Organic Chemistry
1/187
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms
Alcohols Nomenclature
Suffix -ol
Alcohols with two hydroxyl groups are called diols or glycols and are indicated with the suffix -diol
Aldehydes Nomenclature
Suffix -al
Methanal: Formaldehyde
Ethanal: Acetaldehyde
Propanal: Propionaldehyde
Ketones Nomenclature
Suffix -one
Carboxylic Acid Nomenclature
Suffix -oic acid
Esters Nomenclature
___ -yl ____-oate
Amide Nomenclature
Suffix -amide
Anhydride Nomenclature
Replace acid with anhydride
Isomer
Same molecular formula but different structures
Constitutional (Structural) Isomers
Same molecular formula/weight
Stereoisomer
Same structural backbone, differ in how atoms are arranged in space
Conformational Isomer
Differ in rotation around single bonds
Configurational Isomer
Can be interconverted only by breaking bonds
Newman Projection
A molecule is visualized along a line extending through a carbon-carbon bond axis
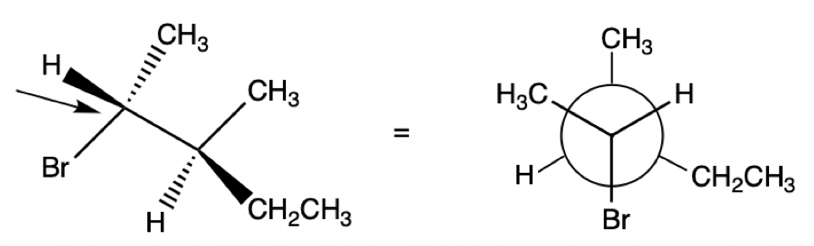
Staggered Conformation
When two functional groups in a Newman projection are oriented 180 degrees away from each other; AKA lowest-energy state
Anti Conformation
In a Newman projection, when the two largest groups are antiperiplanar (in the same plane, but on opposite sides) to each other; Occurs in a staggered conformation
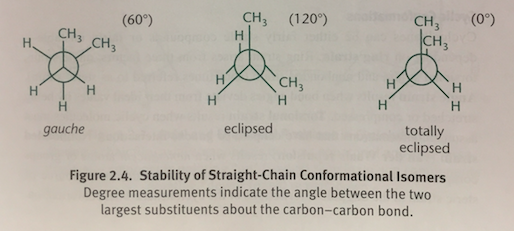
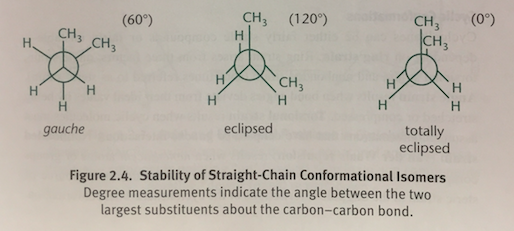
Gauche Conformation
In a Newman projection, when the two largest groups are 60 degrees apart; Occurs in a staggered conformation
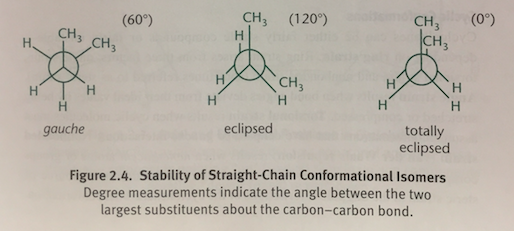
Eclipsed Conformation
In a Newman projection, when two methyl groups are 120 degrees apart and overlap with the hydrogen atoms on the adjacent carbon
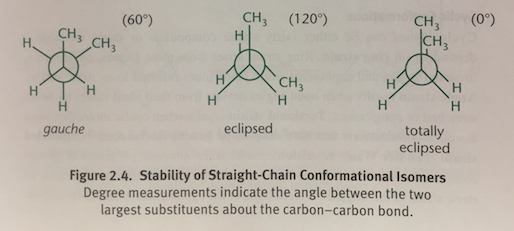
Totally Eclipsed Conformation
In a Newman projection, when two methyl groups directly overlap each other with 0 degrees of separation; The molecule’s highest-energy state
Torsional Strain
Occurs when cyclic molecules must assume conformations that have eclipsed or gauche interactions
Nonbonded Strain (van der Waals Repulsion)
Results when nonadjacent atoms or groups compete for the same space; Dominant source of steric strain in the flagpole interactions of the cyclohexane boat conformation
Axial
In the chair conformation, the hydrogen atoms that are perpendicular to the plane of the ring (sticking up or down)
Equatorial
In the chair conformation, the hydrogen atoms that are parallel to the plane of the ring (sticking out)
