AP Psych 2024-25
1/352
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
353 Terms
Psychology
study of behavior and mental processes
Experimental Method
manipulating a variable in research
Non-Experimental method
non-manipulative research
Qualitative data
In-depth data, asks for explanation
Quantitative data
surface level information; likert scale (1-5)
operational definition
statement that specifies the procedures used to define research variables, serves as common ground
Sampling Bias
sample that’s not representative of the population.
confounding variables
non independent variables that may affect the dependent variable in an experiment, leading to erroneous conclusions.
consent/assent
permission for an experiment (adult/minor)
confidentiality
preserving identity of subject in experiment
debriefing
occurs after experiment, fully explain to participants what the purpose of experiment was
deception
misleading participants in a research study about the purpose/details of the study.
protection from harm
ethical guideline protecting participant from undue harm caused by the experiment
Descriptive statistics
Summarizes and organizes data to highlight its main features.
Inferential statistics
draws conclusions about a population from sample data.
mean
average
median
numbered lowest-highest, number in the middle of the set
mode
most common score from a set
range
difference between lowest and highest score
percentile rank
scale of 1-100 where a score places, lower percentile = higher score
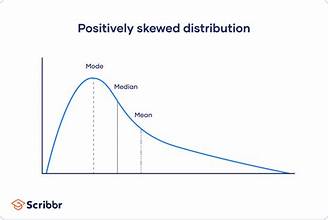
Positive skew
A distribution where most values are concentrated on the left, with a long tail extending to the right.
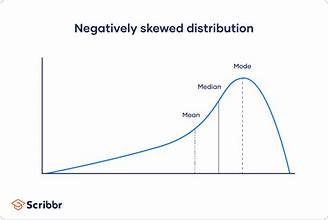
negative skew
A distribution where most values are concentrated on the right, with a long tail extending to the left.
representative sample
1-2 people from a population to represent in a study
statistical significance
how applicable the results of a study are (generalizability)
meta-analysis
combines result from multiple studies
peer review
double checking accuracy of information by peers
standard deviation
variation among scores in a set of values (scale -1 - +1)
Psychodynamic perspective
Behavior is a product of unconscious drives and conflicts, and unresolved issues from childhood.
Cognitive perspective
Behavior is a result of how we process, store and use information to reason and solve problems
Behavioral perspective
Behavior is viewed as a result of learning through associations. Rewards and punishments dictate our behavior
Humanistic perspective
Behavior is a reflection of internal growth and the desire to reach our fullest potential. Nothing determines our behavior but our own free will
Biological perspective
How does the brain and nervous system play a role in our behavior
Neurobiological perspective
Behavior is a result of biological responses
Behavior genetics
Behavior is a result of our “pre-programming” and genetic make up (genetic influence of mental/physical health ex: schizophrenia)
Socio-cultural perspective
Behavior is a result of social, racial, ethnic and religious influences. Behavior and thinking vary with the situation and culture.
Evolutionary perspective
Behavior is a result of favorable traits that promote perpetuation of genes
Nature vs Nurture
debate of what influences and shapes our behavior/mental processes today
Heredity
“nature” argument, what is genetically passed down? shown via adoption/twin studies
Environmental factors
“nurture” argument, what is developed over time through experience? shown via sibling/adoption studies
Natural selection
“survival of the fittest” inspired eugenics movement
Central nervous system
Uses brain and spinal cord to process information and coordinate activity
Peripheral nervous system
Connects the CNS to the limbs and organs, serving as a relay between the brain and spinal cord and the rest of the body (holds peripheral, autonomic, somatic, sympathetic, parasympathetic nervous systems)
autonomic nervous system
Regulates involuntary body functions (heart rate, digestion)
somatic nervous system
Controls voluntary movements and transmits sensory information to the CNS
sympathetic nervous system
Prepares the body for 'fight or flight' response during stress.
