Tundra Biome
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

30 Terms
The climate both wet and dry
The Tundra
Arctic & Alpine
The Two Major Tundras
Arctic
is located in the far north.
Alpine
is found in mountainous areas above tree line
Abiotic factors of the arctic tundra
Extremely low temperatures (-70 to a summer high in the 70s or 80s)
Very short growing season (from 3 weeks in some areas to 6 weeks in others)
Light for half the year while dark the other half. The constant sunshine in the summer does cause some plants to thrive even though the growing season is short.
Low precipitation - could be considered a desert if it had a warmer temperature.
Elevation & Altitude
This diagram explains the connection between
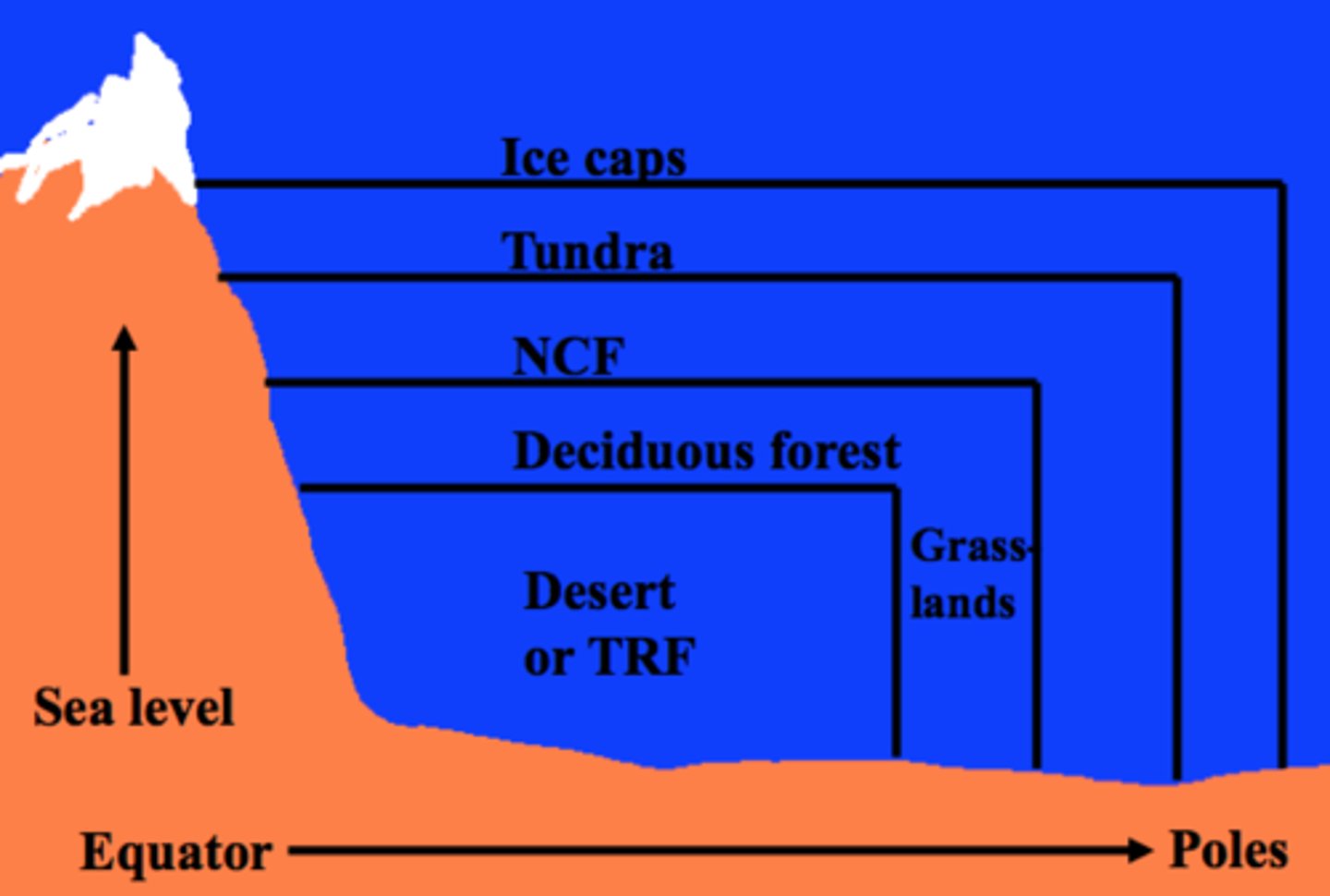
Tundra Biome
is basically a grassland with no dominant species
Tundra plant species
must be adapted for dry conditions as well as freezing cold.
