Lab 4
1/103
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
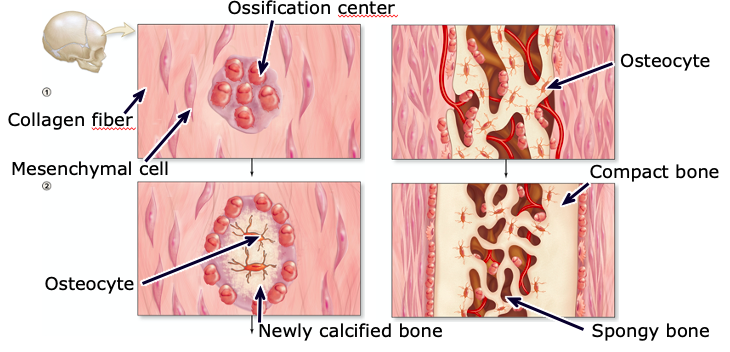
Intramembranous ossification
bone develops directly on a “mat” of collagen fibers (e.g. most of the flat bones of the skull, some facial bones, mandible, part of the clavicle)
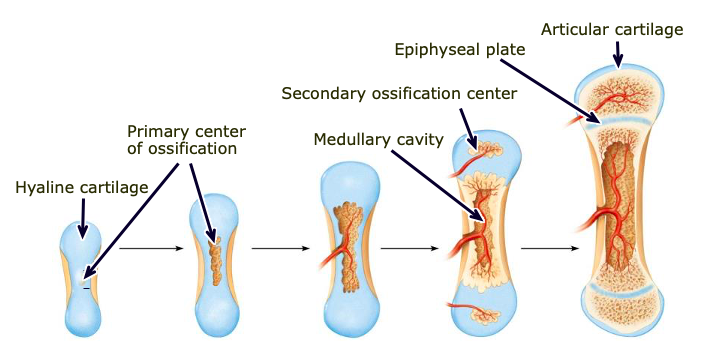
Endochondral ossification
bone that begins as a hyaline cartilage framework (most bones form this way)
Flexion/extension
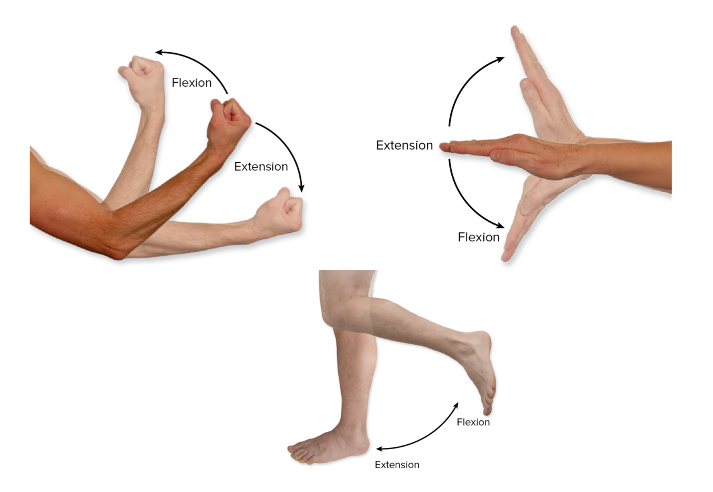
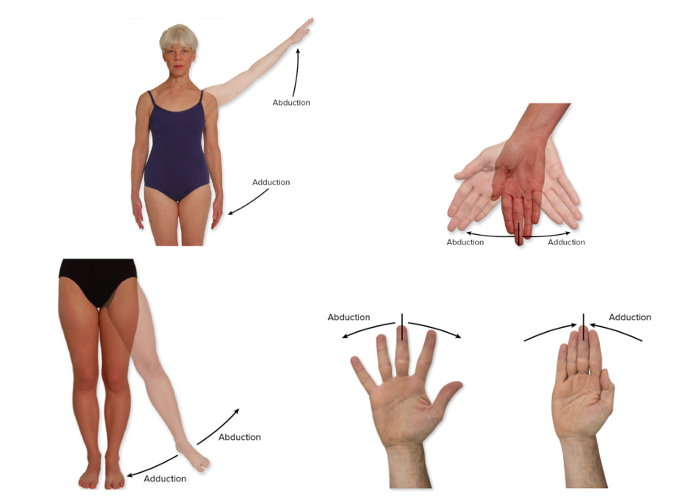
Abduction/adduction
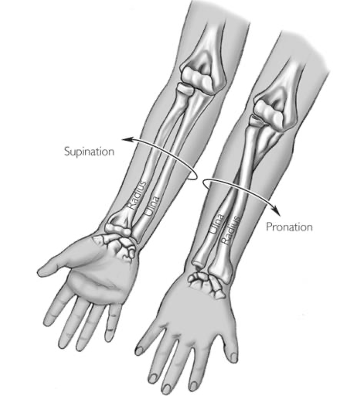
Pronation/supination
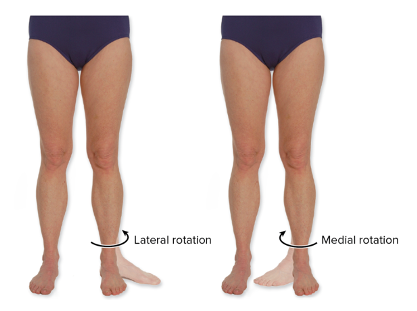
Rotation
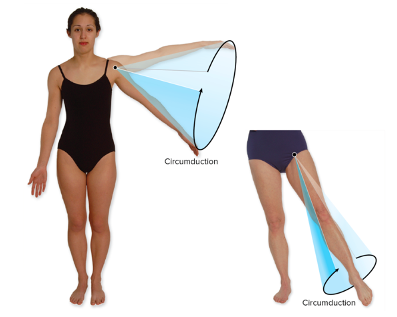
Circumduction
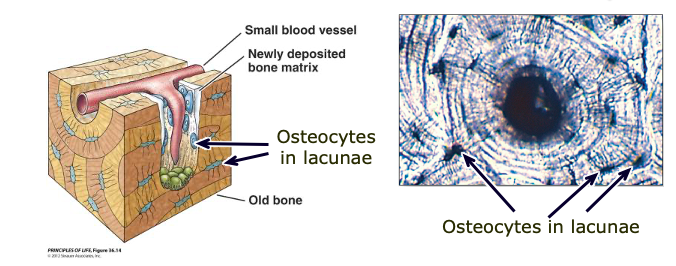
Osteocyte
a cell that lies within the substance of fully formed bone
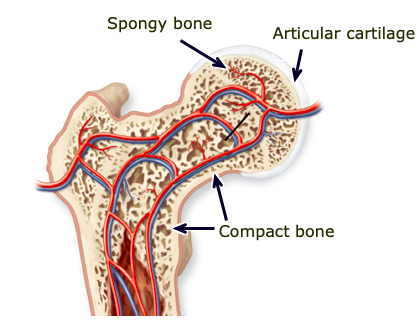
Compact (cortical) bone
dense outer layer of bones; strong and rigid
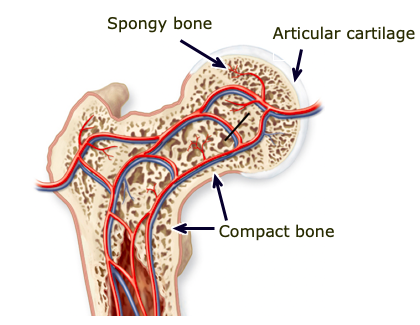
Spongy/trabecular bone
inner tissue of bone, surrounded by marrow, more air pockets; better at shock absorption
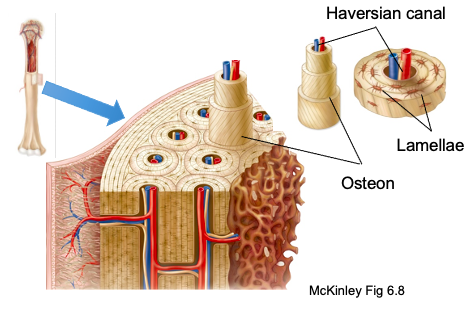
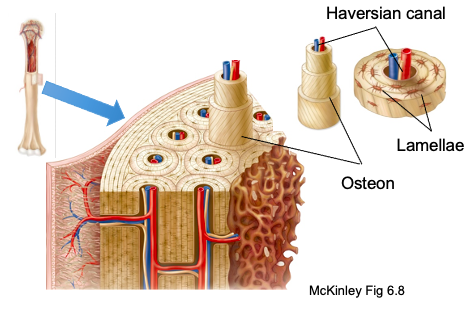
Central (Haversian) canal
runs through core of each osteon and provides blood supply, nutrients, and nerves
Lacunae
a cavity in the bone containing osteocytes
Lamellae/lamellar bone
concentric tubes that make up osteons
Hyaline Cartilage
most common type of cartilage; has tiny, nearly invisible collagen fibers called fibrils; found in ends of long bones, costal cartilages, respiratory structures, and the fetal skeleton
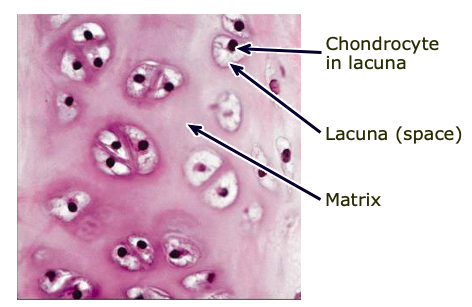
Chondrocytes
