BP - F2024 - Nervous System
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
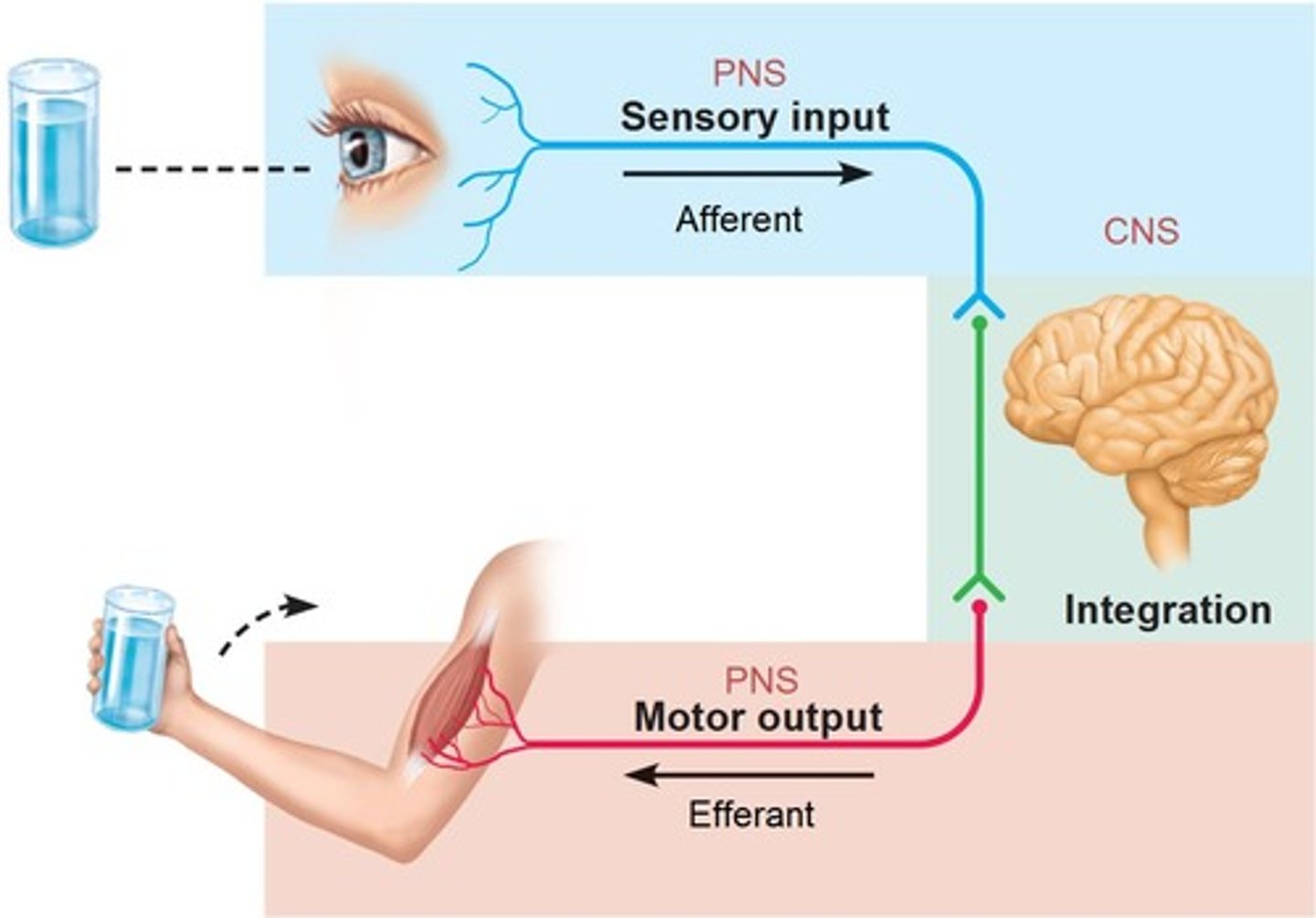
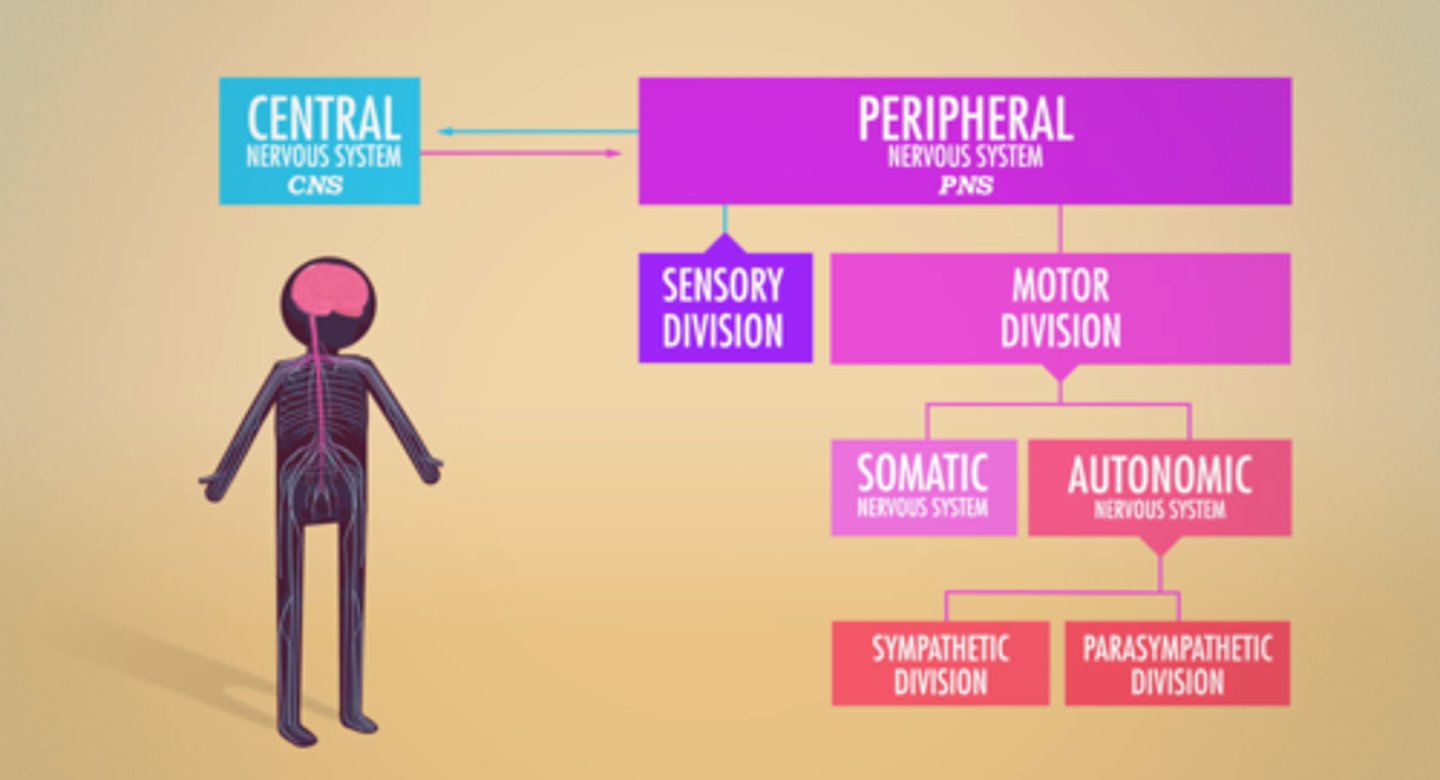
Central Nervous System
consists of brain and spinal cord; processes and responds to all messages from PNS
Spinal cord
bundle of nerves; extension of brain stem
Brain stem
nerve connections of motor and sensory systems from the rest of the body pass through this; includes midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
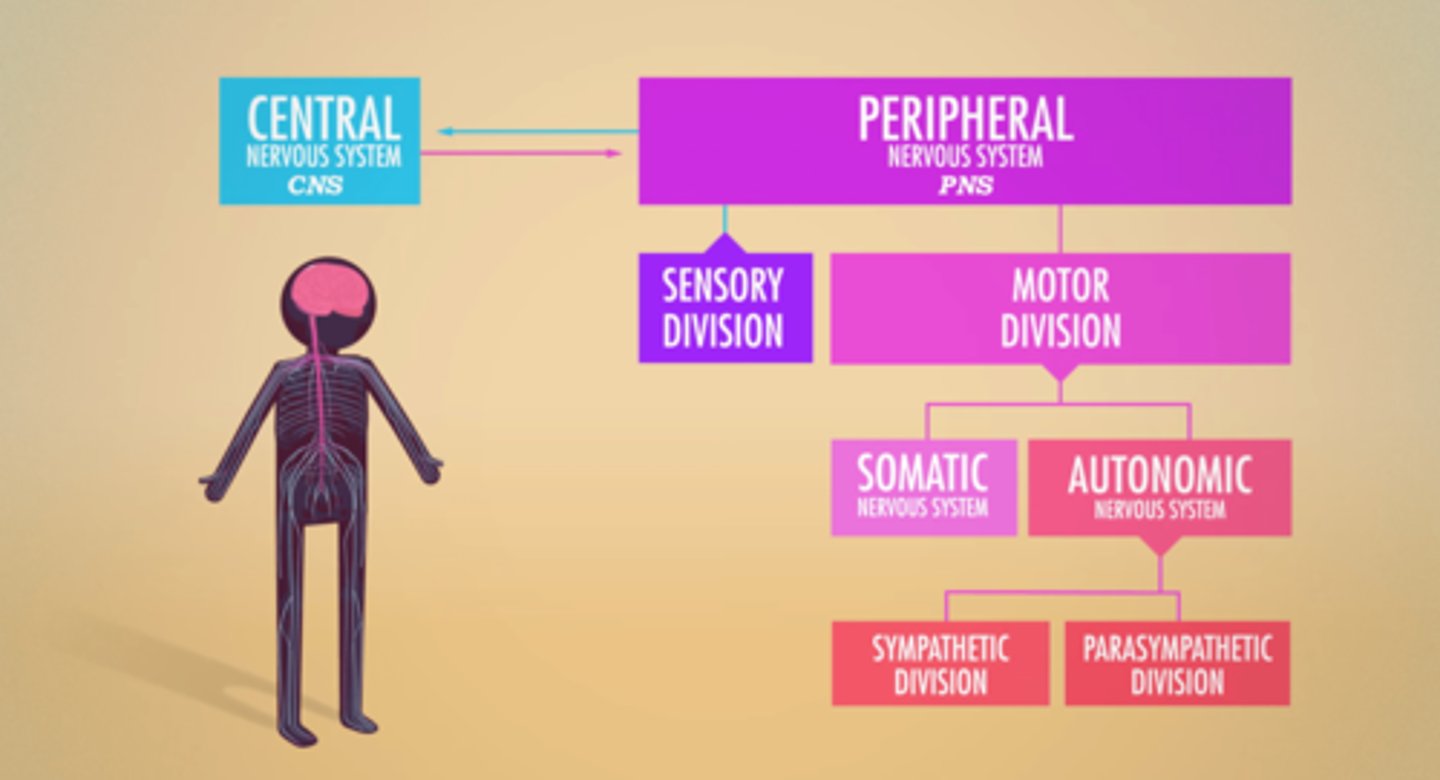
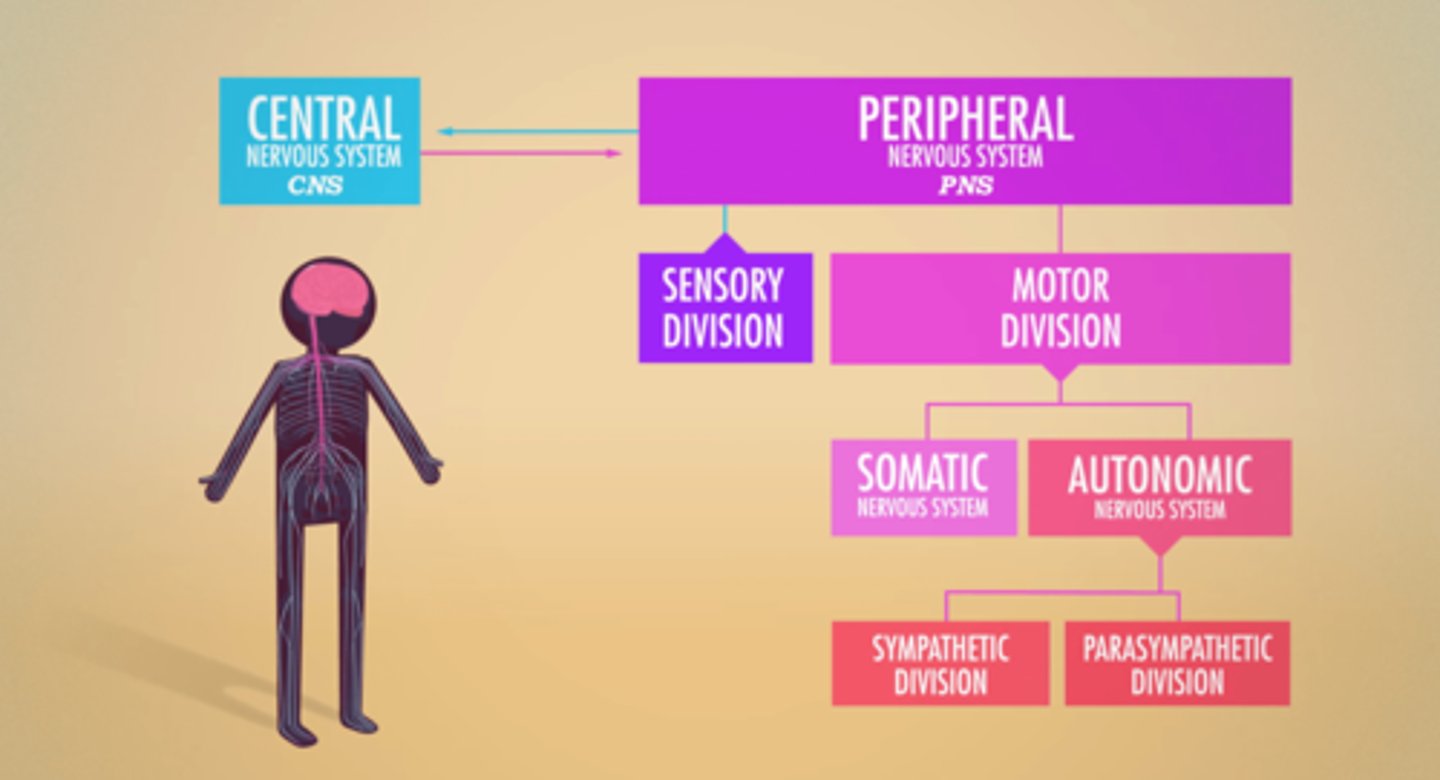
Peripheral Nervous System
