Lab exam 4 (shortened)
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
“Free at last, Free at last, Thank God almighty we are free at last.” ― Martin Luther King Jr.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
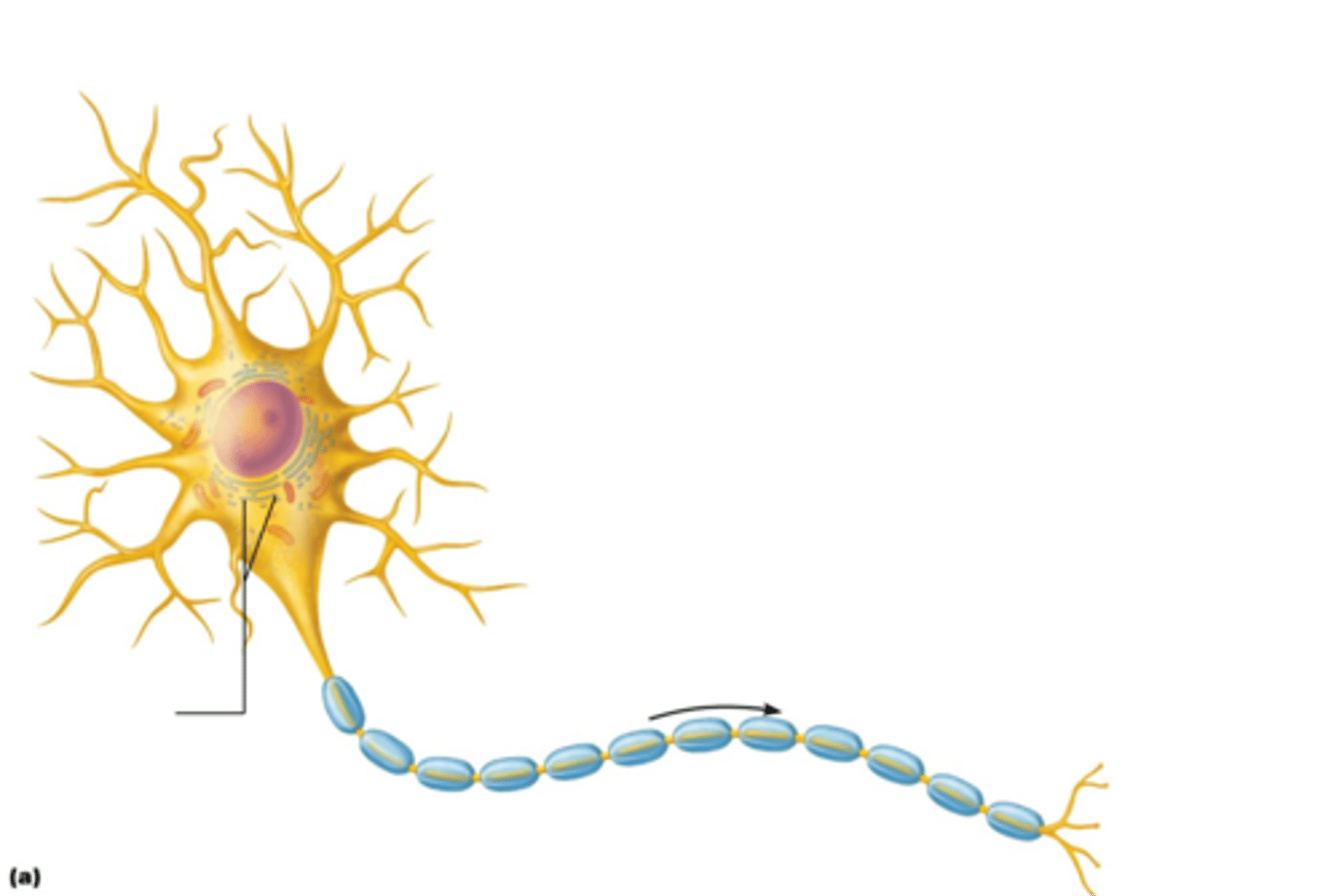
Nissl bodies
Rough endoplasmic reticulum in neuron
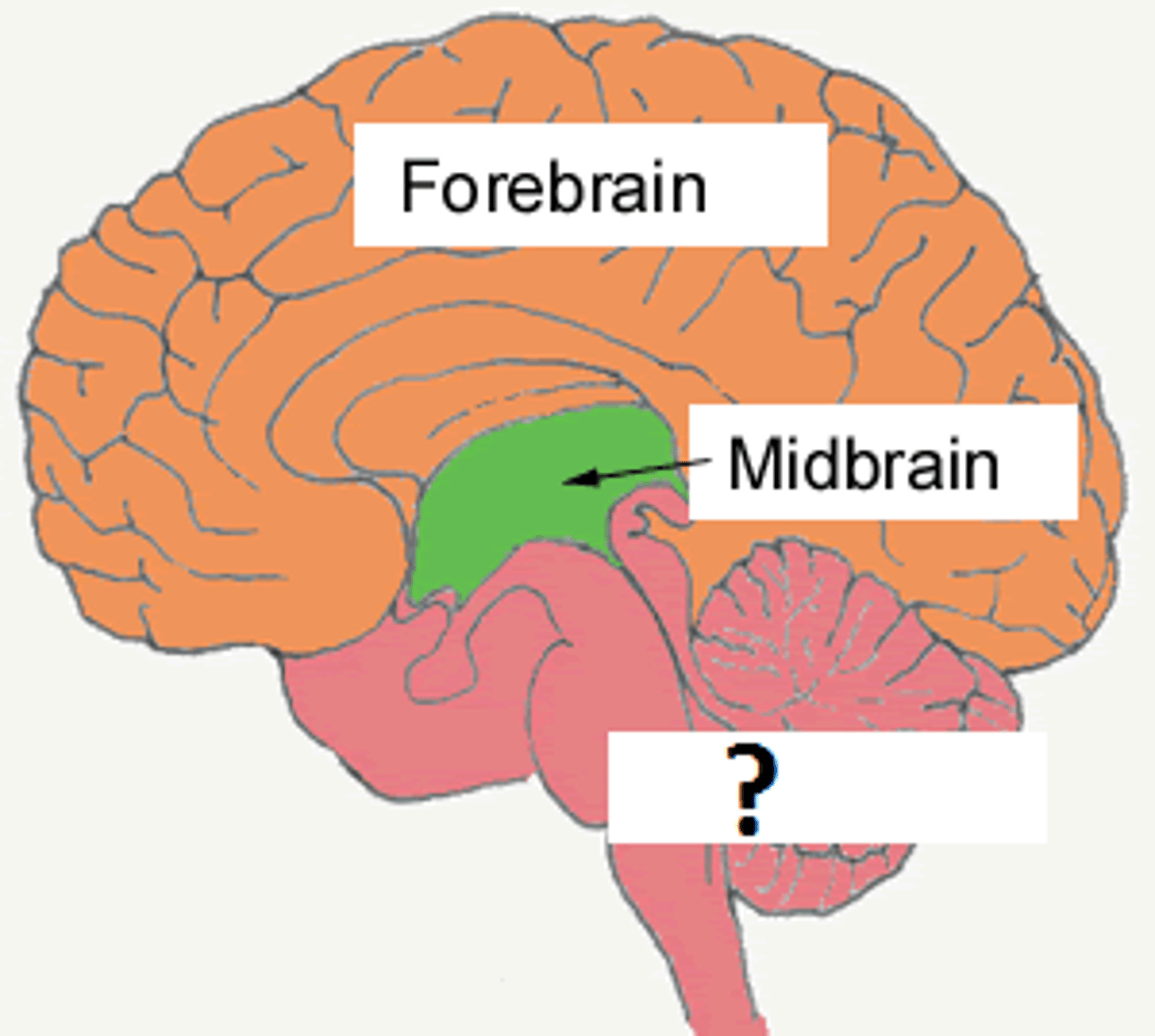
neural tube
an embryonic structure with subdivisions that correspond to the future forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain
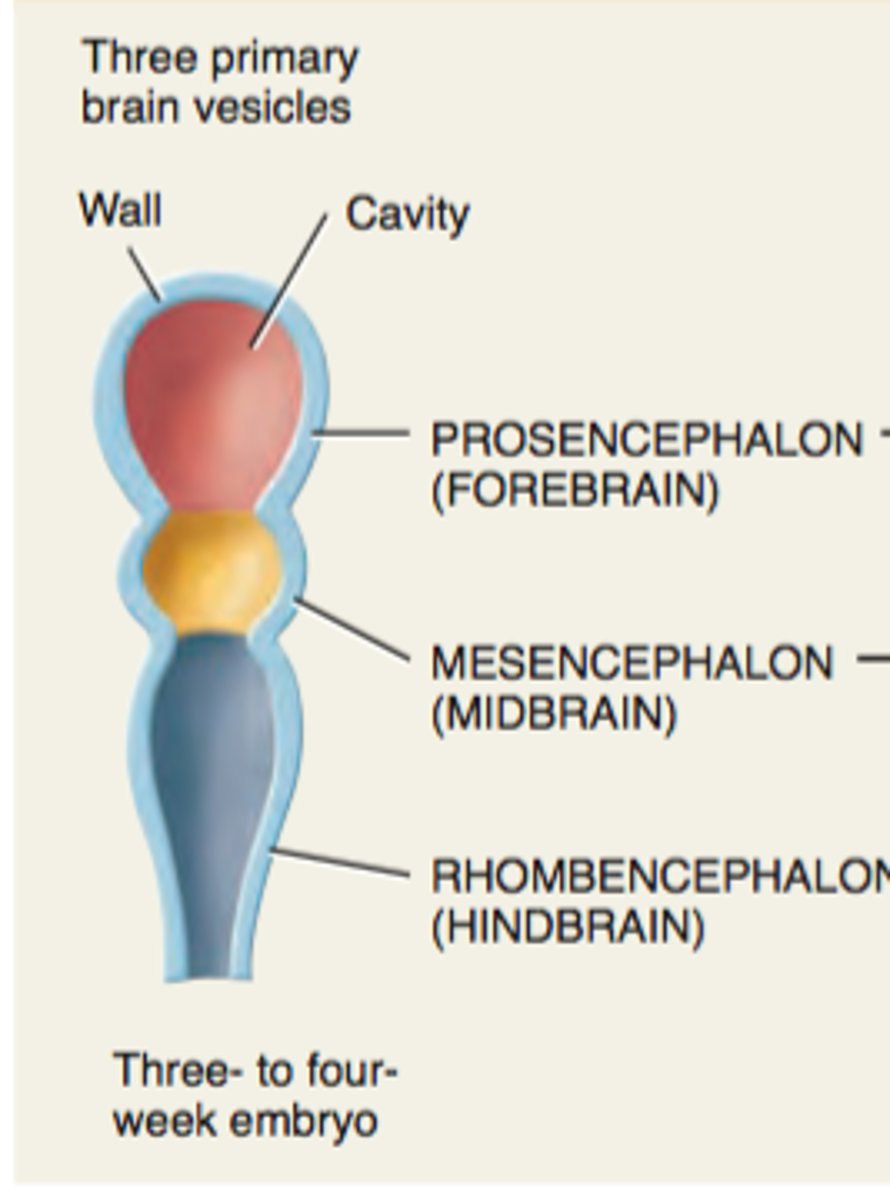
Prosencephalon (forebrain)
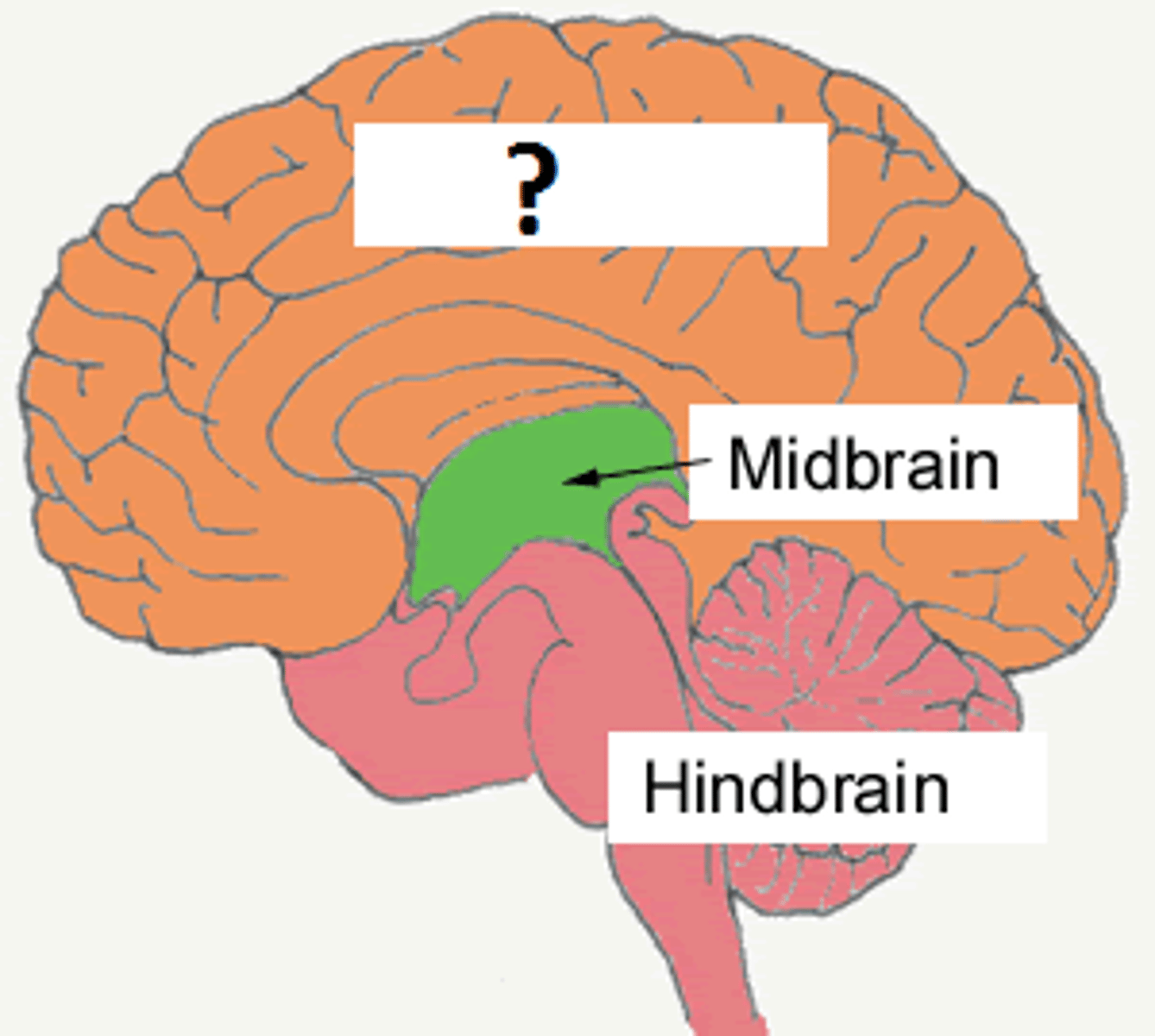
Mesencephalon (midbrain)
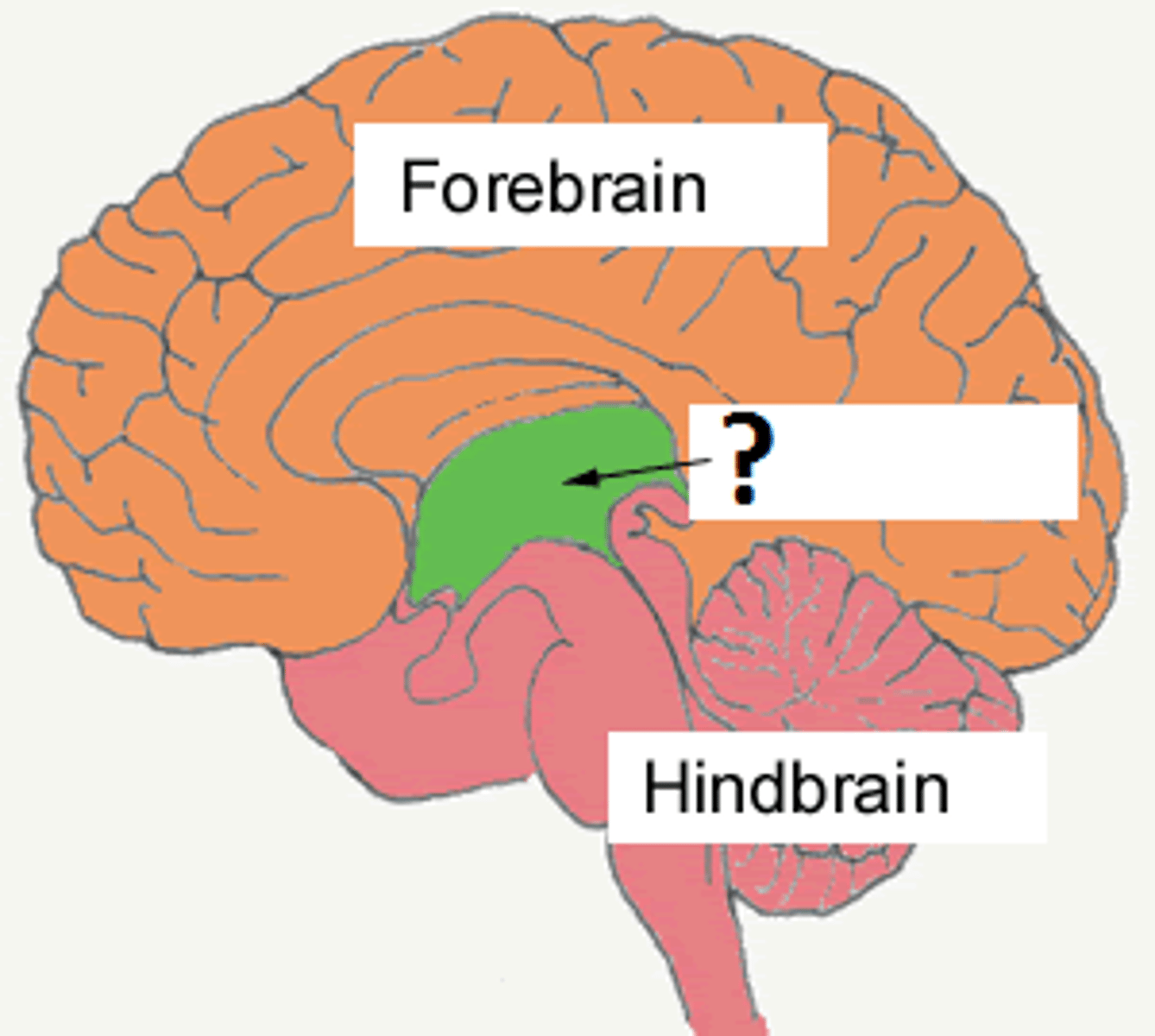
