peripheral nervous system
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
PNS
links cns with the body and external environment
detects sensory stimuli and delivers info to CNS
transmits response impulses from the CNS to effectors
somatic sensory division
sensory neurons transmit signals from the integumentary, muscular, and skeletal systems
as well as special sensory signals
visceral sensory division
sensory neurons transmit signals from organs and abdominopelvic and thoracic cavities
somatic motor division
motor neurons that signal skeletal muscle fibers
controls voluntary motor functions
visceral motor division
autonomic nervous system- ANS
neurons signal cardiac muscle cells, smooth muscle cells, and secretory cells in glands
controls involuntary motor functions to maintain homeostasis
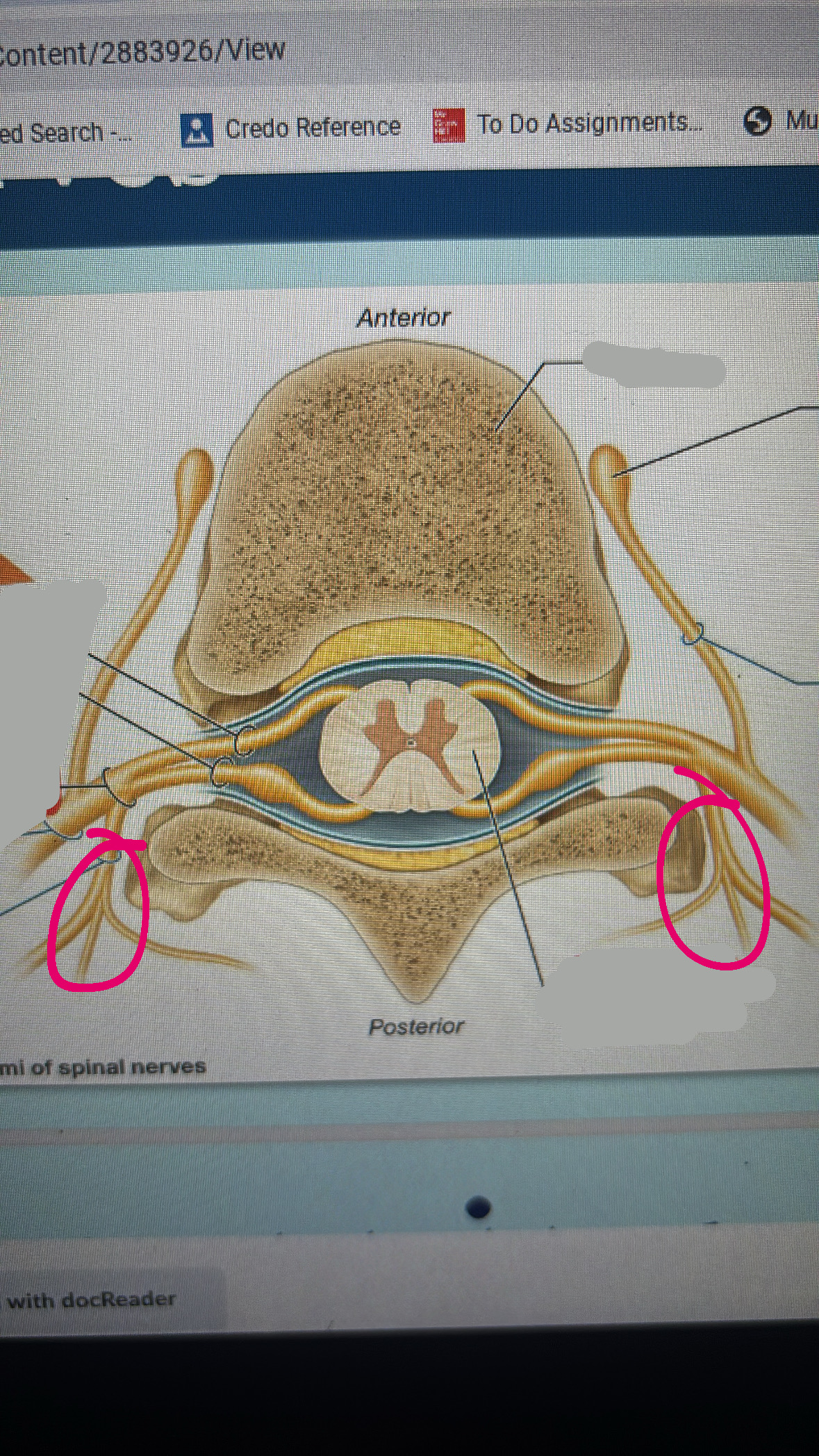
peripheral nerves
