Biochemistry II Lesson 11: Mitosis and Meiosis
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
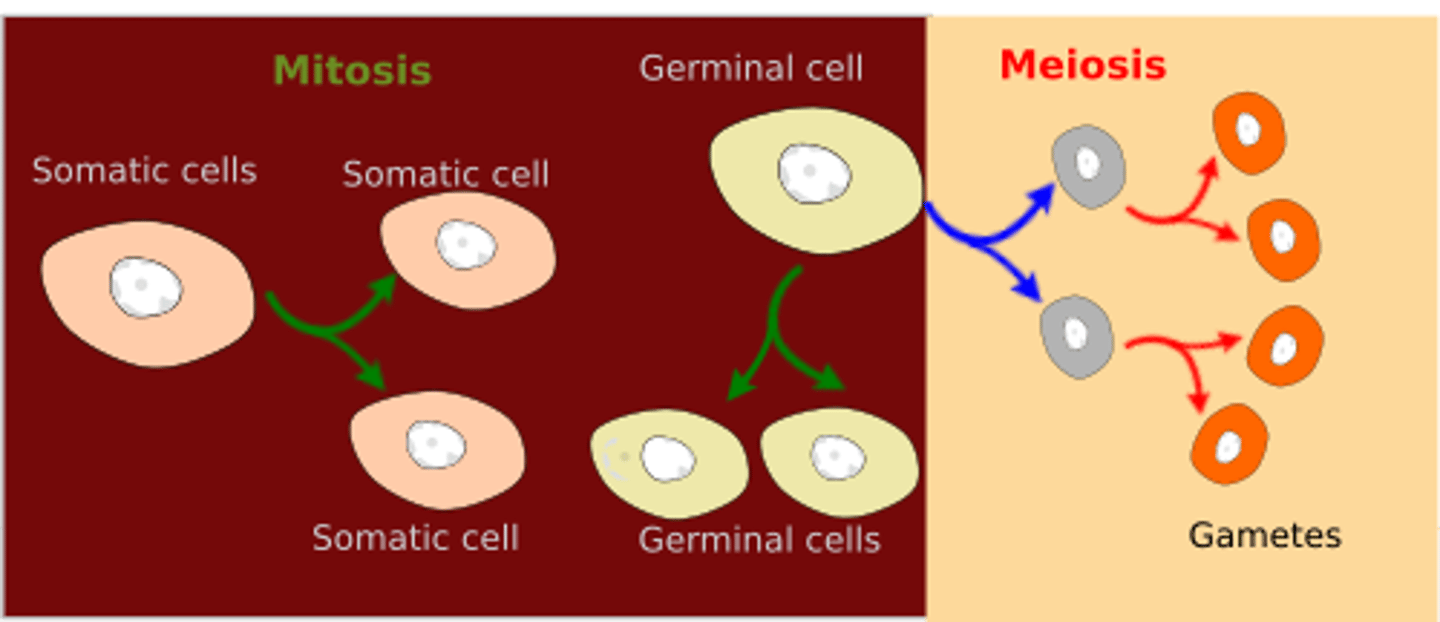
CRB Fill in the blanks: Mitosis occurs in ______________, whereas meiosis occurs in __________________.
(A) Germ Cells, Germ Cells
(B) Germ Cells, Somatic Cells
(C) Somatic Cells, Germ Cells
(D) Somatic Cells, Somatic Cells
(C) Somatic Cells, Germ Cells
Mitosis occurs in Somatic Cells, whereas meiosis occurs in Germ Cells.
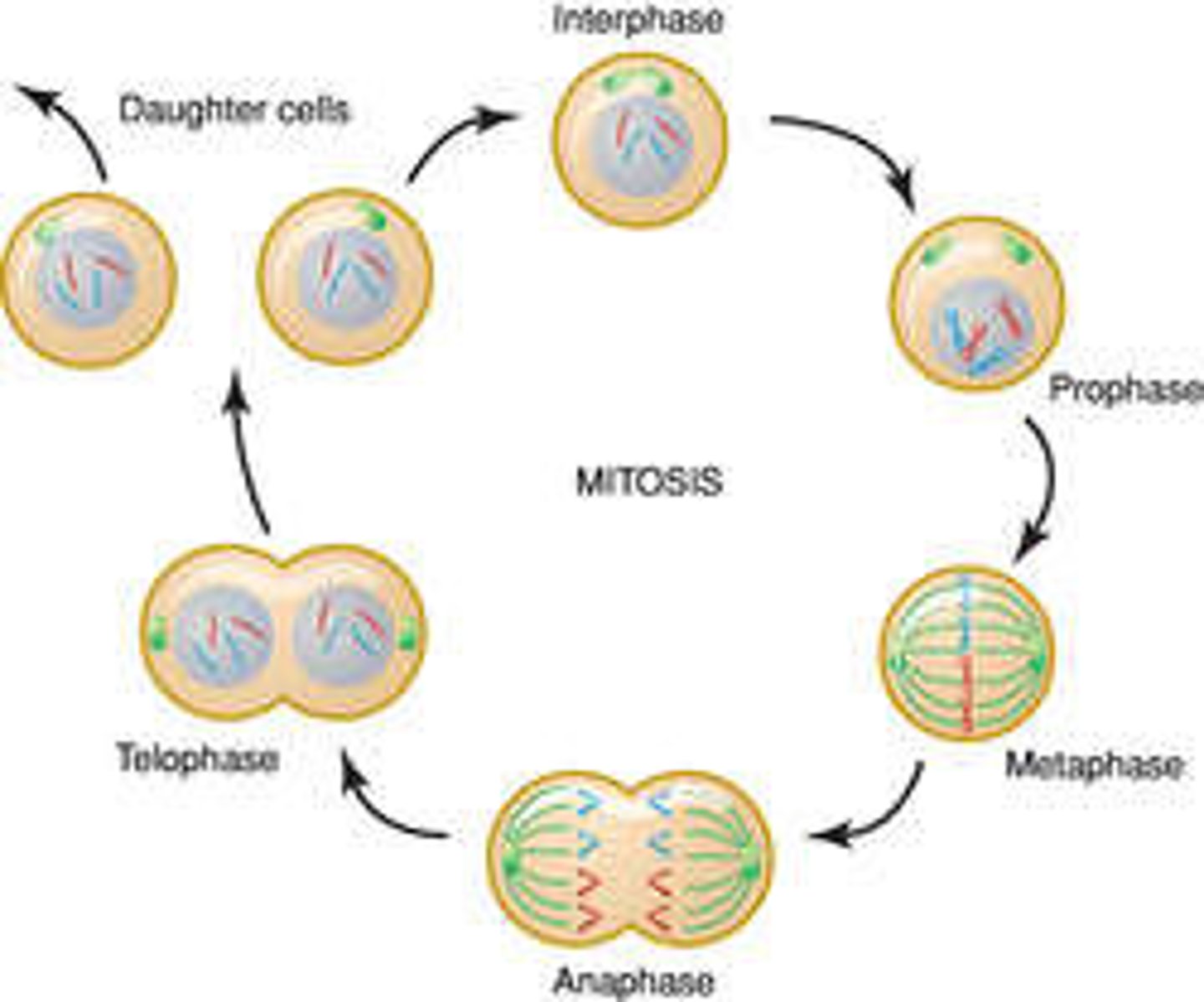
Put the following phases of Mitosis in order from first to last:
I. Prophase
II. Anaphase
III. Telophase
IV. Metaphase
(A) I > IV > II > III
(B) I > II > IV > III
(C) III > IV > II > I
(D) III > II > IV > I
(A) I > IV > II > III
The following are the phases of Mitosis in order from first to last: Prophase > Metaphase > Anaphase > Telophase.
Think PMAT ("Pee on the MAT")
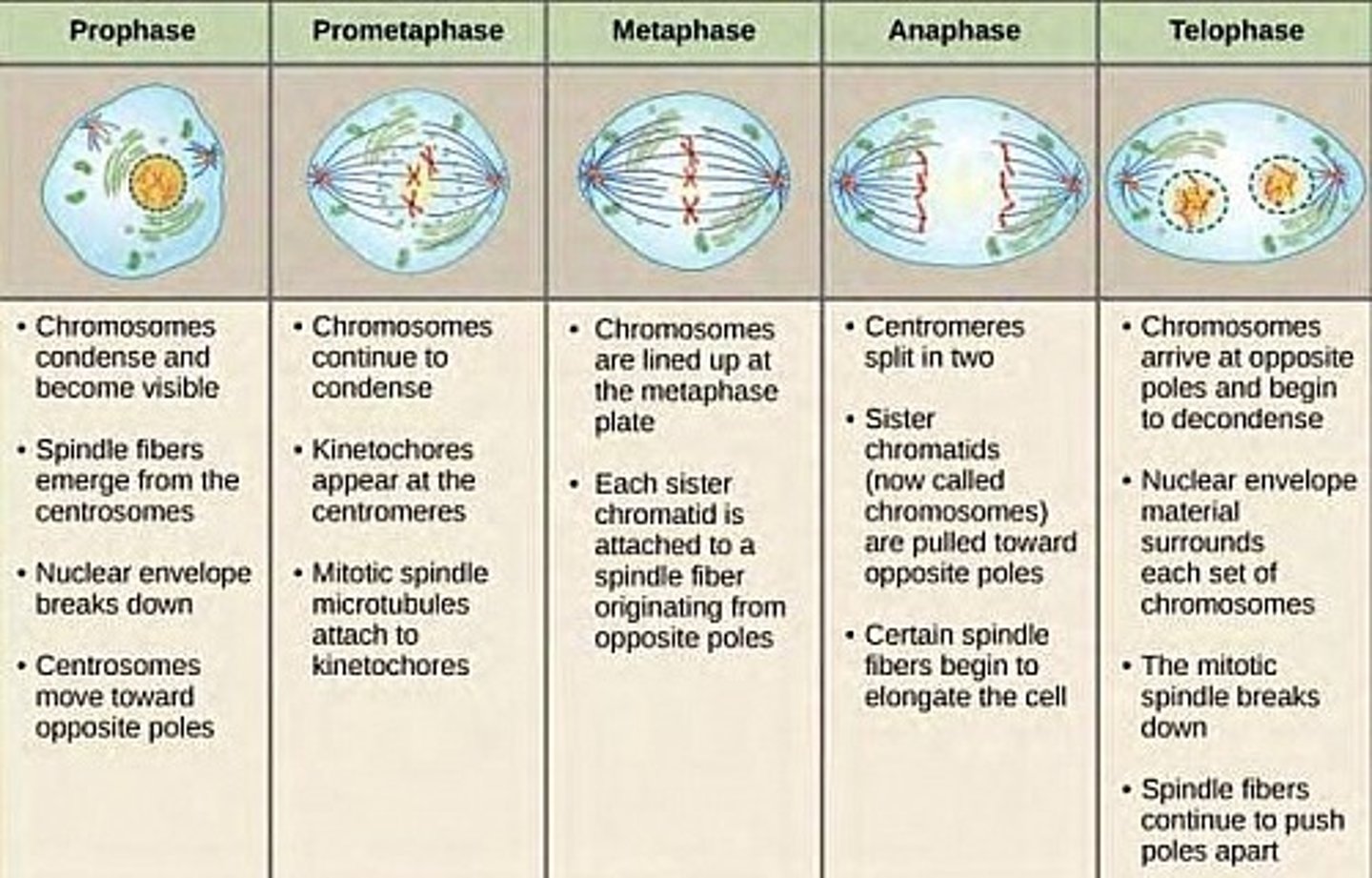
What is happening with the nuclear envelope during each phase of Mitosis?