allows the brain and spinal cord to receive and send information to other areas of the body which allows us to react to stimuli in our environment
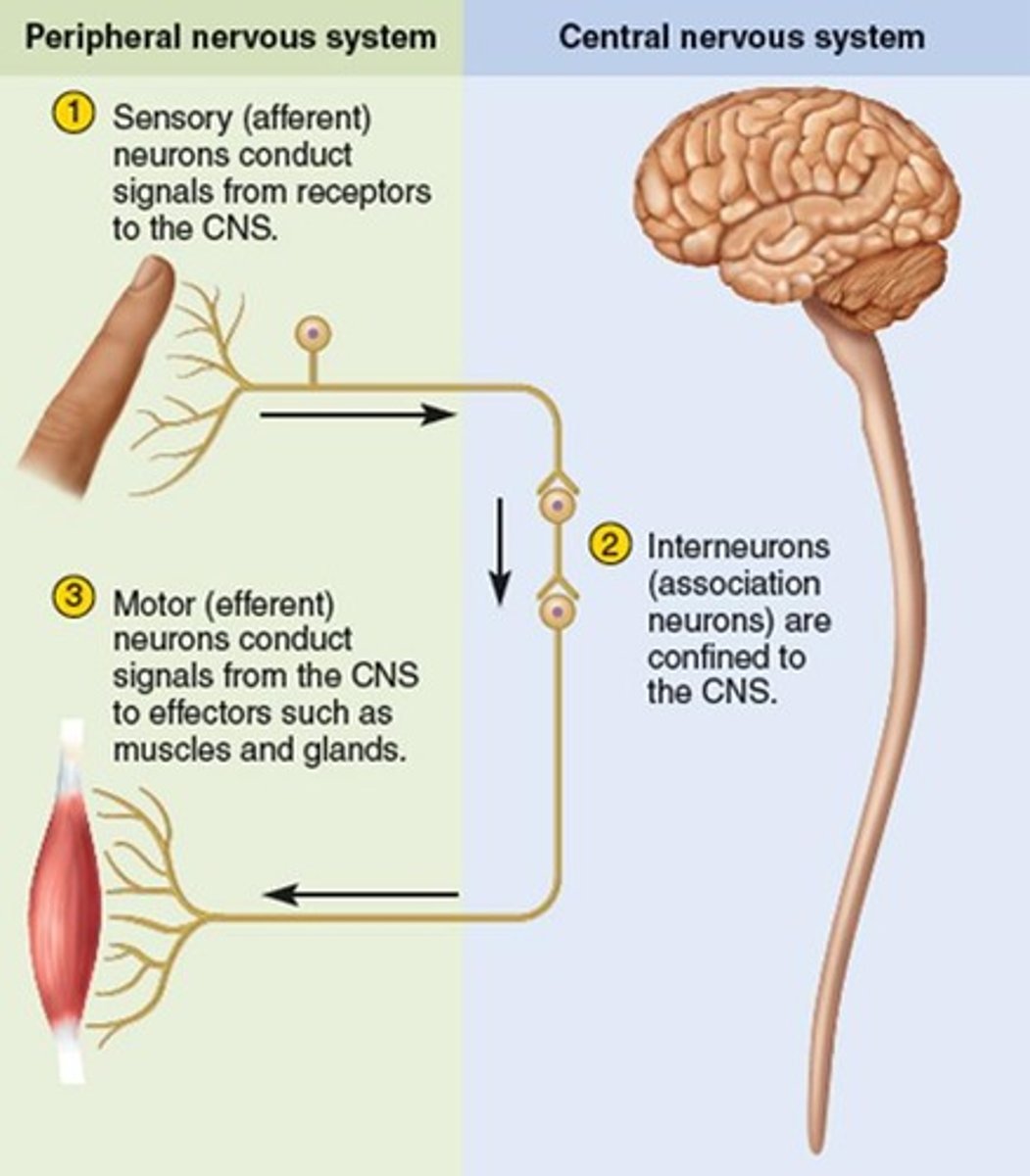
Sensory Division
made up of afferent neurons that conduct impulses to the CNS from receptors that detect changes inside and outside the body; these include receptors for touch, smell, taste, hearing, sight, pain, body position (proprioception), and receptors in the viscera (internal organs) that indicate bladder fullness, stomach aches, blood pressure and more
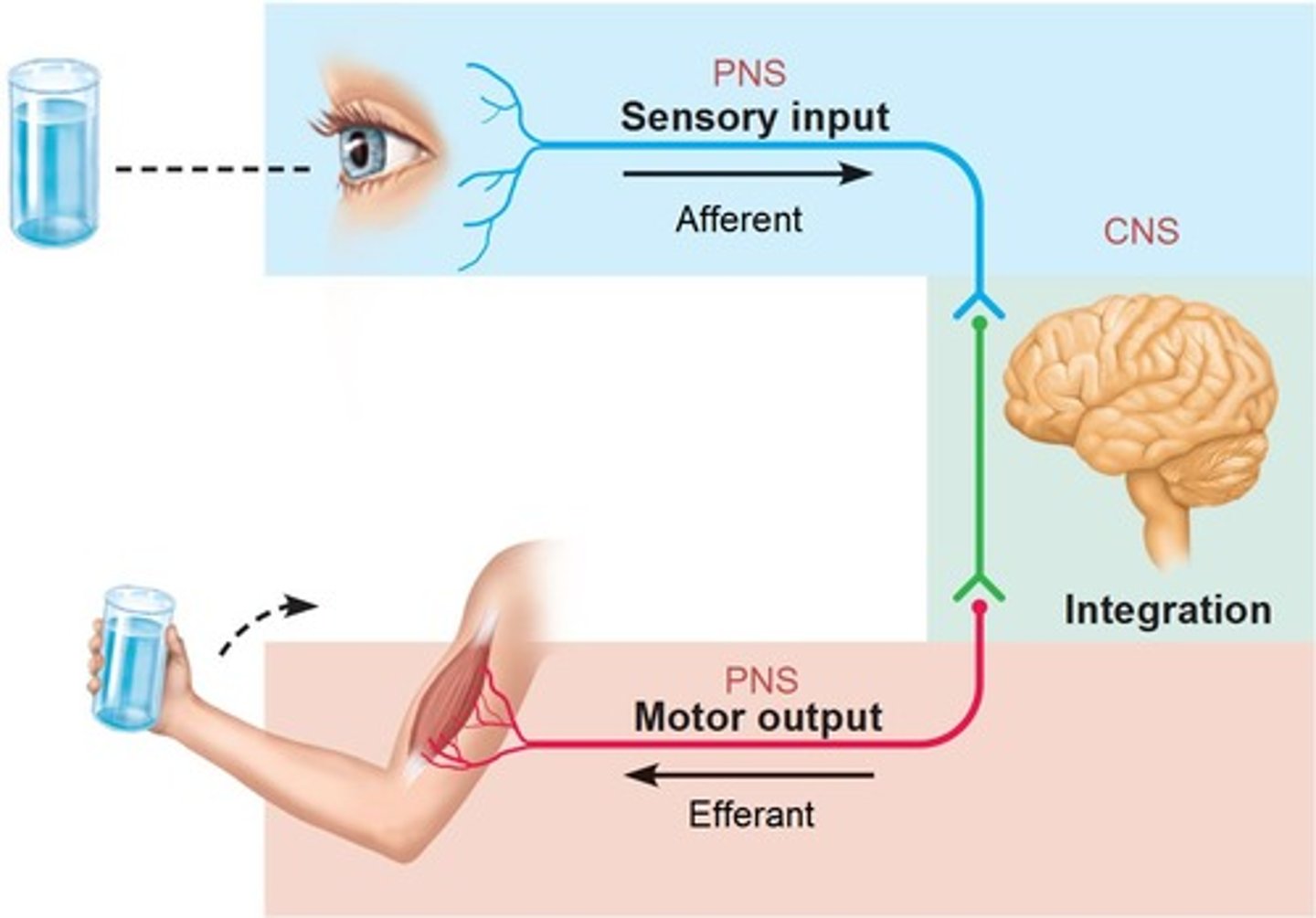
Motor Division