Rhombencephalon (hindbrain)
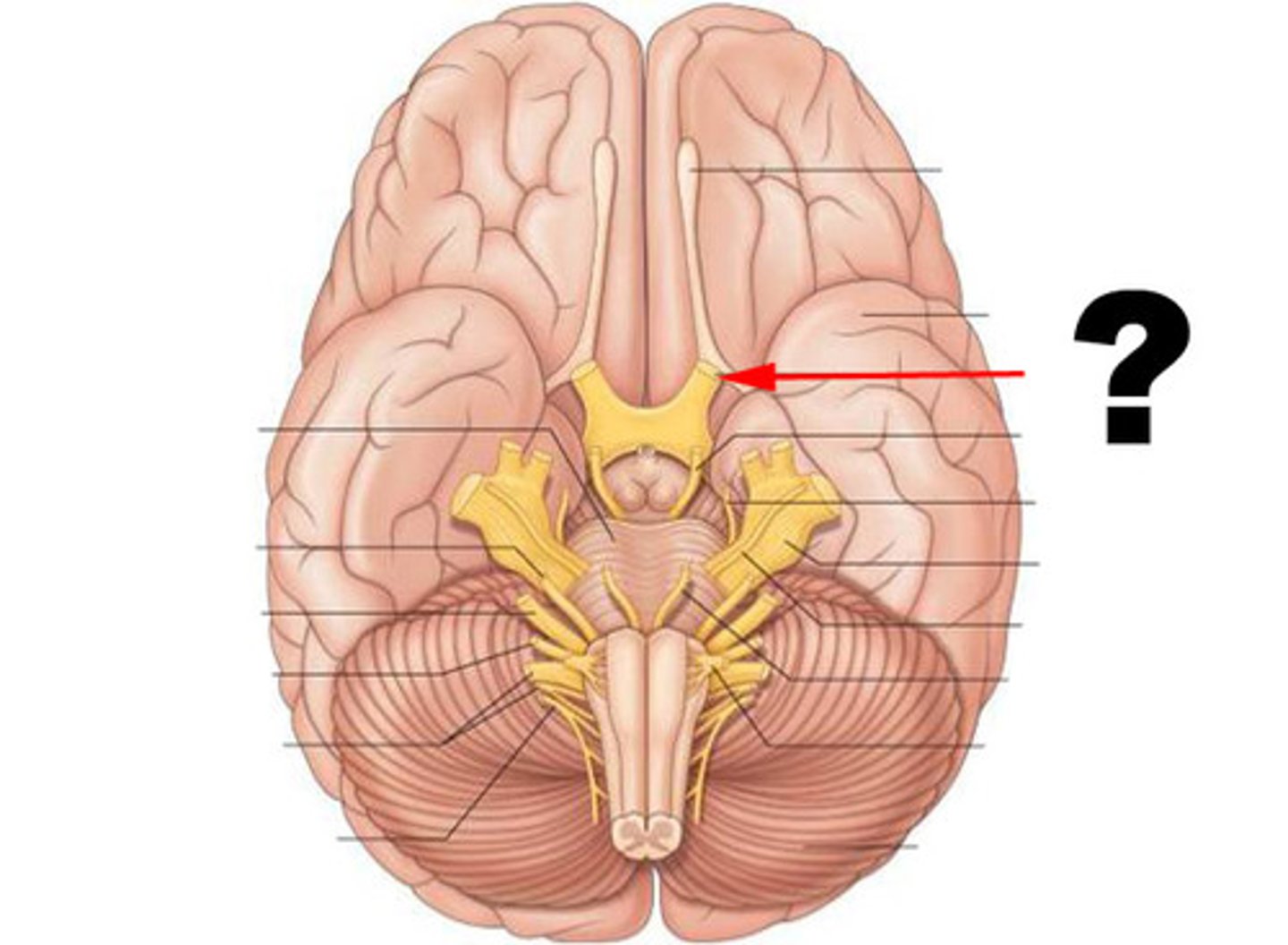
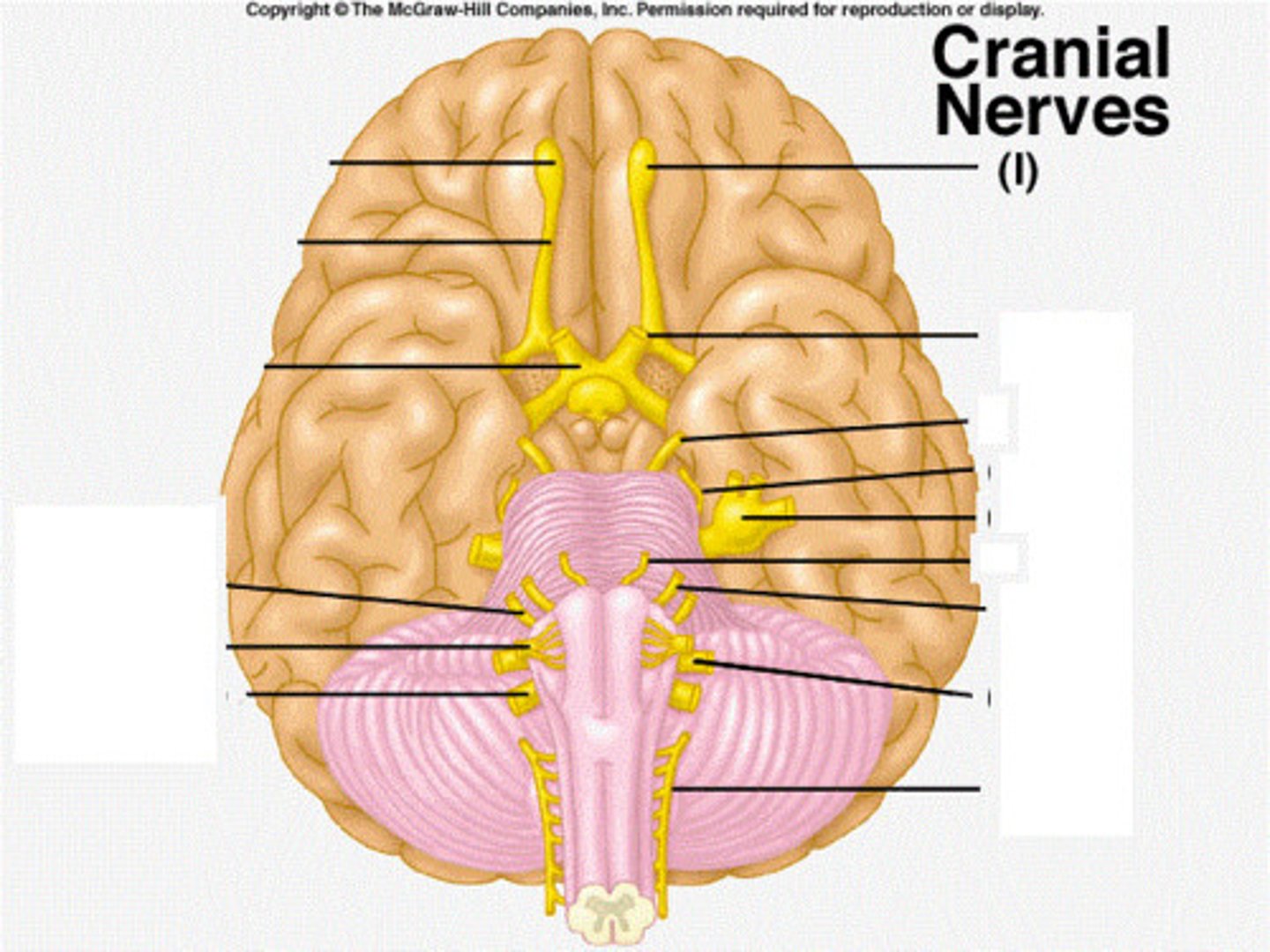
optic nerve
function: purely sensory
testing: vision
olfactory nerve
function: purely sensory
testing: smelling
oculomotor nerve
function: primarily motor (mixed)
testing: eyeball movement
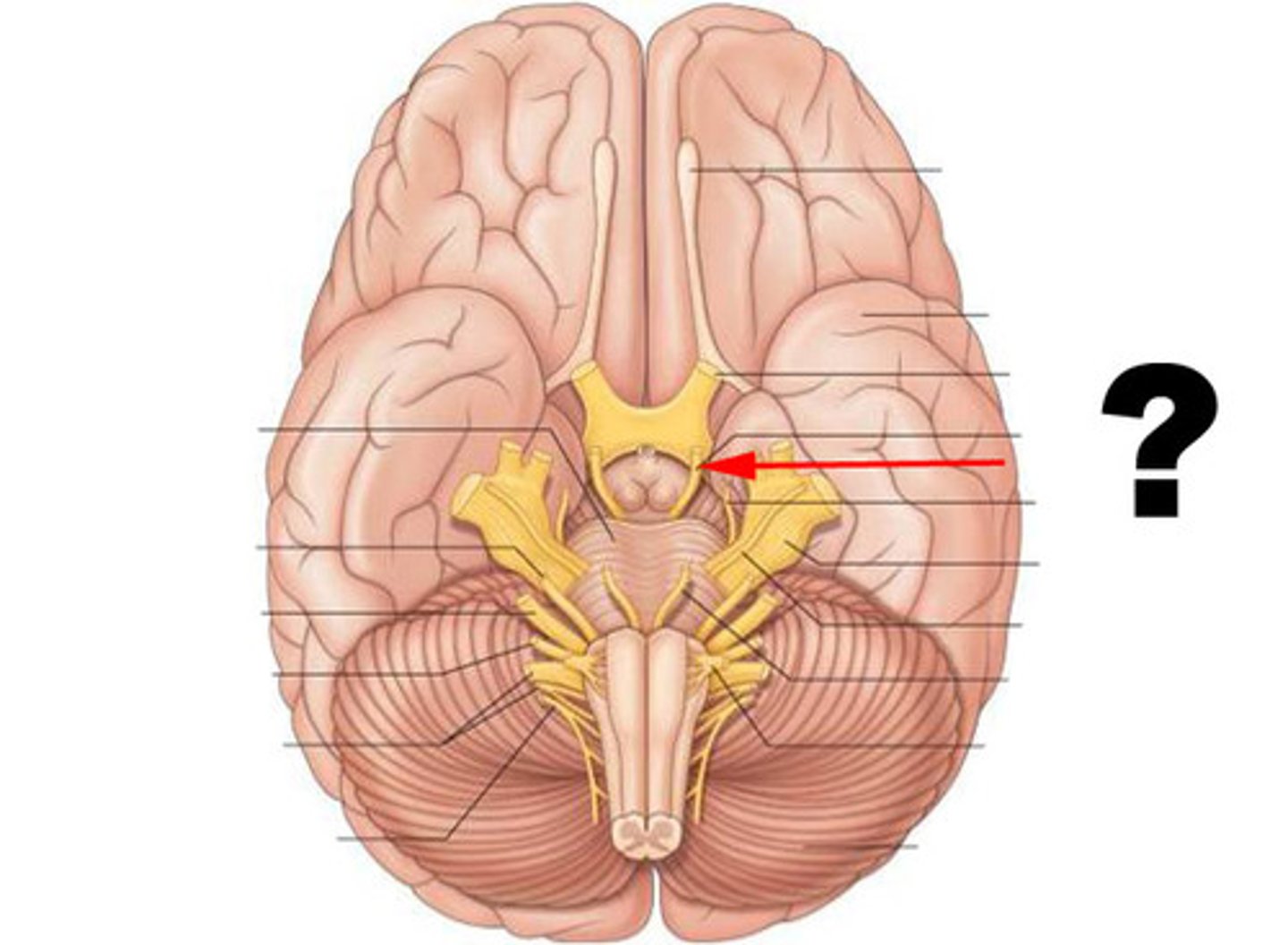
trochlear nerve
function: primarily motor
testing: eyeball movement
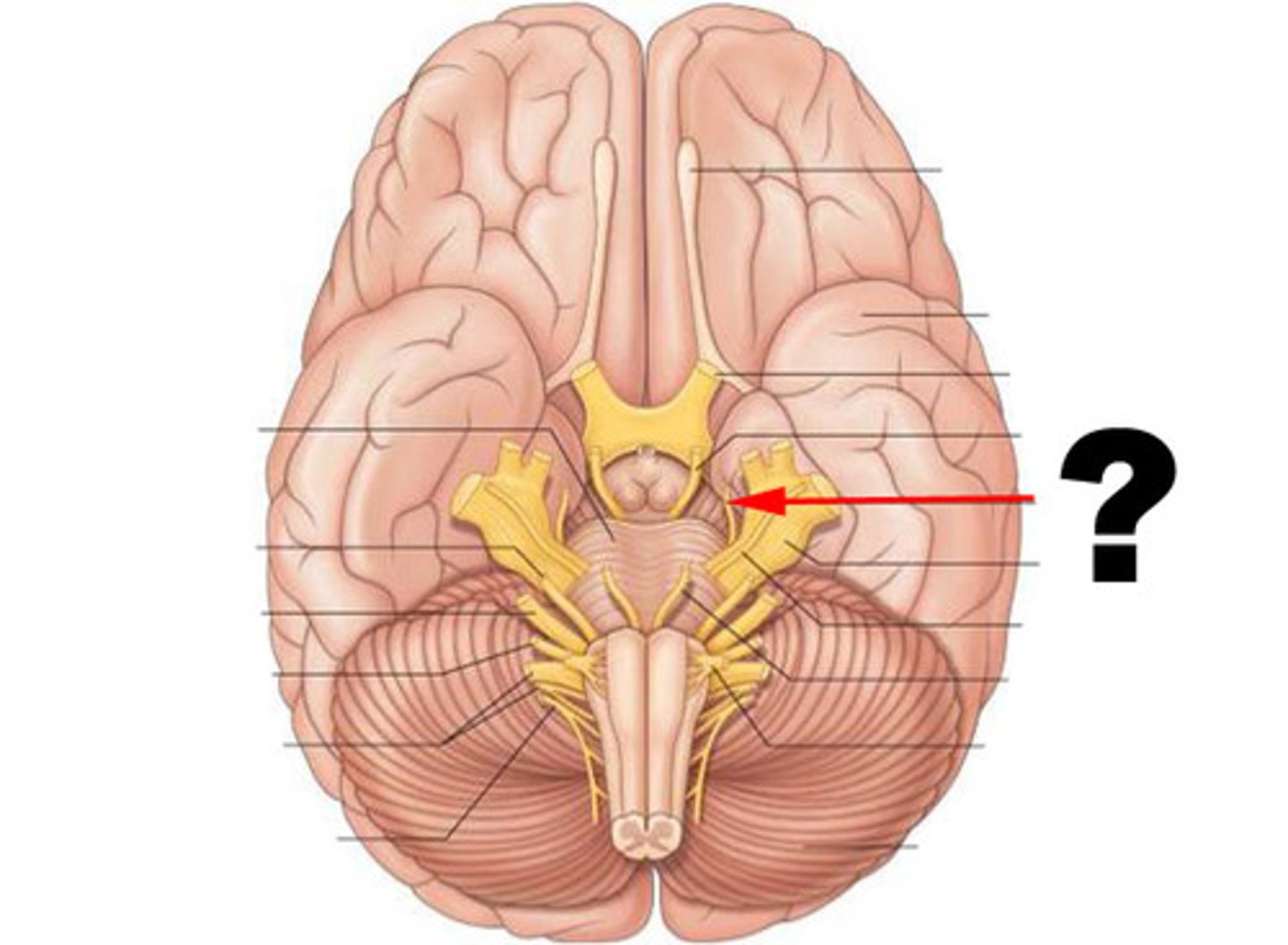
trigeminal nerve
function: mixed
testing: pain, touch, chewing
(biggest)
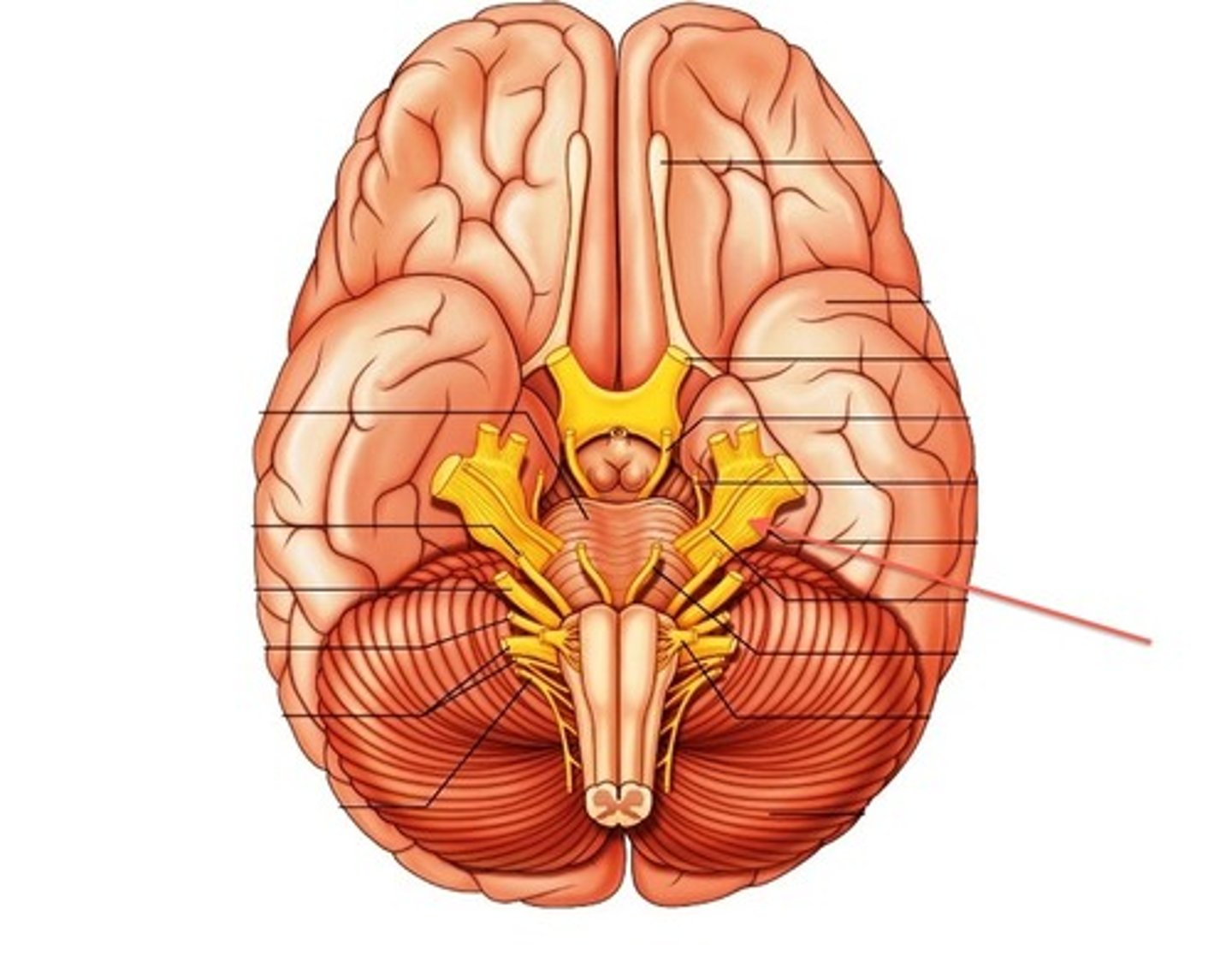
abducens nerve
function: primarily motor (mixed)
testing: eyeball movement
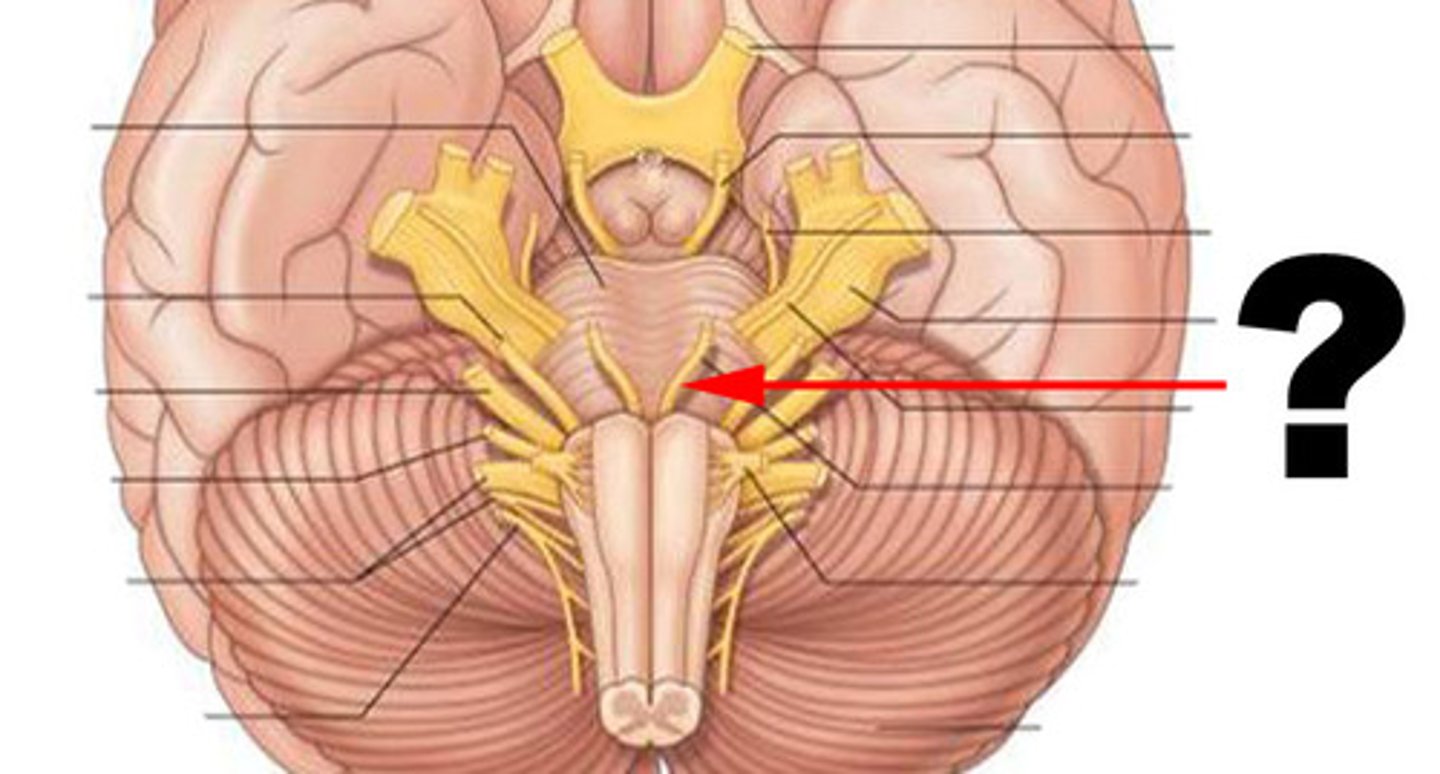
facial nerve
function: mixed
