Environmental Science for AP - Chapter 15
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Air pollution
Introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or microorganisms into the atmosphere at concentrations high enough to harm plants, animals, materials, or alter ecosystems.

SO2
Combustion of fuels that contain sulfur, including coal, oil, and gasoline. Respiratory irritant, can exacerbate asthma and other respiratory ailments. Can harm stomates and other plant tissue. Converts to sulfuric acid in atmosphere, which is harmful to aquatic life and some vegetation.
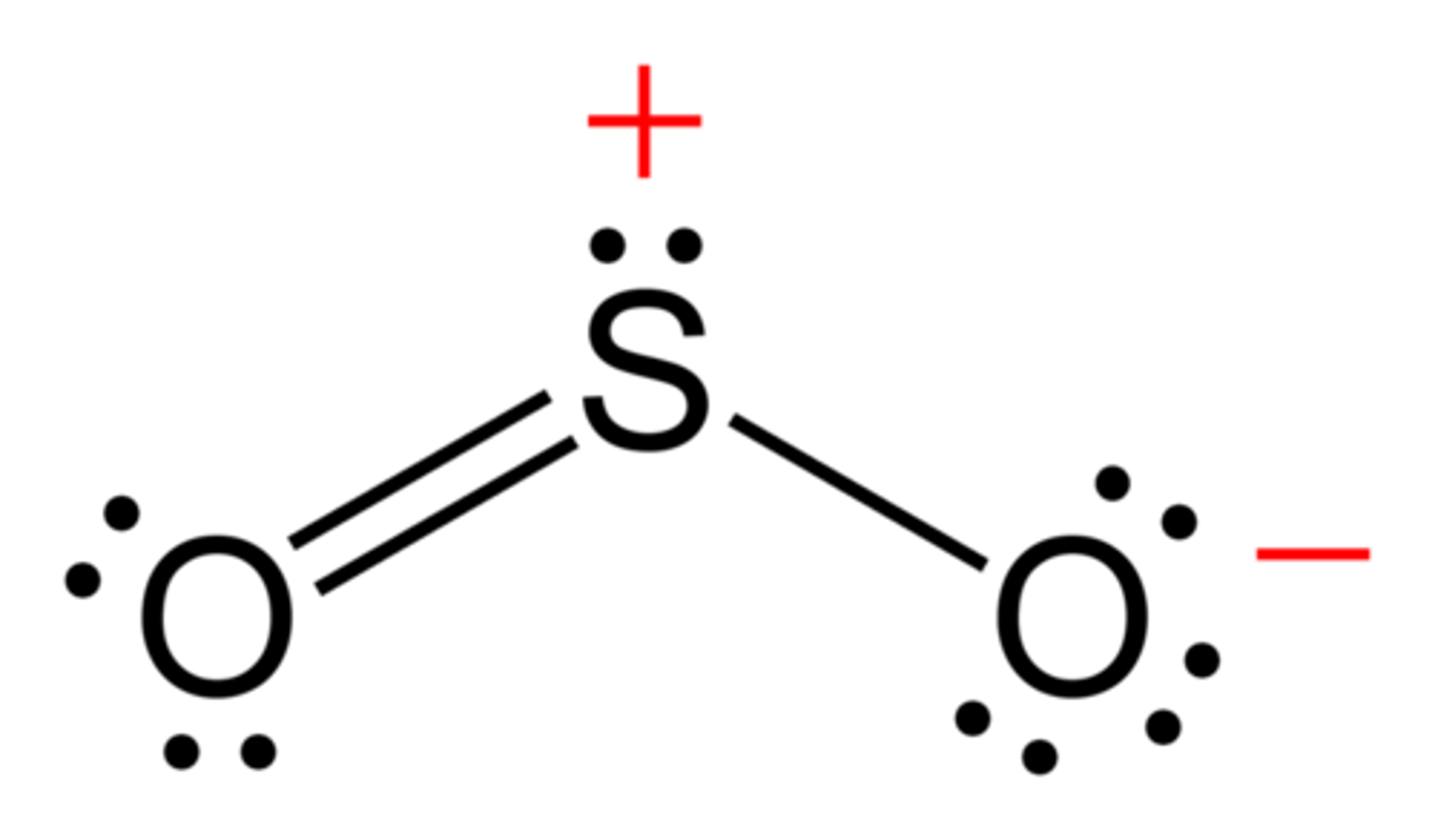
NOx
All combustion in the atmosphere including fossil fuel combustion, wood, and other biomass burning. Respiratory irritant, increases susceptibility to respiratory infection. Ozone precursor, leads to formation of photochemical smog. Converts to nitric acid in atmosphere, which is harmful to aquatic life and some vegetation. Contributes to over fertilizing terrestrial and aquatic systems.
