Quiz 1: PSY 3150
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Distal stimulus
The 3D image that exists in the environment. Constant properties.
Sensation
Receptors are activated via the senses. The basics of the sensory system. No interpretation takes place. Ex: icecream is cold.
How does visual angle change when looking at objects close up?
Objects appear larger when closer so the visual angle becomes smaller.
Is perception active or passive?
Perception is an active process. We move our bodies and eyes to obtain more information.
Principle of Representation
Our perception is influenced by how receptors are activated and make sense of the environment
Photoreceptors
Rods and Cones. A chemical called visual pigment turns light into chemical/electric energy.
Transduction
Turning one form of energy to another. Ex: turning light energy into chemical or electrical energy.
Receptor processes
Sensory receptors respond to the environment
Neural Processing
electrical/chemical energy is transmitted by the receptors to different parts of the brain. The brain communicates these signals, and signals are changed and processed.
Behavioral Response
Occurs when chemical/electric energy is transformed into a conscious experience (perception). Taking action based on the perception.
Perception is influenced by…
Previous knowledge and experiences
Bottom (Data) Up Processing
Stimulus/sensation based. Perception created by light hitting the receptors. Detect the stimulus, something happens and then higher cognitive thinking occurs.
Top-Down Processing
Perception Based. Perception is created on previous knowledge experiences, and expectations. Cognitive thinking occurs, black box, and then stimulus is detected.
Ways in which light perception differs across species
Each species has its own sensory system that comes with its own limitations on how much they can see.
Light is measured in…
In wavelengths and photons
Wavelengths
Measure the color of light.
Short wavelengths correspond to which color(s)
blue and purple
Long wavelengths correspond to which color(s)
red
Photons
Measures the amount of light. Smallest unit of light. Brightness.
The minimum and maximum amount of photons we can see
5 photons - 5 × 10 to the 12 photons
Law of specific Nerve Energies
Sensation depends on the specific nerve fibers (receptors) we have. Perception depends on the specific nervous system of species and individual differences.
The type of thinking that is unique to humans
Higher order thinking
Give an example of individual perceptual differences
color-blindness
Frogs will not eat when surrounded by dead flies. This illustrates…
The law of Specific Nerve Endings: Nerve fibers on this animal differ from ours and influence perceptual processes.
The number of rods we have in our eye
120 million
The number of cones we have in our eye
6 million
The number of receptors we have in our eye
126 million
The function of the eye
detecting light
The Cornea
Bends light to a certain point on the retina (by the same amount) Has a fixed curvature. 80% of the eye’s focusing power.
The (crystallin) Lense
20% focusing power. Changes in thickness and curvature based on distance.
Accommodation
Change of the crystalline lense to help you see based on distance
Far accommodation
Eye muscles relax and lense becomes less curved
Close Accommodation
Eye muscles become more engaged and lense becomes more curved.
The visual impairments that are caused by problems with cornea curvature
Myopia, Hyperopia, and Astigmatism
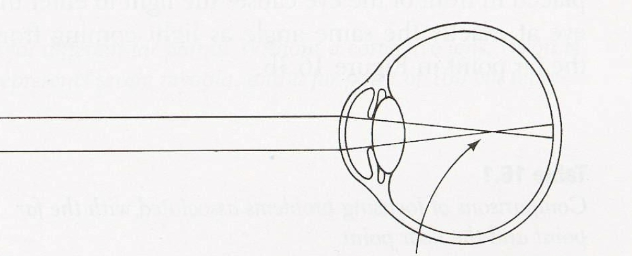
Myopia
Nearsightedness-difficulty seeing far based on the length and curvature of cornea. Requires a negative correction.
Eye Has small far point. Curvature of cornea makes light focus in front of the retina/fovea, making it blurry. Concave lenses push the light out further, to extend the far point. This allows the eye to focus light on the correct spot of the eye.
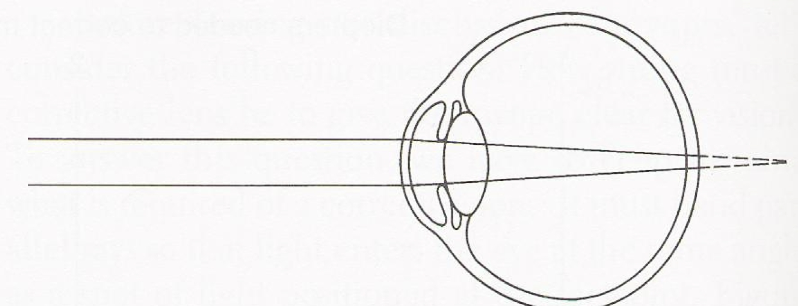
Hyopia
Farsightedness-difficulty seeing close up. Usually caused by a shorter eyeball/cornea. Requires a positive correction.
Eye has small near point. Curvature of cornea makes light focus behind cornea/retina, causing blurriness. Convex lenses bends the light forward so the image is reflected on the retina
This picture is an example of which visual impairment…
hyopia
This picture is an example of which visual impairment…
myopia
The far point
The threshold for the greatest amount of distance that light can focus correctly
The near point
The threshold for the closest that light can focus correctly
Presbyopia
Also called old eye. Failure of the lense to accommodate. Muscles in the lense become weak and must work harder. The near point becomes smaller with age.
The reason why people over 50 need glasses
Presbyopia. The muscles in the lense are not strong enough and cannot accommodate. The near point is small.
Astigmatism
Cornea is not perfectly round. Corrective lenses help bend light so it hits the Fovea
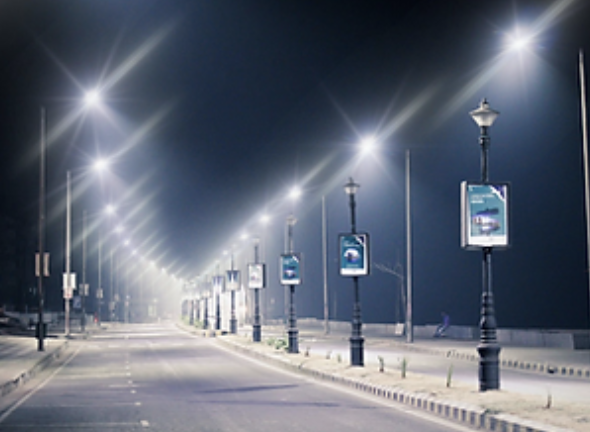

This is a picture of which visual impairment…
Astigmatism

Aqueous humor
A clear liquid-like substance between the cornea and lens. Provides nutrition and cushioning.
Controls the amount of pressure in the eye. Is replaced and flushed out every 4 hours to clear debris. Keeps eye inflated
Glaucoma
The #1 cause of adult blindness. Caused by too much pressure in the eye when aqueous humor won’t drain.
The visual impairment associated with the crystalline lens
presbyopia and cataracts
Cataracts
Visual impairment associated with the crystalline lens. Lens becomes glassy
The visual impairment associated with aqueous humor
glaucoma
Iris
The muscle surrounding the pupil. Contains 2 layers: pigment and blood vessels.
Pupil
Hole that allows light to enter your eye. Size is influenced by the amount of light and emotion. Not great at adjusting light.