(1) Prophase
(2) Metaphase
(3) Anaphase
(4) Telophase
(1) Prophase. The nuclear envelop disintegrates.
(2) Metaphase. Still disintegrated.
(3) Anaphase. Still disintegrated.
(4) Telophase. After Cytokinesis, the nuclear envelop reforms.
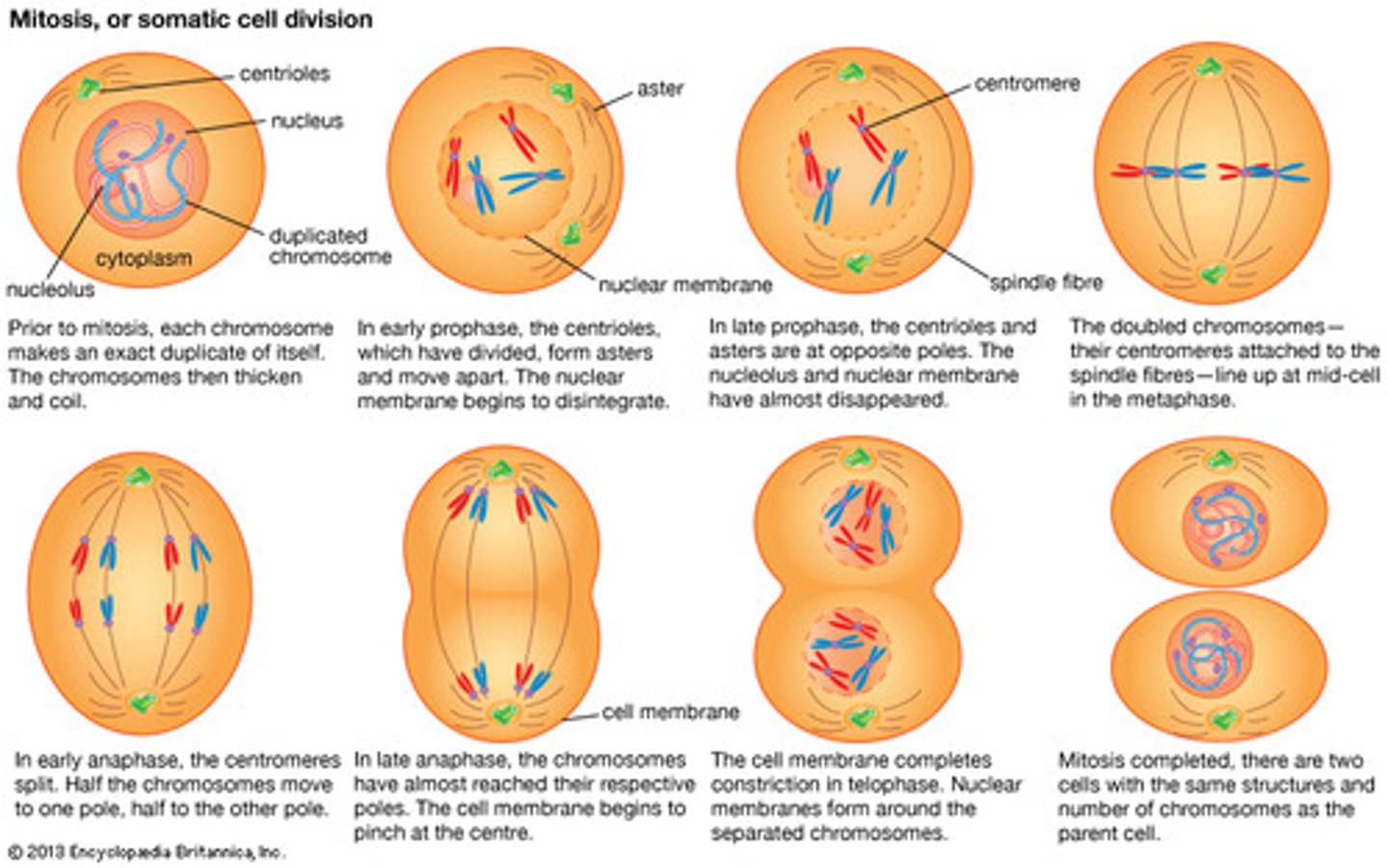
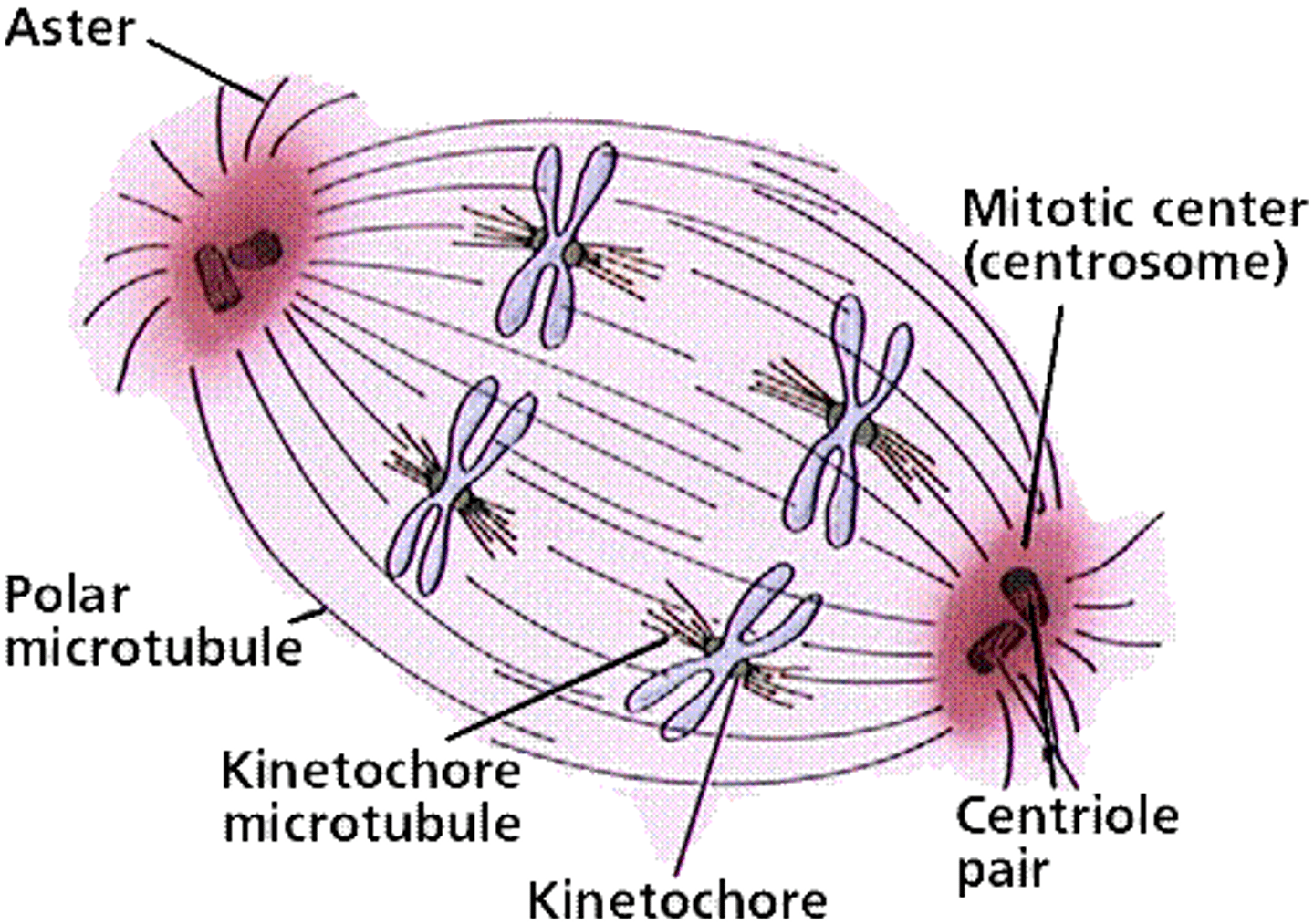
What is happening with the Centrosomes during each phase of Mitosis?
(1) Prophase
(2) Metaphase
(3) Anaphase
(4) Telophase
(1) Prophase - Centrosomes move toward the poles of the cell.
(2) Metaphase - Centrosomes are now at the poles of the cell. The microtubules are attached to the chromosomes lined up in the center of the cell.
(3) Anaphase - The microtubules pull the chromosomes apart from each other to opposite poles of the cell.
(4) Telophase - A single Centrosome (with its centriole pair) ends up in each cell.