testing: sensory- taste/ motor- facial expression
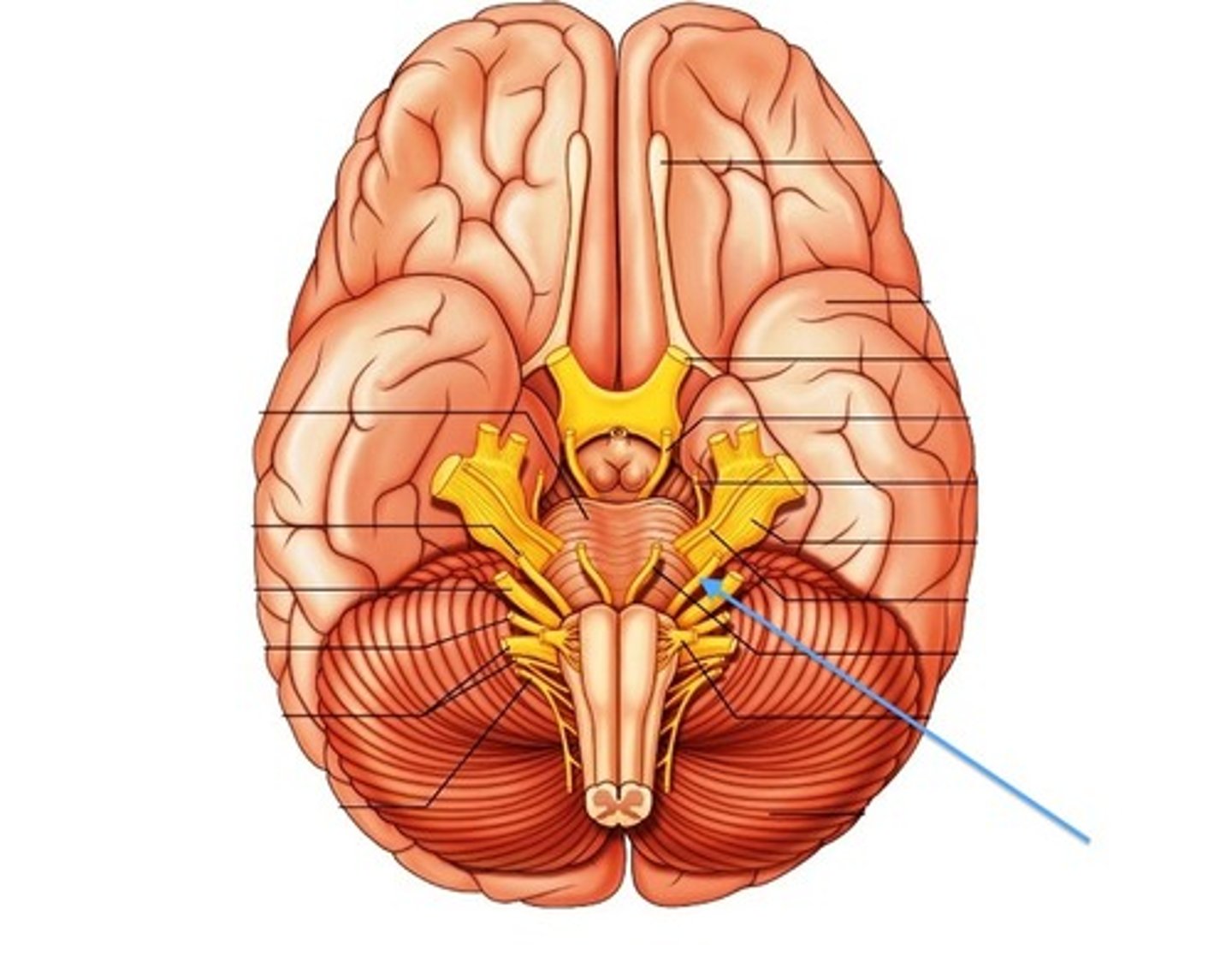
vestibulocochlear nerve
function: mostly sensory (mixed)
testing: balance and hearing
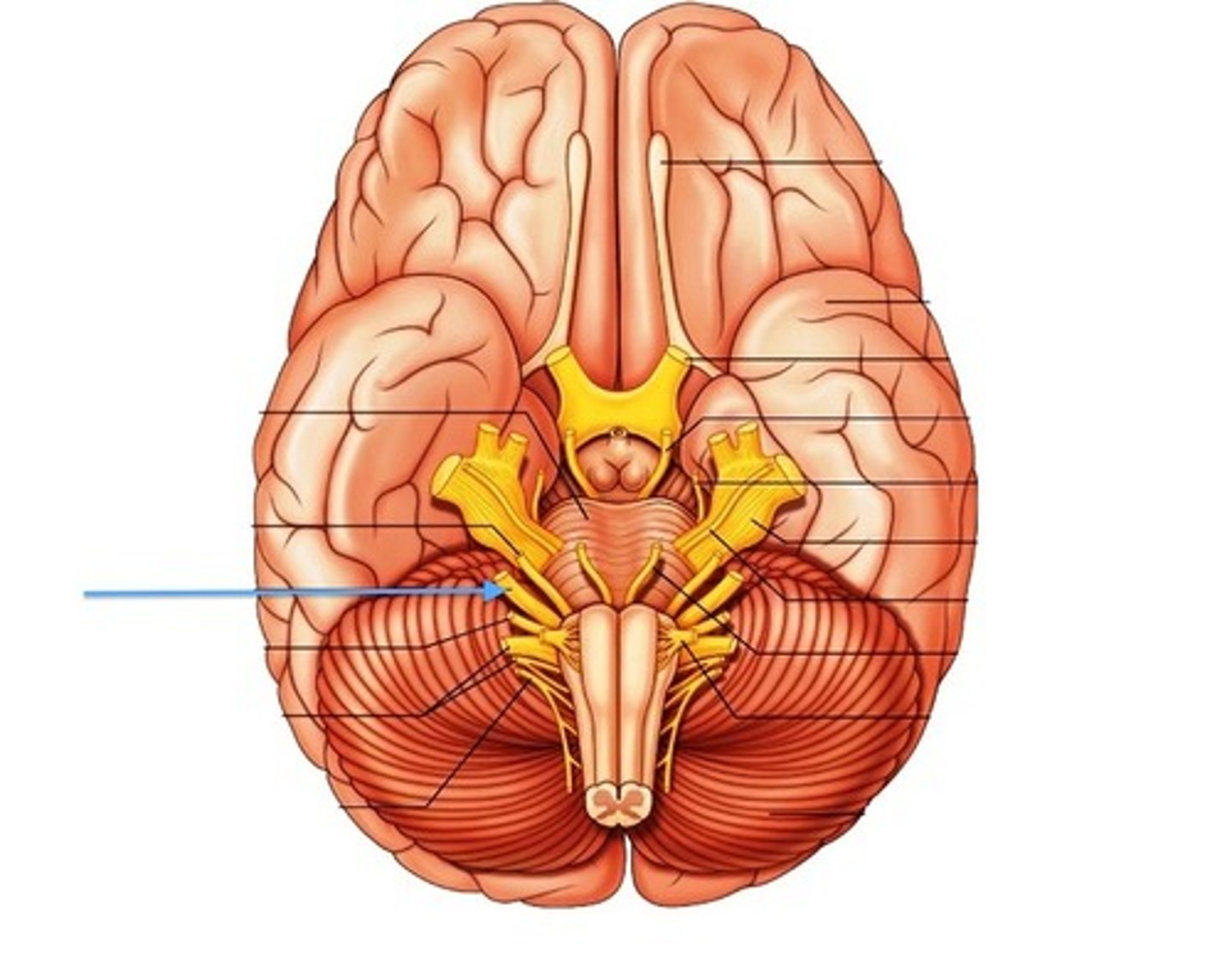
vagus nerve
function: mixed
cardiac and smooth muscle organs. PARASYMPATHETIC
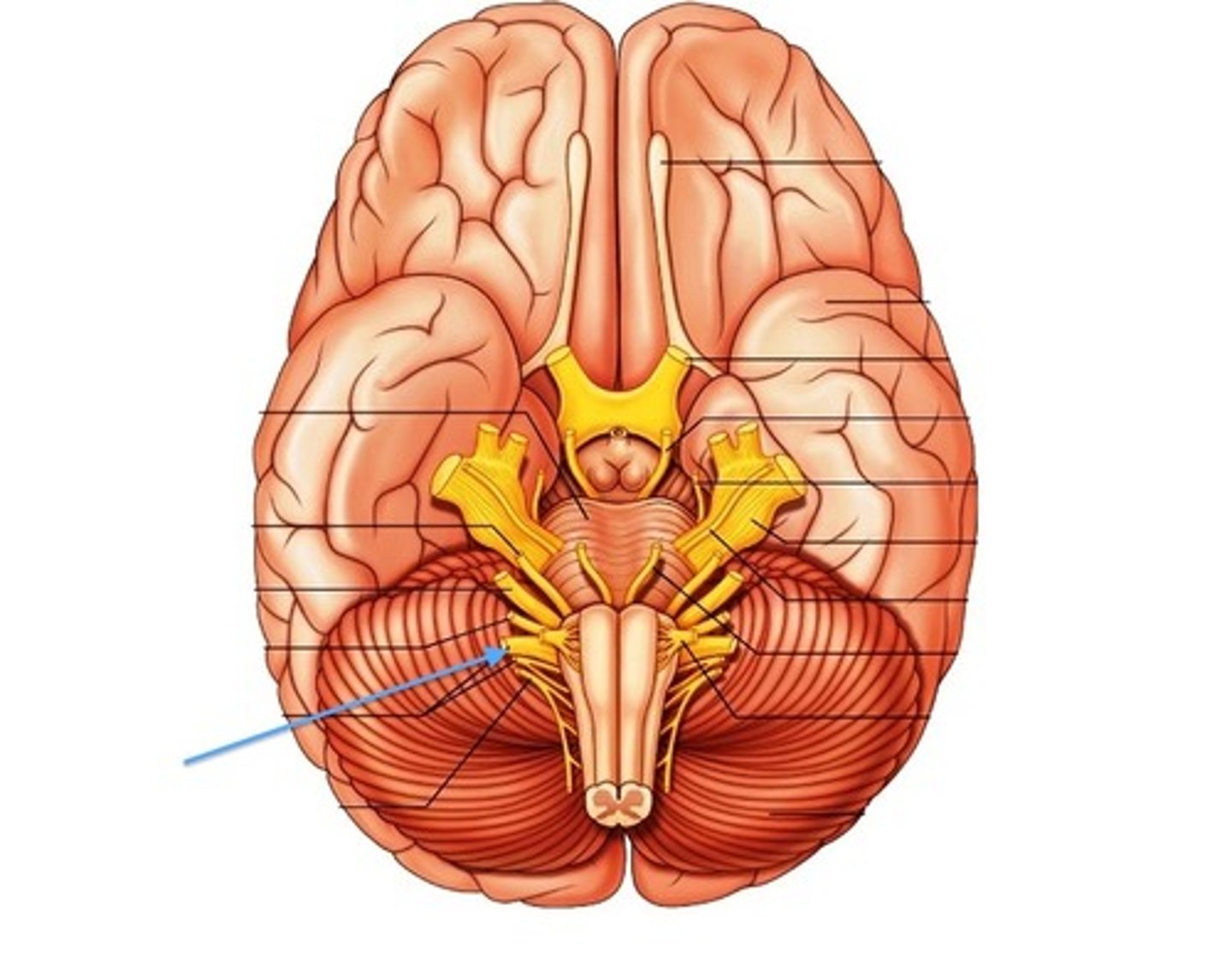
glossopharyngeal nerve
(R)
function: mixed
Posterior tastebuds, Pharyngeal muscles. PARASYMPATHETIC
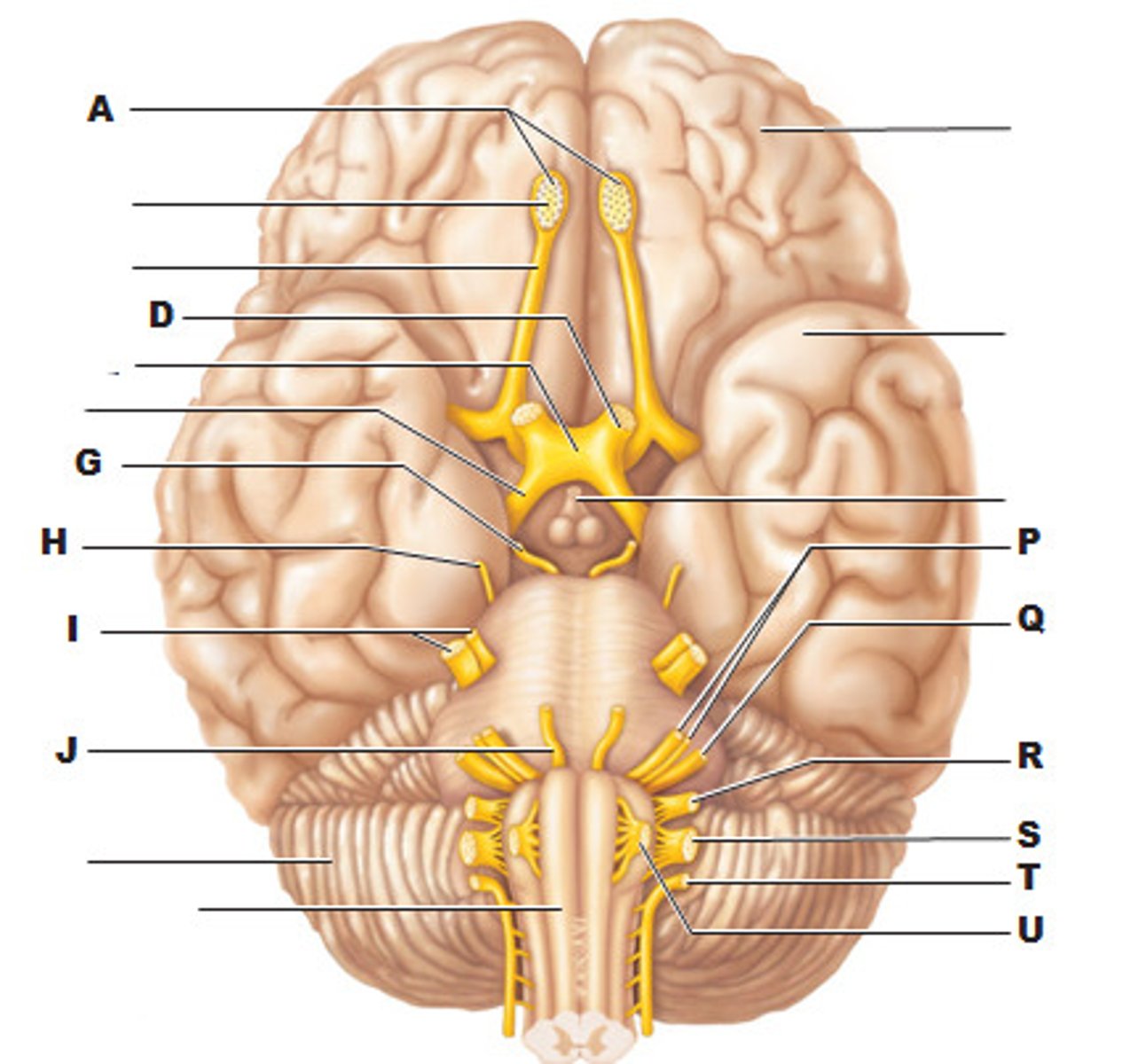
accessory nerve
function: mixed
testing: spinal and cranial nerves
(sternocleidomastoid and trapezius)
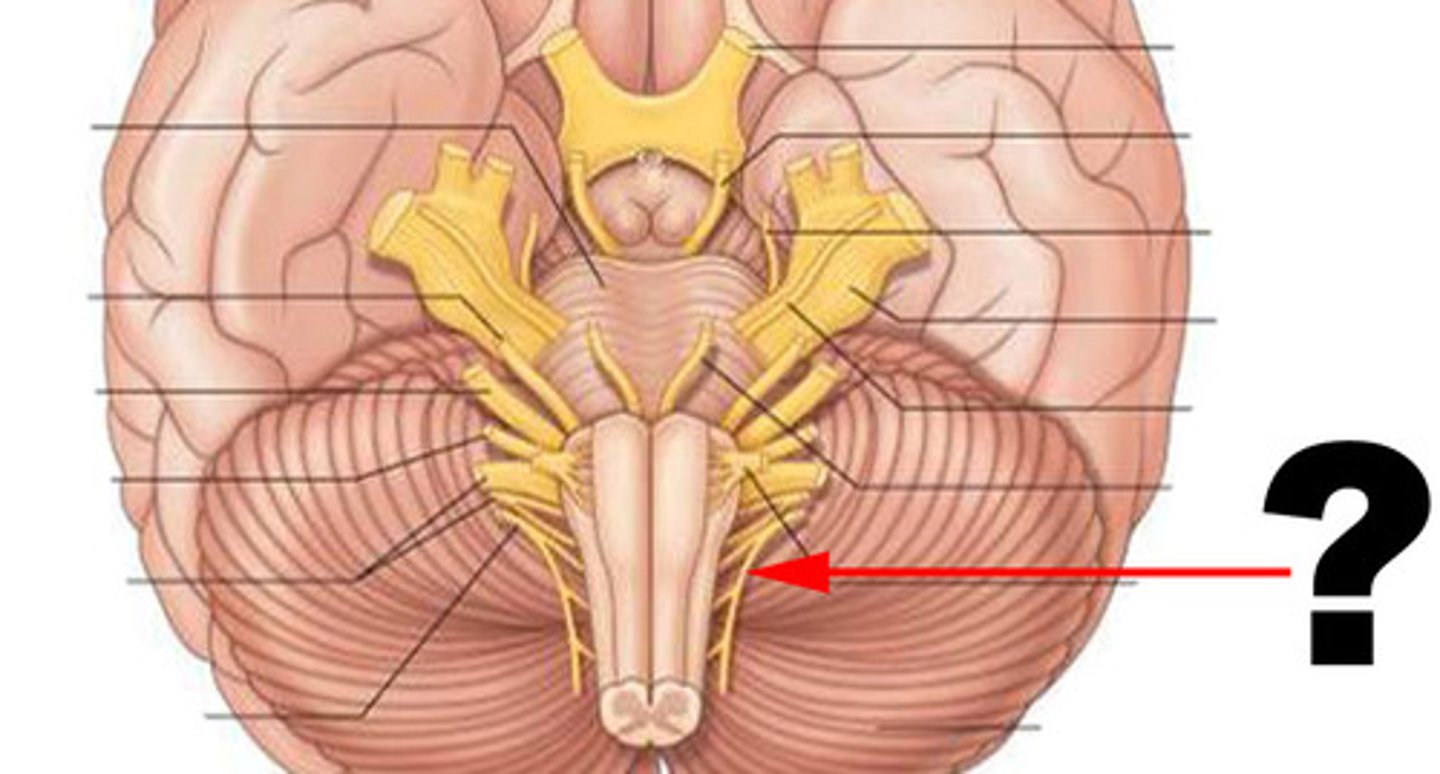
hypoglossal nerve
function: mixed (primarily motor)