parasympathetic nervous system
Conserves energy and restores the body to a state of calm
Nervous vs Endocrine system
Neurotransmitters + Electrical impulses vs Hormones + Bloodstream
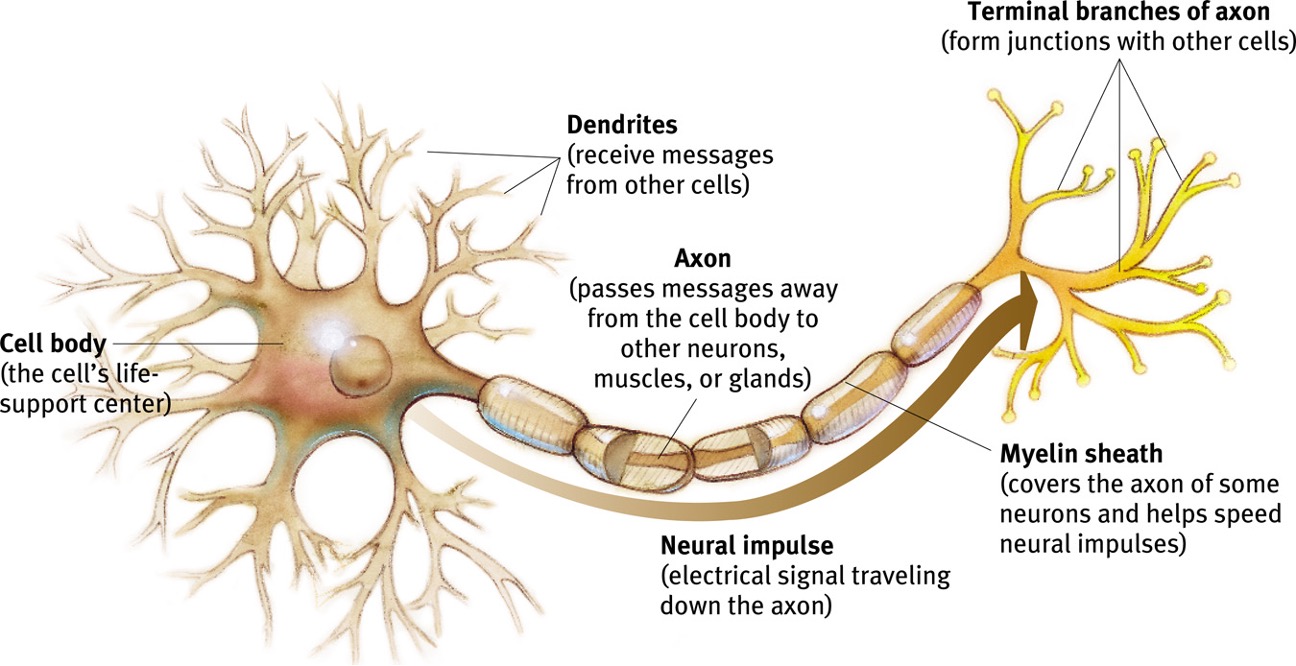
Neuron
sends messages through body of movement and senses
Sensory neuron
sensitive to stimulation (light, sound, touch…) carries message to CNS (ex:touching a flame)
Interneurons
connects neurons to one another, carries messages within CNS (ex: processing pain of touching flame)
Motor neurons
transmits impulse to muscles, carrying messages from CNS to body 9ex: yanking hand back from a burning flame)
reflex arc
the entire process (sensory-inter-motor neuron) of messaging throughout CNS
Glial cells
support neural network producing myelin (helps axon generate)
Neural transmission
electrical impulses sent within each neuron
Polarized neuron
“resting potential state” of a neuron, inside is mostly negative and outside is mostly positively charged
Depolarized Neuron
“Action potential” of a neuron, electrical charge down axon, negative ions move out
Threshold (neuron)
neuron must reach a certain energy level to fire
Excitory signal
a signal that increases the likelihood of a neuron firing, making it more likely that the message will be transmitted (glutamate!)