composed of the axons of many neurons bound together by a common connective tissue sheath
mixed nerves- sensory + motor neurons
sensory nerves- sensory neurons
motor nerves- motor neurons
spinal nerves- 31 pairs
cranial nerves- 12 pairs
spinal nerves
originate from the spinal cord and mainly innervate structure inferior to the head and neck
all mixed nerves
31 pairs
cranial nerves
originate from the brain and mainly innervate structure of the head and neck
12 pairs
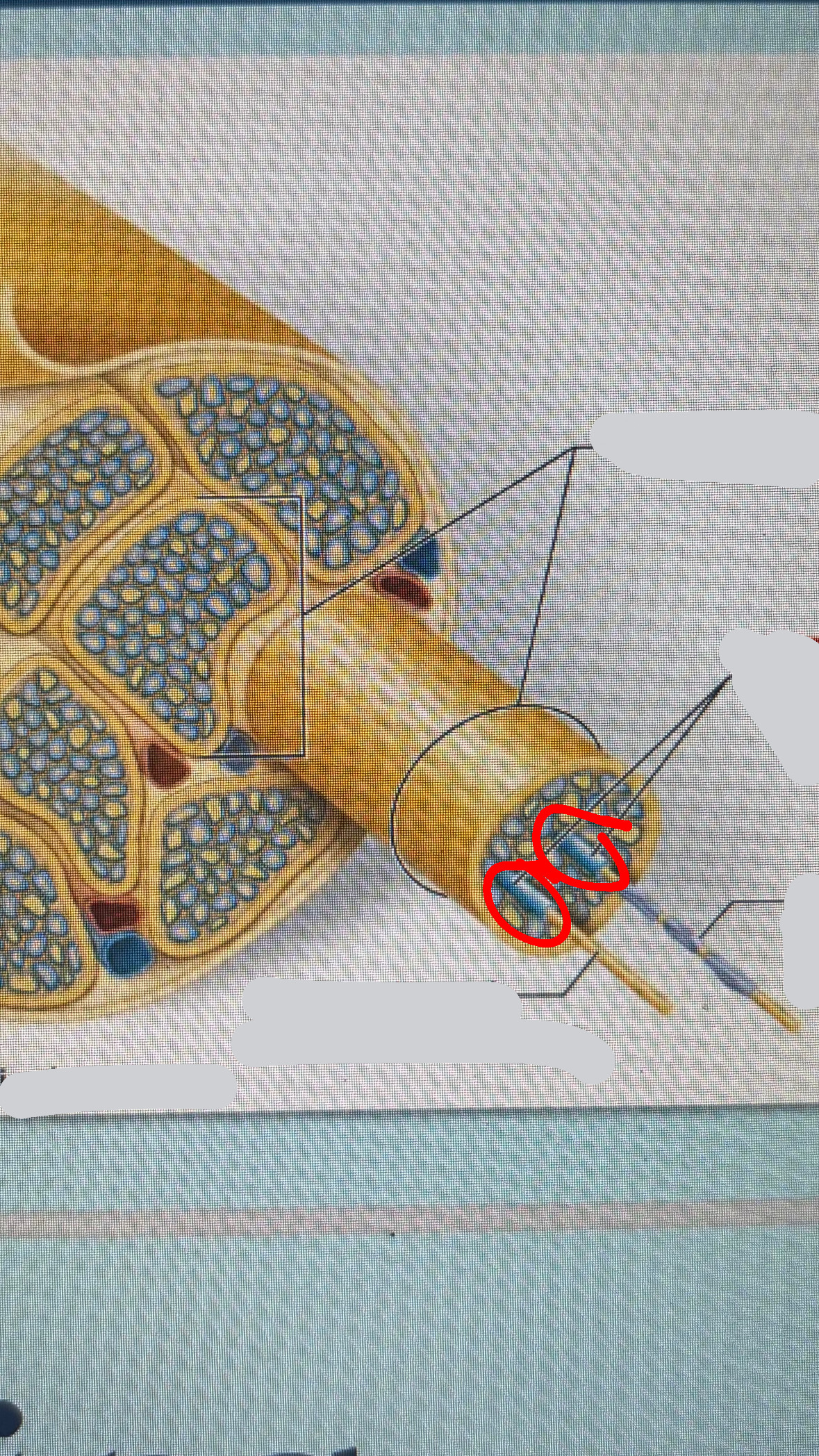
endoneurium
nerve structure
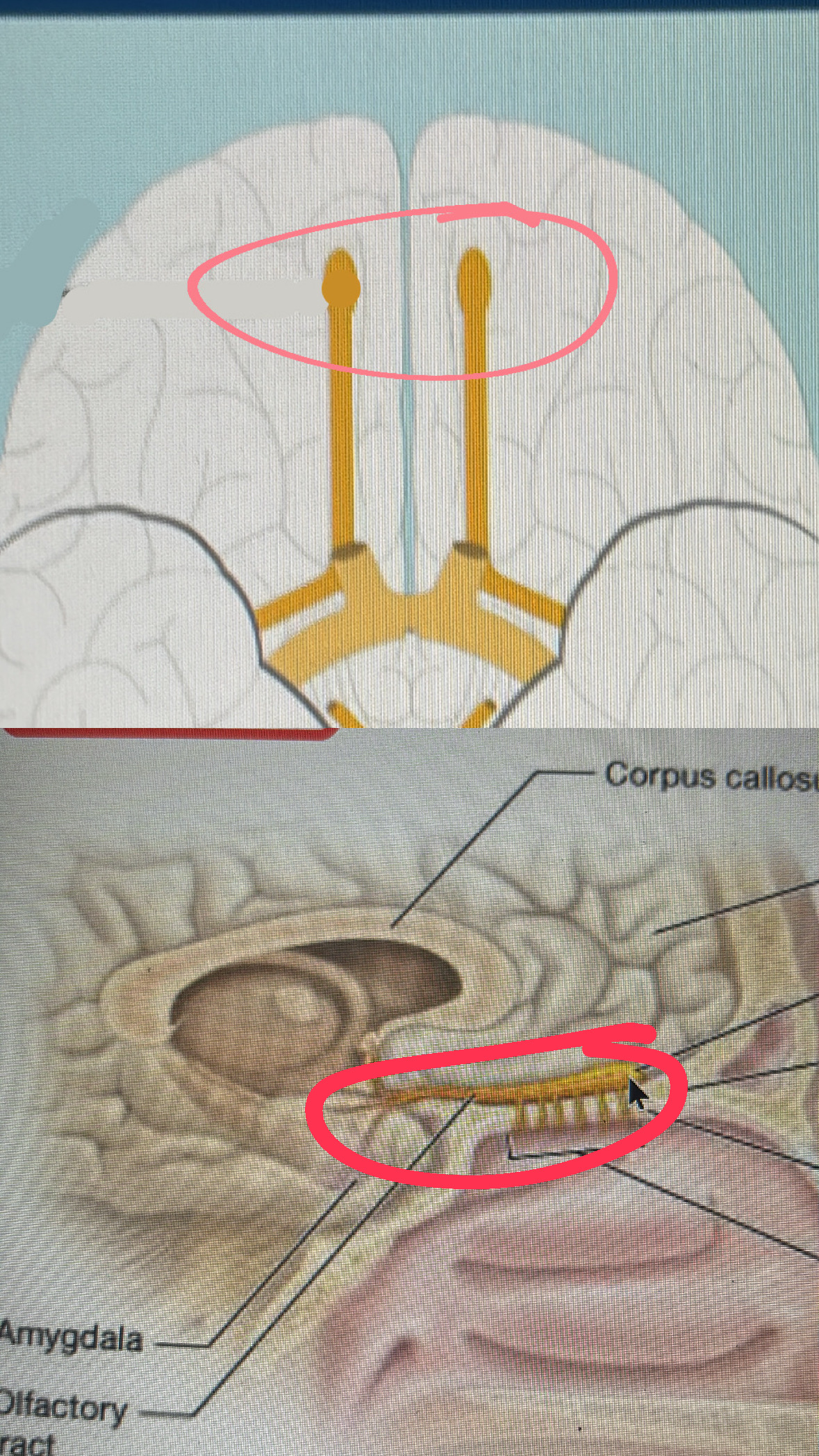
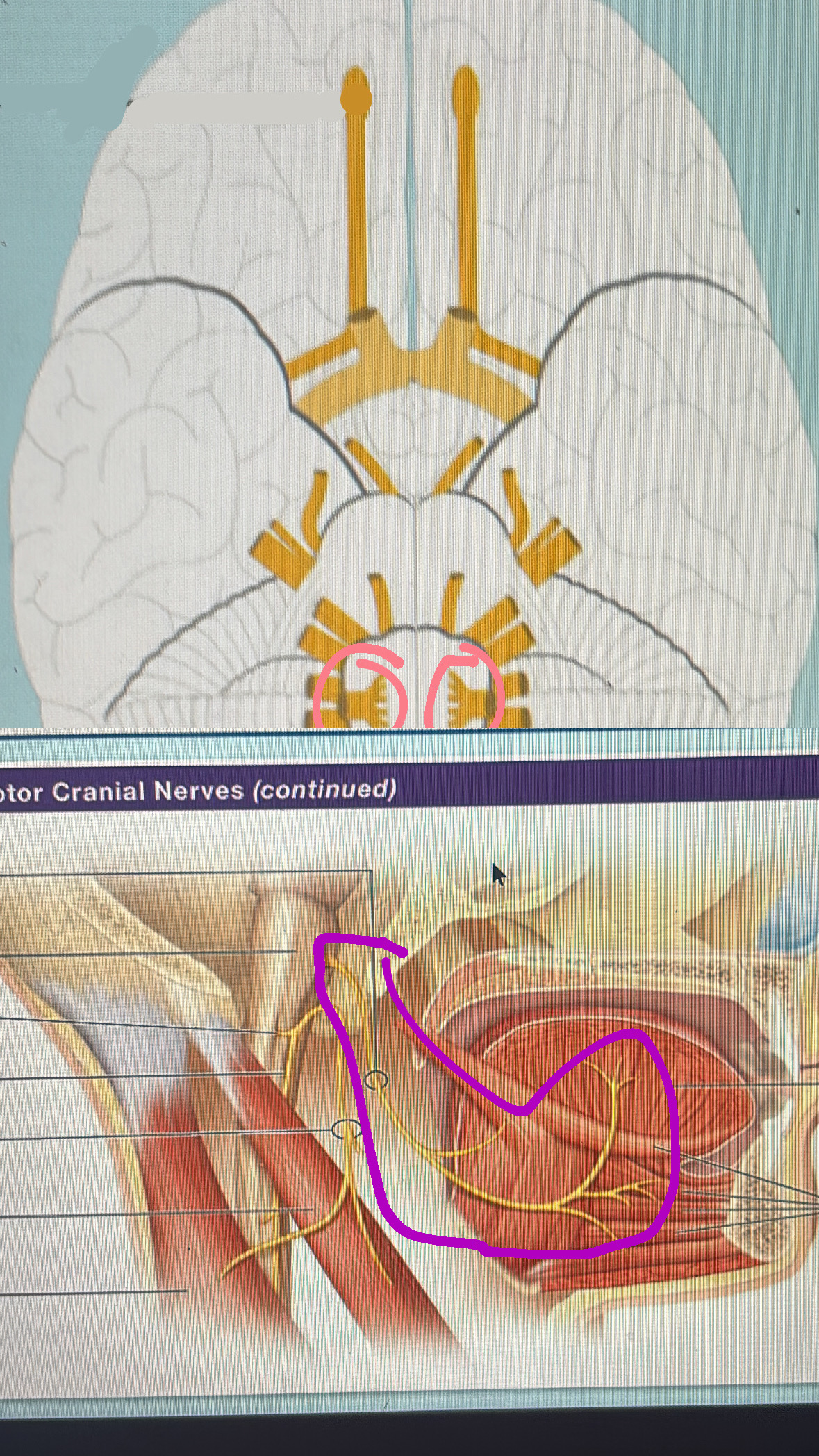
olfactory (sensory)
I. smell
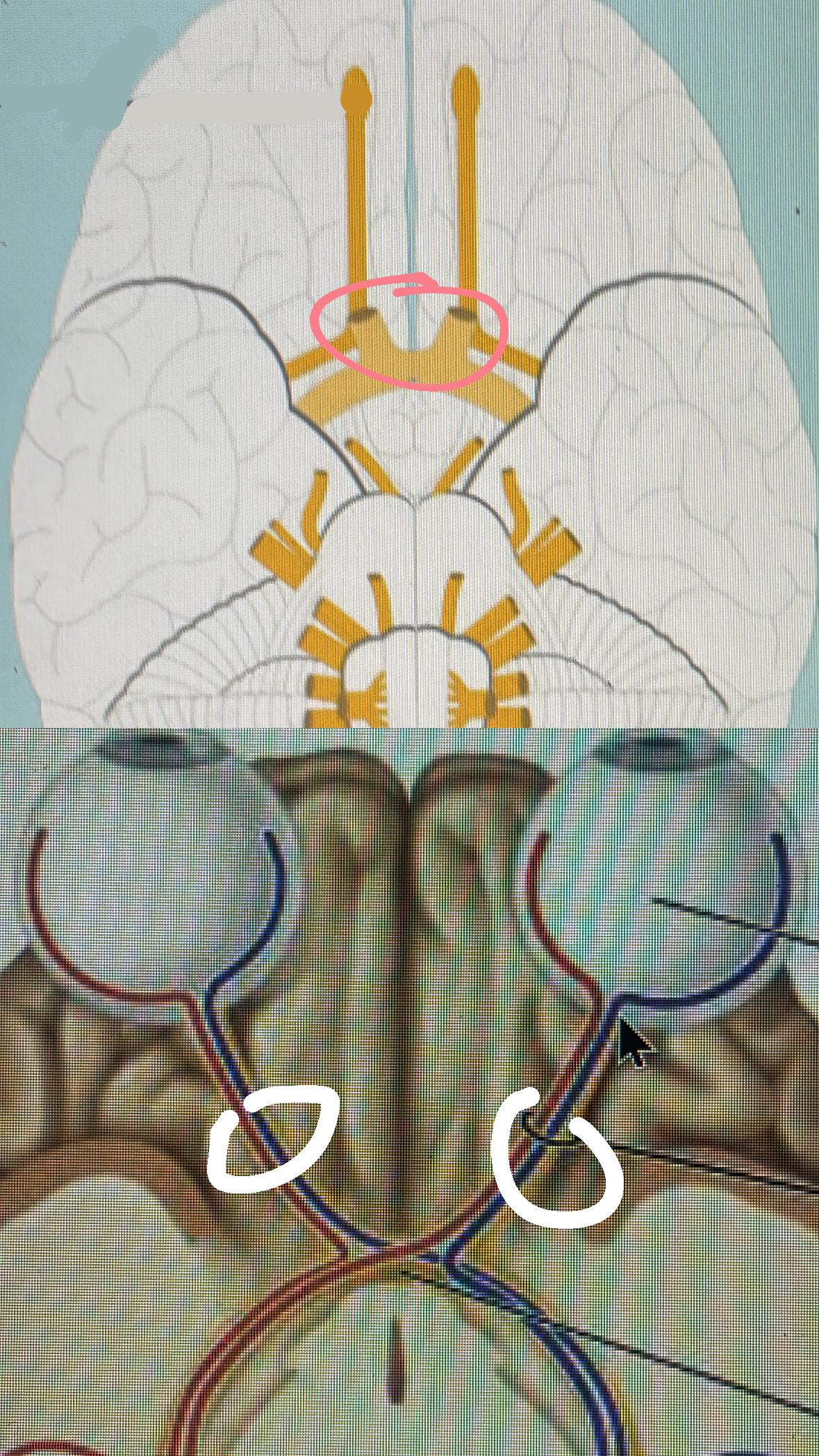
optic (sensory)
II. vision
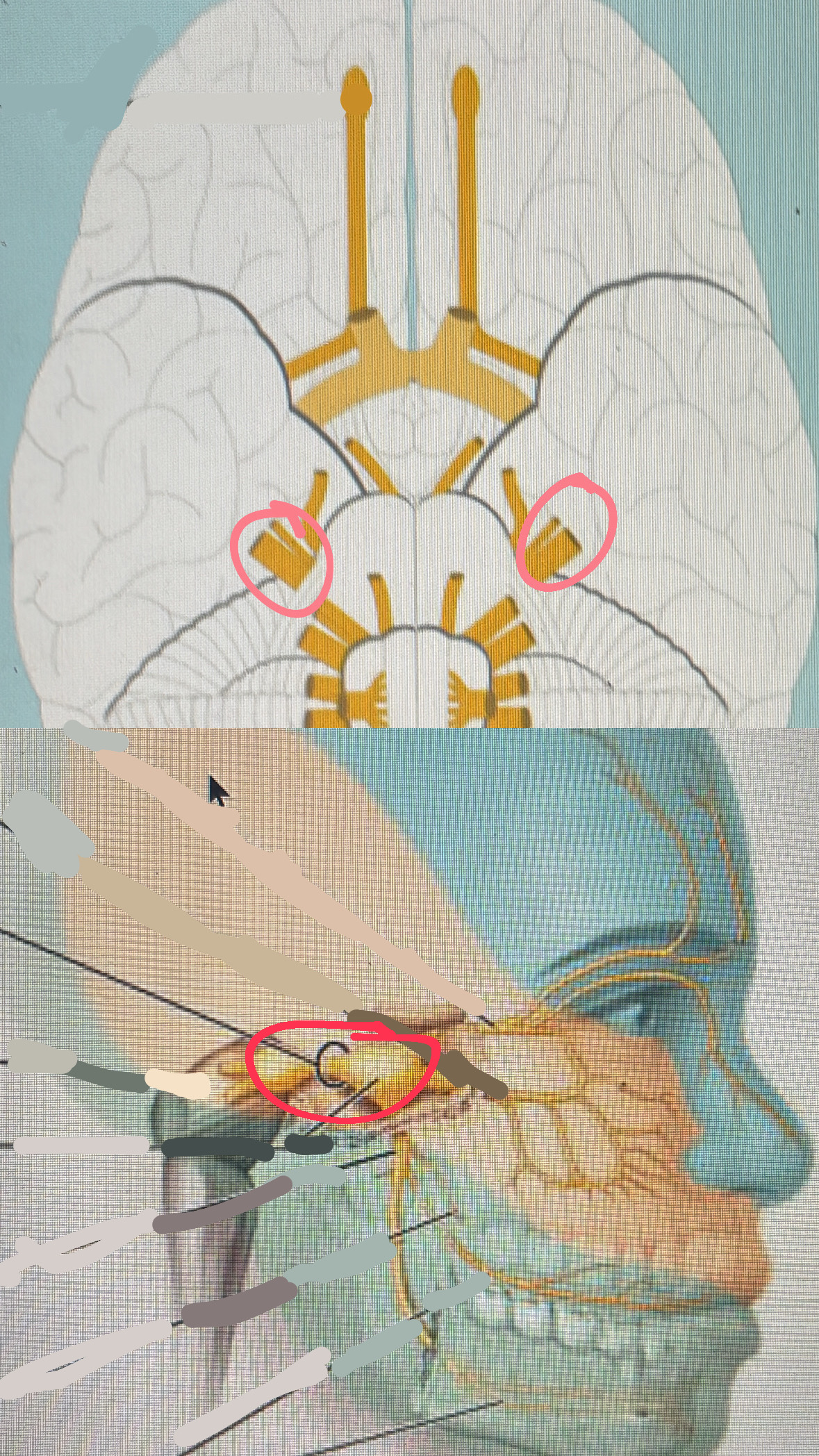
oculomotor (motor)
III. eyes and eyelid movement; pupil constricting
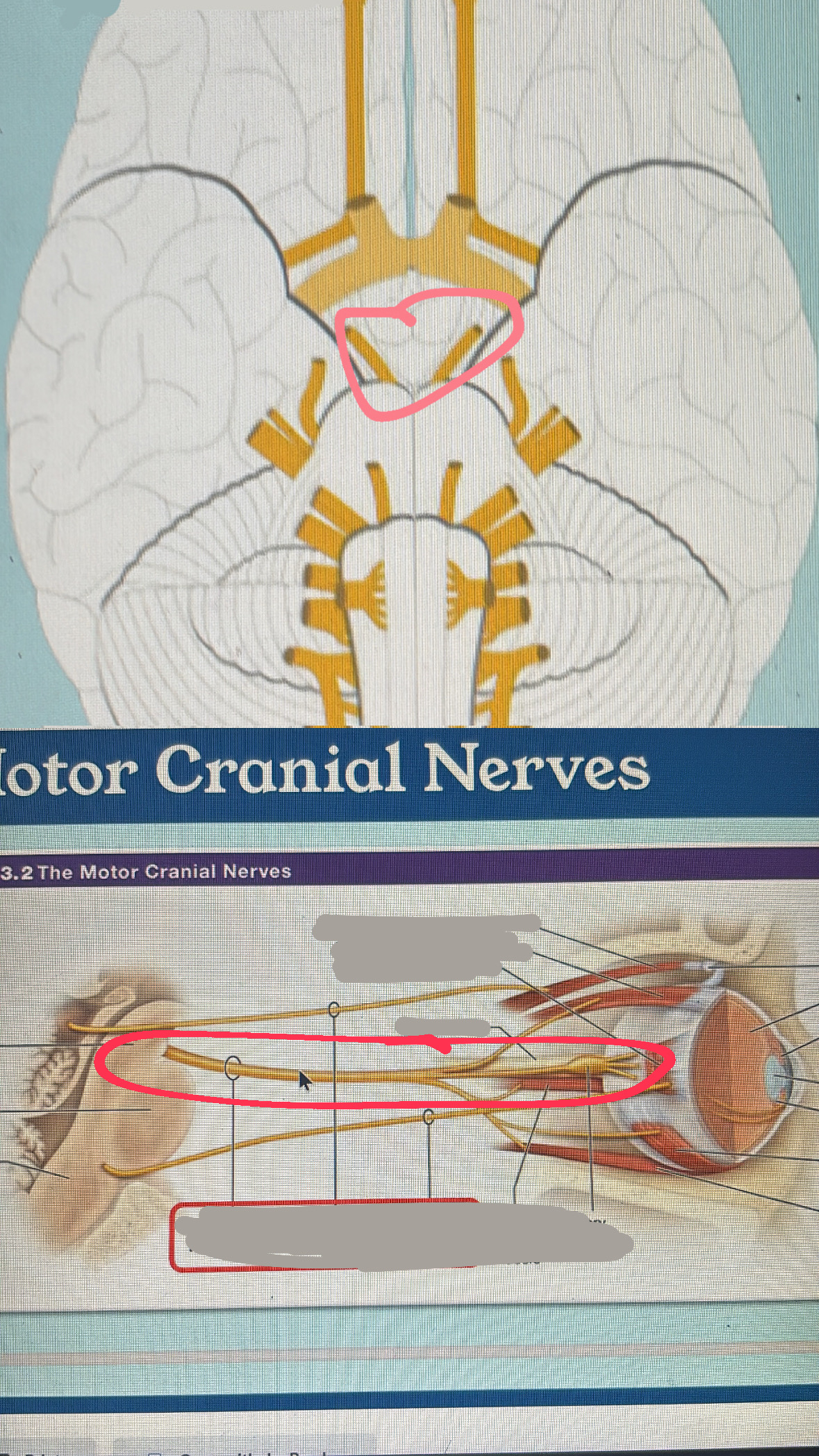
trochlear (motor)
IV. eye movement
