IB chem S2.1, S2.3, S2.4
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
how are ionic compounds formed
when electrons are transferred from one atom to another to form ions with a complete outer shell of electrons
how does an ionic bond work
the positive and negative ions (cation and anion) are attracted to one another by electrostatic forces and build up into a strong lattice
why do ions have high melting points
a very large amount of energy is needed to break the electrostatic forces of attraction between them
how to name ionic compounds
cation-anion+ide
anions are sometimes known as —- because
acid radicals; they are formed when an acid loses one or more H+ ions
what is the ionic bond
the sum of all the electrostatic attractions and repulsions within the lattice
why are many ionic compounds water soluble
the energy given out when they are hydrated is enough to overcome the forces holding the ions together
what increases lattice enthalpy
the smaller the ions and the greater their charge
which ionic compounds can conduct electricity and why
molten or aqueous as they have free flowing ions but as a solid they are held in fixed positions
what is a metallic bond
the electrostatic attraction between a lattice of cations and delocalized electrons
what does the strength of a metallic bond depend on
the charge of the ions and the radius and the number of delocalized electrons
what is the metallic characteristic
the loss of control over the electrons in the outer shell
what are the properties of metals
good electrical conductivity
good thermal conductivity
malleable
ductile
high melting point
shiny
why are metals good electrical conductors
the delocalized electrons are mobile and so they can move through the metal structure in response to an applied voltage
why are metals good thermal conductors
the delocalized electrons are able to efficiently transfer thermal energy because they can move
why are metals malleable
there is non-directional movement of electrons so the lattice remains intact when pressure changes the conformation of the lattice
why do metals have high melting points
a lot of energy is required to overcome the electrostatic attraction in the metallic bond and separate the atoms
why are metals shiny
the delocalized electrons reflect light
what are transition elements
elements whose atoms have an incomplete d-sublevel or can give rise to cations with an incomplete d-sublevel
why do transition metals have high melting points
there is close energy proximity between the outer occupied sublevels so even the d-electrons can be delocalized which leads to a large number of delocalized electrons and a high positive charge that makes a strong metallic bond and high melting point
why do transition metals have high electrical conductivity
more delocalized electrons so more electrical conductivity
what is bonding described as
a continuum between the ionic, covalent and metallic models represented by a bonding triangle
how do you determine the type of bonding
electronegativity differences
how do you calculate the average electronegativity
E1+E2/2
what are alloys
mixtures of a metal and other metals or non-metals. They have enhanced properties
how are alloys produced
when you add a metal element to another metal in the liquid state, so that the different atoms can mix. When the mixture solidifies, the ions of the different metals are scattered through the lattice and form a structure of uniform composition
why is it possible to produce alloys
because of the non-directional nature of delocalized electrons and that the lattice can accommodate different size ions
why are alloys stronger
they are made up of different cations which interrupt to arrangement of the atoms and make it difficult for the atoms to slip over each other.
do alloys have fixed compositions
no
what kind of properties are retained when making an alloy and why
the metallic properties such as thermal and electrical conductivity or magnetism
what are polymers
large molecules or macromolecules made from repeating subunits called monomers
how do we show the structure of a polymer
a repeating unit
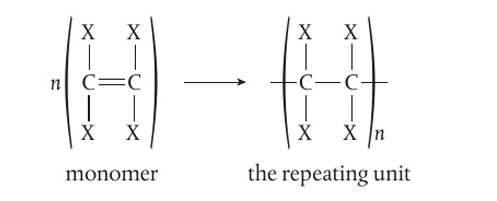
what are plastics
synthetic polymers
what are some properties of addition polymers such as plastic (5)
they have strong LDF depending on length
tend to be soft because the chains are not held in place very strongly
non-polar so they are usually water insoluble
unreactive because the chains are made of polyalkanes
lack delocalized electrons and free ions so they are thermal and electrical conductors
how do addition polymers form
the breaking of a double bond in each monomer
how do condensation polymers form
by the reaction between functional groups in each monomer with the release of a small molecule
how do you know id something will form a condensation polymer
it must have two functional groups where condensation can occur
when does a polyester form
when one monomer has two carboxylic acid groups and the other has two alcohol. this is an ester bond
when does a polyamide form
when one monomer has two carboxylic acid groups and the other has two amines and they form an amide bond
what is hydrolysis
the reverse reaction of condensation reaction where a water molecule is used to break the ester bond