Electric Circuits
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
1
New cards
Symbol, units, alternative units for charge
Q, coulomb (C), 1 e.c \= 1.6x10^-19 C
2
New cards
Symbol and units for electric potential (voltage)
V, volt (V), J/C
3
New cards
Equations not in packet for electric potential- relating Ep/E and q
Ep = qv
E = qV
E = qV
4
New cards
Equations not in packet for electric potential relating W and q
W\= qv
5
New cards
equation not in packet for electric potential relating E and d
v \= Ed
6
New cards
Units/symbols for energy
E, Joule (J). 1 eV \= 1.6x10^-16 J
7
New cards
Units/symbols for current
I, ampere (A), C/s
8
New cards
equation for current not in packet
I \= change in q /change in t
9
New cards
drift speed equation
rearrange I \=nAvq (in packet)
10
New cards
symbol for charge density
n
11
New cards
define charge density
number of charge carriers per unit volume (m^3)
12
New cards
units and symbols for resistance
R, ohm, V/A
13
New cards
units and symbols for resistivity
p, ohm x meter
14
New cards
Units and symbols for power
P, watt (W) 1 W \= 1 J/s, \= 1 VA
15
New cards
units and symbols for energy, work
E, W, Q, joule
16
New cards
How does a battery cause a light bulb to light up?
one battery terminal is at a high electric potential (+), the other is at a low (-) one. this difference in potential makes an electric field in both the wire and the bulb's filament, causing free electrons in the circuit to start moving toward the positive terminal. Along the way they hit the positive stationary lattice ions, transferring kinetic energy. The increase in Ek in lattice ions in the filament becomes thermal energy, and the filament gets hot enough to glow.
17
New cards
Wire R is cut into thirds of equal length, arranged in parallel. What is the equivalent resistance?
R/q
18
New cards
How many MJ in one Kw/Hr?
3.6 x 10^6
19
New cards
A copper wire of diameter .65 mm carries a current of .25 A. There are 8.5x10^28 charge carriers in each cubic meter of copper. Calculate the drift speed of the charge carriers
1. find A using pi r ^2
2. v = I/nqA
3. I = .25, n = 8.5x10^28, q = 1.6x10^-19, A = pir^2
4. =5.5x10^-5 m/s
20
New cards
What is the cross-sectional area equation?
A \= pi x (r ^2)
21
New cards
What is the difference between a source of emf and a potential difference?
EMF \= voltage rise, potential increase. Potential difference \= voltage drop, potential decrease
22
New cards
What does it mean when something is a source of EMF
it converts from some other form of energy into electrical energy
23
New cards
What does it mean when something is a source of potential difference?
it converts from electrical energy into some other form of energy
24
New cards
What is a cell?
a container in which a chemical reaction occurs to convert chemical potential energy into electrical energy. A source of EMF
25
New cards
What is a battery?
Two or more cells connected together
26
New cards
What is a primary cell?
Non-rechargeable cell
27
New cards
What is a secondary cell?
A rechargable cell
28
New cards
A cell-phone battery is marked as 90 Ma h 12 V 1.08 Wh. What quantity is being measured as 90 mAh?
The charge. 90 x 10^-3 c/s x 3600 s \= 324 c
29
New cards
Define (charge) capacity
A quantity used to measure the ability of a cell to release charge
30
New cards
A battery whose capacity is 90 MA h means that before it dies you can run it
a. At 90 mA for x hours
b. at 45 mA for x hours
c. at 9 mA for x hours
a. At 90 mA for x hours
b. at 45 mA for x hours
c. at 9 mA for x hours
a. 1 hour \n b. 2 hours \n c. 10 hours
31
New cards
Ideal cell vs real cell
Ideal has no internal resistance and voltage across the terminals (terminal potential difference) is constant over time
Real has small internal resistance that increases over time as chemicals are used up. Voltage across terminals (terminal potential difference) decreases over time
Real has small internal resistance that increases over time as chemicals are used up. Voltage across terminals (terminal potential difference) decreases over time
32
New cards
Describe the terminal potential difference of a real cell
decreasing over time
33
New cards
Define EMF
electromotive force: the total energy per unit charge supplied around a circuit by the battery
Energy that is used by both the exterior circuit and the interior chemical processes of the cell
Remains constant as the battery charges
Energy that is used by both the exterior circuit and the interior chemical processes of the cell
Remains constant as the battery charges
34
New cards
Define terminal voltage (Vterm)
The potential difference across the terminals of the battery.
