Chapter 11 - Market Structures: Perfect Competition and Monopolies
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Short-Run Costs for Jennifer and Jason's Farm
Ex.
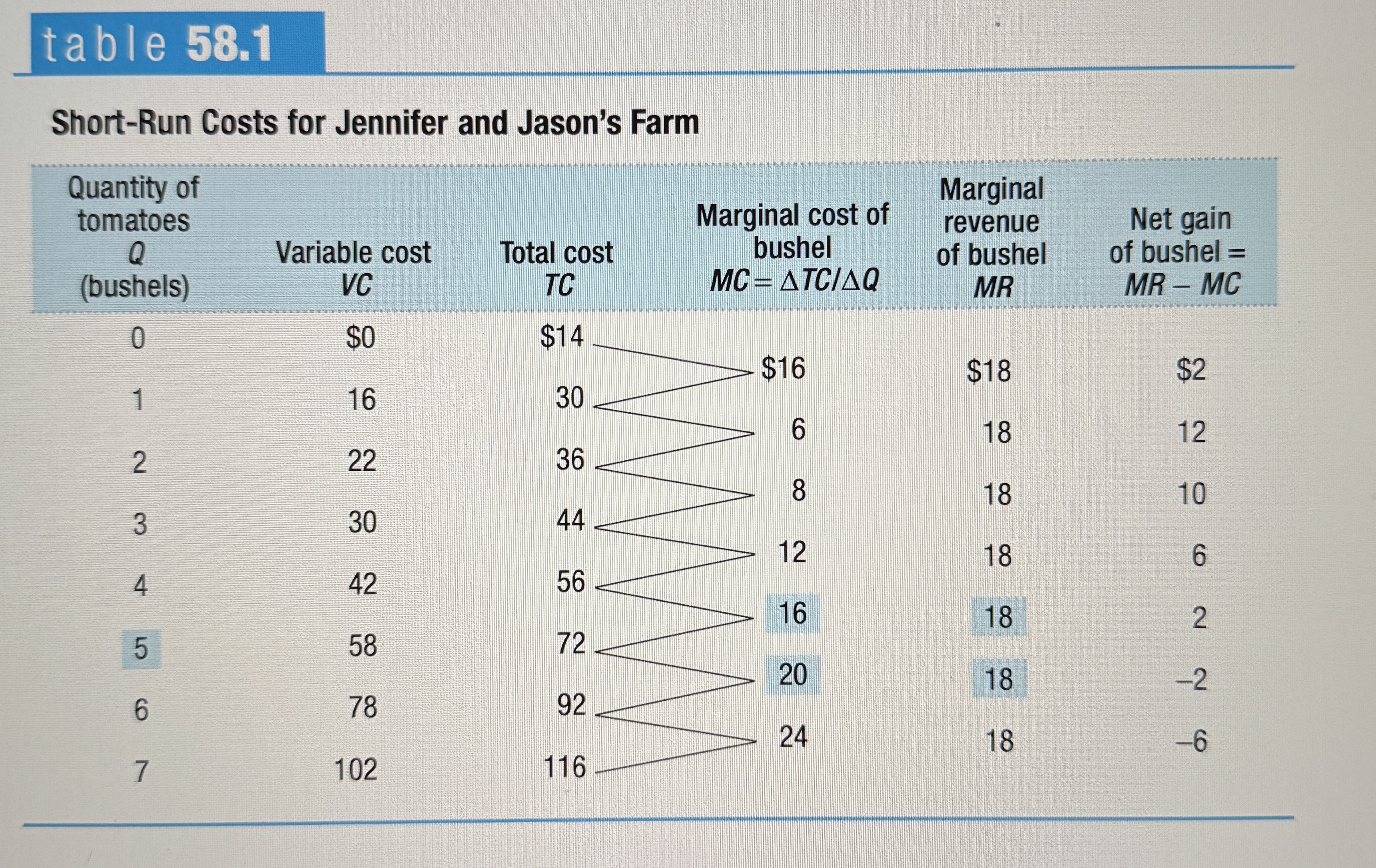
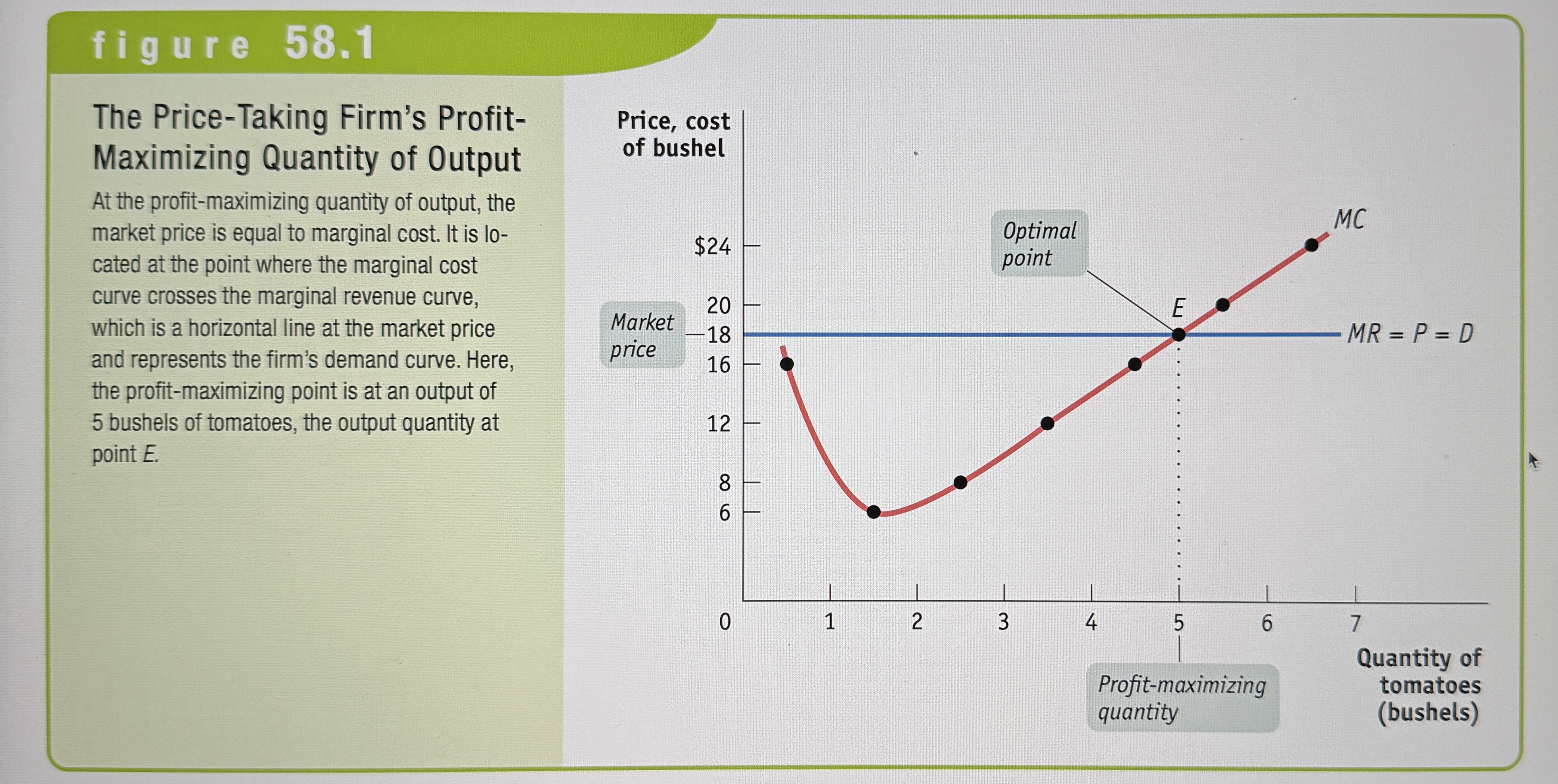
Price-taking firm’s optimal output rule
Says that a price-taking firms profit is maximized by producing the quantity of output at which the market price is equal to the marginal cost of the last unit produced.
The Price-Taking Firm's Profit-Maximizing Quantity of Output
Ex.
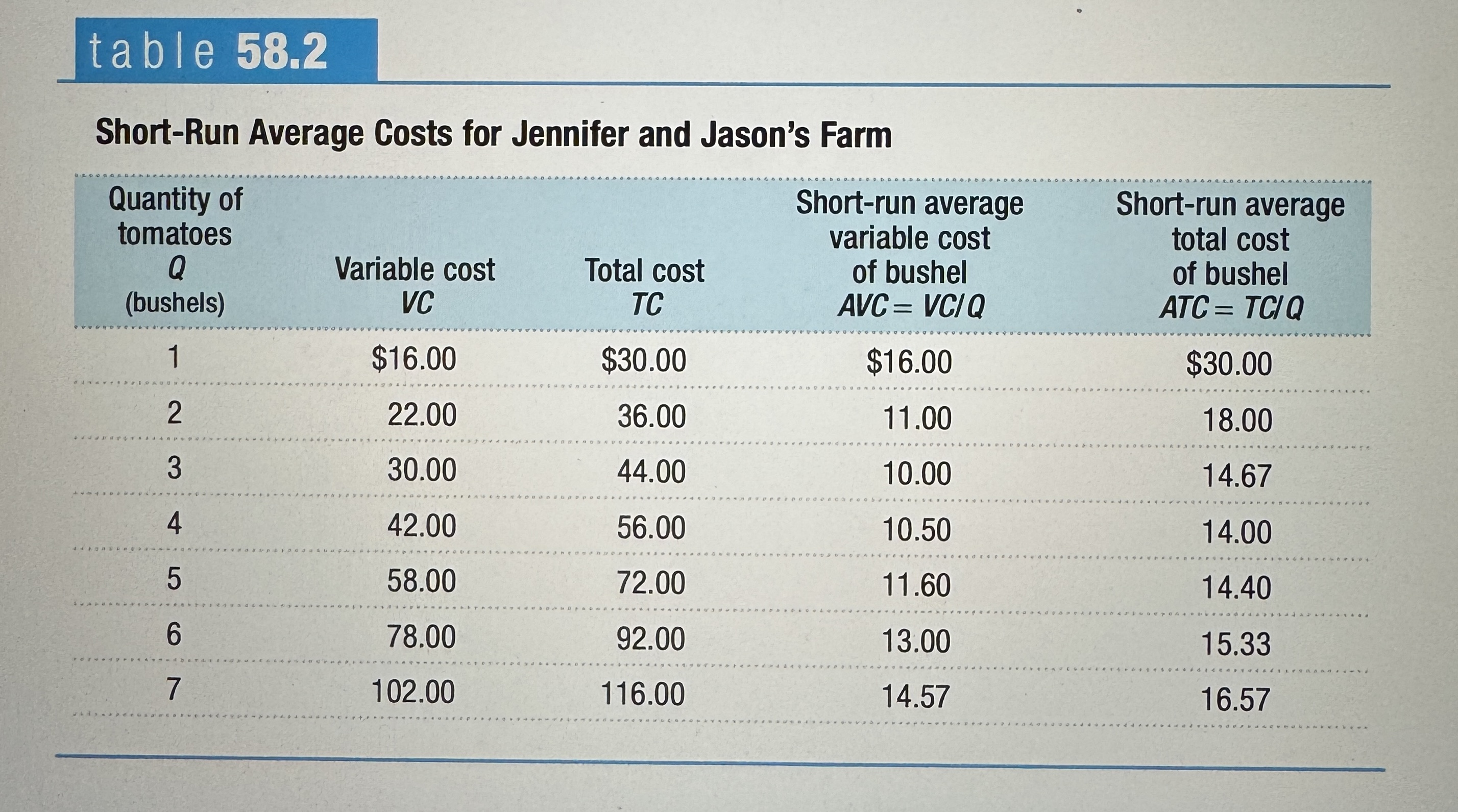
Short-Run Average Costs for Jennifer and Jason's Farm
Ex.
