Business Managment Unit 1- Business Organisations and Environments
0.0(0)Studied by 17 people
Card Sorting
1/108
Earn XP
Last updated 10:36 AM on 2/25/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
1
New cards
Define human resources
Management of the workforce and deals with recruitment, wages, communications and motivation
2
New cards
Define goods
Physical articles that have been produced for sale or use. Three examples are food, clothing, and cars.
3
New cards
Define services
intangible goods
4
New cards
Define finance and accounts
Manage money and assets. Ensure accurate recording and reporting of financial documentation.
5
New cards
Define marketing
Ensure company's product sells. By advertising and making sure customers needs/wants are satisfied
6
New cards
Define operations
In charge of business functions and processes
7
New cards
What are the main inputs in a business?
Capital: Amount of money needed
Land: Space
Labour/ Manpower: Physical and mental efforts of people to produce a product
Entrepreneurship: Management, Organisation and planning
Land: Space
Labour/ Manpower: Physical and mental efforts of people to produce a product
Entrepreneurship: Management, Organisation and planning
8
New cards
What are human resources?
The right quality+Quantity of people required to make a product
9
New cards
What are physical resources?
Raw materials, machinery, land space
10
New cards
What are financial resources?
Cash and other forms of money to make the product
11
New cards
Define primary sector
The production of raw material and basic foods e.g. eggs and wood
12
New cards
Define secondary sector
The processing of raw materials, food manufacturing, textile manufacturing, and industry.
13
New cards
Define tertiary sector
Provides services to its consumers
14
New cards
Define quaternary sector
This includes the high tech industry, with information technology and some forms of scientific research, as well as education and consulting, and information industry.
15
New cards
What us the chain of production?
primary then secondary then tertiary then quaternary
16
New cards
Define industrialisation
When a country moves towards the manufacturing sector as their primary output and employment.
17
New cards
Define integration
Expanding the business through taking over other businesses in the chain of production
18
New cards
What is backwards vertical integration?
Expanding backwards in the chain of production
19
New cards
What is forwards vertical integration?
Expanding forwards in the chain of production
20
New cards
What is horizontal integration?
Expanding across the same level of the chain of production
21
New cards
What is diversification?
The process of firms expanding their operations by entering new markets
22
New cards
Name some reasons to start a business
Profit, fame, benefit society, fulfilment, gap in market, legacy, limited resources
23
New cards
State the process of starting a business.(6 steps)
1. Researching the market
2. Planning the business
3. Establish legal requirements
4. Raising the finance
5. Testing the market
6. Organizing the basics
(This is a cycle)
2. Planning the business
3. Establish legal requirements
4. Raising the finance
5. Testing the market
6. Organizing the basics
(This is a cycle)
24
New cards
State some organisational problems a new business might face
Location of business may not be appropriate, name not good, structure does not work
25
New cards
State some finance problems a new business might face
Raising startup capital was too difficult, accounts not kept well, medium/long term finance was hard to obtain
26
New cards
State some market research problems a new business might face
Too optimistic, target market not appropriate, research was poor, weak channels of communications
27
New cards
State some problems a new business might face with it's business plan
too vague
28
New cards
State some legal problems a new business might face
tax obligations not addressed, registration was too difficult, labor laws not addressed
29
New cards
State some problems with the market that a new business might face
limited success, launch failed
30
New cards
What are the 6 elements of a business plan?
1. The idea, aim, and objectives
2. Business organisation
3. Human resources
4. Finance
5. Marketing
6. Operations
2. Business organisation
3. Human resources
4. Finance
5. Marketing
6. Operations
31
New cards
Distinguish between the public and private sector
Private sector:
- Goal is to make profit
- Owned, financed and run by private individuals
Public sector:
- Goods and services provided by the government
- may be free or require a small fee
- Goal is to make profit
- Owned, financed and run by private individuals
Public sector:
- Goods and services provided by the government
- may be free or require a small fee
32
New cards
State the forms of profit making businesses
1. Sole trader
2. Partnerships
3. Companies/corporations
4. For-profit social enterprise: cooperatives, micro-financiers, public-private partnerships
2. Partnerships
3. Companies/corporations
4. For-profit social enterprise: cooperatives, micro-financiers, public-private partnerships
33
New cards
Equation for profit?
Total revenue-Total costs
34
New cards
Features of a sole trader
The sole trader runs and owns the business, the business and owner are indivisible meaning unlimited liability, limited finance, business is close to customers, privacy, easy to register the business
35
New cards
Advantages of sole-trader
Control, work hours are flexible, privacy guaranteed, owner keeps all profit, being close to customer gives competitive advantage, legal formalities can be kept to a minimum.
