CAPE Chemistry Module 1: 2022-2011
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:02 PM on 5/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
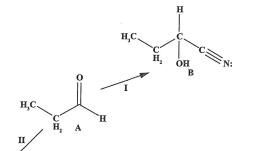
State the reagents and condition for the reaction (2022)
NaCN/HCl, room temperature
2
New cards
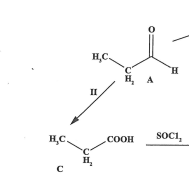
State the reagents and conditions for the reaction (2022)
H+/potassium dichromate, heat
3
New cards
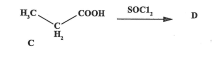
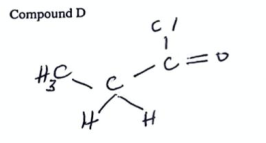
State the name of compound D (2022)
propanoyl chloride
4
New cards
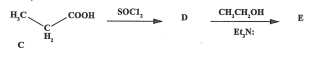
State the name of compound E (2022)
propanoyl chloride
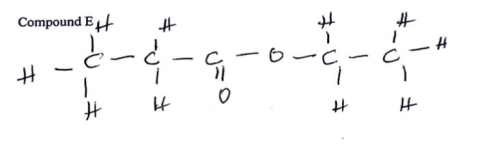
5
New cards
Account for the fact that pKb of phenylamine is greater than ethylamine (2022)
* higher pKb indicating a weaker base.
* ethylamine is stronger base than phenylamine
* electron-withdrawing effect of the phenyl group in phenylamine → decreased availability of the lone pair of nitrogen atom to act as a proton acceptor; reducing its electron density
* ethylamine lacks this electron-withdrawing group→ lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more available for protonation
* ethylamine is stronger base than phenylamine
* electron-withdrawing effect of the phenyl group in phenylamine → decreased availability of the lone pair of nitrogen atom to act as a proton acceptor; reducing its electron density
* ethylamine lacks this electron-withdrawing group→ lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom is more available for protonation

6
New cards
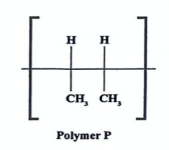
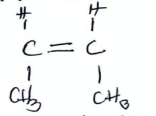
State the name of monomer involved and type of polymerization (2022)
prop-2-ene
Addition polymerization
Addition polymerization
7
New cards
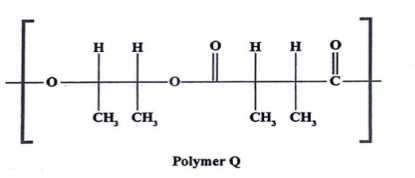
State the type of polymerization and the monomers involved (2022)
* 1,2-dimetyleth-1,2-diol and
* condensation polymerzation
* condensation polymerzation
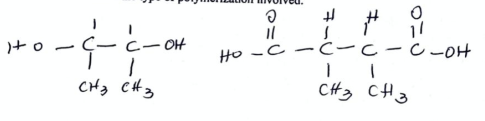
8
New cards
identify a compound which in aqueous solution wil break down polymer Q but not polymer P (2022)
* HCl
* H2SO4
* NaOH
* H2SO4
* NaOH
9
New cards
define structural isomerism (2021)
same molecular formula but different structural formula (connection of atoms)
10
New cards
Define each type of structural isomerism (2021)
* Chain isomerism: carbon skeleton of the molecule differs between isomers
* Position isomerism: the functional group or substituent on the carbon chain is located at different positions in the molecule.
* Functional group isomerism: molecules have different functional groups, leading to different chemical properties.
* Position isomerism: the functional group or substituent on the carbon chain is located at different positions in the molecule.
* Functional group isomerism: molecules have different functional groups, leading to different chemical properties.
11
New cards
State the reaction mechanism for: halogenation of alkane (2021)
Free Radical substitution.
