ID Lecture 17: Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics w/ Emphasis on Aminoglycosides and Vancomycin | Quizlet
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
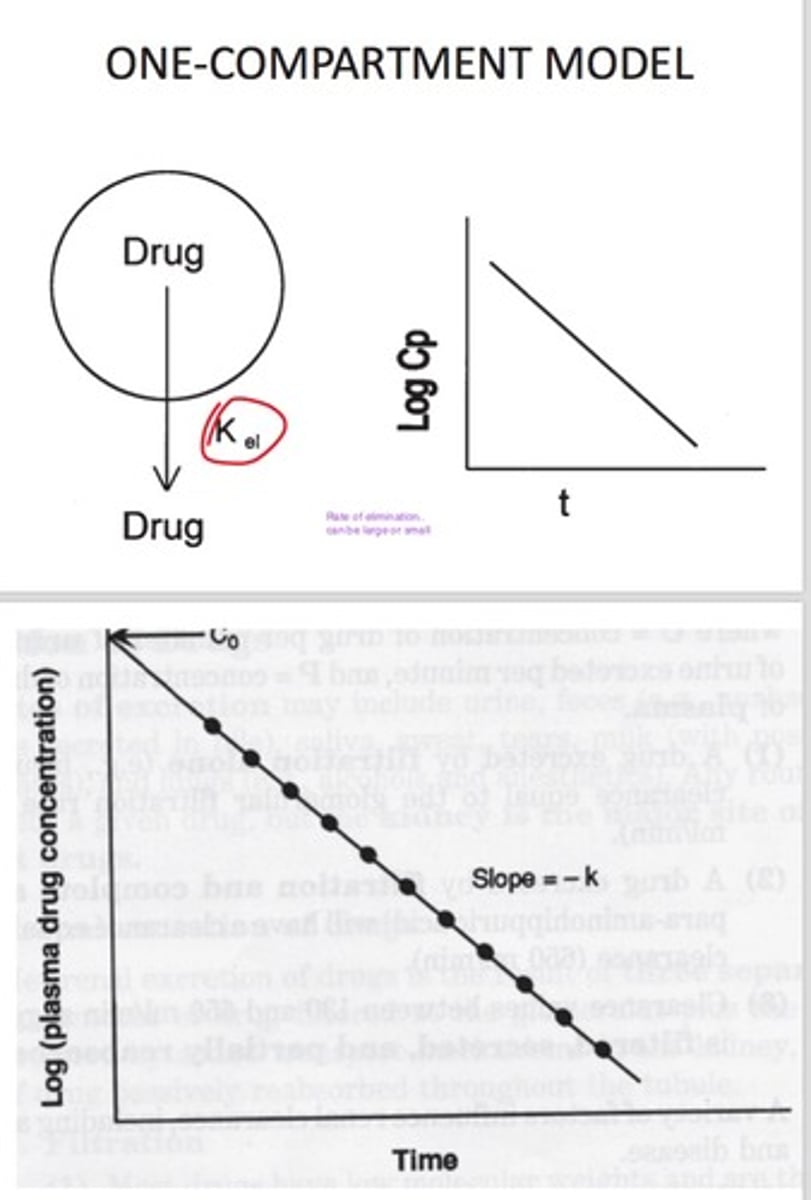
One compartment model
drug undergoes absorption into the blood at a rate constant Ka and elimination at a constant Ke
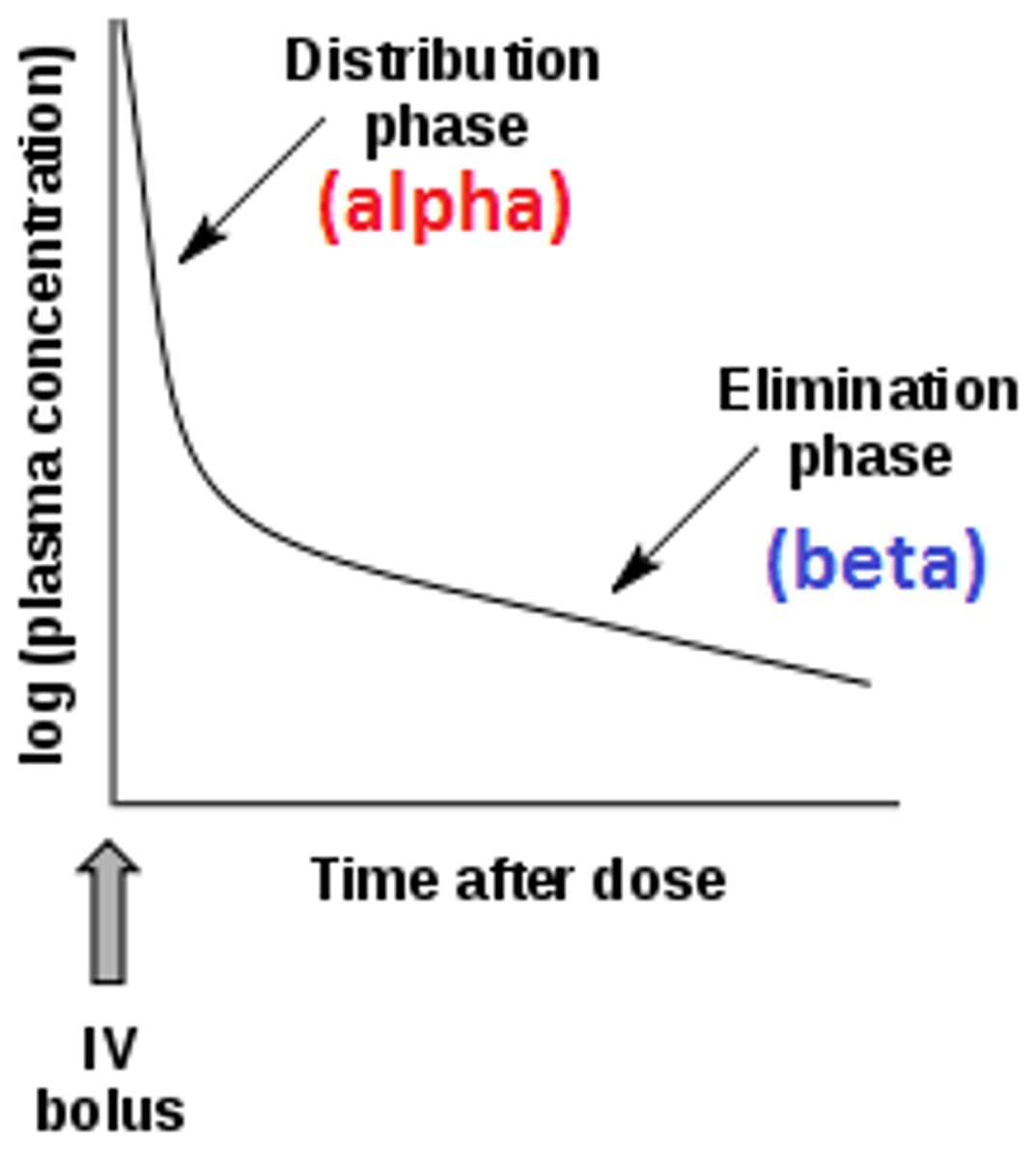
Two compartment model
Drugs are absorbed into the central compartment (blood), distributed from the central compartment to the peripheral compartment (tissues), and eliminated from the central compartment
How many half lives does it take to achieve steady state?
3-5
Are Aminoglycosides concentration or time dependent?
Concentration dependent
Do Aminoglycosides have a post antibiotic effect?
yes
Half life of Aminoglycosides
1.5-3 hours (~2)
How are Aminoglycosides eliminated?
>90% excreted unchanged via glomerular filtration
What is the volume of distribution of Aminoglycosides?