testing: tongue movement
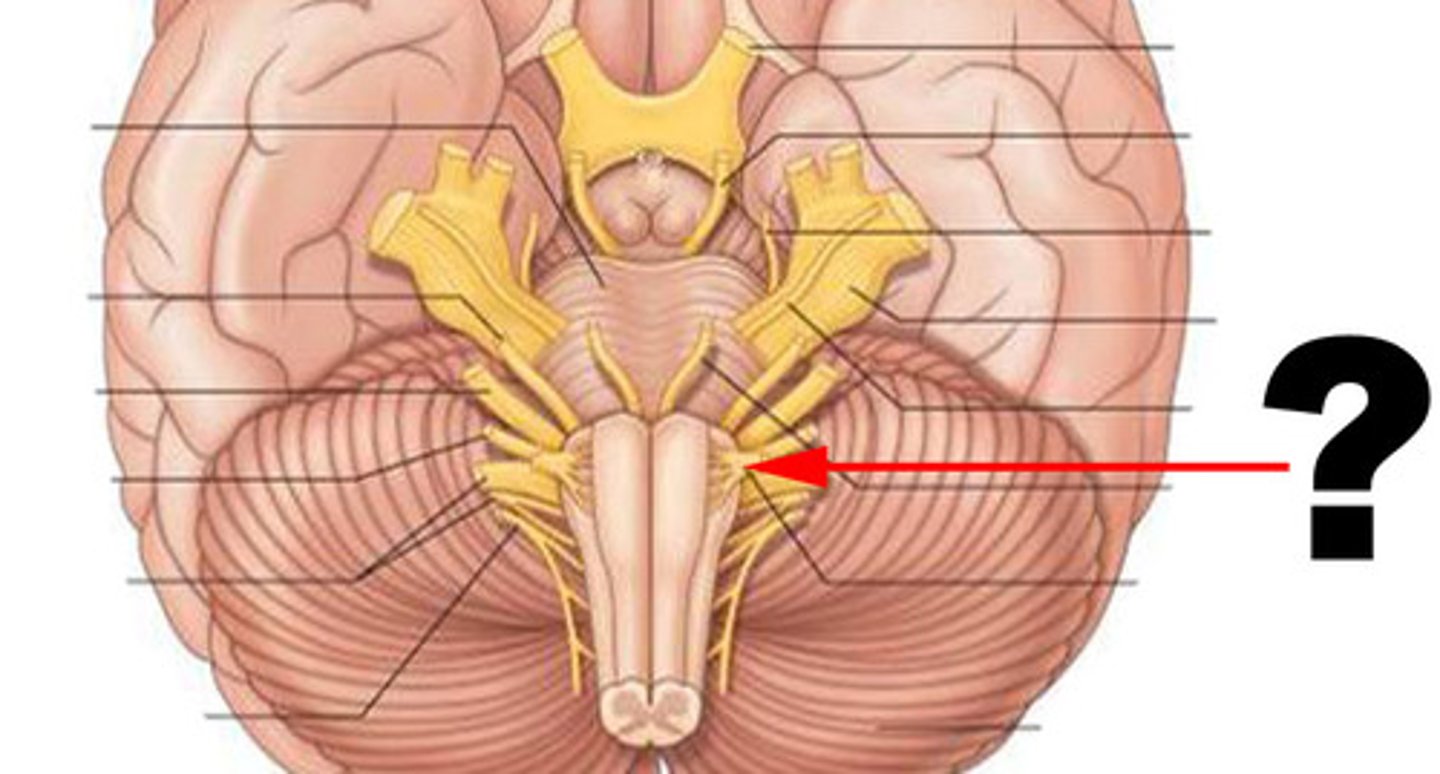
spinal meninges
(E)
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
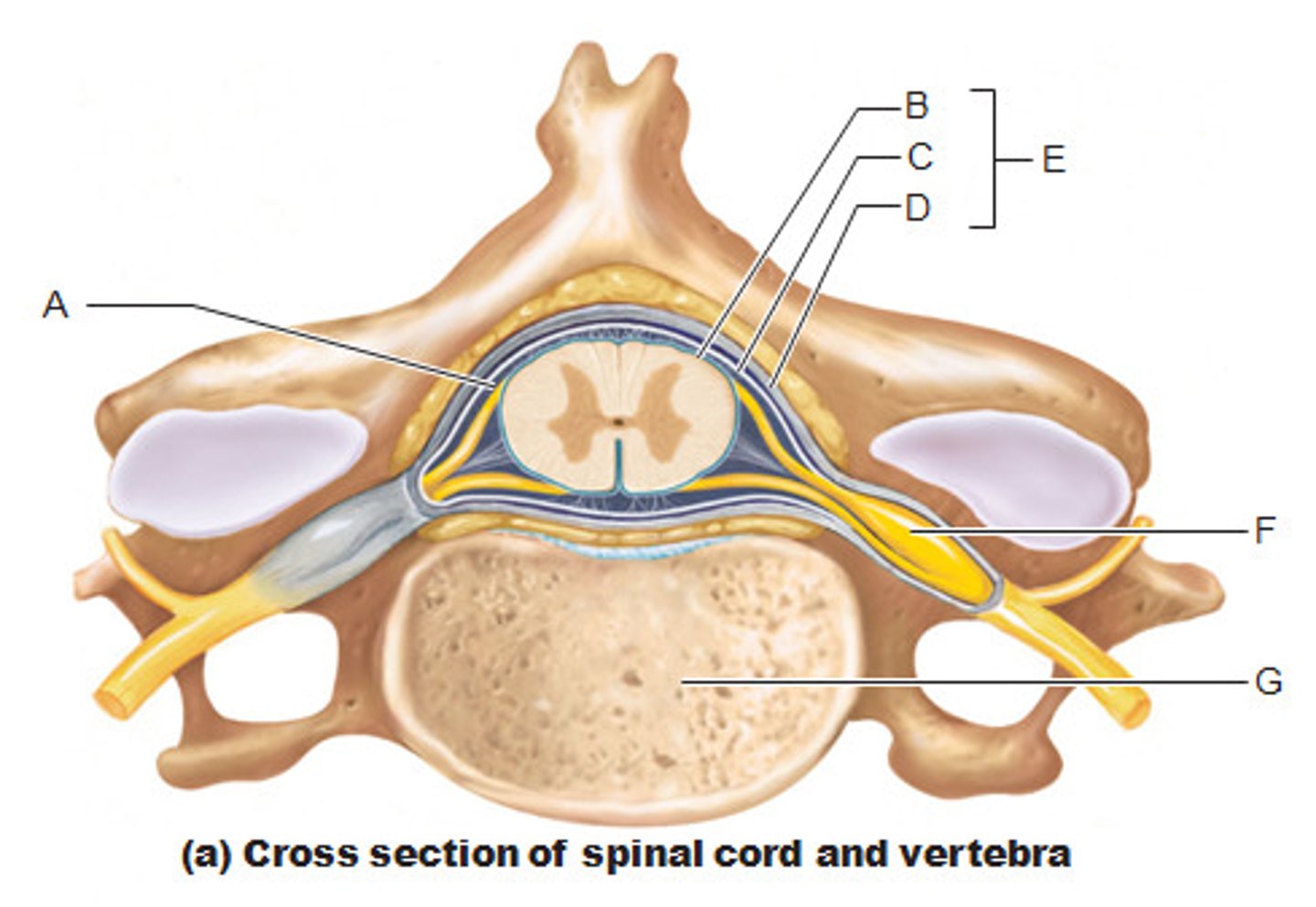
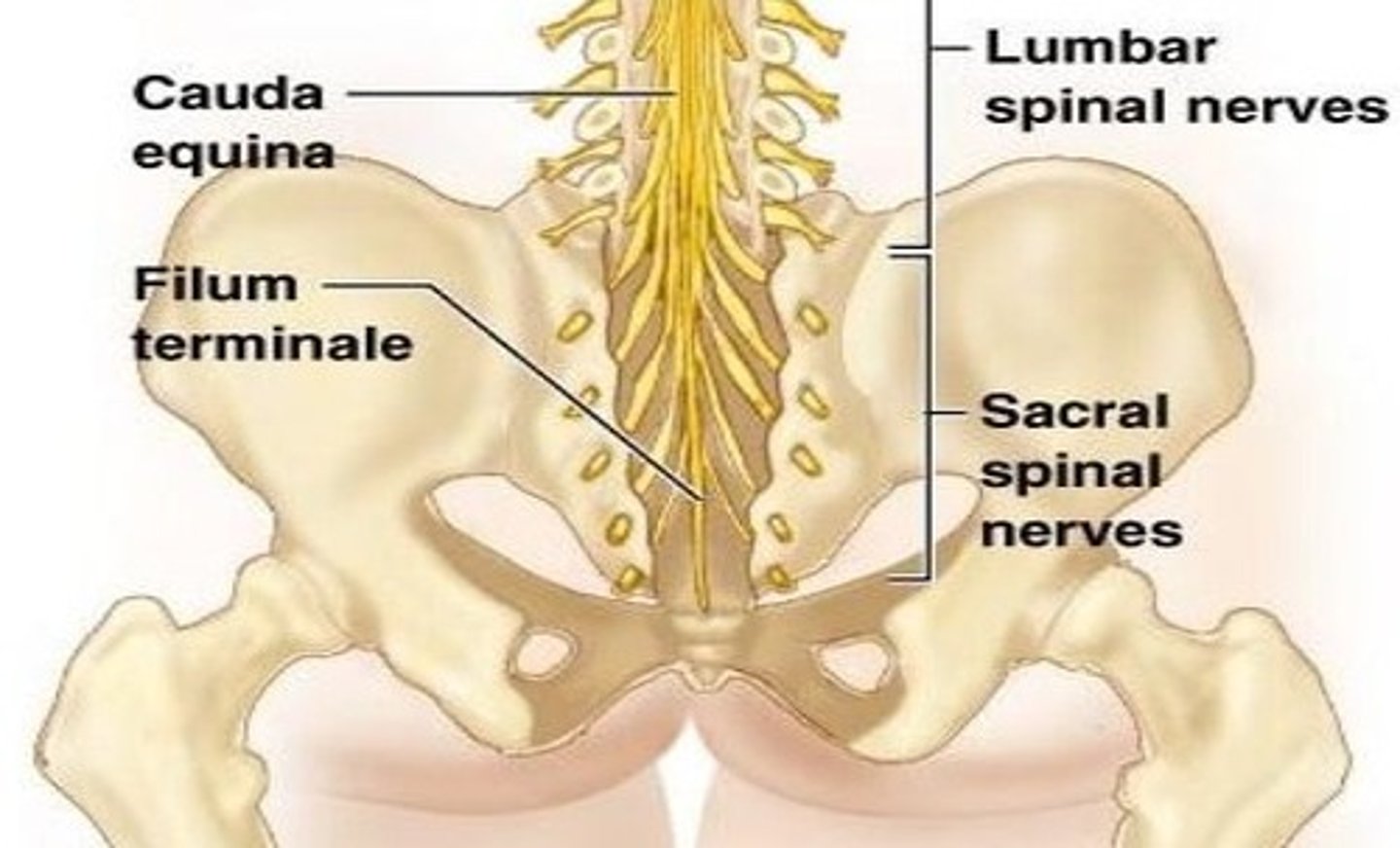
conus medullaris location
between L1 and L2
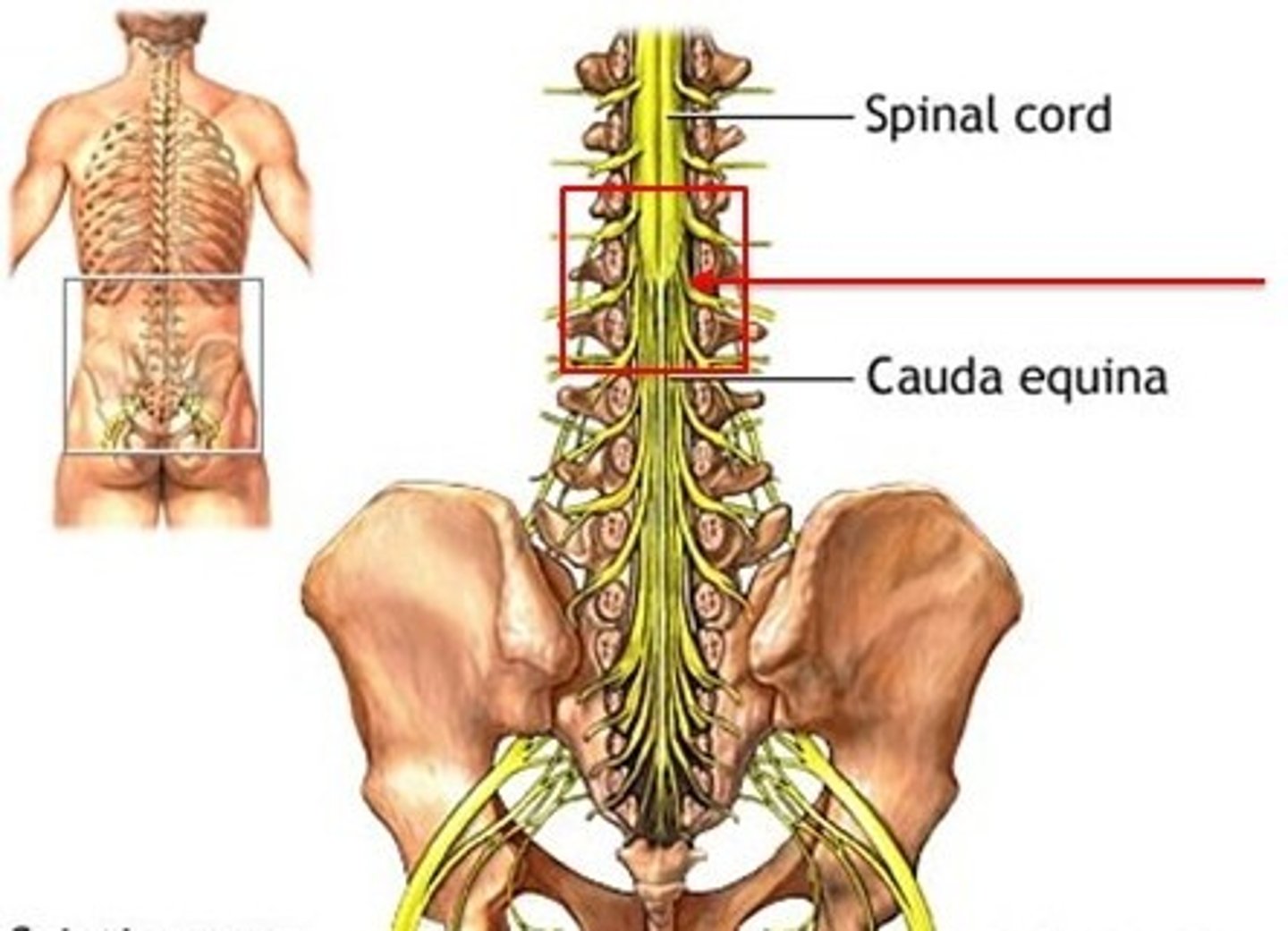
filum terminale
anchors spinal cord to coccyx
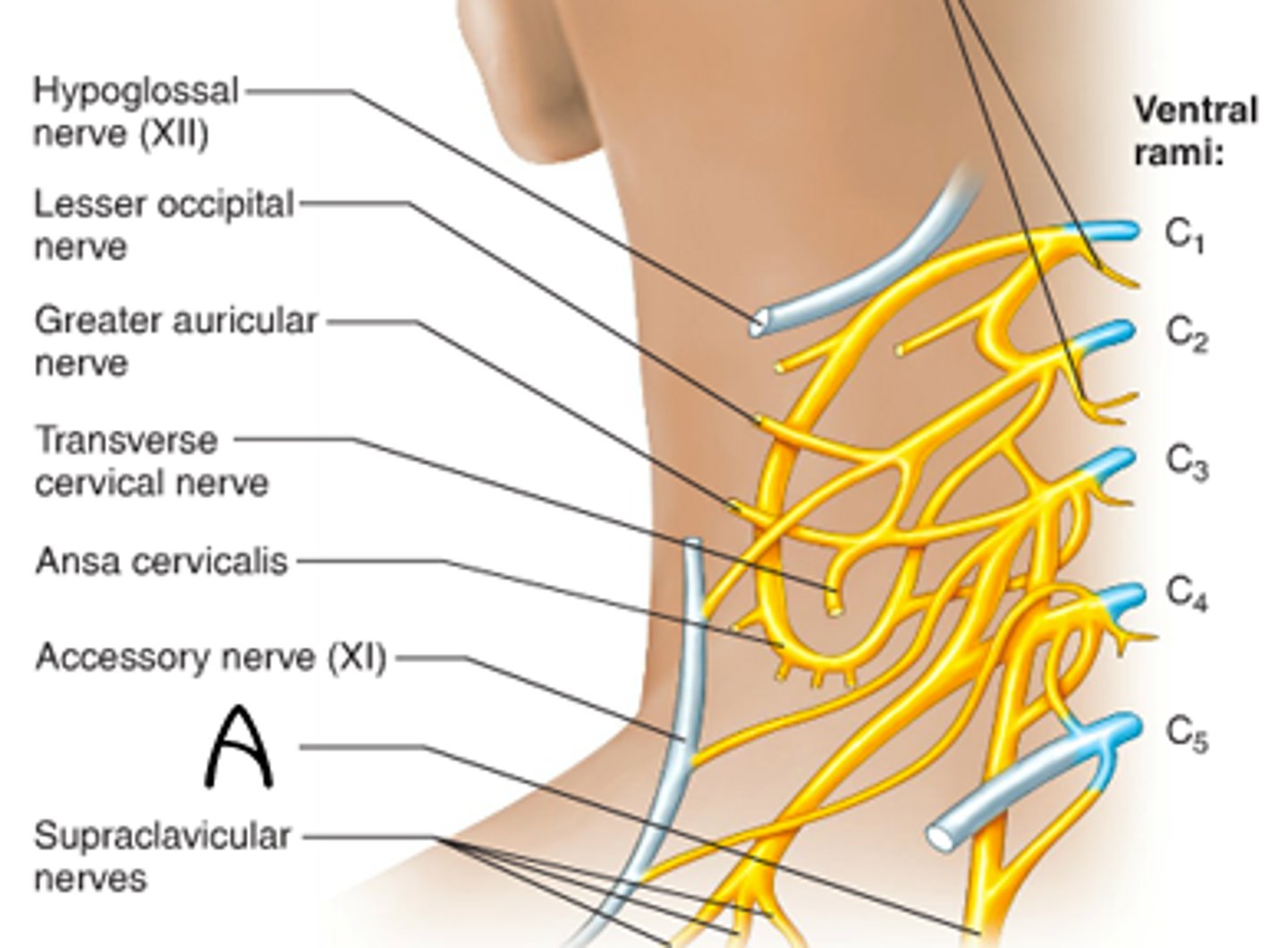
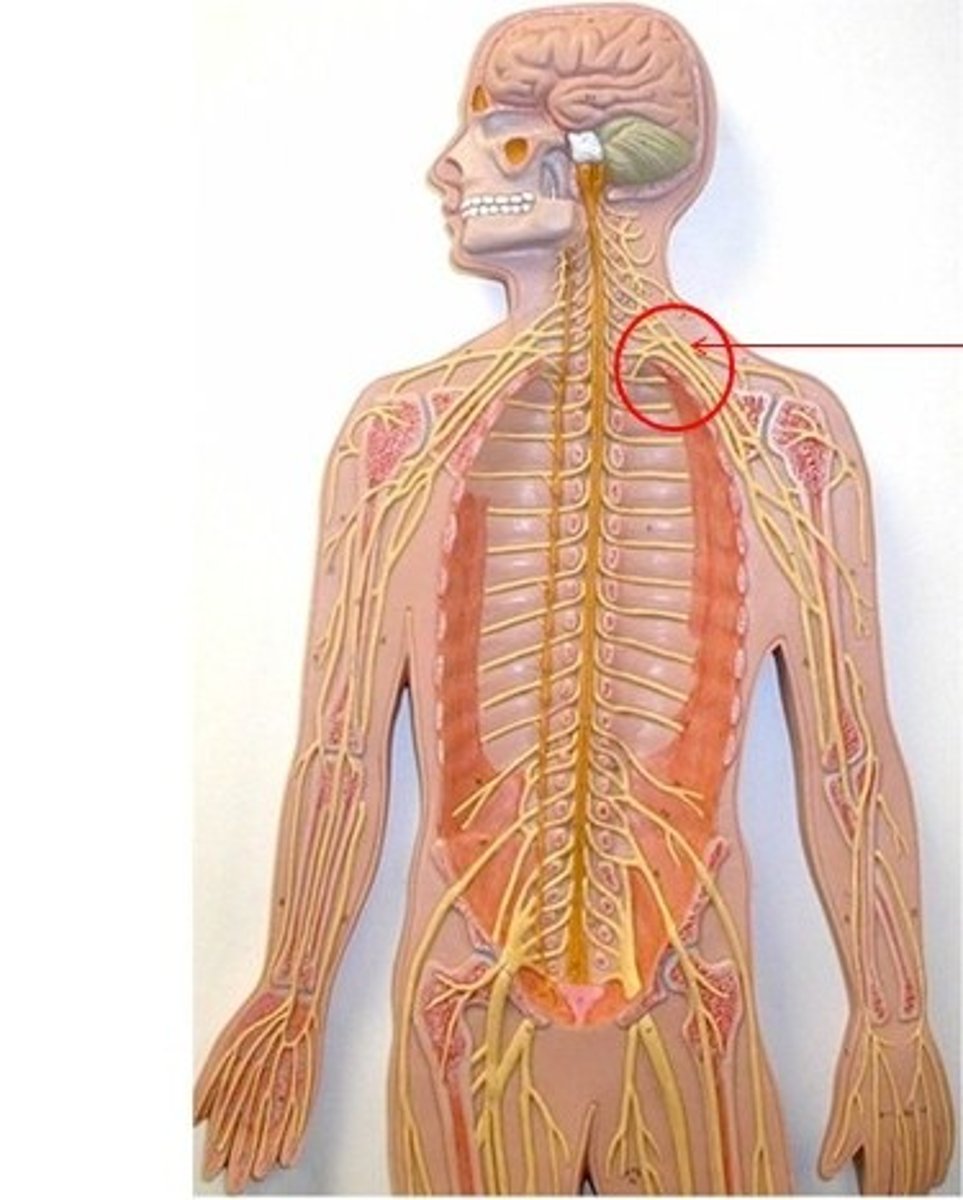
cervical plexus
C1-C5
supplies neck and phrenic nerve to the diaphragm
phrenic
- C3-C5
- Diaphragm
brachial plexus
C5-T1
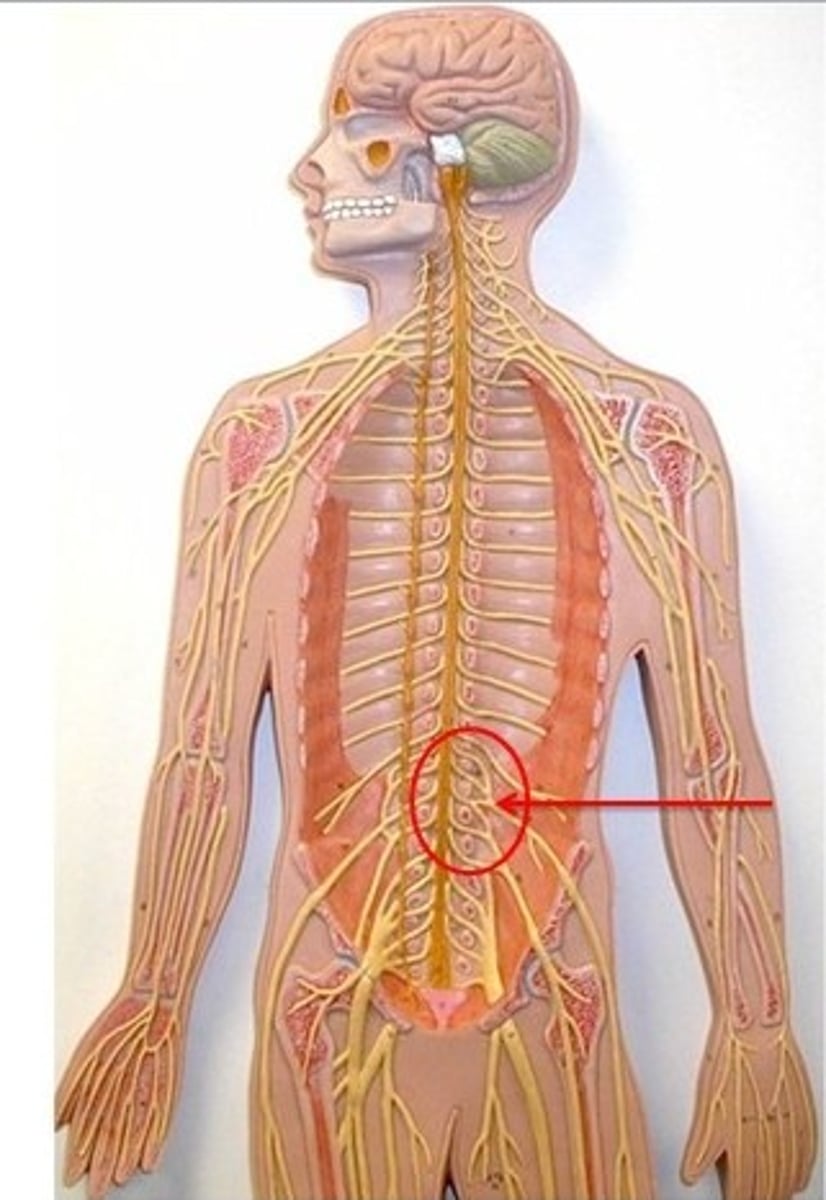
lumbar plexus
L1-L4
sacral plexus
L4-S4
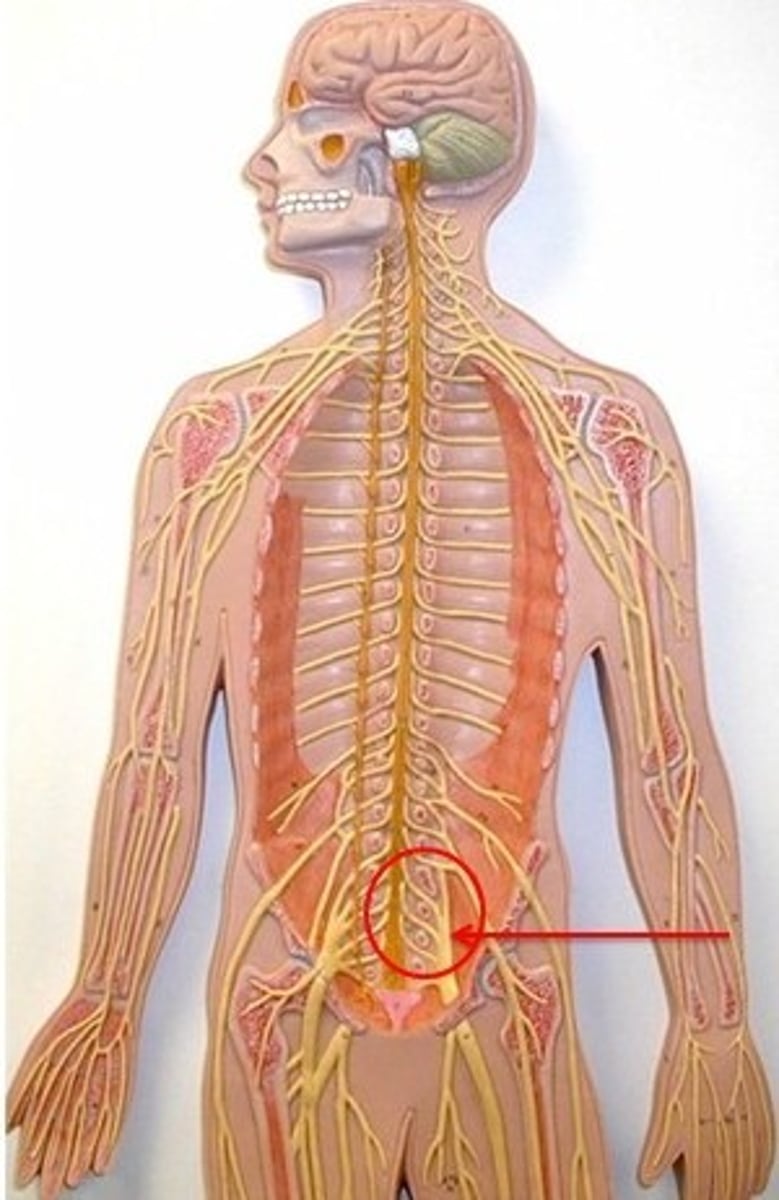
sciatic nerve
- L4-S3.