the cells of cartilage (found in lacunae)
Perichondrium
a layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the cartilage of developing bone
Epiphysis
ends of long bones
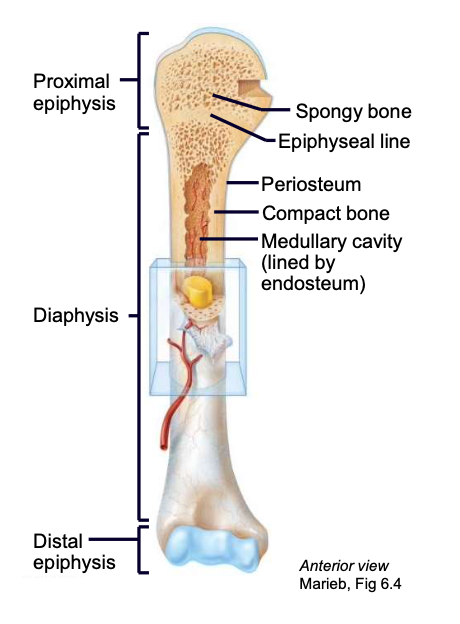
Diaphysis
shaft of long bone
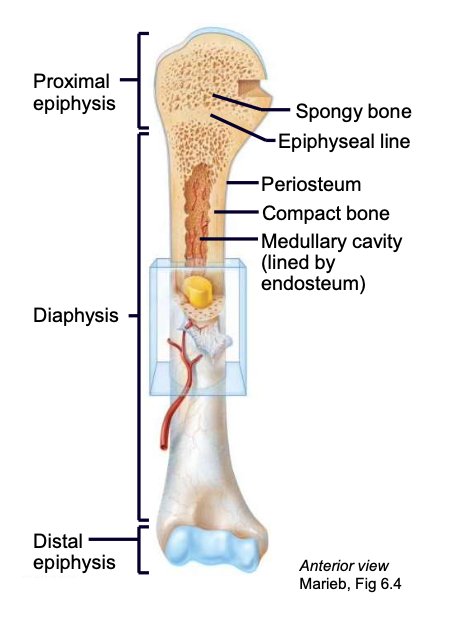
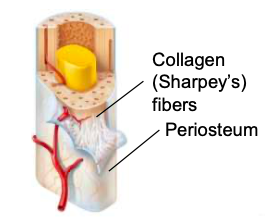
Periosteum
sheath on the outside of a long bone
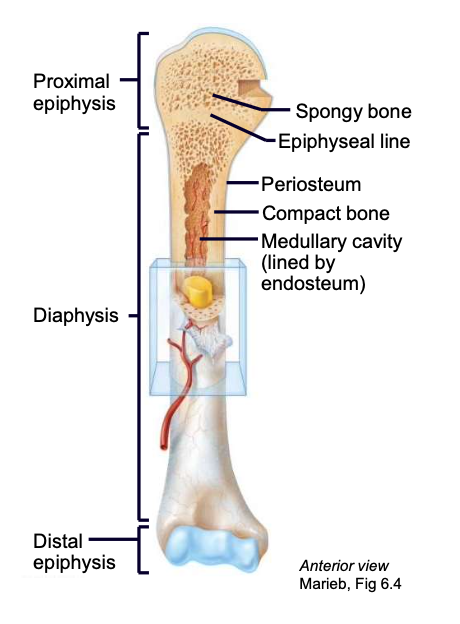
Endosteum
lines the internal medullary cavity of the long bone
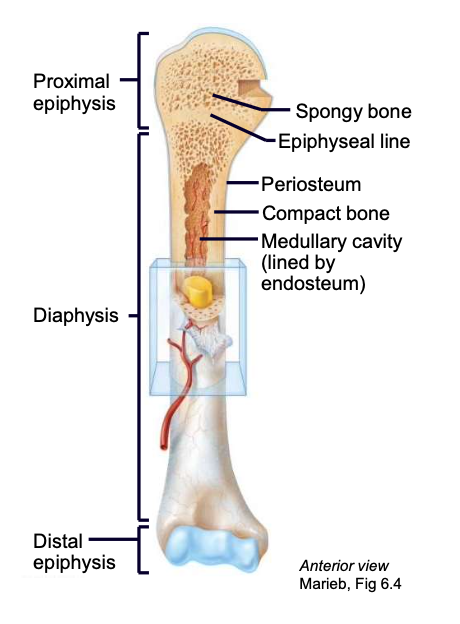
Medullary cavity
cavity of the long bone where bone marrow resides
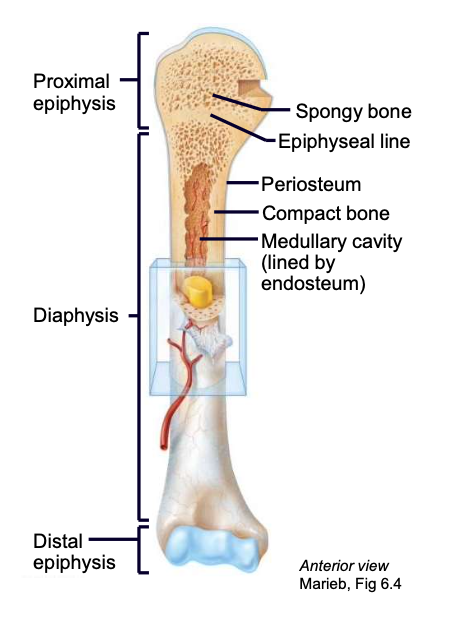
Epiphyseal plate/ line
the “growth” plate; a thin layer of hyaline cartilage found in the epiphysis that ossifies when the bone is done growing
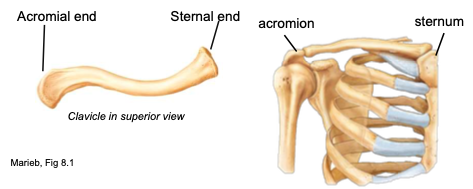
Clavicle
collarbone; spans the superior thorax, S-shaped
attachments: manubrium of sternum, acromion process of scapula
function: provides muscle attachment, acts as brace for the scapula and arms
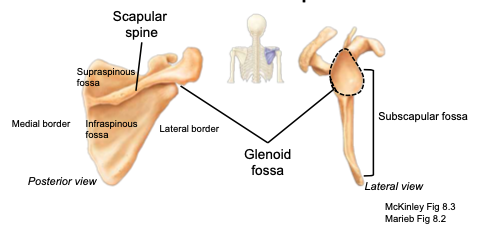
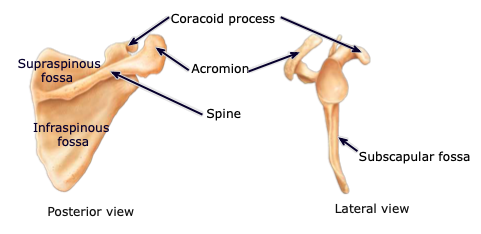
Scapula
shoulder-blade; located on the posterior surface of the rib cage
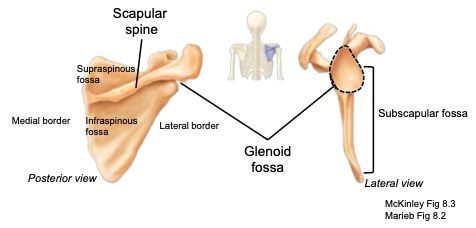
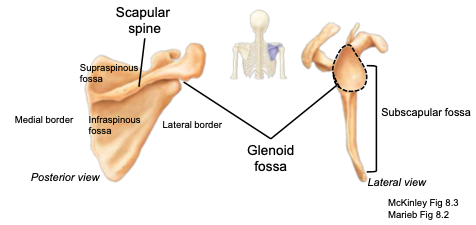
Scapular Spine
located on the posterior side of the scapula; separates the supraspinous from the infraspinous fossa
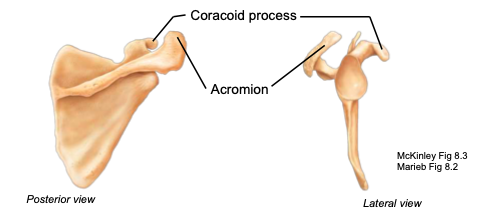
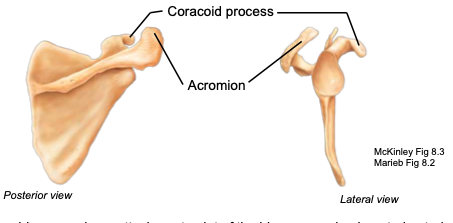
Acromion
part of the scapula articulating with the acromial end of the clavicle; located posteriorly
Glenoid cavity
part of the scapula articulating with the humerus to form the shoulder joint