0.26L/kg
Aminoglycosides are considered to be what?
water soluble
What peak and trough concentrations of Gentamicin, Tobramicin, or Netilmicin do we see ototoxicity or nephrotoxicity?
Peak: >12-14
Trough: >2-3
What peak and trough concentrations of Amikacin do we see ototoxicity or nephrotoxicity?
Peak: >35-40
Trough: >10
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
The process of measuring drug levels to identify a patient's drug exposure and to allow adjustment of dosages with the goals of maximizing therapeutic effects and minimizing toxicity.
IBW equation
Males = 50+ (2.3) (height - 60)
Females: 45 +(2.3) (height - 60)
Male Cockgroft-Gault Equation
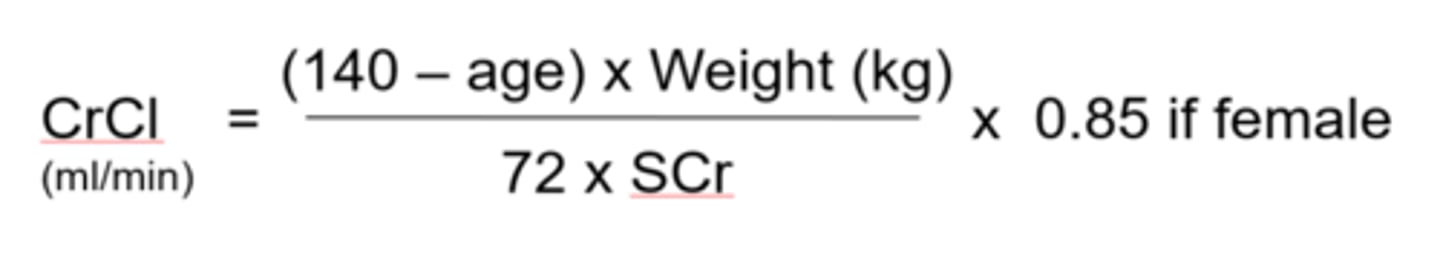
Conventional dosing of Aminoglycosides
reduced doses administered frequently and by using PK parameters to determine dosing to achieve target peak and trough values
Extended spectrum dosing of Aminoglycosides
Hartford Nomogram is typically used to determine this dosing regimen