- LONGEST nerve in the body
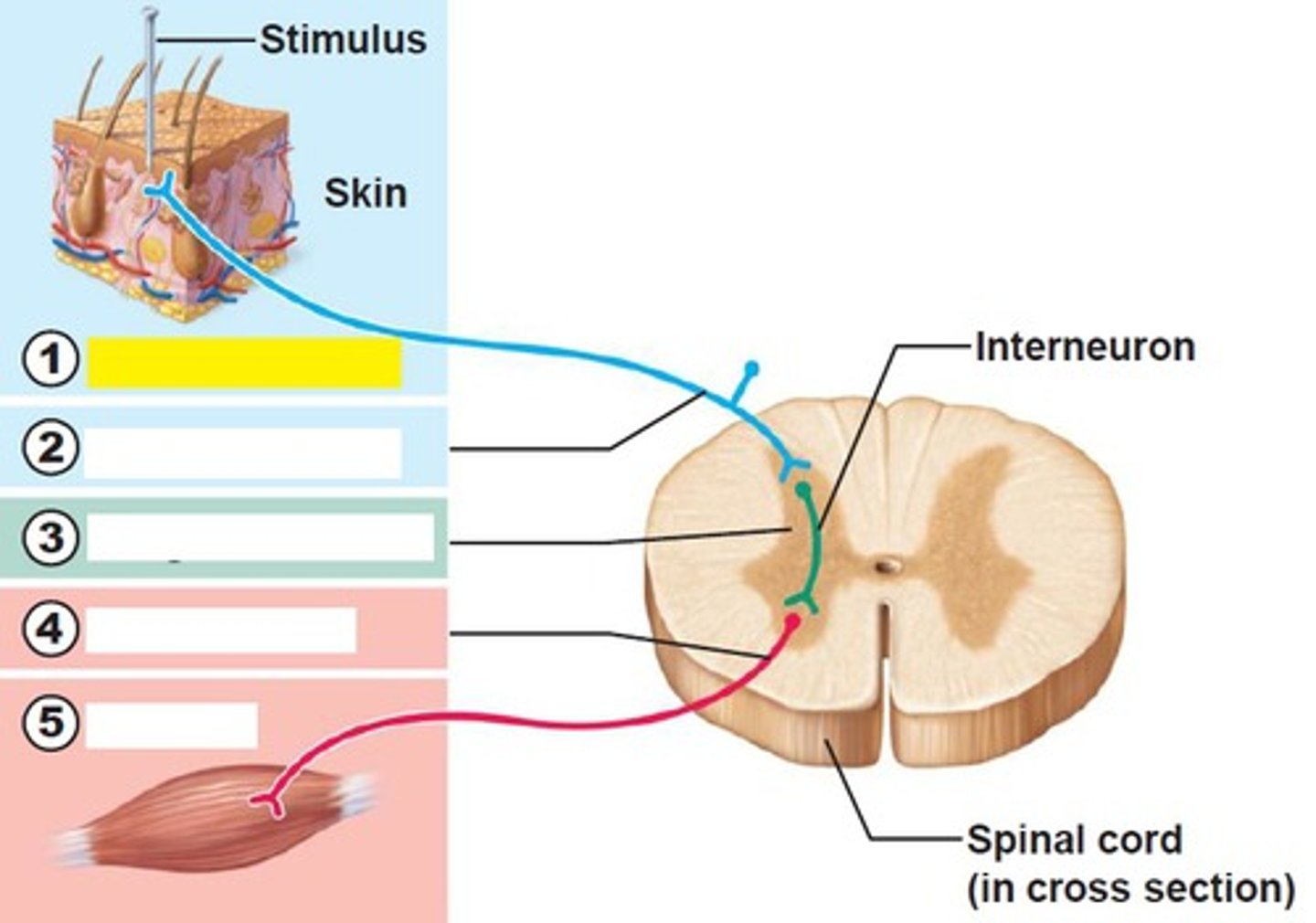
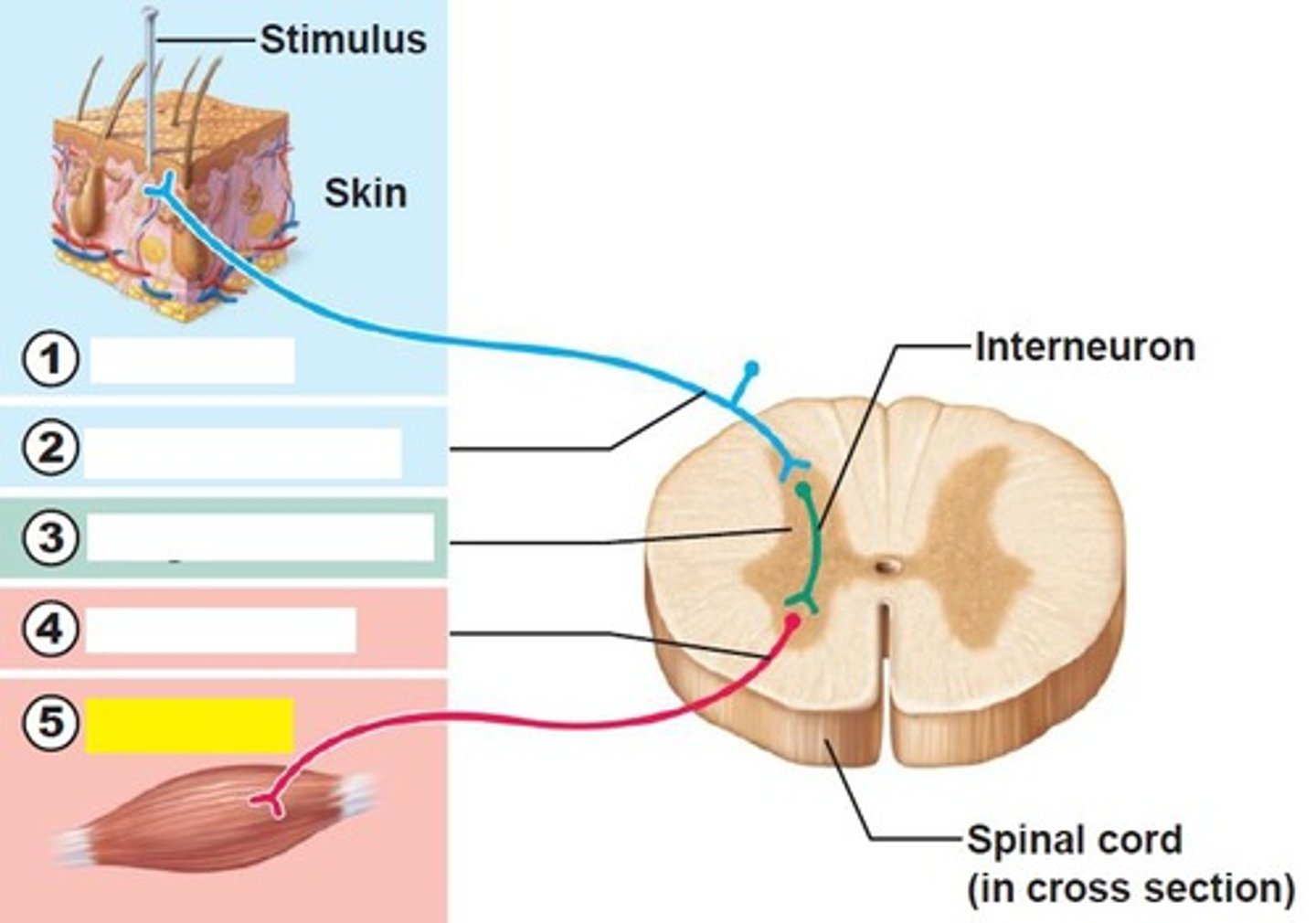
receptor of reflex arc
site of stimulus action
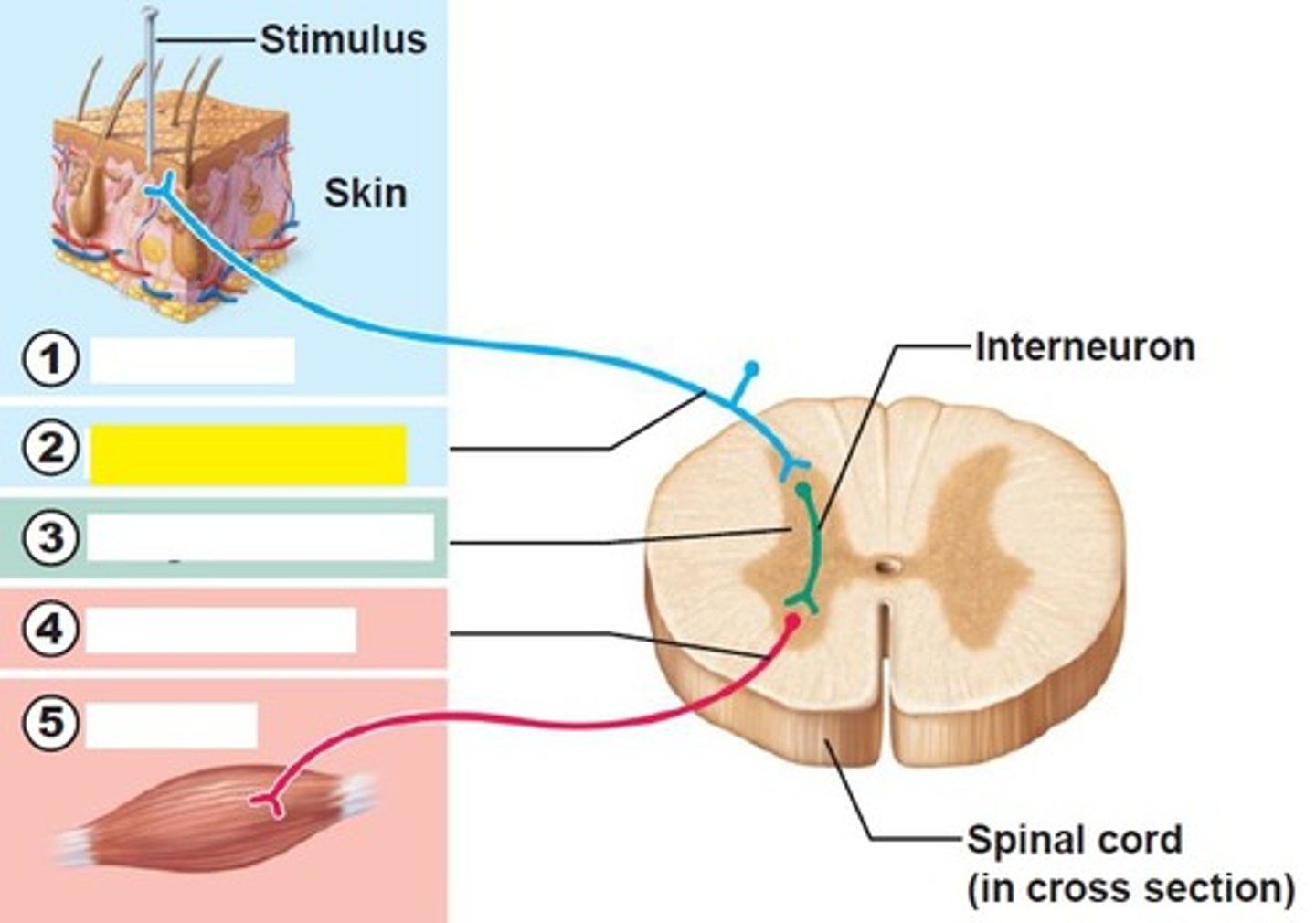
sensory neurons of reflex arc
transmits afferent impulses to the CNS
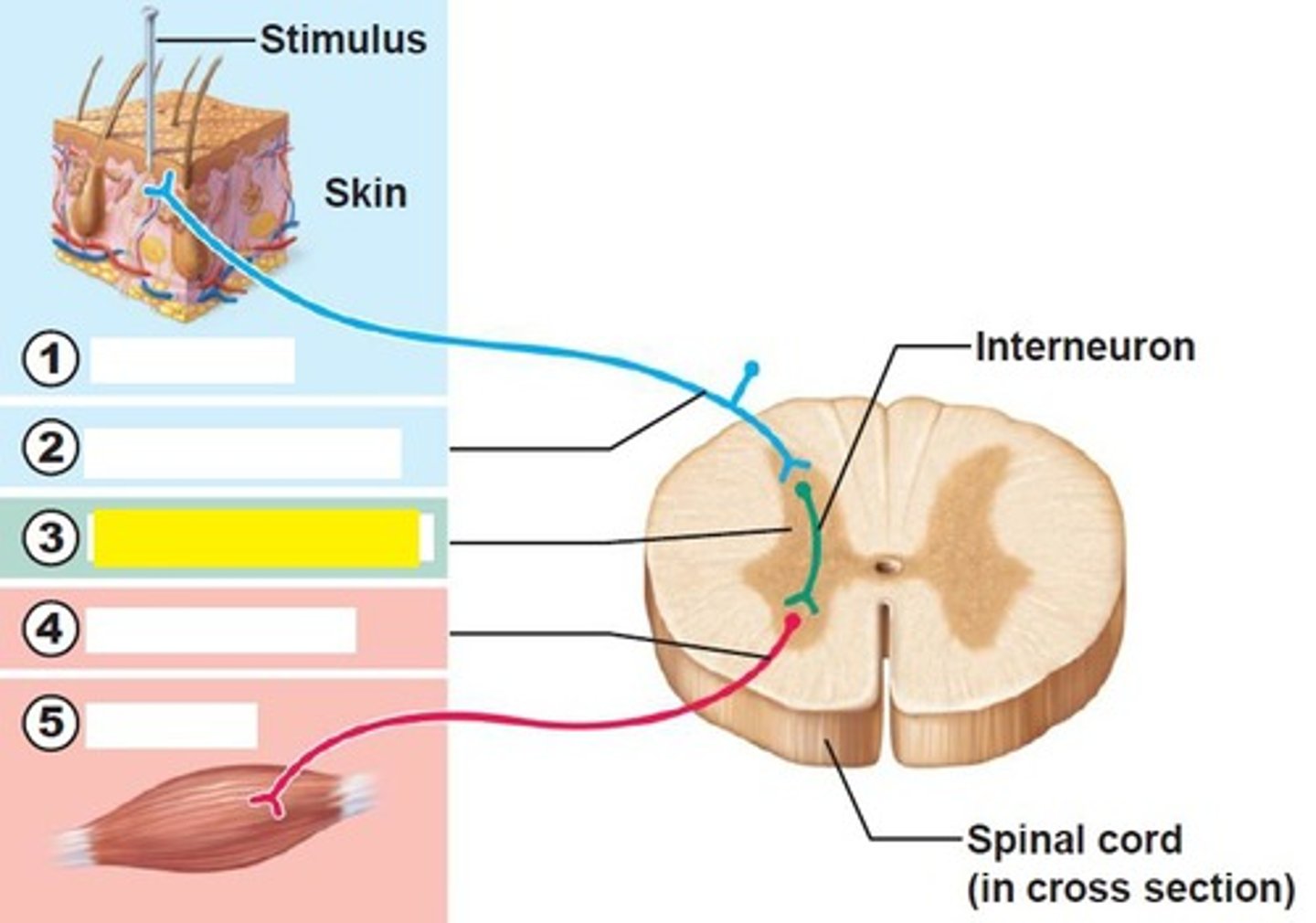
integration center of reflex arc
either monosynaptic or polysynaptic region within the CNS
motor neuron of reflex arc
conducts efferent impulses from the integration center to an effector
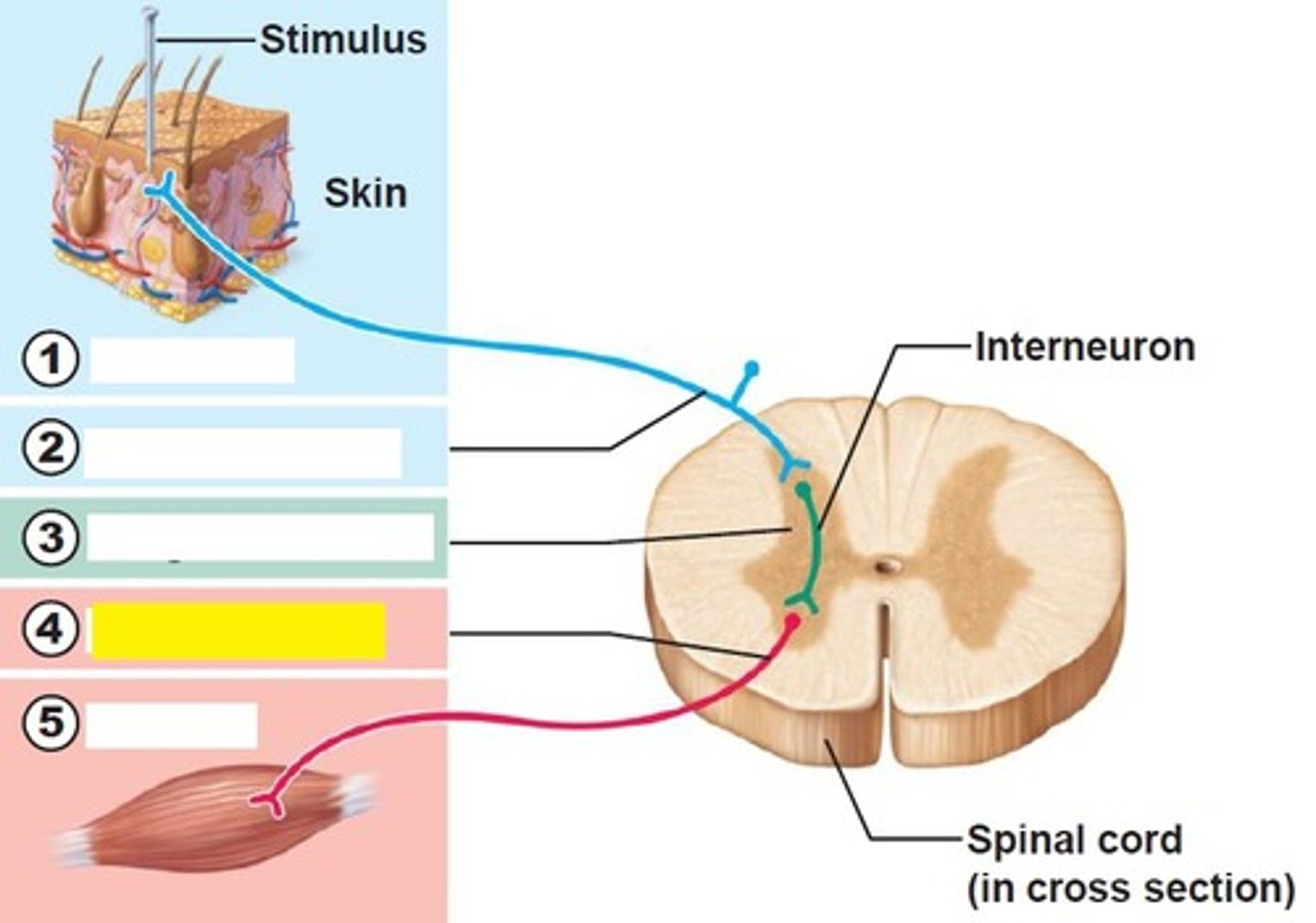
effector of reflex arc
muscle fiber or gland that responds to the efferent impulse