Diastereomers
When two molecules are chiral and share the same connectivity but are not mirror images of each other because they different at some of their multiple chiral centers
For any molecule with n chiral centers, there are 2n possible stereoisomers
Optical Activity
When a chiral compound has the ability to rotate plane-polarized light; One enantiomer will rotate plane-polarized light to the same magnitude but in the opposite direction of its mirror image; Racemic mixtures don’t have this; Molecules with this lack a plane of symmetry
Dextrorotatory (d-)
A compound that rotates the plane of polarized light to the right, or clockwise; Labeled (+); Determined experimentally
Levorotatory (l-)
A compound that rotates light toward the left, or counterclockwise; Labeled (-); Determined experimentally
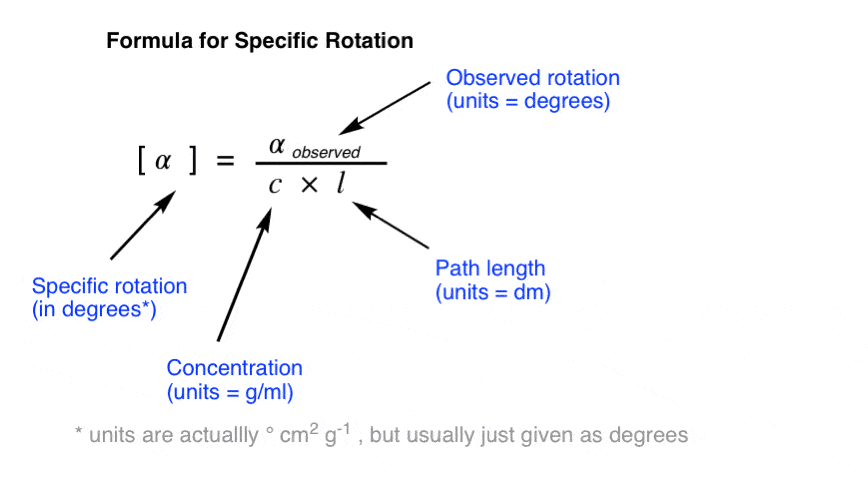
Specific Rotation
Racemic Mixture
When both (+) and (-) enantiomers are present in equal concentration; No optical activity is observed
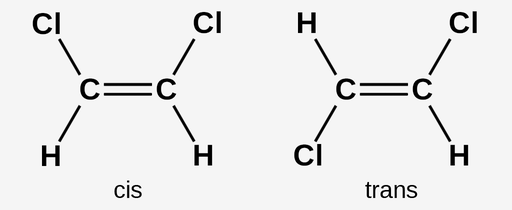
Cis-Trans Isomers
Type of diastereomer in which substituents differ in their position around an immovable bond, such as a double bond, or around a ring structure, such as a cycloalkane in which the rotation of bonds is greatly restricted; In simple compounds with only one substituent on either side of the immovable bond, we use the terms cis and trans
Meso Compound
A molecule with chiral centers that has an internal plane of symmetry
Relative Configuration
The configuration of a chiral molecule in relation to another chiral molecule
Absolute Configuration
The exact spatial arrangement of atoms or groups in a chiral molecule, independent of other molecules
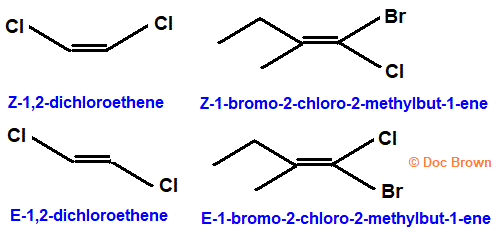
Cahn-Ingold-Prelog Priority Rules (E and Z Forms)
The alkene is named (Z) if the two highest-priority substituents on each carbon are on the same side of the double bond and (E) if they are on opposite sides
The higher the atomic number, the higher the priority
(R) and (S) Nomenclature
Step 1: Assign Priority
Higher atomic number = Higher priority
Step 2: Arrange in Space
Orient the molecule in 3D so that the atom with the lowest priority is at the back of the molecule (Anytime two groups are switched on a chiral carbon, the stereochemistry is inverted; if we switch the lowest-priority group to the back, we need to switch our final answer from (R) to (S), or vice versa)
Step 3: Draw a Circle
Draw a circle connecting the substituents from 1-3
Counterclockwise = (S)