12
New cards
State the reaction mechanism for alkene + HBr (2021)
electrophilic addition
13
New cards
Describe the observation of: aqueous bromine + pentane in sunlight (2021)
red/brown to colourless; Br decolorizes
14
New cards
Describe the observation of: aqueous bromine + pentane without sunlight (2021)
remains brown; no reaction
15
New cards
Describe the observation of: cold acidified potassium manganate + pentane (2021)
purple to colourless
16
New cards
State the reaction mechanism and type of reaction for halohexane + NaOH → alcohol. (2019)
Mechanism: nucleophilic substitution
type: oxidation reaction
type: oxidation reaction
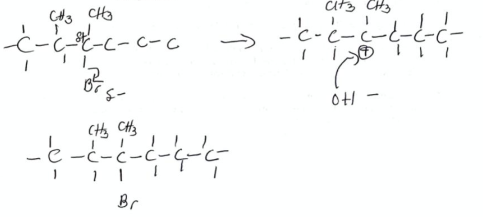
17
New cards
State reagents and conditions for nitration of benzene (2019)
REAGENTS: conc H2SO4, conc HNO3
CONDITION: 50C
CONDITION: 50C
18
New cards
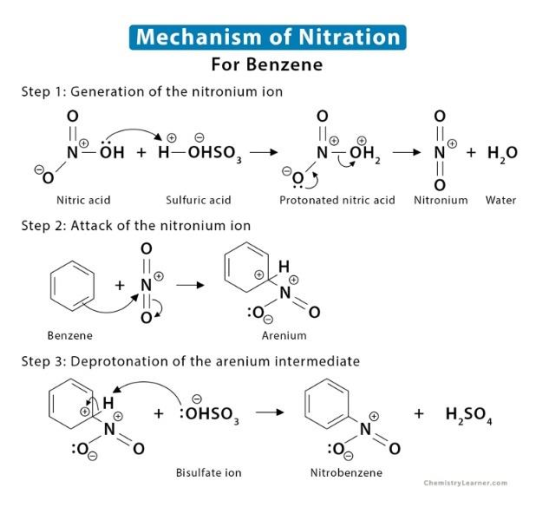
Outline the mechanism of benzene to nitrobenzene (2019)
* Mechanism: electrophilic substitution
* Generate NO2 (nitronium) by taking H from H2SO4 and releasing water
* Attack of nitronium by benzene pi bond.
* H on benzene removed by OHSO3
* nitrobenzene formed; H2SO4 reformed
* Generate NO2 (nitronium) by taking H from H2SO4 and releasing water
* Attack of nitronium by benzene pi bond.
* H on benzene removed by OHSO3
* nitrobenzene formed; H2SO4 reformed
19
New cards
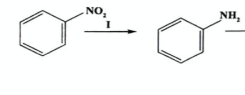
State the Reagents and conditions of reduction of nitrobenzene (2019)
REAGENTS: Sn/HCl
CONDITIONS: reflux, heat
CONDITIONS: reflux, heat
20
New cards
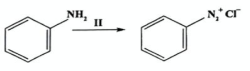
State reagents and conditions for diazotization (2019)
Reagents: NaNO2, HCl
Conditions: 0-5C
Conditions: 0-5C
21
New cards
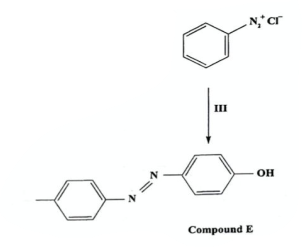
State reagents, condition and name of reaction (2019)
Name of reaction: Coupling (with Diazonium Salt)
Reagents: NaOH
Conditions: 0-5C
Reagents: NaOH
Conditions: 0-5C
22
New cards
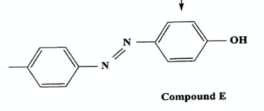
Name the class of compounds, and a use (2019)
azo compounds, used as dyes
23
New cards
Using ethylamine, explain “All amines are weak bases, and aqueous solutions of amines are basic” (2019)
* Amines have a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom
* lone pair allows accepting of proton
* lone pair allows accepting of proton
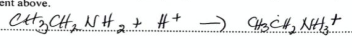
24
New cards
The pKb values of ethanamide, ethylamine, and phenylamine are 14.51, 3.27 and 9.38. Account for the differences (2019) \[4mks\]
* ethanamide (14.51) is weakest base
* ethylamine is strongest base
* phenylamine is middle
* smaller the pKb, the stronger the base
\
*Ethanamide*
* has a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to the nitrogen atom.