Coracoid process
part of the scapula acting as an attachment point of the biceps muscle; located anteriorly
Supraspinous fossa
located on the posterior aspect, above the scapular spine; provides attachment sites for muscles
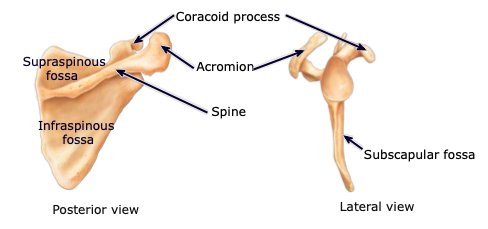
Infraspinous fossa
located on the posterior aspect, below the scapular spine; provides attachment sites for muscles
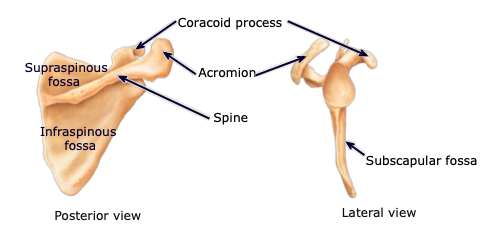
Subscapular fossa
located on the anterior aspect; provides attachment sites for muscles
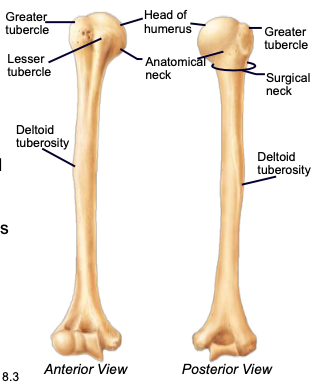
Humerus
longest bone of the upper limb, main bone of the upper arm
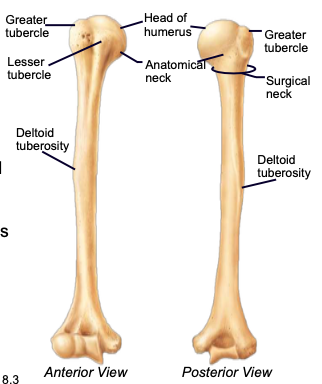
Humeral Head
the highest part of the humerus, supported by the neck; articulates with the scapula at the glenoid cavity
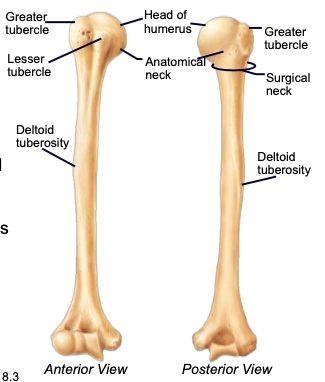
Greater & lesser tubercles
parts of the humerus; sites of muscle attachment
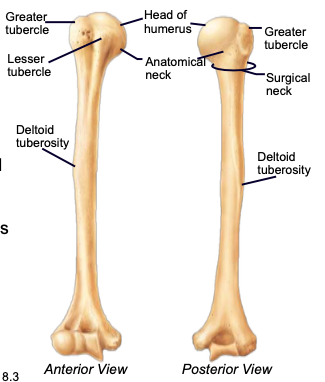
Anatomical neck of humerus
divides the head of the humerus from the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus
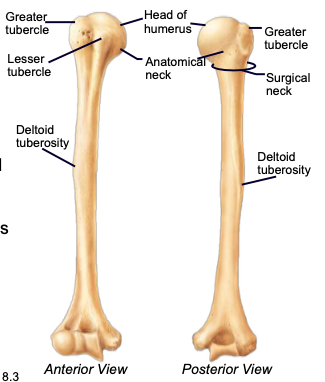
Surgical neck of humerus
bony constriction at the proximal end of the shaft of humerus, where it is frequently fractured
Capitulum
distal part of the humerus articulating with the head of the radius
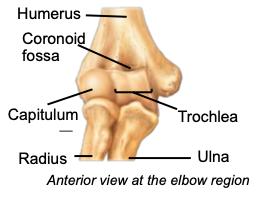
Trochlea
distal part of the humerus articulating with trochlear notch of ulna; creates the hinge joint of the elbow
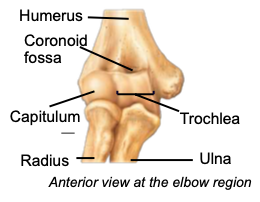
Olecranon fossa
distal part of the humerus articulating with the olecranon process of the ulna
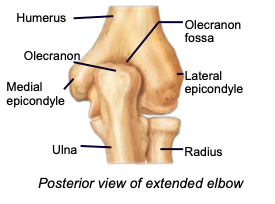