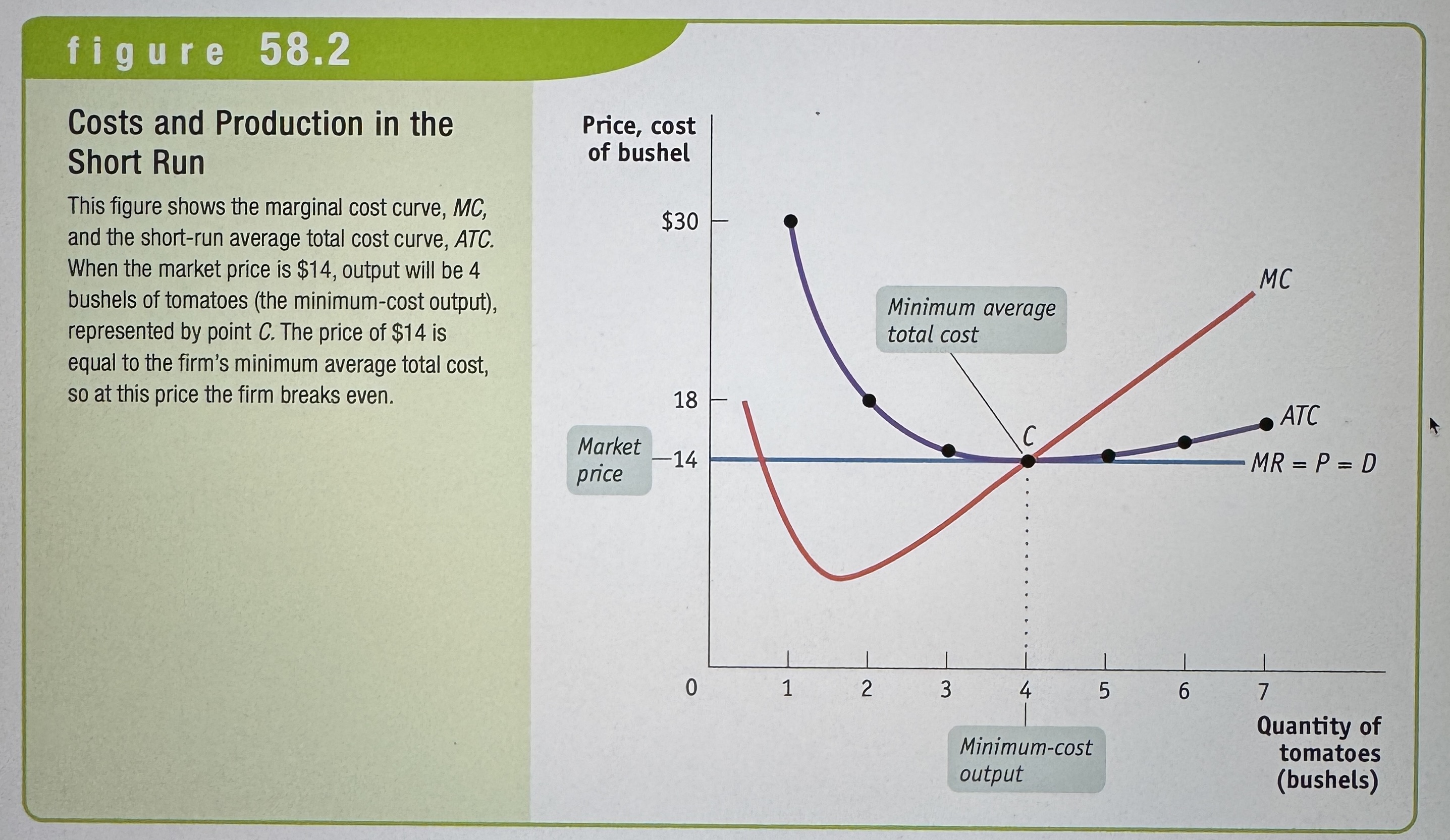
Costs and Production in the Short Run
Ex.
Profitability and the Market Price
Ex.
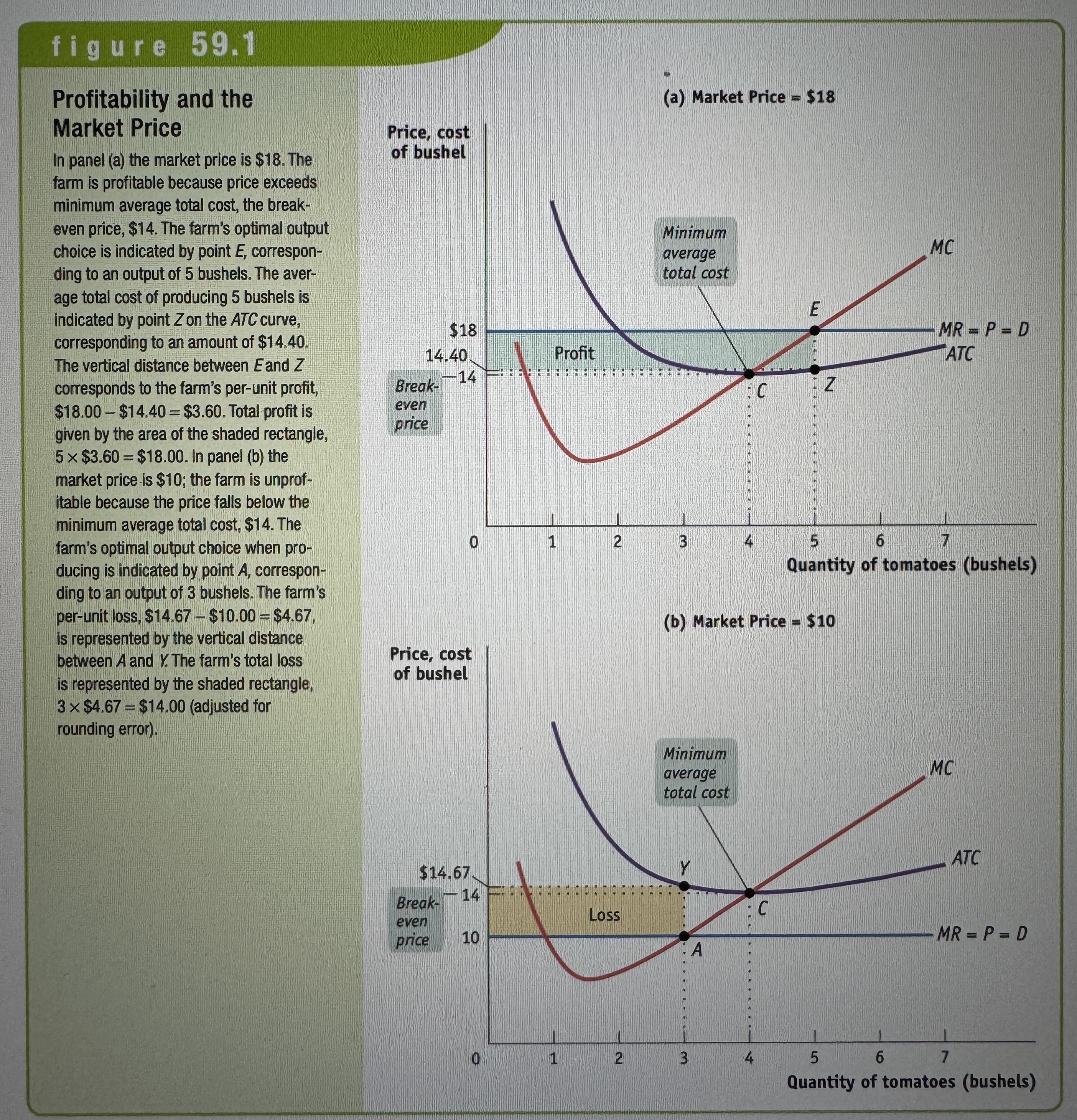
Break-even price
The break-even price of a price-taking firm is the market price at which it earns zero profits.
The Short-Run Individual Supply Curve
Ex.