CO
Incomplete combustion of any kind, malfunctioning exhaust systems, and poorly ventilated cooking fires. Bonds to hemoglobin thereby interfering with oxygen transport in the bloodstream. Causes headaches in humans at low concentrations, can cause death with prolonged exposure at high concentrations.
PM10 or PM2.5
Solid or liquid particles suspended in air. Combustion of coal, oil, biofuels, and diesel. Agriculture, road construction, and other activities that mobilize soil, soot, and dust. Can exacerbate respiratory and cardiovascular disease and reduce lung function. May lead to premature death. Reduces visibility and contributes to haze and smog.
Lead
Pb. Gas additive, oil and gas, coal, old paint. Impairs central nervous system. At low concentrations, can have measurable effects on learning and ability to concentrate.
Ozone
O3. Secondary pollutant formed by combination of sunlight, water, oxygen, VOCs, and NOx. Reduces lung function and exacerbates respiratory symptoms. Degrading agent to plant surfaces. Damages materials like rubber and plastic.

VOC
Hydrocarbons that become vapors at typical atmospheric temperatures. Volatile Organic Compounds. Evaporation of fuels, solvents, paints, improper combustion of fuels like gas. Precursor to ozone formation.
Mercury
Coal, oil, gold mining. Impairs central nervous system. Bioaccumulates in the food chain.

CO2
Combustion of fossil fuels and clearing of land. Affects climate and alters ecosystems by increasing green house gas concentrations.
Haze
Reduced visibility from particulate matter.

Photochemical Oxidants
Air pollutants formed as a result of sunlight acting on compounds such as nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide.

Smog
Mixture of oxidants and particulate matter.

Photochemical Smog
Dominated by oxidants. LA-type smog or brown smog.

Sulfurous smog
Dominated by sulfur dioxide and sulfate compounds. London type or gray smog.
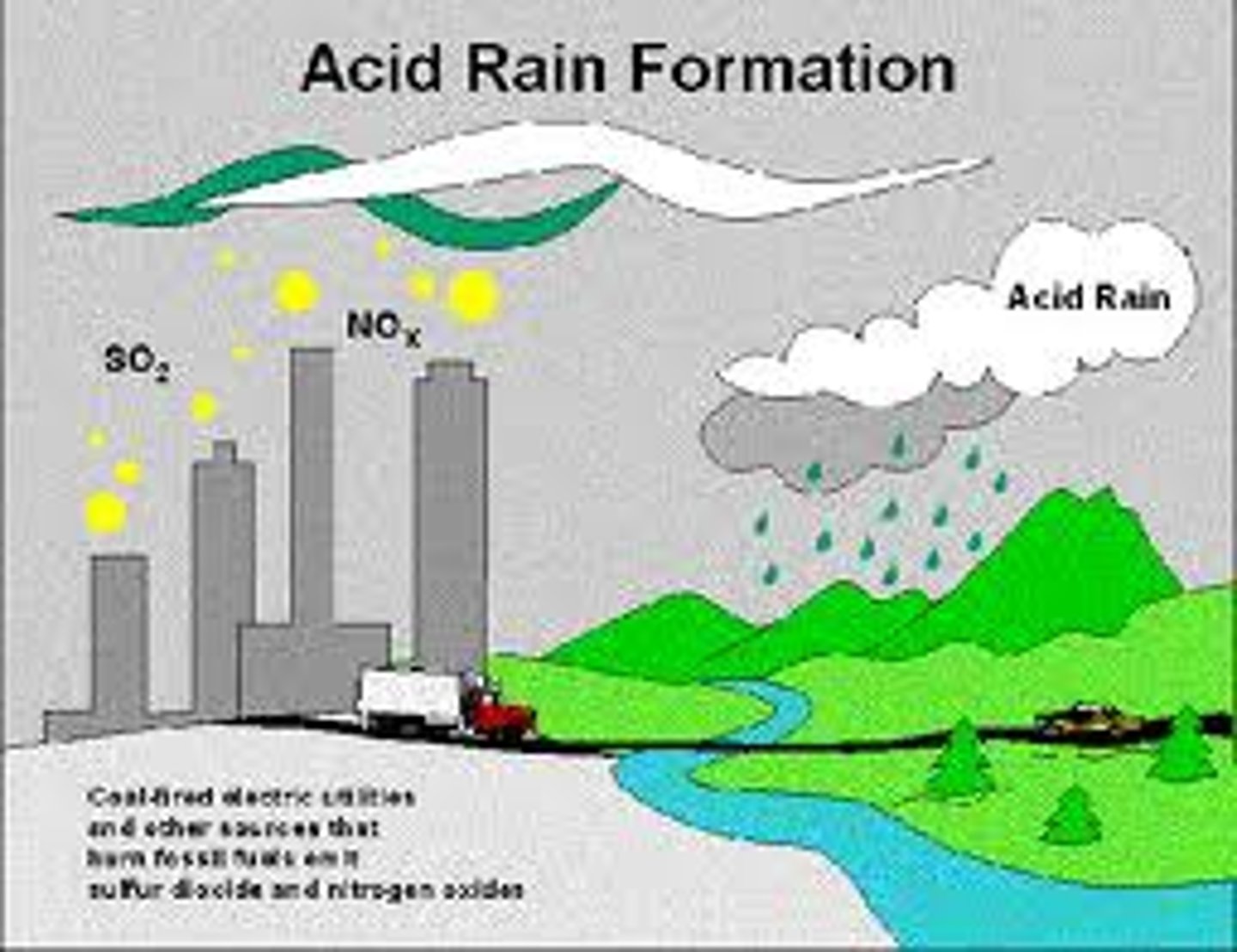
Primary pollutants
Pollutants directly from sources. CO, CO2, SO2, NOx, VOCs.

Secondary Pollutants
Primary pollutants that have undergone transformation in the presence of sunlight, water, oxygen, or other compounds. Ozone, sulfate, nitrate.

Clean Air Act
EPA established standards to control pollutants that are harmful.
Ozone Formation
NO2 turns to NO + O transfers to O + O2 to form O3.