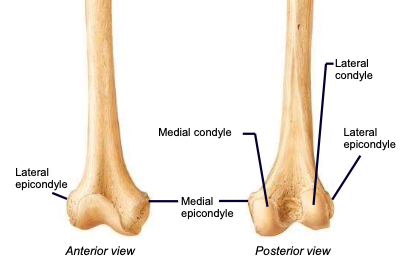
Lateral & medial epicondyles
distal parts of the humerus acting as attachment sites for forearm muscles
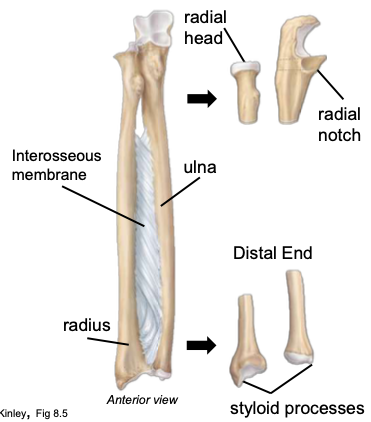
Ulna
medial bone of the forearm
Olecranon process
a projection of the ulna that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus when forearm extends
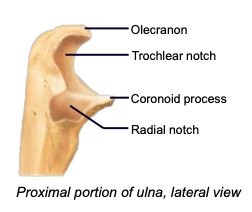
Coronoid process
a projection of the ulna that fits into coronoid fossa when forearm bends
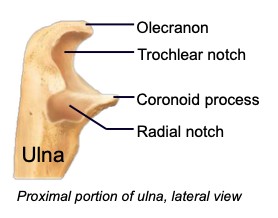
Trochlear notch
the space of the ulna accommodating the trochlea of the humerus; fits over trochlea to create a hinge (allows elbow to bend)
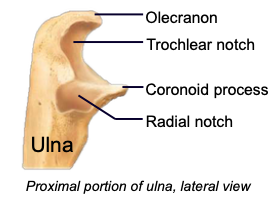
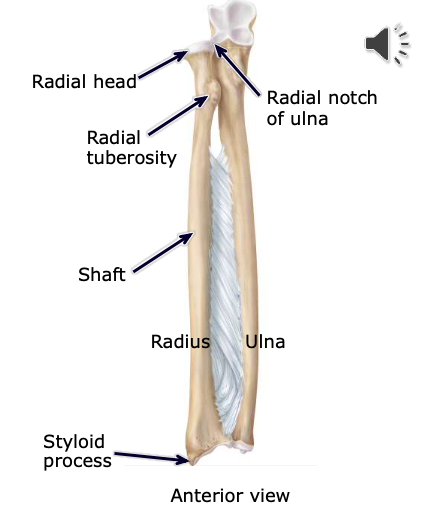
Radial notch
the space of the ulna accommodating the radial head; forms a pivot joint (allows elbow to twist)
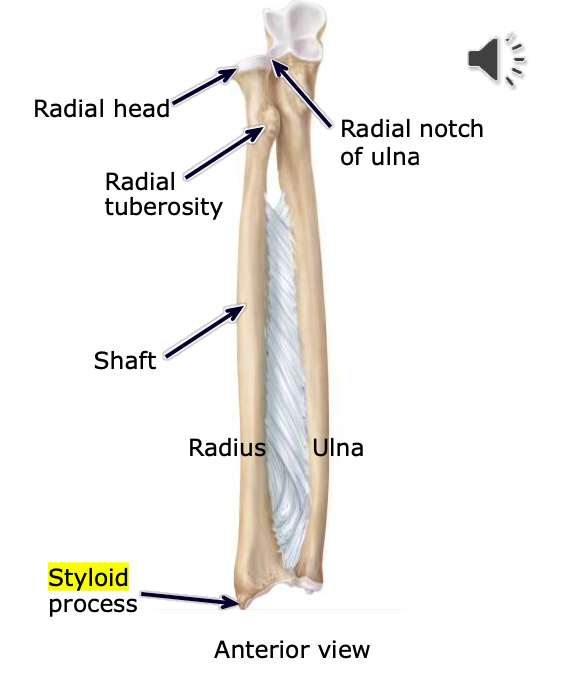
Ulnar Head
located at the lateral, distal end of the ulna; articulates the the ulnar notch of the radius
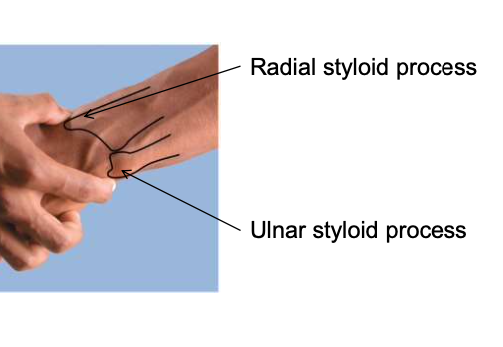
Styloid processes
attachment points for the ligaments that anchor the wrist
Radius
lateral bone of the forearm
Radial Head
located at the proximal, medial end of the radius; articulates the the radial notch of the ulna
Radial Tuberosity
a large bony projection on the medial surface of proximal part of the radius, just distal to the neck
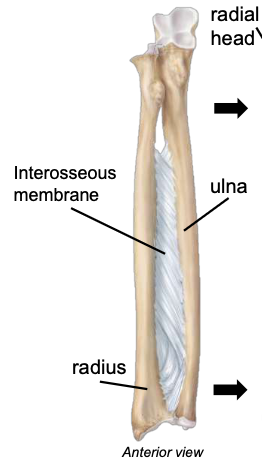
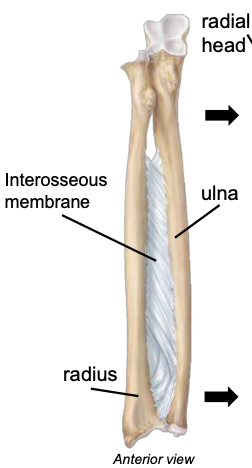
Interosseus membrane (between radius & ulna)
keeps the radius and ulna a fixed distance; allows for rotation
Carpals (8 bones in 2 rows)
Located at the proximal end of the hand; wrist is very flexible because of the gliding motions at the articulations
