Intro to criminology - Chapter 5: Methods and counting crime
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
The 9-step research process
A place to start in talking about research methods
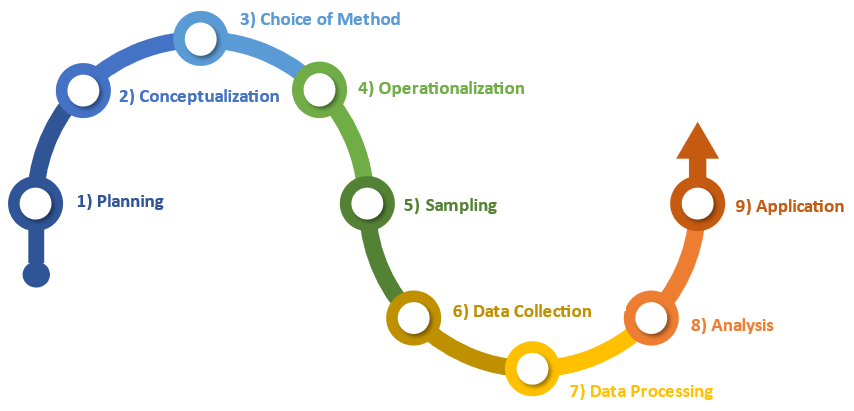
Planning
Figuring out the objectives and what the research question(s) might be
Conceptualization
Envisioning, narrowing down and starting to become clearer and more specific on the key question(s)
Choice of method
Choosing a particular method that is suited to answer your research question and examining methods used in other similar studies
e.g Surveys, field research, observation
Operationalization
Figuring out how to measure the concepts
e.g. If you are doing field research, what specific observations will you be making? If you’re doing a survey, how will you word the questions?
Sampling
Picking which part(s) of a population to focus on and study, and determining if it’s a group of people or an official data set you need to draw from
Data Collection
Collecting the data via the chosen methods and recording information
Data Processing
Processing the raw data into a usable form for easy analysis
Analysis
Making sense of the data and to synthesise and summarise the findings in a way that can be communicated to a larger audience
How can data be summarized
Graphs, tables, and charts can be used to visually present data
Application
Using the conclusions reached from the data to inform or educate others
Quantitative projects
Projects that involve statistical analysis, and tends to use numbers or quantities, along with larger sample sizes and closed-ended questions, as the most important element because this allows for abstraction
Qualitative projects
Projects that involve textual analysis and tend to focus on specific, localized objectives to examine them more in depth, along with smaller sample sizes and open-ended questions
Inductive research
Starts with people’s experiences and then builds ideas around it
Deductive research
Starts with a theory and then tests it
Two-Eyed Seeing
The blending of Indigenous world views and Western science.
Variable
A person, place, thing, or phenomenon you are trying to measure in some way that varies
Hypothesis
An informed thought or expectation of what the relationship is between variables, and it is often written as an “if, then” statement that indicates the directionality of each variable
Academic imperialism
An unequal relation between academics where one group dominates while other groups are ignored or silenced.
Grey literature
Literature or evidence that is relevant to the research question but not published in typical commercial or academic peer-reviewed publications
Uniform Crime Report
Is an official crime data source collected by Statistics Canada and police departments
Uniform Crime Report (con’t)
Crimes discovered by/reported to police are included, along with relevant info like the suspects, victims, offence, etc, are included
Uniform Crime Report (III)
Only the most serious crime will be reported in instances where multiple crimes were committed
Strengths of the Uniform Crime Report
Provides consistent nationwide data
Allows for comparisons of different time periods, provinces, etc
Can be used by governments for policy-making
Weaknesses of the Uniform Crime Report
Only documents reported crimes
General social survey
Captures victimization experiences and certain crimes notoriously under-reported, (e.g.) sexual assault
General social survey (con’t)
Also reveals low reporting rates amongst Indigenous peoples
National victimization survey
Measures responses directly from victims by asking them their about their experiences
National victimization survey (con’t)
Is important as it covers the crimes which go unreported
Self-report data
Captures offender perspective and shows that a majority of seemingly law-abiding individuals engage in crime and deviance
Literature review
A written summary and overview of writings and other sources on a selected topic to gain an understanding of existing research relevant to the topic.
Scientific colonialism
The state in which the transformation of knowledge production is controlled by the colonizers while other ways of knowing, namely Indigenous ways of knowing, are dismissed
Epistemology
The study of knowledge or ways of knowing, which is central to the practice of research (How we know what we know)
Epistemology (con’t)
Delves into the nature of knowledge and truth, and challenges us to consider what it means to know something
Objectivity
Deals with ideas that are based on fact and free from bias or personal opinion; is a cornerstone of of Western research
Empiricism
A method of study based on tangible and observable facts, evidence, and research; is a cornerstone of of Western research
Reliability
The degree to which a measurement or research method produces consistent results
Subjectivity
Perceptions based on one’s own feelings, experiences, and opinions rather than on external, observable facts
Methodology
A system of methods, procedures and principles used in a particular area of study or discipline
Talking circle
A type of discussion with participants sitting in a circle, originated by Indigenous peoples and often used as a part of a healing ceremony; can also be used to value participants’ sharing of personal experiences for the sake of research
Validity
The accuracy of our research methods, and whether they measure what they intend to measure
Generalisability
The degree to which the results of a study can be applied to a larger population