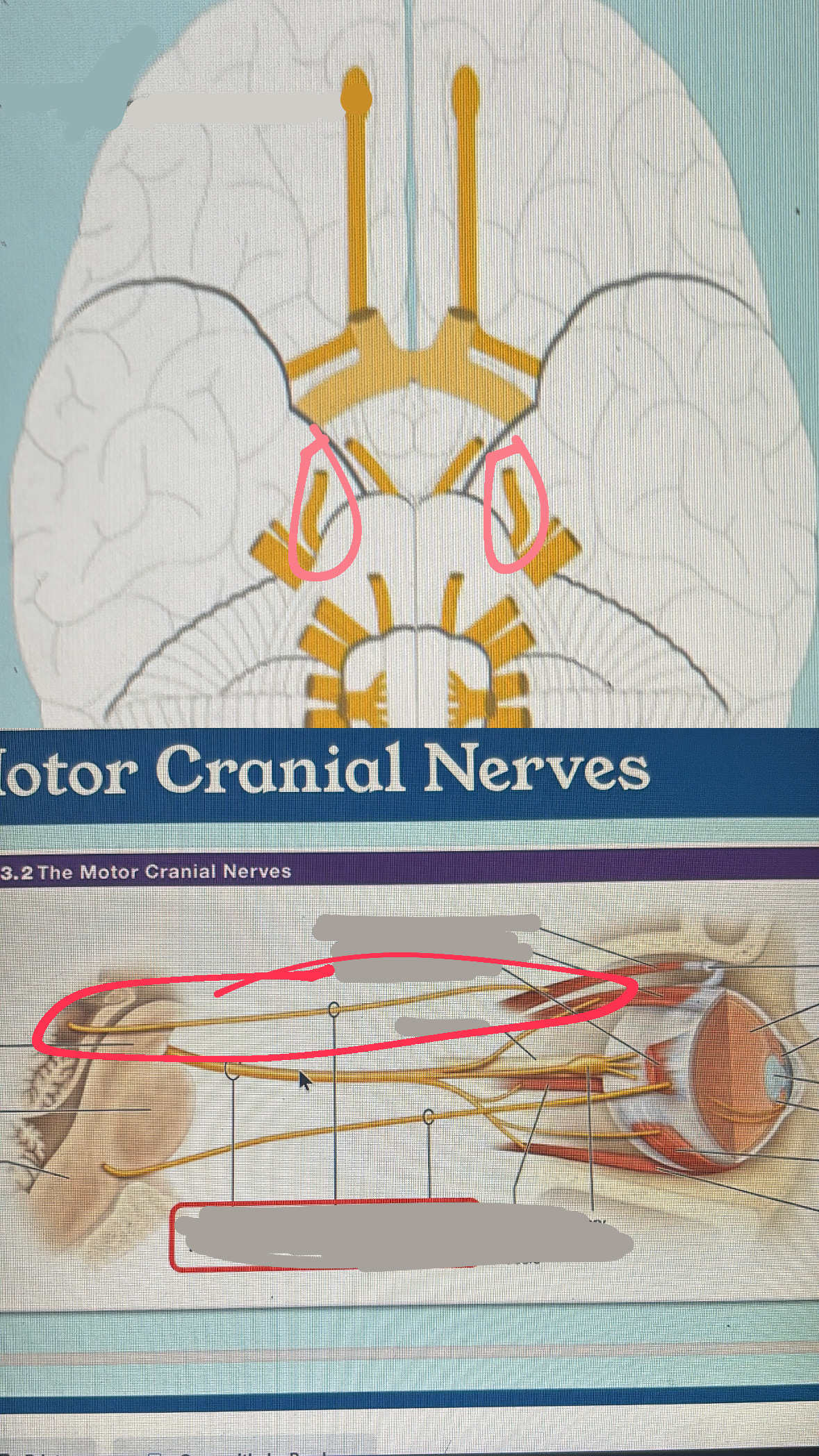
trigeminal (mixed)
V. facial sensation (touch and pain): mastication
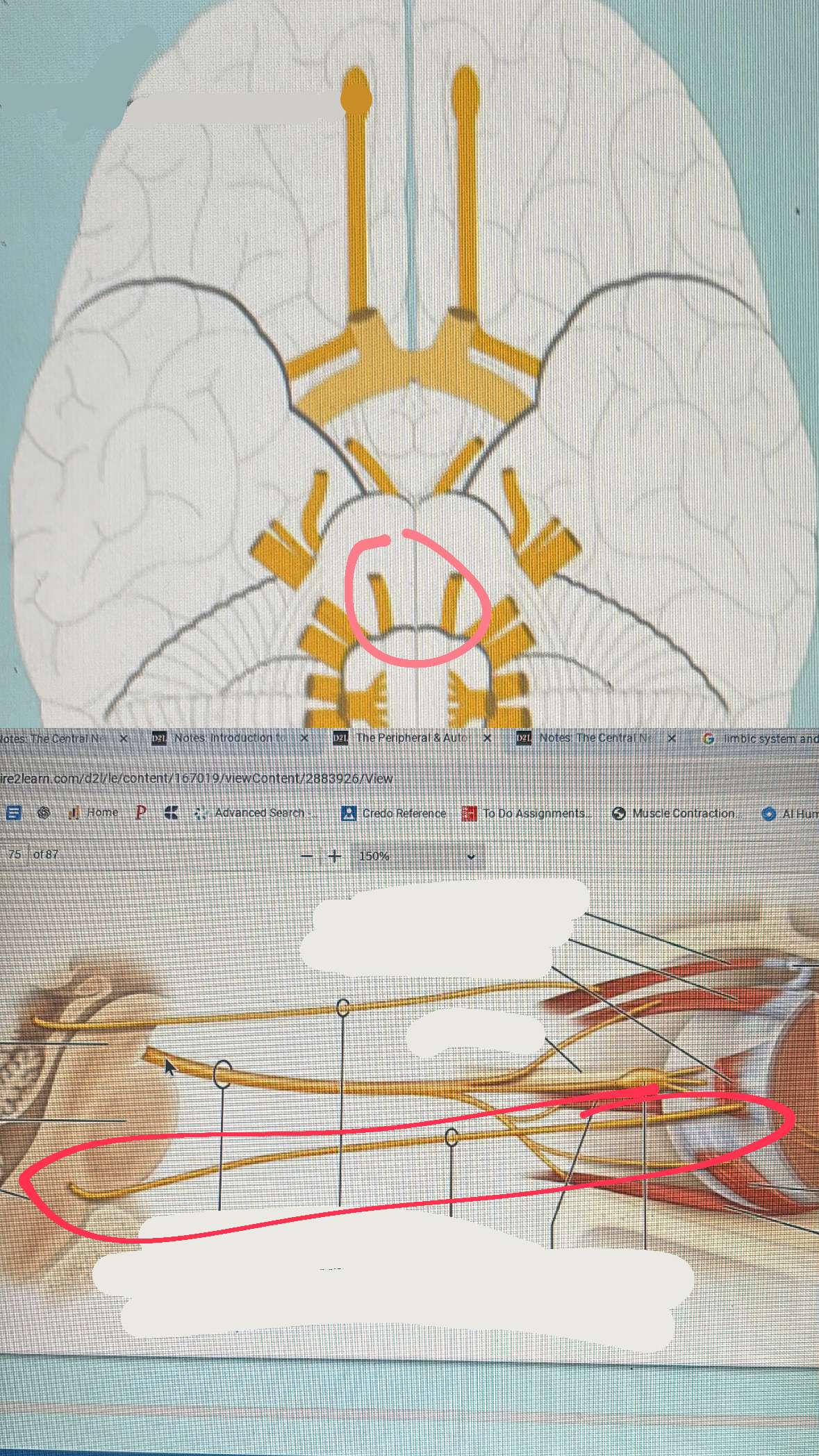
abducens (motor)
VI. eye movement
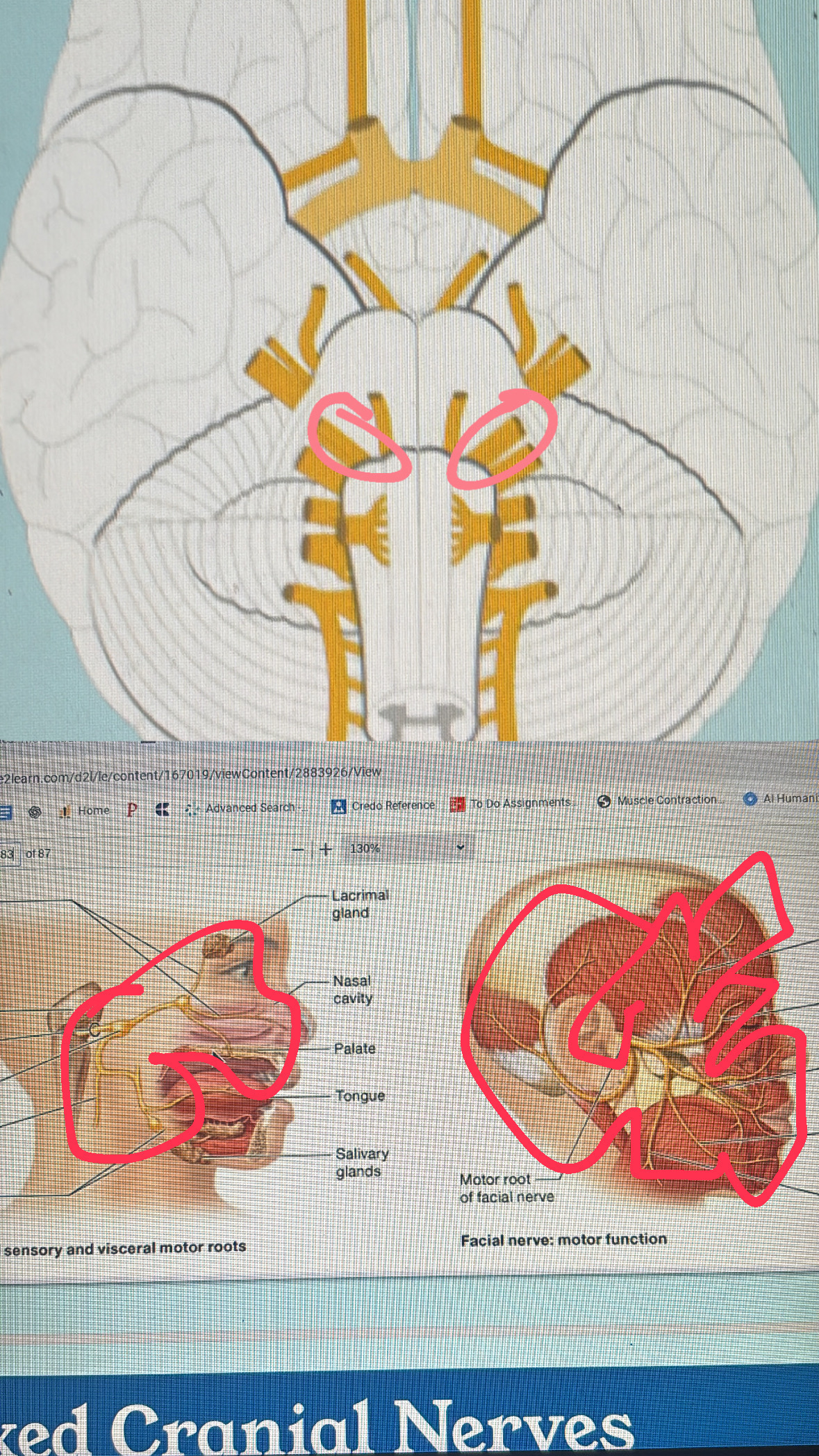
facial (mixed)
VII. facial expressions; taste; salivation; tear secretion
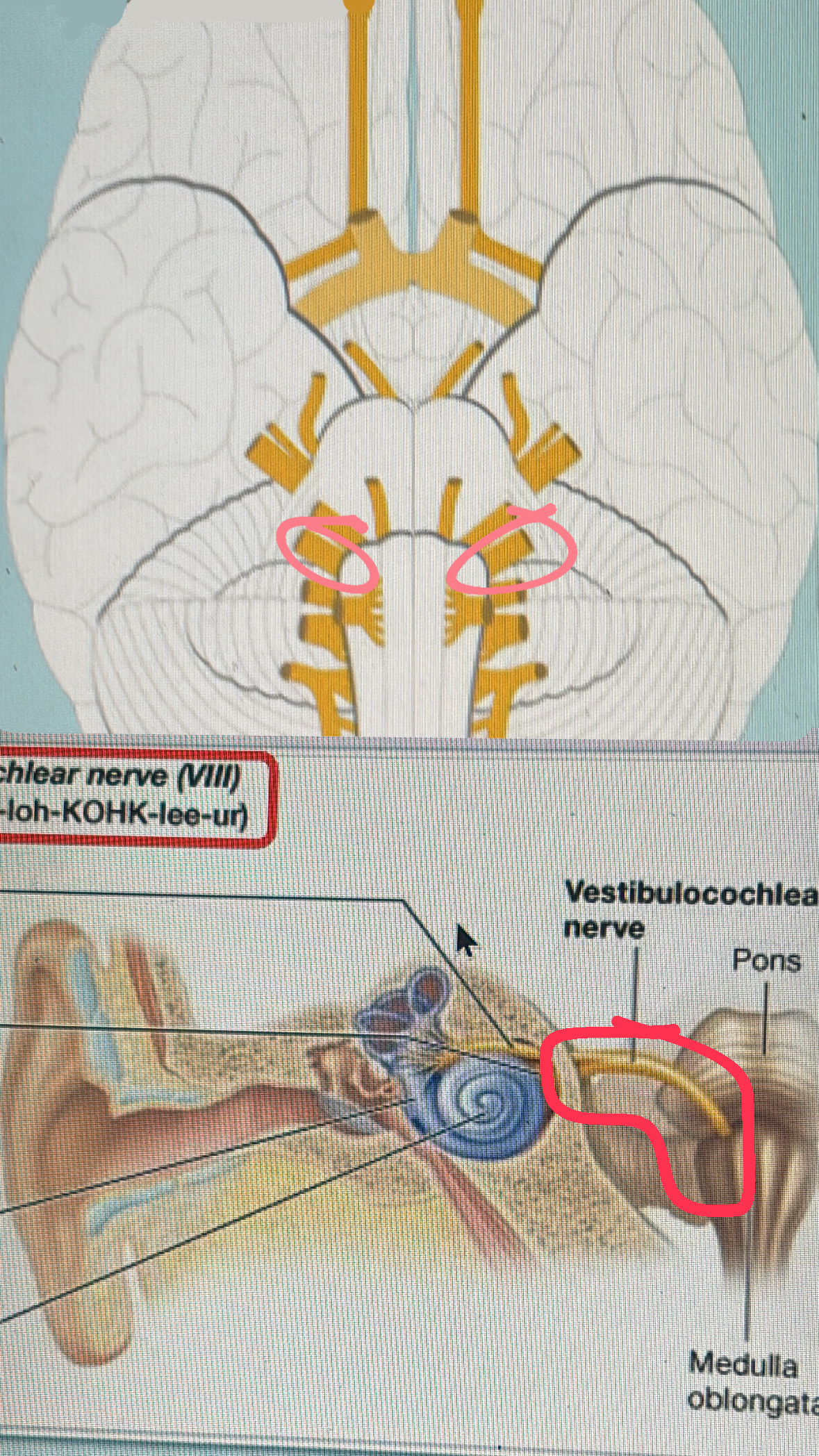
vestibulocochlear (sensory)
VIII. hearing, balance
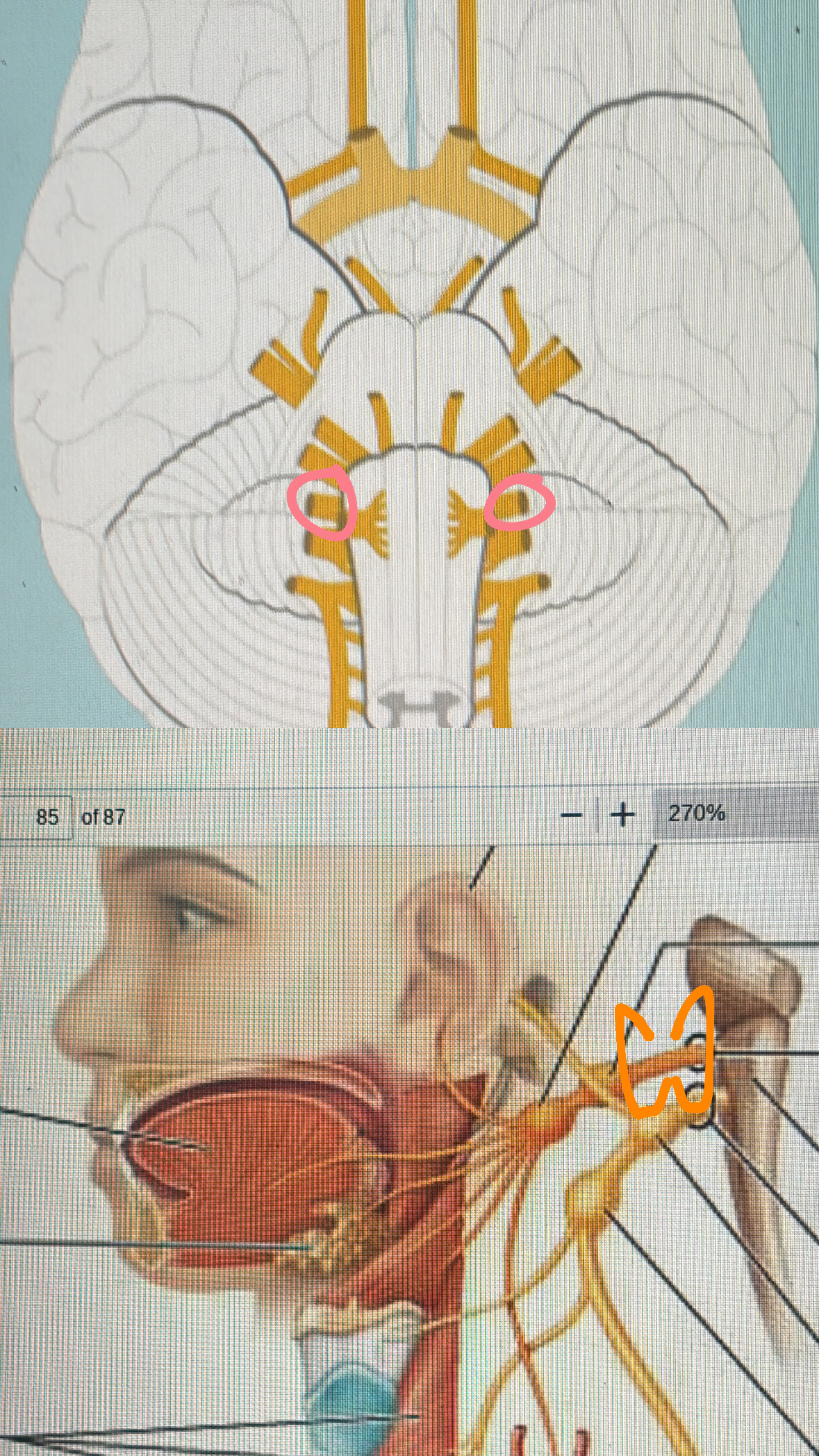
glossopharyngeal (mixed)
IX. taste, tongue, tonsil, and pharynx sensations, salivation, swallowing
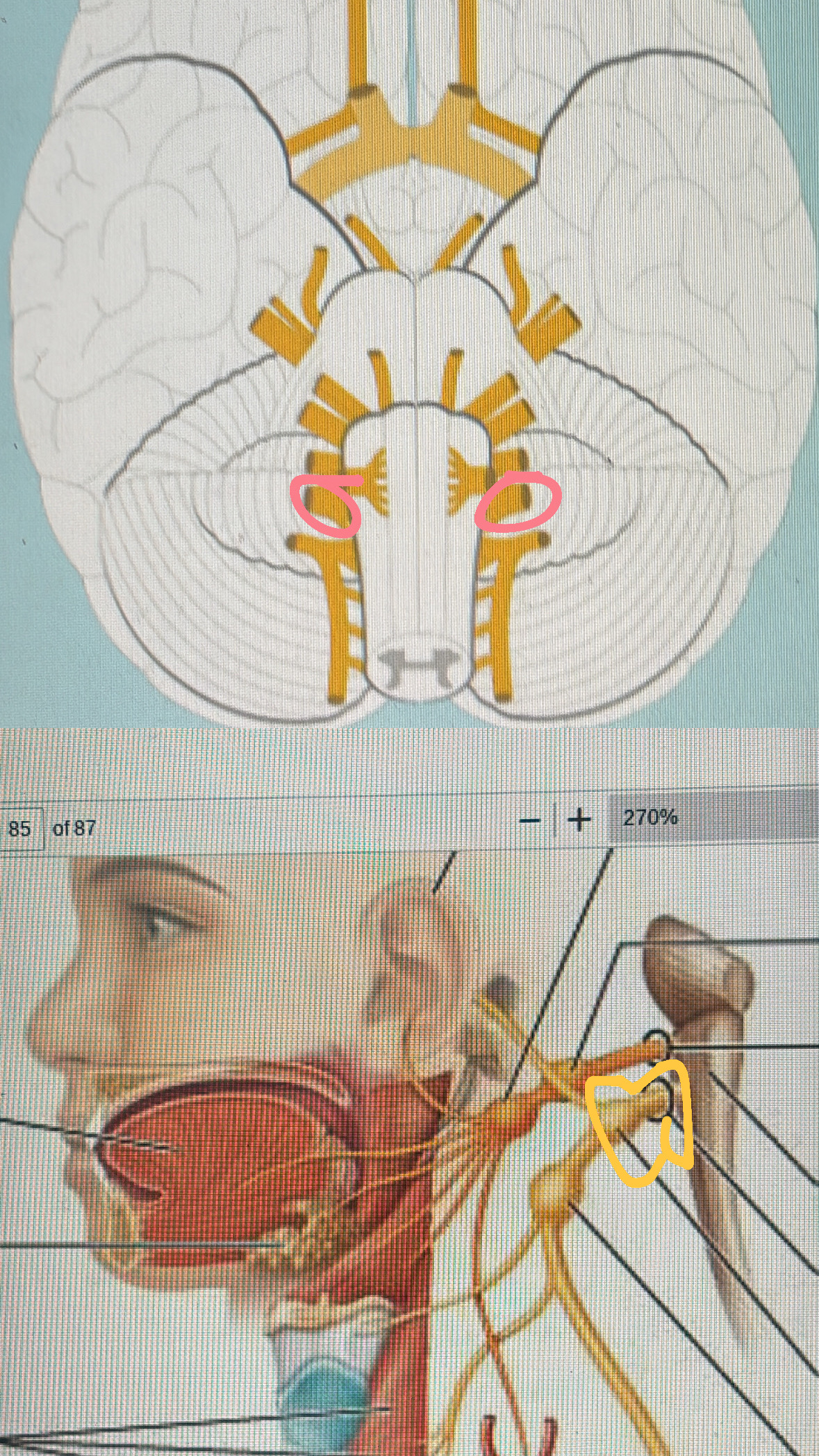
vagus (mixed)
X. autonomic control of viscera( heart, lungs, digestive organs, glands)
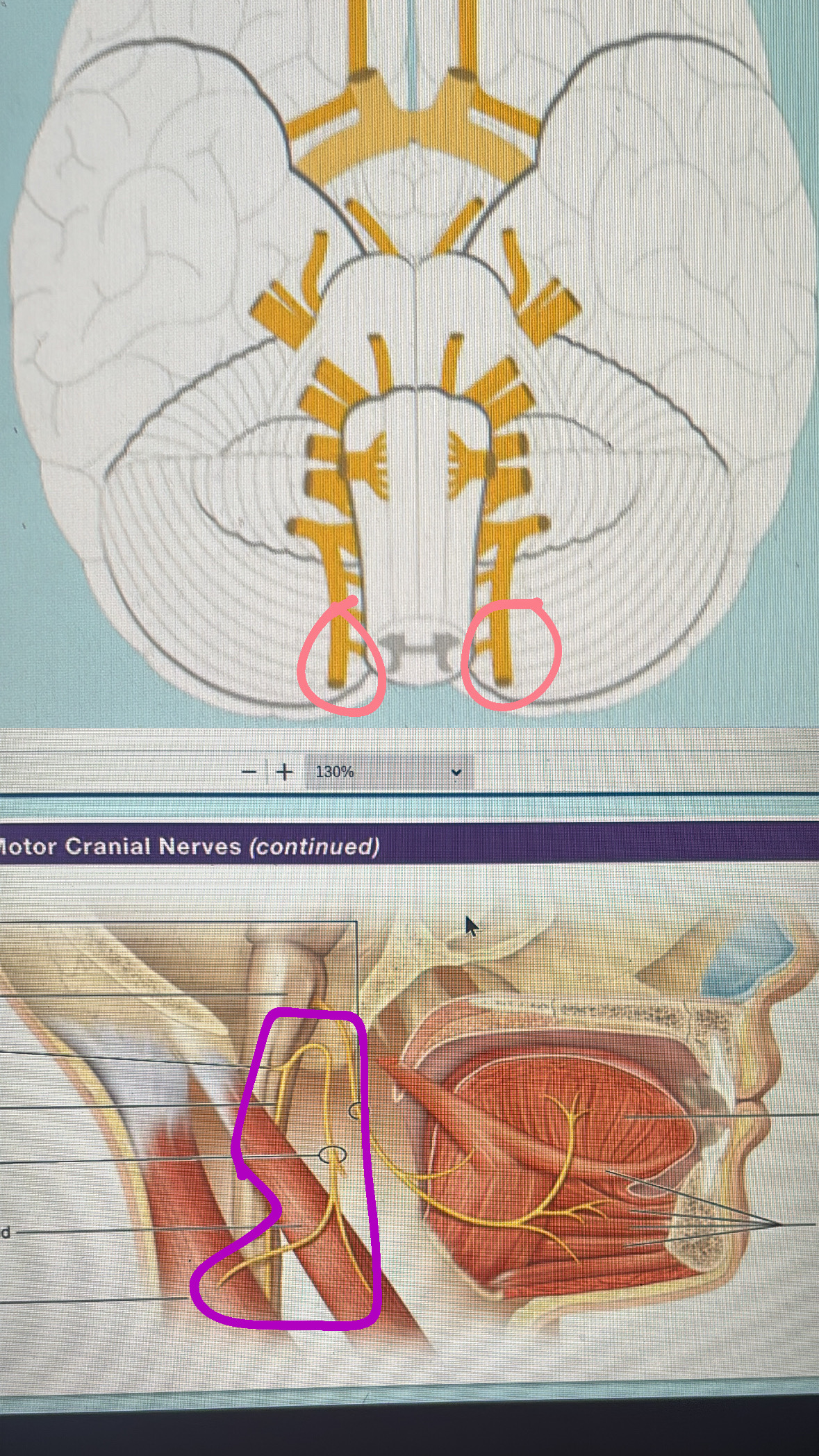
accessory nerve (motor)
XI. spinal component - head and shoulder movement
cranial component- muscle of speech
hypoglossal (motor)
XII. tongue movements
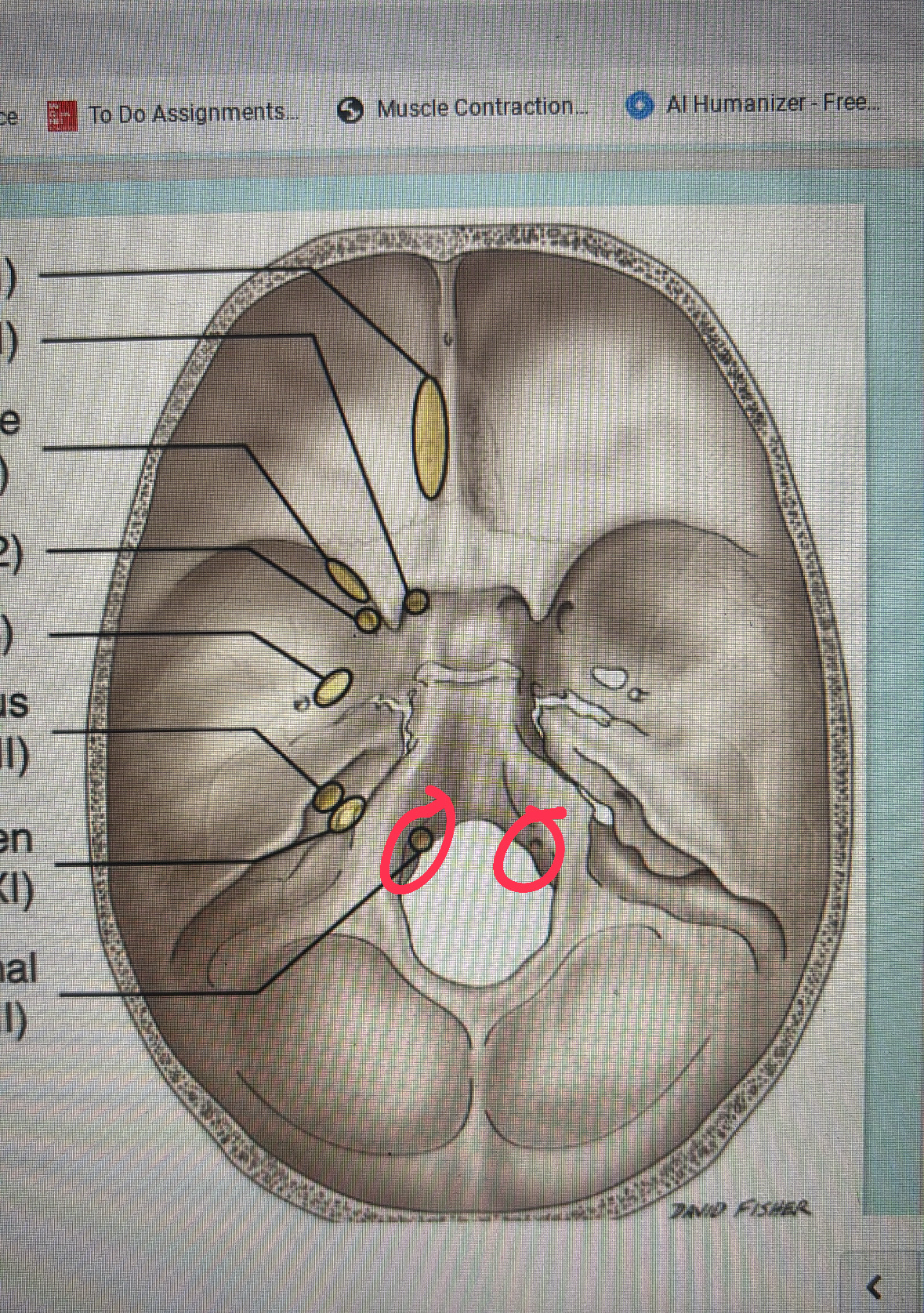