made up of efferent neurons that conduct impulses away from the CNS to the muscles and glands, allowing the brain to control heart rate, blood pressure, breathing rate, sweat production, and hormone release, among other functions
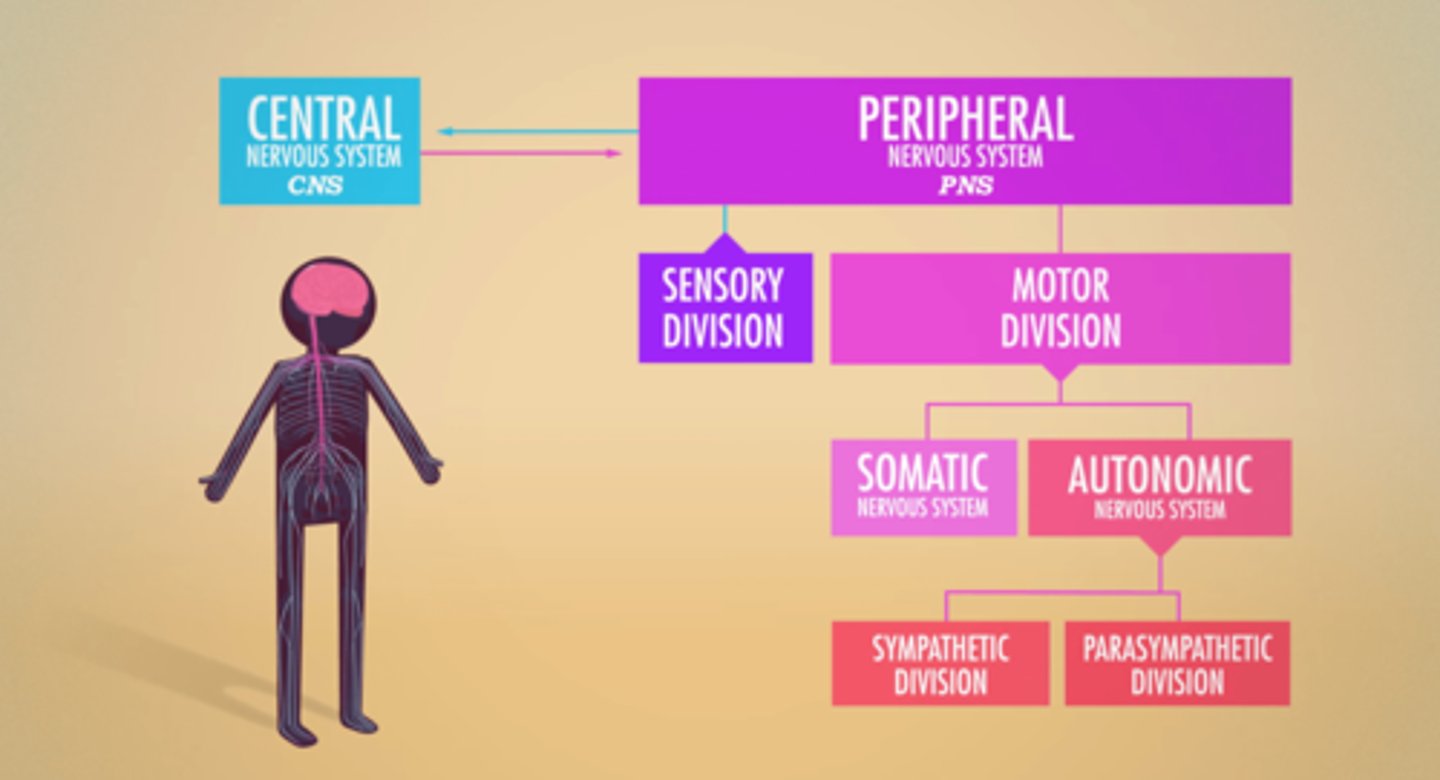
Somatic Nervous System
responsible for voluntary movement of muscles and the process known as a reflex arc, a system that carries nerve impulses back and forth between the CNS and the skeletal muscles, skin, and sensory organs
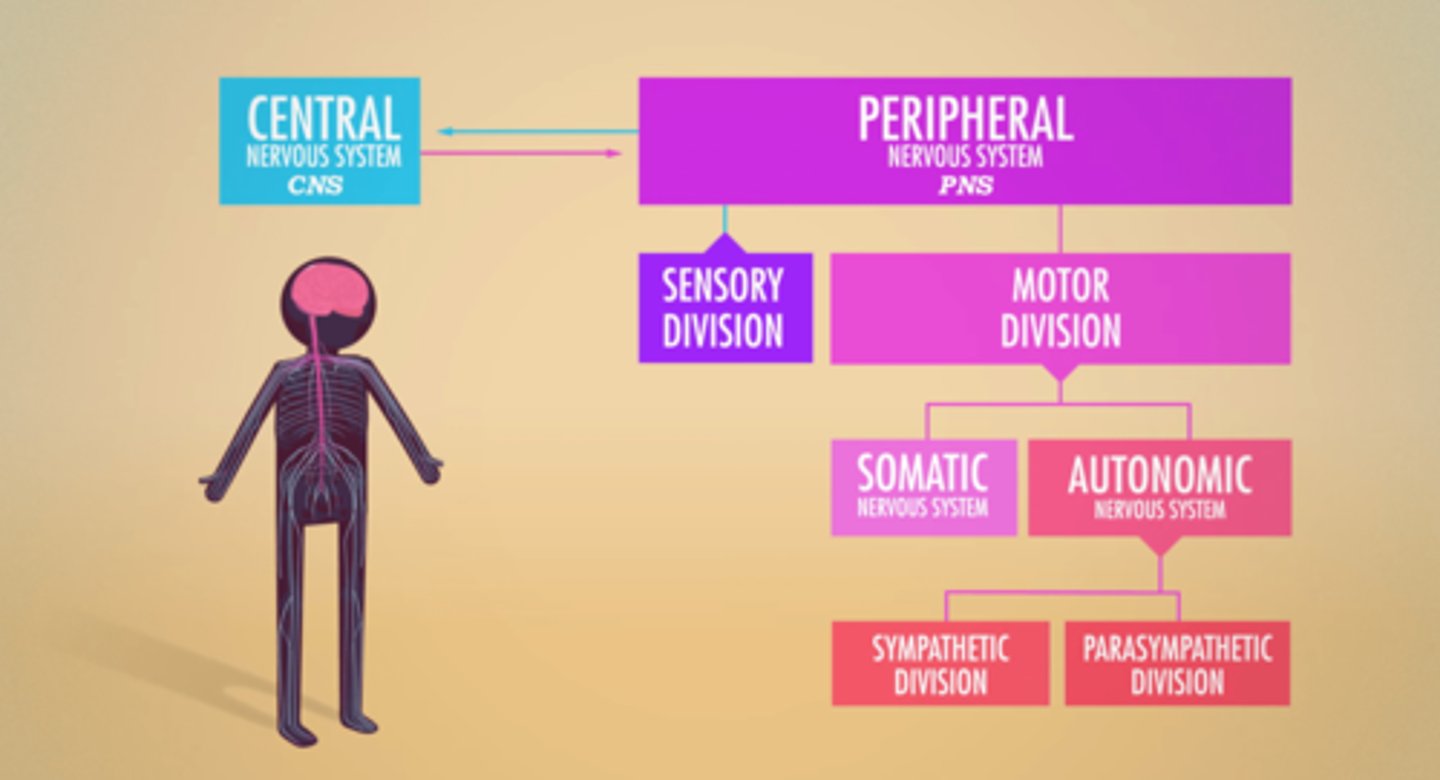
Autonomic Nervous System
