Lecture 2- Psychoanalytic Theory
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Repression
Unconsciously blocking out painful or threatening thoughts and feelings from awareness.
Denial
Refusing to accept reality or facts, acting as if a painful event, thought, or feeling does not exist.
Projection
Attributing one’s own unacceptable thoughts or feelings to someone else, often blaming others for one’s own shortcomings.
Displacement
Redirecting emotions or impulses from the original source to a safer, substitute target.
Reaction Formation
Converting unwanted or dangerous thoughts into their opposites, often exhibiting exaggerated behaviors.For example, showing excessive friendliness towards someone whom one actually dislikes.
Sublimation
bad→ good
Regression
Reverting to behaviors characteristic of an earlier stage of development when faced with stress or anxiety. Eg. childlike behaviors like sucking thumb or throwing tantrums.
What are the three core ideas about mental energy in Freud's view of the mind?
1) There is a limited amount of energy. 2) Energy does not disappear; it gets channeled to other expressions upon blockage. 3) The mind functions to achieve a state of quiescence (tension/drive reduction).
What is the difference between manifest content and latent content in dreams?
Manifest content is the storyline of a dream, while latent content refers to the unconscious ideas, emotions, and drives that are expressed in the dream's storyline.
What are the stages of psychosexual development according to Freud?
1) Oral Stage 2) Anal Stage 3) Phallic Stage 4) Latency Stage 5) Genital Stage.
How does Freud's case study of Anna O illustrate the concept of catharsis?
Anna O's symptoms were relieved when she recalled forgotten traumas, suggesting that pent-up energy can be released through this process.
What are some criticisms of Freud's psychoanalytic theory?
Many ideas are unfalsifiable, rely on subjective interpretations, and early studies supporting the theory often used flimsy methods with small sample sizes.
What did neo-Freudian theorists emphasize in contrast to Freud's ideas?
They emphasized the importance of **later experiences *(adolescence, early adulthood) and* the role of social and cultural forces** in shaping personality.
What are projective tests and what purpose do they serve in psychoanalysis?
Tap into their unconscious
Repression
Unconsciously blocking out painful or threatening thoughts and feelings from awareness.
Denial
Refusing to accept reality or facts, acting as if a painful event, thought, or feeling does not exist.
Projection
Attributing one’s own unacceptable thoughts or feelings to someone else, often blaming others for one’s own shortcomings.
Displacement
Redirecting emotions or impulses from the original source to a safer, substitute target.
Reaction Formation
Converting unwanted or dangerous thoughts into their opposites, often exhibiting exaggerated behaviors. For example, showing excessive friendliness towards someone whom one actually dislikes.
Sublimation
Redirecting unacceptable impulses or thoughts into more acceptable, often constructive, behaviors or forms of expression.
Regression
Reverting to behaviors characteristic of an earlier stage of development when faced with stress or anxiety. Eg. childlike behaviors like sucking thumb or throwing tantrums.
What are the three core ideas about mental energy in Freud's view of the mind?
1) There is a limited amount of energy. 2) Energy does not disappear; it gets channeled to other expressions upon blockage. 3) The mind functions to achieve a state of quiescence (tension/drive reduction).
What is the difference between manifest content and latent content in dreams?
Manifest content is the storyline of a dream, while latent content refers to the unconscious ideas, emotions, and drives that are expressed in the dream's storyline.
What are the stages of psychosexual development according to Freud?
1) Oral Stage 2) Anal Stage 3) Phallic Stage 4) Latency Stage 5) Genital Stage.
How does Freud's case study of Anna O illustrate the concept of catharsis?
Anna O's symptoms were relieved when she recalled forgotten traumas, suggesting that pent-up energy can be released through this process.
What are some criticisms of Freud's psychoanalytic theory?
Many of Freud's psychoanalytic concepts are often unfalsifiable, lack objective measurement, and rely on subjective interpretations. His early studies frequently used flimsy methods with small sample sizes, leading to a lack of robust empirical support, though contemporary research refines some related concepts.
What did neo-Freudian theorists emphasize in contrast to Freud's ideas?
They emphasized the importance of social and cultural forces, conscious influences, personal agency, and later experiences (adolescence, early adulthood) in shaping personality, moving beyond Freud's focus solely on instinctual urges and early childhood.
What are projective tests and what purpose do they serve in psychoanalysis?
Assessment tools that use ambiguous stimuli (e.g., Rorschach inkblots) to tap into an individual's unconscious processes and reveal hidden motives. These tests often face challenges regarding their reliability and validity.
Freud’s Psychoanalytic Theory
A theory positing the mind as an energy system governed by unconscious drives and organized into Id (instincts), Ego (reality), and Superego (morality), shaping personality through dynamic conflicts.
Structural Model of Mind
Freud’s tripartite model that divides the mind into Id, Ego, and Superego, each governing different functions: the Id operates on pleasure, the Ego on reality, and the Superego on moral standards. Their interaction produces psychological tension, anxiety, and defense.