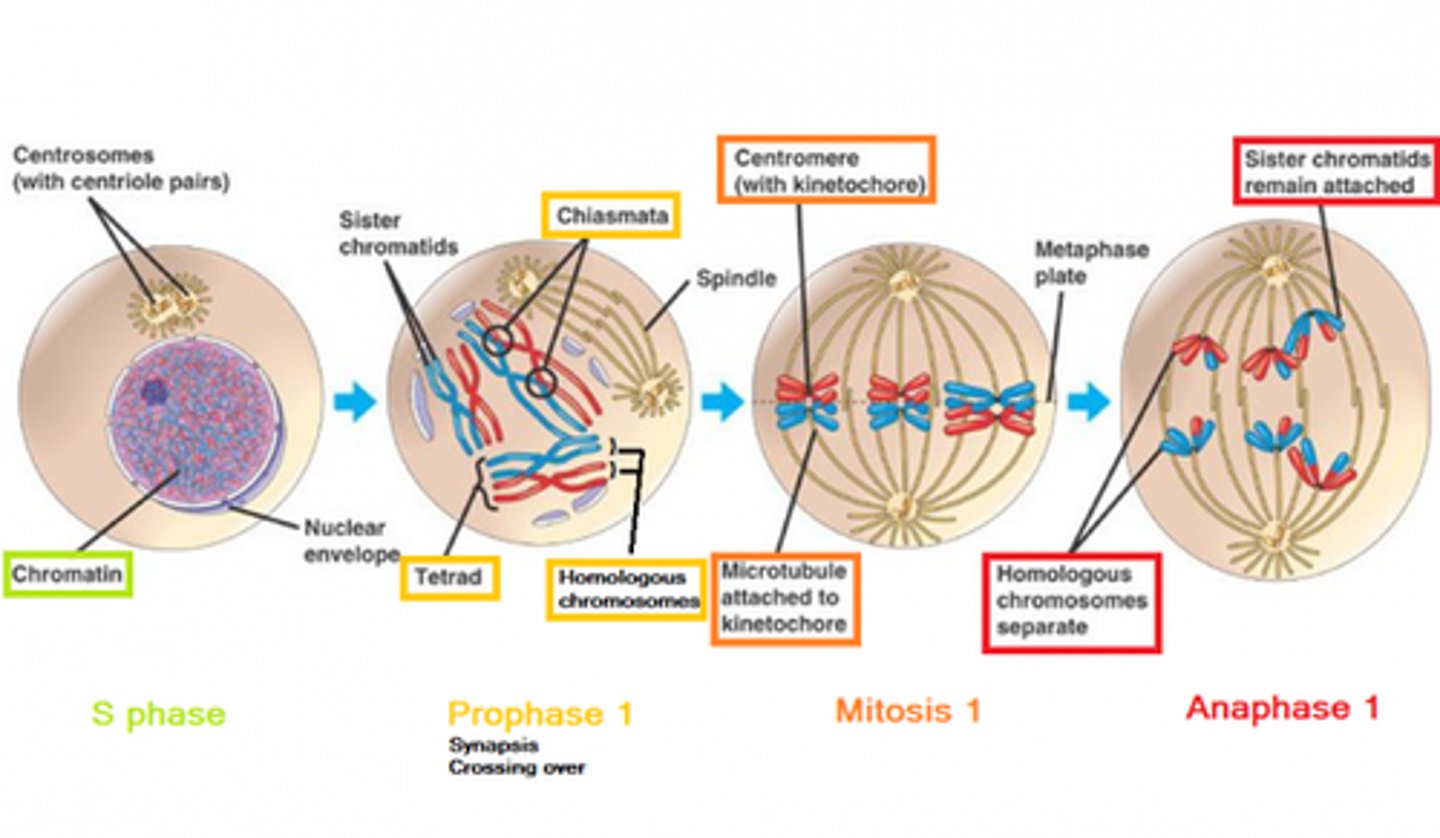
CRB In which of the four stages of Mitosis do Spindle Fibers first appear from the Centrosome?
(A) Prophase
(B) Metaphase
(C) Anaphase
(D) Telophase
(A) Prophase
Spindle Fibers first appear in Prophase.
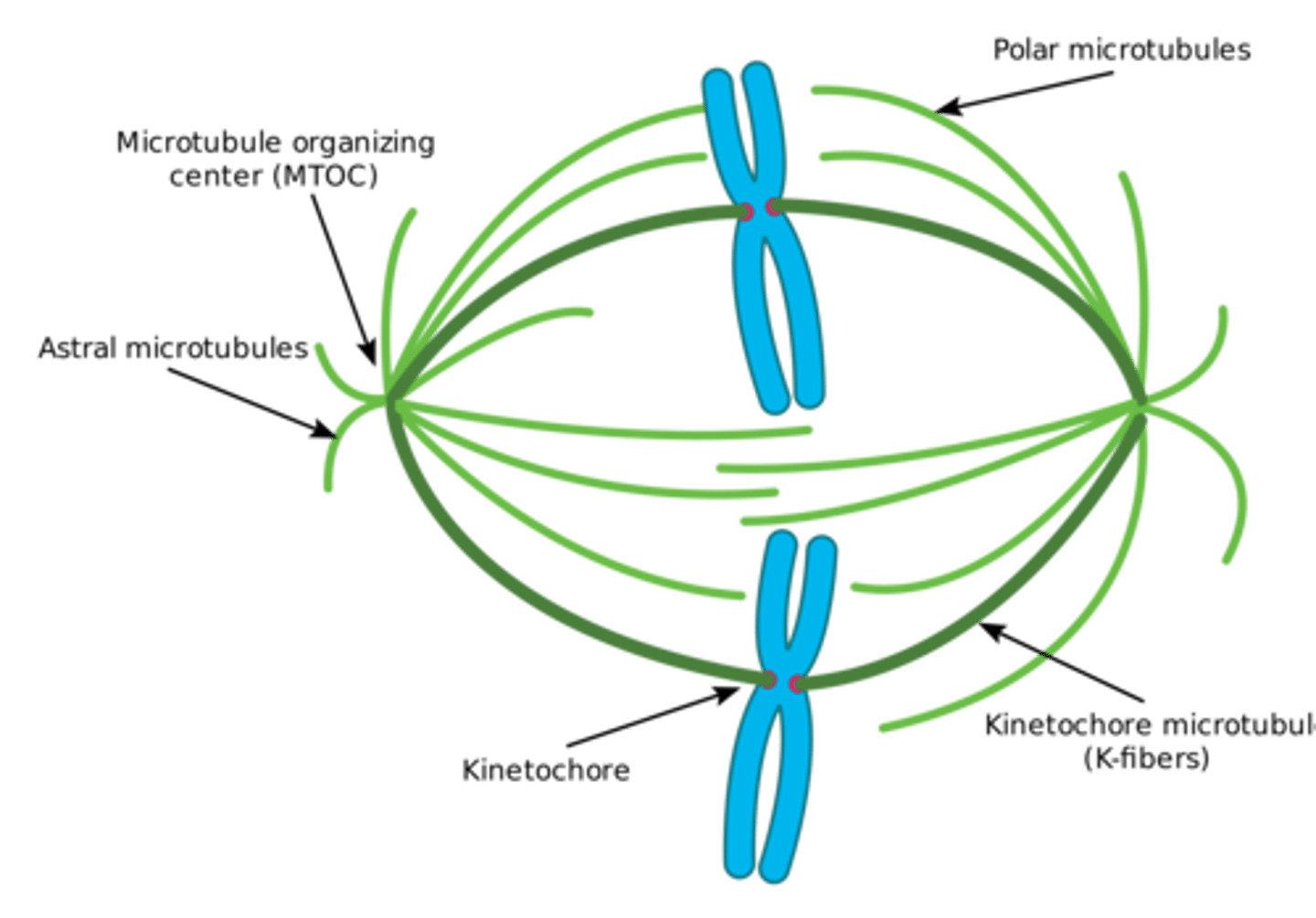
CRB The spindle fibers are made of Microtubules. Which of the following statements about these microtubules are true?
I. The Microtubules that do not form the Asters will anchor centrioles to the Cell Membrane.
II. The other Microtubule Organizing Center in Mitosis is the Cleavage Furrow, providing extra stability.
III. The only Microtubule Organizing Center in Interphase are the two Centrioles near the nucleus.
(A) III only
(B) I and II only
(C) I and III only
(D) II and III only
(A) III only
Each of the following statements are true about Microtubules:
I. The Microtubules that form the Asters will anchor centrioles to the Cell Membrane.
II. The only Microtubule Organizing Center in Mitosis is Centrosome.
III. The only Microtubule Organizing Center in Interphase are the two Centrioles near the nucleus.
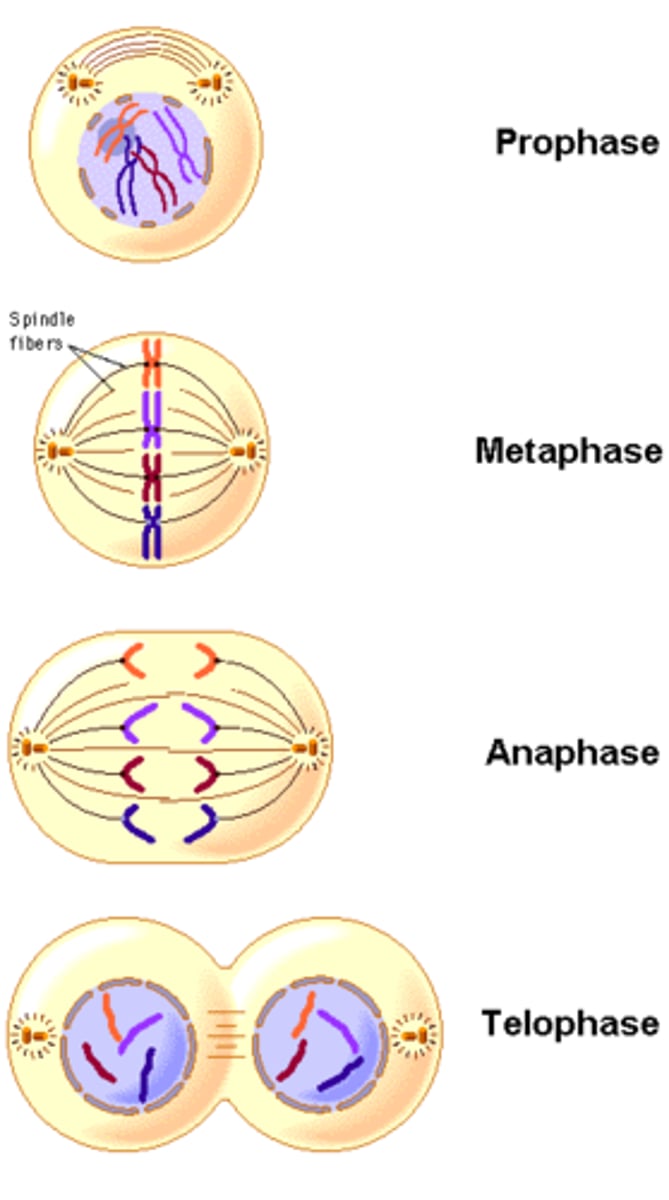
What is happening with the Chromosomes during each phase of Mitosis?
(1) Prophase
(2) Metaphase
(3) Anaphase
(4) Telophase
(1) Prophase. The Chromosomes condense and begin lining up in the center of the cell.
(2) Metaphase. The Chromosomes are now aligned in the center of the cell, attached to the microtubules.
(3) Anaphase. The microtubules pull the chromosomes apart from each other to opposite poles of the cell.
(4) Telophase. The Chromosomes become enveloped by a new nuclear envelope and decondense.