Clockwise = (R)
S-Orbital
Spherical and symmetrical, centered around the nucleus
P-Orbital
Composed of two lobes located symmetrically about the nucleus and contains a node—an area where the probability of finding an electron is zero—at the nucleus
D-Orbital
Composed of four symmetrical lobes and contains two nodes; Four of these orbitals are clover-shaped, and the fifth looks like a donut wrapped around the center of a p-orbital
Molecular Orbitals
When two atomic orbitals combine
Bonding Orbital
Produced when the signs of the wave functions of two atomic orbitals are the same; Lower-energy and more stable
Antibonding Orbital
Produced when the signs of the wave functions of two atomic orbitals are different; Higher-energy and less stable
Single Bonds
All of these are sigma bonds, accommodating two electrons; Requires more energy to break this than one of the two bonds in a double bond
Double Bond
One pi bond on top of an existing sigma bond; Hinders free rotation of atoms around the bond axis; Shorter than a single bond
Hybrid Orbitals
Formed by mixing different types of orbitals
S Character
Example Problem: an sp3 orbital has 25% s character and 75% p character
Lewis Acid
Electron acceptor
Lewis Base
Electron donor
Bronsted-Lowry Acid
A species that can donate a proton
Bronsted-Lowry Base
A species that can accept a proton
Amphoteric
Molecules that can act as either Bronsted-Lowry acids or bases
Ka Equation
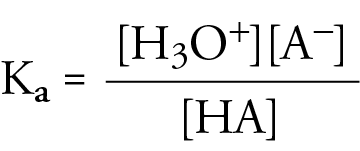
pKa
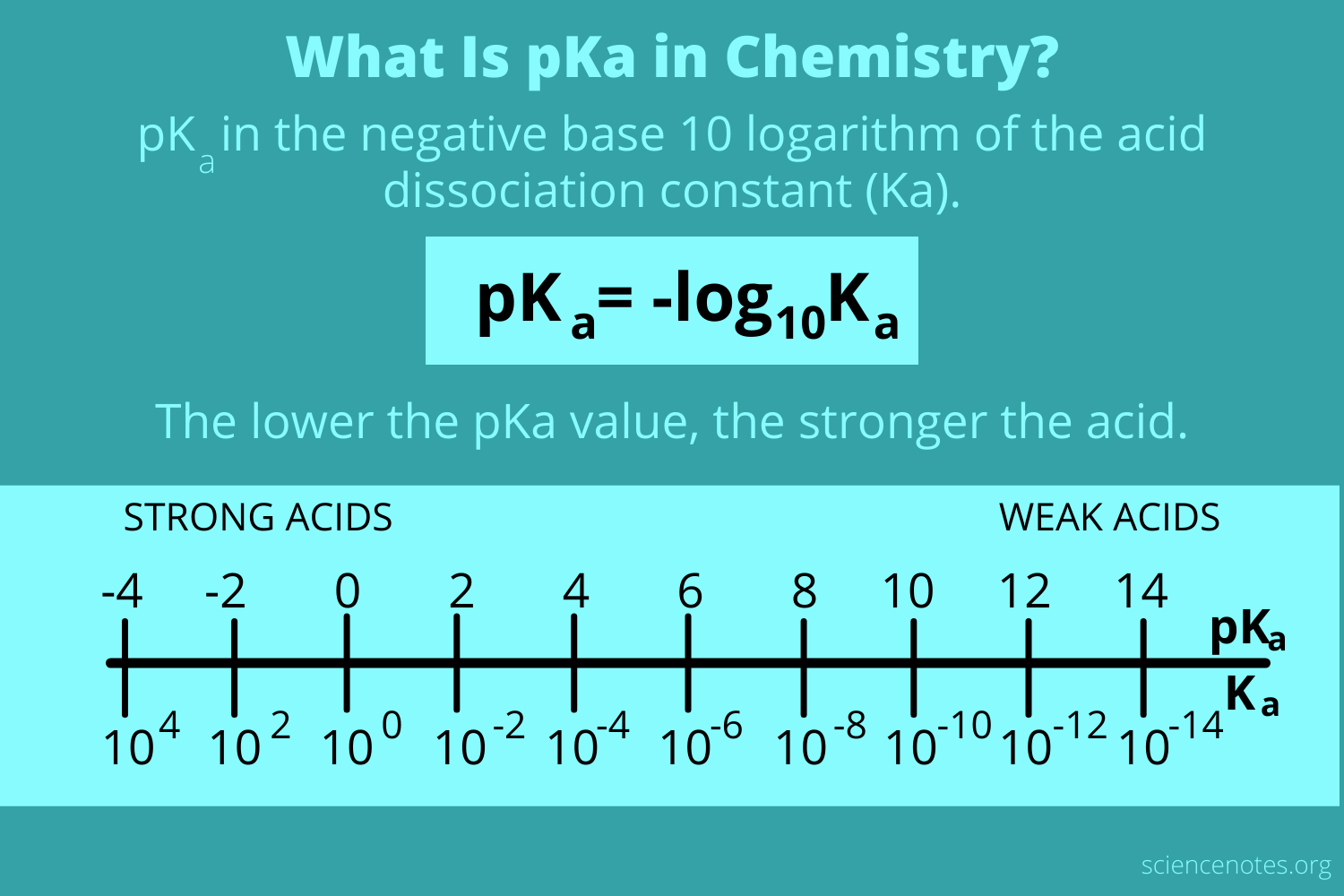
pKa Values
Generally, bond strength decreases down the periodic table, and acidity therefore increases; The more electronegative an atom, the higher the acidity
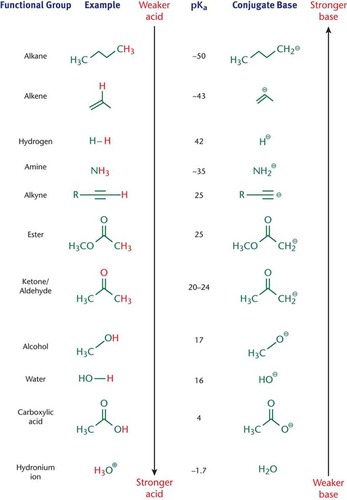
Nucleophiles
Good _____ tend to be good bases
Nucleophilicity determined by:
Charge: Nucleophilicity increases with increases electron density (more negative charge)
Electronegativity: Nucleophilicity decreases as electronegativity increases because these atoms are less likely to share electron density
Steric Hindrance: Bulkier molecules are less nucleophilic
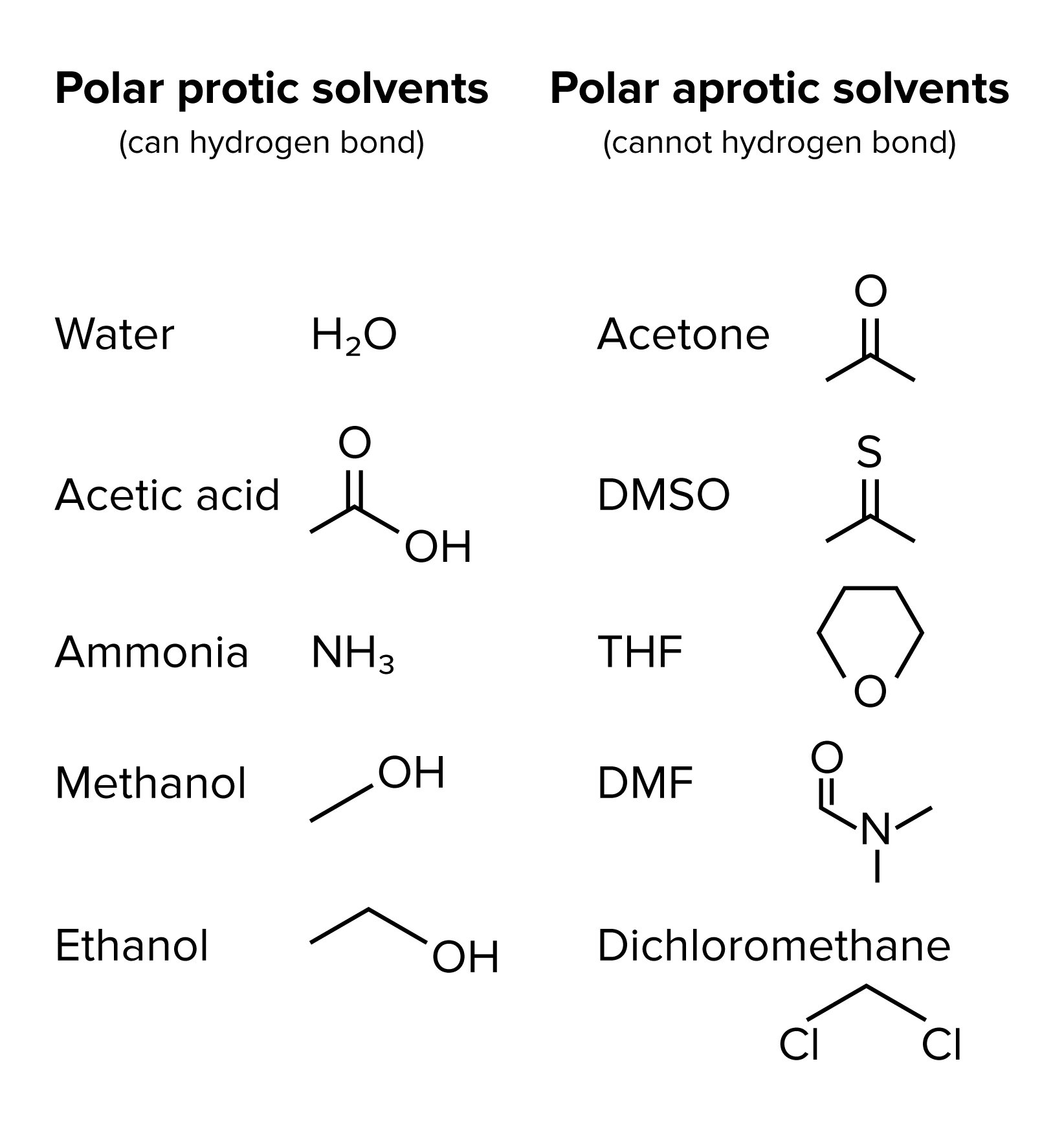
Solvent: Protic solvents can hinder nucleophilicity by protonating the _____ or through hydrogen bonding
In polar protic solvents, nucleophilicity increases down the periodic table (I- > Br- > Cl- > F-). In polar aprotic solvents, nucleophilicity increases up the periodic table (F- > Cl- > Br- > I-). In aprotic solvents, nucleophilicity relates directly to basicity.