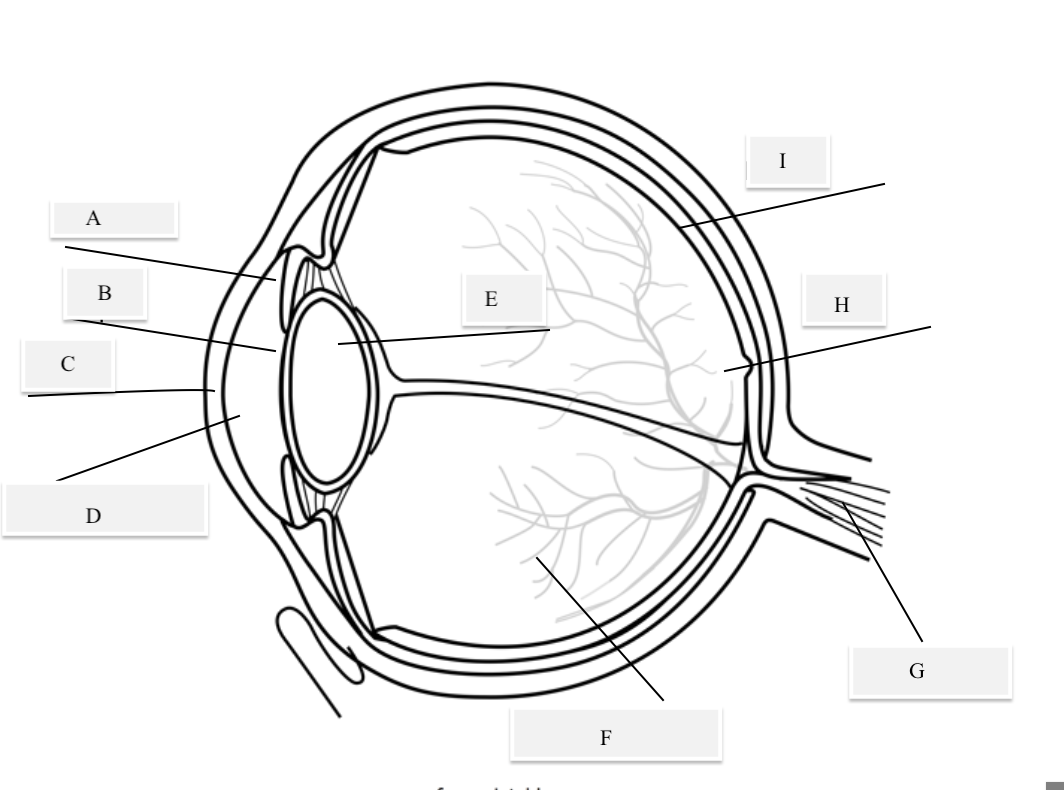
A on the diagram
The iris
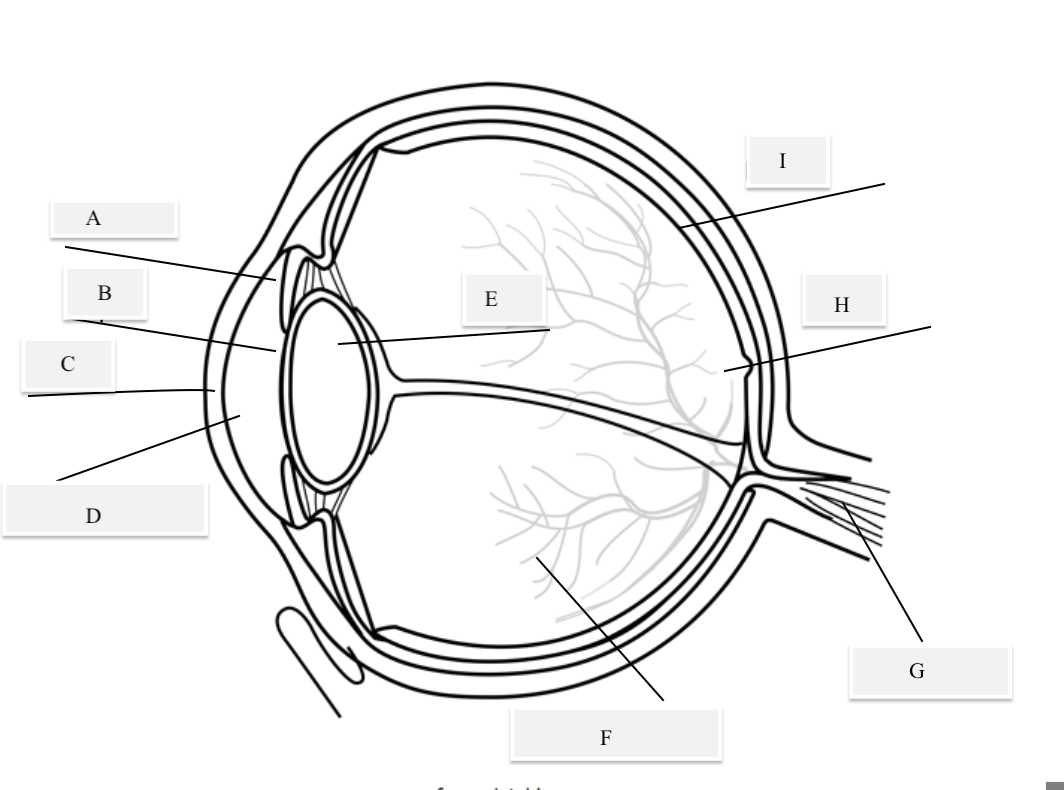
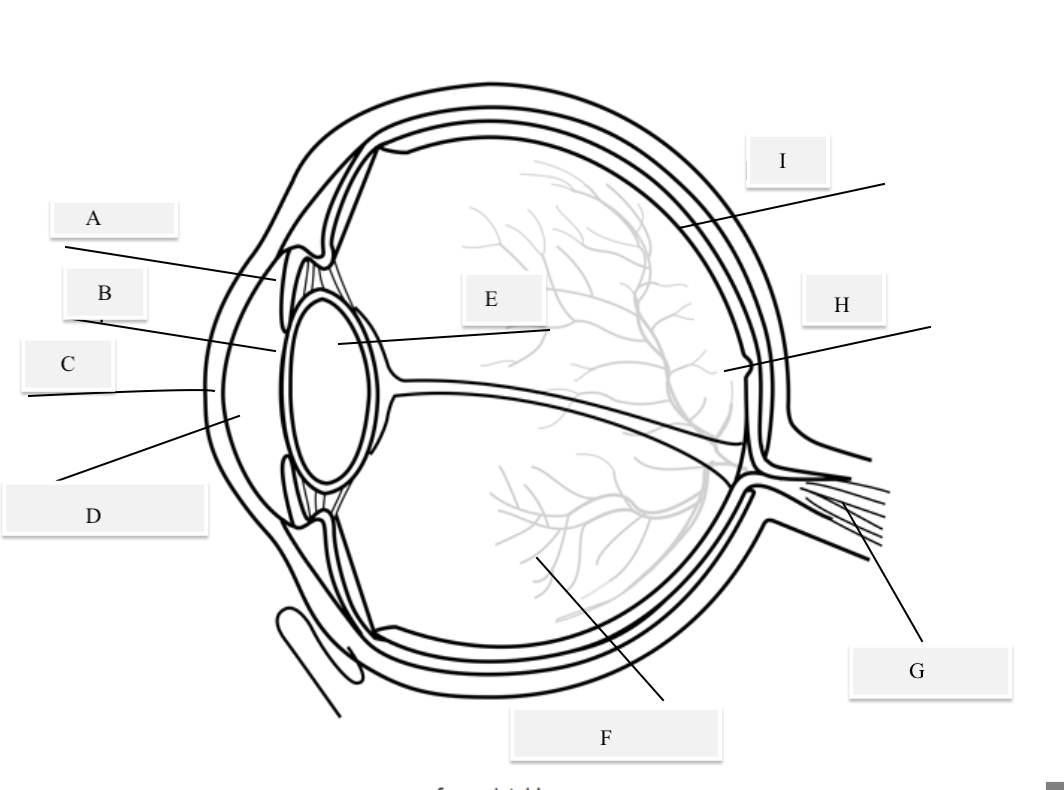
B on the Diagram
Pupil
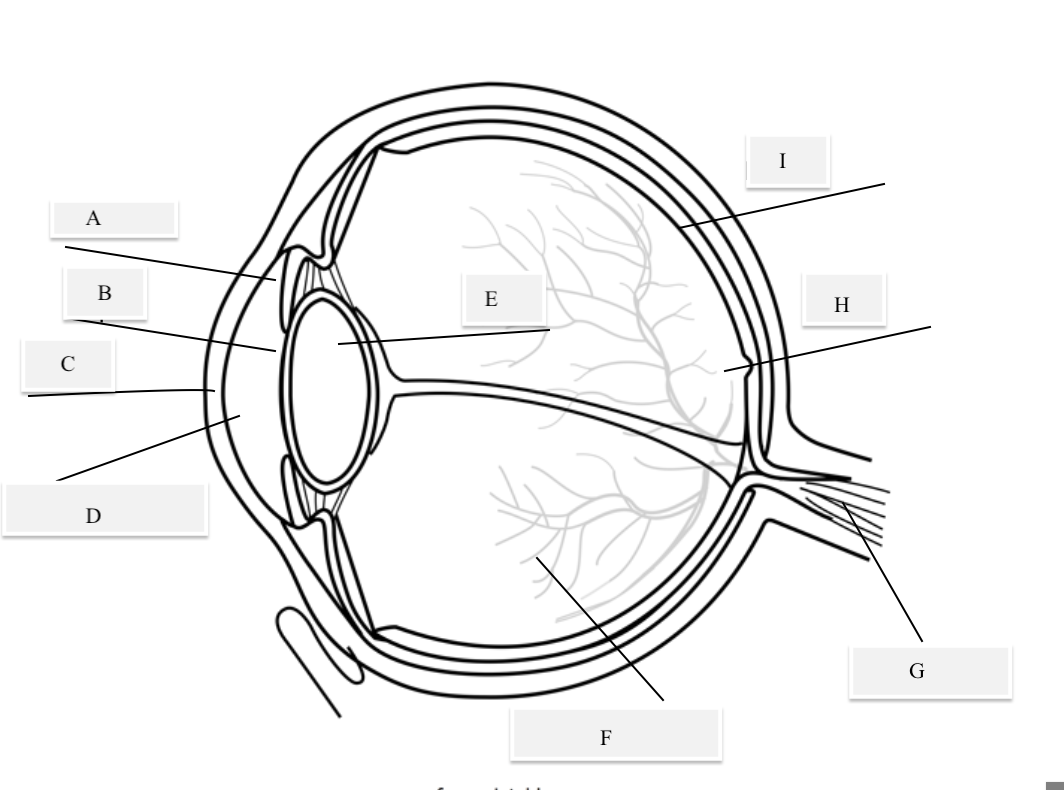
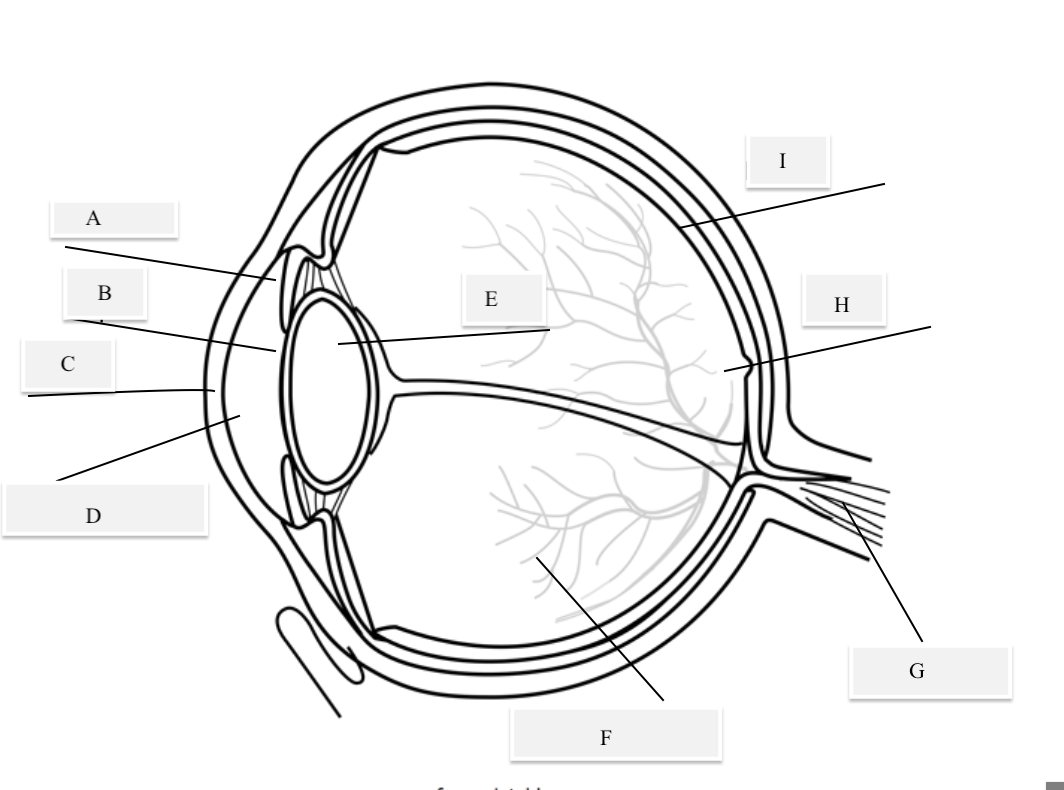
C on the Diagram
Cornea