permafrost
is permanently frozen soil
Permafrost prevents
water from soaking into the ground
Mammals of the tundra
Arctic wolf
Tundra grizzly bear
Arctic fox
Caribou
Fish of the tundra
Arctic char
Salmon
Grayling
Birds of the tundra
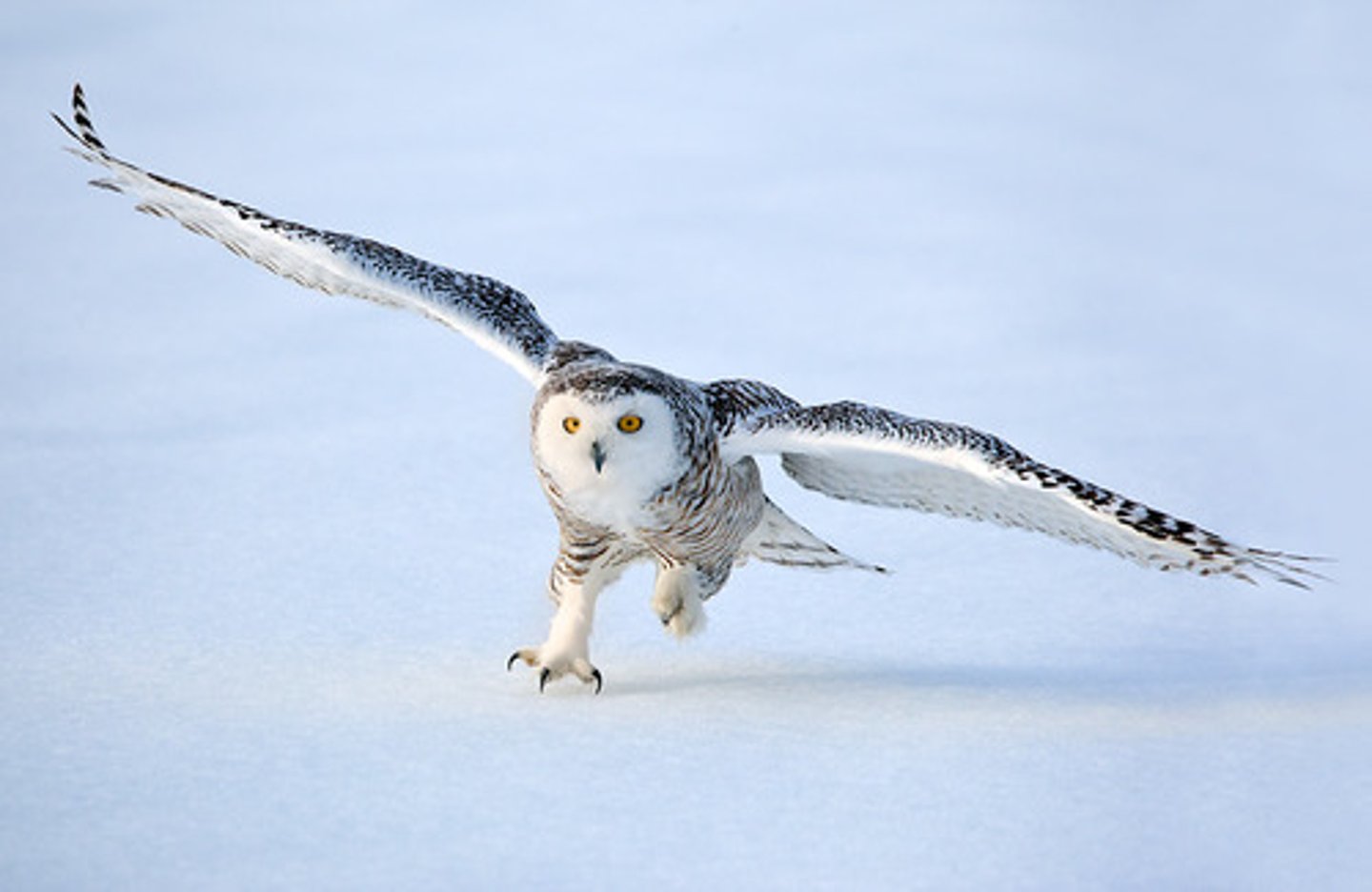
Snowy owl
Willow ptarmigan
Buntings
Organisms not found in the tundra
There are no reptiles and amphibians found in the arctic tundra,
All Vegetation in the tundra is
low to the ground. There are no proper trees
Animal adaptations to the tundra
Insulation
Bergman's law
Polar whiteness syndrome
Animal Biotic Factors
Huddle in groups
Seek shelter
Curl up in a ball to reduce surface area exposed to cold.