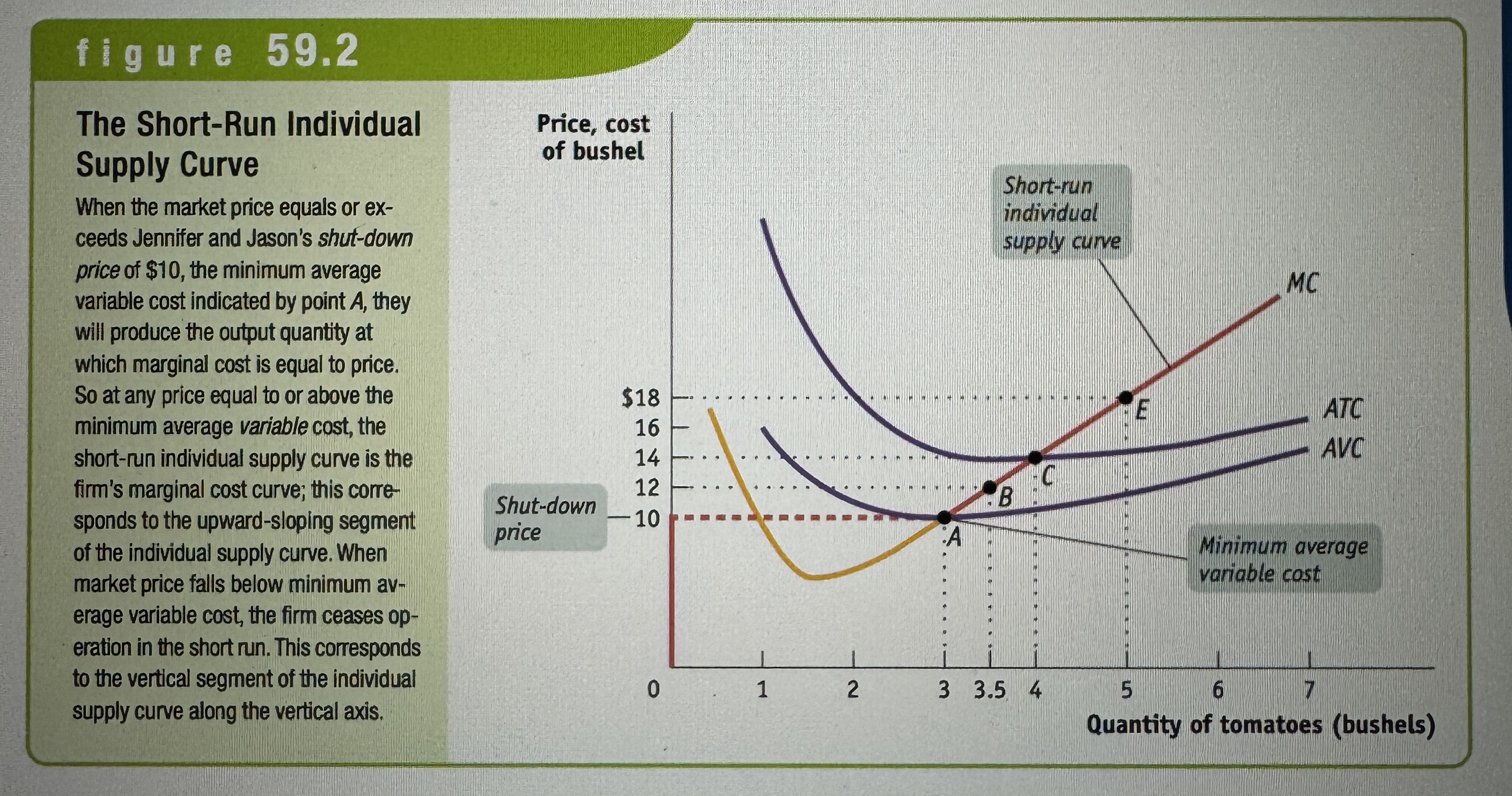
Shut-down price
A firm will cease production in the short run if the market price falls below the shut-down price, which is equal to minimum average variable cost.
Short-run individual supply curve
Shows how an individual firms profit-maximizing level of output depends on the market price, taking fixed cost as given.
How is fixed costs changed?
In the long run
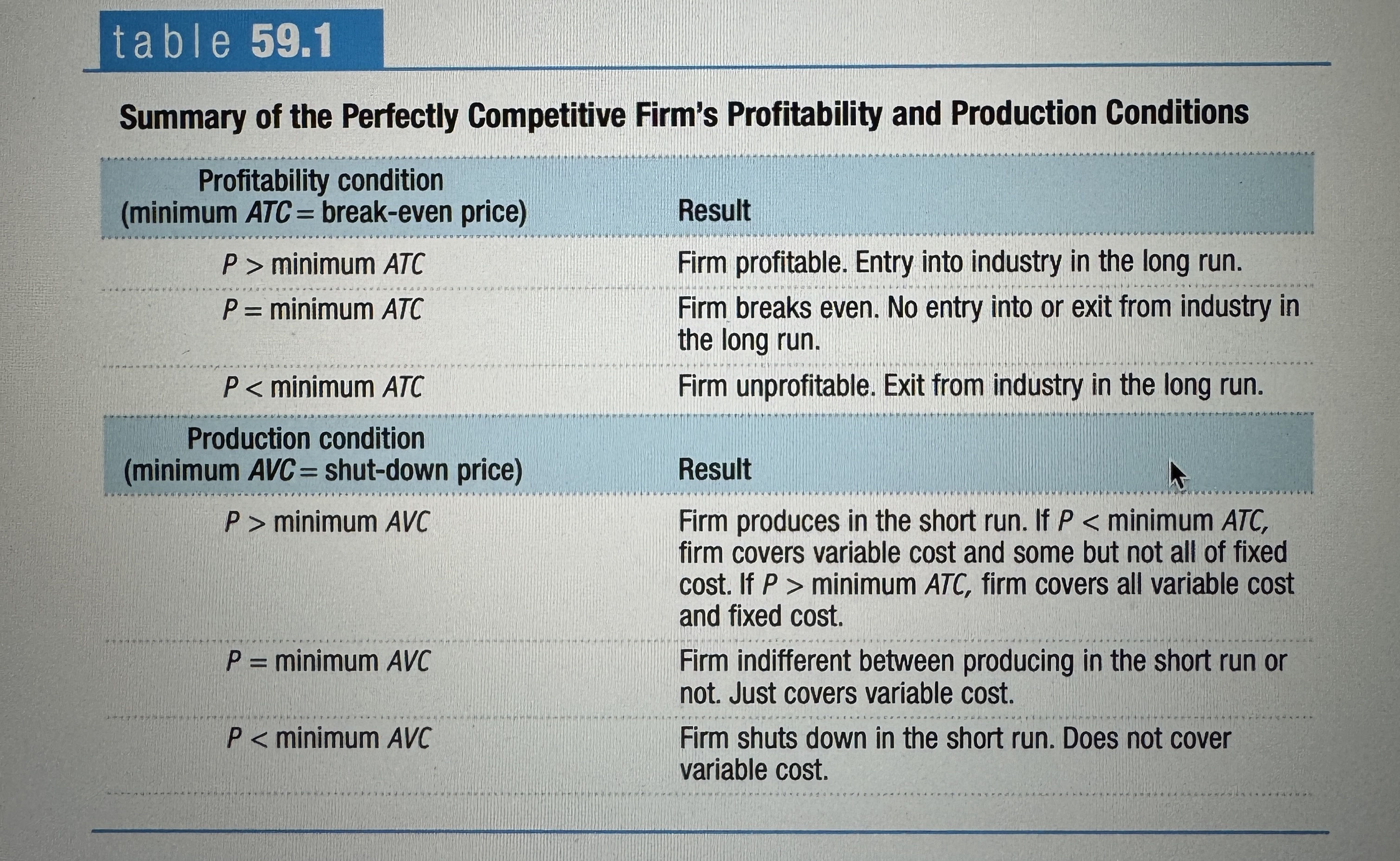
Summary of the Perfectly Competitive Firm's Profitability and Production Conditions
Ex.
Industry supply curve
Shows the relationship between the price of a good and the total output of the industry as a whole.
The Short-Run Individual Supply Curve
Ex.
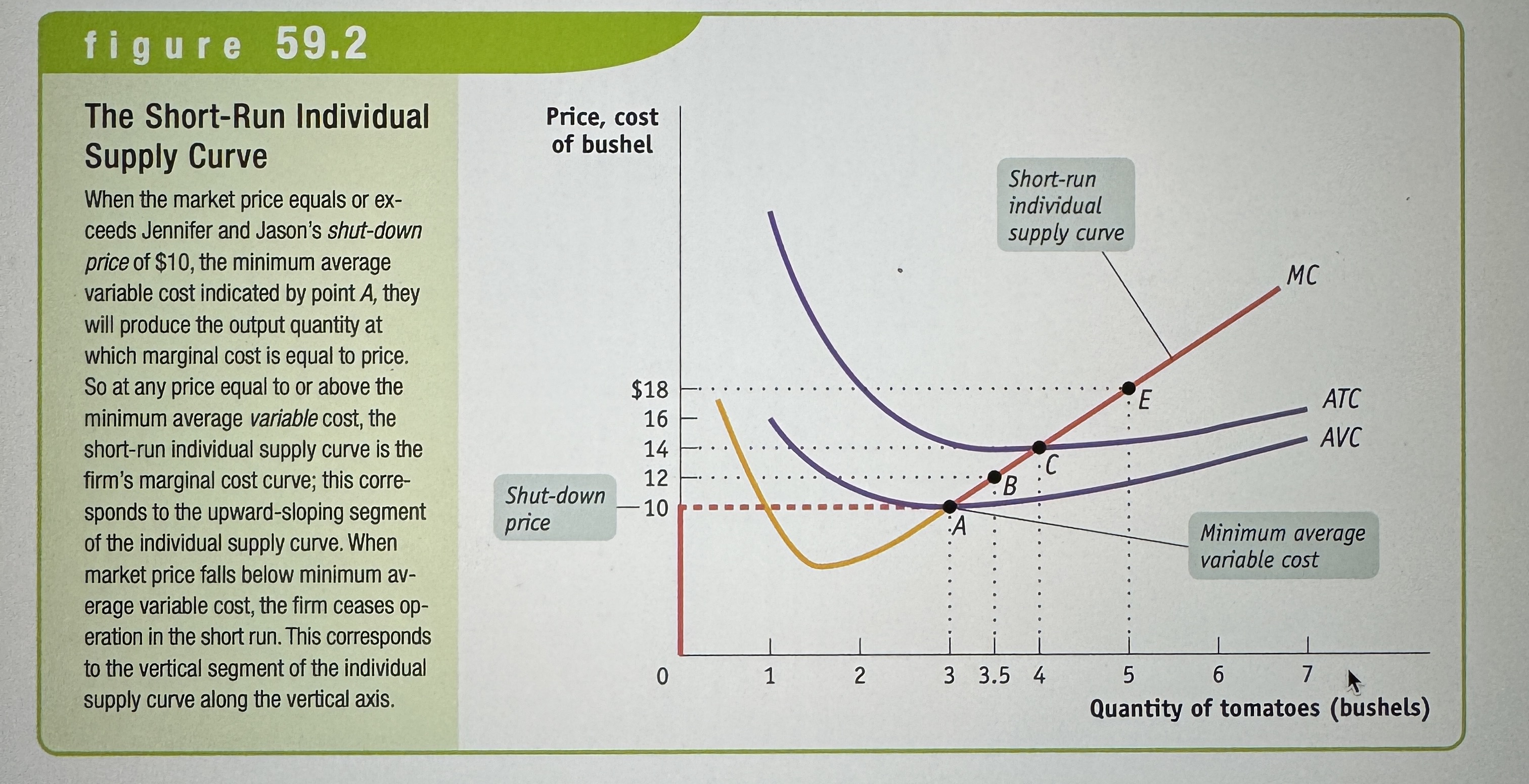
Short-run industry supply curve
Shows how the quantity supplied by an industry depends on the market price, given a fixed number of firms.