The energy that is available for use by the exterior circuit.
Decreases as the battery charges
The energy that is available for use by the exterior circuit.
Decreases as the battery charges
35
New cards
In an ideal cell, how are emf and Vterm related
emf \= Vterm
36
New cards
In a real cell, how are EMF and Vterm related?
emf \> Vterm
37
New cards
How does terminal potential difference vary with time in a cell? Draw the graph on page 4.
Vterm loses its initial value quickly, then has a stable, constant value for most of its life, then rapidly decreases to zero as the cell discharges completely
38
New cards
In which direction should current flow to recharge a secondary cell, and why?
Backwards through the cell, from positive to negative to reverse the chemical reaction within the cell.
39
New cards
describe the current in a series circuit
the same for all resistors. It \= I1 \= I2
40
New cards
describe the voltage in a series circuit
split in proportion to resistance. Vt \= V1 + V2
41
New cards
describe the resistance in a series circuit
The total adds up. Rt \= R1 + R2
42
New cards
describe the power (measure of brightness) in a series circuit
Total adds up. Pt \= P1 + P2
43
New cards
write the Ratio Relationship for series circuits
R1/R2 \= V1/V2
44
New cards
What is a potential divider?
Resistors in series split the potential of the source between them
45
New cards
describe the current in a parallel circuit
split in inverse proportion to resistance. It \= I1+I2
46
New cards
describe the voltage in a parallel circuit
same for all resistors. Vt \= V1 \= V2
47
New cards
describe the resistance in a parallel circuit
total adds down. Rt \= (1/R1 + 1/R2)^-1
48
New cards
describe the power (measure of brightness) in a parallel circuit
total adds up. Pt \= P1 + P2
49
New cards
write the Ratio Relationship for parallel circuits
R1/R2 \= I2/I1 (bigger R gets less current)
50
New cards
What is an ammeter? What is the resistance of an ideal ammeter? Where should an ammeter be placed relative to the battery in a circuit?
Ammeter measures current, ideally 0 R, placement is in series with battery
51
New cards
What is a voltmeter? what is the resistance of an ideal voltmeter? where should a voltmeter be placed relative to the battery in a circuit?
Measures potential difference, ideally infinite R, placement is in parallel with battery
52
New cards
When there are two emfs in series in the same direction, how do you find voltage?
add the voltages
53
New cards
When there are two emfs in series in opposite directions, how do you find the voltage?
subtract the voltages
54
New cards
When there are two cells in parallel how do you find the emf?
same emf, add internal resistances
55
New cards
What are kirchoff's circuit laws?
1. Total voltage rises = total voltage drops
2. total current into a junction = total current out
56
New cards
difference between potentiometer and variable resistor
sliding connector on potentiometer can be a variable resistor. Adding multiple connections onto a potentiometer can create a potential divider (like a light with a dimmer switch)
57
New cards
Define r
Internal resistance- the resistance supplied by materials within the cell
58
New cards
Define V
change in energy over unit charge (joules per coulomb)
59
New cards
define I
change in charge over change in time (coulombs per second)
60
New cards
Define R
the ratio of potential difference applied across a material to the current going through the material
61
New cards
what is the unit for emf
epsilon (E)
62
New cards
what is IR
Vterm, the external voltage drop outside the cell
63
New cards
what is Ir
the internal voltage drop across the cell
64
New cards
what is E\=I(R+r) saying?
total energy supplied around a circuit by the cell is equal to the internal voltage drop across the cell plus the external voltage drop outside the cell
65
New cards
When does emf \= Vterm?