responsible for involuntary functions inside the body; communicates with internal organs and glands to regulate body processes that take place without conscious effort including heartbeat, pupil dilation, blood flow, breathing, and digestion
Sympathetic Division
regulates flight-or-fight responses; performs tasks including relaxing the bladder, speeding up heart rate, slowing digestion, and dilating pupils
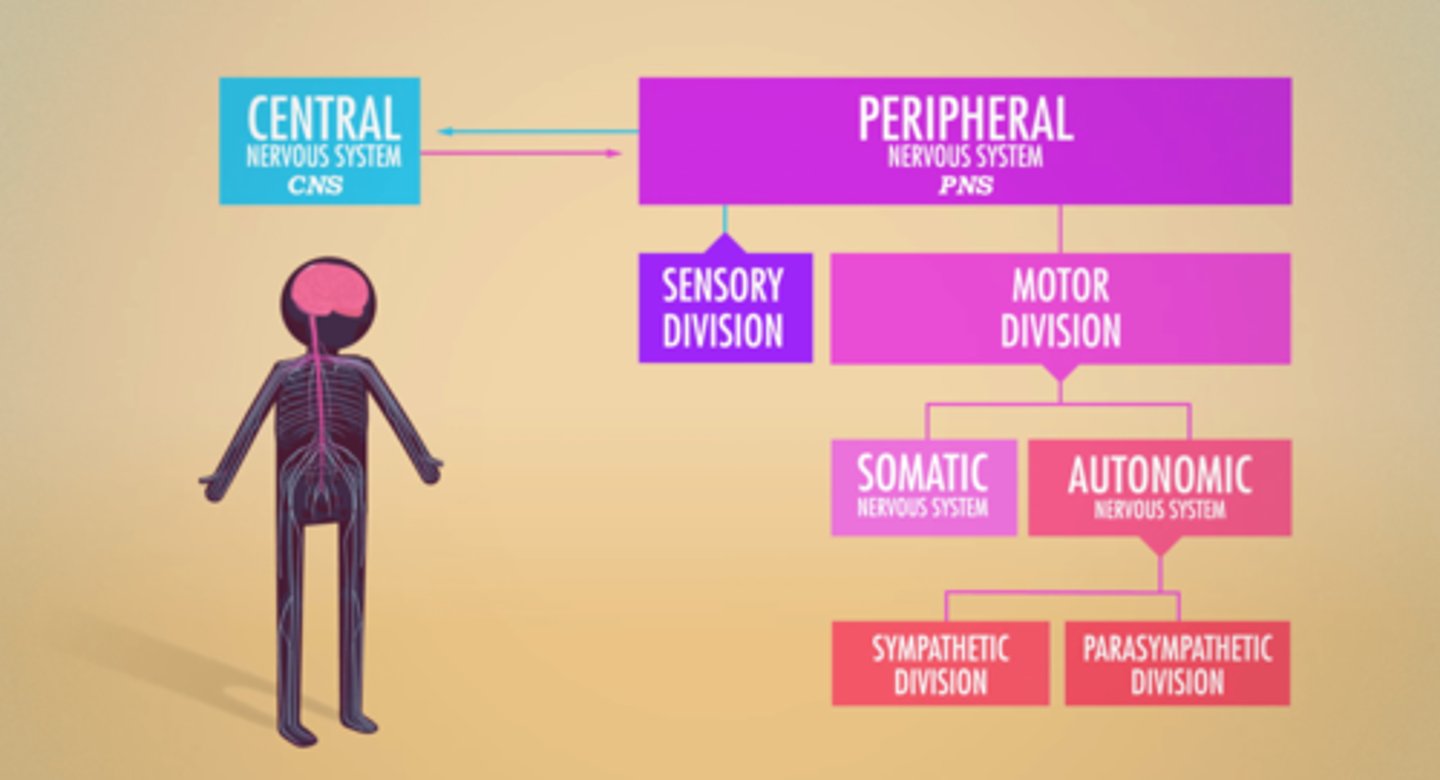
Parasympathetic Division
helps maintain normal body functions and conserves physical resources; performs tasks including controlling the bladder, slowing down heart rate, normalizing digestion, and constricting pupils