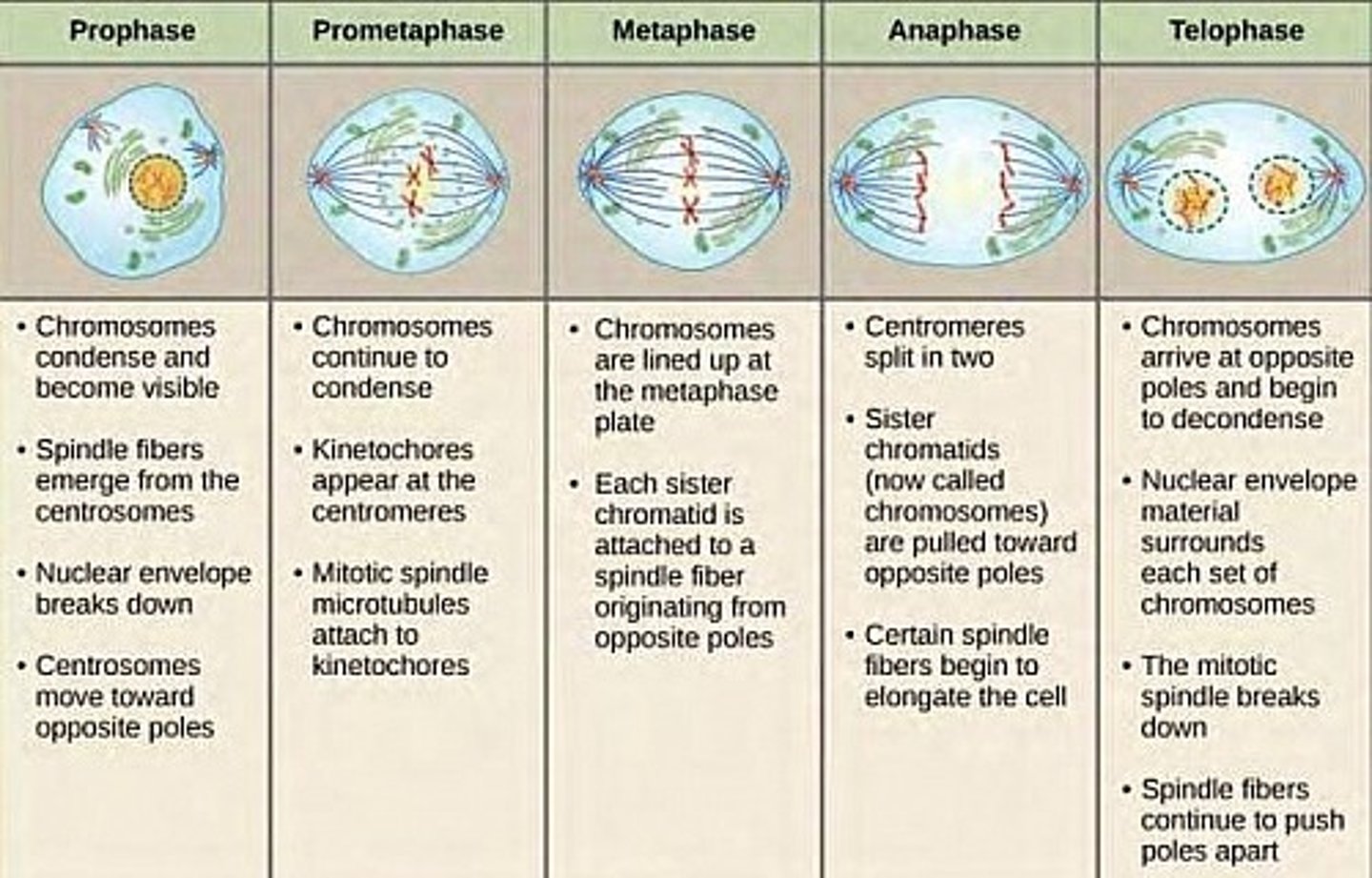
CRB Which of the following statements about how the chromosomes align in Metaphase is INCORRECT?
(A) Where the chromosomes are aligned can be called the Metaphase Plate.
(B) Where the Chromosomes are aligned can be called the Equatorial Plate.
(C) The Chromosomes are anchored by the Aster Spindle Fibers.
(D) The Chromosomes are aligned equidistantly from each of the Centrosomes and poles of the cell.
(C) The Chromosomes are anchored by the Aster Spindle Fibers.
The Chromosomes are anchored by Spindle Fibers, but recall that the Aster Spindle Fibers are the ones that help anchor the Centrosomes.
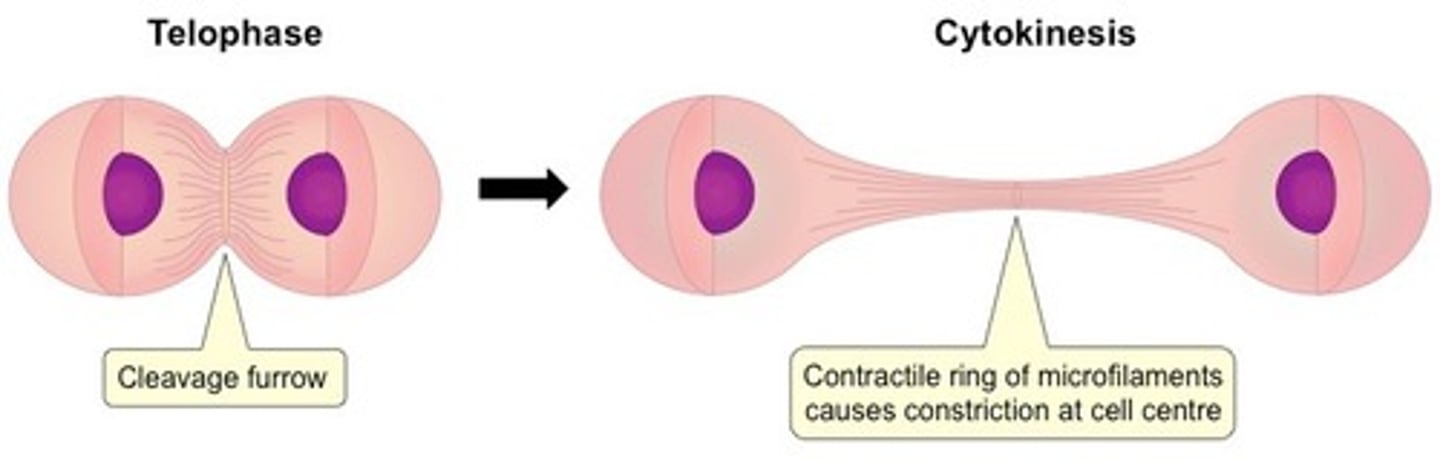
How does Cytokinesis relate to Mitosis?
Cytokinesis is the actual dividing of the cell that occurs during Telophase.
CRB True or false? Most human cells can only divide 20-50 times before programmed cell death will occur.
True. Most human cells can only divide 20-50 times before programmed cell death will occur.
CRB Fill in the blanks: In males, the _______________ undergo meiosis, whereas in females, the ______________ undergo meiosis.
(A) Germ cells, Somatic Cells
(B) Sperm, Egg
(C) Spermatogonia, Oogonia
(D) Testis, Ovary
(C) Spermatogonia, Oogonia
In males, the Spermatogonia undergo meiosis, whereas in females, the Oogonia undergo meiosis.
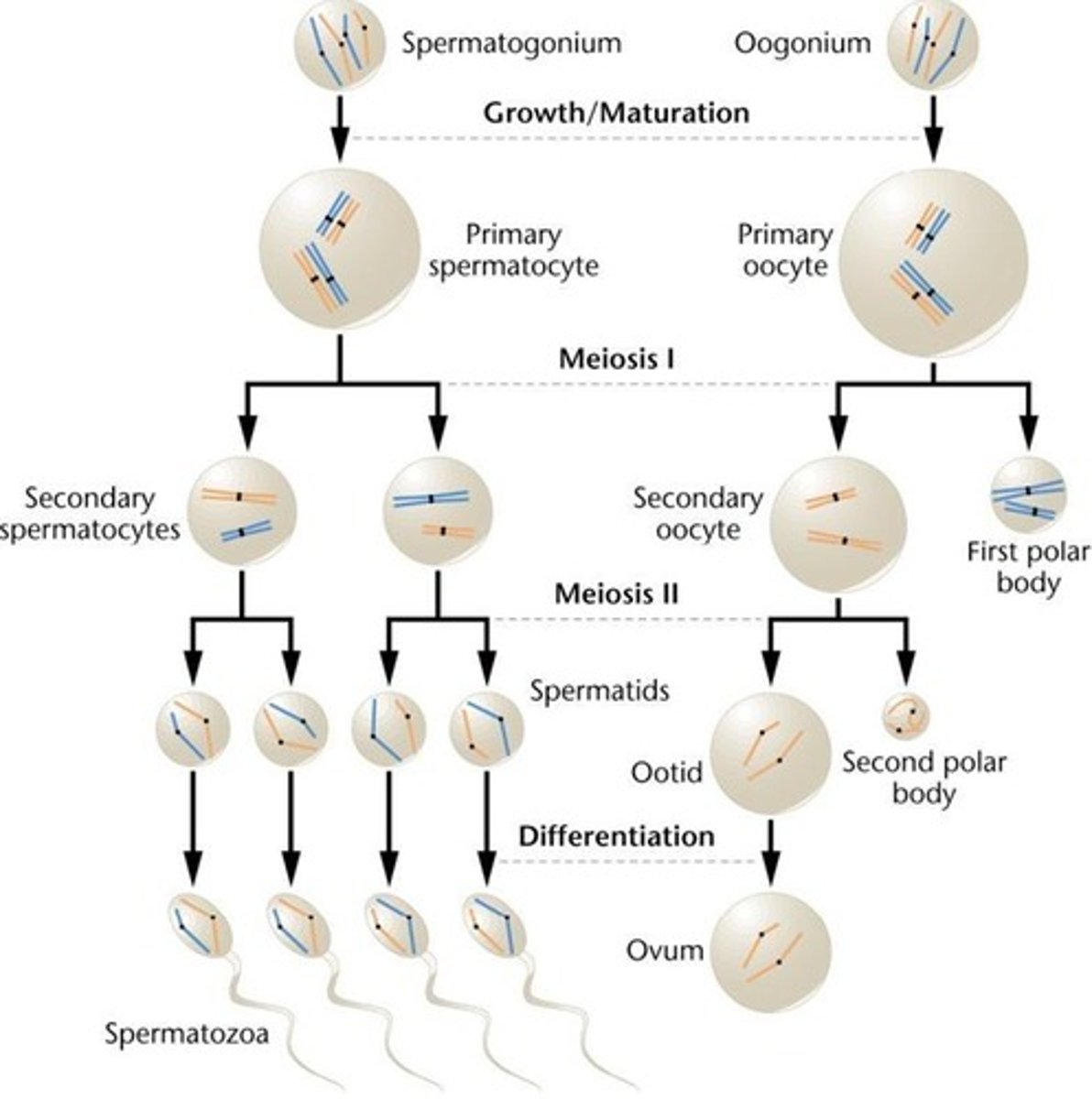
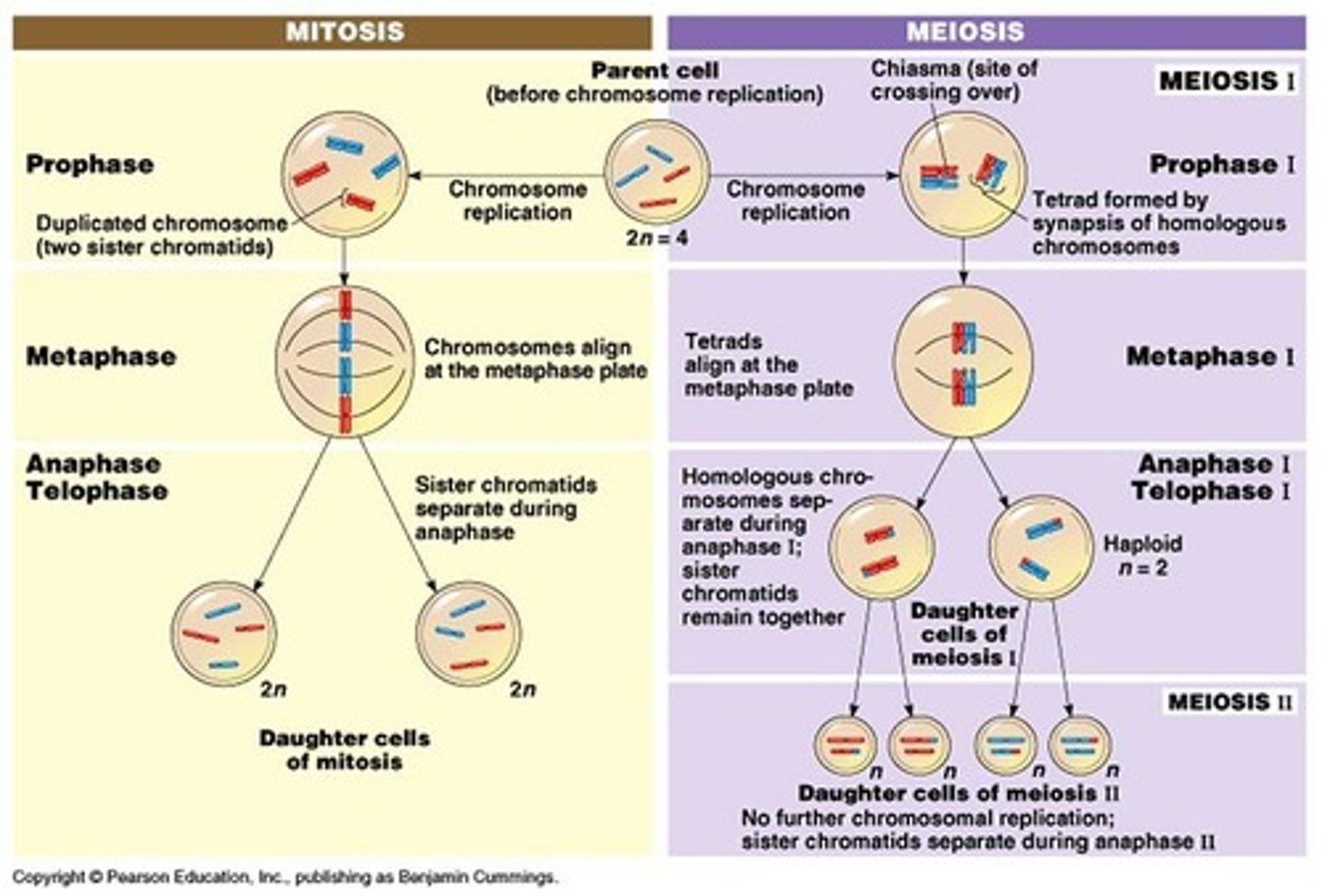
What are the key difference between Prophase I, Metaphase I, and Anaphase I of Meiosis as compared to Mitosis?