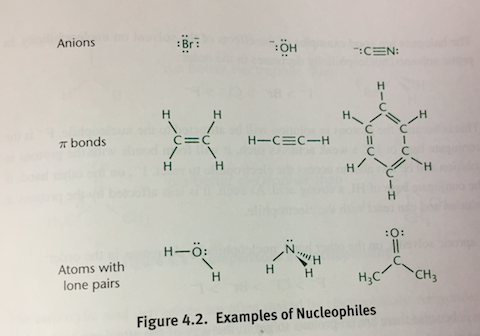
Electrophiles
Species with a positive charge or positively polarized atom that accepts an electron pair when forming new bonds with a nucleophile; Almost always act as Lewis acids in reactions; Greater degree of positive charge increases electrophilicity
Anhydrides > Carboxylic Acids and Esters > Amides

Heterolytic Reactions
Reactions where a bond is broken and both electrons are given to one of the two products; Weak bases are more stable with an extra set of electrons and therefore make good leaving groups (conjugate bases of strong acids like I-, Br-, and Cl-)
SN1 Reactions
Two steps; First step is the rate limiting step in which the LG leaves, generating a positively charged carbocation; The nucleophile then attacks the carbocation, resulting in the substitution product; Formation of the carbocation is the rate-limiting step (rate = k[R-L], where R-L is an alkyl group containing a LG); First order reaction; Planar intermediate; Product will usually be a racemic mixture
![<p>Two steps; First step is the rate limiting step in which the LG leaves, generating a positively charged carbocation; The nucleophile then attacks the carbocation, resulting in the substitution product; Formation of the carbocation is the rate-limiting step (rate = k[R-L], where R-L is an alkyl group containing a LG); First order reaction; Planar intermediate; Product will usually be a racemic mixture</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c877383f-6df5-40fd-92ab-b36ea33d3e6f.png)
SN2 Reactions
One step; The nucleophile attacks the compound at the same time as the LG leaves; Concerted, bimolecular reaction because the single rate-limiting step involves two molecules; Backside attack; Nucleophile must be strong, and the substrate cannot be sterically hindered (less substituted carbon = more reactive)