Glial cells
neuron partner; surround and protect neurons; provide immune defense by destroying pathogens; remove dead neurons; help form myelin sheaths, regulate ions
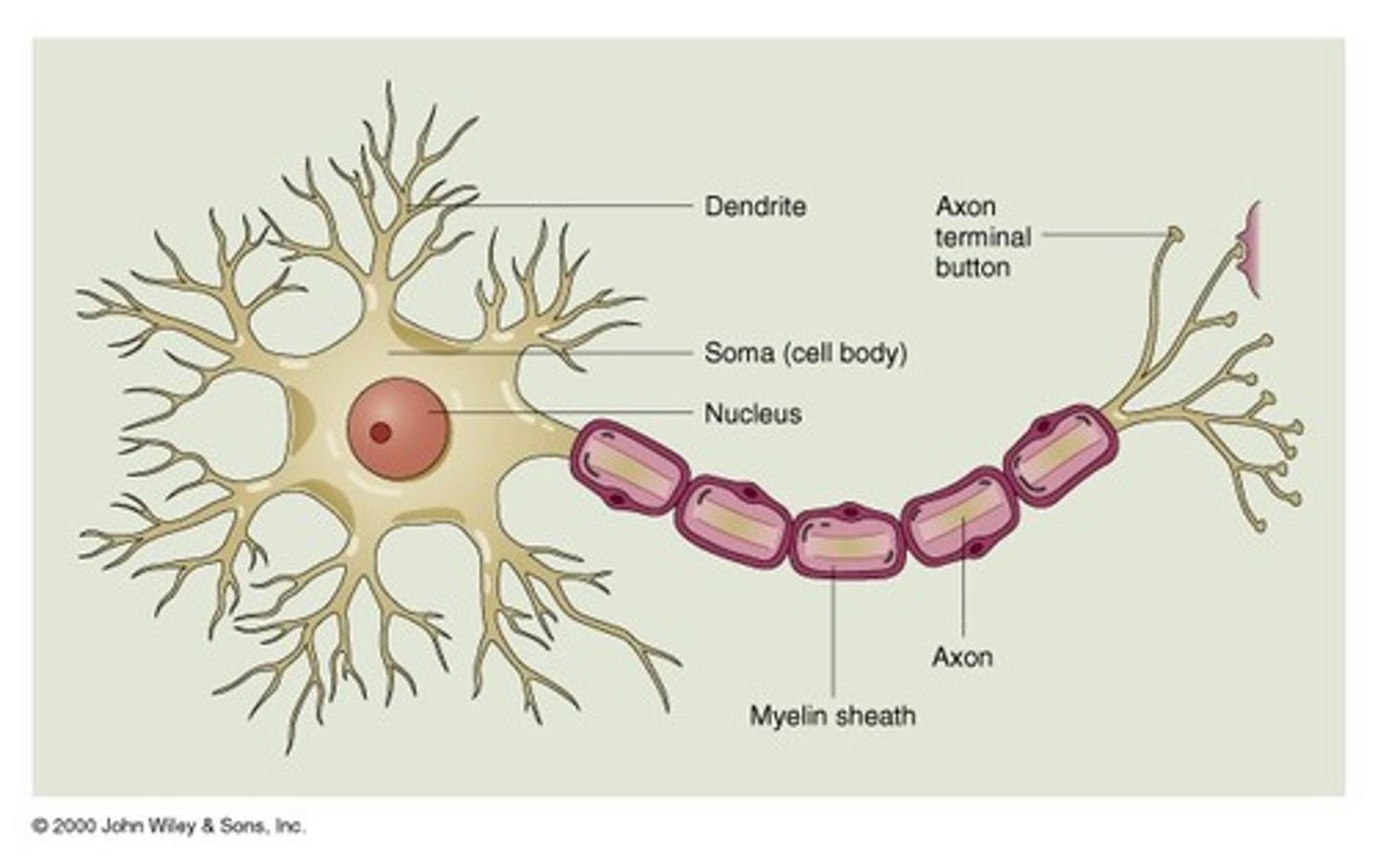
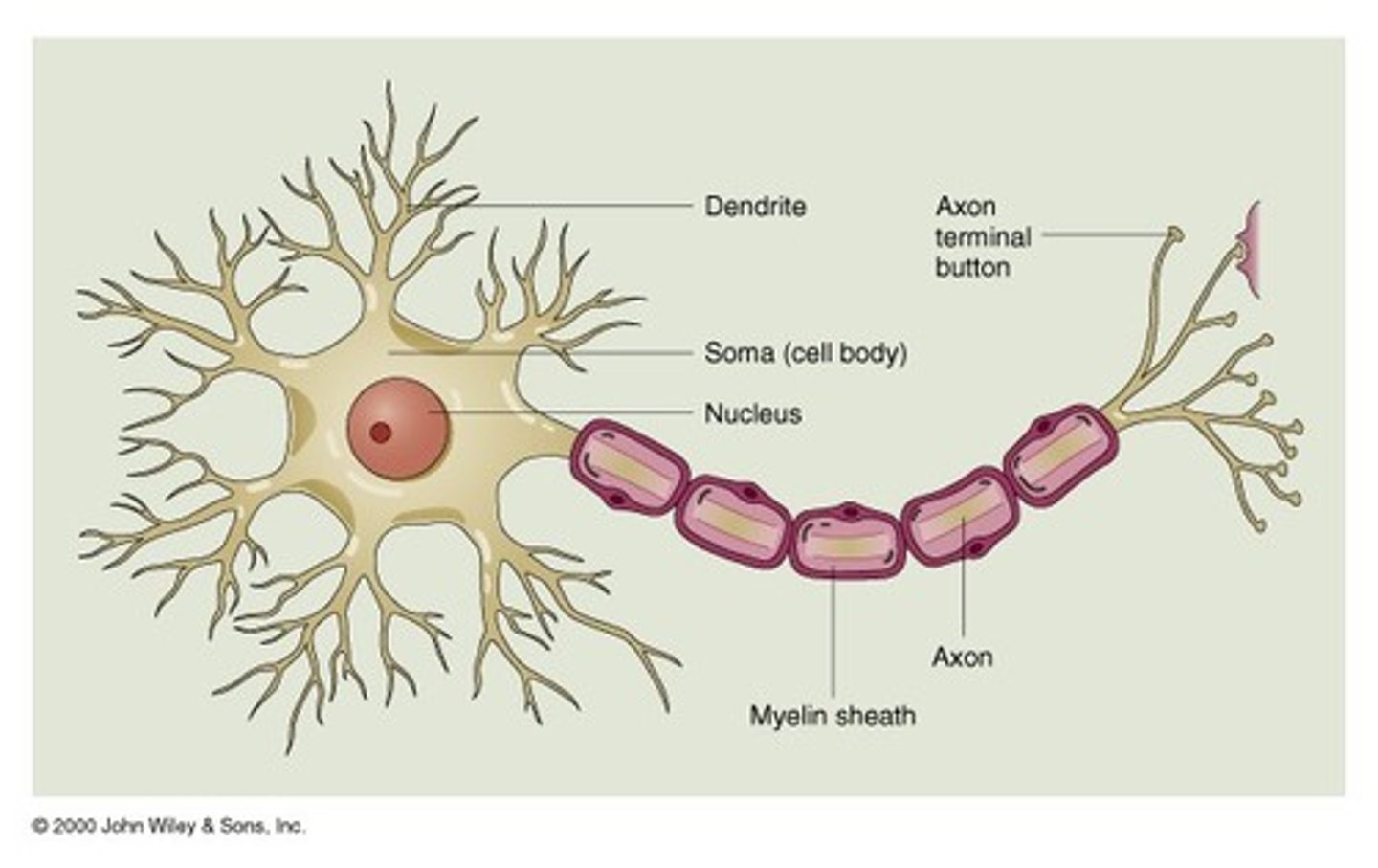
Neuron
electrically excitable cell that transmits information throughout the nervous system through electrical and chemical signals
Interneurons
these are found only in the CNS and transmit messages between the CNS and the sensory and motor neurons of the PNS
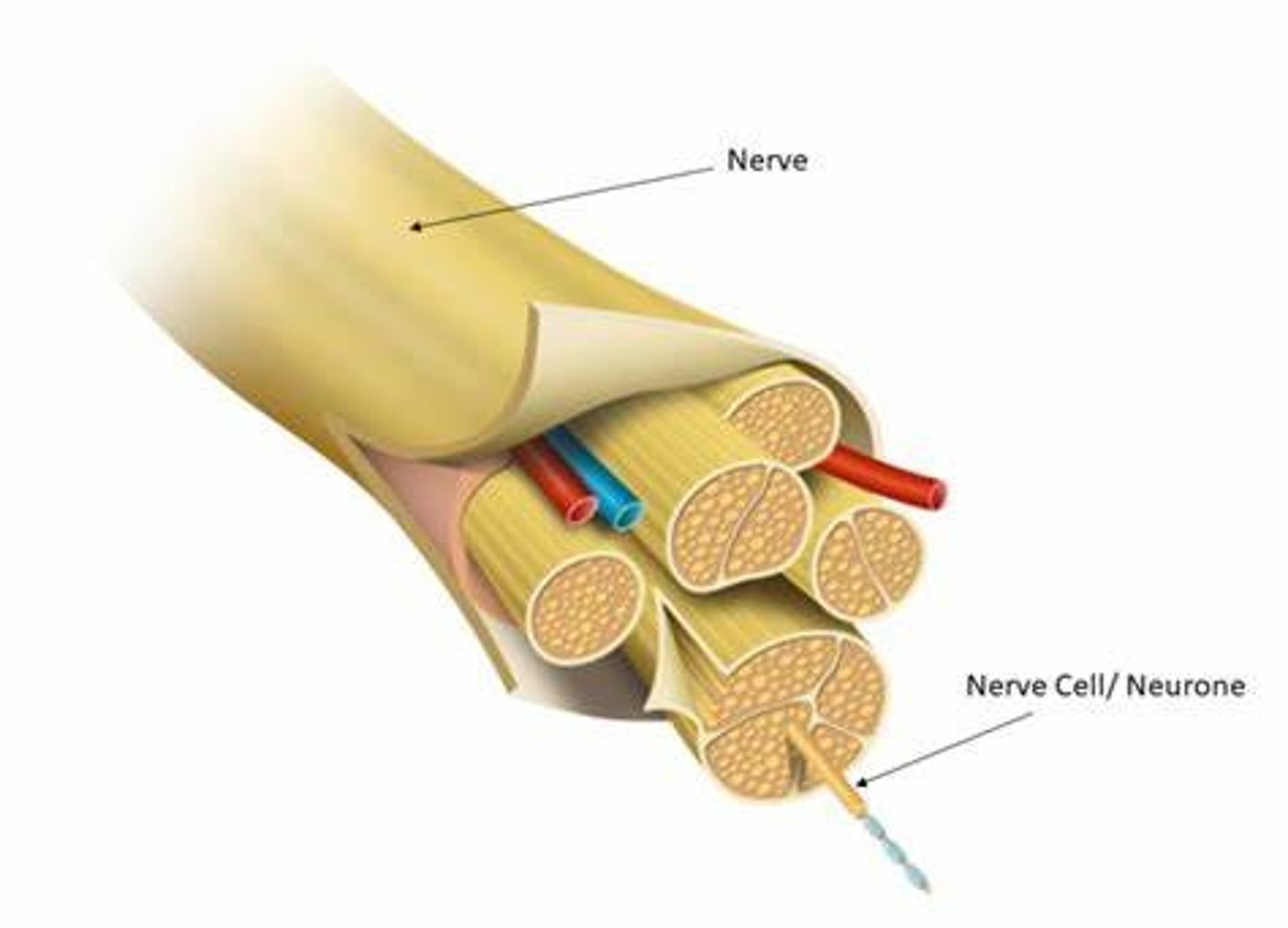
Nerve