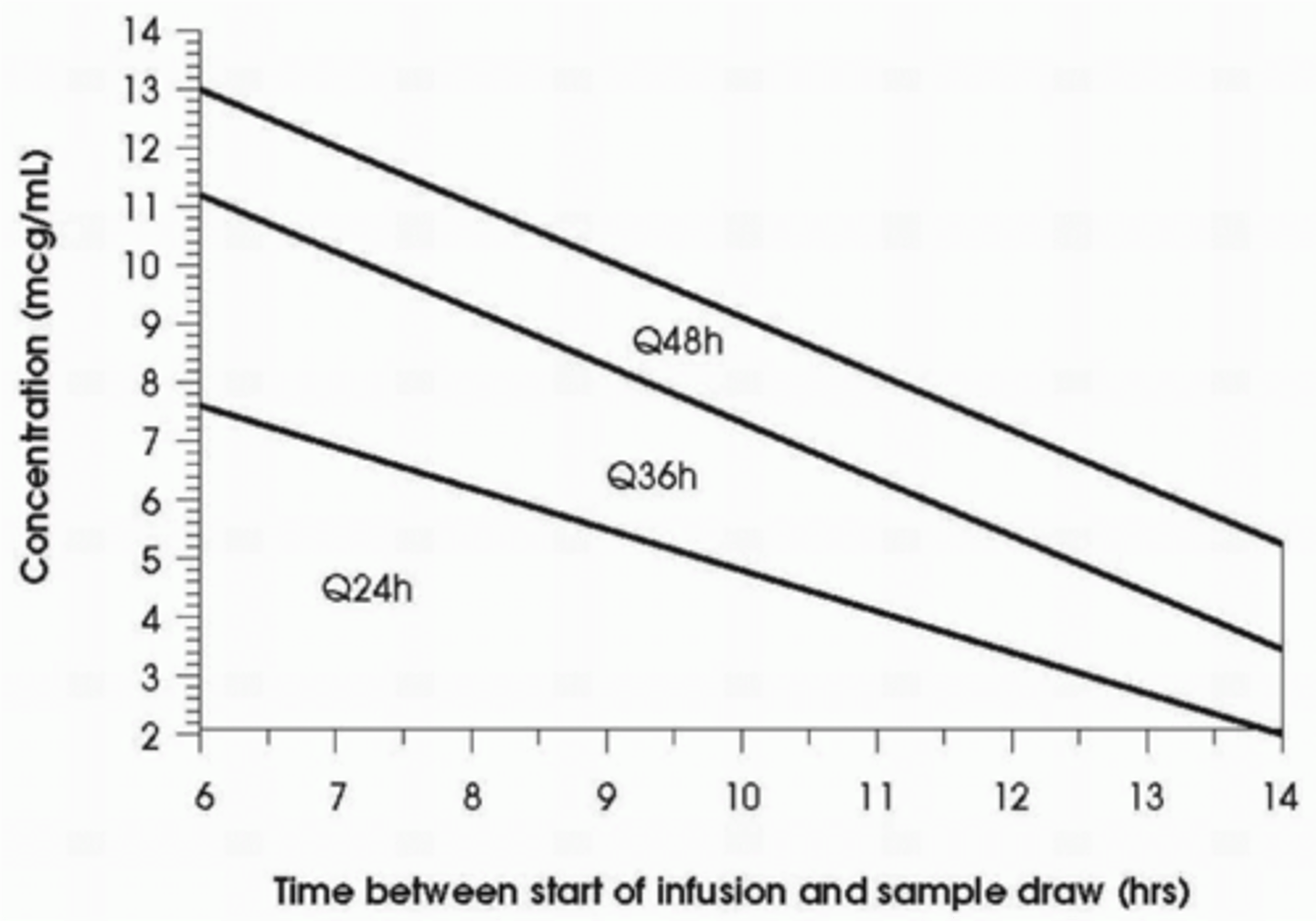
Hartford Nomogram
taking a single random blood sample from a patient to determine dosing of Aminoglycosides
Fixed dose of 4-7mg/kg IBW
When should sampling be done for TDM?
1 hour after the start of infusion
30 mins after infusion if infusion time >40 minutes
Cmin measurements should be taken before the start of the next dose
What describes the PK of Vancomycin?
2-3 compartment body model
What is the half life of Vancomycin?
~8 hours
What is the clearance of Vancomycin?
nearly the same a CrCl (primary renally eliminated)
What are the Vancomycin dosing guidelines?
25-35 mg/kg in non-obese patients
20-25 mg/kg for obese patients
What is the maximum loading dose for Vancomycin?
3 grams
How long are Vancomycin infusions?
Typically 2-3 hours
What is Vancomycin's volume of distribution?
0.7 L/kg
What is the desired peak and trough concentrations of Vancomycin?
Peak: 25-40 mg/L
Trough: 5-15 mg/L