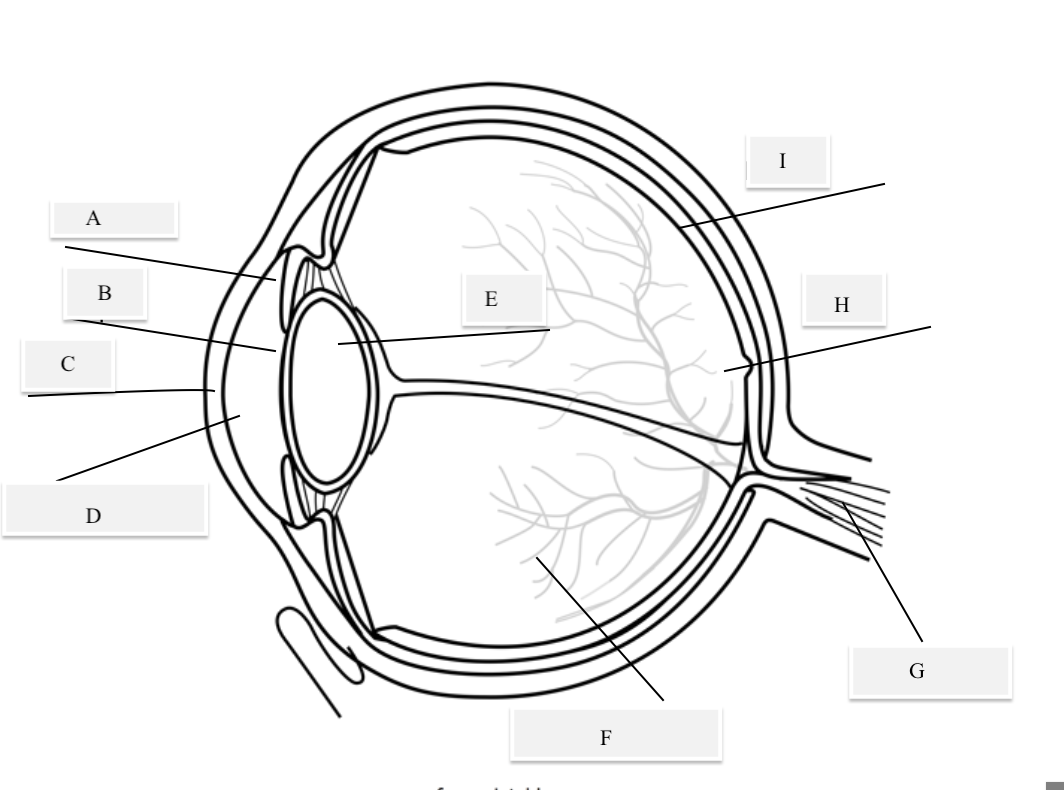
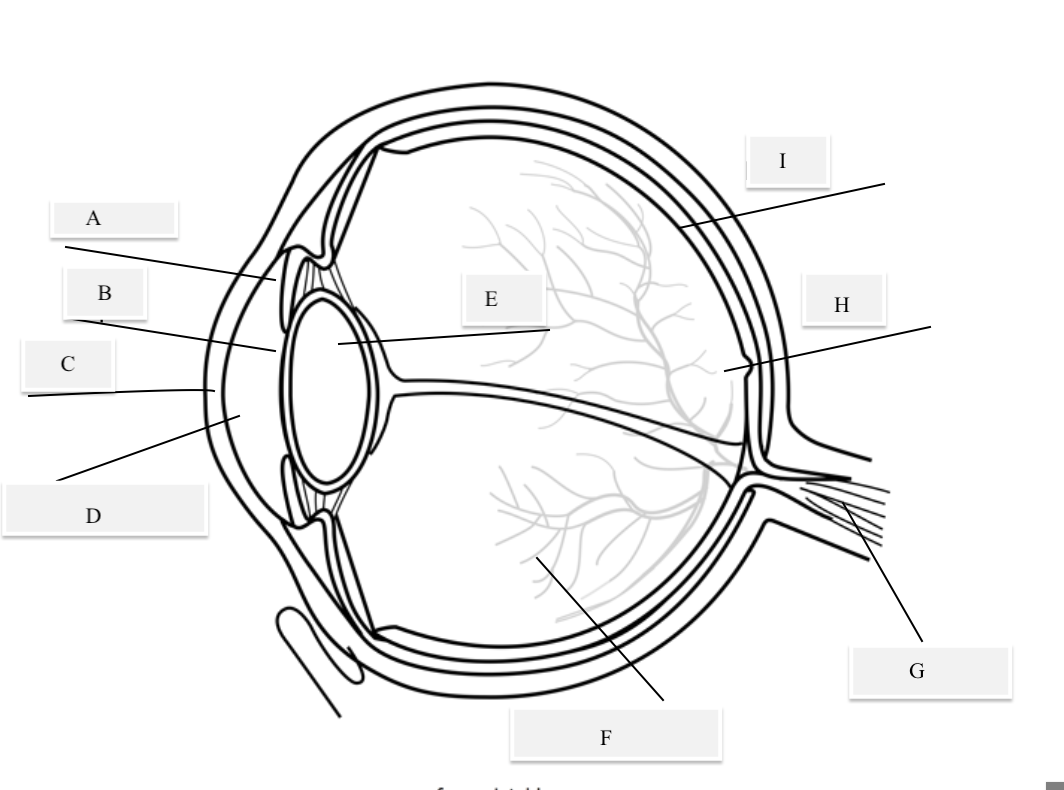
D on the Diagram
Aqueous Humor
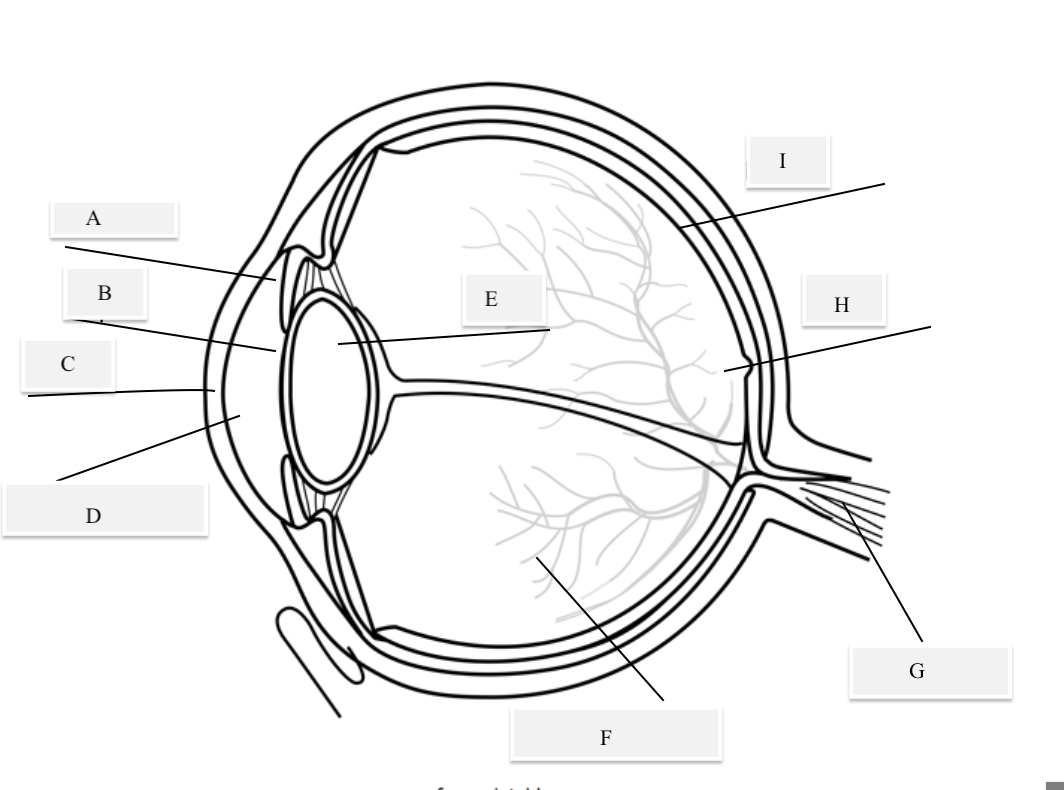
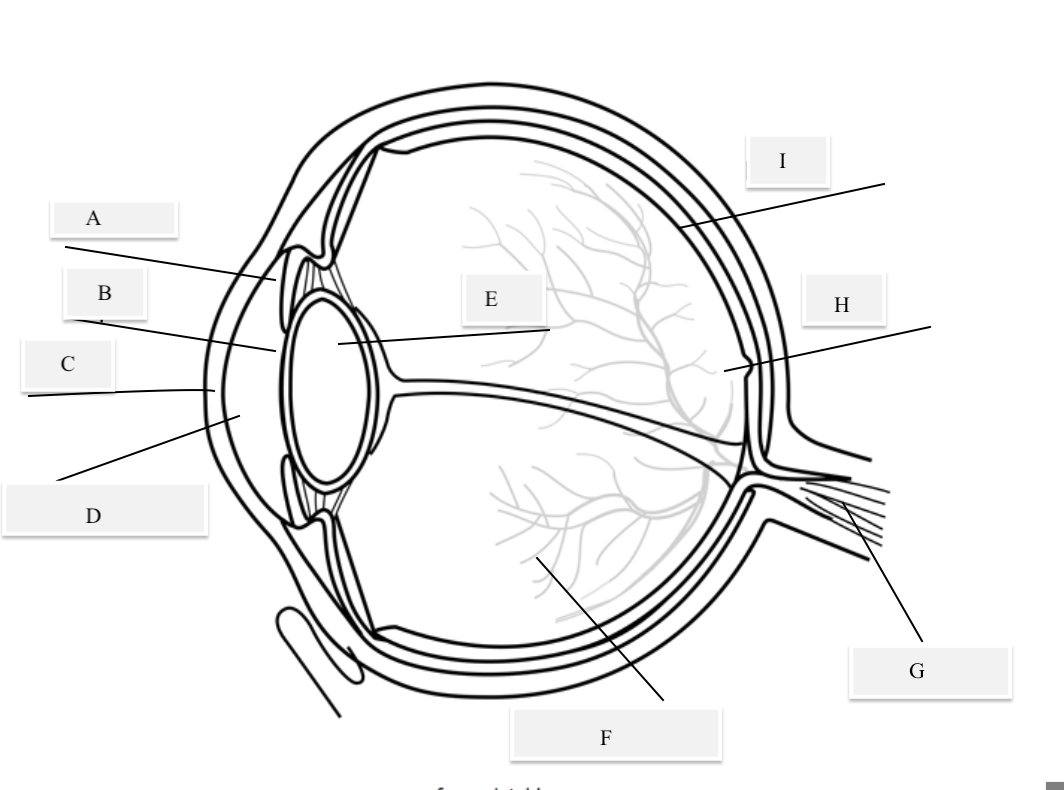
E on the Diagram
Lens
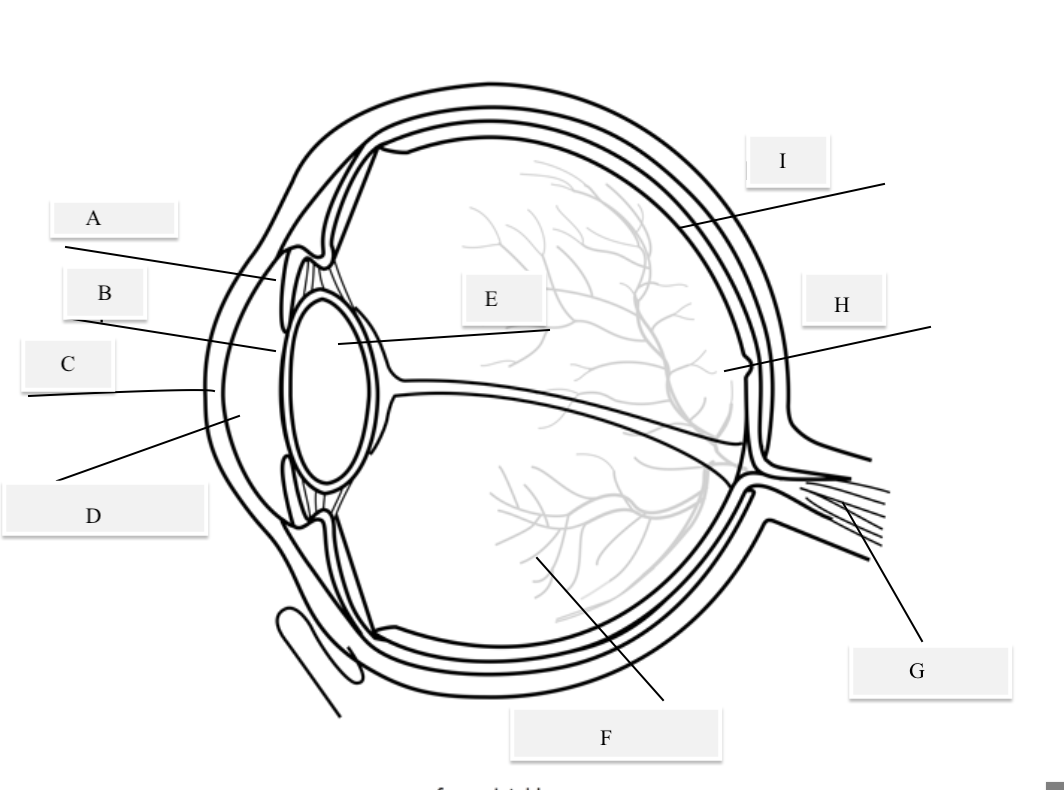
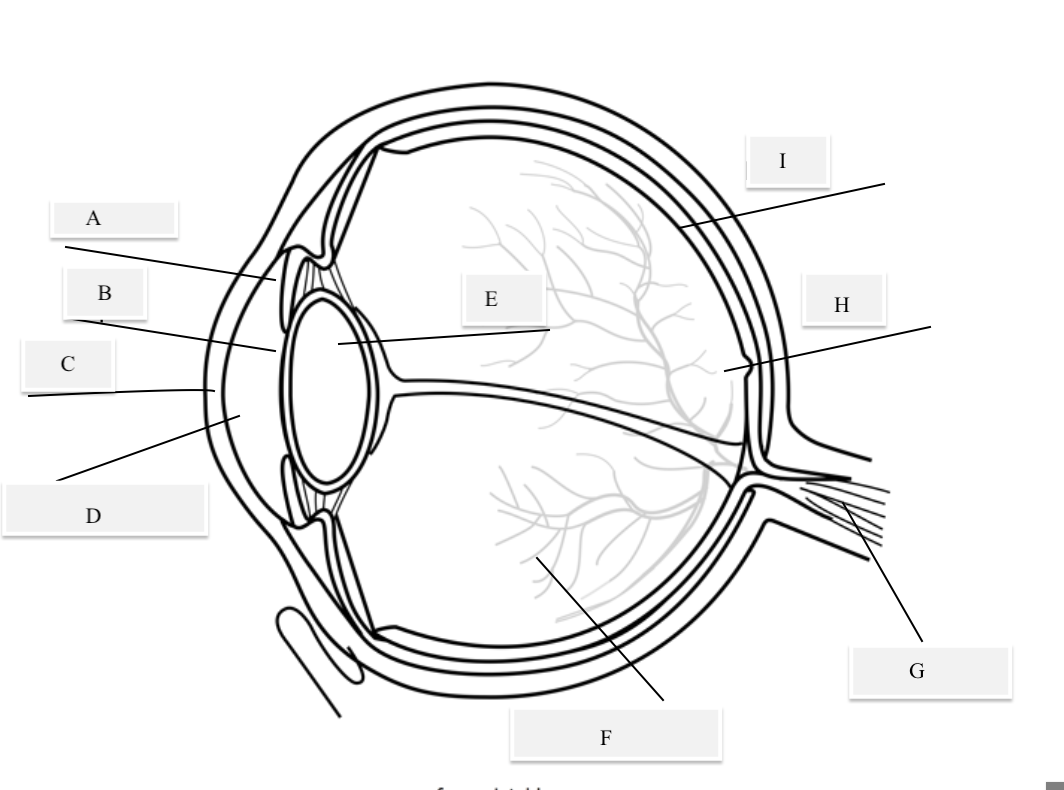
