AP Psychology Unit 0: Research and Data Methods
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab from AP Psychology Unit "0", Research and Data Methods.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Limits of Intuition
People may rely too much on their intuition, or “gut feelings,” when making decisions.
Hindsight Bias
This is the “I knew it all along” phenomenon. After learning the outcome of an event, many people believe they could have predicted that very outcome. Ex: 911 terrorist attack
Psychological Science
This helps make examined conclusions, which leads to our understanding of how people feel, think, and act as they do!
Scientific Attitude
The BLANK is composed of curiosity, skepticism, and humility (ability to accept responsibility when wrong).
Critical Thinking
BLANK does not accept arguments and conclusions blindly. It examines evidence and assesses conclusions.
Scientific Method
Psychologists, like all scientists, use this to construct theories that organize, summarize and simplify observations.
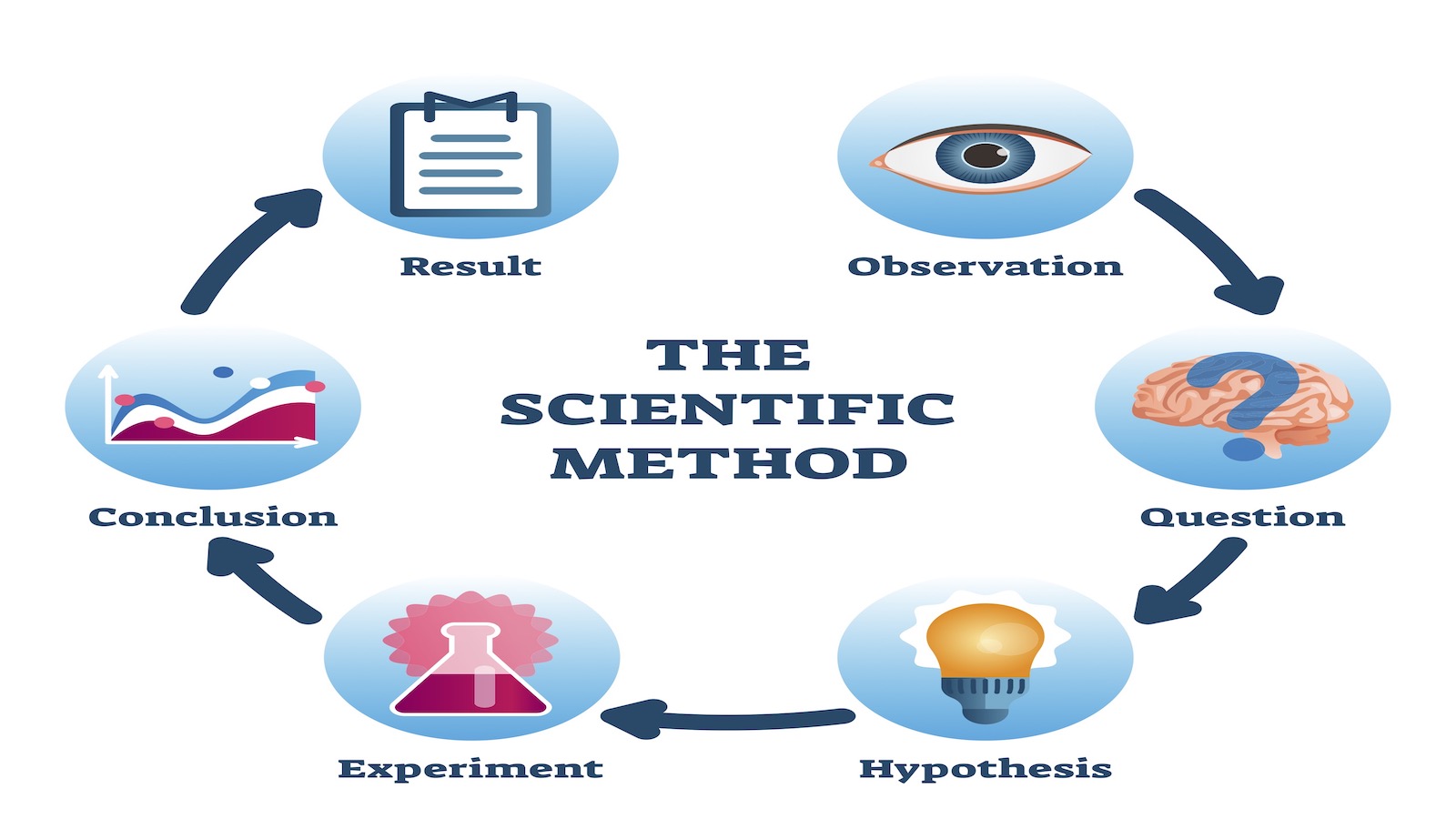
Theory
An explanation that predicts behavior or events.
Hypothesis
is a testable prediction, often prompted by a theory, to enable us to accept, reject, or revise the theory.
Operational Definition
Written instructions describing how to conduct the experiments. Leads to exact “replication”.
Overconfidence
Sometimes we think we know more than we actually do.
Case study, survey, observation
3 types of experimentation
Case study
one person is studied in depth to reveal underlying behavioral principles
Therapist actively interacts with a client
takes place over many years
Survey
1 of the 3 types of experiments
Pros: quick, can collect lots of data in a short time
Cons: people lie with them, are not very specific, and weird working can confuse people.
One type of BLANK is a random sample:
If each member of a population has an equal chance of inclusion into a sample, it is called a random sample (unbiased).
False Consensus Affect
A tendency to overestimate the extent to which others share our beliefs and behaviors.
Observation (naturalistic)
Observing and recording the behavior of animals and people in their natural environment WITHOUT interacting in any way with them.
Scatterplot
This is a graph comprised of points that are
generated by values of two variables.
Correlation
This tells you that two variables are related, but not WHY they are related. It does not mean causation.
Regression Toward the Mean
Following an extreme random event, the next random event is likely to be less extreme.
Illusory Correlation
The perception of a relationship where no relationship actually exists.
Experimentation
This is a research technique. It is designed to isolate causes and their effects.
Experimental Group
This is the group that gets the variable
Control Group
This is the group that doesn’t the variable. They get the “placebo”.
Effect Size
How meaningful the relationship between variables or the group is.
Independent Variable
This is the factor that is manipulated or changed by the experimenter.
Dependent Variable
This is what you are measuring. In psychology, it is usually a behavior or mental process.
Single Blind
The experimenter knows which test subjects are getting the variable (like medicine), but the test subjects don’t know what they are getting.
Double Blind
Neither the experimenter nor the test subjects know who is getting what. This removes “experimenter bias”.
Placebo Effect
When people believe they are getting the treatment, they actually start to get better for a short time.
Validity
does the experiment measure what it was designed to measure?
Quantitative Research
the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data.
Qualitative Research
Inquiry that seeks an in-depth understanding of social phenomena within their natural setting. Asks “Why” not “what”.
Histogram
A chart that plots the distribution of a numeric variable’s values as a series of bars.
Mode
The most frequently occurring score in a distribution.
Mean
The arithmetic average of scores.
Median
The middle score in a rank-ordered distribution.
Standard Deviation
A measure of how much scores vary around the mean score. It measures consistency.
Range
The difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution.
Statistical Difference
For psychologists the difference is measured though an alpha level set at 5 percent.
Meta-Analysis
The statistical combination of results from two or more separate studies.