Inhibitory signal
a signal that decreases the likelihood of a neuron firing, making it less likely that the message will be transmitted (GABA/Glyceine)
reuptake inhibitor
prevents absorption of neurotransmitter (ex: anti depressants block serotonin from being absorbed so your body has more of it)
Refractory period
after depolarized, neuron must reset
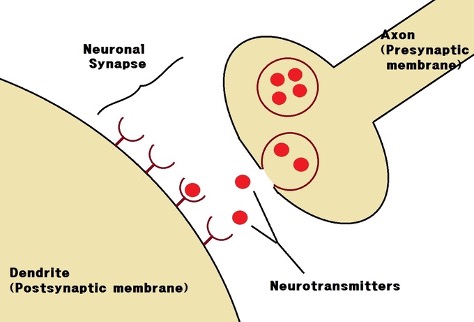
synaptic gap
space between axon of a neuron and receiving neuron
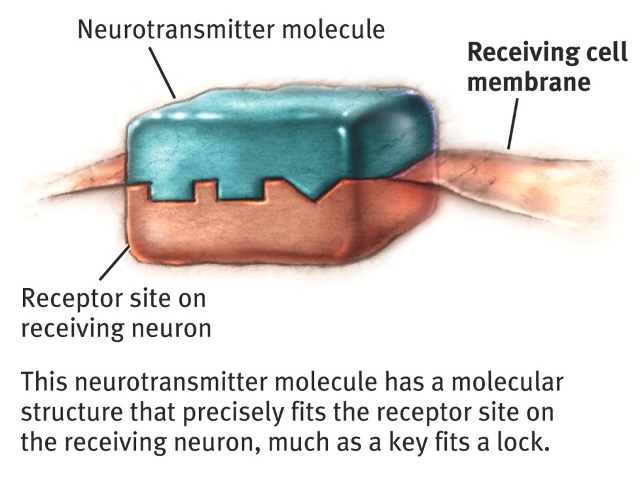
Neurotransmitter
triggers chemical release when action potential reaches synaptic gap
Norepinephrine
neurotransmitter; body's stress response, regulating arousal, attention, and mood, influencing fight-or-flight response. Abnormal levels have been linked to conditions such as anxiety and depression.
Glutamate
Excitory neurotransmitter, cognition, learning, memory, synaptic plasticity
Acetylcholine
transmitter influencing both CNS and PNS; excitory, muscle contraction, attention, arousal, memory
dopamine
reward, motivation, pleasure neurotransmitter; regulates mood, attention, and motor control; abnormal levels linked to depression/schizophrenia
serotonin
neurotransmitter; regulates mood, apetite, sleep, memory. low levels linked to anxiety and depression
GABA
Inhibitory neurotransmitter; CNS, regulates muscle tone and anxiety, calms brain activity
Adrenaline
neurotransmitter/hormone released by adrenal glands, excitory (fight or flight) increased heart rate, blood pressure, energy
Melatonin
Hormone; sleep/wake cycle
oxytocin
“love” hormone, bonding, care
Endorphins
acts as neurotransmitter in pain relief, natural response to stress/discomfort “feel good” hormone
leptin
hormone; low level = hunger
ghrelin
hormone; high level = hunger
hallucinogens
class of drug, affects audio/visual perception
Depressants
class of drug, slows brain activity and bodily function
stimulants
class of drug amplifying brain activity and bodily function
caffeine
a stimulant that increases alertness and energy
cocaine
a stimulant that increases energy, alertness, and euphoria, often leading to addiction.
nicotine
a stimulant found in tobacco that enhances alertness and can lead to dependence.
alcohol
a depressant that affects the central nervous system, leading to relaxation, impaired judgment, and decreased coordination.
marijuana
a psychoactive drug /hallucinogen that can produce relaxation, altered perception, and increased appetite, often used for both recreational and medicinal purposes.
heroin
a highly addictive opioid that produces intense euphoria, pain relief, and can lead to severe physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms.
Brainstem
structure of the brain that regulates vital functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and blood pressure, and connects the brain to the spinal cord. (includes the thalamus, reticular formation, and medulla)
Frontal lobe
the lobe of the brain associated with reasoning, planning, problem-solving, and emotional regulation, located at the front of the cerebral cortex.
brocas area
a region in the left frontal lobe responsible for language production and speech.
wernickes area
a region in the left temporal lobe involved in language comprehension and understanding.
motor cortex
a region in the frontal lobe responsible for controlling voluntary movements of the body's muscles.
Parietal lobe
the lobe of the brain responsible for processing sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain, located behind the frontal lobe.
sensory cortex
a region in the parietal lobe that processes sensory information from the body, including touch, temperature, and pain.
occipital lobe
the lobe of the brain responsible for processing visual information, located at the back of the brain.
association areas
regions of the parietal lobe involved in higher cognitive functions such as thinking and problem-solving.
somasensatory cortex
a part of the sensory cortex that specifically processes tactile information from the body.
visual cortex
the area within the occipital lobe that processes visual information from the eyes.
auditory cortex
the region in the temporal lobe that processes auditory information from the ears.
temporal lobe
the lobe of the brain responsible for processing auditory information and is involved in memory and emotion, located beneath the lateral fissure.
corpus callosum
layer of brain connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, allows communication between them.
hippocampus
a part of the brain involved in the formation of new memories and spatial navigation, located in the medial temporal lobe.
amygdala
a part of the brain involved in emotional processing, particularly fear and pleasure responses, located near the hippocampus.