collection of neuron fibers (axons) bundled with blood vessels and connective tissue; carry impulses between the CNS and other parts of the body; most have axons of both sensory and motor neurons
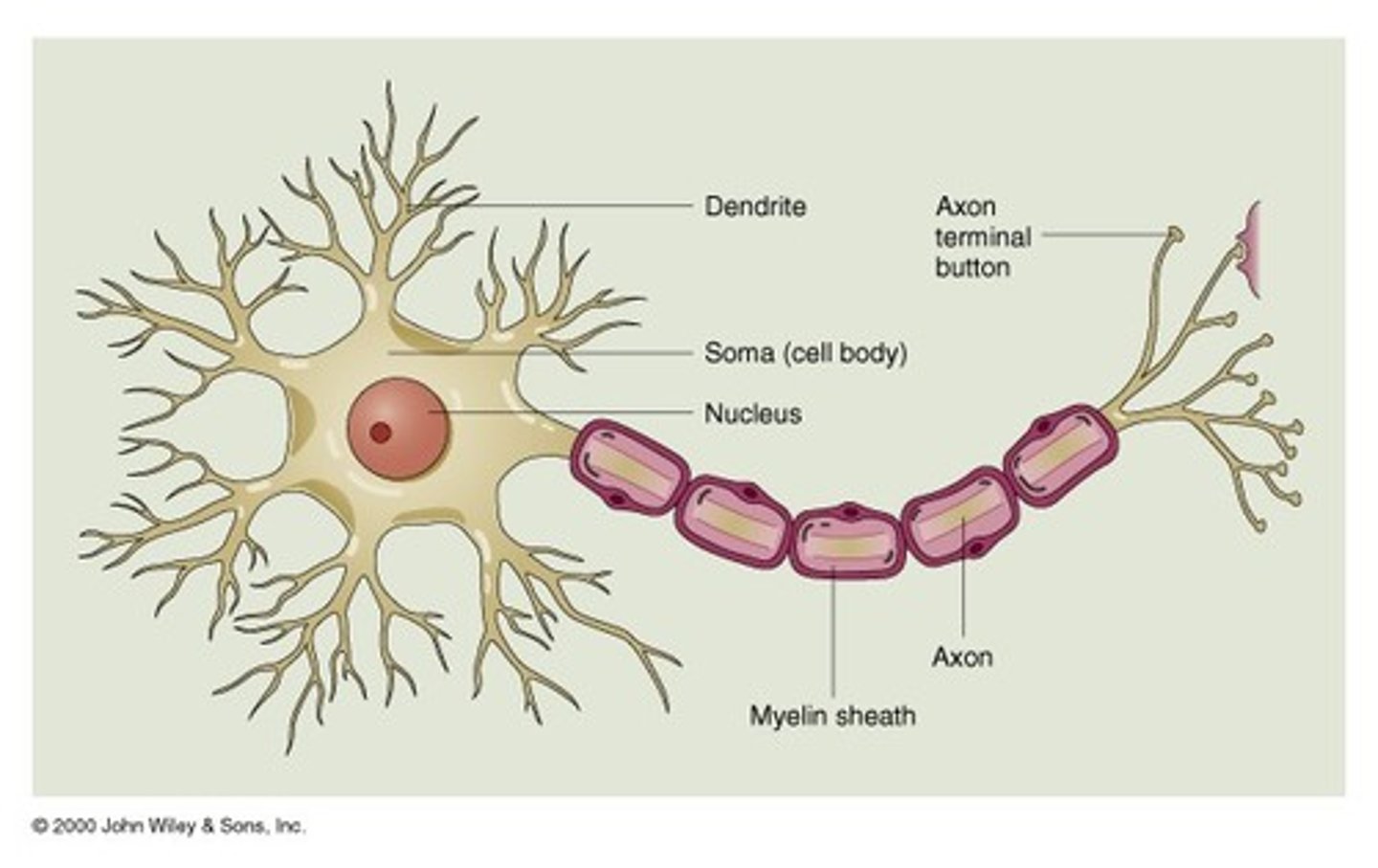
Axon
long threadlike part of a neuron that sends impulses to other cells
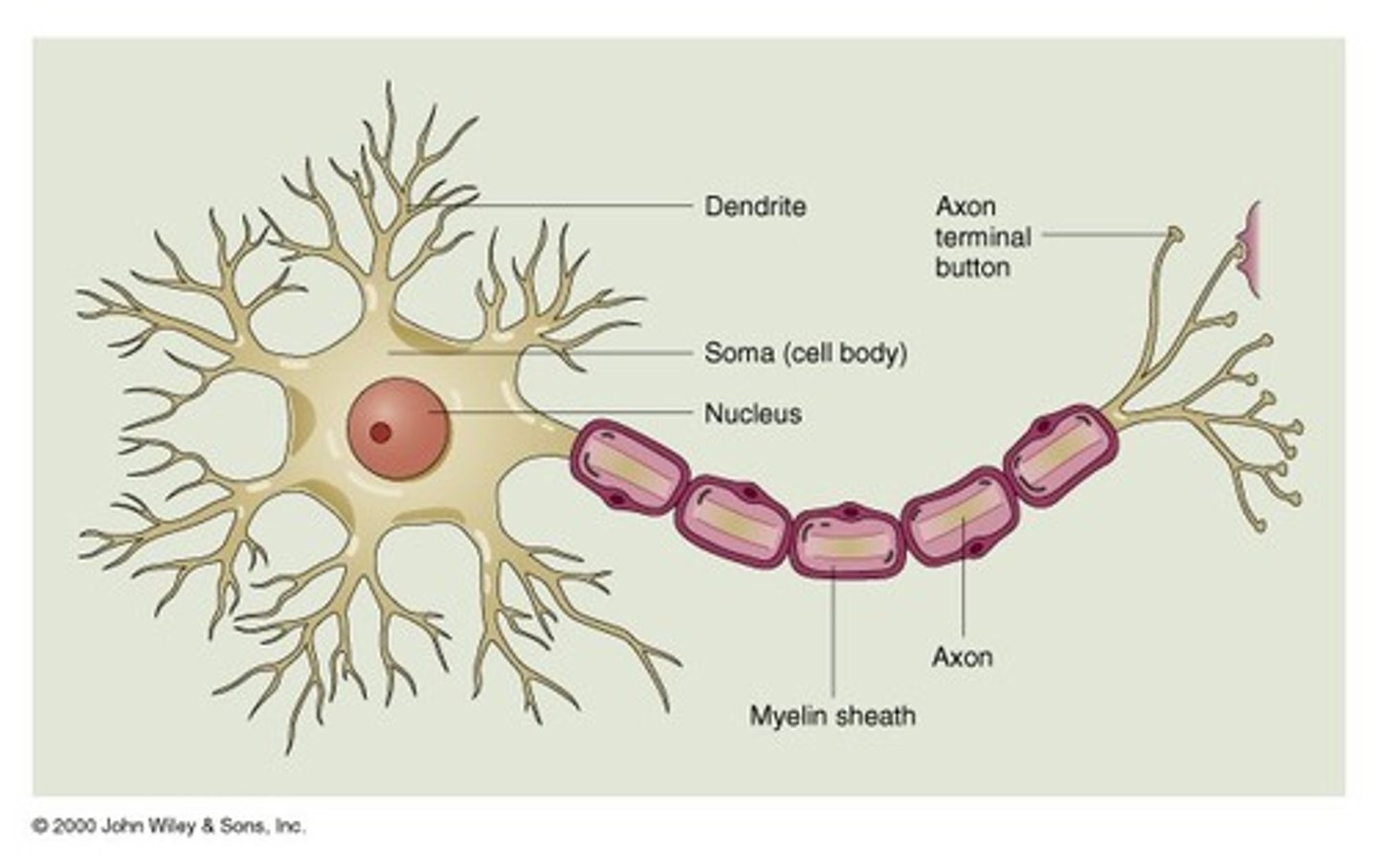
Dendrite
short branched extension of neuron that receives impulses from other cells at synapses
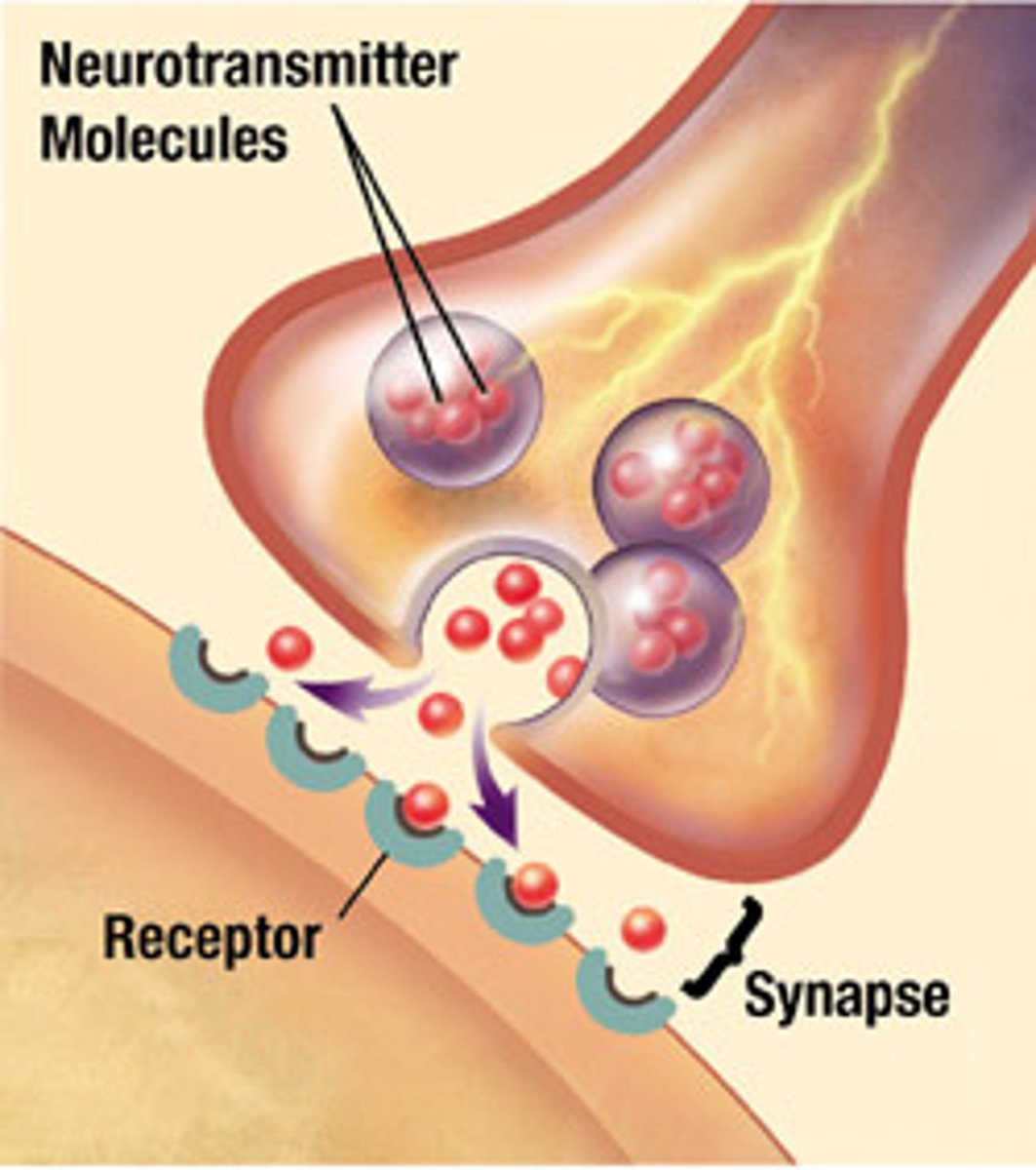
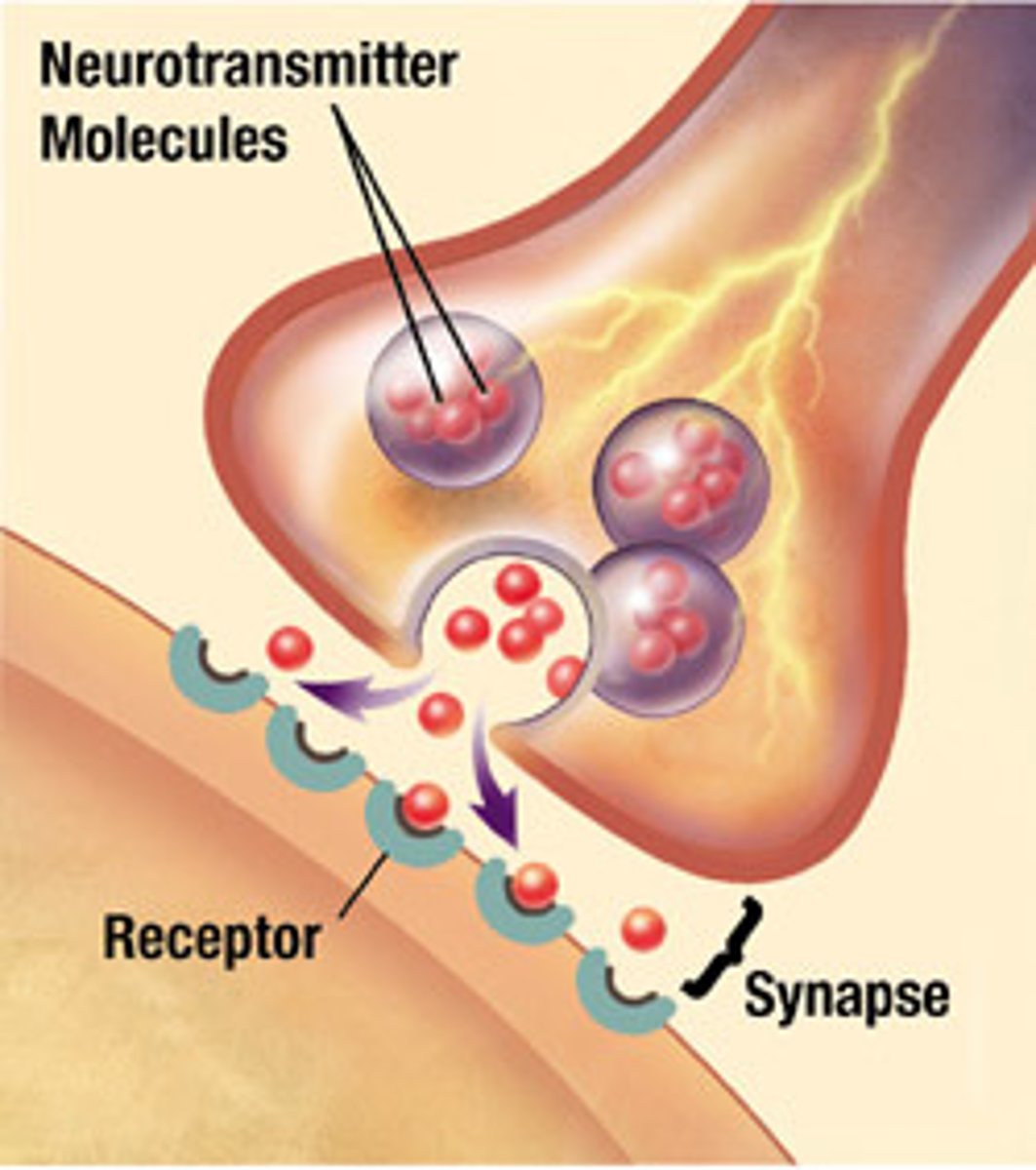
Synapse
site of transmission of electric nerve impulses between two neurons or between a neuron and a gland or muscle cell