Levels of Consciousness
Freud's model categorizing mental content as conscious (aware), preconscious (accessible), and unconscious (containing anxiety-provoking material defended from awareness, only accessible through dreams or psychoanalysis).
Psychodynamic Energy
In Freud's view, psychological energy is limited and can be redirected or blocked, producing tension and symptoms. Upon blockage, this energy can channel into hysterical symptoms or be released through catharsis (emotional release).
Defense Mechanisms
Ego strategies for managing anxiety by distorting reality or excluding feelings from awareness. Mechanisms include denial, projection, isolation, reaction formation, sublimation, repression, and displacement—all working to reduce inner conflict.
Psychosexual Stages of Development
Freud’s theory of five developmental stages (oral, anal, phallic, latency, genital) based on erogenous zones, where fixation at any stage can lead to specific adult personality traits (e.g., oral-demandingness or anal-retentiveness).
Oedipal Complex
A phallic stage conflict where a child develops sexual desires for the opposite-sex parent and rivalrous feelings towards the same-sex parent. Its resolution typically involves identification with the same-sex parent and the development of gender identity.
Adler’s Theory
Individual Psychology, which emphasizes** social motives** and the innate striving to** overcome feelings of inferiority. **This theory highlights the profound impact of the **family environment and conscious efforts in shaping personality.
**
Jung’s Analytical Psychology
**Collective unconscious
** universal, inherited symbols (e.g., hero, mother, trickster) appearing in myths and dreams across cultures.
Karen Horney’s Feminine Psychology
A critique of Freud’s male-centric theories, particularly the concept of 'penis envy.' Horney advocated for concepts like 'womb envy,'
identifying neurotic styles such as moving toward, against, or away from others.
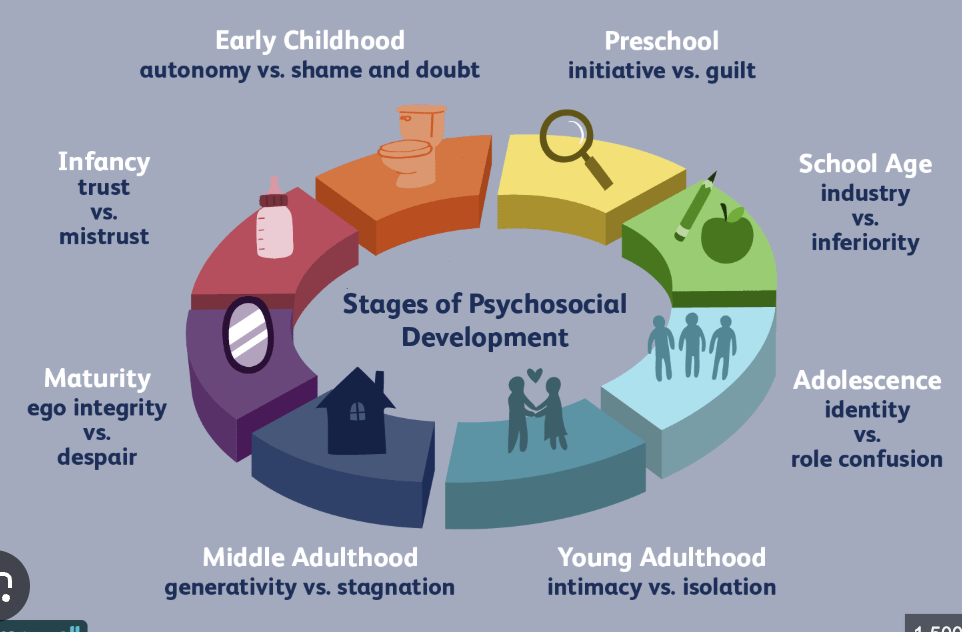
Erikson’s Psychosocial Development
eight psychosocial crises, each involving a conflict (e.g., trust vs. mistrust, autonomy vs. shame) that must be resolved to achieve healthy personality growth throughout life.
Object Relations Theory
Relationships with significant others ('objects') are fundamental to personality development.
**narcissism
** and self-esteem develop through the internalization of early relationships and the establishment of boundaries between the self and others.
Attachment Theory
Developed by Bowlby and Ainsworth, this framework posits that early relationships with caregivers form 'internal working models' of relationships. Secure attachment typically leads to trust and positive relationship orientations, while anxious or avoidant attachments can shape adult relationship patterns and relational styles.
Narcissism
overt grandiose subtypes and covert vulnerable subtypes.
Fixation Theory
In psychosexual development, fixation refers to remaining 'stuck' in a particular stage due to unresolved conflicts, leading to lasting personality traits (e.g., oral-demandingness, anal-retentiveness).
Anna O case
Catharsis as emotional release, showing how past events affect unconscious processes and manifest as hysterical symptoms.