Hibernation
is not very prominent. Bears are not true hibernators.
Migration
is very prominent (leave the area) - caribou, water fowl, with carnivores following the herds.
Plant's 2 major problems
the cold and drying out
Plant adaptations
Short and bunched together - keeps them out of the wind.
99% of plants are annual - don't have to waste time each year starting over.
Ephemerals - plants that grow quickly when the conditions are right, spend harsh times of the year as seeds, or dormant.
Insulation
Bergmans law
Polar whiteness syndrome
This owl demonstrates all three of these traits

Average Yearly Precipitation
6 to 10 inches.
Average Yearly Range Temperature
-30 F in winter and 37-54 F in summer.
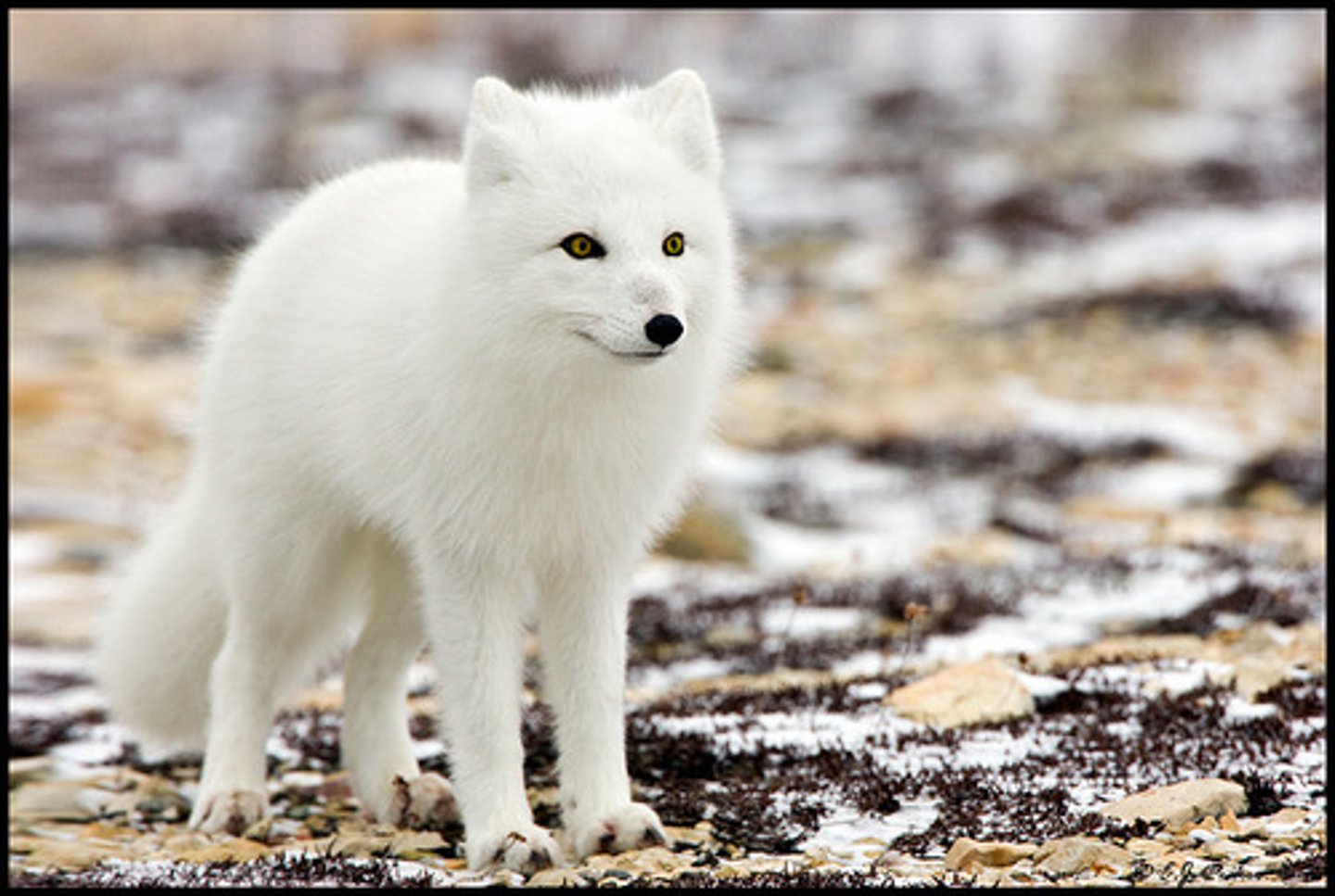
Arctic Fox
Has a long and bushy tail for warmth, their feet are lined with fur to conserve heat.