“Straight Line To Pinky, Here Comes The Thumb”
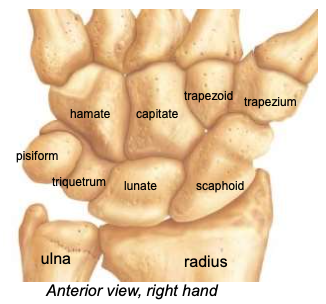
Scaphoid
the most frequently fractured carpal, especially in FOOSH
Metacarpals (1-5)
each digit has one; numbered I-IV, thumb to pinky finger
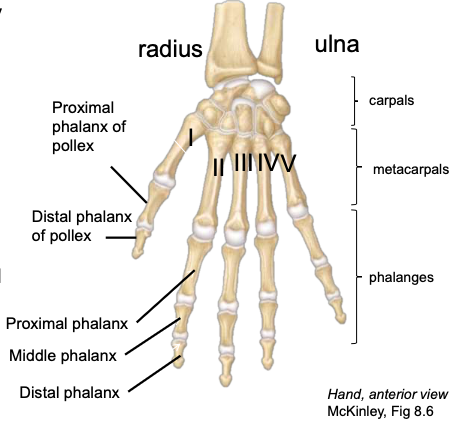
Proximal Phalanges
the most proximal of the three phalanges in digits II-V
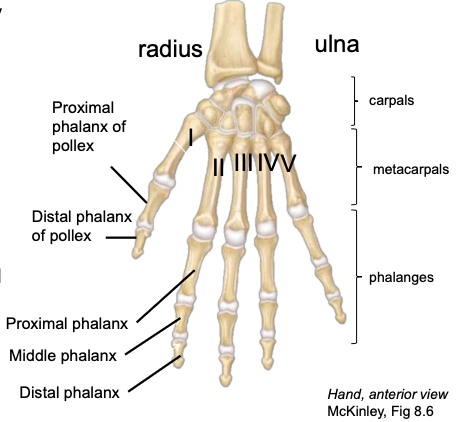
Middle Phalanges
the middle-most of the three phalanges in digits II-V
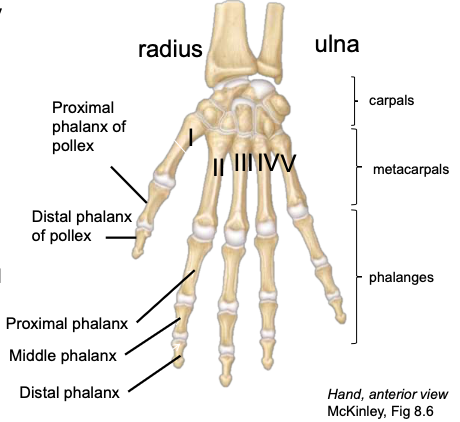
Distal Phalanges
the most distal of the three phalanges in digits II-V
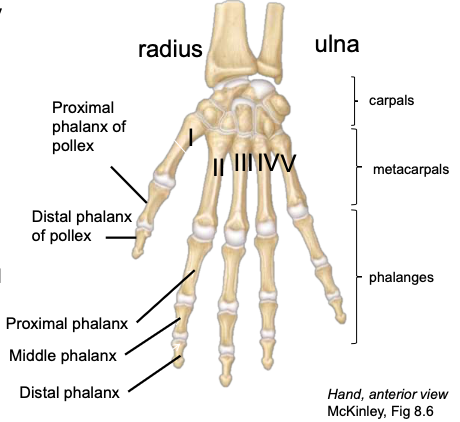
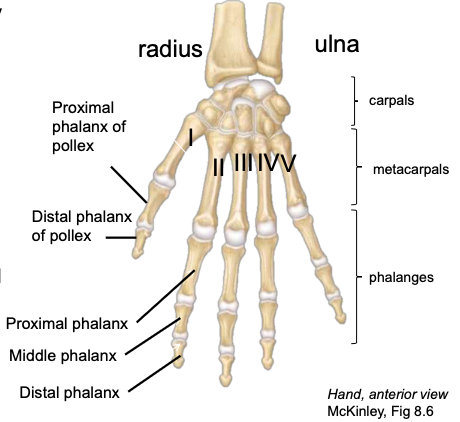
Pollex
thumb, digit 1; has only 2 phalanges (proximal and distal)
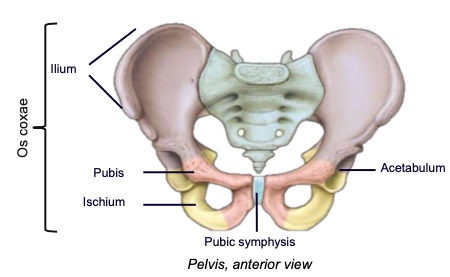
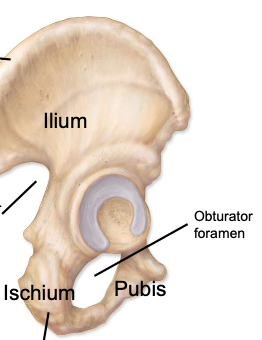
Os coxa
hip bone; a complex-shaped bony structure formed after the fusion (synostosis) of three bones: ilium, ischium, and pubis
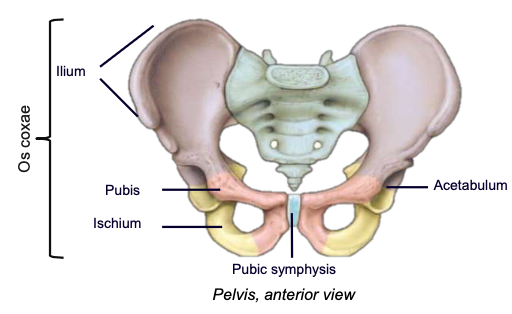
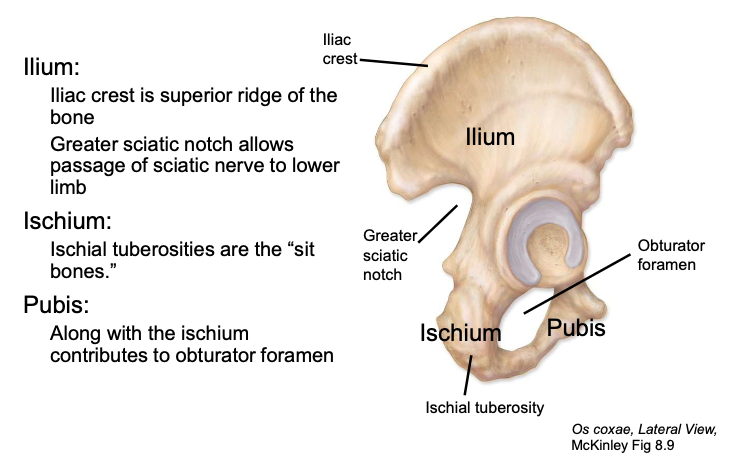
Ilium
the main, most superior component of the os coxa
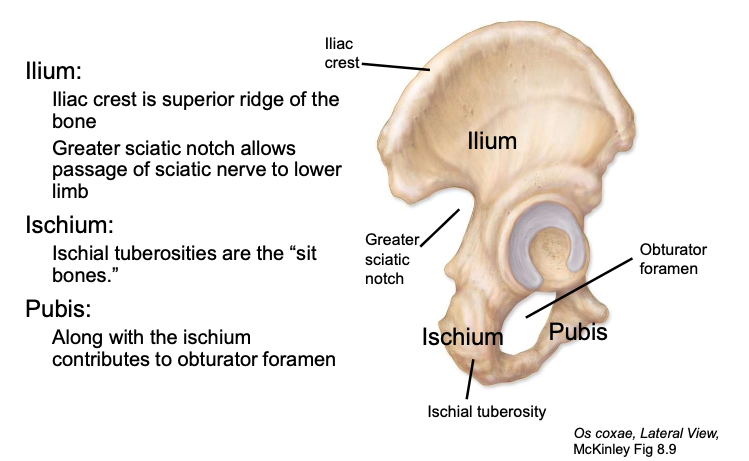
Ischium
the posterioinferior component of the os coxa
Ischial tuberosity
“sit bones”
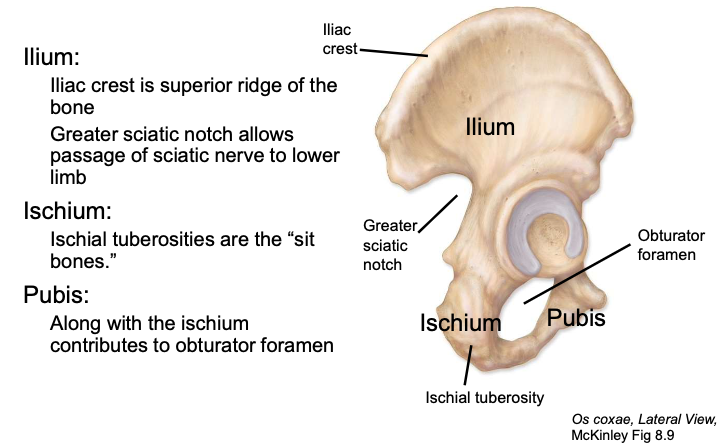
Pubis
the smallest, anterioinferior component of the os coxa
Pubic symphysis
the cartilaginous anterior articulation site of the left and right pubis bones
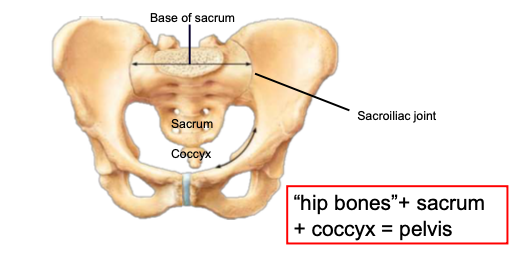
Pelvis (= 2 os coxae + sacrum + coccyx)
Includes both appendicular and axial bones (the sacrum and coccyx are part of the axial skeleton)
