Body Fluids Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:48 PM on 9/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
1
New cards
What is the principle of operation of most semi-automated urine dipstick readers?
Reflectance photometry
2
New cards
What is the normal pH range of urine?
4.5-8.0
3
New cards
How might starvation or vomiting affect a urine's pH? What is present in the urine to cause this change?
It may become more acidic due to the presence of ketones
4
New cards
How might a UTI or an old urine affect urine pH and why?
The pH might rise due to the production of bacterial waste products
5
New cards
What substance, when detected in urine, is most indicative of renal disease?
Protein
6
New cards
What major protein is detected up by a urine dipstick?
Albumin
7
New cards
What are Bence Jones proteins, and in what condition are they often present?
Free kappa or lambda light chains, common in multiple myeloma
8
New cards
What are small amounts of albumin in urine which might not be picked up by the dipstick called?
Microalbumin
9
New cards
What is the significance of a positive test for microalbumin?
Warning sign of renal problems, notably in diabetics
10
New cards
What is another tern for postural proteinuria?
Orthostatic
11
New cards
What are the typical protein findings in someone with postural proteinuria?
First urine upon rising: protein negative;
Urine after being upright: protein positive
Urine after being upright: protein positive
12
New cards
How will a highly alkaline urine affect the protein dipstick?
Falsely elevate
13
New cards
Other than proteins, what 2 substances can cause an SSA test to be positive?
Drugs & dyes
14
New cards
At what plasma level will glucose begin to appear in urine?
160 mg/dL
15
New cards
What 2 conditions or substances can cause a falsely decreased glucose dipstick reaction?
Ascorbic acid (Vit. C) & unpreserved samples (glycolysis)
16
New cards
On what population of patients might a Clinitest (copper reduction test) be ordered?
2-3 yrs or younger
17
New cards
A dipstick is 1+ positive for glucose, however the Clinitest is negative. With is most likely causing this combination of results?
Low levels of glucose
18
New cards
A dipstick is negative for glucose but the urine reacts strongly reactive with the Clinitest. What might be causing these results?
Galactose or another sugar besides glucose
19
New cards
What are 4 conditions that can cause the urine to be ketone positive?
Uncontrolled diabetes, starvation, prolonged vomiting or diarrhea, some diets
20
New cards
Why does leaving the cap off of a urine container cause falsely decreased ketone results?
Ketones will evaporate
21
New cards
What 3 things will cause a dipstick to be positive for blood?
Hemoglobin, myoglobin, and intact RBCs
22
New cards
What are 2 conditions that could cause the appearance of myoglobin in urine?
Heart attack or muscle injury
23
New cards
What 2 substances will cause the urine to appear clear and red/reddish-brown?
Hemoglobin & myoglobin
24
New cards
What type of bilirubin will filter through the glomerulus?
Conjugated (direct) bilirubin
25
New cards
Which urine chemical reacts with Diazo reagent?
Bilirubin
26
New cards
Where does bilirubin originate?
From the heme within RBCs
27
New cards
Which 2 urine chemicals are most sensitive to light exposure?
Bilirubin & urobilinogen
28
New cards
In what organ is urobilinogen formed?
Intestines
29
New cards
Is bilirubin or urobilinogen normally found in the the urine in small volumes?
Urobilinogen
30
New cards
What is the expected urine bilirubin and urobilinogen results in a case of bile duct obstruction?R
Bilirubin positive, urobilinogen negative
31
New cards
What is the expected urine bilirubin and urobilinogen results in a case of hemolytic anemia?
Bilirubin negative, urobilinogen positive
32
New cards
What do you see in a urine microscopic if the nitrate is positive?
Bacteria
33
New cards
Is a negative nitrite confirmation that bacteria are absent? Why or why not?
No, because not all bacteria produce nitrate
34
New cards
What 2 conditions are consistent with a positive nitrite result?
UTI & unpreserved urine
35
New cards
Other than nitrite, what other dipstick result is consistent with infection?
Leukocyte esterase
36
New cards
What is the term for the presence of WBCs in urine?
Pyuria
37
New cards
What characteristic of a substance will determine whether or not it will react with the SG portion of a dipstick?
Must be iconic in nature
38
New cards
What 3 substances will not react with the SG pad on a dipstick, but can be measured by refractive index?
Glucose, dyes, & urea
39
New cards
What type of white cells are seen in (non-bacterial) inflammation?
Lymphocytes
40
New cards
What WBCs do not react well with a dipstick?
Lymphocytes
41
New cards
What is the term for an infection within the kidney nephron?
Pyelonephritis
42
New cards
What is the term for a bladder infection?
Cystitis
43
New cards
What 2 conditions are most likely to cause the presence of bilirubin in urine?
Liver disease & bile duct obstruction
44
New cards
What would most likely be causing the dipstick to be strongly positive for glucose, but negative on the Clinitest?
Interfering substance or testing error
45
New cards
What metabolic process creates ketones?
Fat metabolism
46
New cards
What does speckling on the blood dipstick pad indicate?
Intact RBCs
47
New cards
What area of the nephron receives and filters blood?
Glomerulus within Bowman's capsule
48
New cards
Which part of the nephron is the primary site of reabsorption of essential substances?