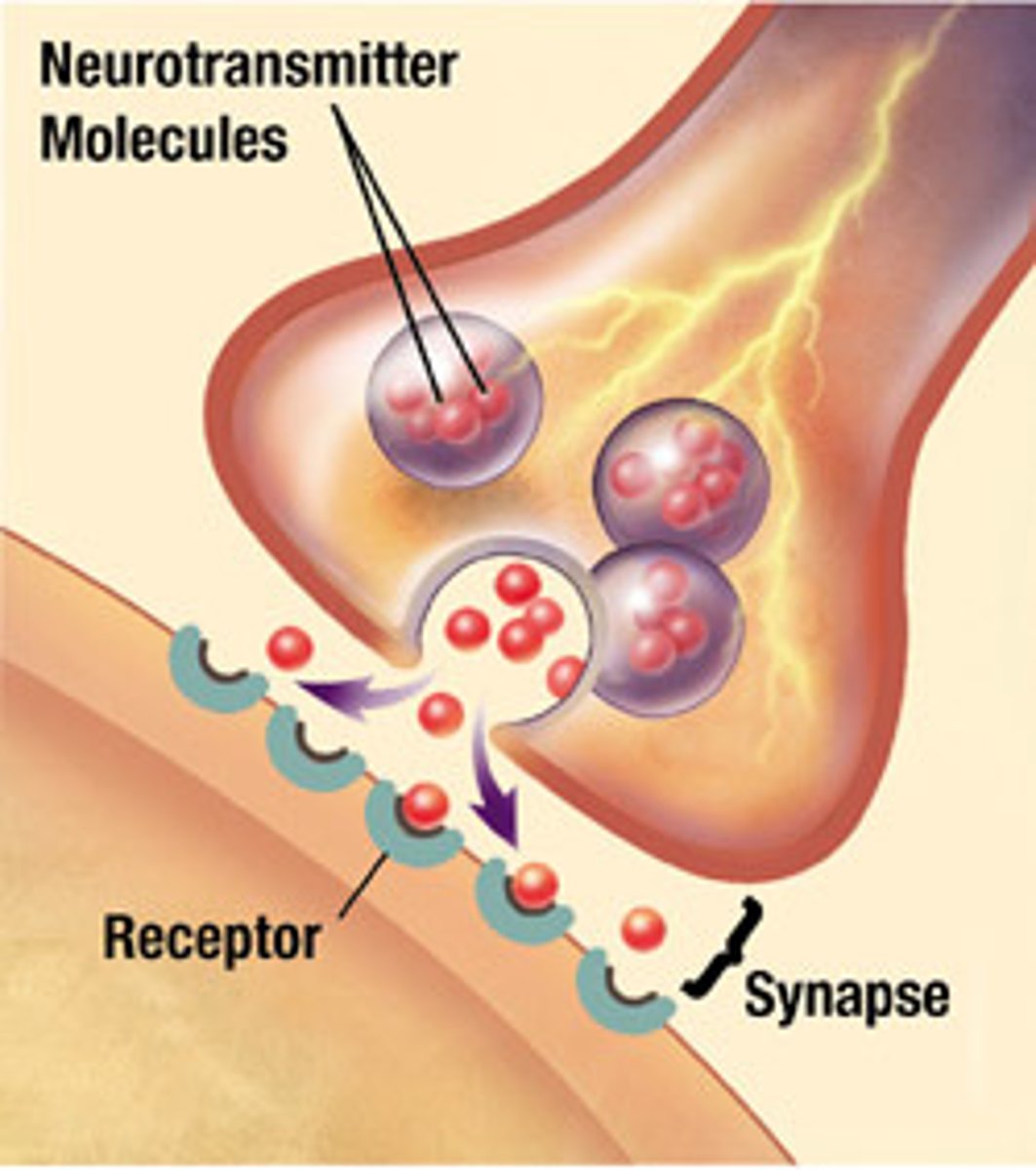
Neurotransmitter
chemical substance that is released at the end of a nerve fiber by the arrival of a nerve impulse and transfers the impulse to another neuron, gland, or muscle cell
Action potential
the brief (~1/1000 of a second) reversal of electric polarization of the membrane of a neuron or muscle cell; in the neuron it produces the nerve impulse; in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for movement
Myelin sheath
fatty white substance that forms protective coating around axons in the CNS; insulates and protects and helps speed transmission of nerve impulses
