Ch. 20 Gram - Bacilli
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
What are a couple examples of where I would find these gram - bacilli bacteria
aerobes
facultative anaerobes
Obligate anaerobes
Do any of these form endospores?
no bacteria in this chapter
Are they all true pathogens? Yes or no
some are true pathogens, and some are opportunist
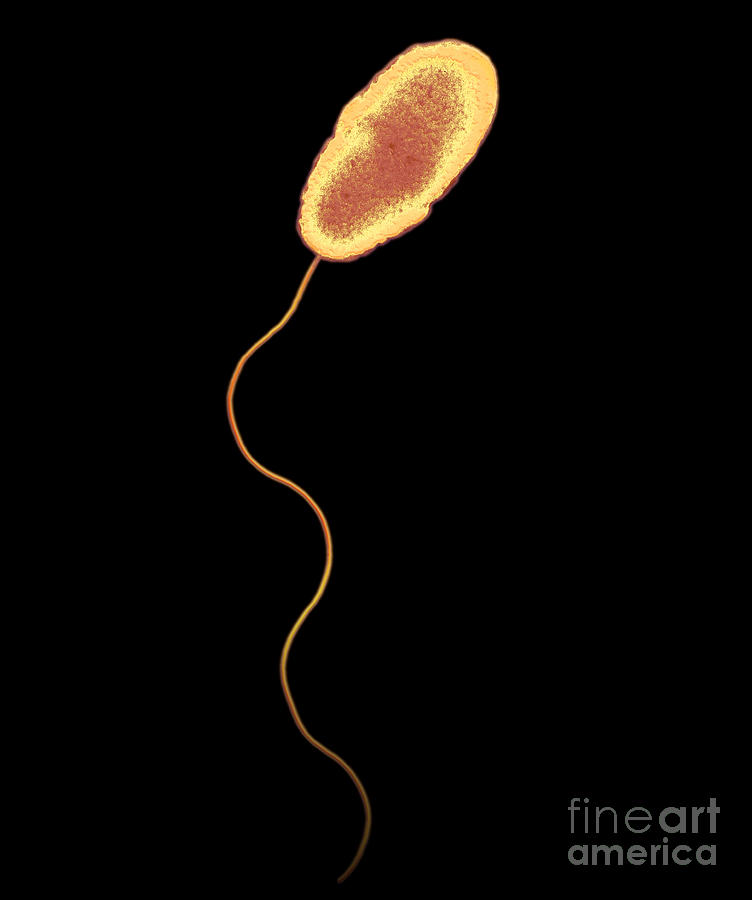
Are Pseudomonas motile?
they are motile, they have a single polar flagellum
Can Pseudomonas be a problem in standard households?
Pseudomonas are frequent contaminants in homes and clinical settings
Are Pseudomonas coliforms?
NO pseudomonas are not coliforms
Where would I find Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Pseudonomas aerginosa are a common inhabitant of soil and water, they are also an intestinal resident flora in 10% of normal people
What household product did I say could aid in causing a skin infection?
Loofah sponge can aid in causing a skin infection
You may sit these out in the sun to treat the bacteria or simply replace them throughout the year
Are Pseudomonas aeruginosa a problem with respiratory equipment in the hospitals?
Yes they are frequent contaminants of ventilators, IV solutions, and anesthesia equipment
Can Pseudomonas aeruginosa cause nosocomial infections?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a common cause of nosocomial infections in hosts with burns, pneumonia, and UTI
What kind of infections are seen in healthy individuals from Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Infections in healthy people from Pseudomonas aeruginosa is
rash
external ear infections from either hot tubs or swimming pools
foliculitis
What odor is given off in Pseudomonas aeruginosa?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa gives off a grapelike odor
What pigment is produced from Pseudomonas aeruginosa? What color is it? Some of you have used this repeatedly in a lab.
They produce a greenish/blue pigment, called pyocyanin
Is Pseudomonas aeruginosa easy to treat with drugs?
NO, Pseudomonas aeruginosa is multidrug resistant
the species common to cattle, pigs, and the species that causes human brucellosis
Brucella abortus
Brucella suis
Brucella melitinsis
How is Brucellosis transmitted?
Animal to human
Brucellosis is a zoonosis transmitted to humans from infected animals
What is the characteristic symptom of Brucella melitensis? What causes this?