* C=O, electron-withdrawing group, reduces the availability of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom
* resonance stabilization of the C=O bond; delocalizes the electron density away from the nitrogen atom.
\
*Ethylamine*
* ethyl group attached to the nitrogen atom
* electron-donating group increases the availability of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom
\
*Phenylamine*
* phenyl group attached to the nitrogen atom
* electron-donating group and increases the availability of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom
* some e- delocalizes around benzene ring
* ethylamine is strongest base
* phenylamine is middle
* smaller the pKb, the stronger the base
\
*Ethanamide*
* has a carbonyl group (C=O) attached to the nitrogen atom.
* C=O, electron-withdrawing group, reduces the availability of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom
* resonance stabilization of the C=O bond; delocalizes the electron density away from the nitrogen atom.
\
*Ethylamine*
* ethyl group attached to the nitrogen atom
* electron-donating group increases the availability of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom
\
*Phenylamine*
* phenyl group attached to the nitrogen atom
* electron-donating group and increases the availability of the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom
* some e- delocalizes around benzene ring
25
New cards
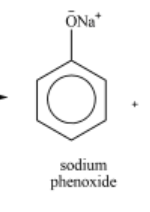
State the reagents and observation for phenol to sodium phenoxiate ion (2019)
REAGENTS: NaOH
OBSERVATION: raise in temp
OBSERVATION: raise in temp
26
New cards
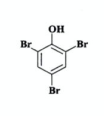
State reagents and observations for phenol to following compound(2019)
REAGENTS: aqueous Bromine
OBSERVATIONS: brown to colourless; white ppt
OBSERVATIONS: brown to colourless; white ppt
27
New cards
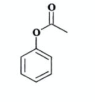
State reagent for phenol to organic ester
acyl halide ( acid halide )
28
New cards
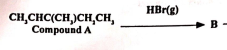
State the reaction mechanism for B to occur, and the class of compounds to which B belongs. Note A: 3-methylpent-2-ene (2019)
Mechanism: electrophilic addition
B: haloalkane
B: haloalkane
29
New cards
Given that compound B is 3-bromo-3methylpentane, identify the reaction mechanism leading to C. Also identify the class of compounds that C belongs (2019)
Mechanism: nucleophilic substitution
C: alcohols
C: alcohols
30
New cards
State 3 characteristics of homologous series (2017(
* Same functional group
* Similar chemical properties
* Gradation in physical properties: Members of a homologous series exhibit a gradation in their physical properties such as boiling points, melting points, density, and solubility. This is because as the molecular weight increases, the intermolecular forces between the molecules also increase.
* Same general formula
* Increase in molecular size: Compounds in a homologous series have a gradual increase in molecular size as the number of carbon atoms in the molecule increases.
* Similar chemical properties
* Gradation in physical properties: Members of a homologous series exhibit a gradation in their physical properties such as boiling points, melting points, density, and solubility. This is because as the molecular weight increases, the intermolecular forces between the molecules also increase.
* Same general formula
* Increase in molecular size: Compounds in a homologous series have a gradual increase in molecular size as the number of carbon atoms in the molecule increases.
31
New cards
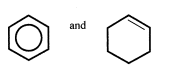
Describe an experiment to distinguish between the compound(2017)
Reaction with bromine:
Benzene: remains brown
cyclic hexene: brown to colourless.
Benzene: remains brown
cyclic hexene: brown to colourless.