The Short-Run Market Equilibrium
When the quantity supplied equals, the quantity demanded, taking the number of producers as given.
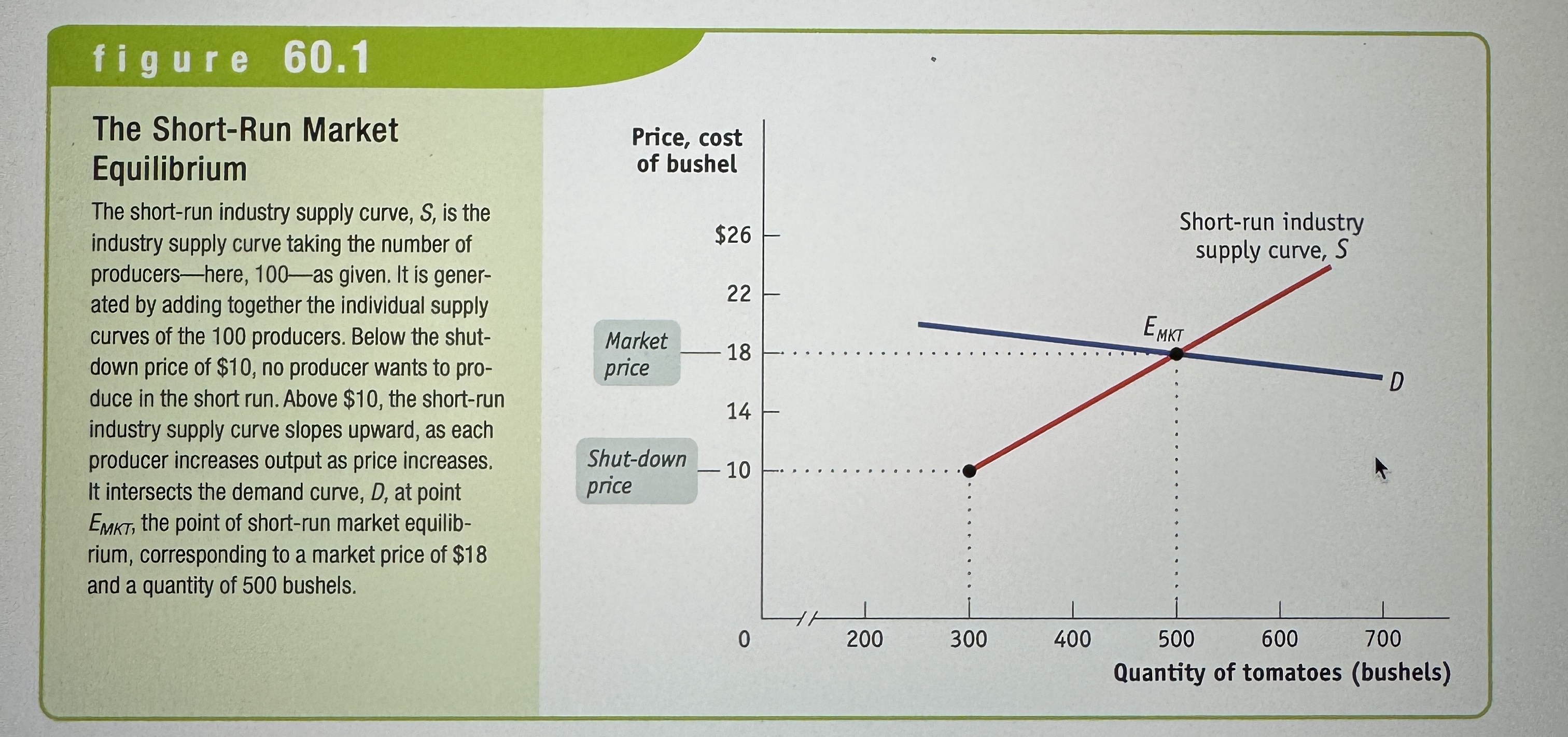
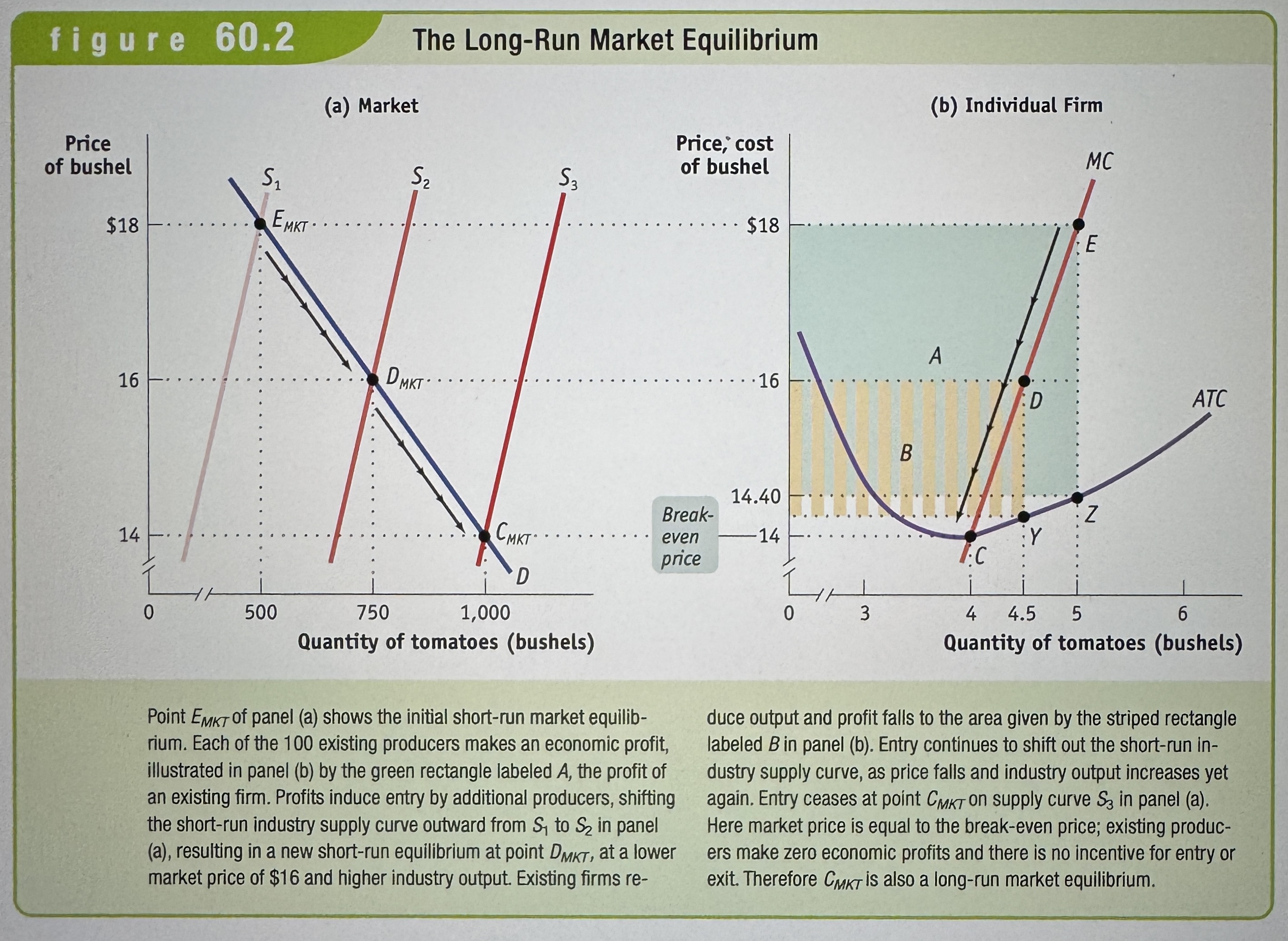
The Long-Run Market Equilibrium
When the quantity supplied equals, the quantity demanded, given that sufficient time has elapsed for entry into and exit from the industry to occur.
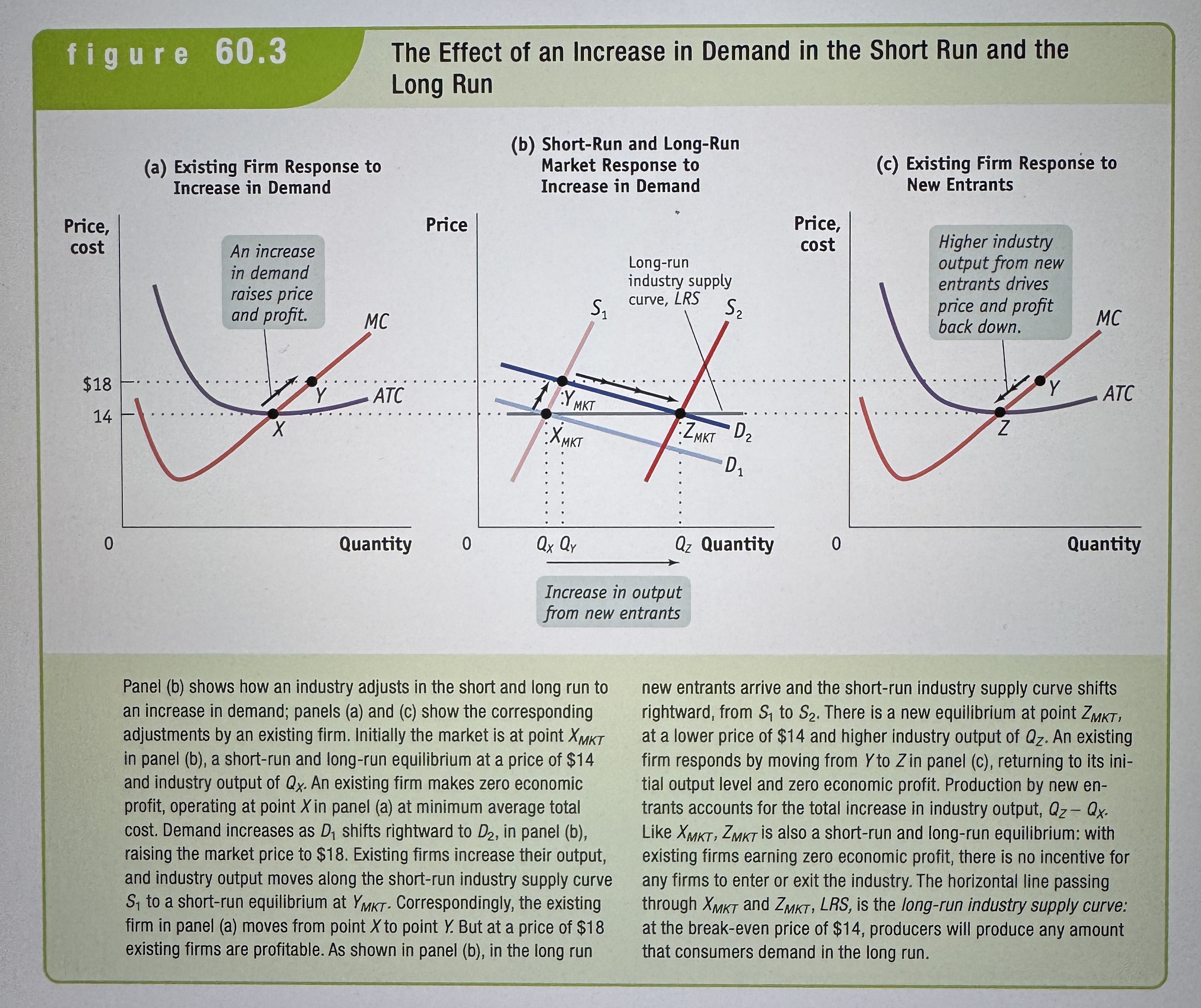
The Effect of an Increase in Demand in the Short Run and the Long Run
Ex.