Attaches the lower limbs to the trunk (body weight passes through pelvis to the lower limbs) and supports viscera.
Strong attachment to axial skeleton at the sacroiliac joint (very stable). Less freedom of movement compared to pectoral girdle.
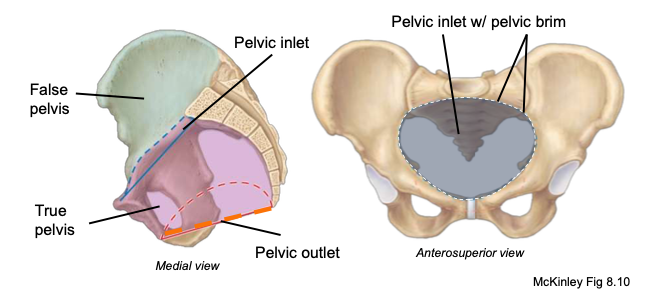
Pelvic inlet
space between pelvic and abdominal cavities (true and false pelves)
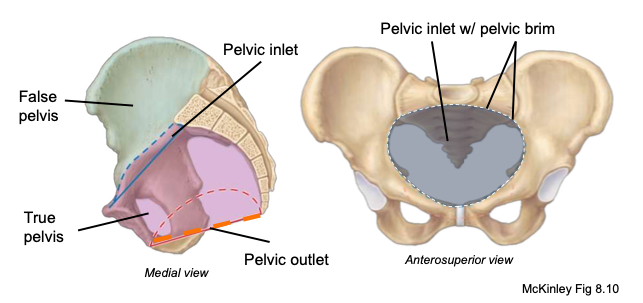
Pelvic outlet
inferior opening defined by ischial tuberosities; the size of this outlet is important for a successful birth
Acetabulum
the lateral socket where the head of the femur articulates; composed of all three of the pelvic bones
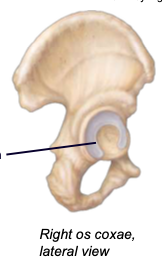
Obturator foramen
a large opening in the pelvic or hip bone, lies just below the acetabulum
Greater sciatic notch
allows passage of sciatic nerve to lower limb
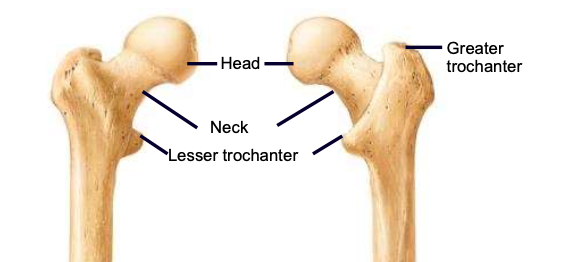
Femur
thigh bone; largest and strongest bone in the body
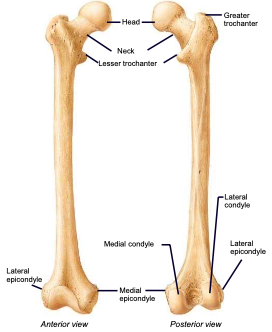
Femoral Head
the highest part of the femur, supported by the neck; articulates with the acetabulum
Fovea capitis
a small, concave depression within the head of the femur that serves as an attachment point for the ligamentum teres
Femoral Neck
weakest part of the femur; angles laterally to join the shaft, carries the head
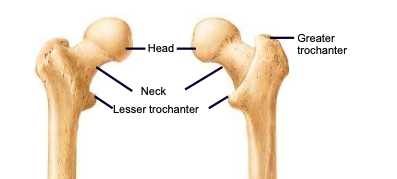
Greater & lesser trochanters
sites of muscle attachment on the femur
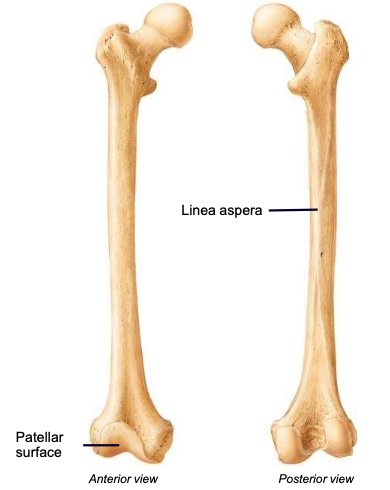
Linea aspera
the ridge along the posterior diaphysis of the femur; used for muscle attachment
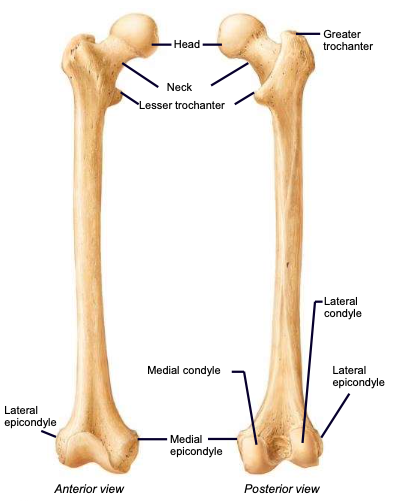
Femoral Condyles