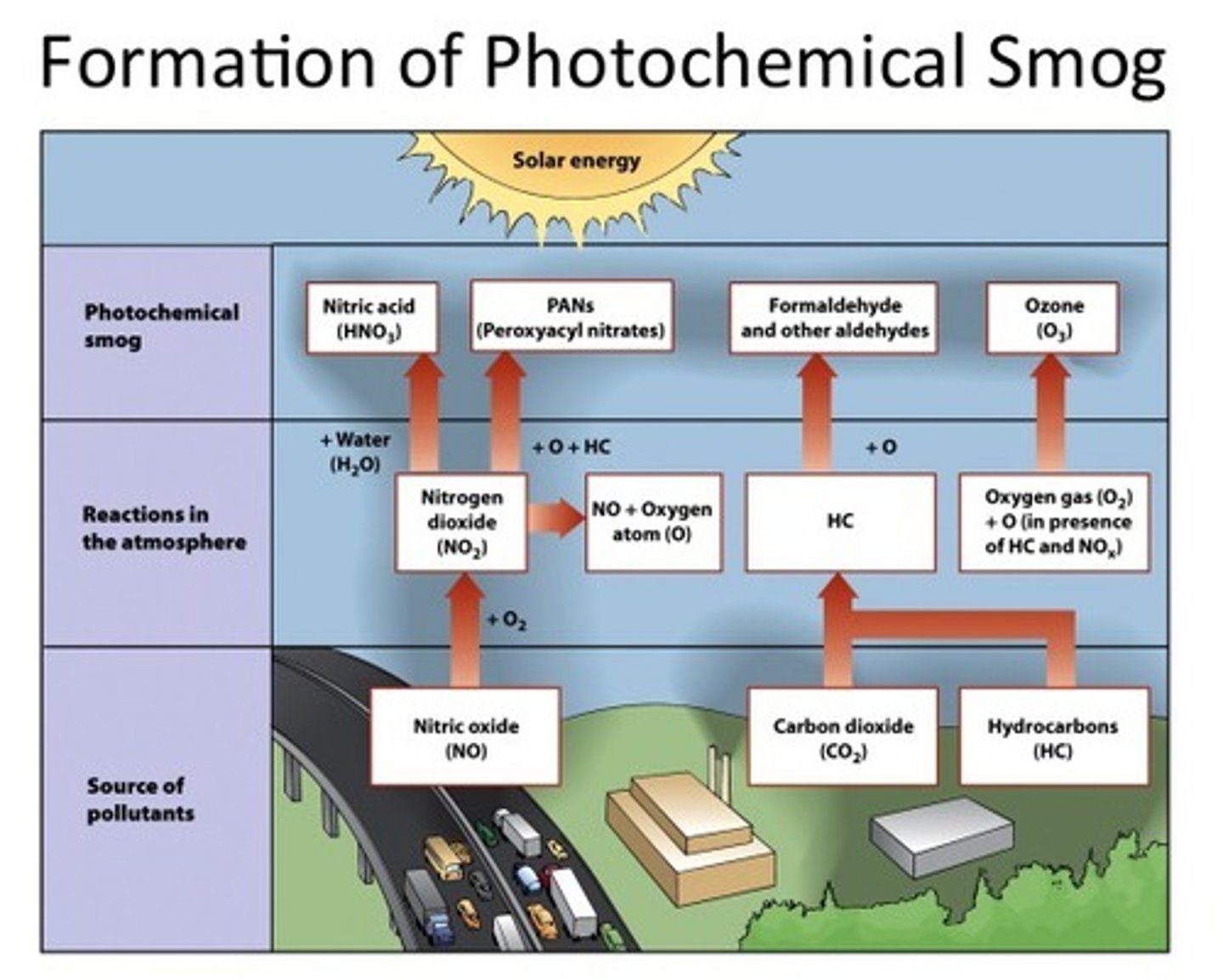
Photochemical Smog Formation
NO2 turns to NO + O transfers to O + O2 to form ozone. NO transfers to NO + VOCs to form Photochemical oxidants. Photochemical oxidants + Ozone = Photochemical smog.