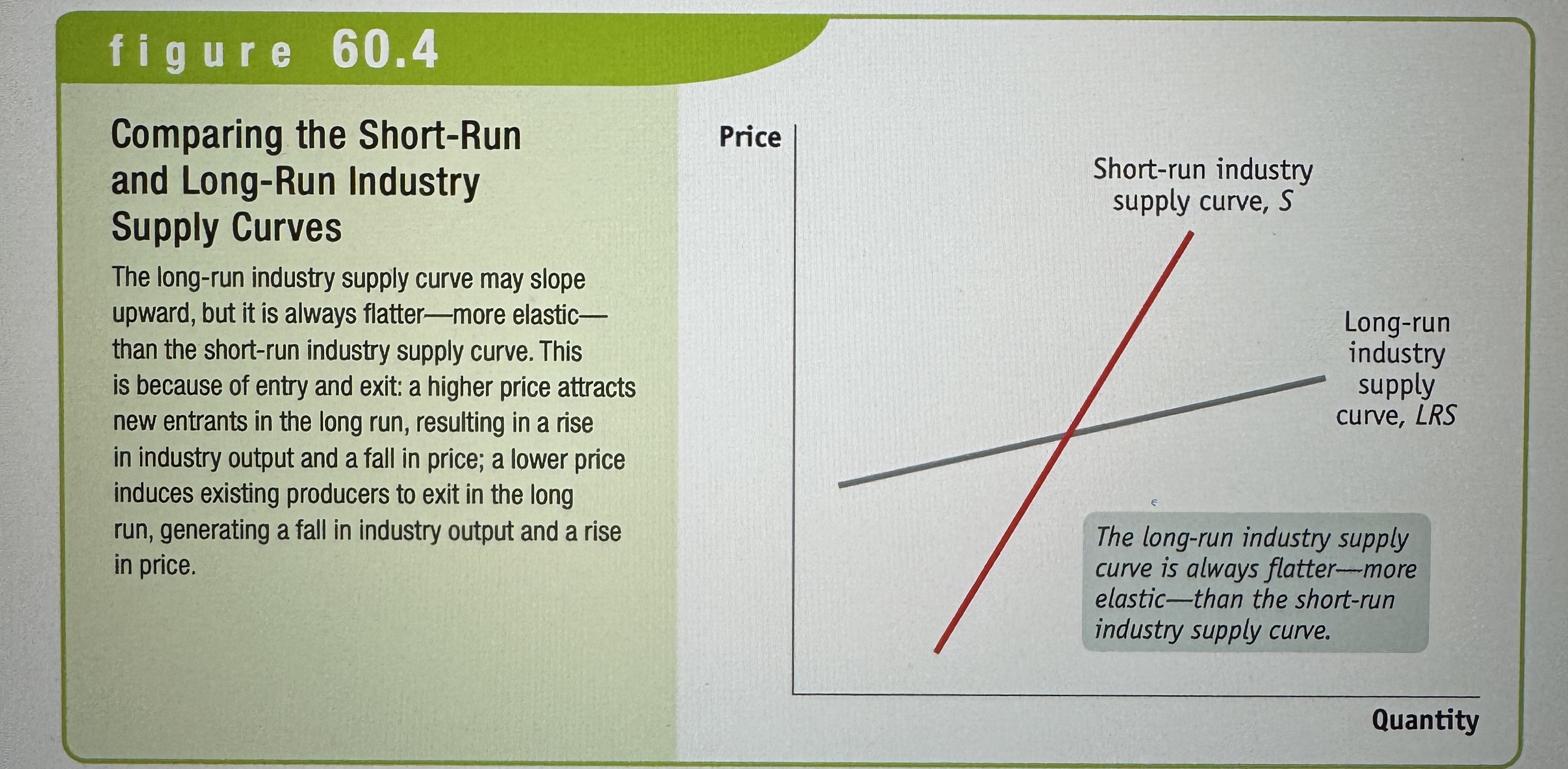
Long-run industry supply
Shows how the quantity supplied responds to the price once producers have had time to enter or exit an industry.
Comparing the Short-Run and Long-Run Industry Supply Curves
Ex.
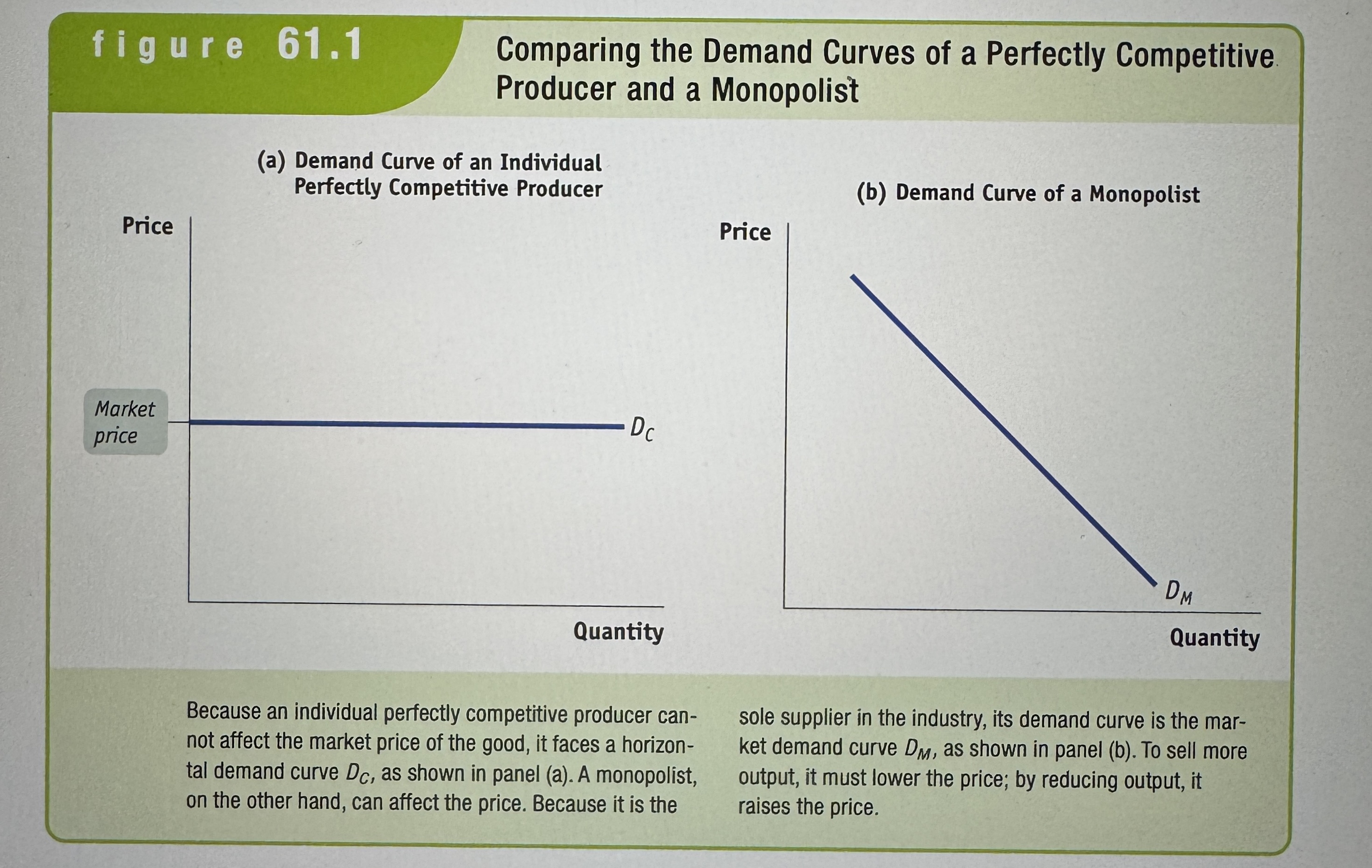
Comparing the Demand Curves of a Perfectly Competitive Producer and a Monopolist
Ex.