32
New cards
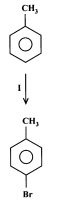
State the type of reaction, reagents and conditions
Type: Bromination/Halogenation
Reagents: Br2
Condition: Fe3+ or Al3+ catalyst
Reagents: Br2
Condition: Fe3+ or Al3+ catalyst
33
New cards

State observation of carboxylic acid + SOCl2, and the products (2014)
PRODUCTS: acid chloride, SO2, HCl
OBSERVATIONS:
* bubbling and heat generation
* pungent smell from HCl
* colourless to yellow
OBSERVATIONS:
* bubbling and heat generation
* pungent smell from HCl
* colourless to yellow
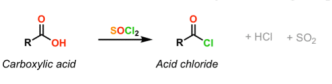
34
New cards

State the observations of C-I bond and silver nitrate (2014)
* yellow ppt (of AgI)
35
New cards

State observation of bromination of phenol (2014)
* brown to colourless
36
New cards

State observation of halogentaion( bromine) of alkene (2014)
* brown to colourless
37
New cards
State the reaction mechanism for bromoalkane refluxed in aqueous sodium hydroxide. (2014)
nucleophilic substitution
38
New cards
State the products, mechanism of bromoalkane refluxed in NaOH (2014)
PRODUCTS: alcohol and NaBr
Mechanism: nucleophilic substitution
Mechanism: nucleophilic substitution
39
New cards
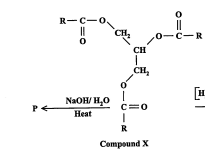
State the products of P, type of reaction and a use of the non-alcoholic product (2013)
Type of Reaction: Alkaline Hydrolysis (Saponification)
Products: glycerol \[ C3H5(OH)3 \], soap (acid salt)
Use of soap: cleaning purposes
Products: glycerol \[ C3H5(OH)3 \], soap (acid salt)
Use of soap: cleaning purposes
40
New cards
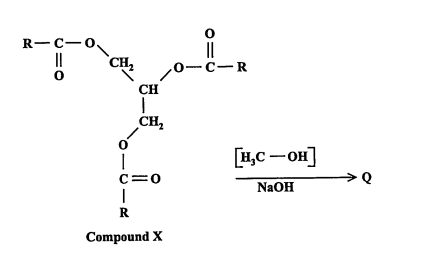
State the products of P, the type of reaction and a use of the non-alcoholic product formed. (2013)
Type of Reaction: transesterification
Products: acyl ester and glycerol
Use of acyl ester: biodiesel
Products: acyl ester and glycerol
Use of acyl ester: biodiesel
41
New cards
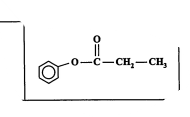
State the reagent to form the product below (2013)
Reagent: acyl halide \[ halogenated carbonyls \],
42
New cards
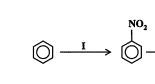
State the reagents, conditions, type and mechanism of reaction. (2013)
Reagents: conc H2SO4. conc HNO3
Conditions: 50C
Type: substitution or nitration
Mechanism: electrophilic substitution
Conditions: 50C
Type: substitution or nitration
Mechanism: electrophilic substitution
43
New cards
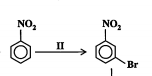
State the reagents, conditions, type and mechanism of reaction. (2013)
Reagents: Br2
Conditions: Fe3+ or Al3+ catalyst
Type: substitution or nitration
Mechanism: electrophilic substitution
Conditions: Fe3+ or Al3+ catalyst
Type: substitution or nitration
Mechanism: electrophilic substitution
44
New cards
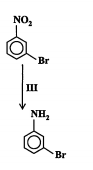
State the reagents, conditions and type of reaction. (2013)
Reagents: Sn/conc HCl, treated w/ NaOH
Conditions: heat, reflux
Type: reduction
Conditions: heat, reflux
Type: reduction
45
New cards
Arrange benzene, methylbenzene and nitrobenzene in order of reactivity with halogen. Justify your answer. (2013)
ORDER: methylbenzene > benzene > nitrobenzene
\
*methylbenzene*
* presence of a methyl group (-CH3) which is an electron-donating group.