F on the Diagram
Vitreous Humor
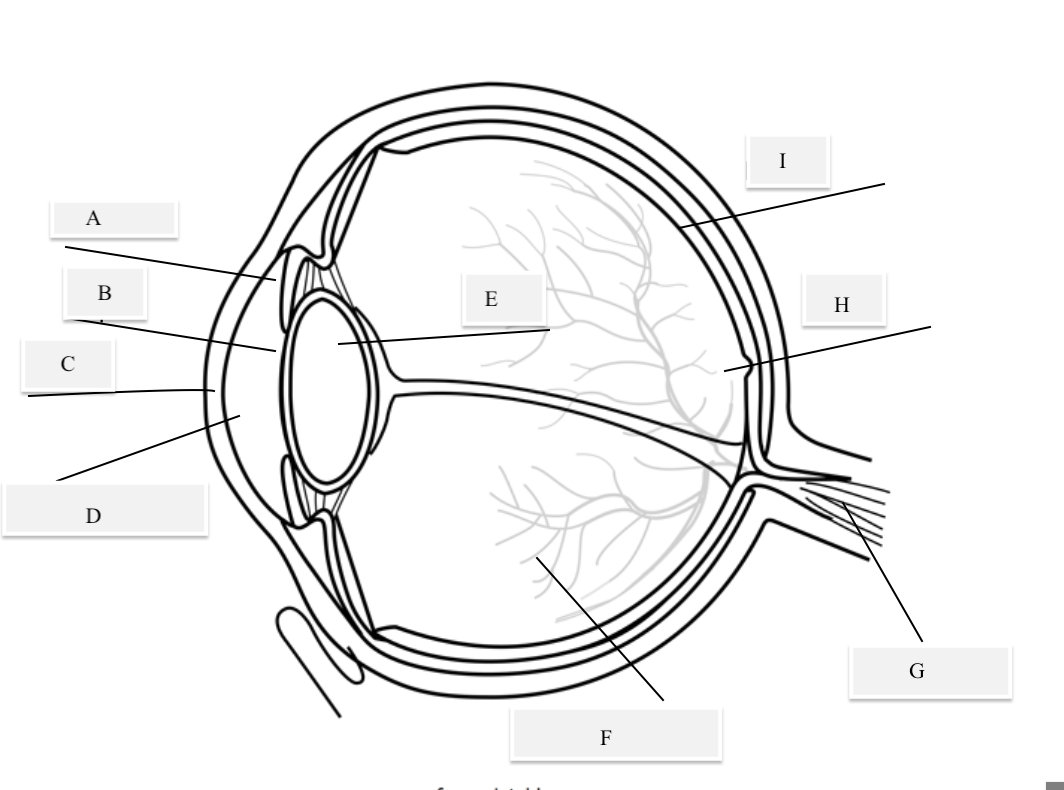
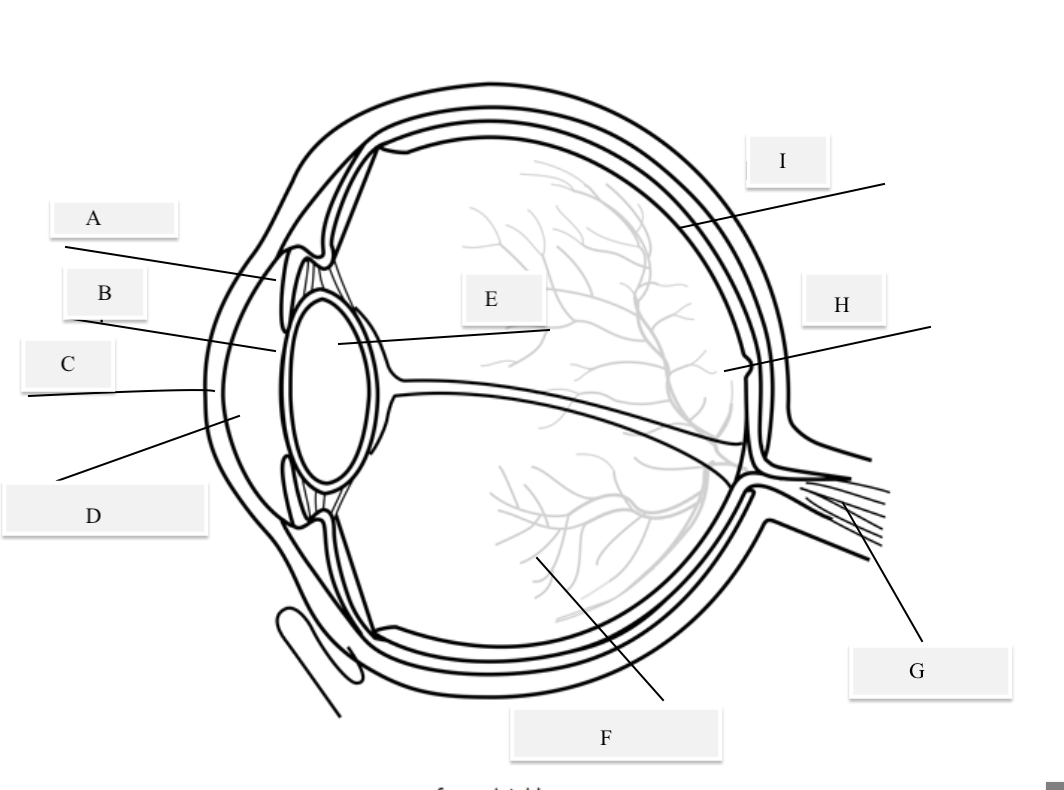
G on the Diagram
Optical Nerve
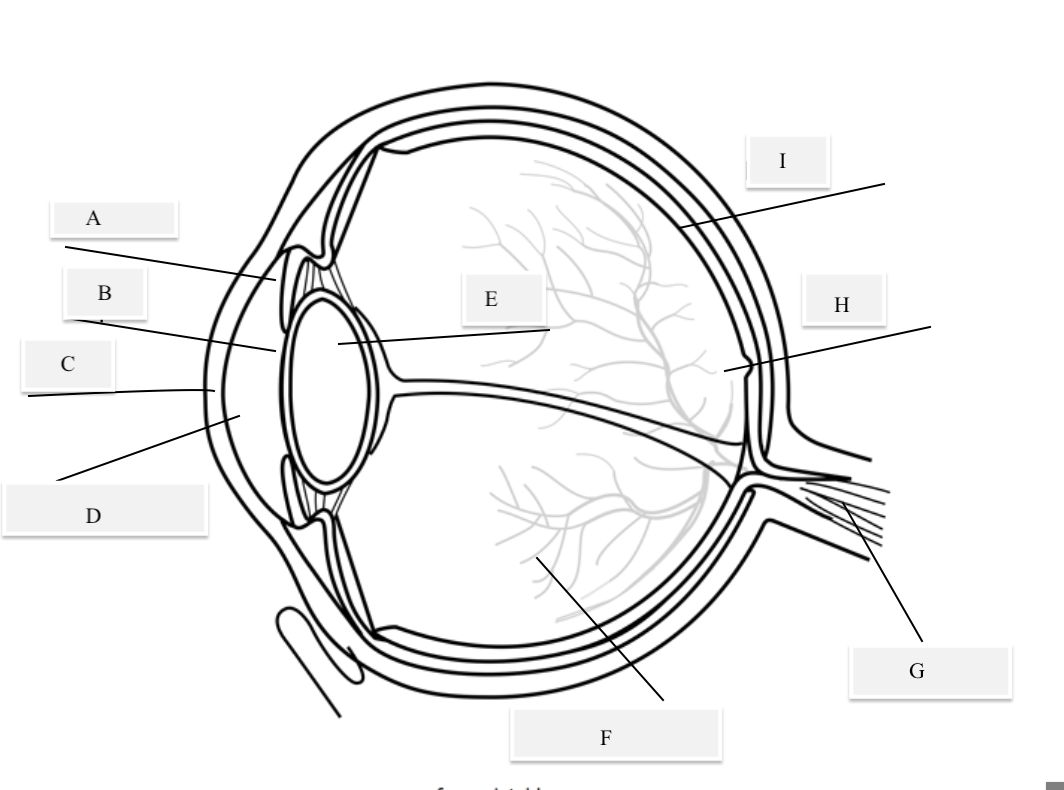
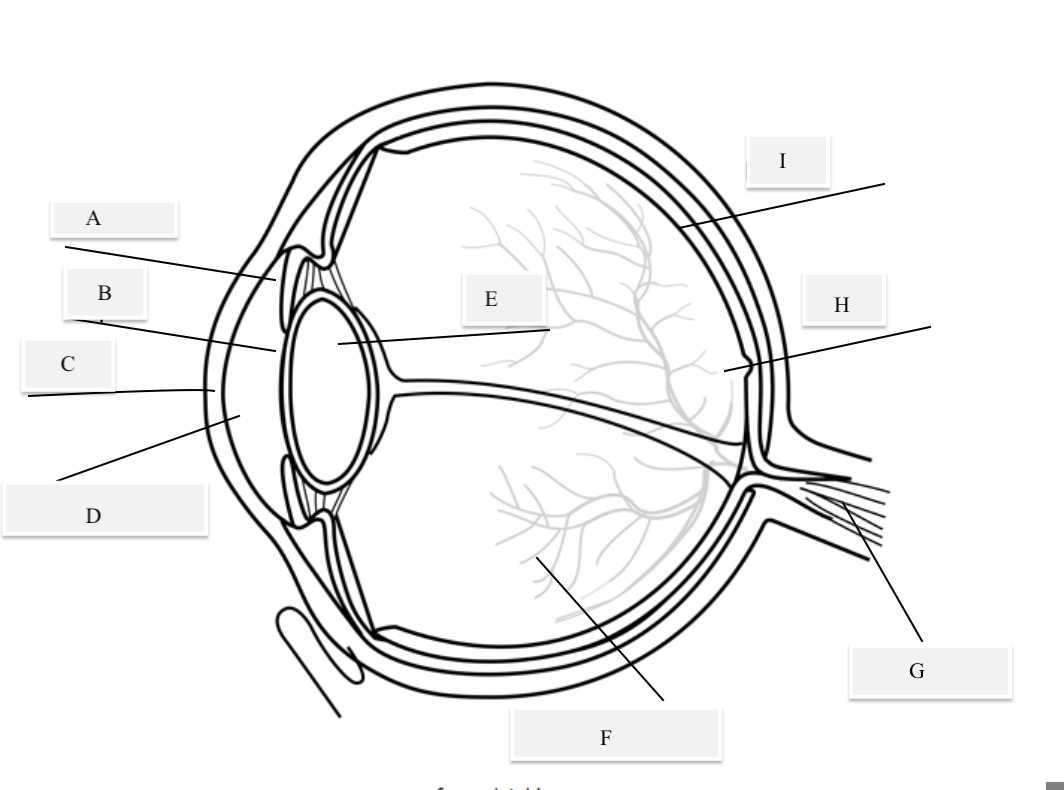
H on the Diagram
Fovea