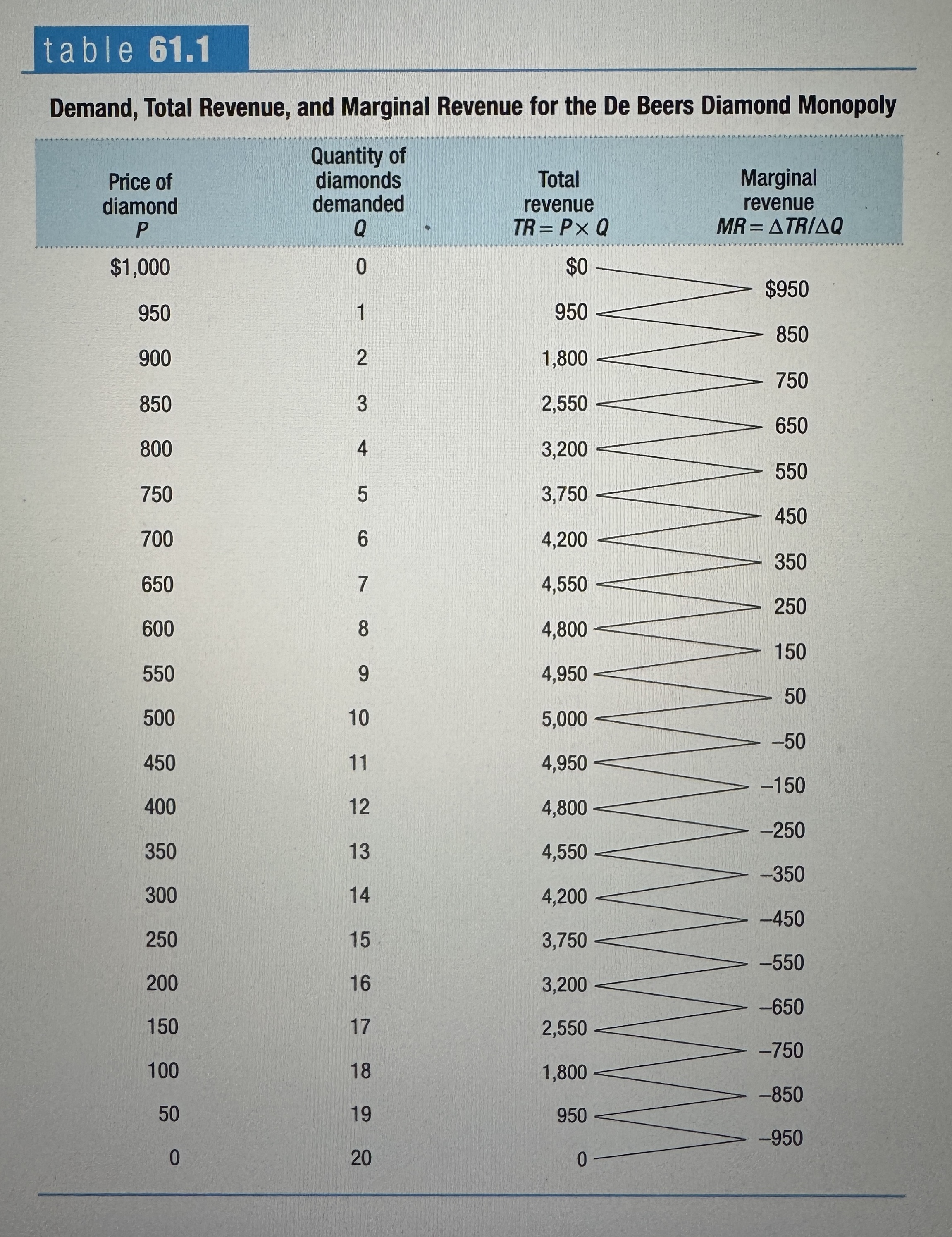
Demand, Total Revenue, and Marginal Revenue for the De Beers Diamond Monopoly
Ex.
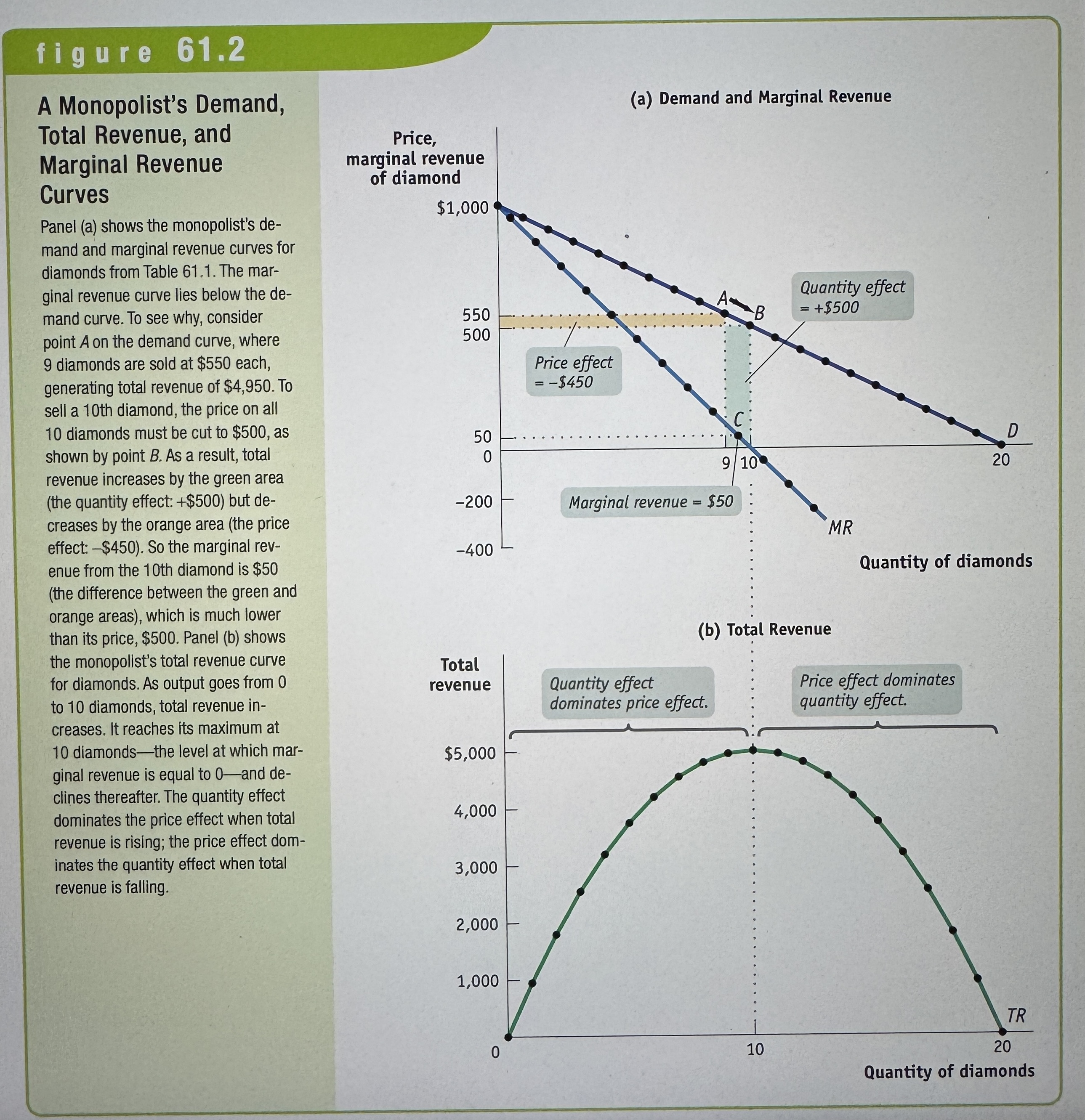
A Monopolist's Demand, Total Revenue, and Marginal Revenue Curves
Ex.
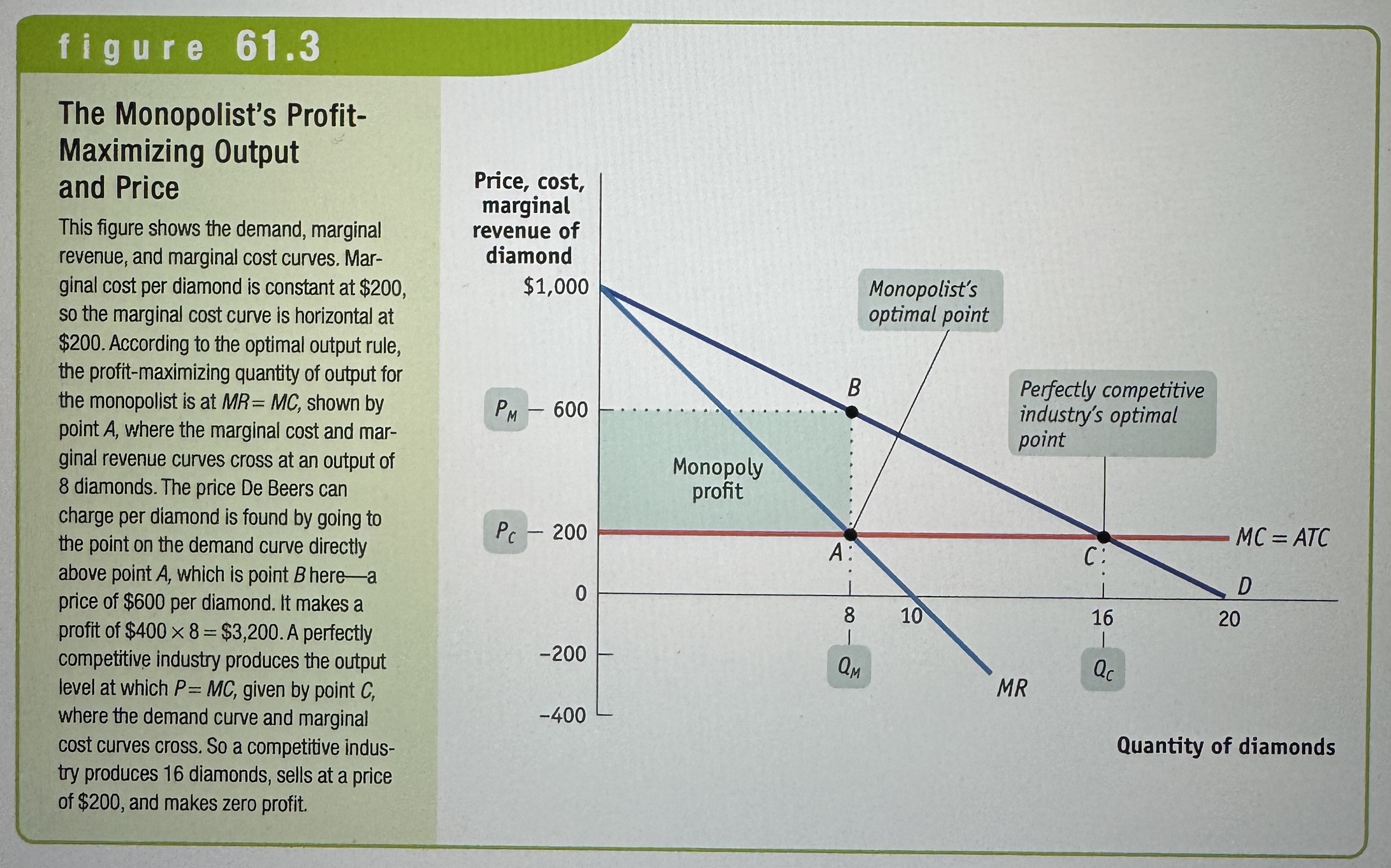
The Monopolist's Profit-Maximizing Output and Price
Ex.