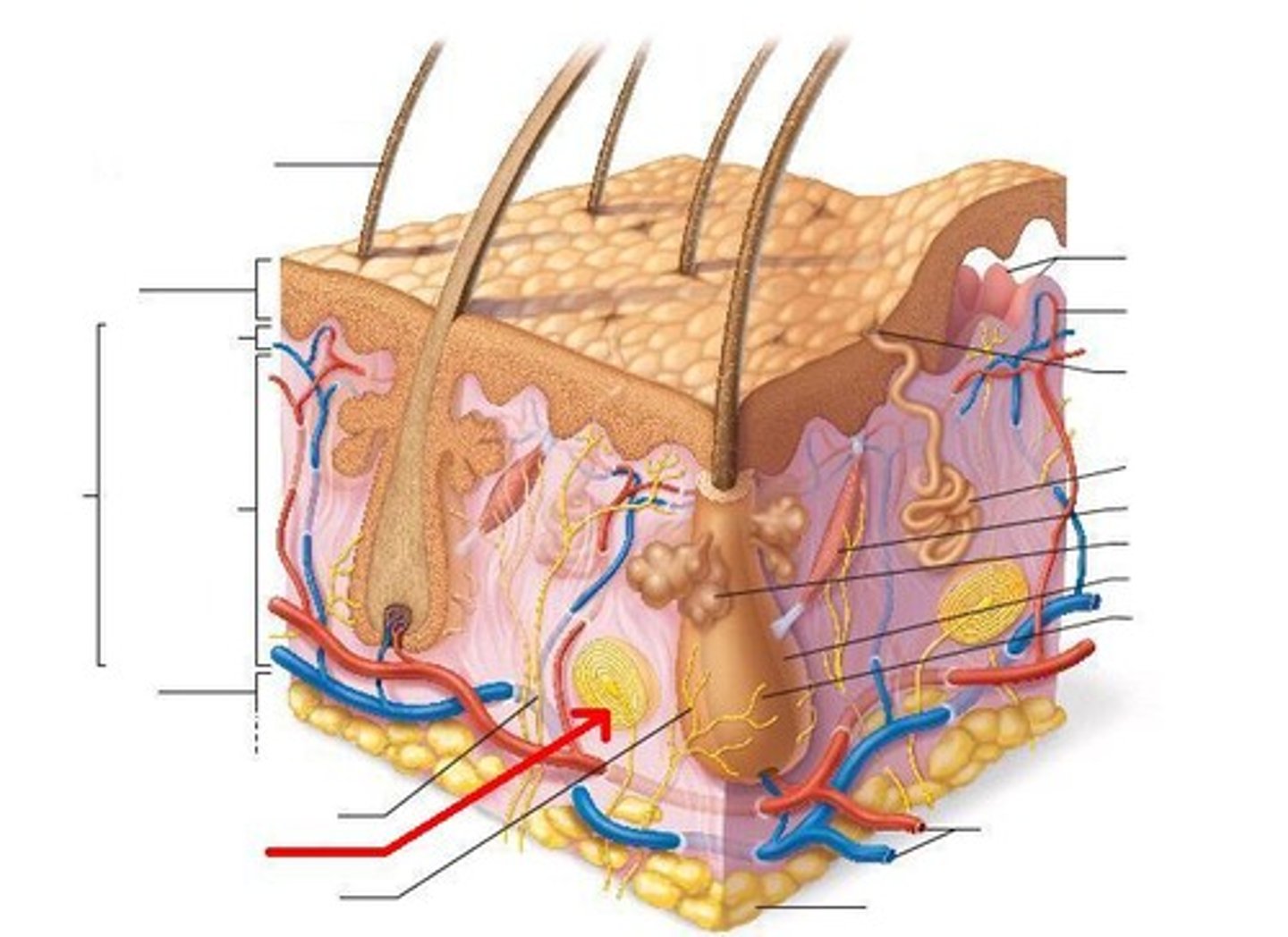
bulbous corpuscles
(6)
deep CONTINUOUS pressure
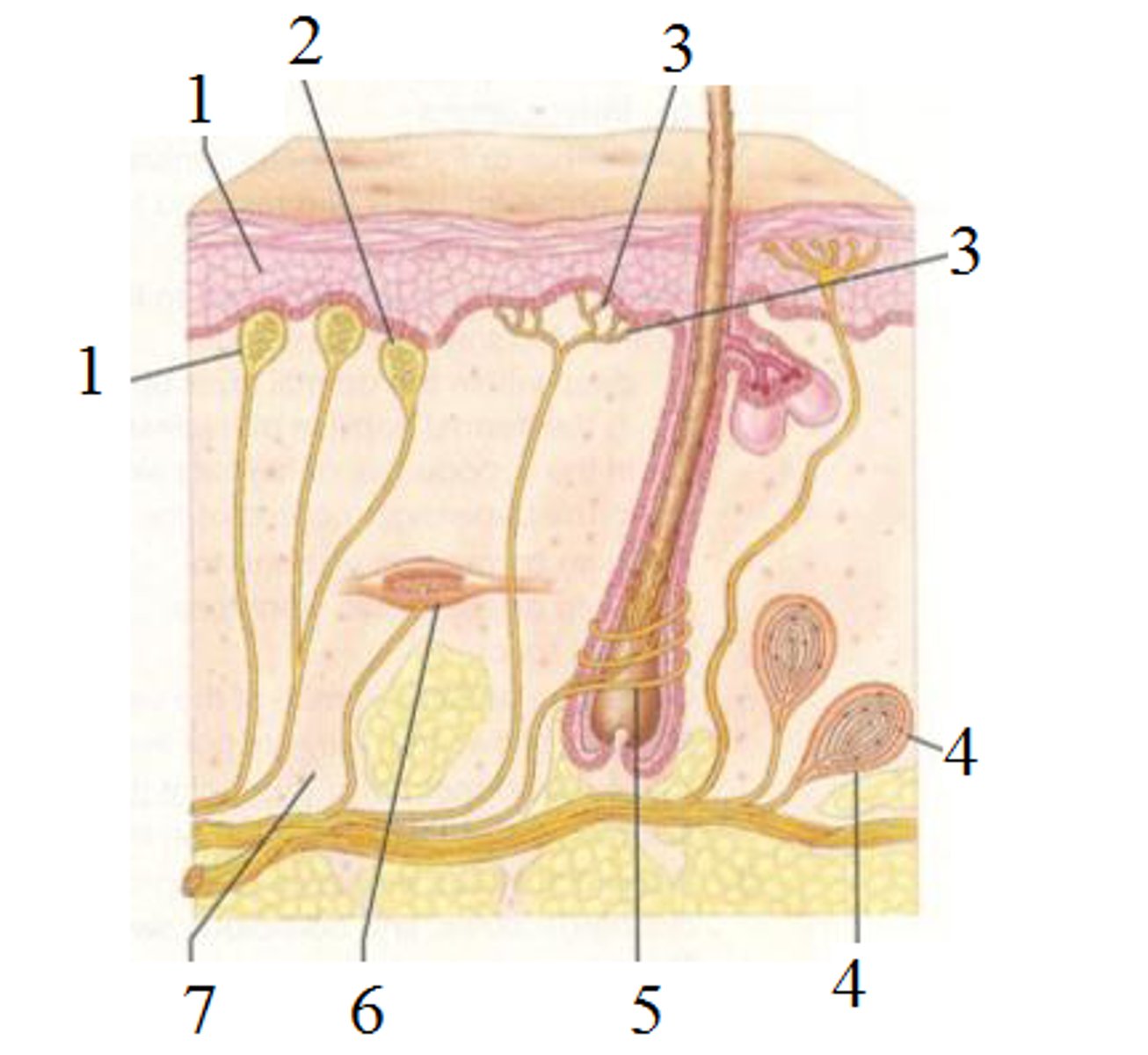
hair follicle receptors
hair movement, light touch
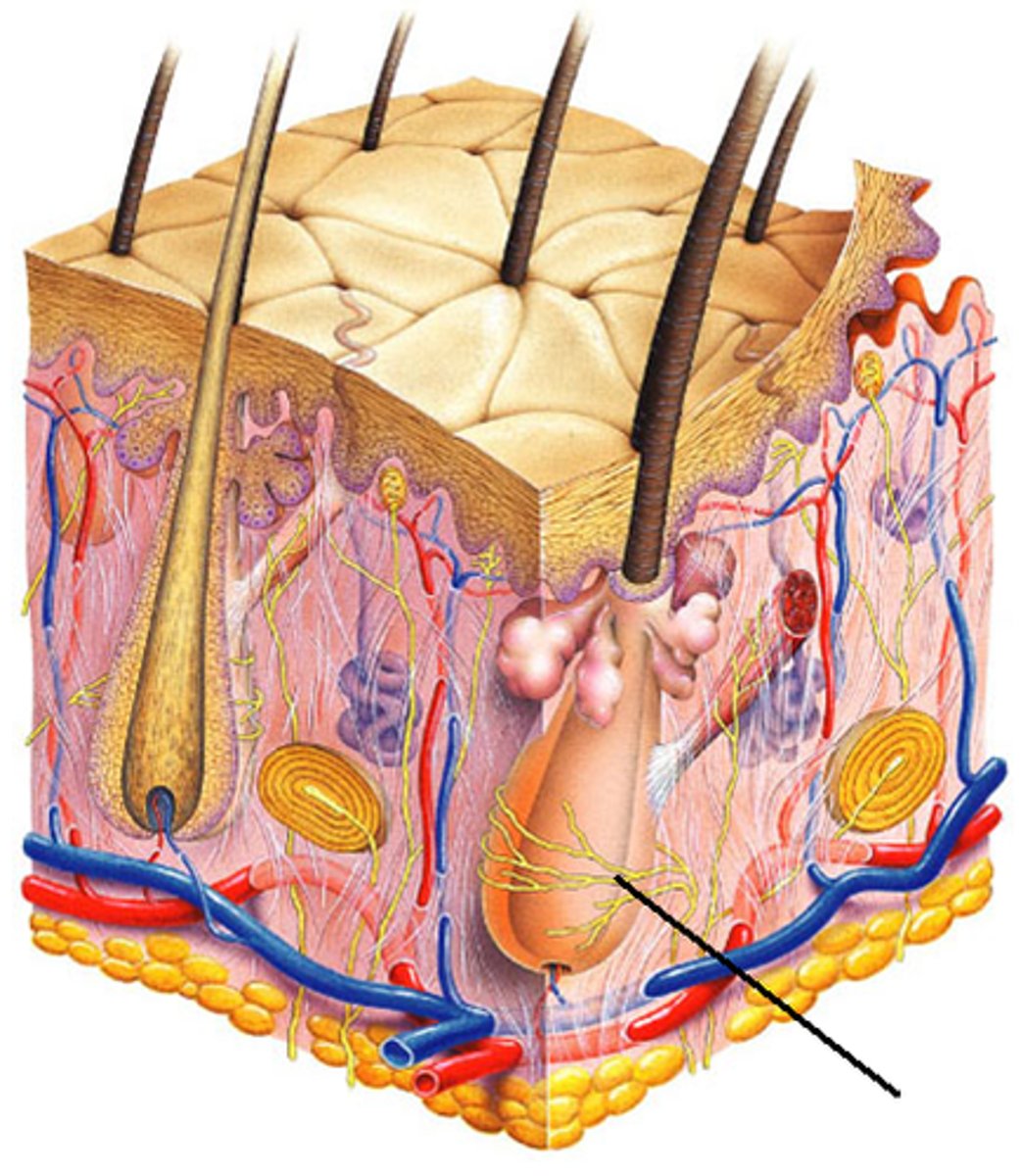
lamellar corpuscle
deep pressure receptor
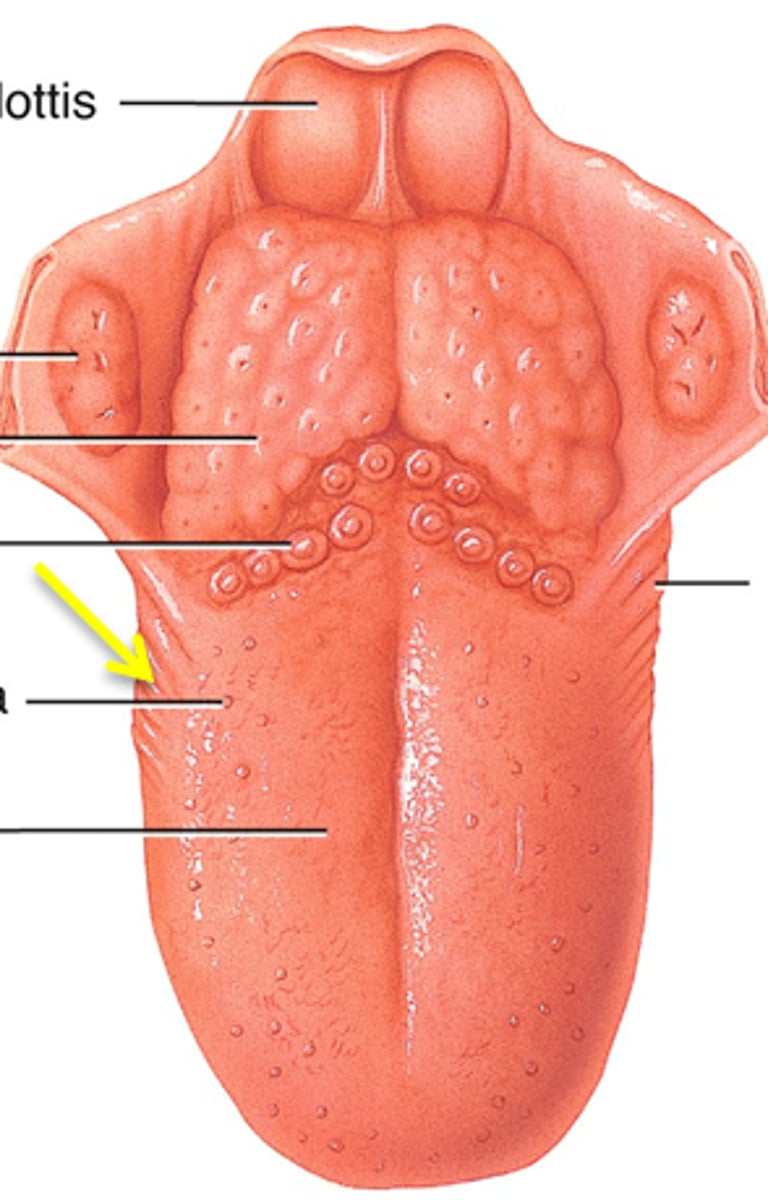
Foliate Papillae
on side walls of tongue; contain taste buds
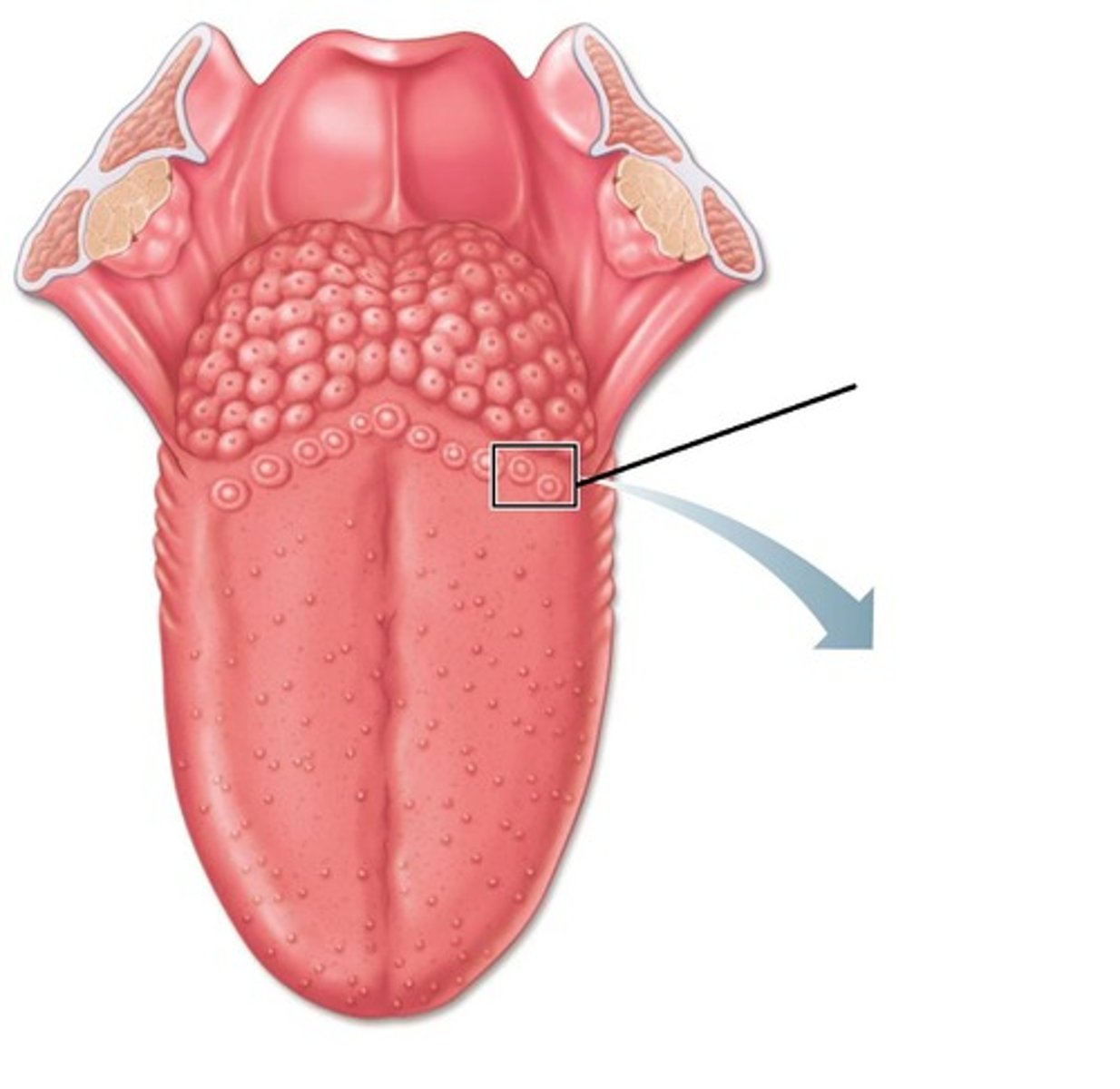
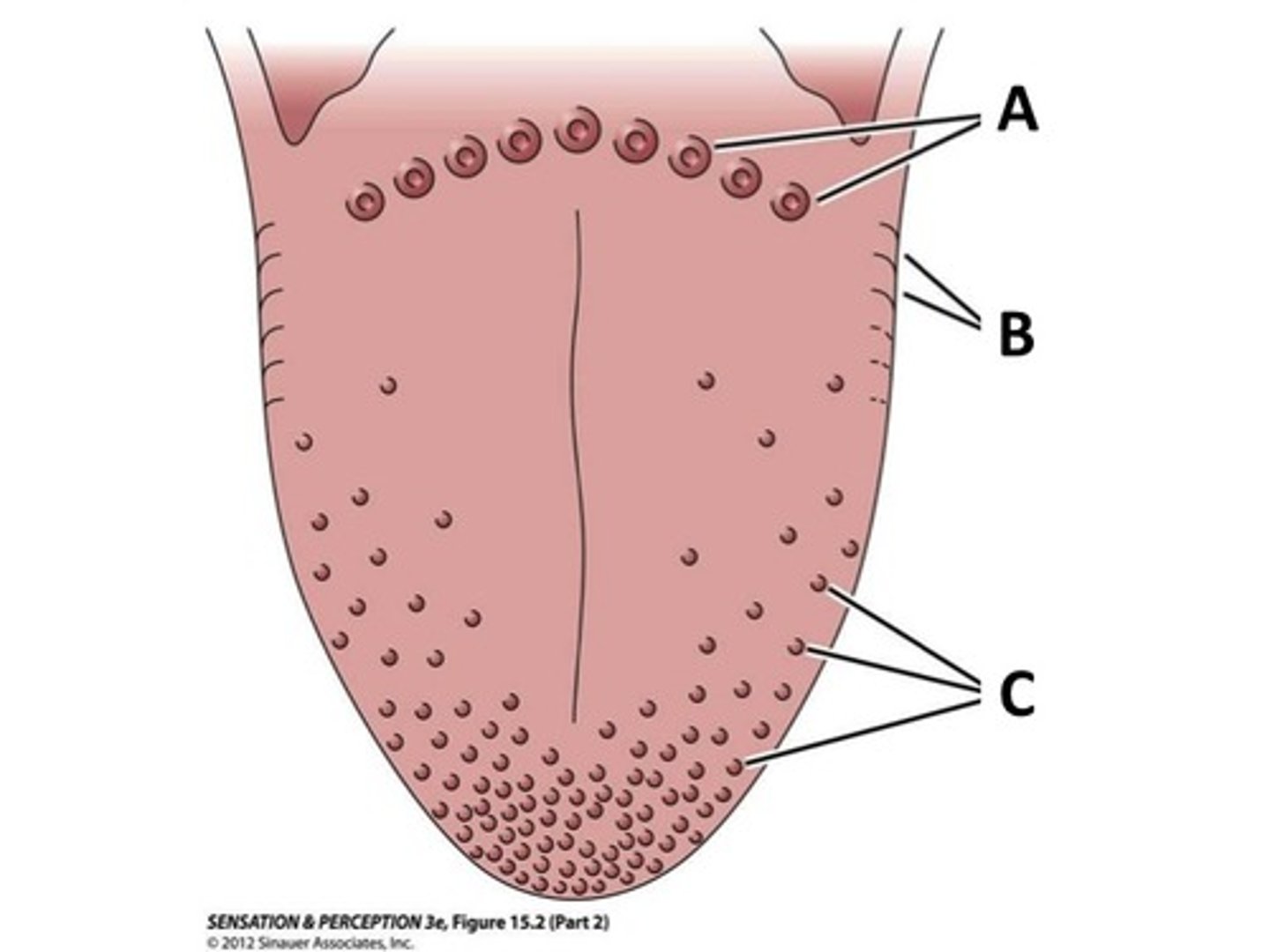
vallate papillae
largest taste buds with 8-12 forming "V" at back of tongue
fungiform papillae
(C)
Mushroom-like protuberances often containing taste buds and located on the sides and tip of the tongue.