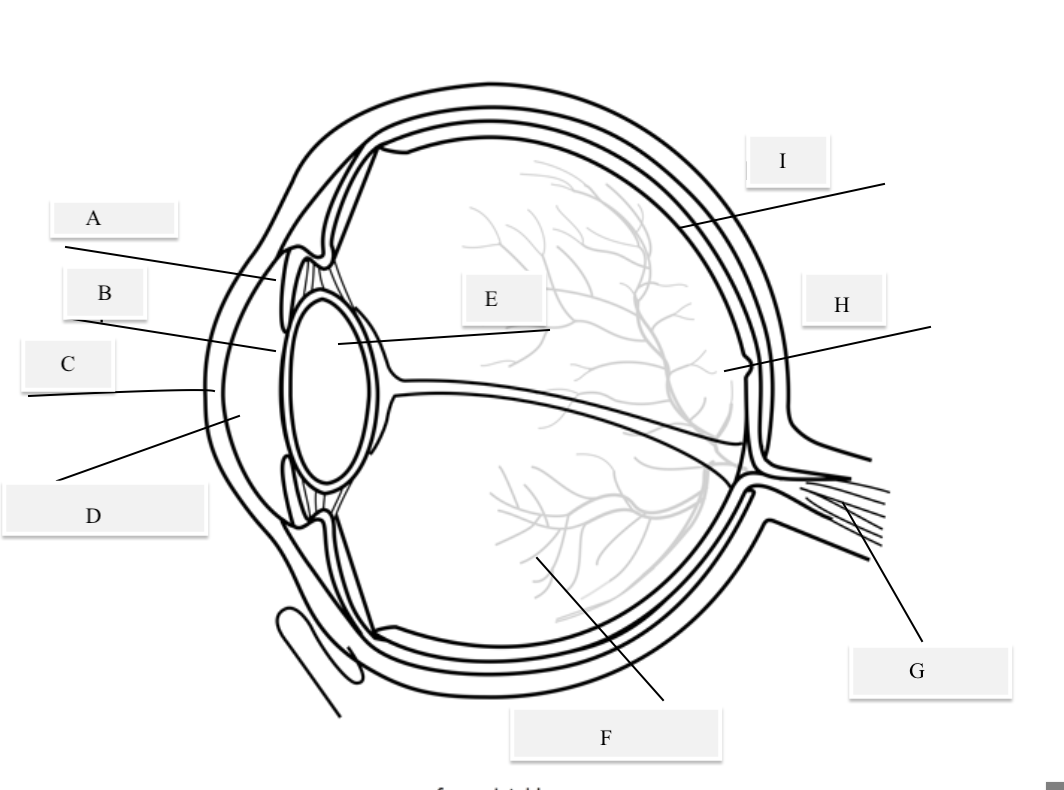
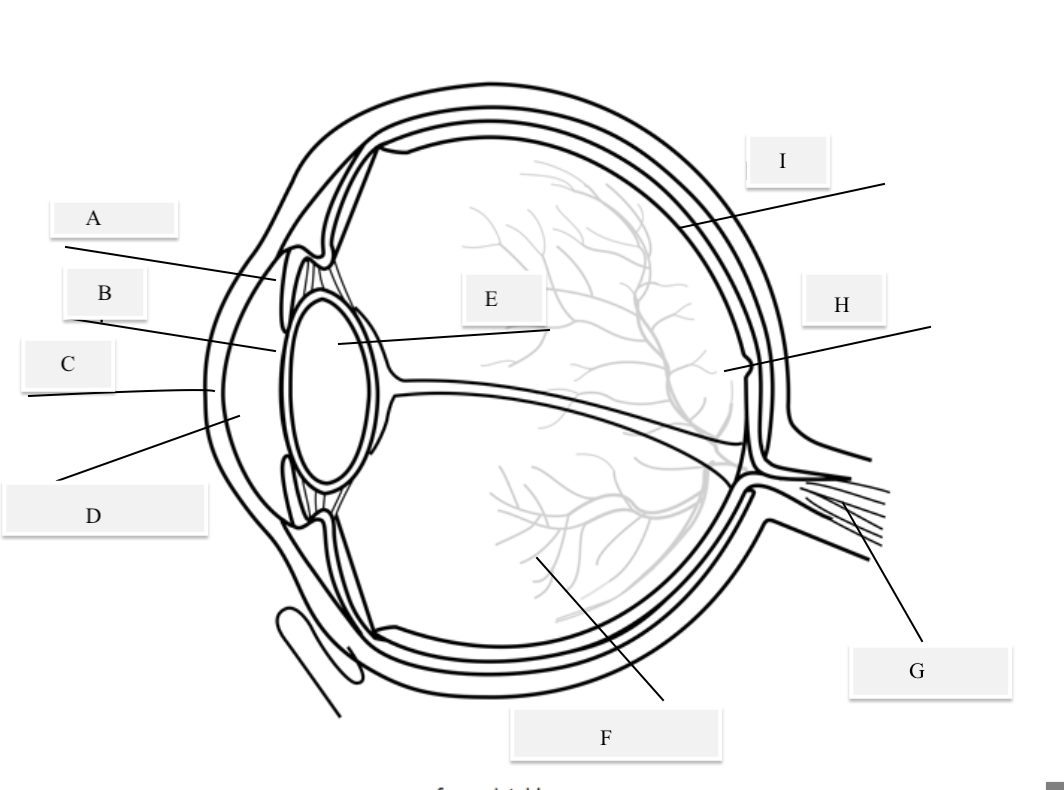
I on the Diagram
Retina
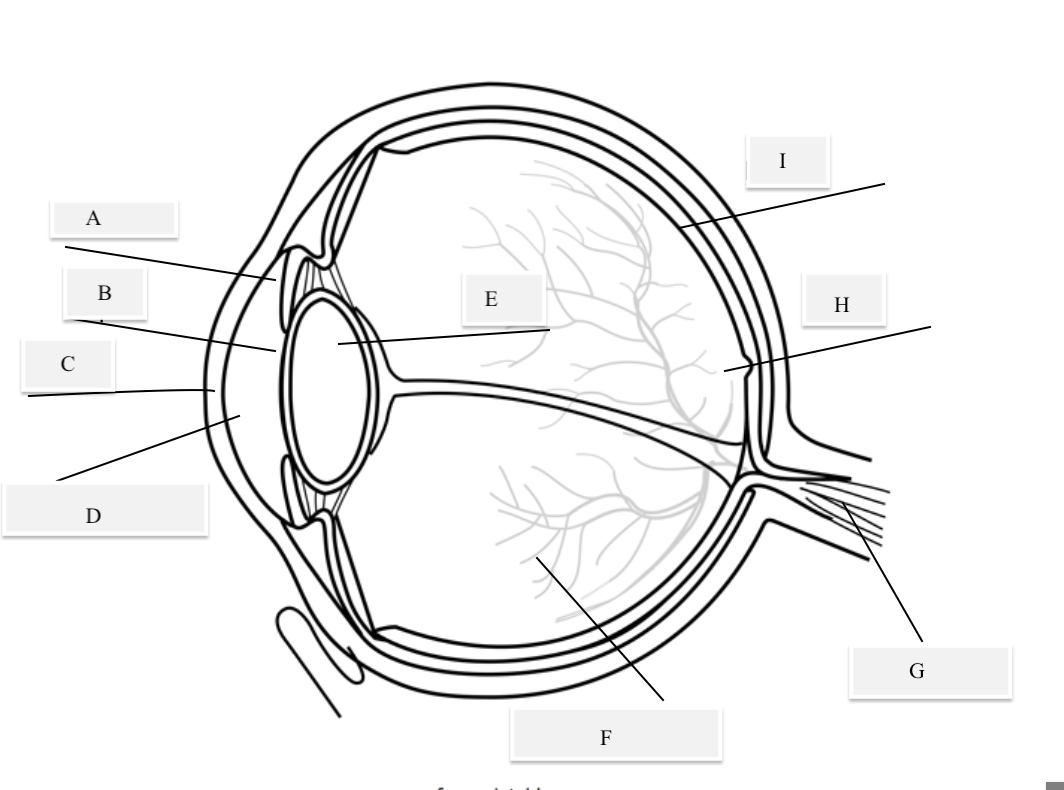
Fovea
Tiny area of the back of the eye, responsible for the center of central vision. Sits at around 0 degrees and covers about 1-2 degrees in bandwith
Retina
The layers of tissue that outline the back surface of the eye. Light must pass through many layers to hit the retina where it is eventually reflected. Photoreceptors are in one layer of the retina
Photoreceptors
Sit in the retina. Contains photopigments that are sensitive to light. Neurons that converts light to a neural impulse
Rods
Highly concentrated in central and peripheral vision. None in fovea. Great at detecting low light and works well at detecting motion. Cannot detect color. Slow dark adaption, but greater sensitivity to dark.