Rate = k[Nu][R-L]
Inversion of relative configuration; If the nucleophile and LG have the same priority in their respective molecules, this inversion will also correspond to a change in absolute configuration from (R) to (S); Stereospecific reaction where the configuration of the reactant determines the configuration of the product
Won’t occur with tertiary substrates
![<p>One step; The nucleophile attacks the compound at the same time as the LG leaves; Concerted, bimolecular reaction because the single rate-limiting step involves two molecules; Backside attack; Nucleophile must be strong, and the substrate cannot be sterically hindered (less substituted carbon = more reactive)</p><p>Rate = k[Nu][R-L]</p><p>Inversion of relative configuration; If the nucleophile and LG have the same priority in their respective molecules, this inversion will also correspond to a change in absolute configuration from (R) to (S); Stereospecific reaction where the configuration of the reactant determines the configuration of the product</p><p>Won’t occur with tertiary substrates</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/40daa696-af6f-4c88-a4c5-a6be0458cf0e.gif)
Oxidation State
An indicator of the hypothetical charge that an atom would have if all bonds were completely ionic
Oxidation Reaction
This type of reaction tends to feature an increase in the number of bonds to oxygen, and oxidizing agents often contain metals bonded to a large number of oxygen atoms
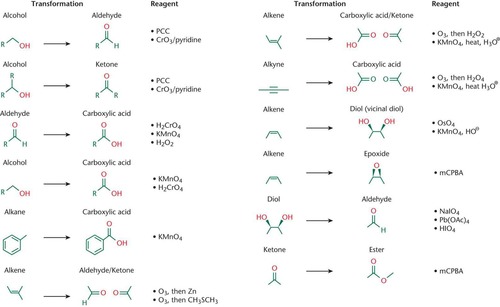
Reduction Reaction
This type of reaction tends to feature an increase in the number of bonds to hydrogen, and reducing agents often contain metals bonded to a large number of hydrides
Chemoselectivity
The preferential reaction of one functional group in the presence of other functional groups