* methyl group increases the electron density of the ring
* makes it more nucleophilic
\
*benzene*
* presence of only the delocalized pi-electrons
\
*nitrobenzene*
* nitro group (-NO2) is an electron-withdrawing group
* nitro group reduces the electron density of the ring
* less nucleophilic and less reactive
\
*methylbenzene*
* presence of a methyl group (-CH3) which is an electron-donating group.
* methyl group increases the electron density of the ring
* makes it more nucleophilic
\
*benzene*
* presence of only the delocalized pi-electrons
\
*nitrobenzene*
* nitro group (-NO2) is an electron-withdrawing group
* nitro group reduces the electron density of the ring
* less nucleophilic and less reactive
46
New cards
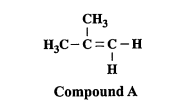
State the class of compounds formed with cold & hot H+/KMnO4 (2013)
Cold: alcohol (diol)
Hot: methanal → methanoic acid → CO2 + H2O
Hot: methanal → methanoic acid → CO2 + H2O
47
New cards
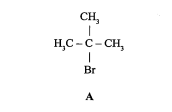
State the reaction mechanism for compound + NaOH (2011)
nucleophilic substitution
48
New cards
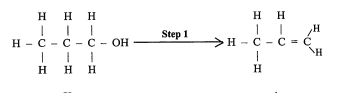
State the reagents and condition used. (2011)
conc H2SO4, 180C
49
New cards
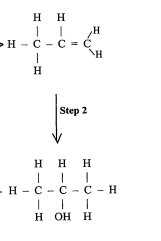
State the reagents and conditions (2011)
REAGENTS: conc H2SO4, water
CONDITIONS: heat
CONDITIONS: heat
50
New cards
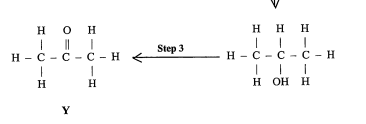
State the reagent and type of reaction.
REAGENT: any oxidizing agent
Type: Oxidation
Type: Oxidation
51
New cards
Explain the difference in acidity of alcohols, phenol and carboxylic acids. (Include acid strength, inductive and conjugative effects ) (2011) \[5mks\]
*Alcohols*
* weak acidity
* oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group is highly electronegative
* C-O bond is polarized towards oxygen.
* The oxygen atom withdraw electron density from the carbon atom through inductive effects, which weakens the O-H bond and makes it less acidic.
*Phenols*
* more acidic than alcohols
* hydroxyl group is directly attached to an aromatic ring, which stabilizes the resulting phenoxide anion through resonance.
* The phenoxide anion has a delocalized negative charge over the aromatic ring
* The presence of the aromatic ring provides additional resonance stabilization through the conjugative effect.
*Carboxylic acids*
* most acidic
* presence of the carboxyl group (-COOH).
* carbonyl group is highly polarized, and the oxygen atom withdraws electron density from the adjacent carbon atom through the inductive effect, making the C-O bond more polar and weakening the O-H bond.
* The carboxylate anion is also stabilized through resonance, where the negative charge is delocalized over both oxygen atoms and the adjacent carbon atom.
* weak acidity
* oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group is highly electronegative
* C-O bond is polarized towards oxygen.
* The oxygen atom withdraw electron density from the carbon atom through inductive effects, which weakens the O-H bond and makes it less acidic.
*Phenols*
* more acidic than alcohols
* hydroxyl group is directly attached to an aromatic ring, which stabilizes the resulting phenoxide anion through resonance.
* The phenoxide anion has a delocalized negative charge over the aromatic ring
* The presence of the aromatic ring provides additional resonance stabilization through the conjugative effect.
*Carboxylic acids*
* most acidic
* presence of the carboxyl group (-COOH).
* carbonyl group is highly polarized, and the oxygen atom withdraws electron density from the adjacent carbon atom through the inductive effect, making the C-O bond more polar and weakening the O-H bond.
* The carboxylate anion is also stabilized through resonance, where the negative charge is delocalized over both oxygen atoms and the adjacent carbon atom.