36
New cards
Disadvantages of sole-trader
intimidating to compete against others by yourself, decision making can be stressful, success depends on owner's drive, cannot continue after owner dies, lack of capital, unlimited liability
37
New cards
Features of partnerships
The partners own and run the company together, owned by more than one person, partners are indivisible from the business meaning there is unlimited liability, more finance available , may have sleeping partners, more varied services can be offered, more accountability due to deed of partnership
38
New cards
Advantages of partnerships
more efficient as partners can specialise, access to more finance, can rely on partners, business will not end if one partner dies
39
New cards
Disadvantages of partnerships
Unlimited liability, limited access to funds, no one has complete control, profits, must be shared, disagreements may occur
40
New cards
Features of companies/corporations
can either be private limited or public limited, shareholders provide finance and have a limited input, limited liability, memorandum of associations and articles of association must be provided, greater finance available
41
New cards
Advantages of companies/corporations
greater finances, limited liability, stronger chance business will continue, stability
42
New cards
Disadvantages of companies/corporations
takes time to setup and costs money, IPO may not generate expected value of sales, owners must give up control(PLC), reliant on stock market, PLC has limited control over who buys shares
43
New cards
Features of a cooperative
A form of partnership whereby the business is owned and run by all the 'members' but unlike the partnerships there may be more than 20 members and each member participates actively in the running of the business.
44
New cards
What are the types of cooperatives?
Financial co-op: A financial institute whose ethical and social aims are prioritised over profits
Housing co-op: run to provide housing for it's members
Workers co-op: failed business taken over by workers whose main aim is to provide employment
producer co-op: druducers collaborate in production
Consumer co-op: provide services to customers who are also part owners
Housing co-op: run to provide housing for it's members
Workers co-op: failed business taken over by workers whose main aim is to provide employment
producer co-op: druducers collaborate in production
Consumer co-op: provide services to customers who are also part owners
45
New cards
Features of micro-financiers
Provide small amounts of finance to thoes who normally would not otherwise have access to it. The money is lent w/ conditions of use and repayments and the micro-financier expects to make a profit on the loans.
46
New cards
Features of public-private partnerships
Profit important but not priority, collab. between business and community, democracy in business, same functions as other business
47
New cards
Advantages of public-private partnerships
socio-economic needs more easily met, helps gov., communal identity leads to an increase in motivation
48
New cards
Disadvantages of public- private partnerships
decision making can be complex, not sustainable in the long term, may cost a lot
49
New cards
Define surplus
Excess money which is put back into the business
50
New cards
Equation for surplus?
total revenues-total cost
51
New cards
Features of NGO's
A social enterprise which redistributes majority of their surplus revenue to a cause which is considered socially desirable
52
New cards
Features of charities
profits are not generated, importance of donations, unclear ownership and contol
53
New cards
Advantages of charities
provide outlet for direct action, can innovate, help those in need
54
New cards
Disadvantages of charities
lack of control, legal issues, reliant on donations
55
New cards
Describe the two types of objectives
Strategic: aka global- these are medium term objectives set by senior management to set the right direction in order to achieve aims
Tactical: aka operational- these are the short term objective and are set by middle management in order to achieve the strategic objectives.
Tactical: aka operational- these are the short term objective and are set by middle management in order to achieve the strategic objectives.
56
New cards
State possible changes in the internal environment.
1. Leadership
2. Human resources
3. Organisations
4. Production
5. Finance
6. Operations
2. Human resources
3. Organisations
4. Production
5. Finance
6. Operations
57
New cards
State possible changes in the external environment that could affect the business
1. Social
2. Technological
3. Economical
4. Ethical
5. Political
6. Legal
7. Ecological
(STEEPLE)
2. Technological
3. Economical
4. Ethical
5. Political
6. Legal
7. Ecological
(STEEPLE)
58
New cards
Define mission
Statement explaining why a company exists
59
New cards
Define vision
a statement that outlines the aspirations and values of the business
60
New cards
Define corporate social responsibility
Organisations consider the interest of society by taking responsibility for the impact of their activities on various stakeholders
61
New cards
Describe some of the impacts of implementing ethical objectives.
may be short term costs to pay, competitors may feel the need to respond, customer loyalty may increase business will have stronger ties with local community, and create positive image
62
New cards
What is the difference between CSR and ethical objectives?
CSR is a concept that a business has no obligation to stick to strictly where as ethical objectives are specific goals that a business may set based on established codes of behaviour.