In Prophase I of Meiosis, crossing over occurs between the chromosomes (as opposed to Mitosis in which crossing over does not occur), resulting in the mixing of genetic material between the two chromosomes that end up lined up next to each other. Then in Metaphase I, the chromosomes line up side by side, making 23 rows of 2 chromosomes each (instead of 46 rows of a single chromosomes as in Mitosis). Finally during Anaphase I, the chromosomes (as opposed to Chromatids in Mitosis) are pulled to opposite poles of the cell.
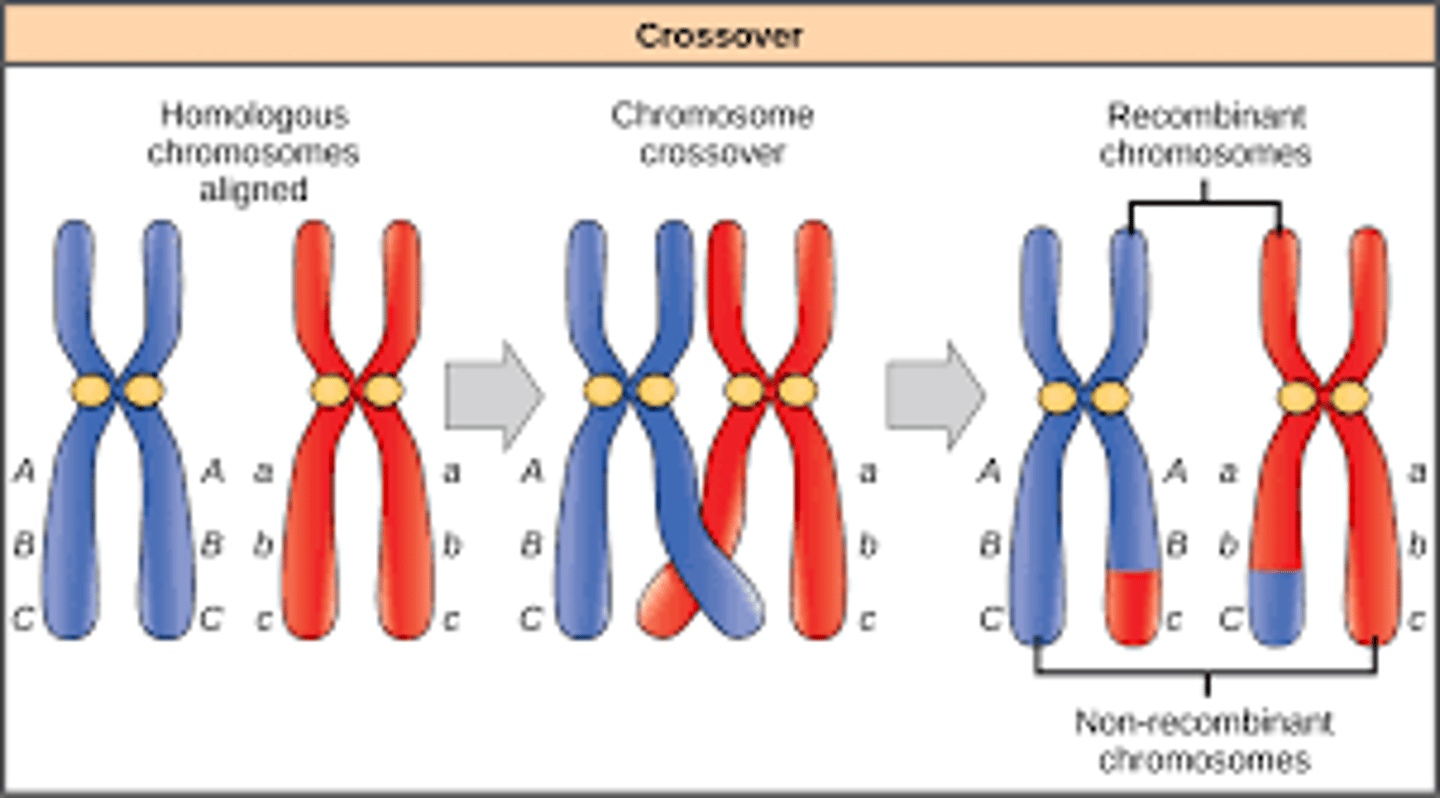
CRB Which of the following statements about Crossing over is Incorrect.?
(A) Homologous chromosomes come together in Synapsis, forming a Tetrad (two chromosome containing two sister chromatids each).
(B) The exchange of equivalent pieces of DNA happens at the chiasmata.
(C) The homologous chromosomes are held together by the Synaptonemal Complex.
(D) Crossing Over only occurs between the sister chromatids, and NOT between the homologous chromosomes.
(D) Crossing Over only occurs between the sister chromatids, and NOT between the homologous chromosomes.
In reality, Crossing Over only occurs between the homologous chromosomes, and NOT between the sister chromatids of the same chromosome.
Sister chromatids of the same chromosome are identical to one another, and any crossing over that occurs does not change the genetic information encoded on the chromosomes.
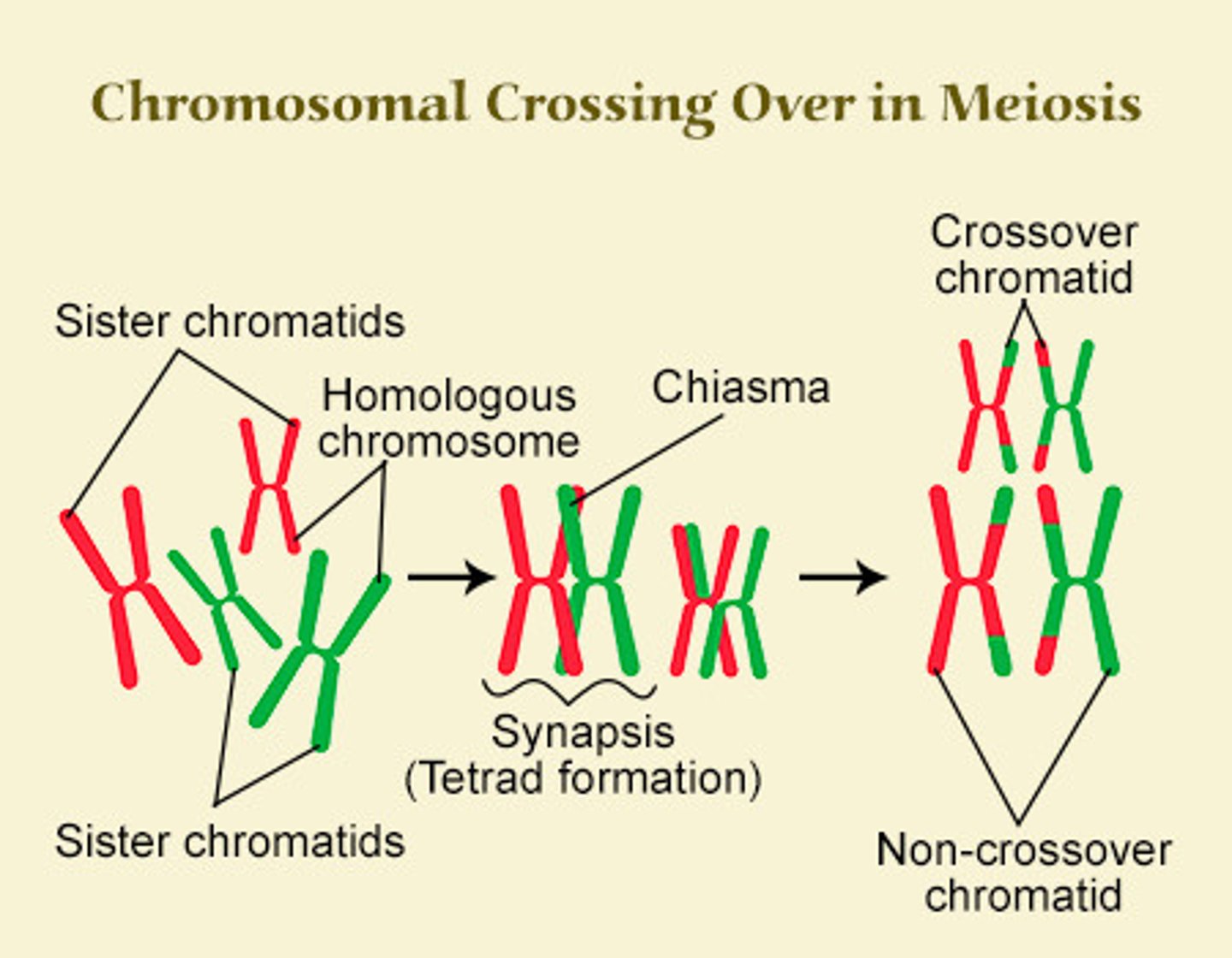
CRB True or false? Crossing over can happen multiple times in the same Tetrad, and can unlink previously-linked genes.