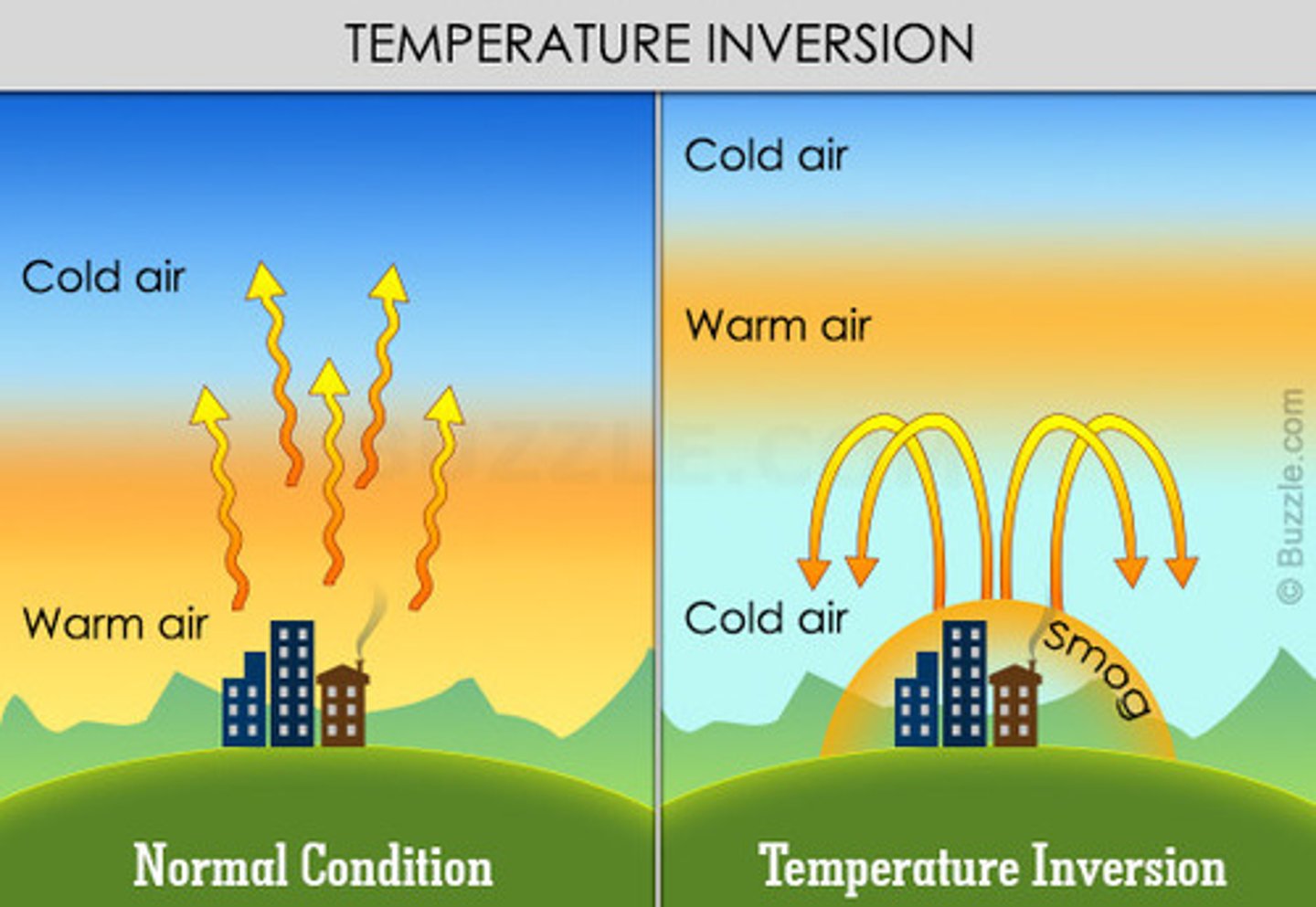
Thermal inversion
Warm inversion layer from cities traps emissions below it at night.
Baghouse Filter
Dirty air enters, combustion exhaust stream moes through and dust particles are trapped in a series of filter bags, cleaner and filtered air moves out of unit, shaker mechanism activated periodically to dislodge trapped particles which can then be collected from below unit.