Brucella melitensis SX:
Initial symptoms:
fever
chills
sweating
HA
myalgia
weight loss
Persisting symptoms:
fever undulant (comes and goes)
depression
swelling of: teste, scrotum, heart, liver, & spleen
What is one way of preventing zoonotic diseases?
cooking your food will prevent brucellosis and vaccinate animals
How is Brucellosis bacterium specifically transmitted to humans? Which is most common?
Brucellosis is most commonly transmitted through eating undercooked meat or consuming unpasteurized/raw dairy products
also by inhalation of bacteria
labs, slaughterhouse employees, meatpacking employees
skin wounds
mucous membranes of digestive tract and conjuctiva
Remember that it can localize in the mammary glands which aids in the importance of dairy product pasteurization.
What kind of infection would result from occupational hazards of handling infected animals?
zoonosis
Is Francisella tularensis another zoonotic disease?
Francisella tularensis is another zoonotic disease
What animals is of concern in the US for Tularemia?
rabbits, “rabbit fever”
How is Francisella tularensis acquired?
Francisella tularensis acquired by:
tick or fly bite, skin contact with infected animals
ingestion of contaminated water, lab, inhalation of dust or aerosols
Is transmission from Francisella tularensis ever from person to person?
NEVER FROM PERSON/PERSON
What symptoms results from infection from skin contact with infected animals?
Headches, backache
Fever 104 F and chills
malaise, weakness, skin ulcer, swollen lymph glands, conjunctival inflammation
Painful eyes or sore throat
Is Francisella tularensis a concern for the CDC as a potential bioterrorism agent?
YES, Francisella tularensis can be used as a potential bioterrorism agent via inhalation and contamination of water sources
What disease is caused by Bordatella pertussis?
causes the disease Pertussis
AKA “whooping cough”
What is an infection of bordatella pertussis?
Whooping cough
Who is the reservoir for Bordetella pertussis?
the reservoir is healthy carriers
How is Bordetella pertussis transmitted?
By direct contact or inhalation of aerosols given off during coughing stage of infection
What age group is most affected if Bordetella pertrussis is present?
Half of cases occur from birth to 4 yrs of age
How are severe cases prevent? What is the specific name?
What types of cells are the bacteria binding to destroying?
Ciliated respiratory epithelial cells
What does the pertussis toxin do?
The infected cells produce more receptors for FHA
it enters the cells and interferes with metabolism, thus increases in mucous production
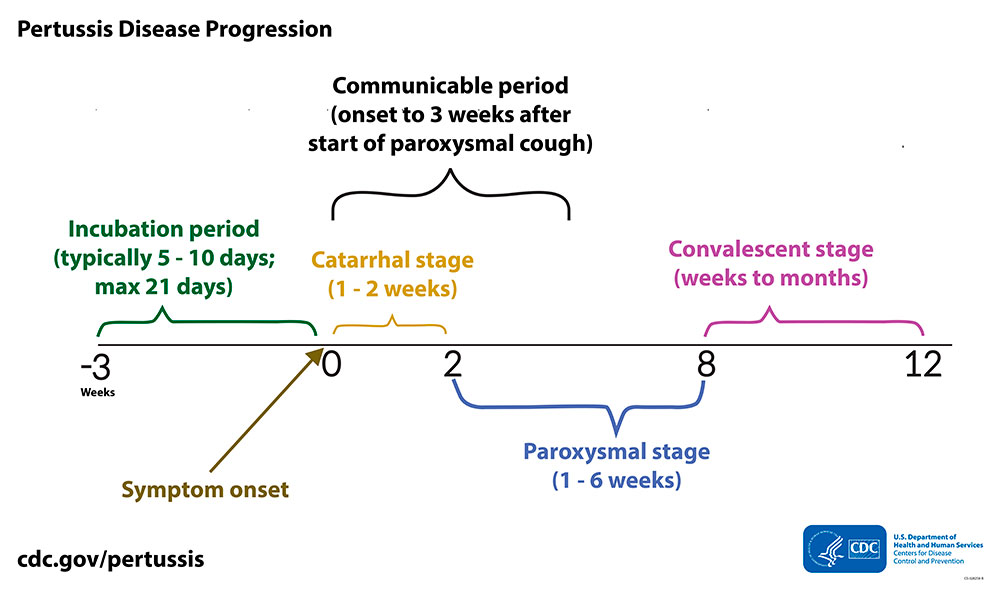
What is occurring during the catarrhal phase and paroxysmal stages?
Catarrhal phase: symptoms resemble a cold, bacteria are more abundant and the patient is more contagious.