Reaction Locations
A redox reagent will tend to act on the highest-priority functional group; For a reaction involving nucleophiles and electrophiles, reactions also tend to occur at the highest-priority functional group because it contains the most oxidized carbon; A nucleophile is looking for a good electrophile, the more oxidized the carbon, the more electronegative groups around it, and the larger partial positive charge it will experience; Aldehydes are generally more reactive toward nucleophiles that ketones; Carbon of a carbonyl
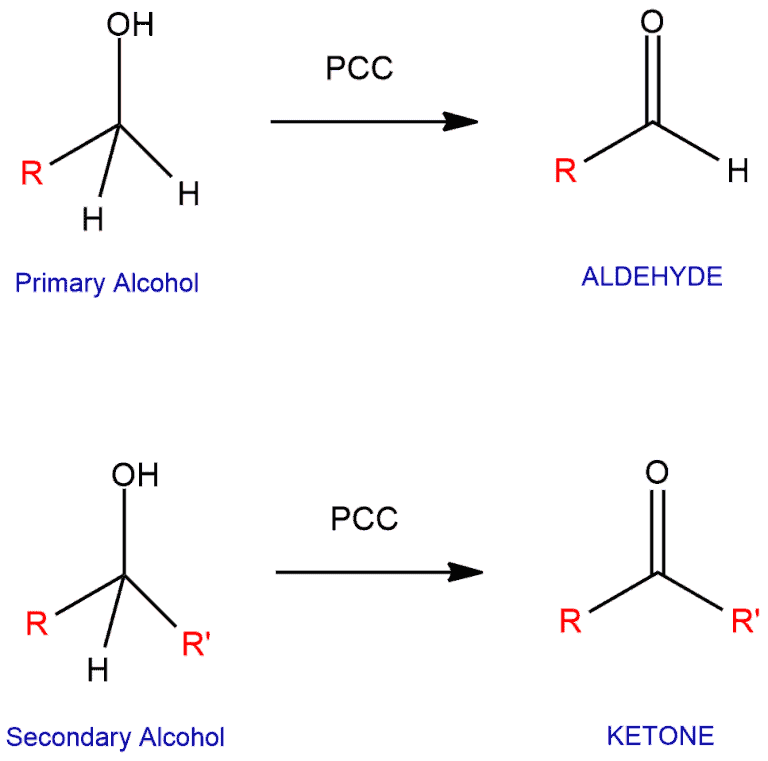
Pyridinium Chlorochromate
Weak oxidizing agent (PCC); Can oxidize primary and secondary alcohols
Polar Protic and Aprotic Solvents
PCC (Pyridinium Chlorochromate)
Oxidizing agent; Is the only oxidizing agent that can oxidize primary alcohols to aldehydes (does not oxidize the aldehyde)
Primary Alcohols
Oxidized into an aldehyde by PCC; Oxidized into a carboxylic acid by stronger oxidizing agents (i.e. chromium)
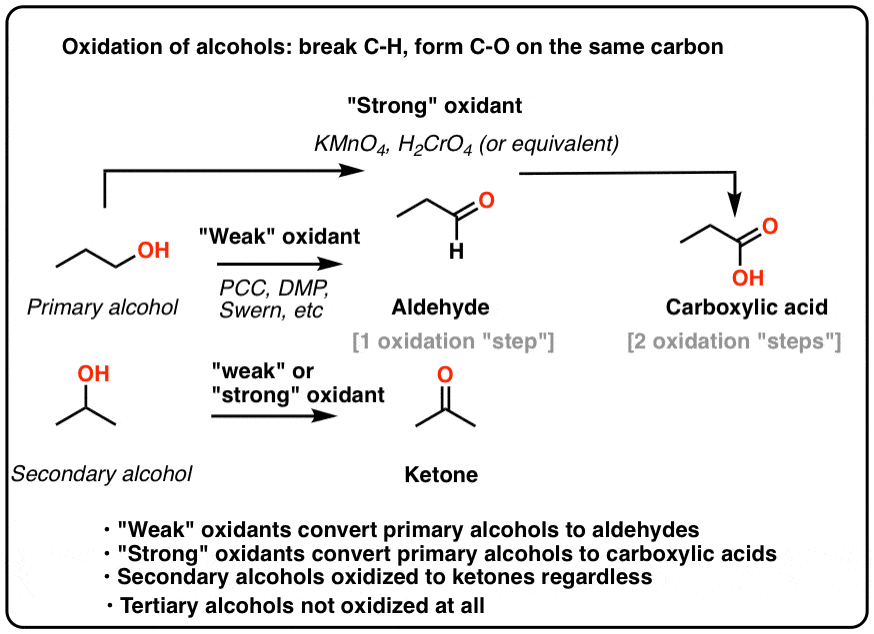
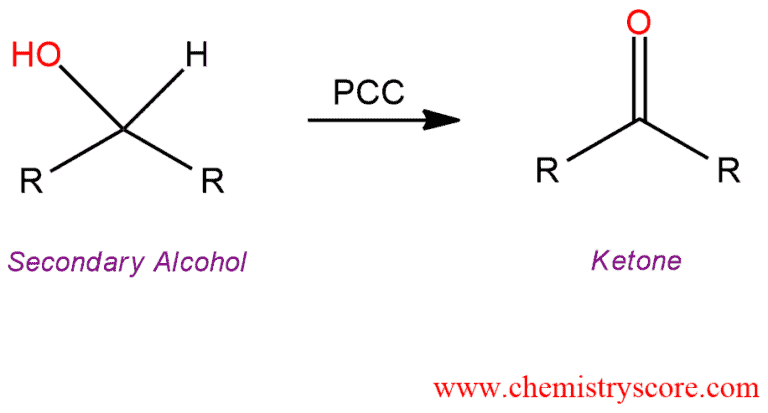
Secondary Alcohols
Can be oxidized to ketones by PCC or any stronger oxidizing agent
Tertiary Alcohols
Cannot be oxidized because they are already as oxidized as they can be without breaking a carbon-carbon bond
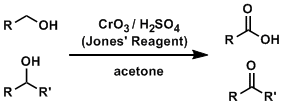
Jones Oxidation
CrO3, dilute sulfuric acid, and acetone oxidizes primary alcohols to carboxylic acids and secondary alcohols to ketones
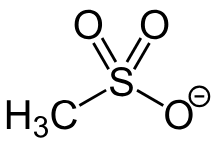
Mesylate
A compound containing the functional group -SO3CH3; Better LG that hydroxyl; Removed using a strong acid
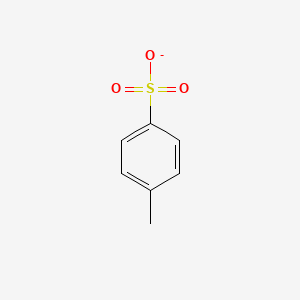
Tosylates
Contain the functional group -SO3C6H4CH3; Better LG than hydroxyl; Removed using a strong acid
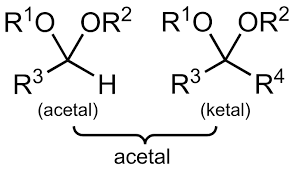