cribriform plate
cranial nerve I
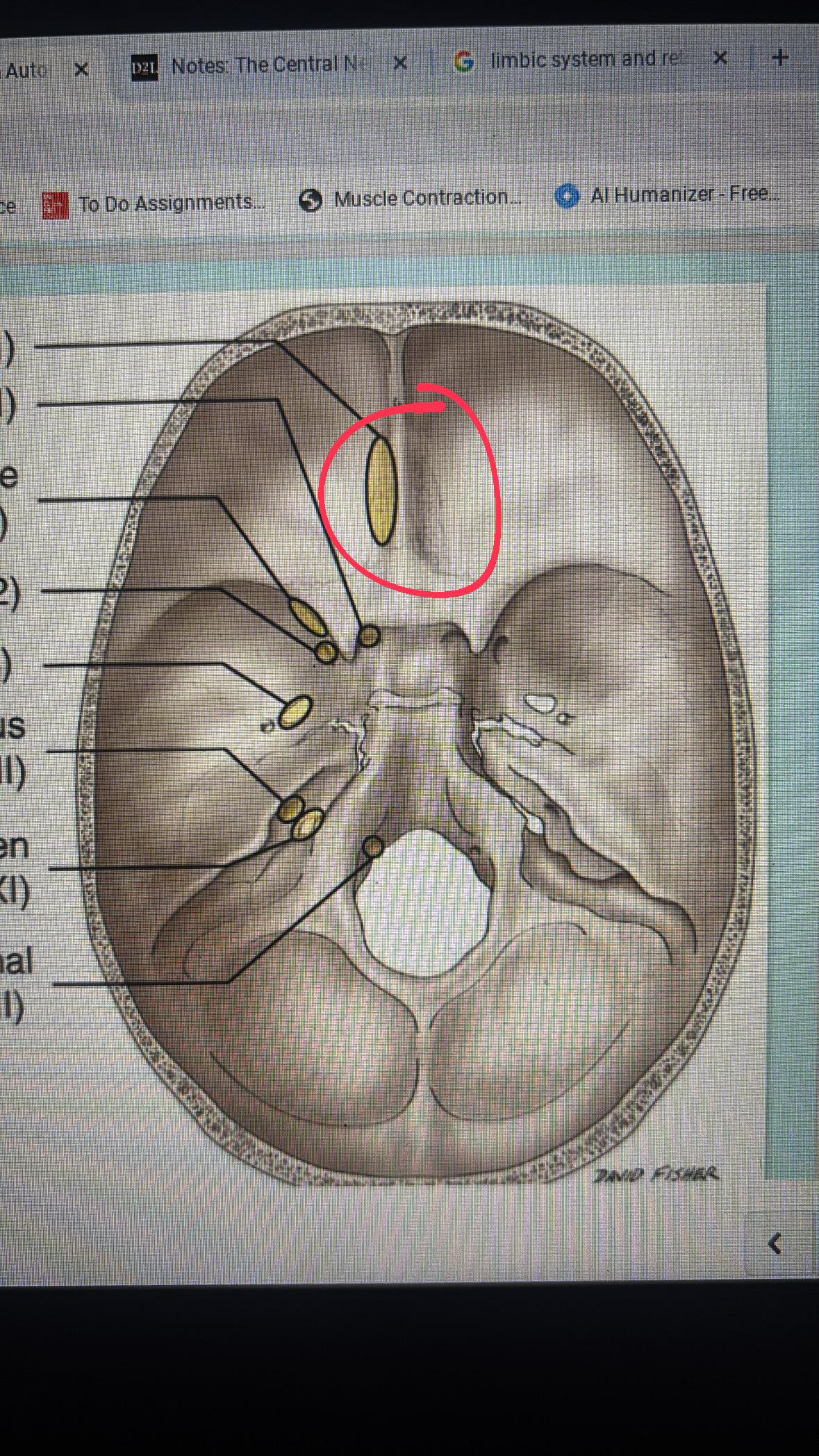
optical canal
cranial nerve II
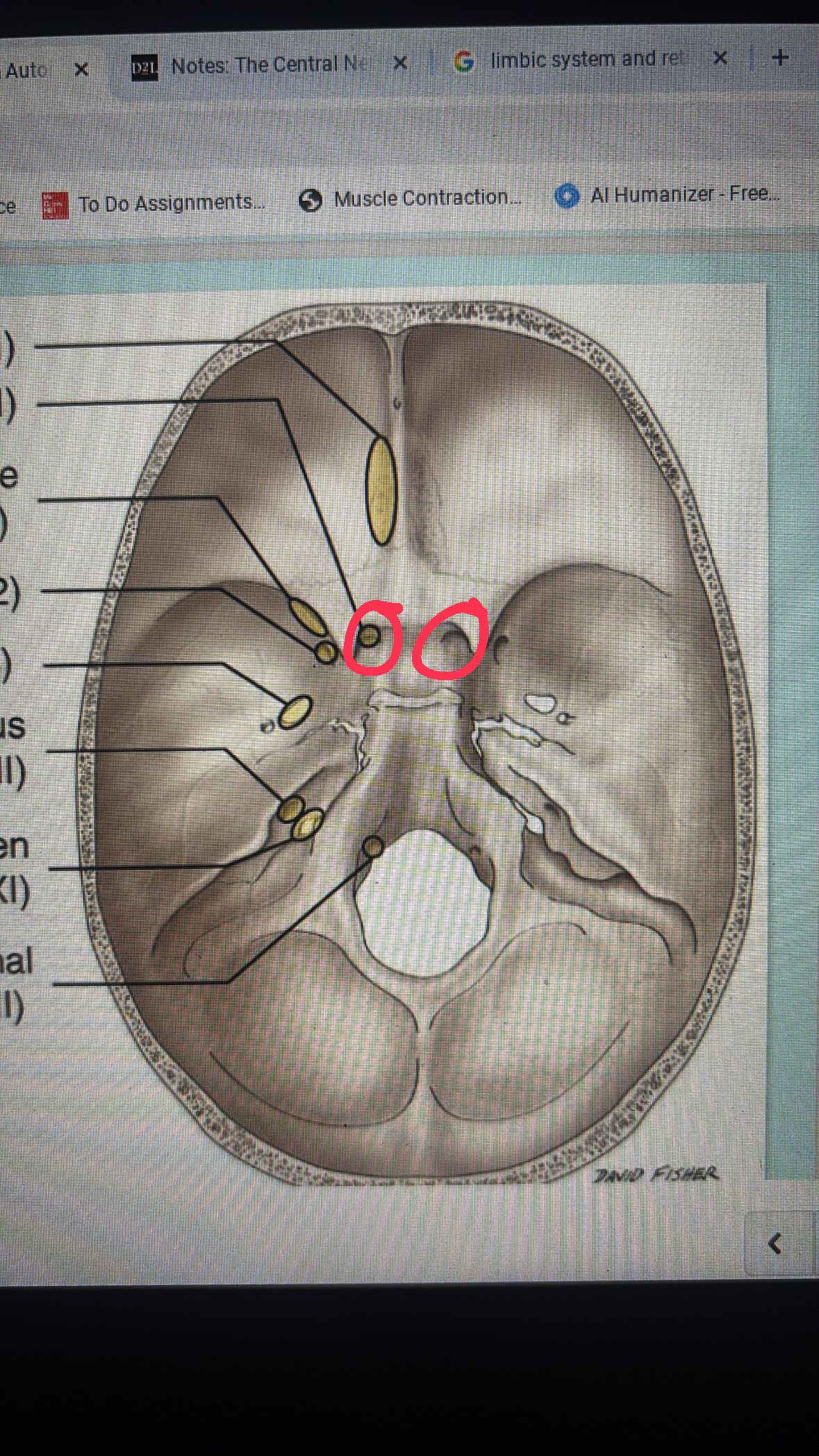
superior orbital fissure
cranial nerve III, IV, VI, and V1
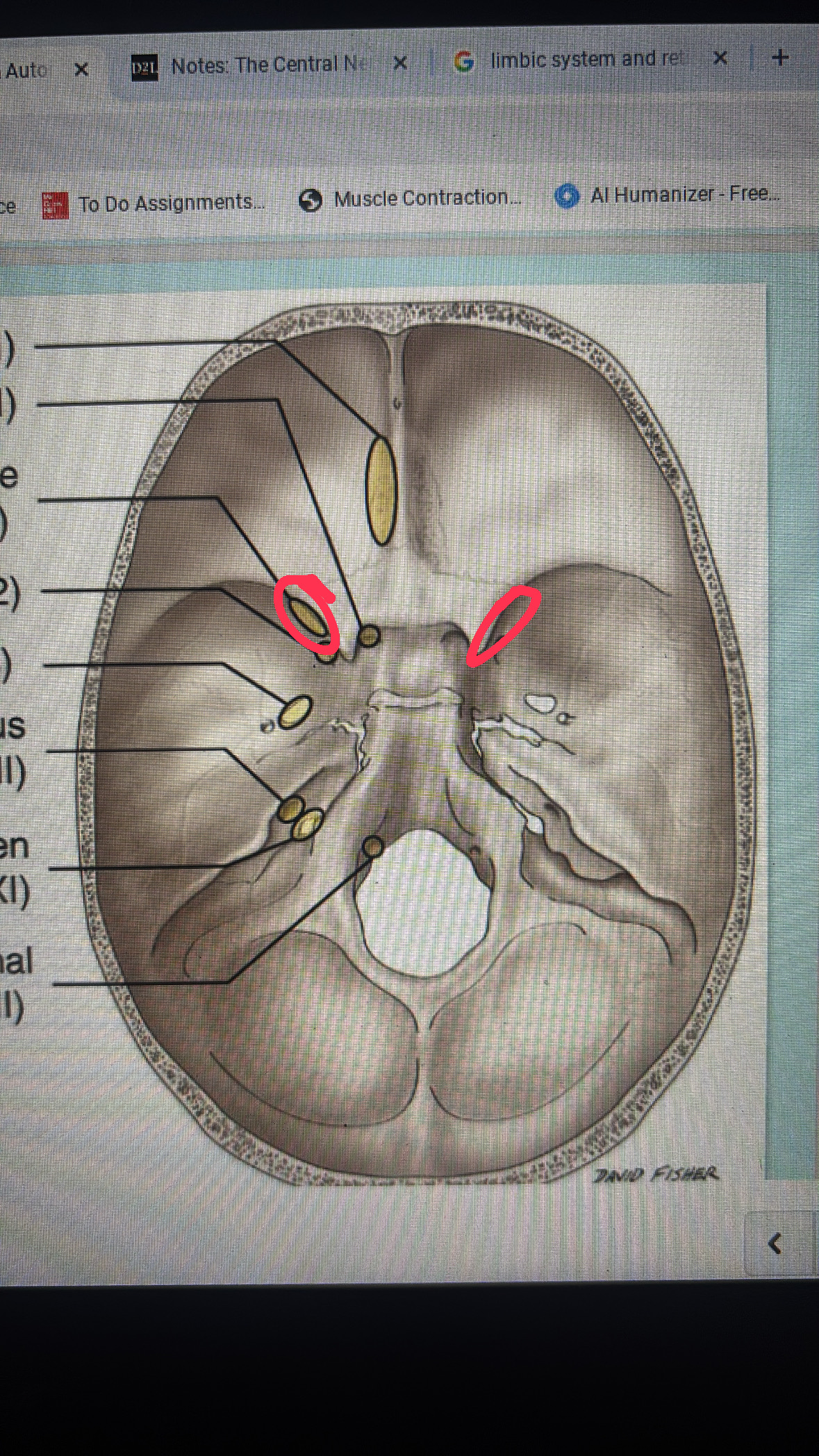
foramen rotundum
maxillary division
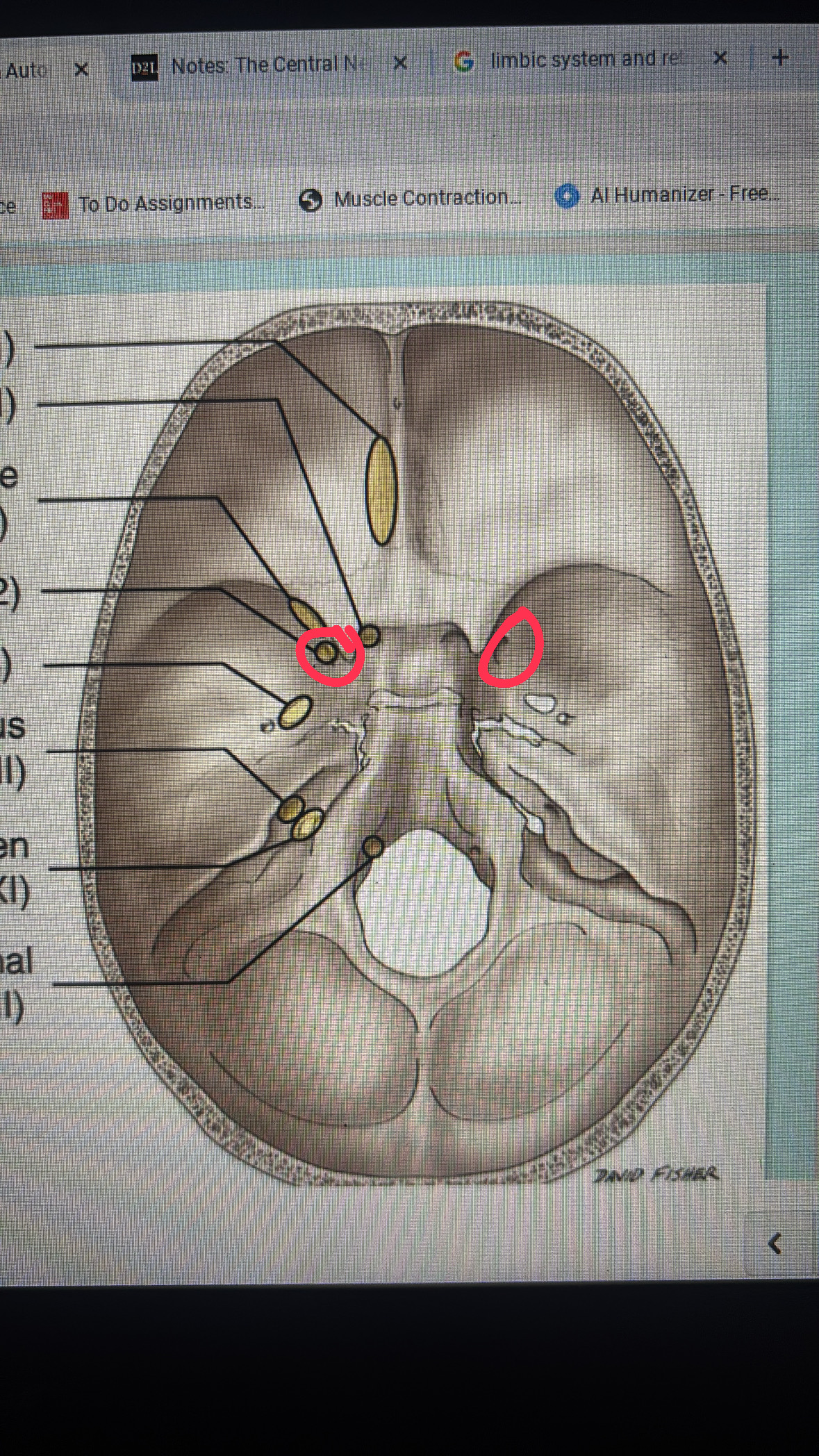
foramen ovale
mandibular division
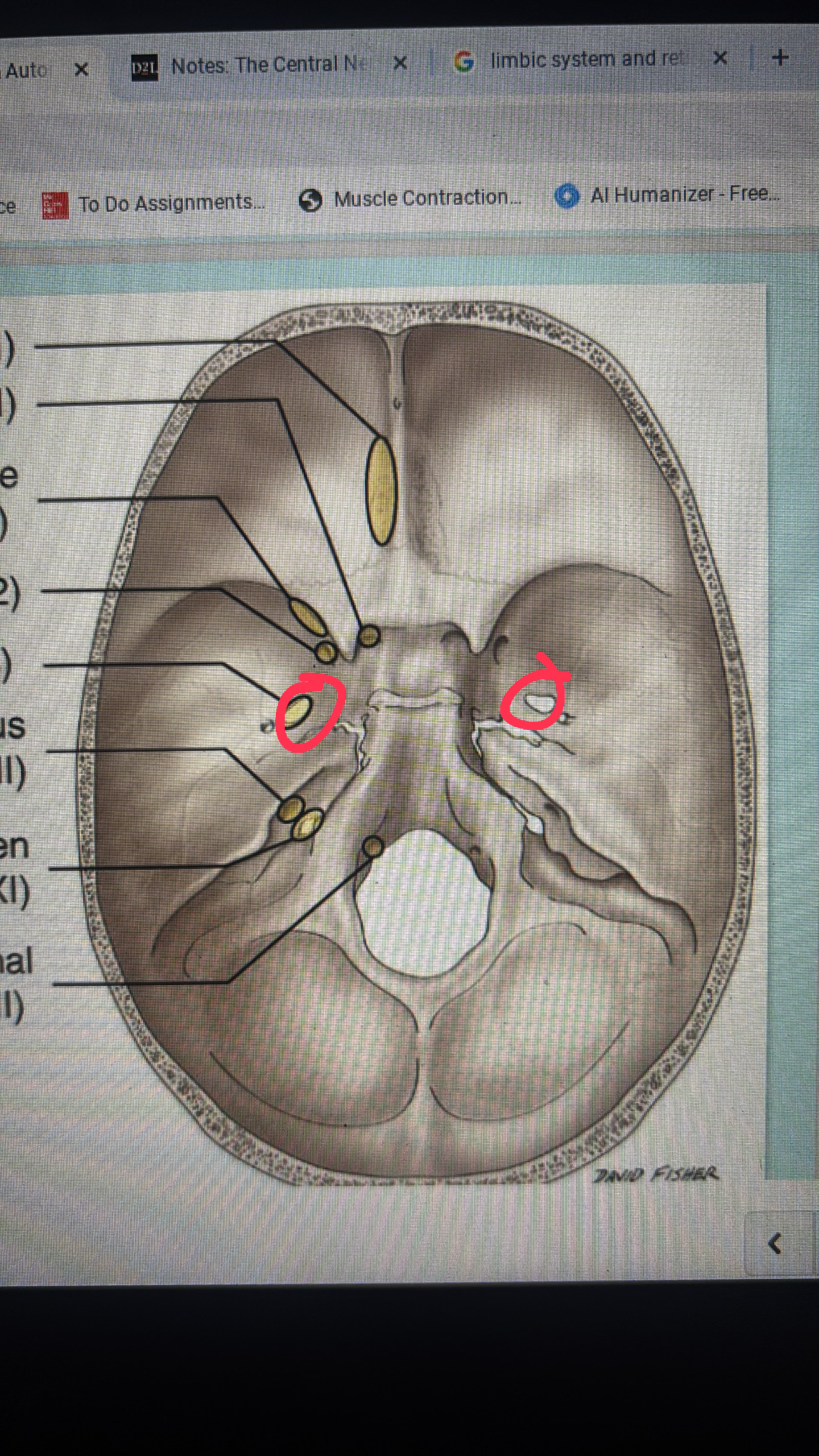
internal acoustic meatus
cranial nerve VII AND VIII
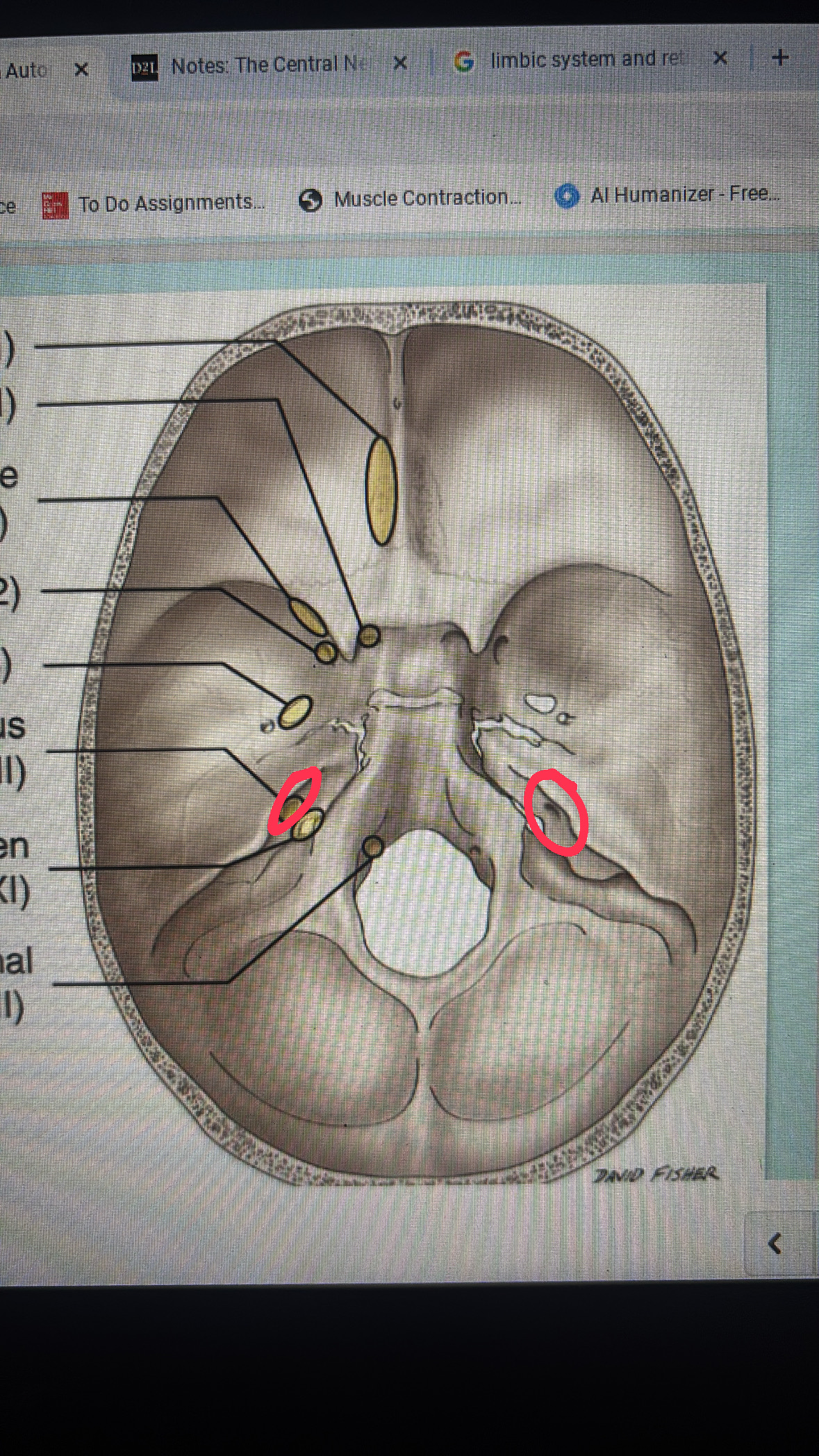
jugular foramen
cranial nerves IX, X, AND XI
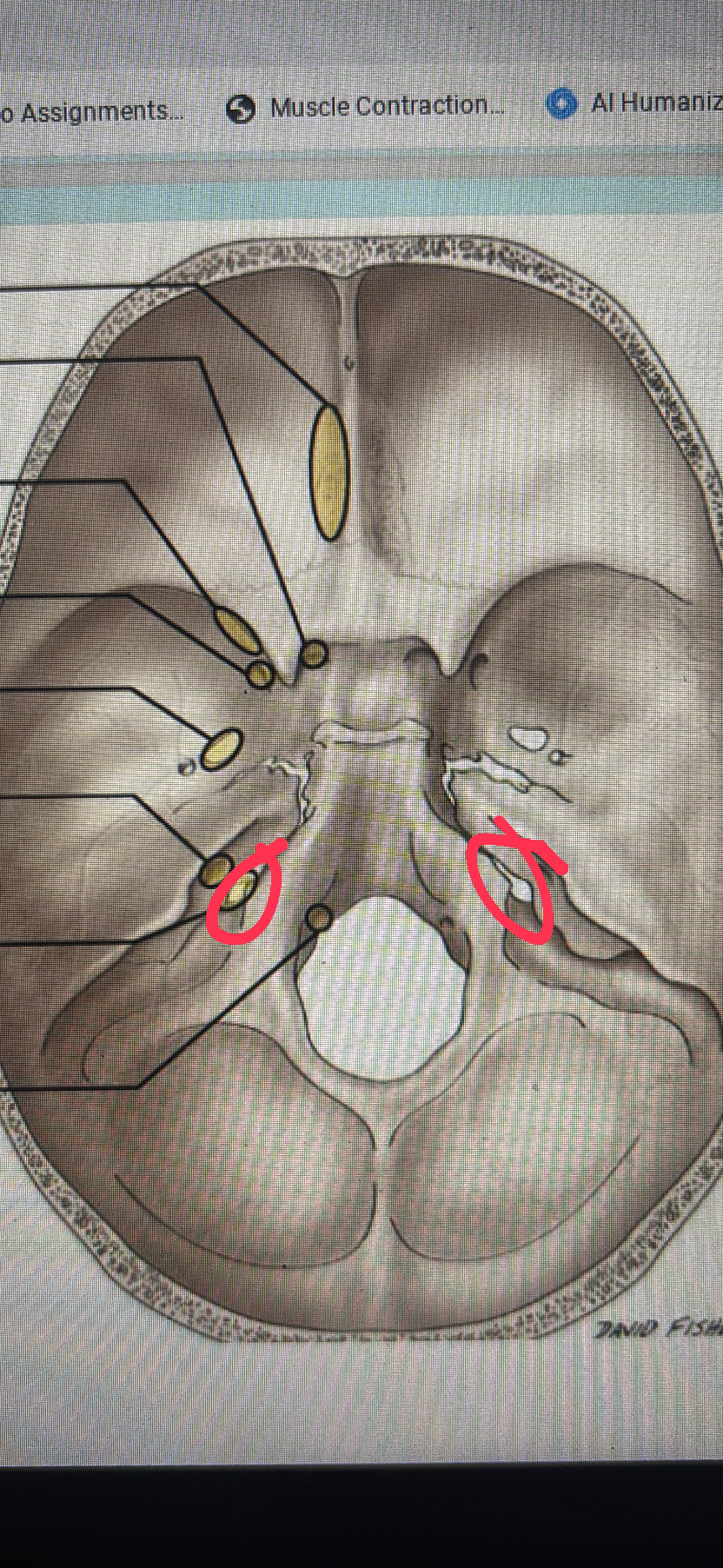
hypoglossal canal
cranial nerve XII
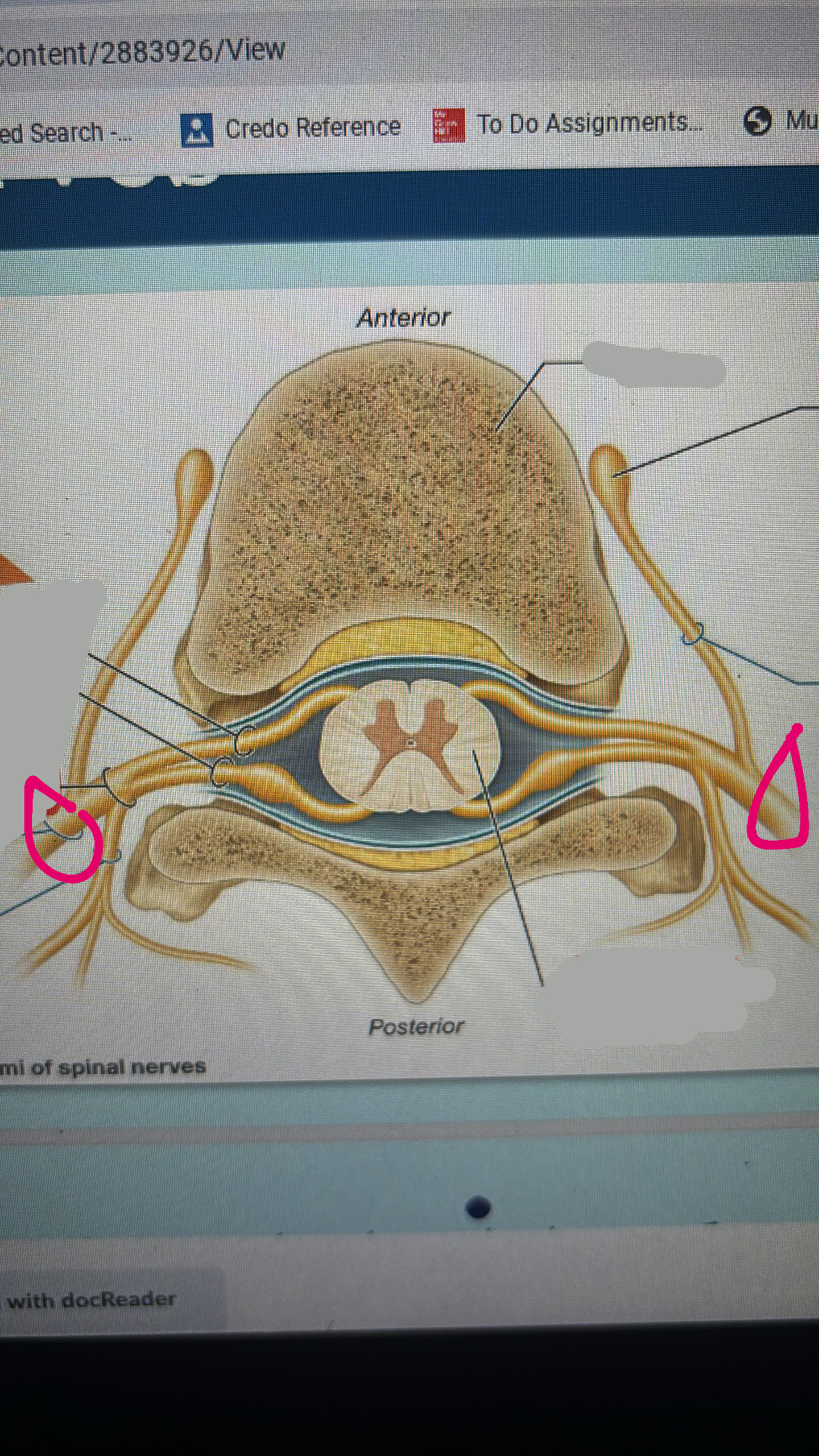
anterior root
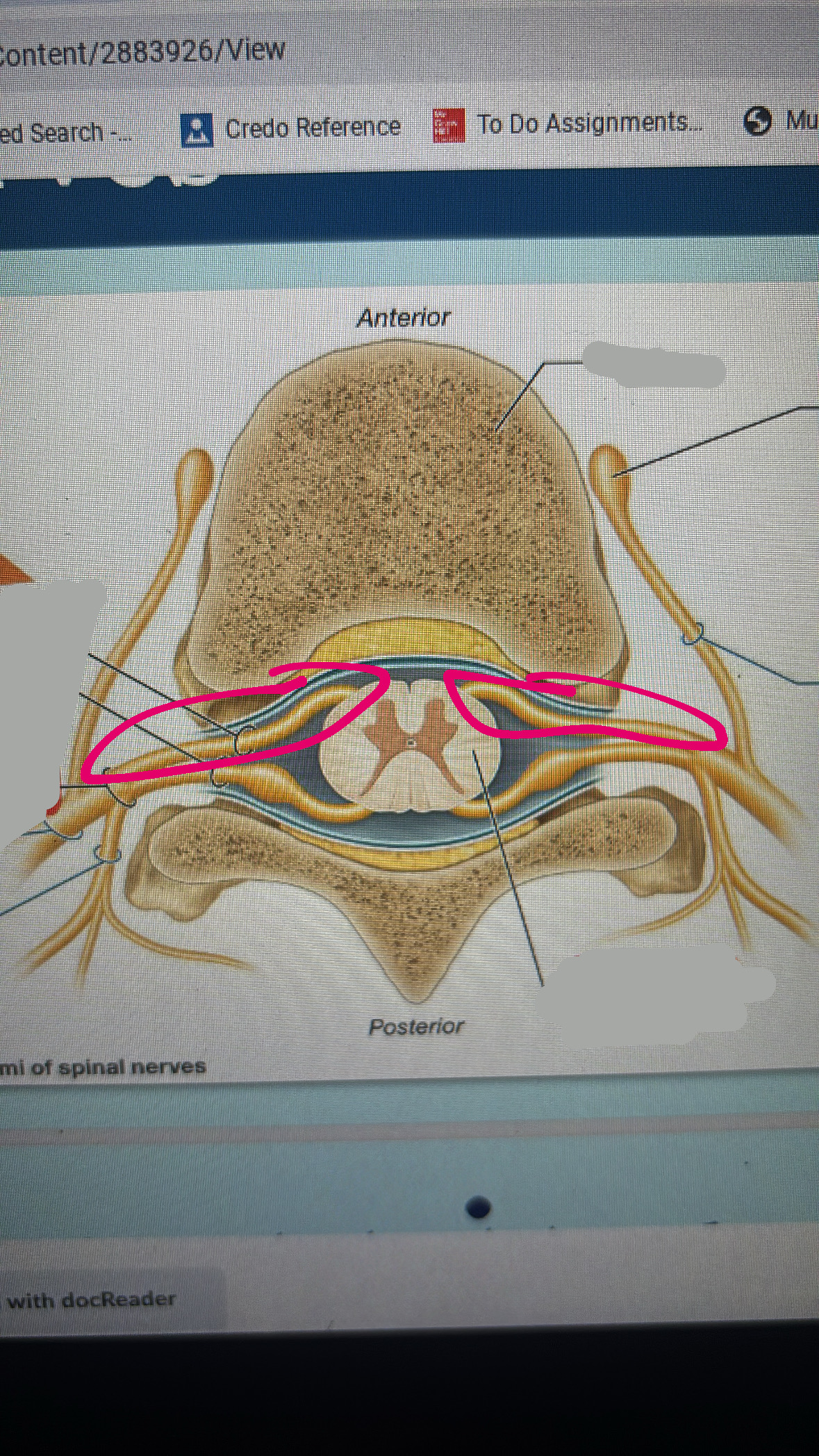
posterior root
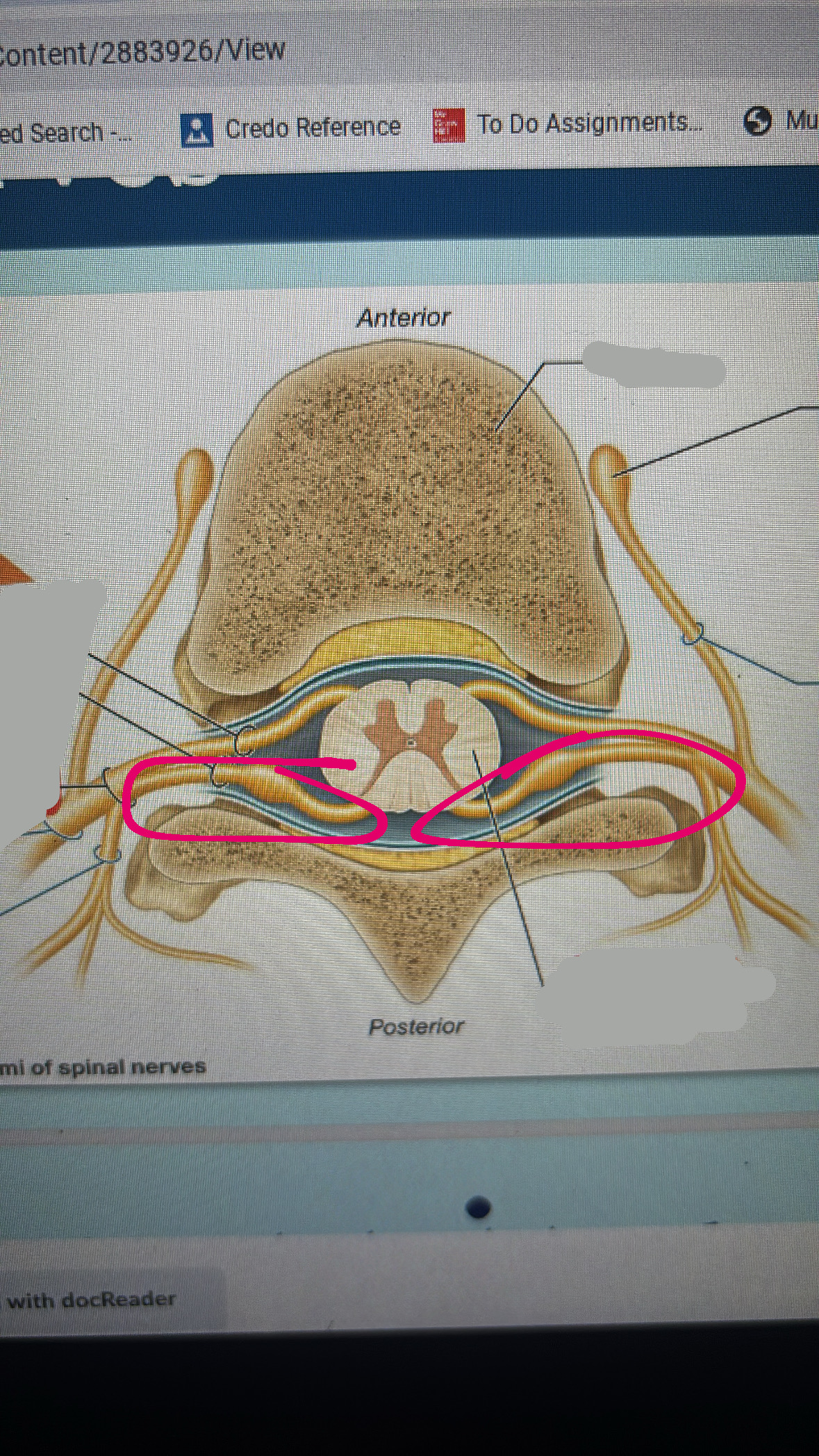
spinal nerve
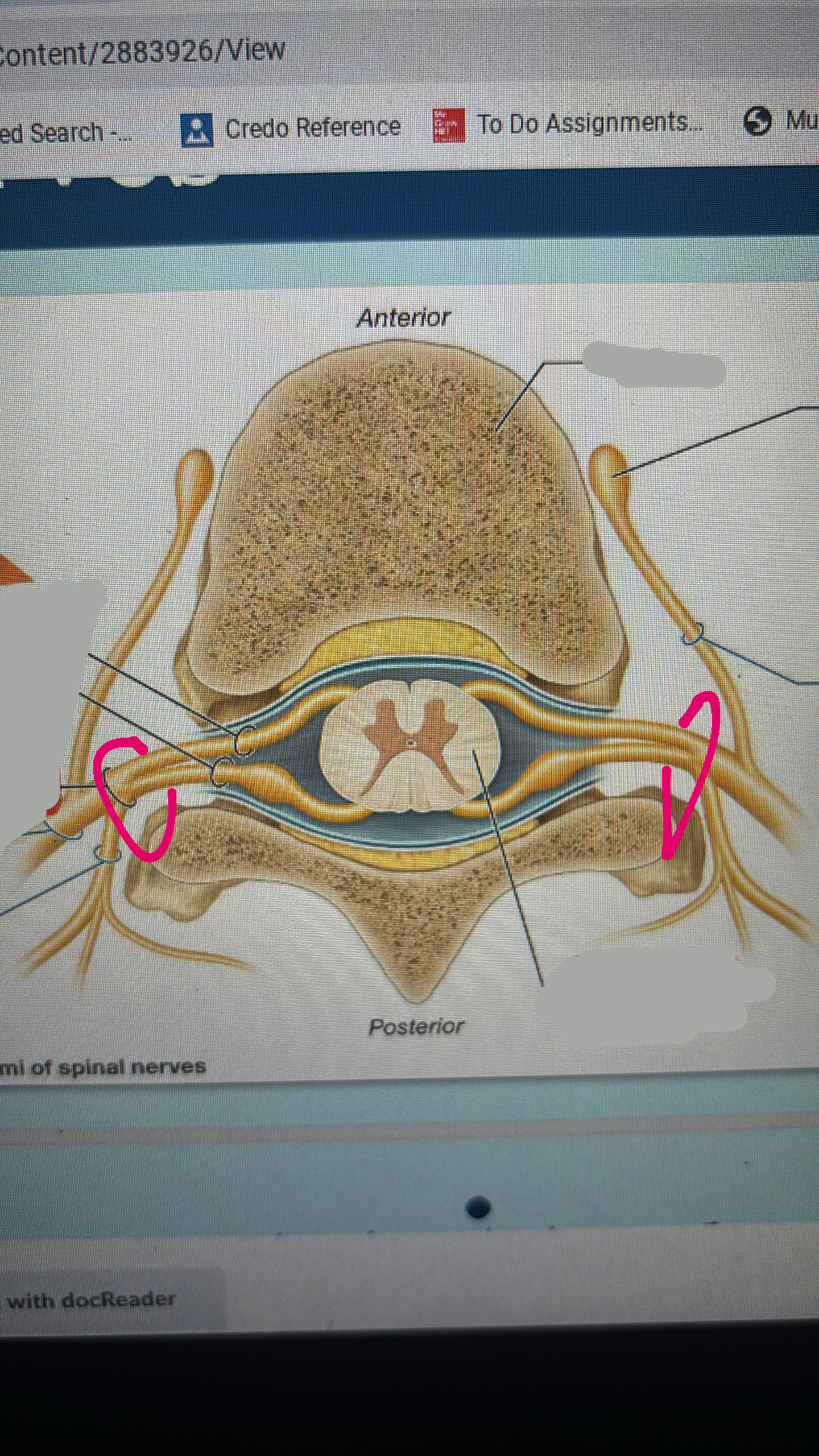
spinal cord
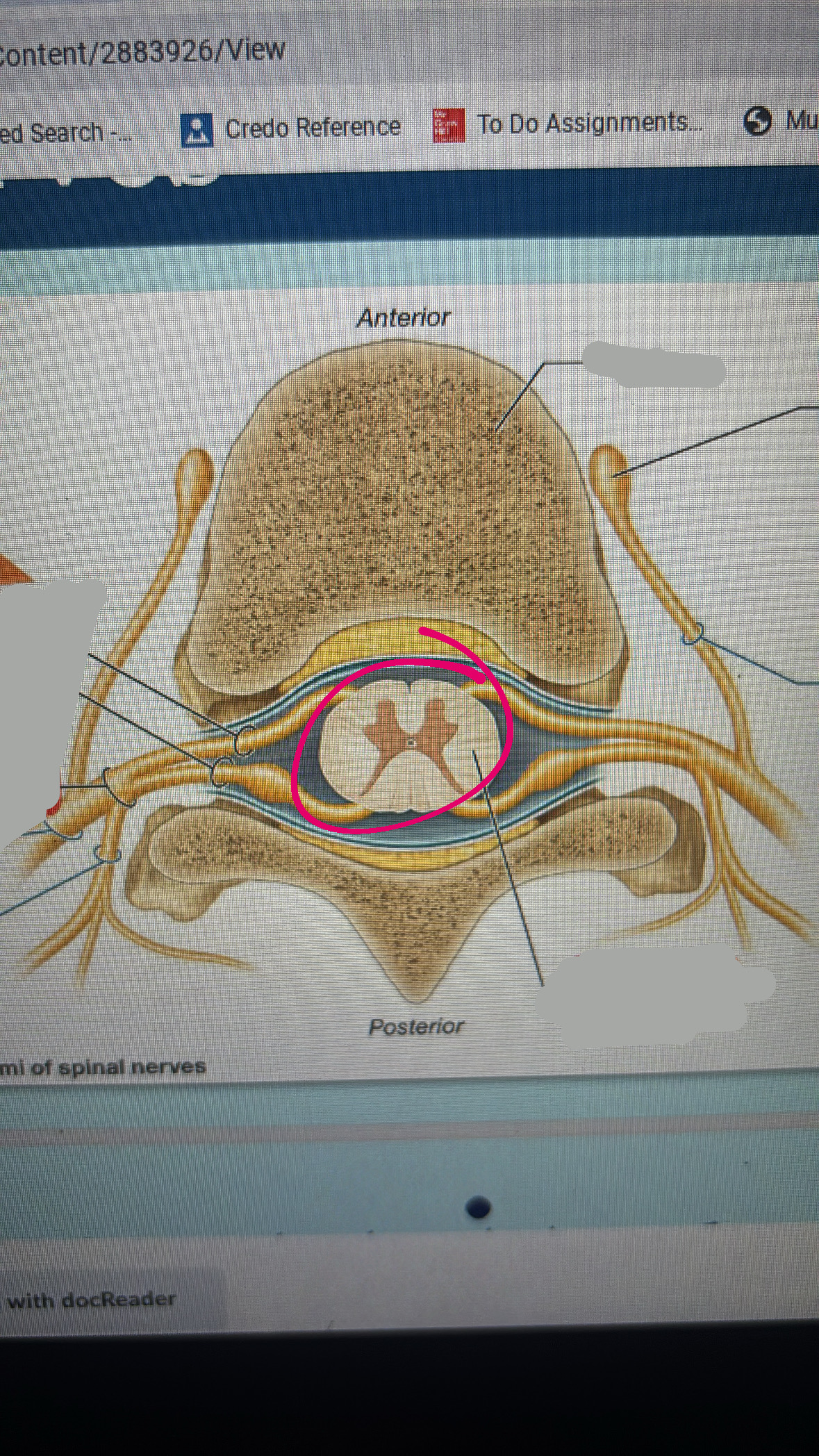
anterior ramus