When no current is flowing- infinite resistance, an ideal cell, or an open circuit
66
New cards
When does emf \= IR + Ir?
When external resistance R is much greater than internal resistance r
67
New cards
When does emf \= Ir
during a short circuit, when I \= Imax
68
New cards
what is a short circuit
When maximum current flows through the circuit
69
New cards
What is Ohm's law?
when a conductor is at a constant temperature the current flowing through it is proportional to the potential difference across it (V is proportional to I)
70
New cards
What is an ohmic device? give an example
a device that obeys ohm's law- has a constant resistance. EX: a resistor
71
New cards
What is the slope on a graph at any given point with I as the y value and V as the x value?
1/R
R= V/I at any given point, regardless of ohmic or non-ohmic characteristics
R= V/I at any given point, regardless of ohmic or non-ohmic characteristics
72
New cards
What is a non-ohmic device? Give an example
A device that doesn't obey ohm's law- resistance isn't constant. EX: a filament lamp
73
New cards
Describe the slope of a filament bulb with I as the y-value and V as the x-value
starts at a constant rate, then decreases into a plateau after a certain point (when the lightbulb filament heats up)
74
New cards
Which variable increases faster on an I-V graph for a non-ohmic device?
V increases faster than I
75
New cards
What is the relationship between slope and resistance for an I-V graph of a non-ohmic device?
no relationship (except at start when slope is linear)
76
New cards
What is a diode?
a semiconductor device that only lets current flow in one direction
77
New cards
What is a light-dependent resistor (aka light sensor)?
a photo-conductive cell. When light strikes it, charge carriers are released- the more light that strikes it, the more carriers are released, and the more resistance decreases.
Relationship: as light intensity increases, effective resistance decreases
Relationship: as light intensity increases, effective resistance decreases
78
New cards
A circuit is set up so a regular resistor is above a light-dependent resistor. A voltmeter is connected in parallel with the regular resistor.
As light intensity increases, what happens to the reading on the voltmeter and the total current across the circuit?
As light intensity increases, what happens to the reading on the voltmeter and the total current across the circuit?
The voltmeter's reading would increase. The voltage across the light-dependent resistor would decreases because the voltage drop across a resistor is proportional to its resistance. Because the total voltage must match the voltage supplied by the cell, the voltage drop across the regular resistor must increase.
Current would decrease as Rtotal decreases
Current would decrease as Rtotal decreases
79
New cards
What are some practical applications for LDRs
night lights, security lights
80
New cards
What is a thermistor/temperature sensor
a sensor that works based on temperature. As the thermistor gets hotter, more charge carriers are released and its resistance goes down
81
New cards
A circuit is set up so a regular resistor is below a thermistor. A voltmeter is connected in parallel with the regular resistor.
As temperature increases, what happens to the reading on the voltmeter and the total current across the circuit?
As temperature increases, what happens to the reading on the voltmeter and the total current across the circuit?
The reading on the voltmeter increases. The voltage across the thermistor would decrease as its resistance decreases, and so the voltage drop across the regular resistor would have to increase so the total voltage drop across the two is still equal to Vterm.
The total current through the circuit would decrease as the total resistance decreases.
The total current through the circuit would decrease as the total resistance decreases.