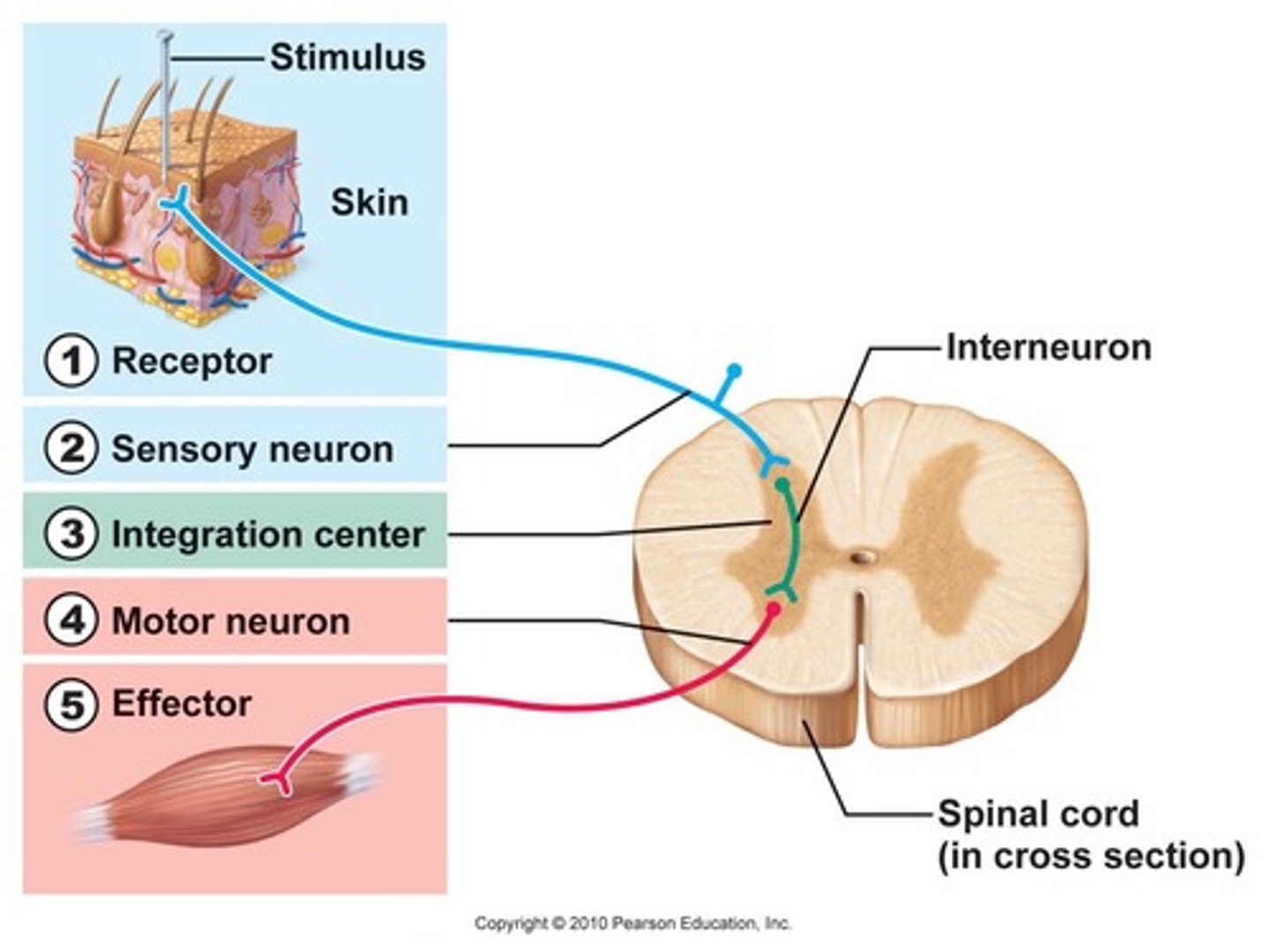
Reflex arc
results when sensory neurons activate spinal motor neurons which activate muscles cells before routing signals through the brain for analysis
PNS branches
Sensory & Motor Divisions
Motor Division branches
Somatic & Autonomic Nervous Systems
Autonomic Nervous System branches
Sympathetic & Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
synaptic terminal
the location where axons terminate at the synapse for transmission of information by the release of a chemical transmitter