fibers to and from anterior side of body and or upper and lower limbs
posterior ramus
fibers to and from posterior side of body
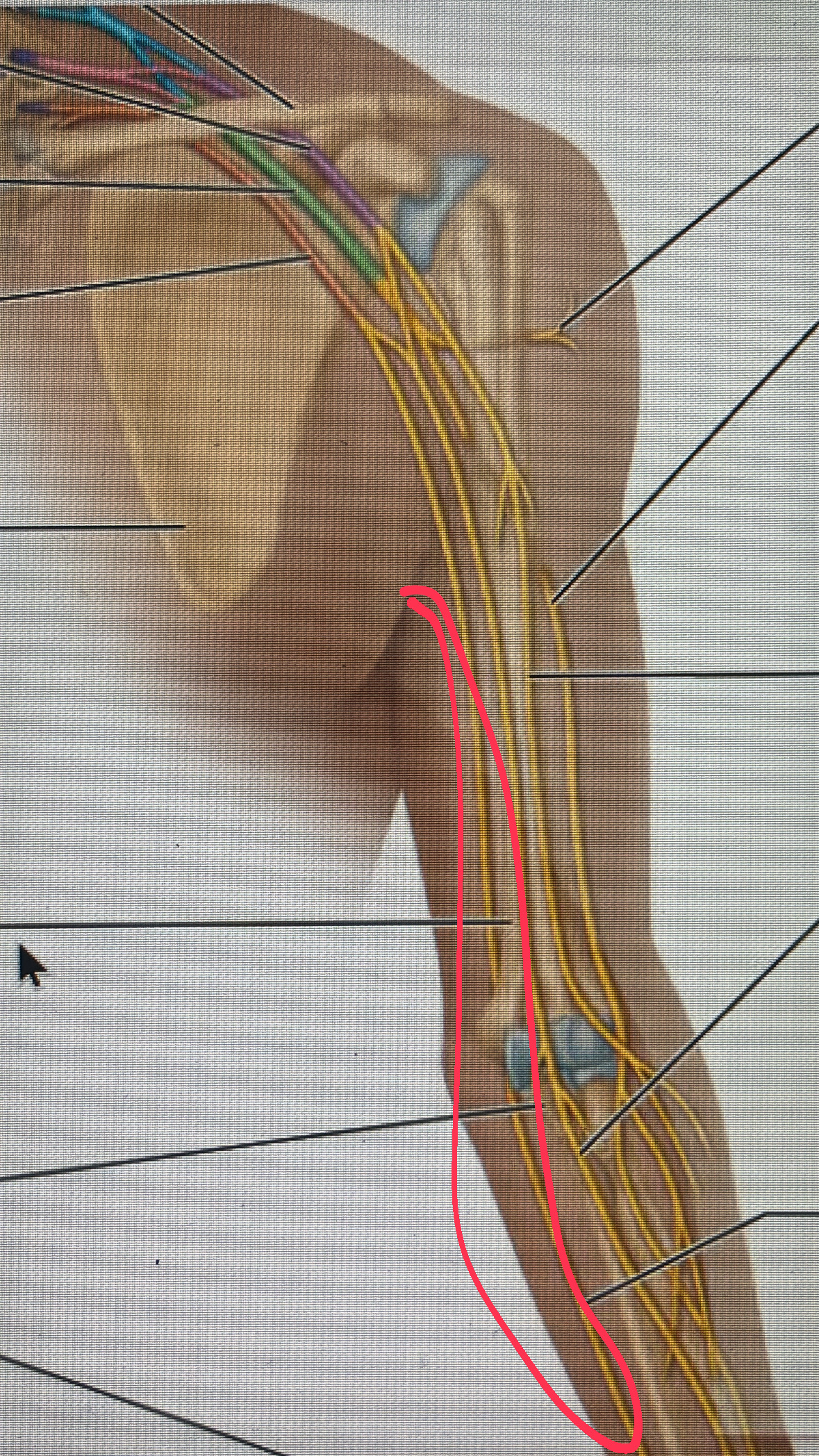
axillary nerve
motor to the deltoid and teres minor muscle and sensory to the skin of the deltoid
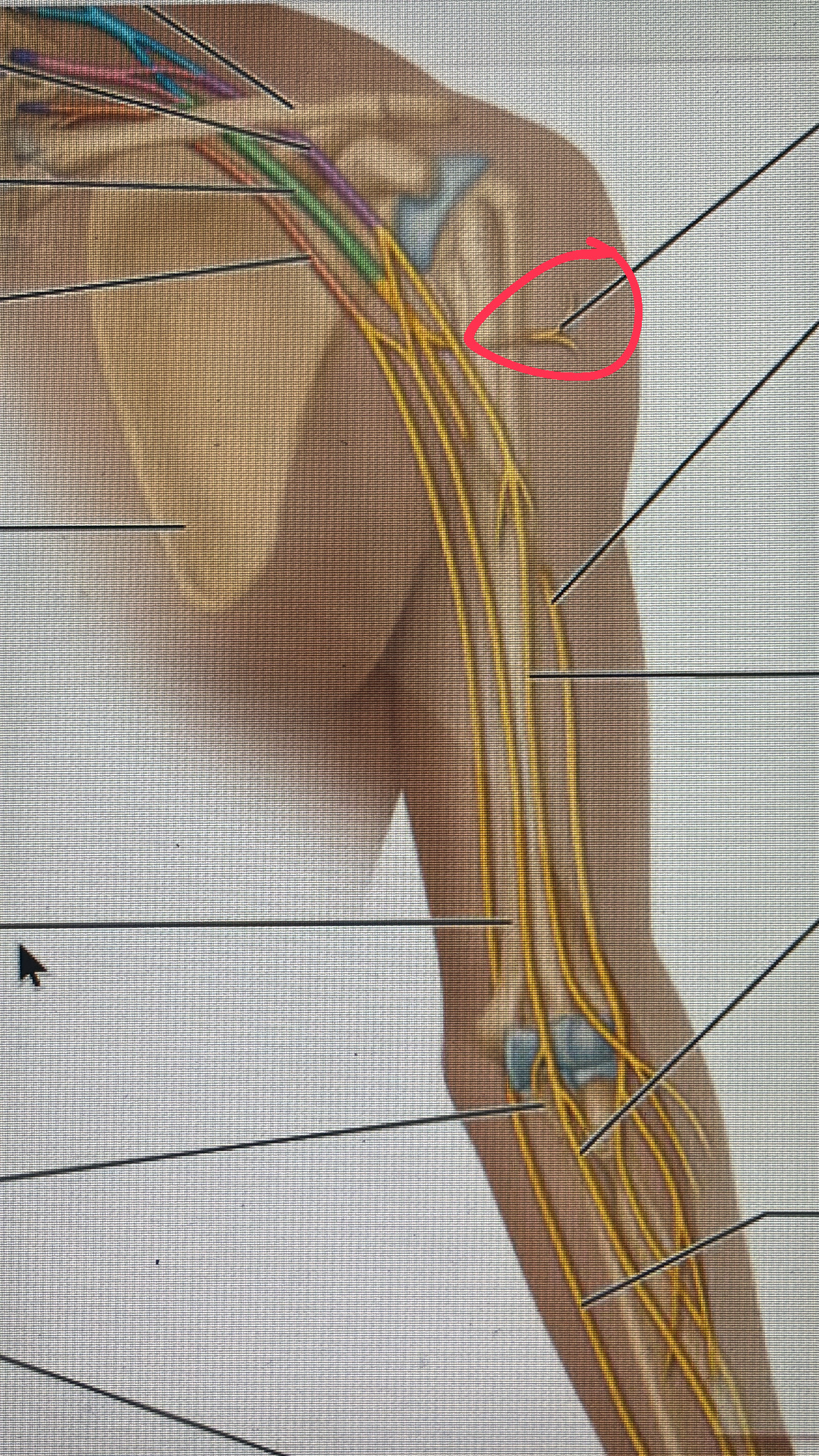
radial nerve
motor to the triceps brachii, brachioradialis, and the extensor muscle
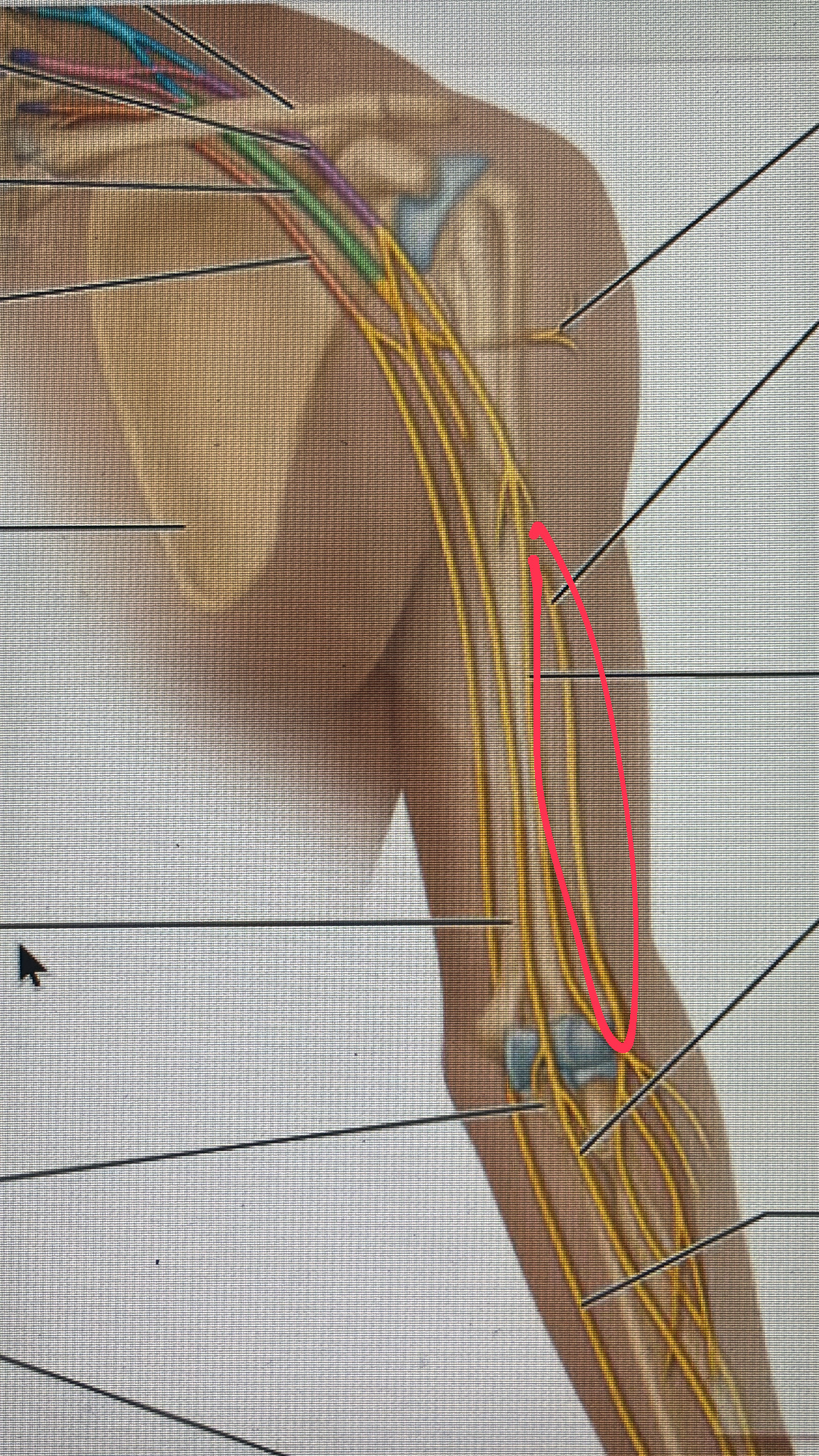
median nerve
motor to most muscles the flex the wrist and fingers
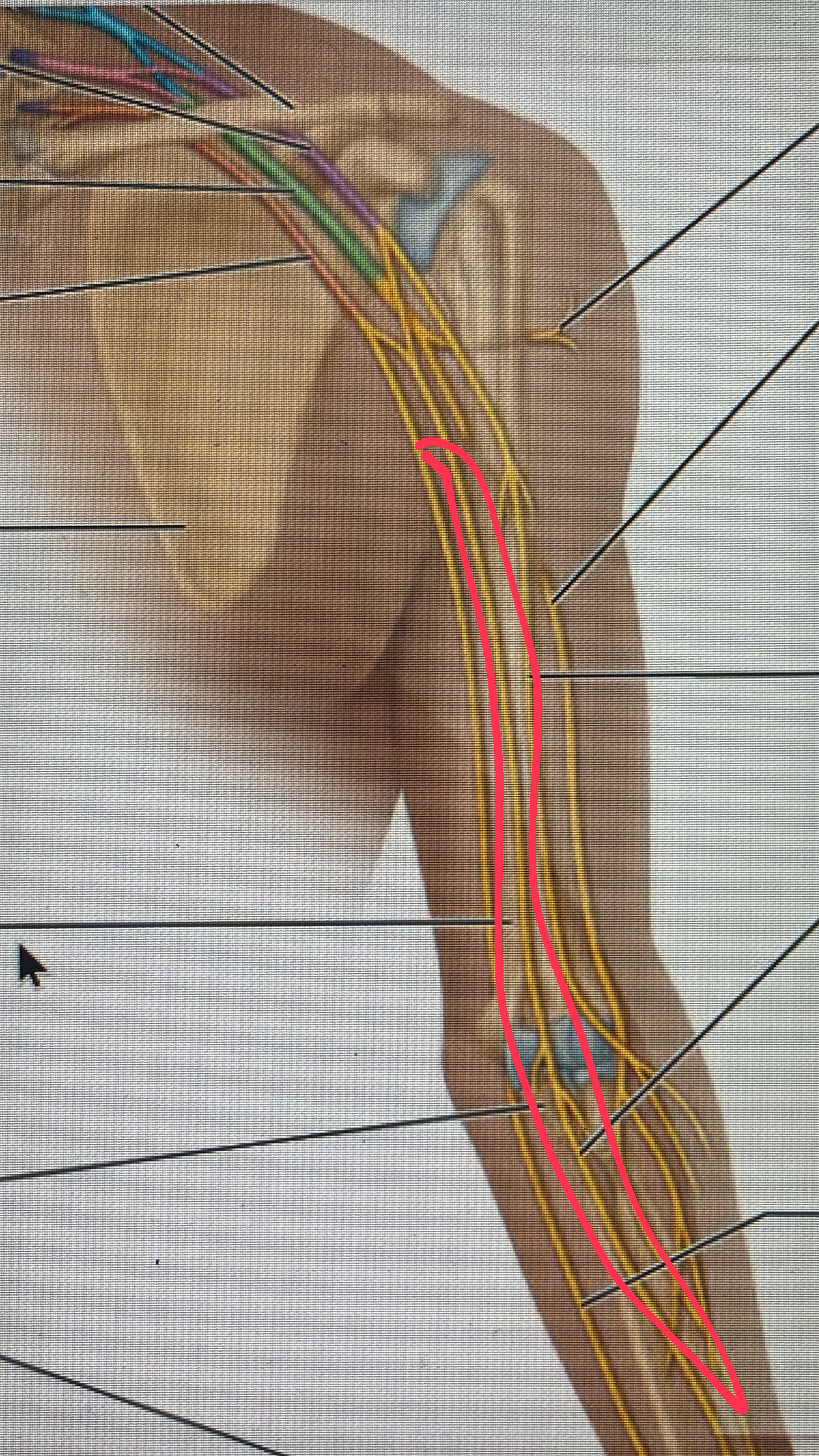
ulnar nerve
motor to certain forearm flexors and to most hand muscles
femoral nerve
anterior motor nerve to que quadriceps femoris, iliopsoas and sartorius
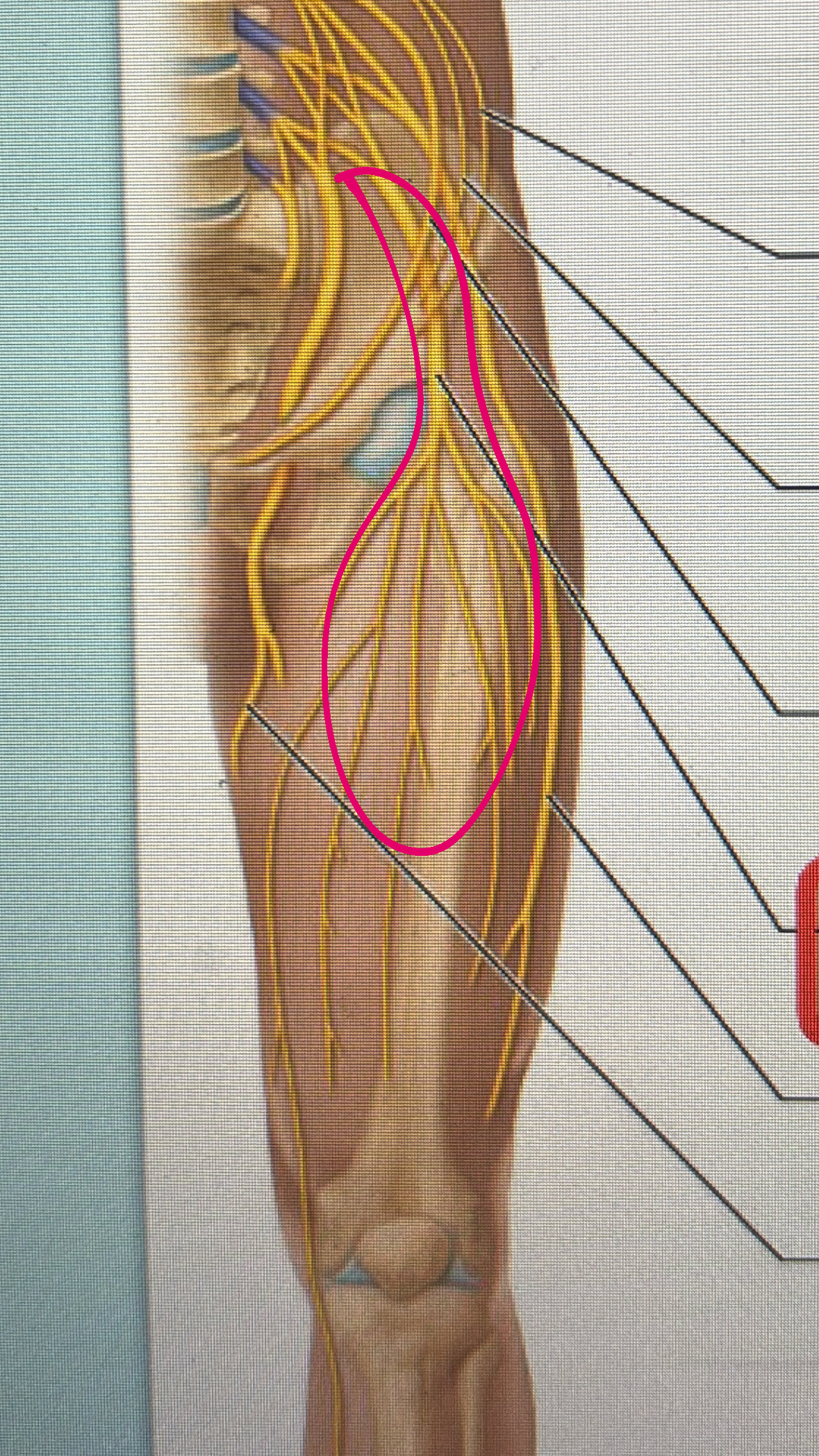
sciatic nerve
sensory to the hip joint
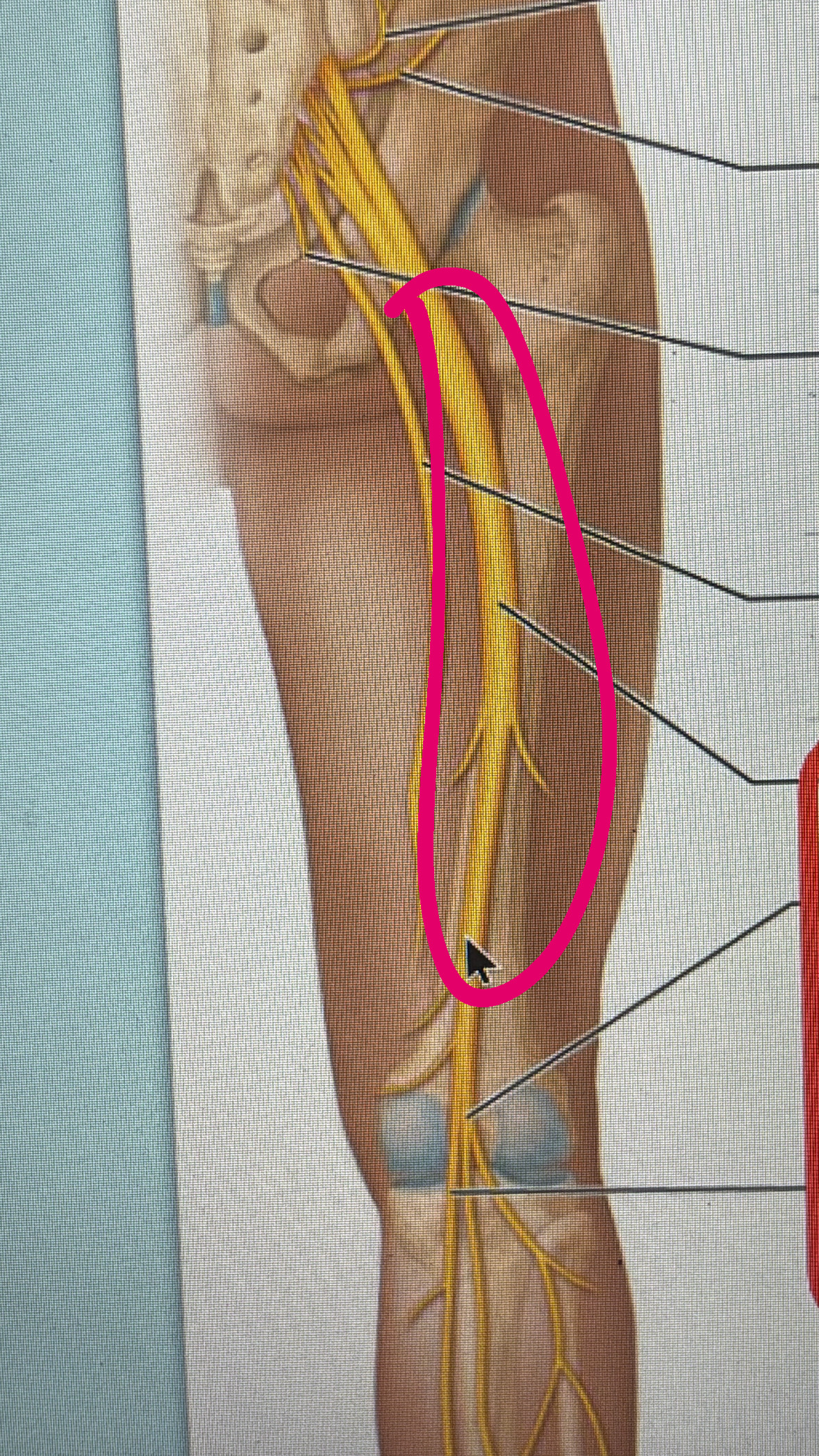
common fibular nerve
motor to the lateral leg muscles