Cones
Highly concentrated in the fovea, but can be found in the fovea and central vision. Fast to adapt to light, is only effective in bright light. Detects color. Fast to adapt to dark, but then sensitivity tapers off.
The photoreceptor that is good for nighttime vision
rods
The photoreceptor that is specialized in daytime vision
Cones
Outersegments
The outer structure on the outside of photoreceptors. Contains proteins and photopigments. The photopigments change their composition when light hits these sensitive proteins.
Vitreous humor
Clear colorless fluid that is inside of the eye. Helps maintain eye shape. Provides nutrition and support. This is where you may get floaters.
Macula
Central vision. Encompasses about 20 degrees (excluding the optic disk)
Optic Disk
Area of the eye where there are not receptors Covers around 15-19ish degrees.
Optic Nerve
A bundle of nerve fibers that transmit visual information from the retina to the brain
Blindspot
No photoreceptors exist here- so no vision can be picked up here.
Retinal Processing
Explains why we don’t notice the blind spot. Because we have two eyes, the blindspots converge and both eyes pick up the slack of the other one.
Cognitive processing
Explains why we don’t notice our blind spot. The brain ignores the absence of information. fills in the blind spot based on our expectations and experience.
A-modal Completion
Ability to see an object even when another object covers parts of it.
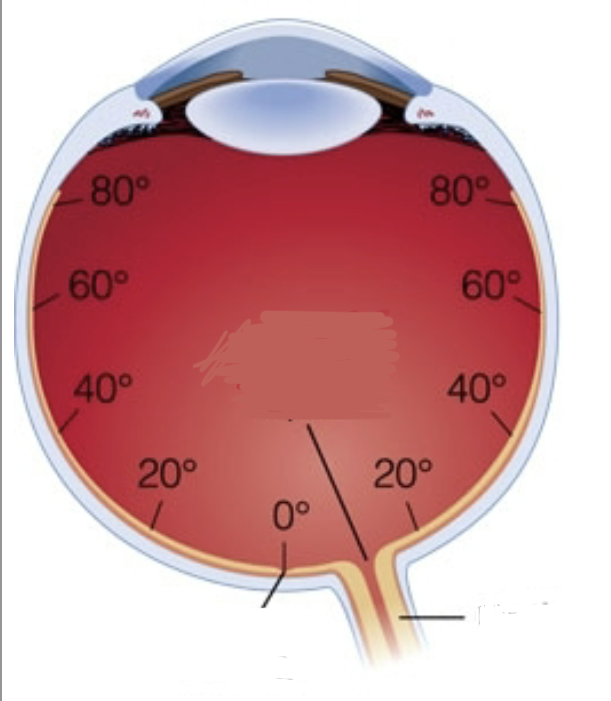
Where is the fovea?
0 Degrees
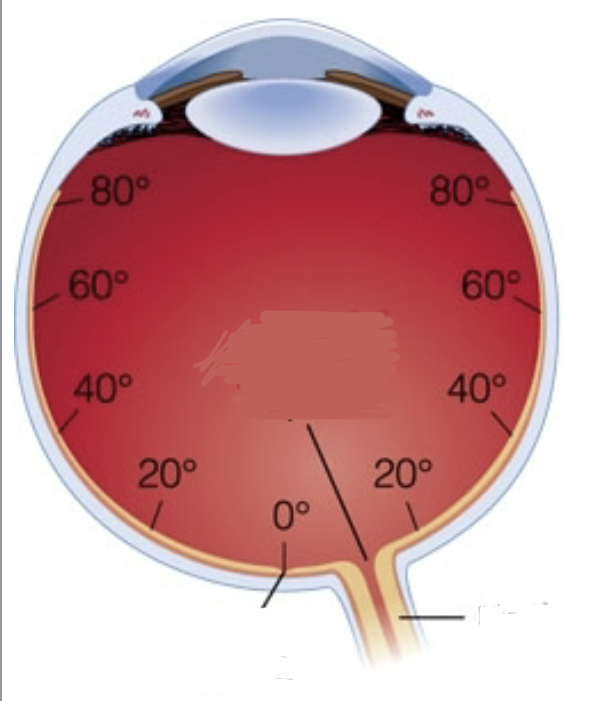
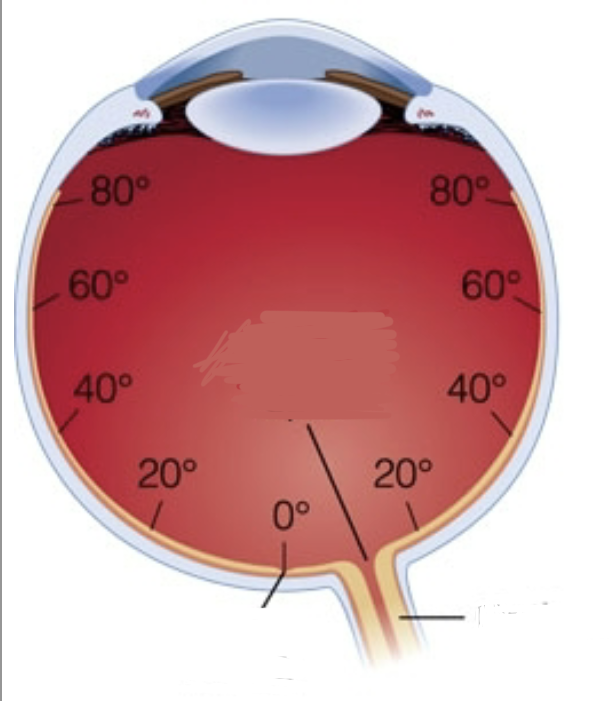
Where is central vision
20 degrees
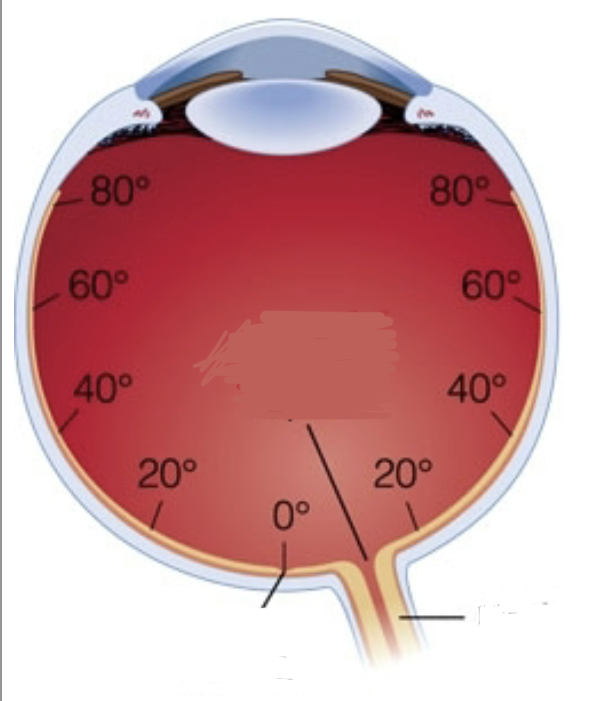
Psychophysics
Studies the relationship between the stimulus and one’s perceptual experience by measuring the absolute threshold.
Rule of thumb
When looking at your thumb from an arm’s length away, only your thumbnail hits the fovea.