True. Crossing over can happen multiple times in the same Tetrad, and can unlink previously-linked genes.
This is called Recombination.
True or False: Meiosis I produces diploid cells, and meiosis II produces haploid cells.
False. Meiosis I produces HAPLOID cells, and meiosis II produces haploid cells.
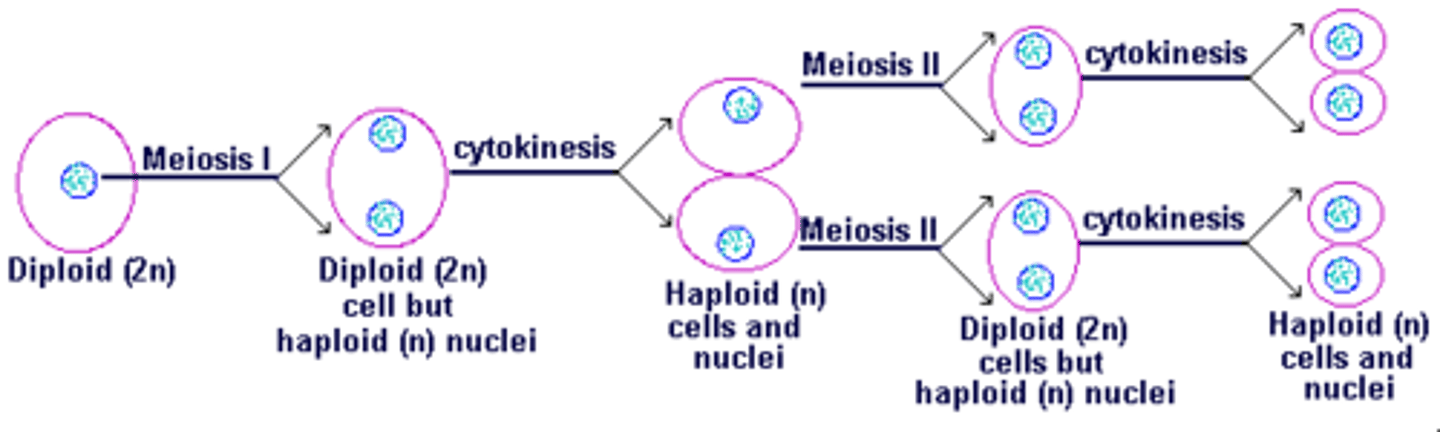
CRB True or false? There may be a rest time between Meiosis I and II, called Interkinesis, where the chromosomes may start to uncoil.
True. There may be a rest time between Meiosis I and II, called Interkinesis, where the chromosomes may start to uncoil.
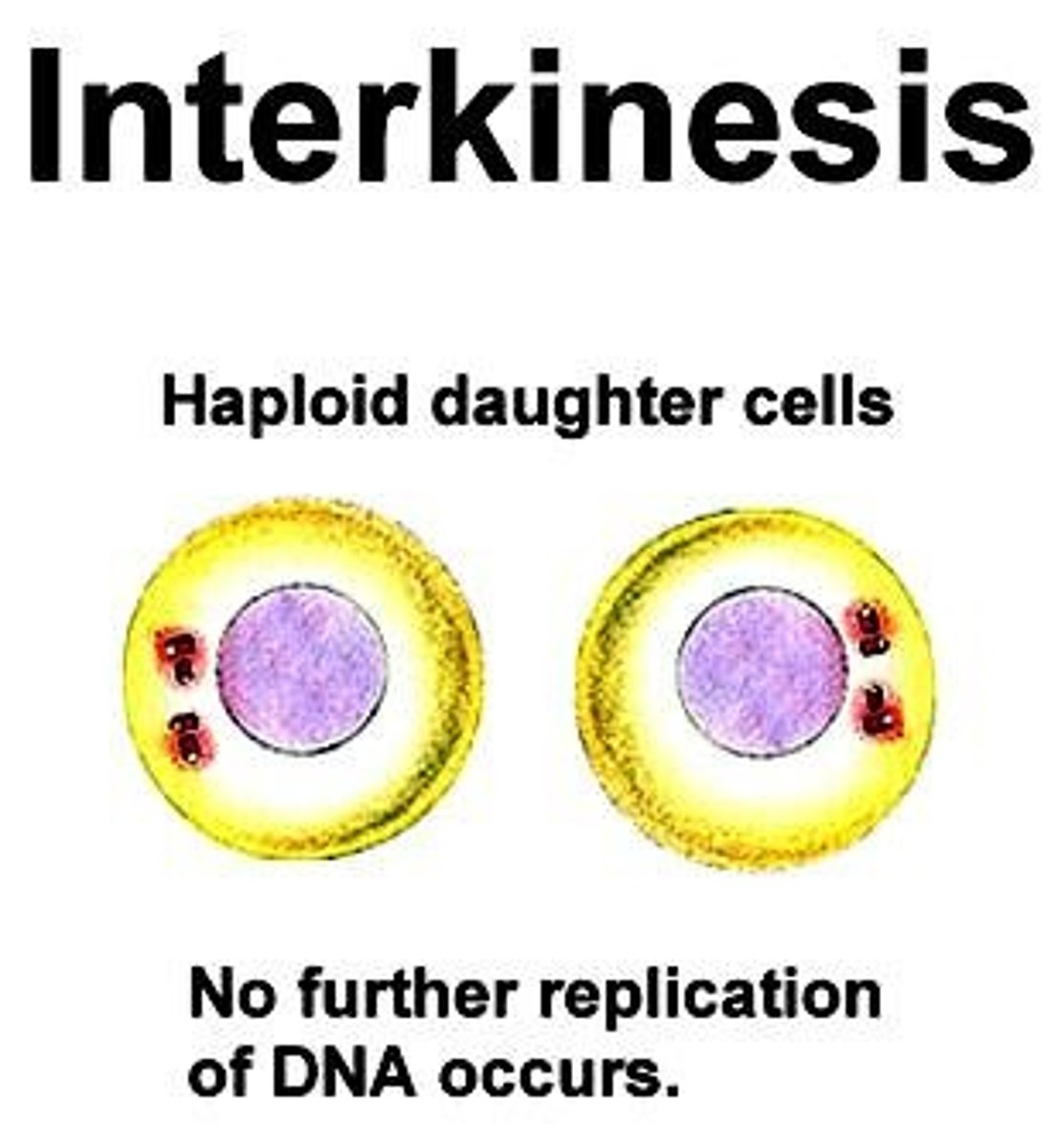
What are the key difference between Prophase II, Metaphase II, and Anaphase II of Meiosis as compared to Mitosis?
Basically, they are exactly the same except that in Meiosis II, you are dealing with half as many chromosomes. This means you will end up with 4 haploid daughter cells in Meiosis II as compared with the 2 diploid daughter cells in Mitosis.
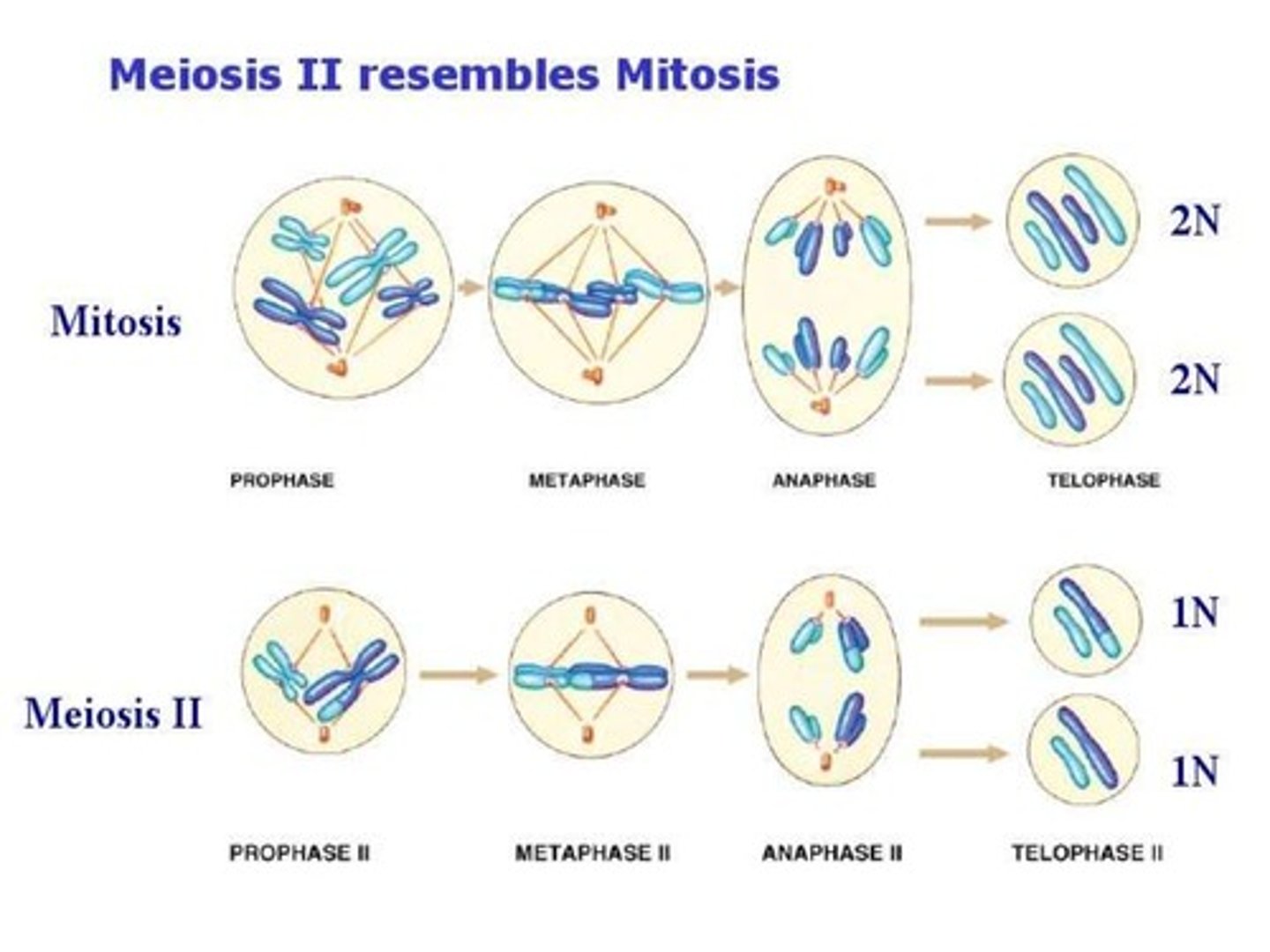
CRB Fill in the blanks: Meiosis I generates haploid daughter cells in a process called _______________ division; Meiosis II results in the separation of sister chromatids and conserves the number of chromosomes, known as _____________ division.