Paroxysmal phase: when you see the characteristics signs and symptoms
accumulation causes uncontrolled coughing fits occurs suddenly.
Which is more contagious?
the catarrhal phase is more contagious
Which shows more cold-like symptoms?
the catarrhal phase shows cold like SX
Which express your characteristic symptoms?
The Paroxysmal phase shows the characteristic symptoms
What vaccine is empathically given to prevent Bordetella pertussis disease?
vaccine is DTaP, which helps prevent it
Should parents get vaccinated even if they have never had whooping cough?
Older children and adults should get vaccinated
What 2 diseases are caused by Legionella pneumophilia?
Legionnaire disease and Pontiac fever
Where did Legionella pneumophilia get its name?
It got its name when 200 legion members attended a convention in Philly and an epidemic of pneumonia ocurred
What age group is more affected by Legionella pneumophilia?
Legionella pneumophilia is prevalent in males over 50
In what environment distributes Legionella pneumophilia? What are a couple examples?
It is widely distributed in water
EX: AC cooling showers, evaporative coolers, spas, moist showers, supermarket veggies sprayers
What organism is Legionella pneumophilia associated with?
Legionella pneumophilia lives in close association with amoebas
How is Legionella pneumophilia transmitted?
Legionella pneumophilia is transmitted by Airborne Transmission
NOT PERSON TO PERSON
Which disease is more severe, Legionnaire disease or Pontiac fever?
Legionnaire disease is more severe
Same symptoms:
cough, diarrhea, and abdominal pain
Fatality rate of 3-30%
What environments are members of the Enterobacteriaceae family found?
many members inhabit
soil
water
decaying matter
are common occupants of large bowel of animals including humans
What is Enterobacteriaceae’s role in causing nosocomial infections?
Enterics and Pseudomonas sp. account for more than 30% of nosocomial infections
What are the 2 divisions in Enterobacteriaceae?
they are divided into coliforms (lactose fermenters) and non-coliforms
What substance is being fermented in coliforms by Enterobacteriaceae? Remember they all ferment glucose.
All ferment:
glucose
reduce nitrates to nitrites
oxidase negative
catalase positive
What kind of media is used to screen samples for pathogens? – we even used this in lab!
enrichment, selective, and differential media are used for screening samples for pathogens
What are “enterics”?
organisms which occupy the digestive tract
what are the names correlating with locations of inflammation – 3
inflammation of the:
Stomach → Gastritis
Small intestine → Enteritis
Large intestine → Colitis
What is a disease caused by enterics? What is the symptom of the disease?!
Gastroenteritis, and diarrhea is a symptom of it
Which are coliforms? Noncoliforms?
E. coli = Coliforms
Klebsiella = Coliforms
Shigella = NON- coliforms
Yersinia = NON- coliforms
Salmonella = NON- coliforms
Know the letters associated with surface antigens – H, K, O and what part of the bacterium it represents. (ex. Flagellum)
H - flagellar antigen
K - capsule and/or fimbrial antigen
O - somatic or cell wall antigen
Enterotoxins cause?
Toxigenic disease causes watery diarrhea
Cholera and some types of E. coli and Shigella
Invasive disease causes bloody diarrhea
Salmonella, shigella, E. coli, Campylobacter, Entamoeba histolytica.
Exoenzymes cause?
Which is more invasive, enterotoxins or exoenzymes?
How prevalant is E. coli?
it is the most common aerobic and non-fastidious bacterium in the gut
Where is E. coli located ?
located in the gut
Is E. coli fastidious?
E. coli is non-fastidious
What are 5 infections that are caused by E. coli?
5 infections caused by E. coli
gastroenteritis
septicemia
pneumonia
meningitis
endocarditis
How does E. coli contribute to the number of UTI cases?
50 - 80% of UTI cases are caused by E. coli
What are coliform counts an indicator of?
coliform count is used as an indicator of fecal contamination in the water
Is E. coli a primary pathogen?
No, it is an opportunistic pathogen
How are pathogenic strains differentiated from one another?
various strains can be differentiated on the basis of antigens (H, K, O serotyping)
What does enterotoxigenic E. coli cause? IMPORTANT
ETEC
Causes severe diarrhea (watery)
Heat labile: increase fluid secretion
Heat stable: decrease fluid reabsorption
Enteroinvasive E. coli causes?
EIEC
causes inflammatory disease of the large intestine
destroys epitheium
Enteropathogenic E. coli causes?