sensory to the knee joint, the skin of distal leg
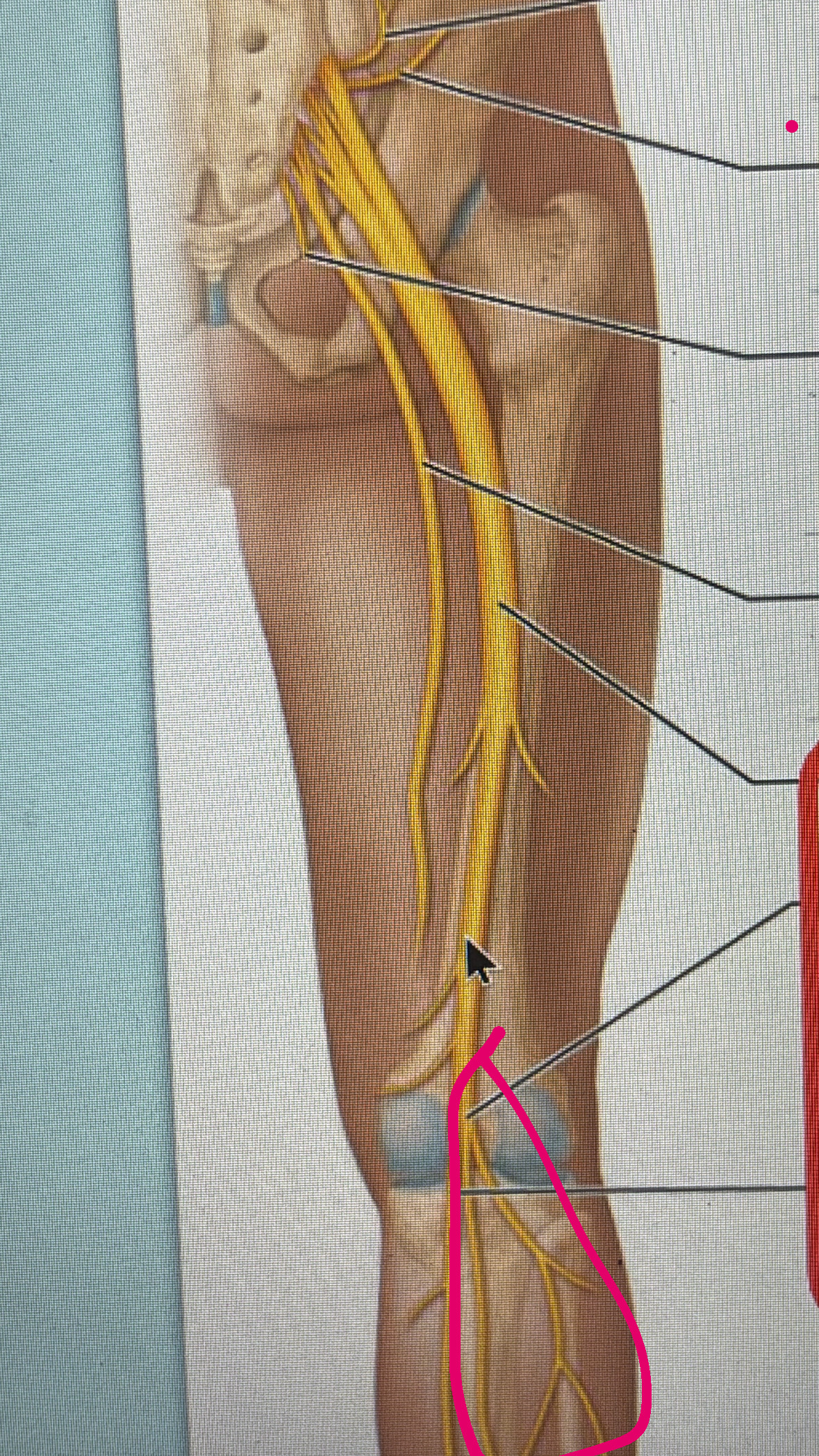
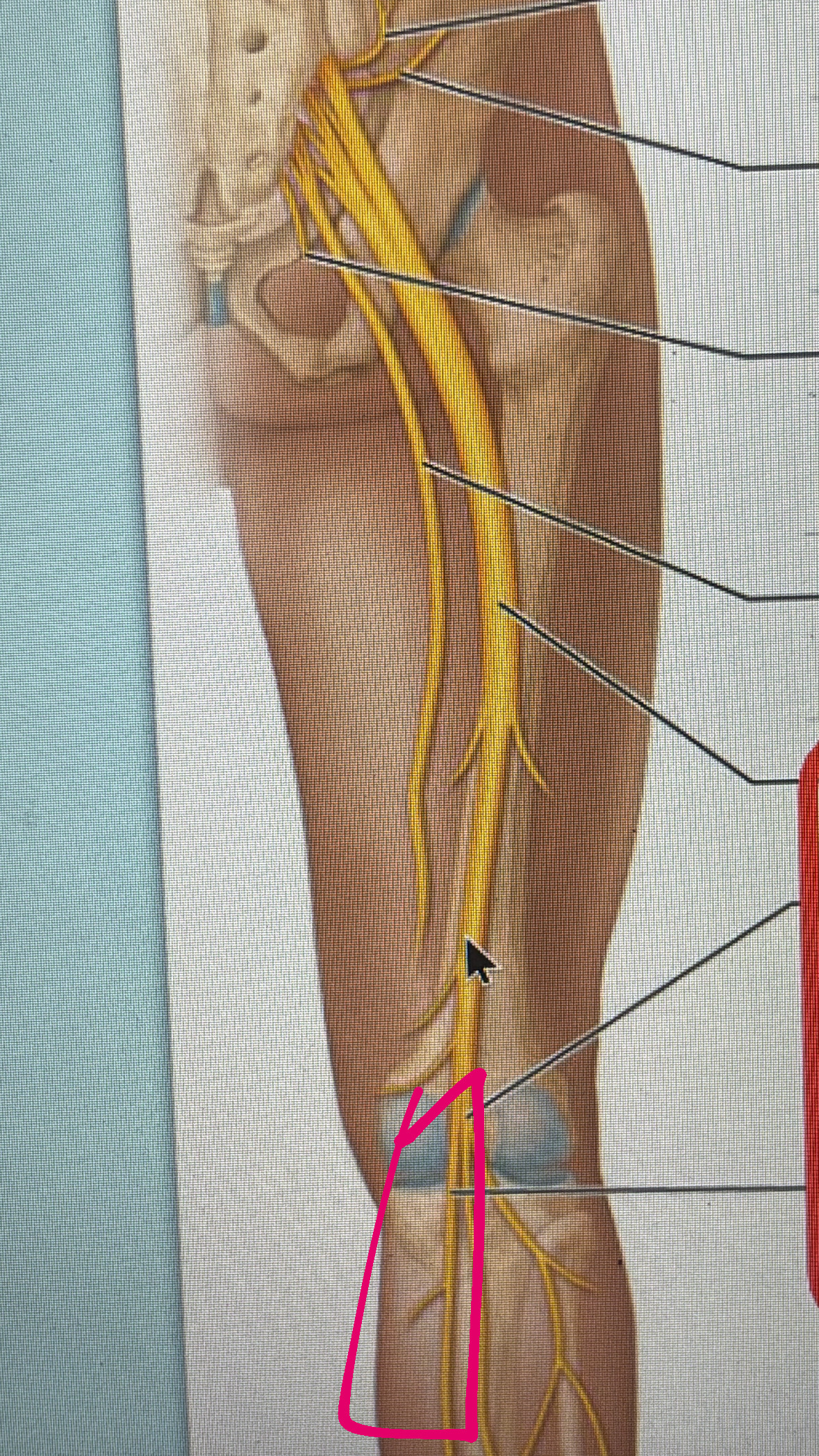
tibial nerve
motor to hamstring and plantar foot
sensory to knee joint ankle joint and skin of posterior lateral leg, and skin on plantar
exteroceptors
detects external stimuli
interoceptors
detect internal stimuli
mechanoreceptor
responds to mechanical force
thermoreceptors
responde to temp changes
photoreceptors
responde to light
chemoreceptors
responde to chemicals (in the air or fluids in body)
nociceptors
responds to damaging stimuli, causing pain
what leads to sensation and perception
peripheral process transmits an action potential from the sensory receptor to neurons other axon, the central process
the central process transmits an action potential from the peripheral process to the posterior horn, eventually synapsing on a neuron in the spinal cord or brainstem