(A) Haploid, Diploid
(B) Nonconservative, Conservative
(C) Reductional, Equational
(D) Gametocyte, Gamete
(C) Reductional, Equational
Meiosis I generates haploid daughter cells in a process called Reductional division; Meiosis II results in the separation of sister chromatids and conserves the number of chromosomes, known as Equational division.
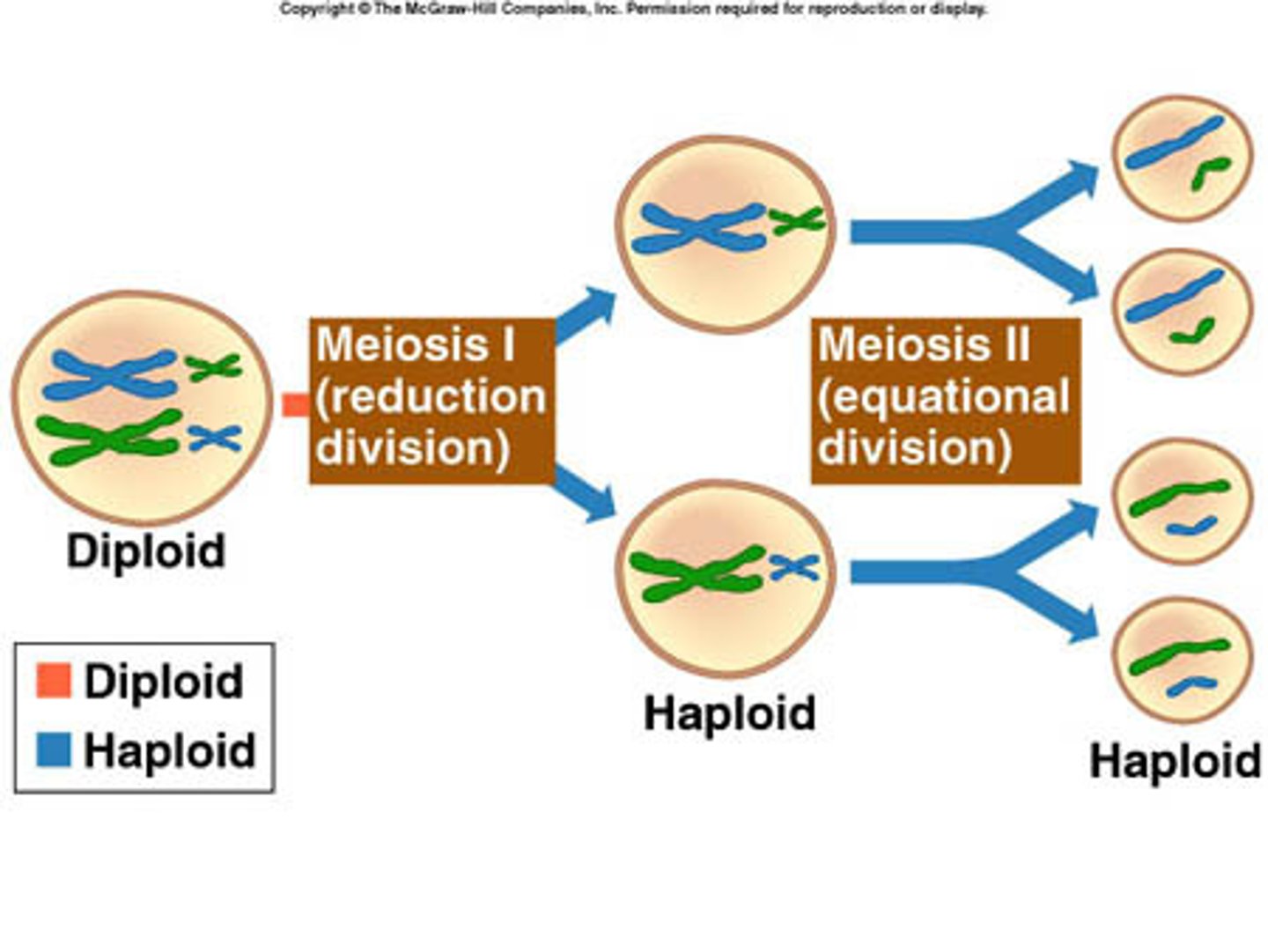
True or false: Meiosis II is like Mitosis in that the number of chromosomes are conserved.
True. Meiosis II is like Mitosis in that the number of chromosomes are conserved.
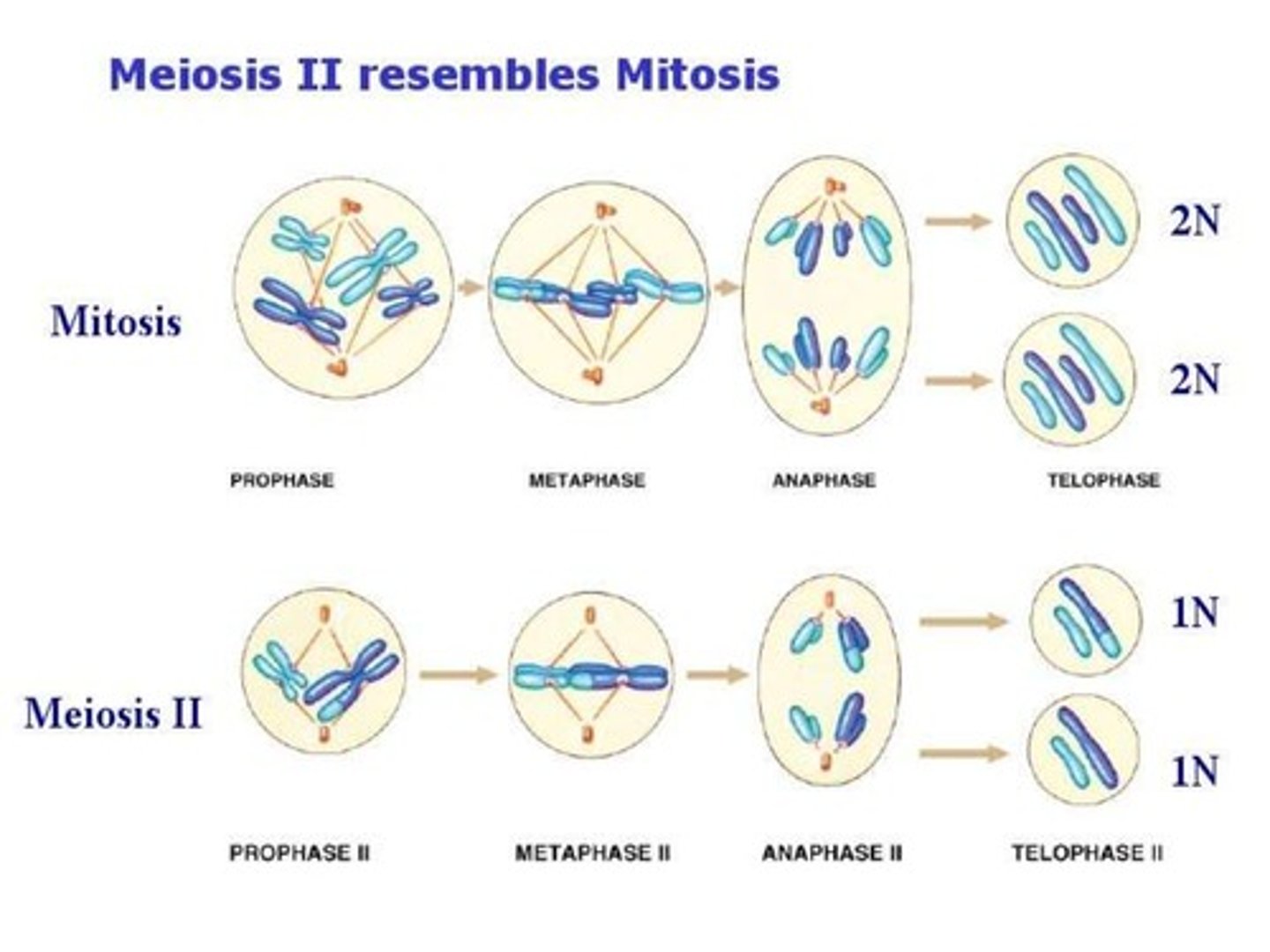
CRB A Nondisjunction event is when homologous pairs do not separate and are not pulled to separate poles of the cell. When could a nondisjunction event affect the number of chromosomes in the daughter cell or gamete?