Acetals
Primary carbons with two -OR groups and a hydrogen atom; Not as reactive to reducing agents as carbonyls
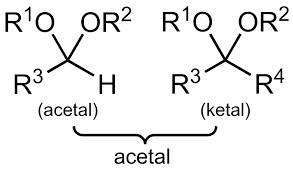
Ketals
Secondary Carbons with two -OR groups; Not as reactive to reducing agents as carbonyls
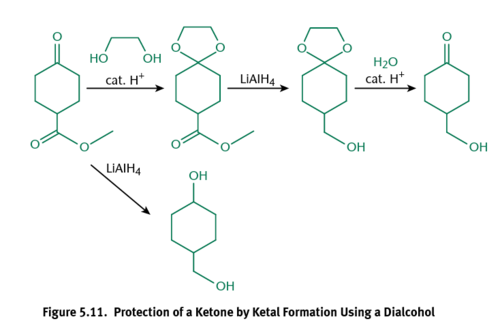
Deprotection
Reverts an acetal or ketal back to a carbonyl with aqueous acid
Quinones
Produced by treating phenols with oxidizing agents
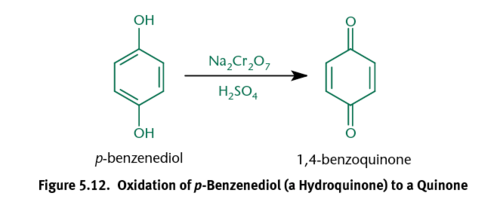
Hydroxyquinones
Quinones can be further oxidized to form these; Share the same ring and carbonyl backbone as quinones, but also have 1+ hydroxyl groups; Slightly less electrophilic than quinones

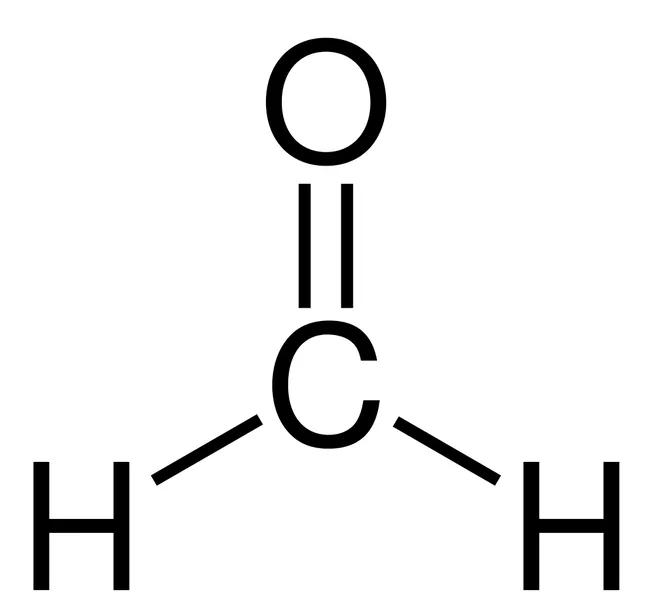
Formaldehyde
Methanal
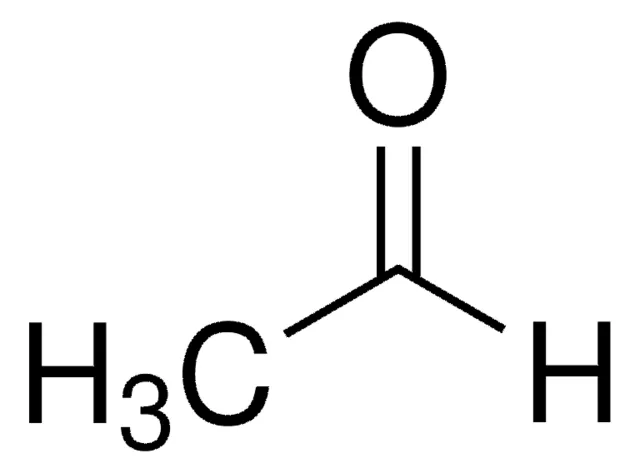
Acetaldehyde
Ethanal
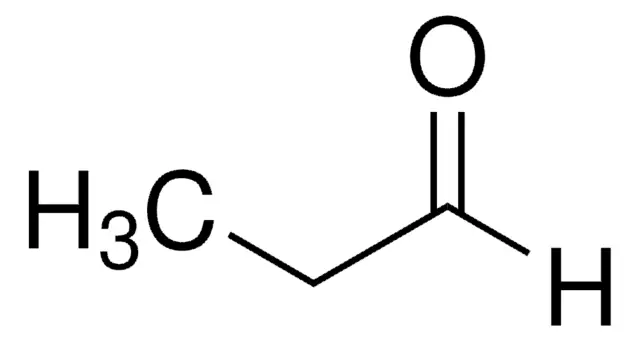
Propionaldehyde
Propanal
Butyraldehyde
Butanal
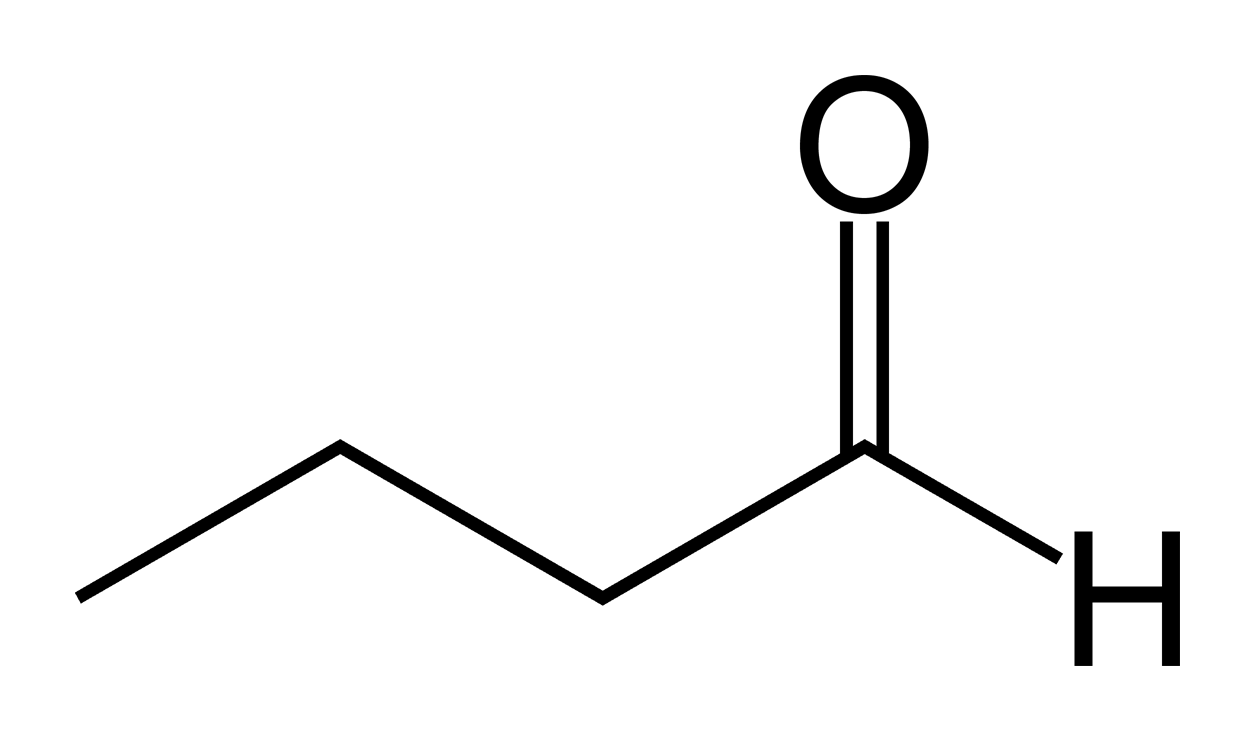
Valeraldehyde
Pentanal
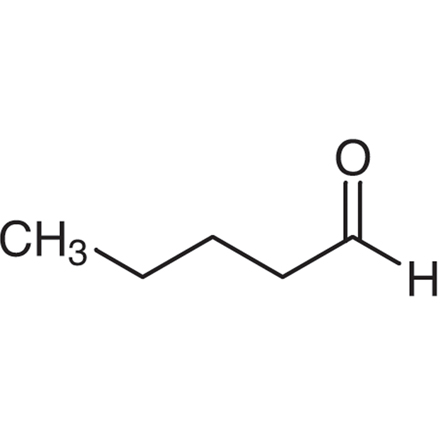
Cyclopentanecarbaldehyde
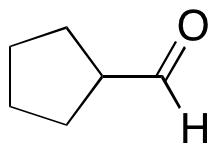
2-Propanone
Dimethyl ketone/acetone
Ketones are named by replacing the -e with -one
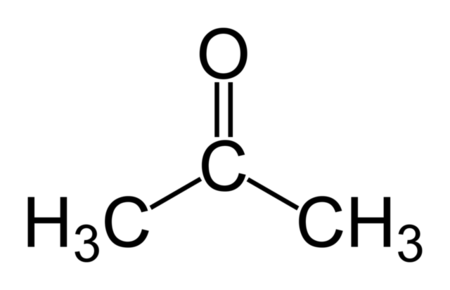
2-Butanone
Ethylmethylketone
Naming Ketones: The two alkyl groups are named alphabetically, followed by -ketone
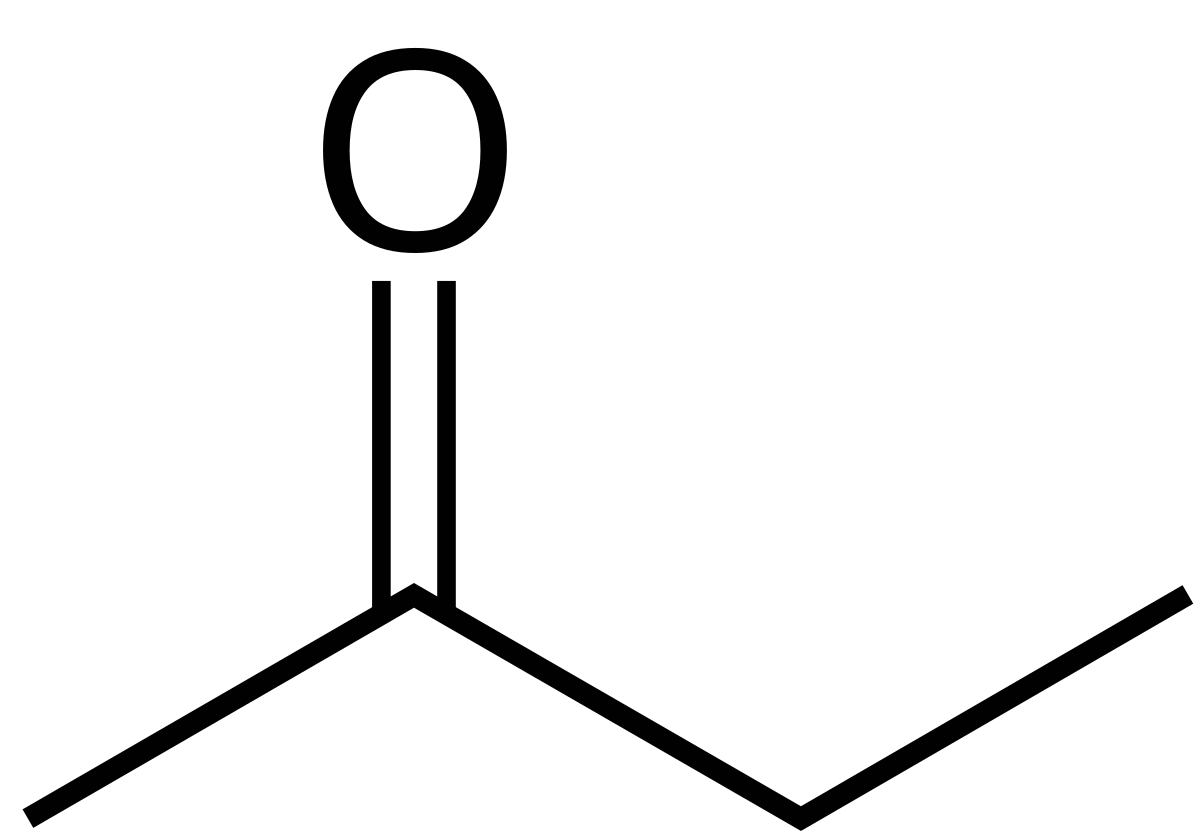
3-Oxobutanoic Acid
When ketones are named as substituents, use either the prefix oxo- or keto-
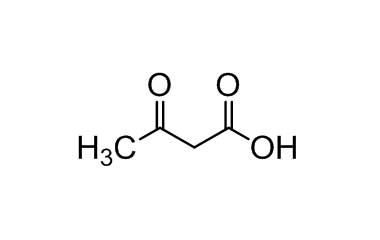
Physical Properties of Ketones and Aldehydes
Dipole moments associated with polar carbonyl groups increase intermolecular attractions, causing an elevation in boiling point relative to their parent alkanes (lower bp than alcohols because no hydrogen bonding)
Both act as electrophiles (EWD oxygen)