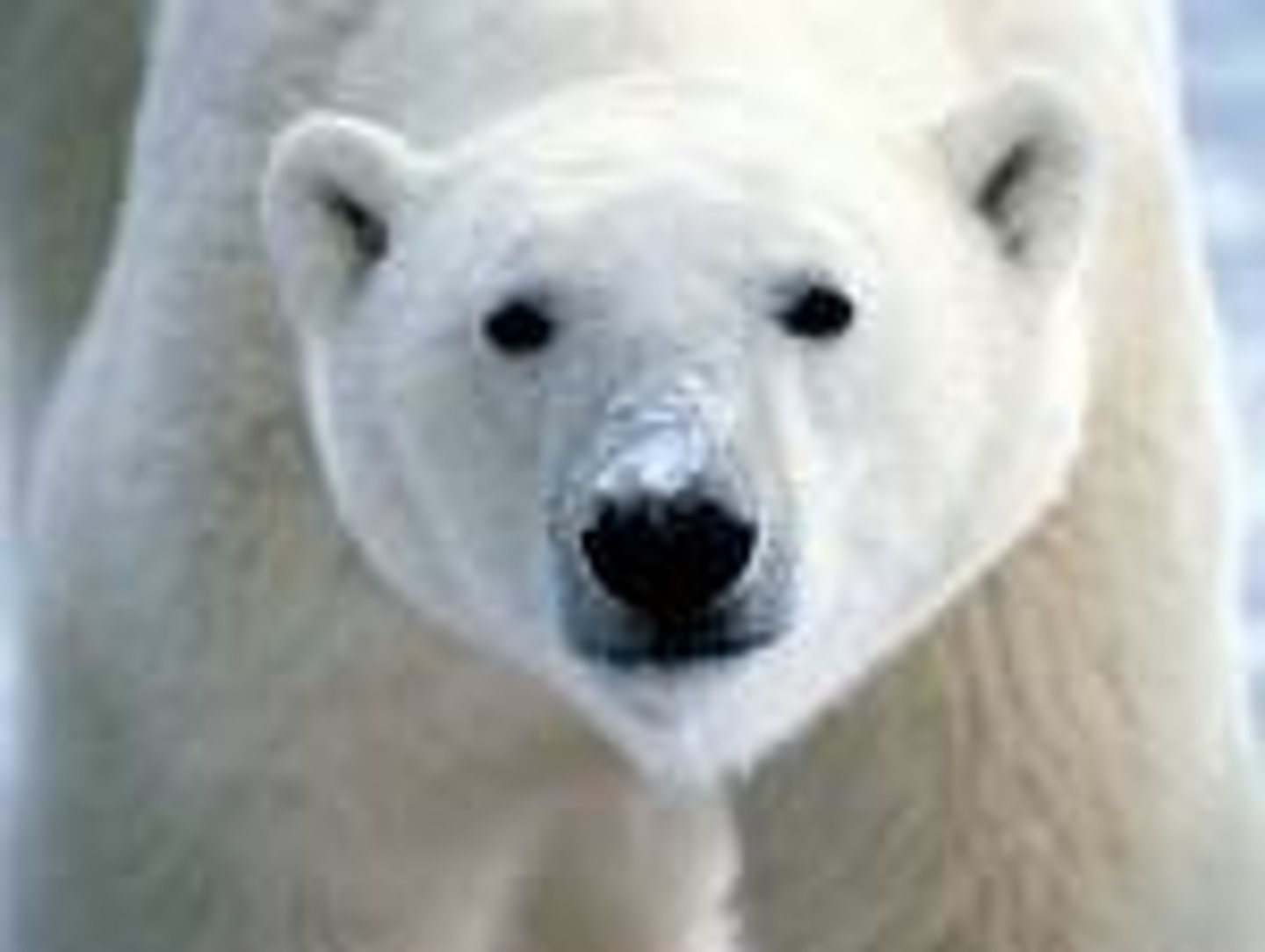
Polar Bear
Thick layer of blubber, hallow shafts of their hair provide insulation, short ears and tail reduces heat loss, long necks so their heads stay above water when swimming.