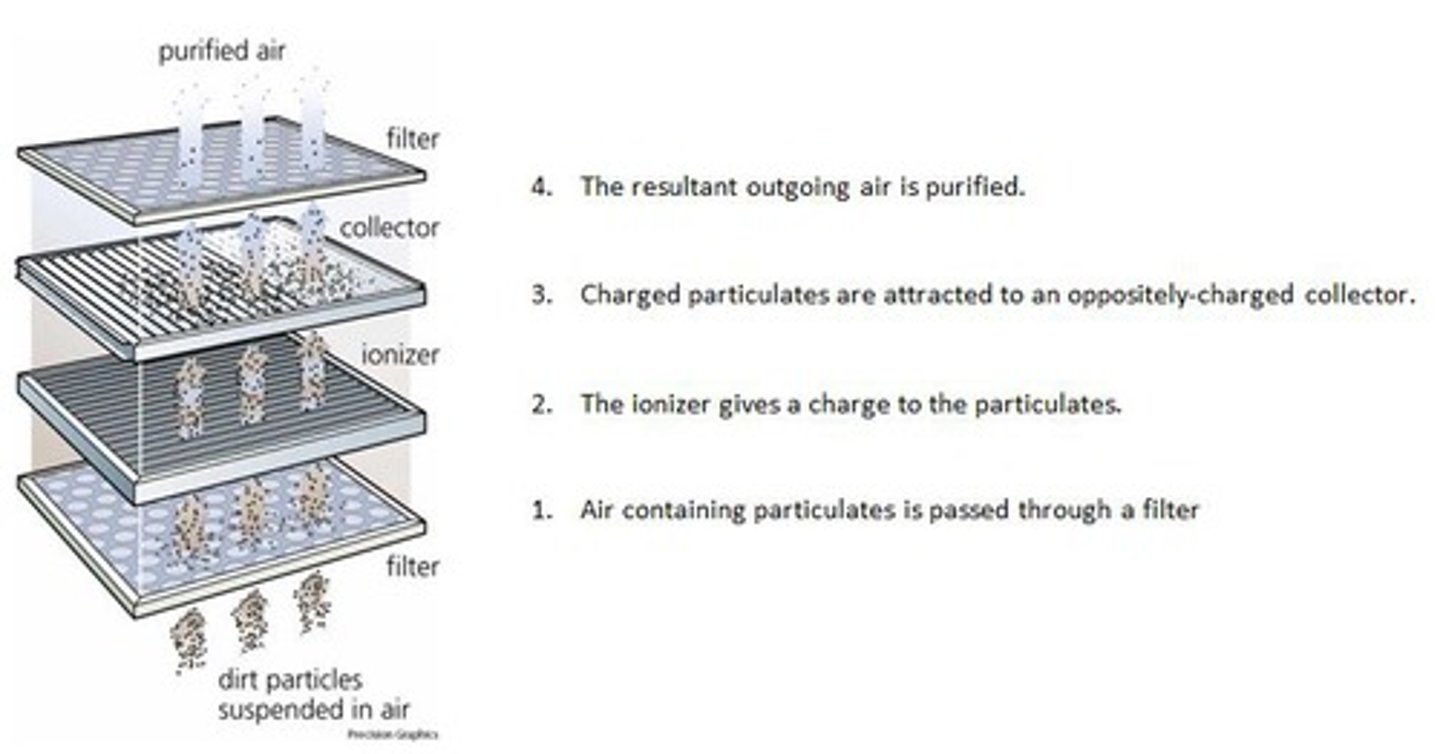
Electrostatic Precipitator
Dirty air enters, particles in combustion exhaust stream pass by negatively charged plates which give them that charge, then these particles are attracted to positively charged collection plates, cleaner air moves out, plates are occasionally discharged so particles fall out and be removed.

Sick Building Syndrome
Buildup of toxic compounds and pollutants indoors because of better insulation to save energy. Proved when symptoms subside when leave building.

Indoor Pollutants
Furniture, Carpets, foam insulation, pressed wood: VOCs
Tobacco Smoke: Toxic and carcinogenic compunds
Old Paint: Lead
Floor and ceiling Tiles, pipe insulation: Asbestos
Rocks and soil beneath house: Radon
Household Products, pesticides, paints, cleaning fluids: VOCs and other compounds.
Fireplaces, wood stoves: Particulate Matter
Leaky or unvented gas or wood stoves and furnaces, running cars left running: CO.