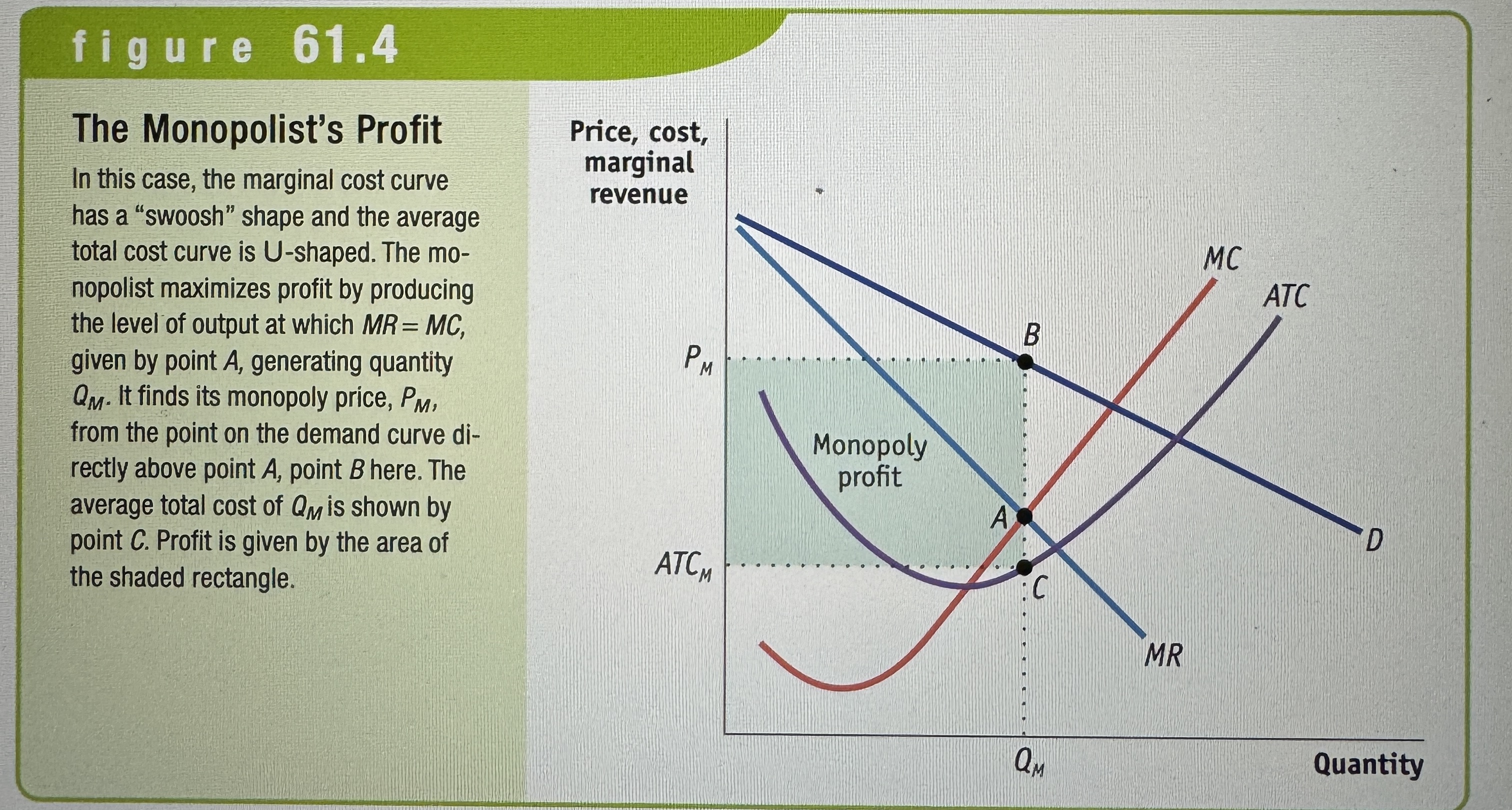
The Monopolist's Profit
Ex.
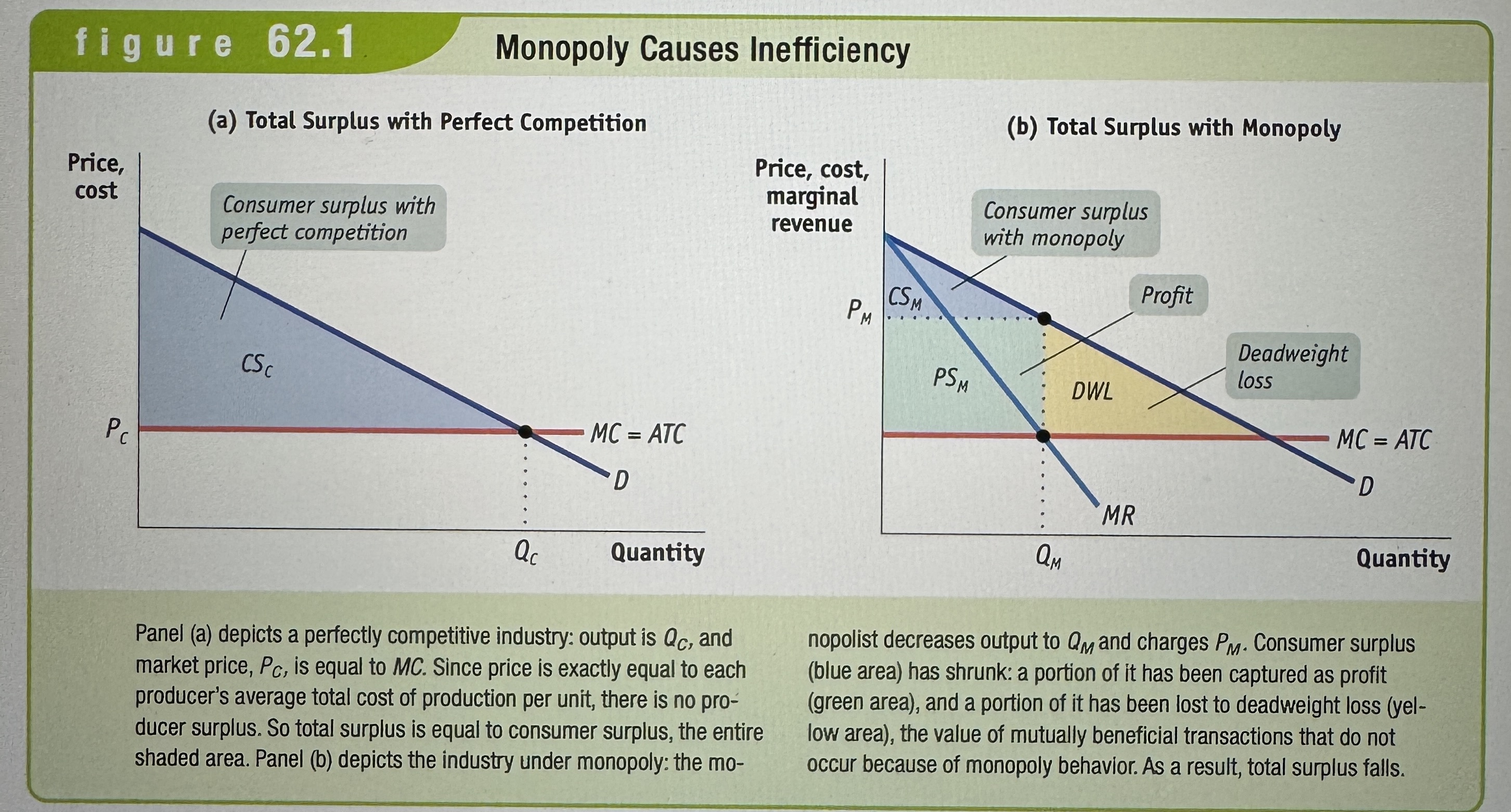
Monopoly Causes Inefficiency
Ex.
Public Ownership
In public ownership of a monopoly, the good is supplied by the government or by a firm owned by the government.
Price regulation
Limits the price that a monopolist is allowed to charge.
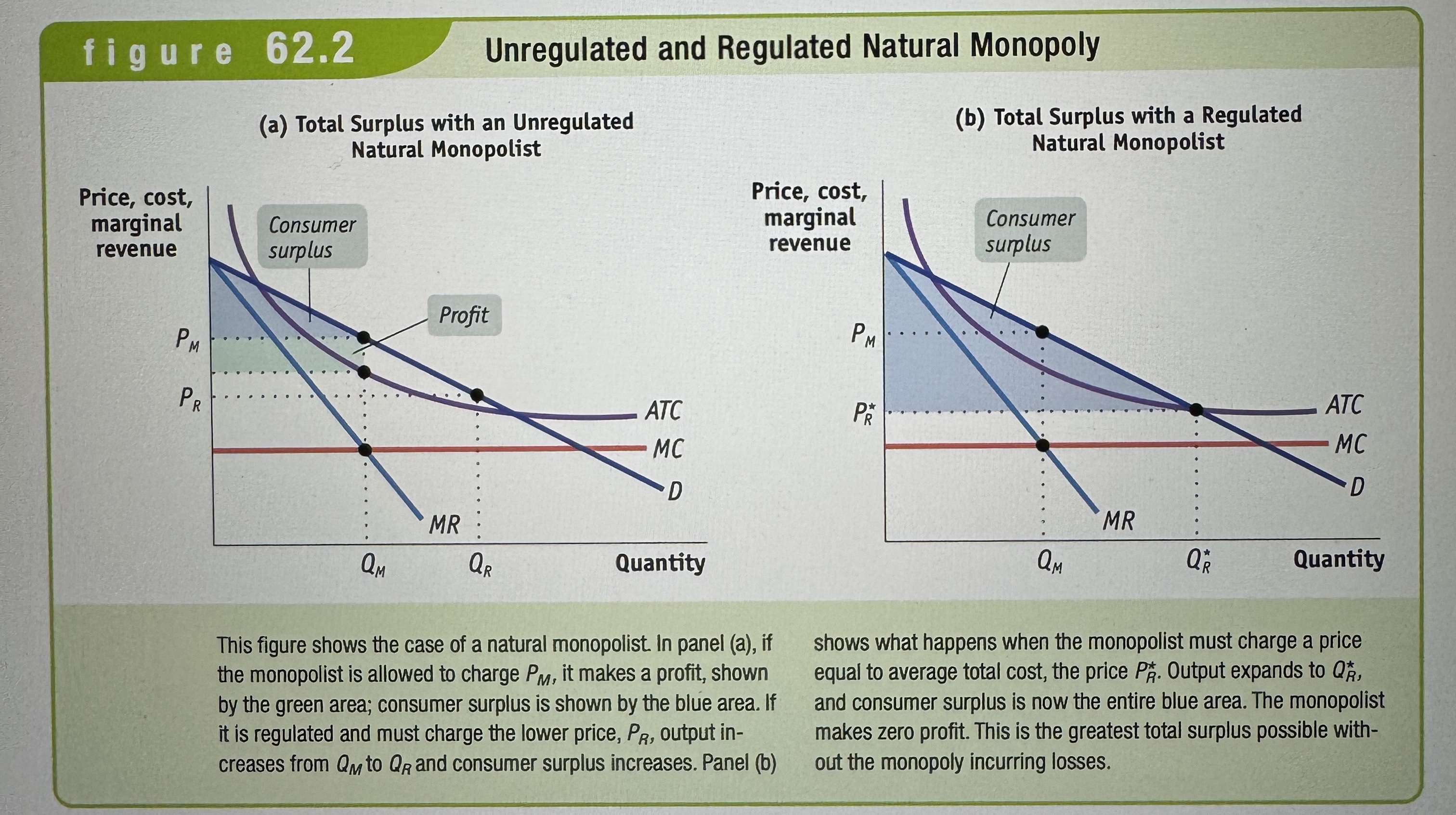
Unregulated and Regulated Natural Monopoly
Ex.