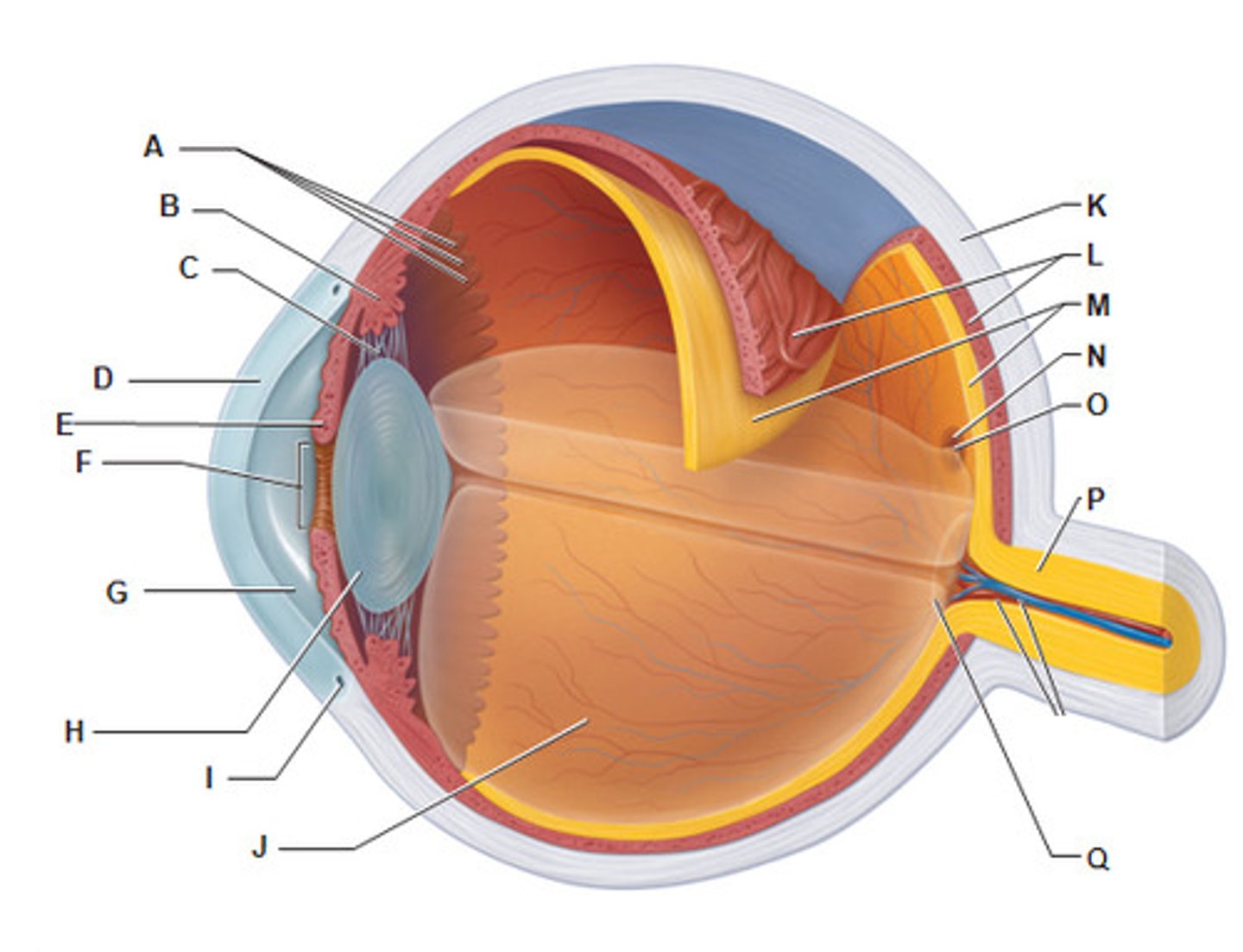
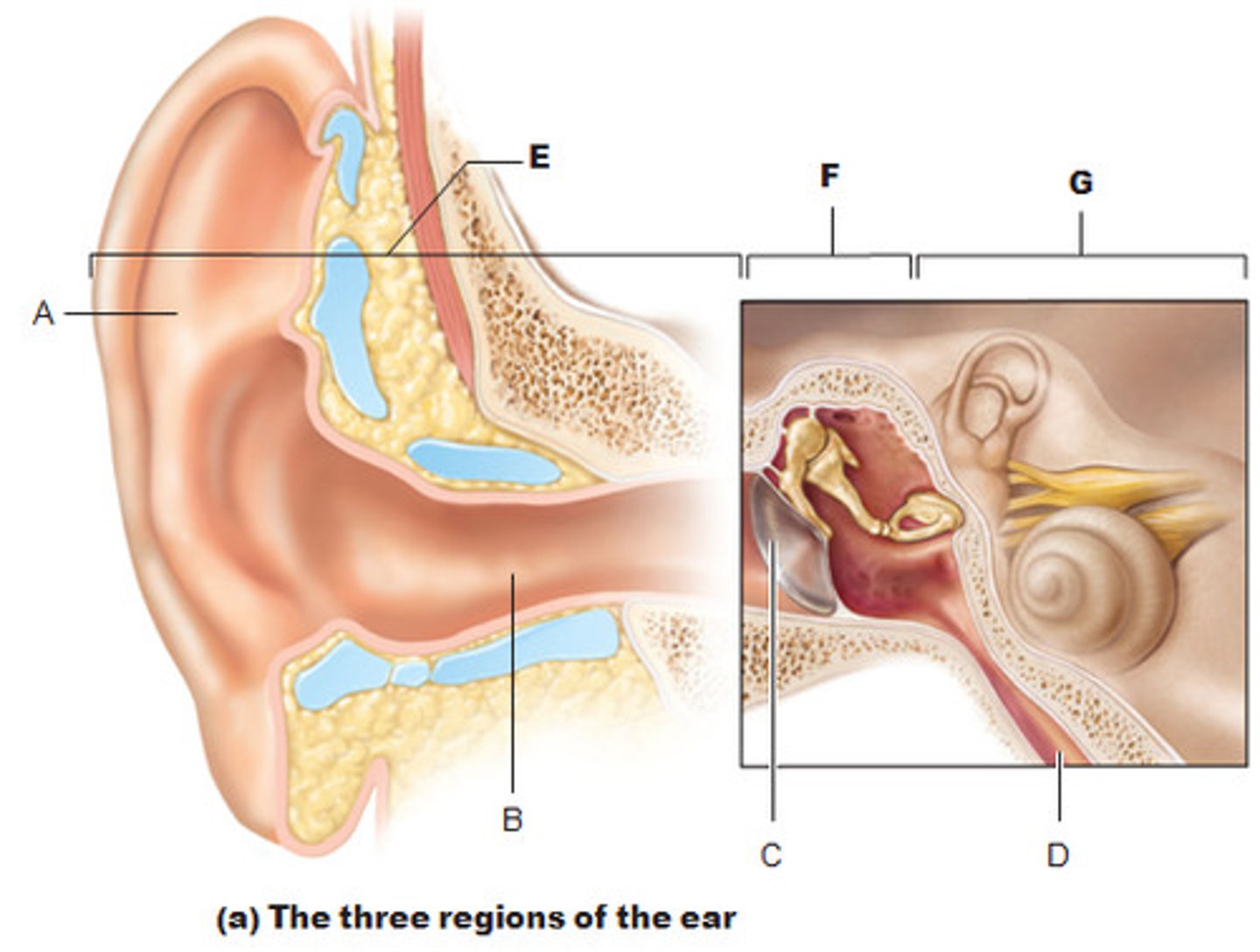
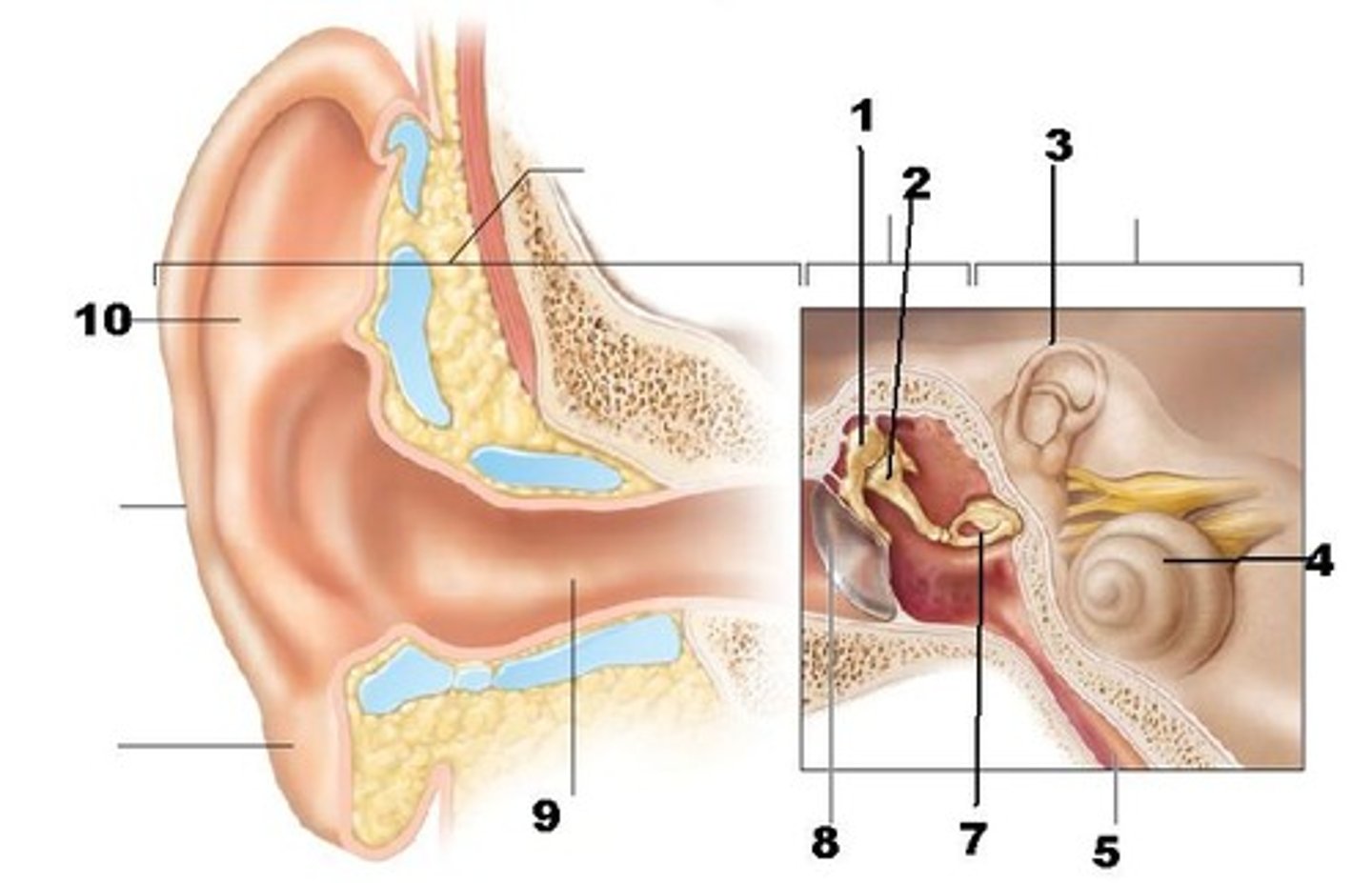
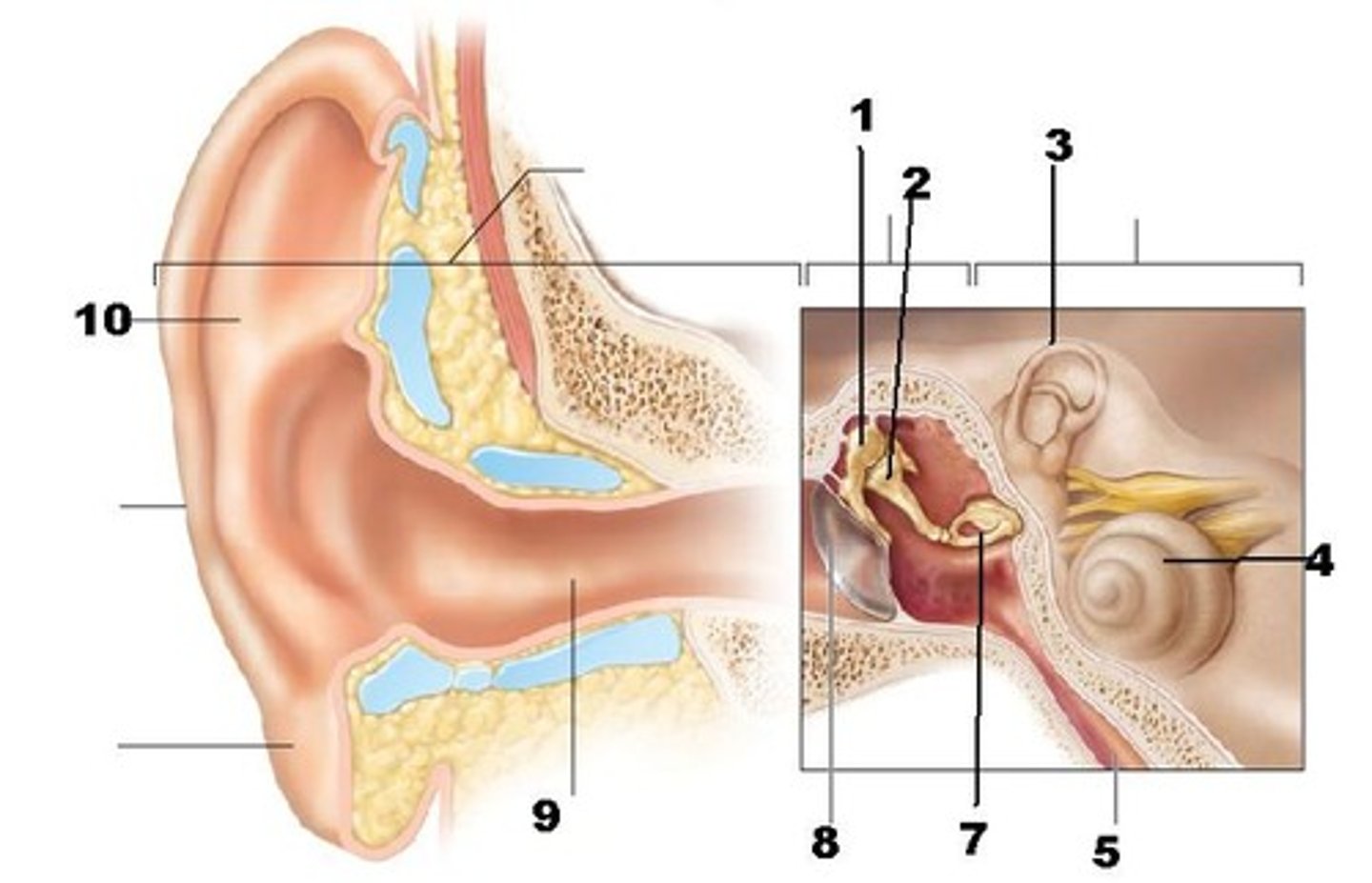
Pinna (auricle)
(A)
directs sound waves into external acoustic meatus
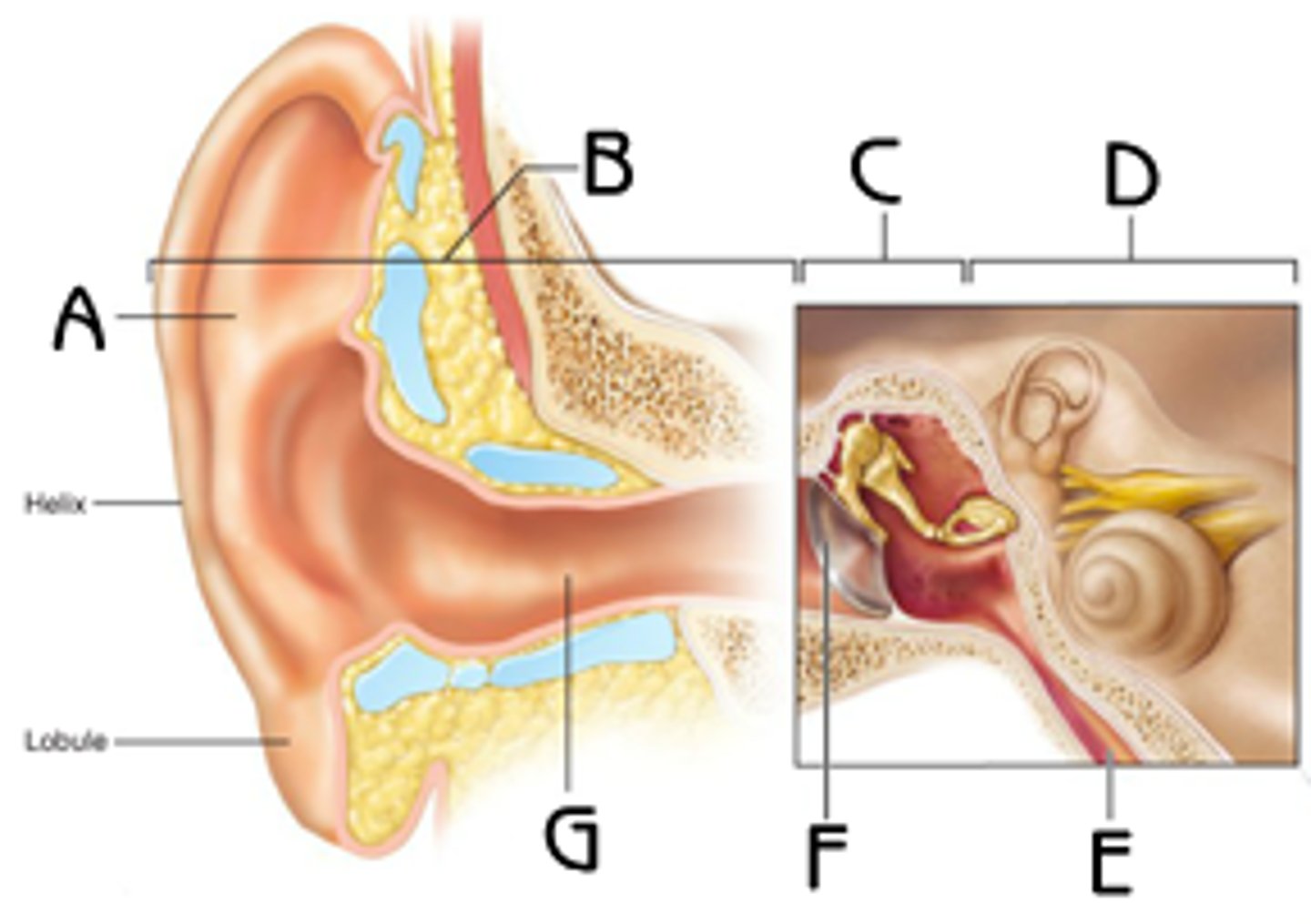
tympanic membrane (eardrum)
- separates the external ear from the middle ear
- transmits vibrations to the auditory ossicles
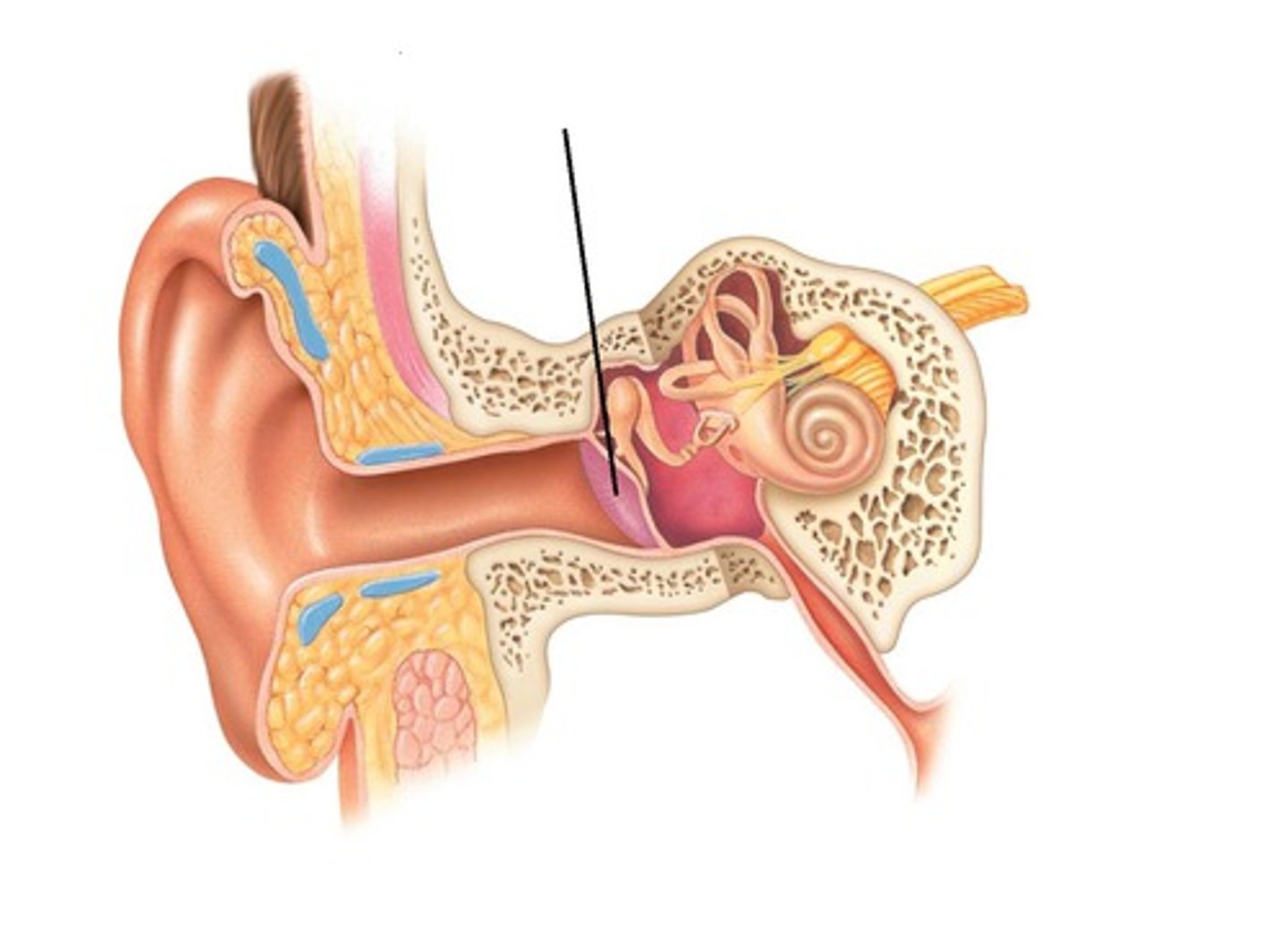
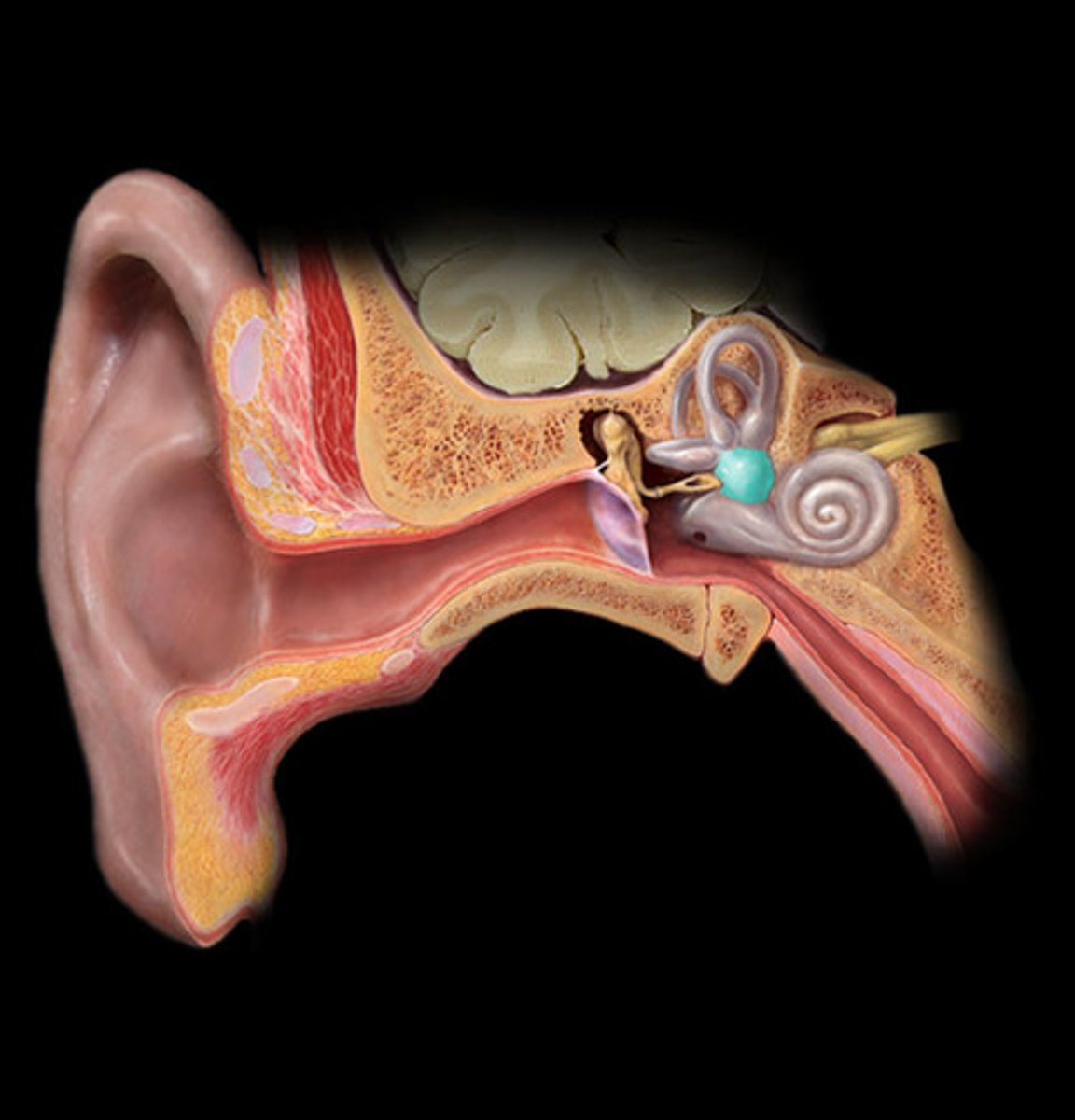
middle ear
filled with air
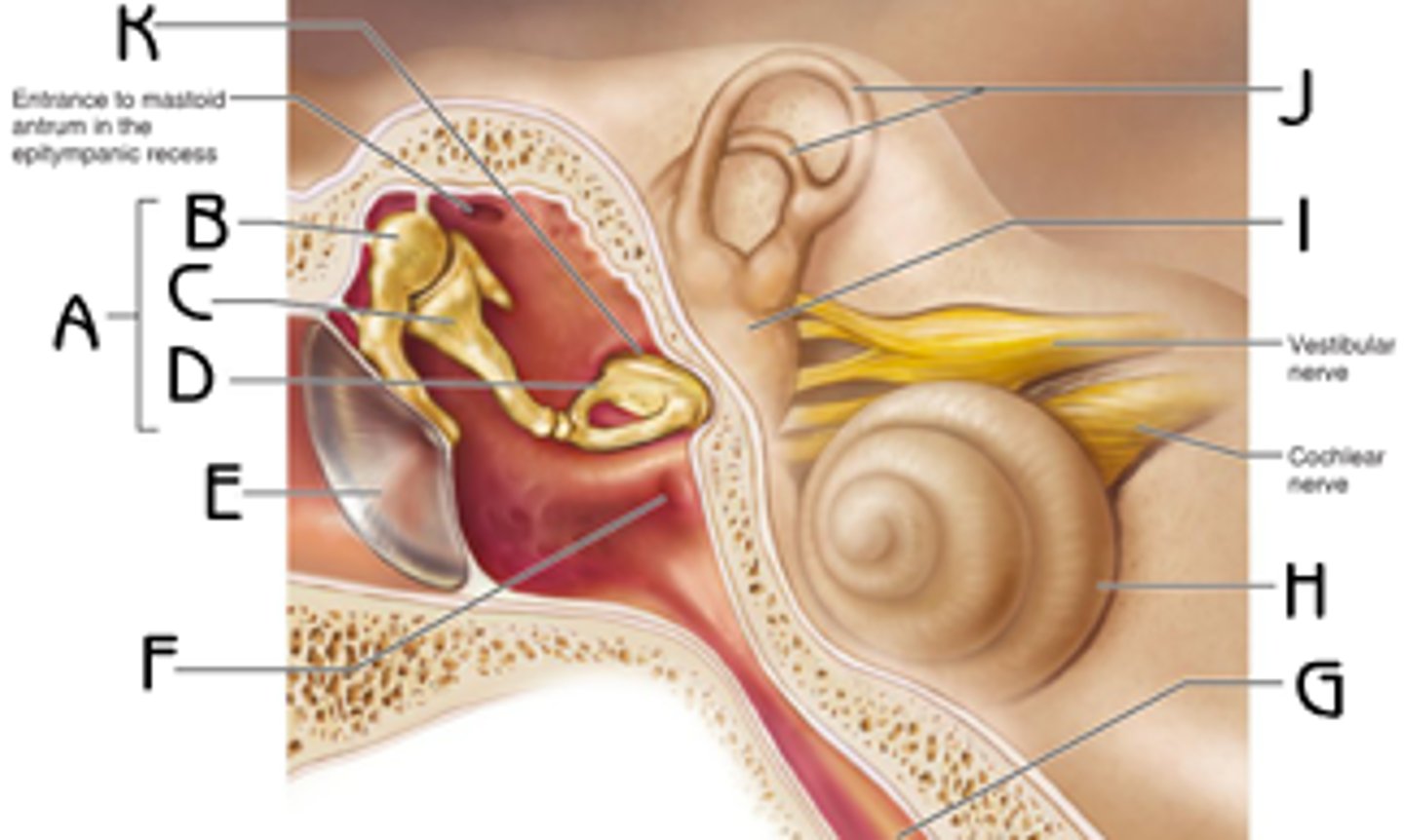