Proximal convoluted tubule
49
New cards
What is the average amount of blood that flows through the kidneys each minute?
1200 mL/min
50
New cards
In response to a decreased blood pressure of blood volume, what hormone is secreted by the kidneys?
Renin
51
New cards
What type of arteriole feeds blood into the glomerulus?
Afferent
52
New cards
What type of arteriole feeds blood out of the glomerulus?
Efferent
53
New cards
What adrenal hormone is secreted upon stimulation by angiotensin?
Aldosterone
54
New cards
What analyte is reabsorbed under the influence of aldosterone?
Sodium
55
New cards
What is not normally allowed to filter through the glomerulus?
Cells, protein, & protein-bound substances
56
New cards
What is the normal average glomerular filtration rate?
120 mL/min
57
New cards
What is the term used to describe the level of a substance when it can no longer be absorbed by the renal tubules?
Renal threshold
58
New cards
What is the normal plasma level of glucose?
75-105 mg/dL
59
New cards
What is the normal renal threshold of glucose?
>160 mg/dL
60
New cards
What process allows unfilterable wastes to pass into the tubules for elimination?
Tubular secretion
61
New cards
The final reabsorption of water is directly under the influence of what hormone?
Antidiuretic hormone (Vasopressin)
62
New cards
What influences the secretion of ADH from the pituitary gland?
The concentration (osmolality) of the plasma
63
New cards
What triggers ADH release?
Sodium plasma increase
64
New cards
In what area of the nephron does the final concentration of urine occur?
Distal tubules/collecting ducts
65
New cards
What waste product is normally present in protein metabolism?
Urea
66
New cards
What waste product is normally present in muscle metabolism?
Creatinine
67
New cards
What waste product is normally present in purine metabolism?
Uric acid
68
New cards
What is the term for decreased urine output?
Oliguria
69
New cards
What is term for painful urination?
Dysuria
70
New cards
What is the term for no urine output?
Anuria
71
New cards
What is the cause of anuria?
Renal failure
72
New cards
What is the term for increased urine output?
Polyuria
73
New cards
What is the average normal output of urine in 24 hours?
1200 mL
74
New cards
What are 2 diseases that may cause a high volume, pale-looking urine?
Diabetes mellitus & diabetes insipidus
75
New cards
What is the most common cause of a dark yellow urine?
Dehydration
76
New cards
What would a urine containing bilirubin look like?
Brown/amber with yellow foam
77
New cards
What 2 substances will cause a clear red to reddish-brown urine?
Hemoglobin & myoglobin
78
New cards
What appearance will a urine that contains a lot of intact RBCs have?
Red & hazy/cloudy
79
New cards
What are causes of having intact RBCs in urine?
Glomerular disease, kidney/bladder trauma or infection, & menstrual contamination
80
New cards
Urine that turns brown-black upon standing might contain what 2 substances?
Melanin & homogentisic acid
81
New cards
A lot of white foam on a urine is a clue to the presence of what substance?
Protein
82
New cards
What appearance will a urine that contains certain porphyrins have?
Burgundy or port wine
83
New cards
Why must urine be mixed before determining color and clarity?
Cells & other substances may have settled to the bottom, giving the urine a clearer appearance
84
New cards
What are 3 insignificant causes of a hazy urine?
Presence of creams or powders, squamous epithelial cells, & certain crystals or sperm
85
New cards
What are significant causes of a hazy/cloudy urine?
RBCs, WBCs, certain crystals, fats, renal cells, bacteria, or other micro-organisms
86
New cards
What urine test is a reflection of the body's state of hydration?
Specific gravity
87
New cards
What is the normal range of urine specific gravity?
1.003-1.035
88
New cards
If a patient is severely dehydrated, would the SG be higher or lower?
Higher
89
New cards
What SG reading (when measured at various times) is consistent with the kidneys inability to concentrate urine?
1.010
90
New cards
What term describes the angle of light as it passes through a urine sample?
Refractive index
91
New cards
What property will increase the angle in refractive index?
Density
92
New cards
If a urine was diluted 1:4 and the SG read 1.012, what is the SG of the undiluted urine?
1.048 (.012 x 4)
93
New cards
What could cause an elevated refractive index?
Proteins, glucose, dehydration, dyes, or IV solutions
94
New cards
Renal anatomy
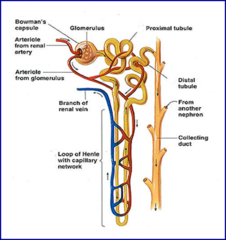
95
New cards
What process leads to the formation of bilirubin?
Red cell lysis
96
New cards
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
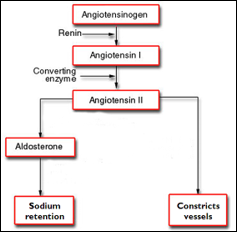
97
New cards
Anti-diuretic hormone release
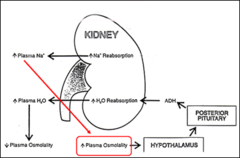
98
New cards
What gives urine its yellow color?
Urochrome
99
New cards
What gives urine an amber color?
Bilirubin
100
New cards
What gives urine an orange color?
Pyridium