Single-price monopolist
A monopoly who charges all consumers the same price.
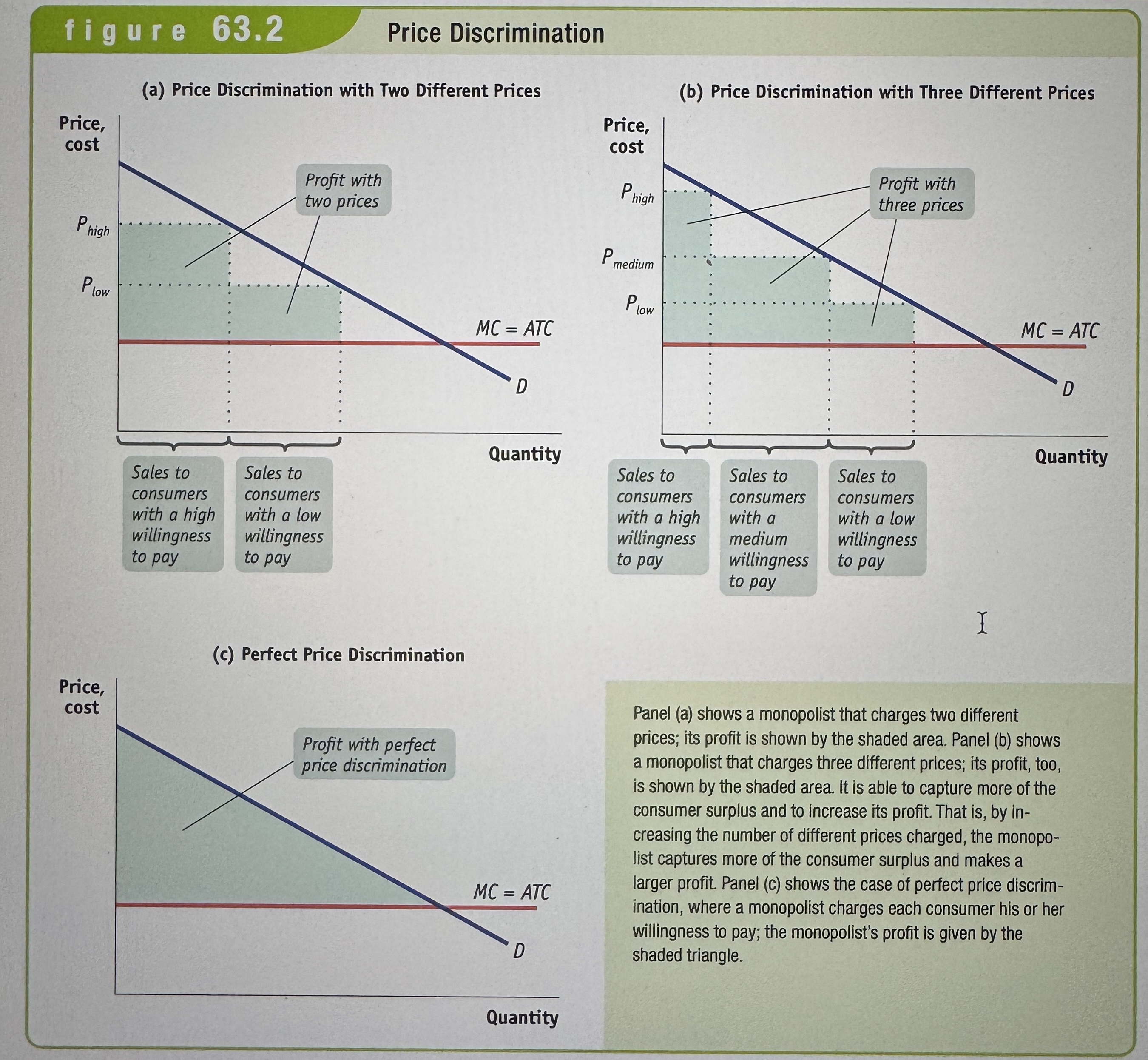
Price discrimination
This happens when sellers change different prices to different consumers for the same good.
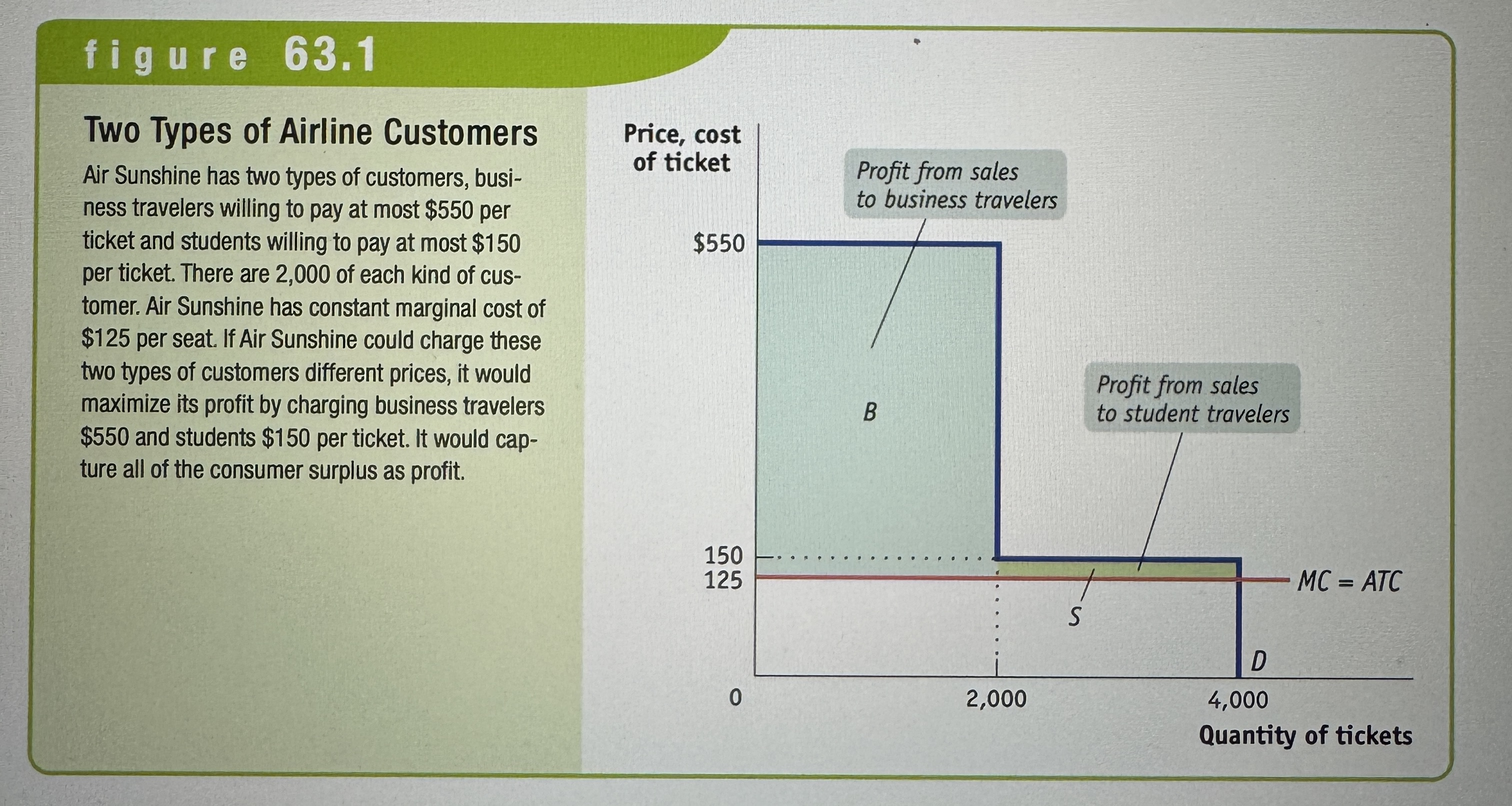
Two Types of Airline Customers
Ex.
Perfect Price Discrimination
Takes place when the monopoly charges each consumer his or her willingness to pay – the maximum that the customer is willing to pay.
Advance purchase restrictions
Prices are lower for those who purchase well in advance. This separates those who are likely to shop for better prices from those who won’t.
Volume discounts
Often the price is lower if you buy a larger quantity. For a consumer who plans to consume a lot of a good, the cost of the last unit – the marginal cost to the consumer – is considerably less than the average price.
Price Discrimination Examples
Ex.
Two-part tariffs
In a discount club like Costco or Sam’s Club you pay an annual fee in addition to the price of the items you purchase. So the full price of the first item you buy is in effect much higher than that of subsequent items.