
These connect the sensory neurons which receive the sensory input to the motor neurons which lead to a movement output