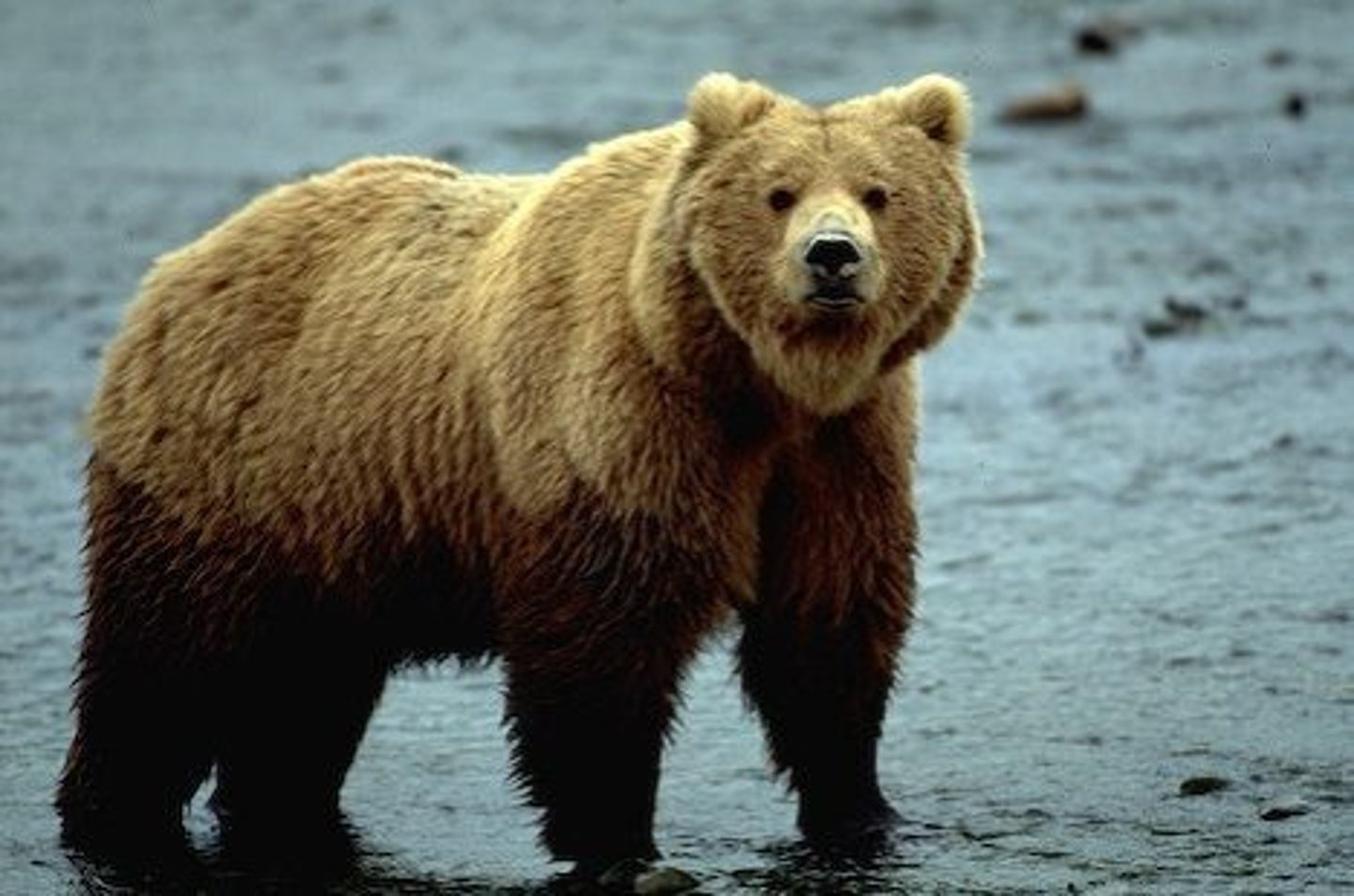
Grizzly Bear
Thick coat with layers of fat and they hibernate.

Insulation
Material used to restrict the flow of heat, cold, or sound from one surface to another.
Bergman's law
farther from the equator, the larger the body size
Polar whiteness syndrome
change to white color in winter. Adds camouflage as well as warmth. White fur and feathers are better insulators and white radiates less heat.