Lateral and medial condyles articulate with the tibia; lateral and medial epicondyles are the more raised parts of these condyles
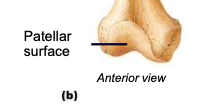
Patellar surface
anteriorly separates the condyles; site of articulation between the femur and patella
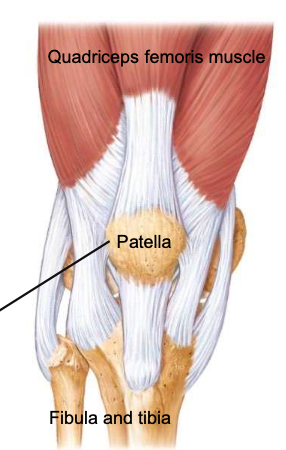
Patella
a sesamoid bone (formed within connective tissue) enclosed in the tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscles; protects knee joint and improves leverage of the quadriceps muscles
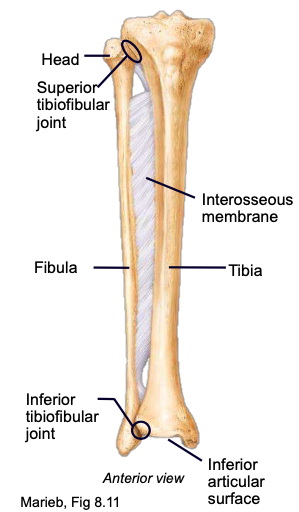
Tibia
the medial, larger, more sturdy bone of the lower leg
Tibial Plateau
shinbone; the triangular diaphysis of the tibia (sharp anterior border)
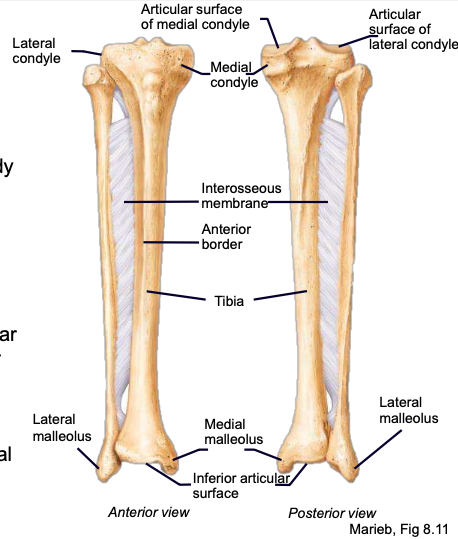
Tibial Condyles
articulation points of the tibia and femoral condyles
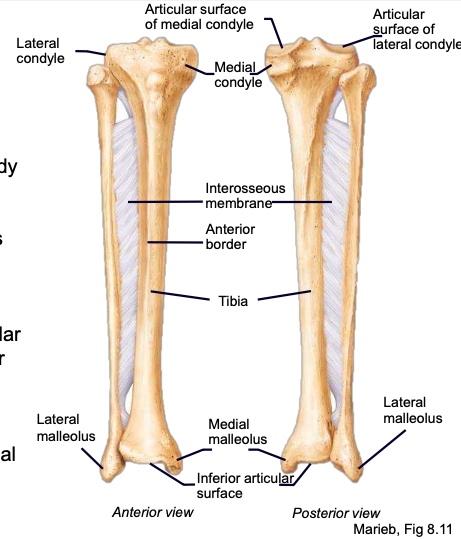
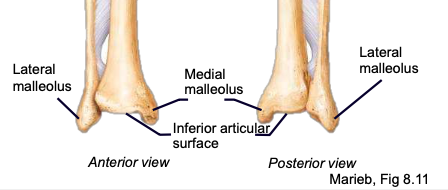
Medial malleolus
the largest of the three bone segments that project to form the ankle bone
Fibula
the thin, lateral, non-weight-bearing bone of the lower leg
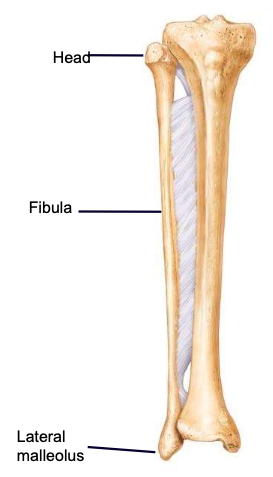
Fibular Head
the highest part of the fibula, supported by the neck; articulates with the tibia
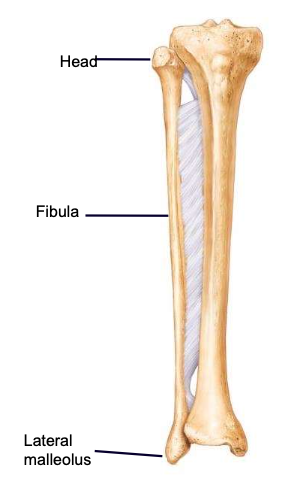
Lateral malleolus
the outermost lower part of the fibula, forming the ankle bone
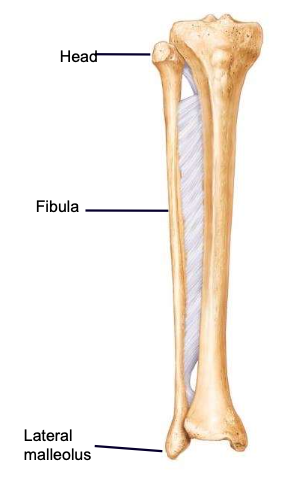
Interosseous membrane (between tibia and fibula)
keeps the tibia and fibula a fixed distance

Tarsals (7 Bones)
Located at the proximal end of the foot
“Tiger Cubs Need M I L C”
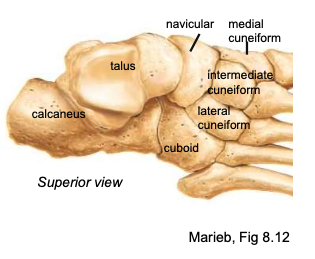
Talus
the bone at the top of the foot that articulates with the tibia + fibula superiorly and the calcaneus inferiorly; carries the majority of the body’ weight