Generally, aldehydes are more reactive toward nucleophiles than ketones because they have less steric hindrance and fewer electron-donating alkyl groups
PCC
Can oxidize a primary alcohol into an aldehyde
Stronger oxidants would oxidize the aldehyde into a carboxylic acid
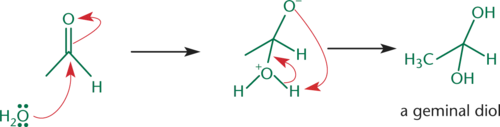
Geminal Diols
Formed from hydration reactions with aldehydes and ketones
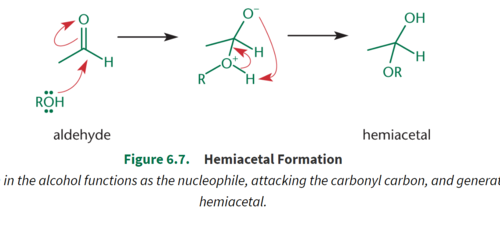
Hemiacetal/Hemiketal
Formed from a reaction between one equivalent of alcohol and an aldehyde or a ketone; Retain the hydroxyl group
Acetal/Ketal
Formed when two equivalents of alcohol react with an aldehyde or ketone; SN1 reaction; Hydroxyl group of hemiacetal/hemiketal is protonated and lost as a molecule of water
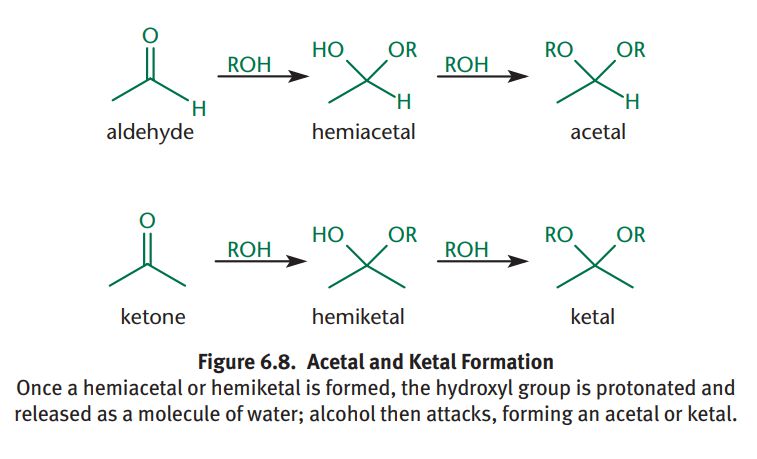
Imine
A compound with a nitrogen atom double-bonded to a carbon atom
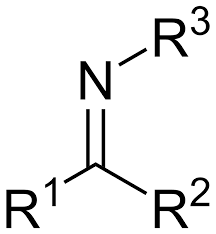
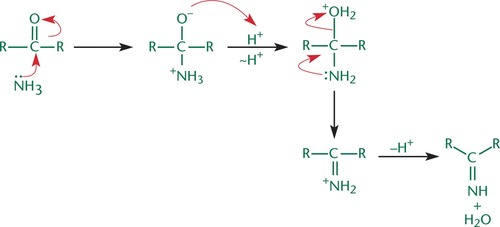
Condensation Reaction
i.e. Imine formation; When a small molecule is lost during the formation of a bond between two molecules
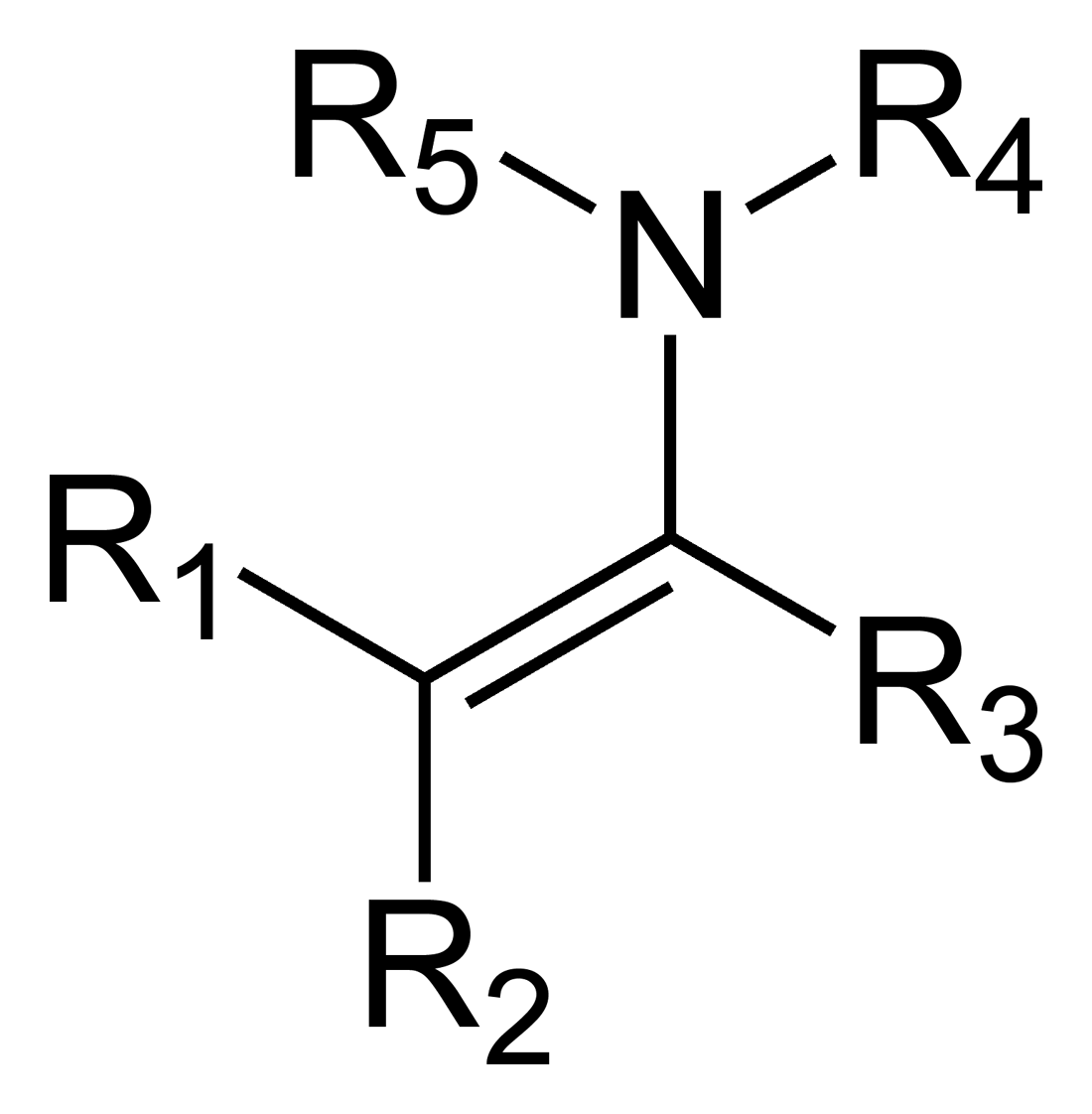
Enamines
Imines can tautomerize to form these; Contain both a double bond and a nitrogen-containing group
Cyanohydrins
Formed from reactions with aldehydes and ketones and HCN
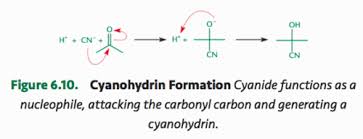
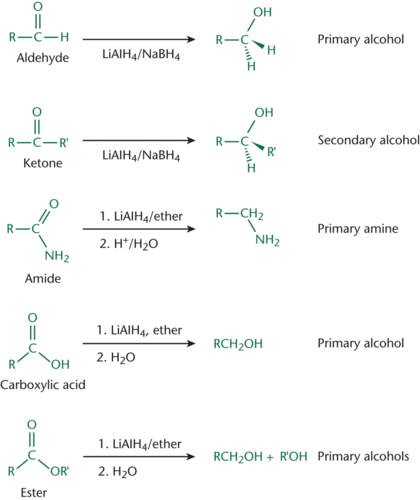
Hydride Reagents
Can reduce aldehydes or ketones to form alcohols; LiAlH4 and NaBH4
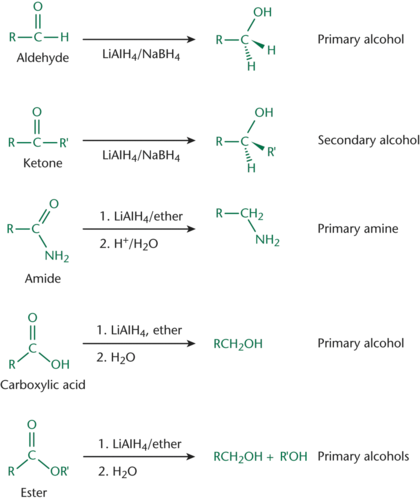
Oxidizing Agents
Reducing Agents

Carbanion
A molecule with a negatively charged carbon atom
Alpha-Hydrogens
When in basic solutions, _____ will easily deprotonate; The _____ of ketones tend to be slightly less acidic than those of aldehydes due to the electron-donating properties of the additional alkyl group in a ketone
Enol Form
Has a carbon-carbon double bond (en-) and an alcohol (-ol)