63
New cards
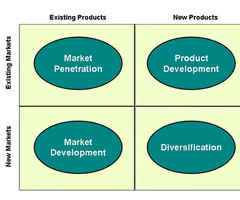
What is Ansoff's Matrix used for?
A marketing planning model that helps a business determine its product and market strategy.
64
New cards
Draw Ansoff's matrix
show the arrows going outwards on both sides with increased risk as well
65
New cards
What interests do entrepreneurs have in a business?
Focus on achieving mission
66
New cards
What interests do shareholders have in a business?
Focus on return on investment
67
New cards
What interests do CEOs/managing directors have in a business?
Focus on coordinating strategy
68
New cards
What interests does senior management have in a business?
Focus on strategic objectives for functional area
69
New cards
What interests does middle management have in a business?
Focus on tactical objectives for functional area
70
New cards
What interests do supervisors have in a business?
Focus on organising tactical objectives
71
New cards
What interests do employees have in a business?
Focus on protecting rights of working conditions
72
New cards
What interests do the government have in a business?
Focus on how the business operates in the country and how it is beneficial to the country
73
New cards
What interests do suppliers have in a business?
Focus on maintaining a stable relationship
74
New cards
What interests do customers have in a business?
Focus on getting the best product that meets their needs
75
New cards
What interests do the local community have in a business?
Focus on business impact on the local area
76
New cards
What interests do financiers have in a business?
Focus on return on investment
77
New cards
What interests do pressure groups have in a business?
Focus on how business impacts the area of concern for them
78
New cards
What interests do the media have in a business?
Focus on the impact of business in terms of new stories
79
New cards
Equation for total cost?
fixed cost + variable cost
80
New cards
Equation for average cost?
total cost/quantity produced
81
New cards
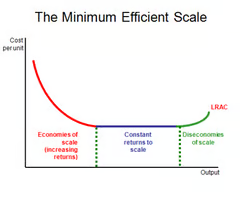
Draw an economies of scale graph.
82
New cards
Define economies of scale
Cost advantages associated with large operations
83
New cards
Define diseconomies of scale
The cost disadvantages that firms and governments accrue due to an increase in firm size or output, resulting in production of goods and services at increased per-unit costs.
84
New cards
What are the 3 factors that make a business hard to control?
Communication, control, coordination
85
New cards
State some advantages of being a big business.
more sales, survival, higher status, market leader, higher market share
86
New cards
State some advantages of being a small business.
Don't spend much, high end products= high profit margin, high satisfaction from job, personalised advantages, serve a niche market
87
New cards
How does a business grow?
Internal (organic) growth and external (fast track) growth(getting money from angel investors or other fast ways of getting money to grow)
88
New cards
Define merger
Two companies joining together
89
New cards
Define joint venture
Two companies join together for one or two products. e.g. sony erikson
90
New cards
Define strategic alliances
not financially joining together but they support eachother
91
New cards
Define franchise
Franchiser does nothing, franchisee does a lot and makes the business
92
New cards
State some market drivers
Con vergence of lifestyle and tast, per capita income converging amoung industrialised natins, more travel, establishment of world brands, push to develop global advertising
93
New cards
Define market drivers
A driver is a factor that has a material effect on the activity of another entity.
94
New cards
State some cost drivers
continuing to push for economies of scale, accelerating tech innovations, advances in transportation
95
New cards
Define cost drivers
cost driver is any factor which causes a change in the cost of an activity
96
New cards
State some competition drivers
increase in world trade, growth on global network
97
New cards
Define competition drivers
Are defined by the actions of competing firms, such as the extent to which competitors from different continents enter the fray, globalize their strategies and corporate capabilities, and create interdependence between geographical markets.
98
New cards
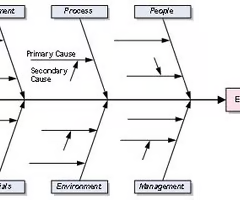
What is the function of a fishbone diagram?
Link problem with the potential root cause
99
New cards
How do you make a fishbone diagram?
1. Get people who know the problem
2. Draw skeleton
3. Enter problem statement
4. Select categories (Manufacturing:men, method, materials, machine. Services:place, procedure, people, politics. Administration: surroundings, suppliers, system, skill)
5. Continue brainstorm on next category
6. Repeat 5
2. Draw skeleton
3. Enter problem statement
4. Select categories (Manufacturing:men, method, materials, machine. Services:place, procedure, people, politics. Administration: surroundings, suppliers, system, skill)
5. Continue brainstorm on next category
6. Repeat 5
100
New cards
Draw a fishbone diagram
(Manufacturing:men, method, materials, machine. Services:place, procedure, people, politics. Administration: surroundings, suppliers, system, skill)