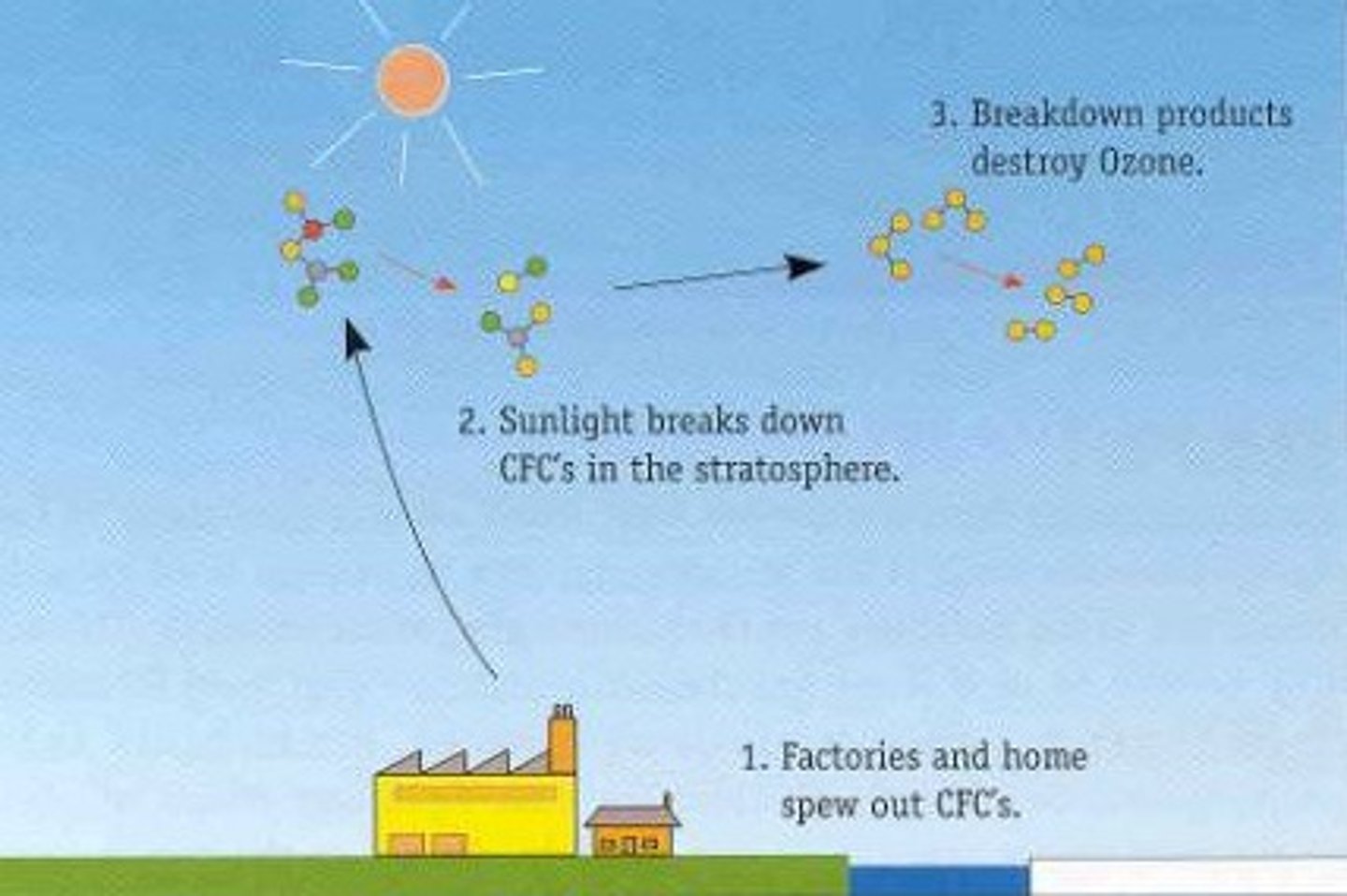
CFC and Stratospheric Ozone Equations
O3 + Cl turns into ClO + O2. Then ClO +O turns into Cl +O2.
CFCs
Used to be used in refrigeration and propellants but destroys stratospheric ozone. Phased out
Scrubber
Dirty air enters, combustion exhaust stream moves upward in shower of water mist, mist collects particles and brings to bottom of unit, dirty water moves to a sludge removal system, sludge is separated from water and disposed of, water moves back into scrubber for reuse, excess mist collects on screen and clean air leaves.