EPEC
linked to wasting form infantile diarrhea
destroys microvilli of Small Intestine
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli causes? IMPORTANT
EHEC
Worse case
has over 50 serotypes
it is an O157:H7 strain
causes hemolytic Uremic syndrome (HUS) and kidney damage
destroys intestinal villi and causes dysentery
How are infantile and traveler’s diarrhea acquired? Why isn’t pepto-bismol used in infantile? What is it acting on?
Infantile and traveler’s diarrhea is acquired through contaminated food or water
Pepto-Bismol is not used because it counteracts enterotoxin
How are Urinary Tract Infections acquired?
UTI’s are acquired through your own normal flora or nosocomially
What contaminated material is ingested that results in bloody Diarrheal illness?
Bloody Diarrheal Illness is acquired through contaminated meat that is not properly cooked
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS) can lead to what type of failure?
HUS can lead to kidney damage and failure
What is the cause of HUS pathogenicity?
pathogenicity is due to new toxins picked up from Shigella
What symptoms are caused by E. coli: Serotype O157:H7 infection?
SX of Serotype O157:H7
bloody diarrhea, UTI, septicemia, HUS
How is E. coli: Serotype O157:H7 transmitted?
MOT:
consumption of undercooked ground beef
unpasteurized milk
fruit juice that is contaminated with feces
What kind of toxin is produced by E. coli: Serotype O157:H7?
a Shiga-like toxin that hitches a ride on neutrophils via surface attachment
How do you prevent infections that lead to diarrhea?
Avoid contaminated water and raw veggies. Drink bottled water or boil water
Where is Klebsiella pneumonia found? What can it cause?
it is a normal inhabitant of the intestines and respiratory tract
can cause nosocomial pneumonia, meningitis, bacteremia, wound infections, and UTIs
What is the color and name (in lab manual) of the pigment produced by Serratia marcescen?
Pigment produced is called Serratia marcescens and it has a red color
Which species of Salmonella is the most serious species? What does it cause?
Salmonella bongori
Salmonella enterica
Typhimurium
enteritidis
typhi: most serious pathogen of the genus
causes typhoid fever
How is Salmonella typhi acquired? What kind of damage is caused to the small intestine?
Salmonella typhi is acquired through contaminated water or food; close personal contact, carriers
SX: fever, diarrhea, abdominal pain
ulcerations and hemorrhage with perforation of small intestines
Who was typhoid mary? What was her occupation? What is removed from carriers?
Typhoid Mary was a cook in households during the early 1900s
she was an asymptomatic carrier, she harbored Salmonella typhi for years in her gallbladder and shed in feces
What primary animals should precautions be taken when handling to prevent animal Salmonella Enteritidis? – think pets and the white meat : )
Animals to take precautions
cattle
poultry
rodents
reptiles
animals (like hedgehogs)
dairy products
What are a couple ways to prevent Salmonella?
Ways to prevent Salmonella
cook chicken well, clean utensils, used, and wash hands
avoid foods w/ raw eggs
Homemade mayo, egg nog, cookie dough
DO NOT USE CRACKED EGGS
Does perforation occur in the intestine when having Shigella?
Perforation does not occur when having Shigella
What is produced in Shigella?
Shigella produces exotoxin instigating severe inflammation and ulceration of small intestine and colon
What is the name of the toxin produced in Shigella?
Shiga toxin
Is Shigella similar to what is seen in E. coli 0157:H7?
Shigella is similar to E. coli 0157:H7 because that produces Shiga-like toxins
Shigella dysenteriae causes?
Shigella dysenteriae causes a bacterial dysentery or shigellosis
What symptoms occur with Shigella dysenteriae?
SX of Shigella dysenteriae
Large intestine invaded
inflammation of lining
degeneration of villi
bleeding and heavy mucus
fever abdominal cramps
pain
Yersinia enterocolitica causes?
Yersinia enterocolitica causes enterocolitis
Yersinia enterocolitica infection can mimic what?
it can mimic appendicitis
What are the 2 clinical manifestations in Yersinia pestis?
Bubonic plague: MOT Vector to Human
Pneumonic plague: MOT human to human
What animal population is plague found in?
Animal population are mammals, rodents without causing disease and flea vectors
What insect vectors the disease for Yersinia pestis?
flea vectors
Know the different symptoms and acquisition of the manifestations in Yersinia pestis.
Acquired: by flea bite and enters the lymph
SX: causes necrosis and swelling called a bubo in groin or axilla