I. Mitosis
II. Meiosis I
III. Meiosis II
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
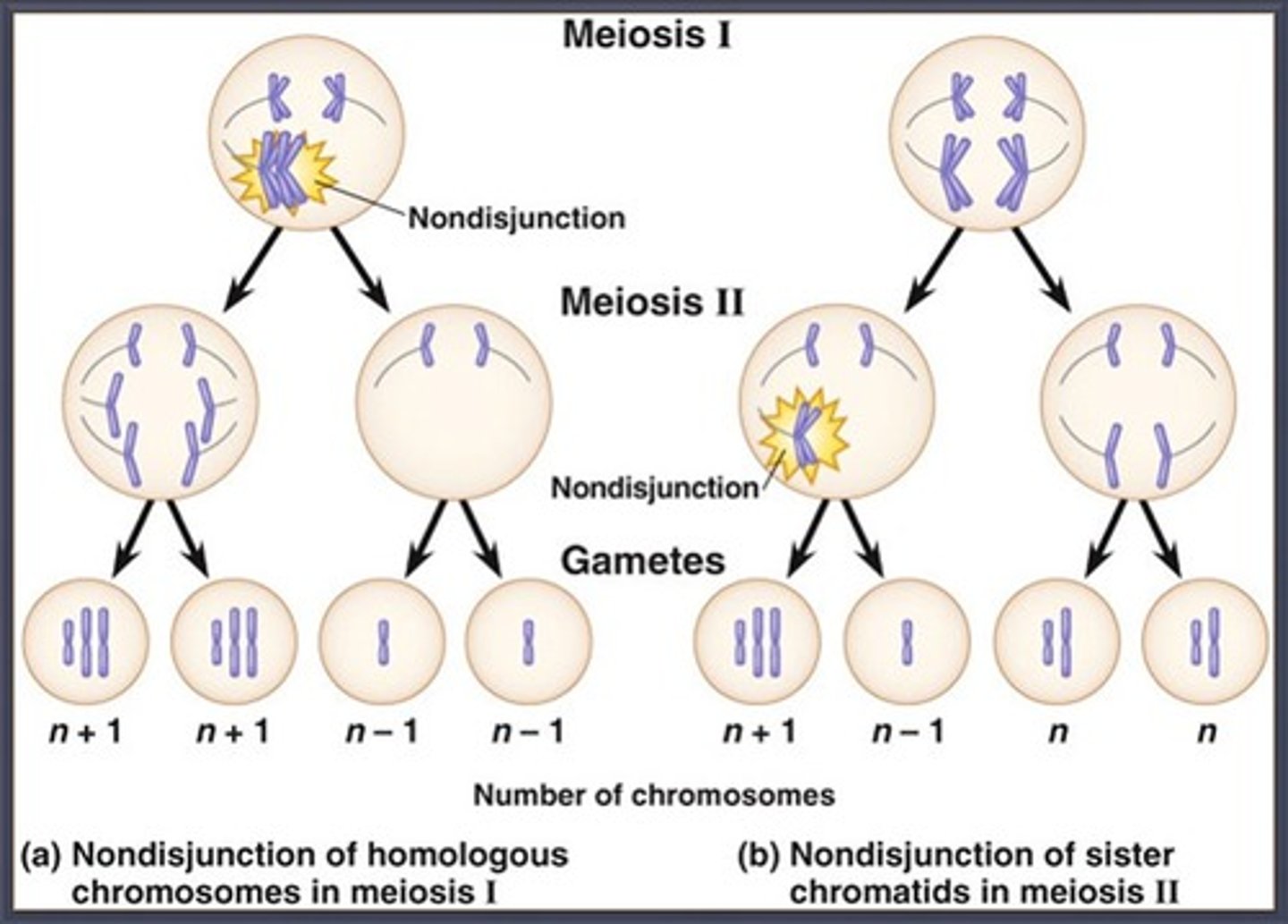
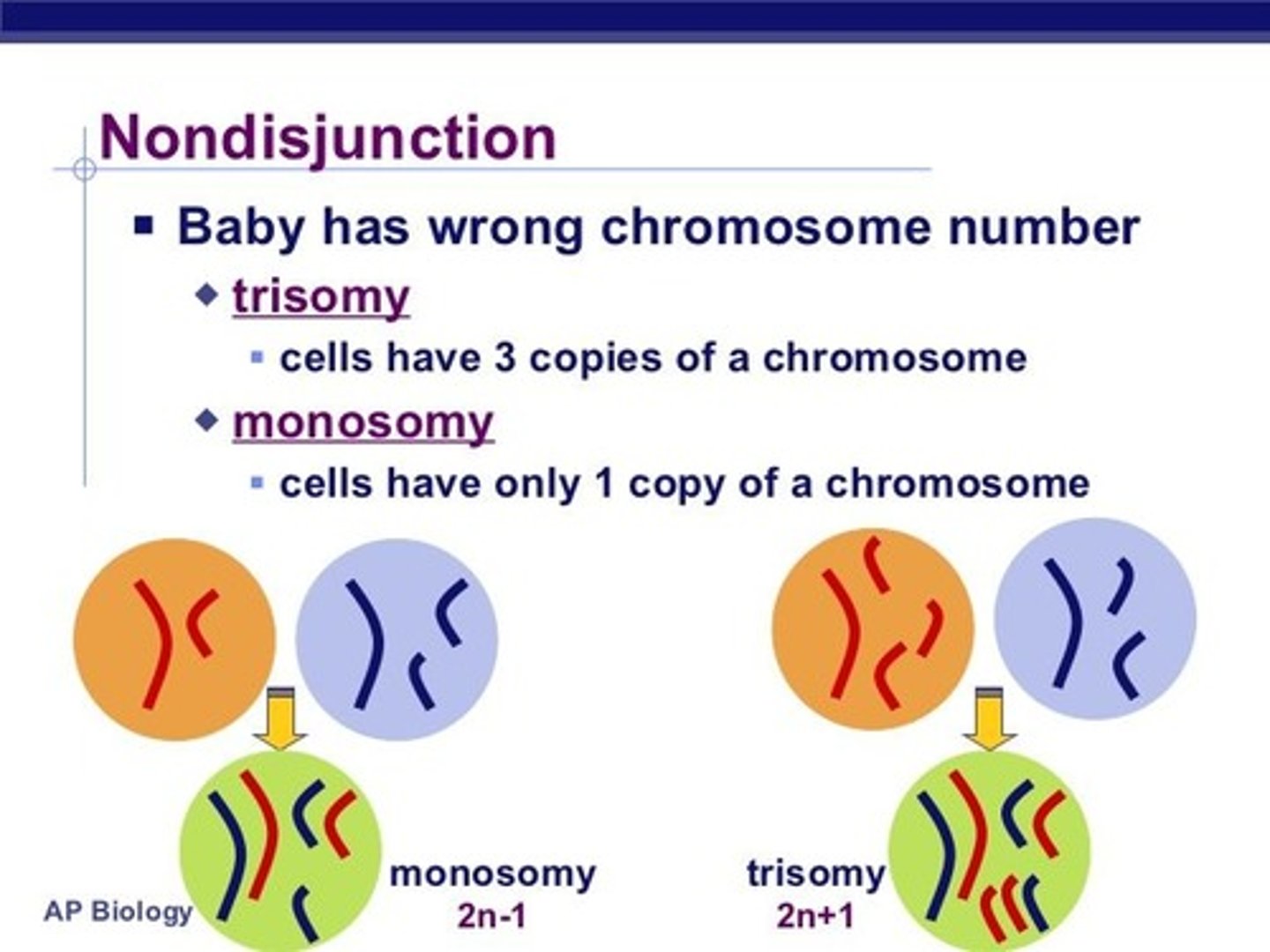
CRB Fill in the blanks: If a nondisjunction event resulted in both copies of a chromosome in the fertilizing gamete, then the zygote will have ___________; if the fertilizing gamete had neither copy of a chromosome, the zygote will have ___________.
(A) Autism, Down Syndrome
(B) Turner's Syndrome, Klinefelters Syndrome
(C) Trisomy, Monosomy
(D) Monosomy, Trisomy
(C) Trisomy, Monosomy
If a nondisjunction event resulted in both copies of a chromosome in the fertilizing gamete, then the zygote will have Trisomy; if the fertilizing gamete had neither copy of a chromosome, the zygote will have Monosomy.
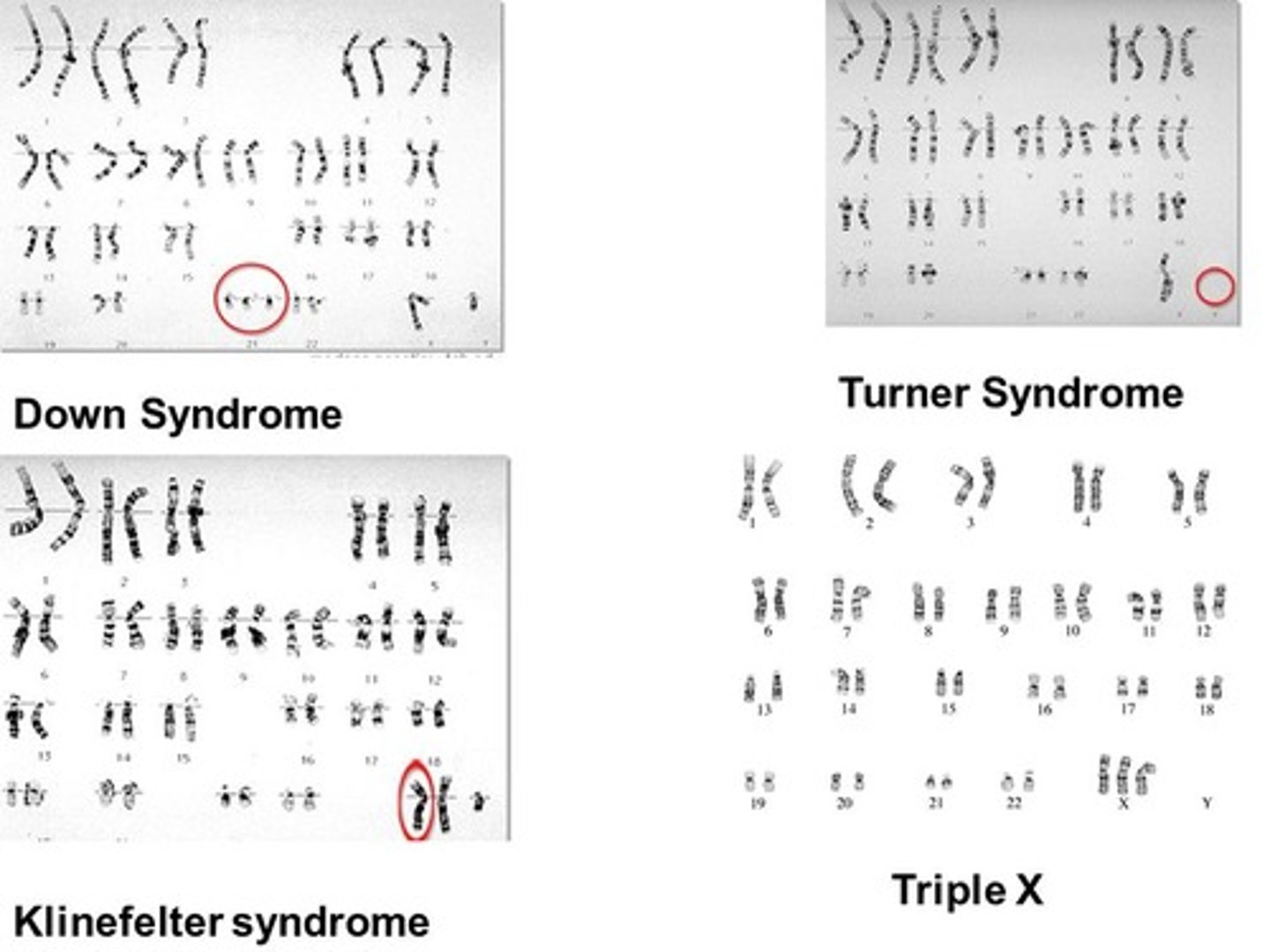
CRB Match each of the following Trisomy/Monosomy diseases with their genotype.
I. Down Syndrome
II. Turner Syndrome
III. Klinefelters
(A) 47 total chromosomes, XXY
(B) 47 total chromosomes, Trisomy of chromosome 21
(C) 45 total chromosomes, XO
I. Down Syndrome - (B) 47 total chromosomes, Trisomy of chromosome 21
II. Turner Syndrome - (C) 45 total chromosomes, XO
III. Klinefelters - (A) 47 total chromosomes, XXY
CRB In Meiosis I, Homologous chromosomes lined up at opposite ends of the Equatorial Plate. What happens to Homologous chromosomes in Mitosis?
In mitosis, there is no need for Homologous Chromosomes to pair or line up. They are treated individually by the cell.