82
New cards
What is a practical application for a thermistor
stovetop heat lights (lights that turn on when a stove is hot)
83
New cards
What is the symbol for a light-dependent resistor
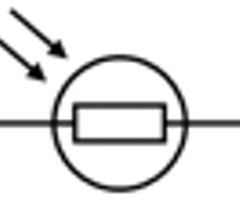
84
New cards
What is the symbol for a thermistor
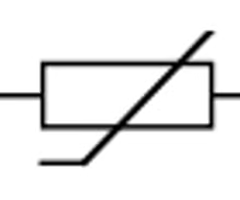
85
New cards
Picture a circuit with a lamp in series with a variable resistor (0-10 ohms), and a battery with an emf of 12 volts. Describe the current and voltage drop across the lamp when R \= 0
Lamp gets maximum current and potential difference
Realistically, it still doesn't get 12 volts because of the internal resistance of the battery and the variable resistor
Realistically, it still doesn't get 12 volts because of the internal resistance of the battery and the variable resistor
86
New cards
Picture a circuit with a lamp in series with a variable resistor (0-10 ohms), and a battery with an emf of 12 volts. Describe the current and voltage drop across the lamp when R \= max
The potential difference is divided between the lamp and the variable resistor. The lamp gets the minimum amount of current and potential difference.
This minimum amount can never be zero though.
This minimum amount can never be zero though.
87
New cards
What is a potentiometer?
a type of variable resistor with 3 contact points
88
New cards
Define variable resistor and identify its symbol
a resistor that allows you to change how much resistance it supplies
89
New cards
What are potentiometers commonly used for?
a potential divider to measure the I-V characteristics (the relationship between current and voltage) of a device
90
New cards
Draw a diagram of a dimmer switch with a potentiometer, labeling contact points
check the diagram on page 19.
Should have a circle with a knob indicating the dimmer switch, 3 circuit lines representing a resistive strip connecting the circle to contact 3 points of a rectangle which symbolizes the potentiometer
Should have a circle with a knob indicating the dimmer switch, 3 circuit lines representing a resistive strip connecting the circle to contact 3 points of a rectangle which symbolizes the potentiometer
91
New cards
Picture a potentiometer connected to a dimmer switch. Think of the 3 points of contact as A, B, and C. As the slider is rotated towards point C, what happens to the resistance between points AB, BC, and AC?
AB: resistance increases
BC: resistance decreases
AC: stays the same (its the total resistance)
BC: resistance decreases
AC: stays the same (its the total resistance)
92
New cards
What is the symbol for a potentiometer
When you turn the knob of a dimmer switch, you're changing where the arrow is.
Total resistance stays the same
Resistance at each point changes as arrow moves
Total resistance stays the same
Resistance at each point changes as arrow moves
93
New cards
A lamp is connected in parallel with variable resistor, so that the connecting arrow is above the resistor entirely. Describe the total resistance and the voltage, current, and brightness of the lamp
Total resistance is at its lowest (because they're completely in parallel)
The lamp has its maximum voltage drop. Vl = Vtotal (except for internal resistance of the batteries/wires)
The lamp has its maximum current and brightness
The lamp has its maximum voltage drop. Vl = Vtotal (except for internal resistance of the batteries/wires)
The lamp has its maximum current and brightness
94
New cards
A lamp is connected in parallel with a variable resistor so that the connecting arrow is halfway down the variable resistor. Describe the voltage, current, and brightness of the lamp
The voltage of the lamp is less than the total voltage of the circuit
The lamp is dim
The current across the lamp is less than the total current in the circuit
The lamp is dim
The current across the lamp is less than the total current in the circuit
95
New cards
A lamp is connected in series with a variable resistor so that the connecting arrow is beneath the variable resistor. Describe the voltage, current, and brightness of the lamp
There is no voltage drop across the lamp (assuming lamp has 0 internal resistance)
There is no current across the lamp
Lamp goes out
There is no current across the lamp
Lamp goes out
96
New cards
What happens to bulb brightness as voltage drop across it increases?
it gets brighter
97
New cards
What happens to bulb brightness as current across it increases?
it gets brighter
98
New cards
What happens to bulb brightness as total resistance increases?
it gets dimmer
99
New cards
Solve through the final hard quizlet problem to make sure you really understand solving circuits with matricies
whew done
100
New cards
What equation would you use to determine how much energy is in a battery given its mAhr and v?
E = qV
1. find q- we know that A = j/c and 3600s in 1 h
2. solve
1. find q- we know that A = j/c and 3600s in 1 h
2. solve