main aspects of sensory perception
the stimulus (pressure) is detected by receptors, generative a receptor potential, which triggers an action potential
action potential is conducted along the peripheral process and transferred to the central process
central process transmits the action potential to 2nd order sensory neurons of the CNS
second order sensory neurons synapse on third order sensory neurons in the thalamus
third order sensory neurons synapses on other interneurons in the primary somatosensory cortex
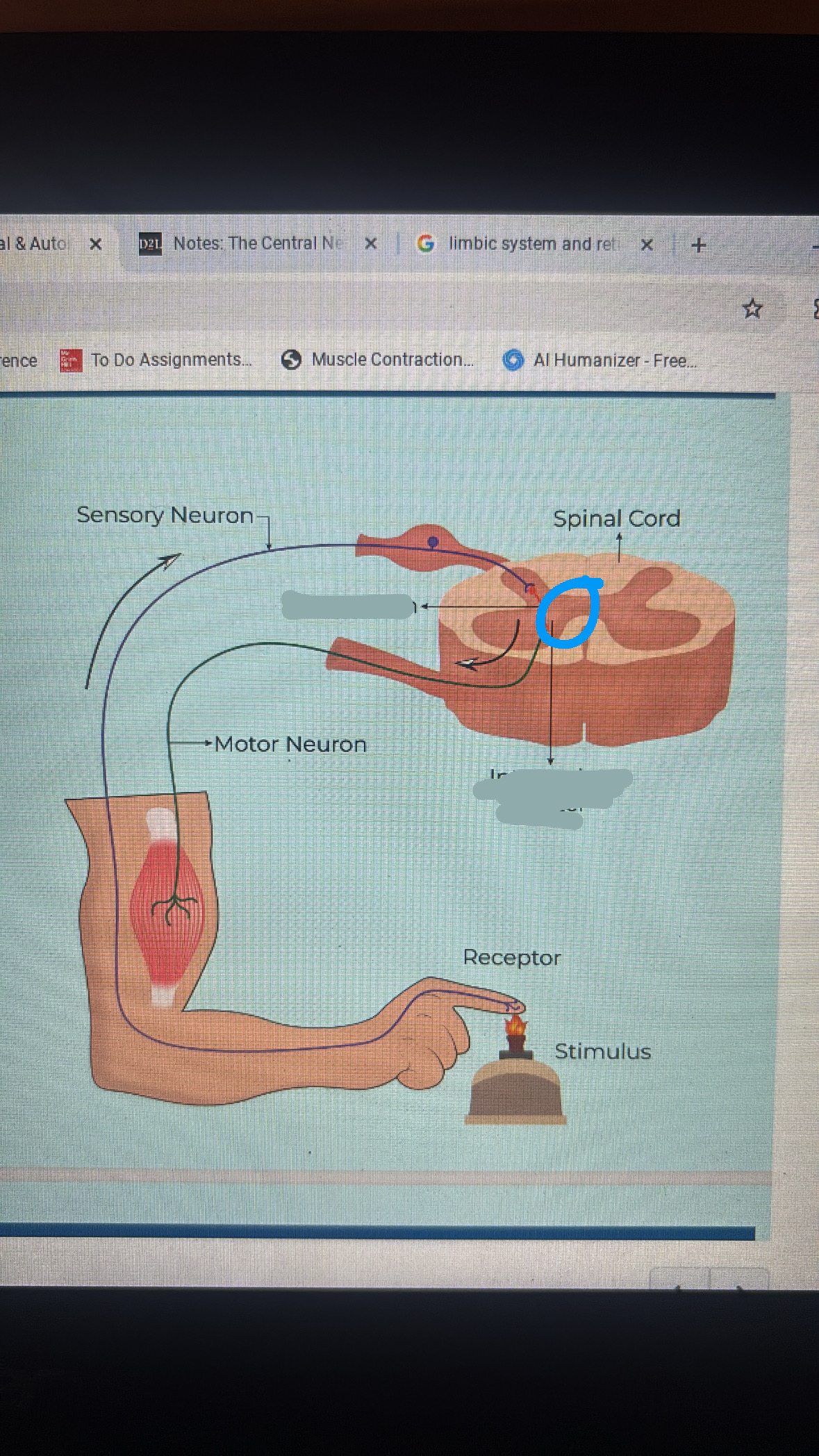
reflex arc
a neuronal pathway that controls a reflex action
sensory receptors detect stimulation
sensory neurons transmit info from receptors to CNS
integration center processes the info
motor neuron conducts a response impulse
effector responds to the motor neuron signal
interneuron
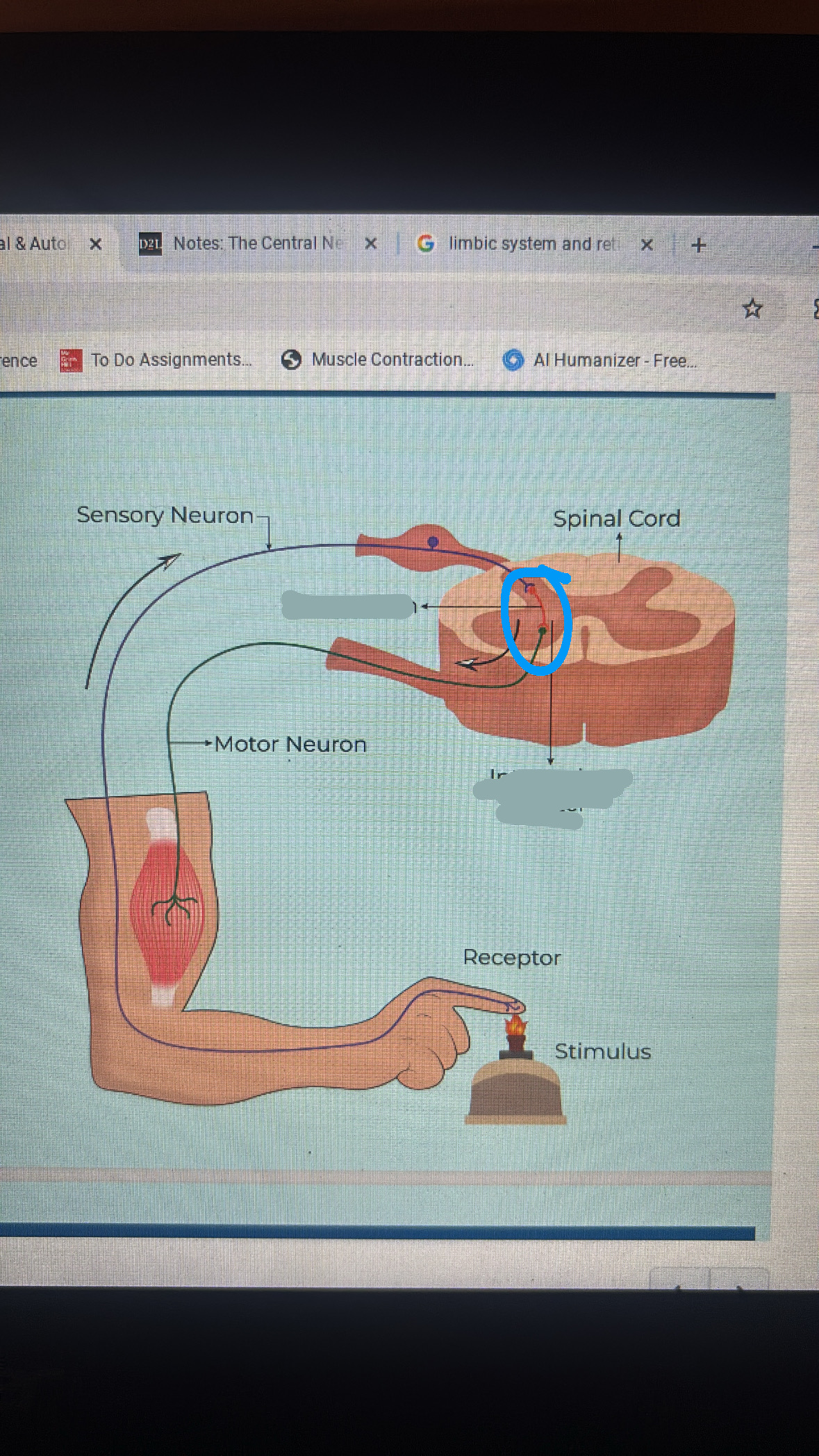
integration center
somatic nervous system
voluntary movements
touch, pain, temp, body postition
one motor neuron straight from muscle to the spinal cord
autonomic nervous system
involuntary movements
heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, digestion, swallowing, and pupil size
senses internal environment
used 2 neurons in “chains”
two divisions- sympathetic and parasympathetic
sympathetic
“fight or flight”
located in thoracic, lumbar, and spinal cord
a bunch of postganglionic cell bodies along the vertebral- SYMPATHETIC CHAIN GANGLIS
ganglion
neuron(nucleus) cell bodies outside CNS
parasympathetic
“rest and digest”
located in brainstem or sacral spinal cord
adrenergic receptors
bond epinephrine and norepinephrine
INCLUDES ALPHA AND BETA RECEPTORS
cholinergic receptors
bind acetylcholine (ACh)
INCLUDES MUSCARINIC RECEPTORS AND NICOTINIC RECEPTORS