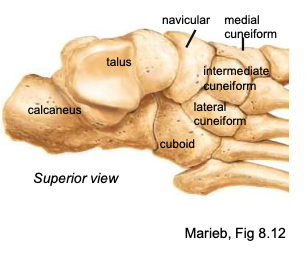
Calcaneus
heel bone; carries the majority of the body’ weight
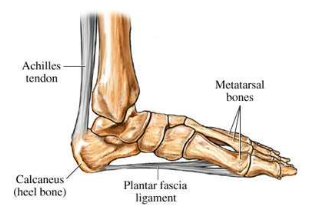
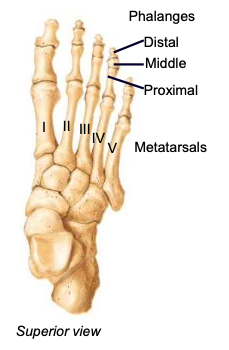
Metatarsals (1-5)
each digit has one; numbered I-IV, big toe to pinky toe
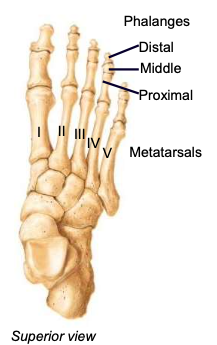
Hallux
big toe, digit 1; has only 2 phalanges (proximal and distal)
Articular (fibrous) capsule
envelope surrounding a synovial joint
2 parts: outer fibrous layer continuous with periosteum; inner synovial membrane that secretes synovial fluid
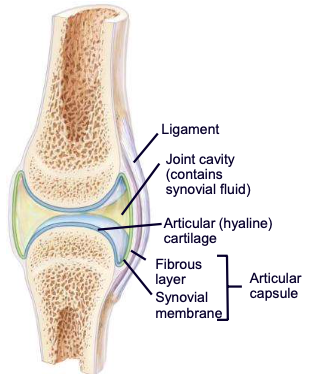
Synovial membrane
a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints and tendon sheaths: makes direct contact with the fibrous membrane on the outside surface and with the synovial fluid lubricant on the inside surface
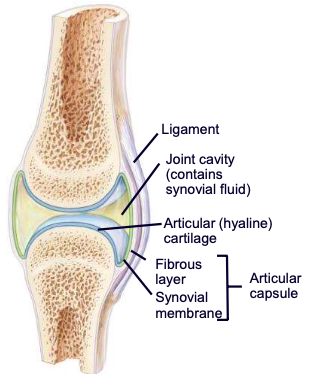
Synovial fluid
liquid in joint cavity and cartilages: provides lubrication for joints
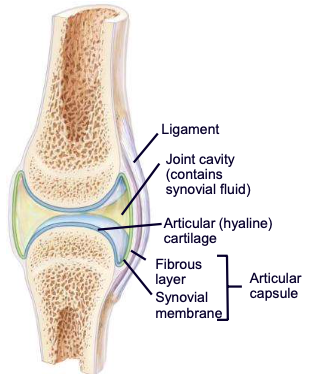
Articular cartilage (in terms of synovial joints)
absorbs forces on the joint, protects bone
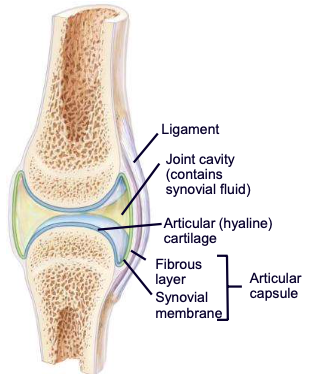
Knee joint
largest and most complex joint; usually acts as a hinge, but can rotate slightly
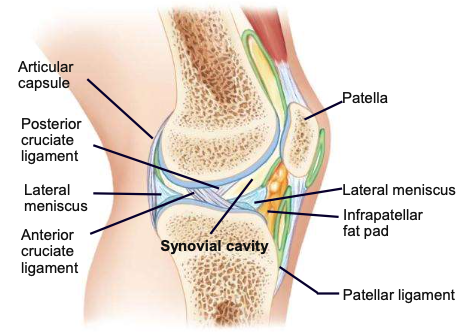
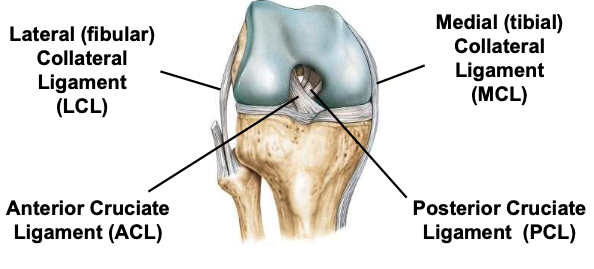
Anterior cruciate ligament
one of 2 cruciate ligaments that aids in stabilizing the knee joint
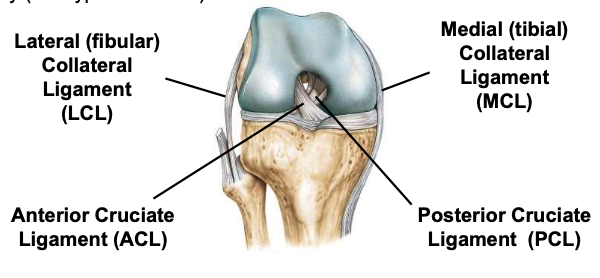
Posterior cruciate ligament
one of 2 cruciate ligaments that aids in stabilizing the knee joint
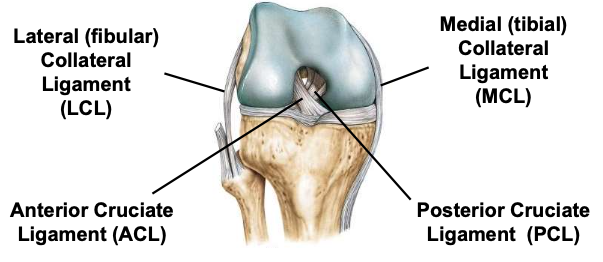
Medial collateral ligament
connects tibia and femur