Incus (anvil), malleus (hammer), stapes (stirrup)
(C)
transmits and amplifies vibrations from the malleus to the stapes
internal ear
filled with fluid
pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube
(D)
equalizes the pressure in the middle ear cavity with the external air pressure so that the tympanic membrane can vibrate properly
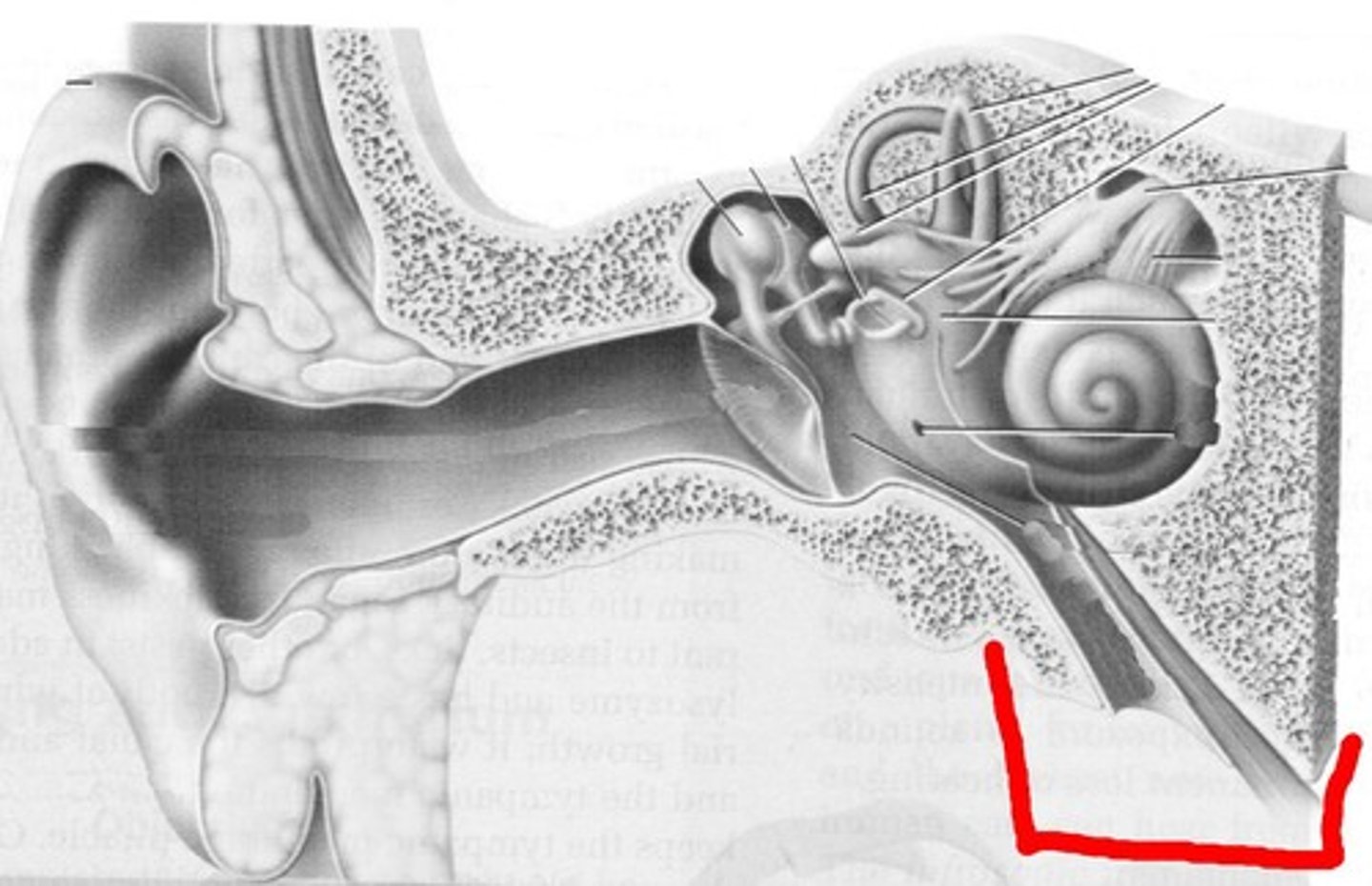
vestibule
balance
cochlea
(4)
hearing
semicircular canals
(3)
balance
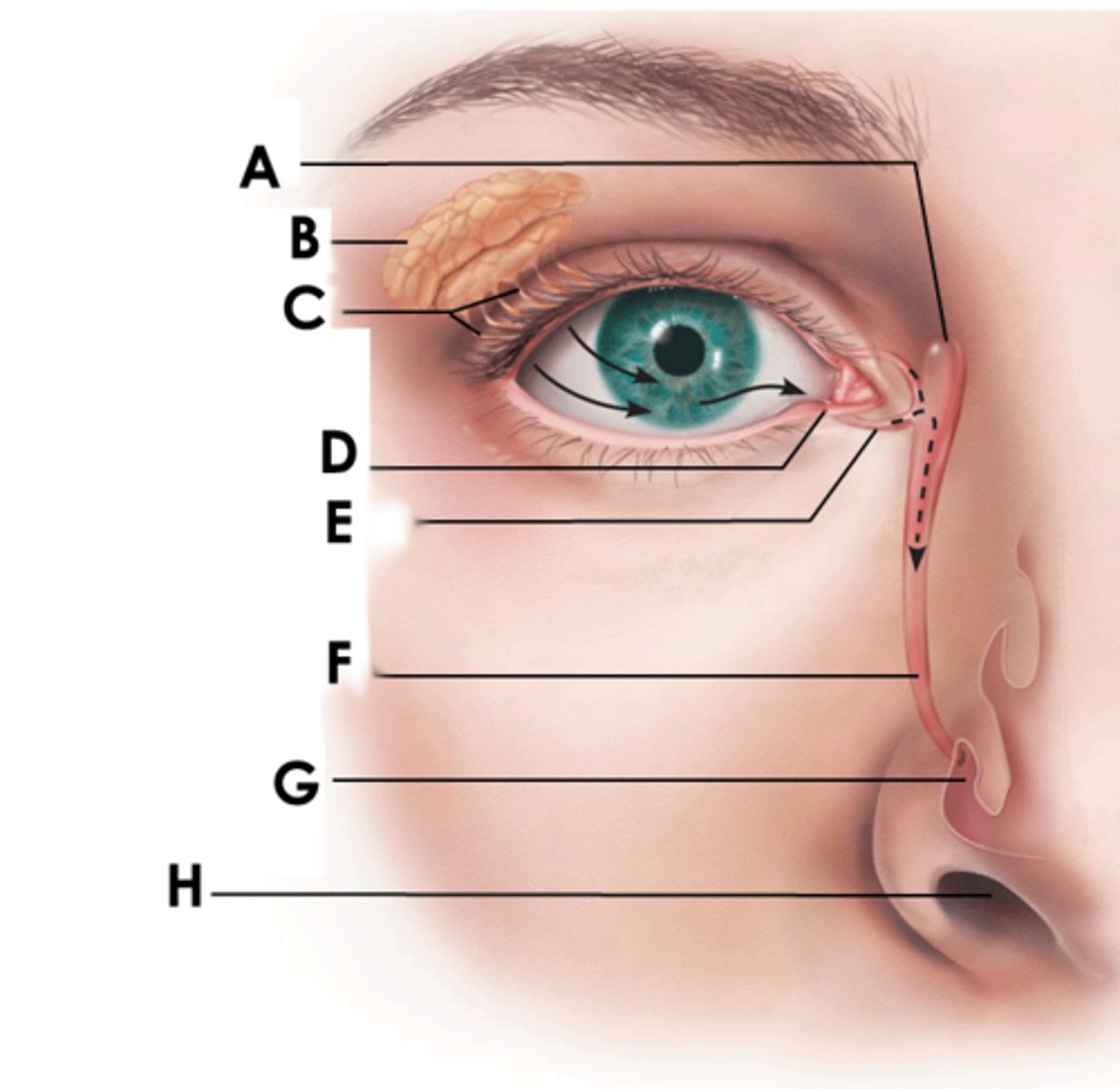
eyebrow
function: shade and prevent sweat from entering eye
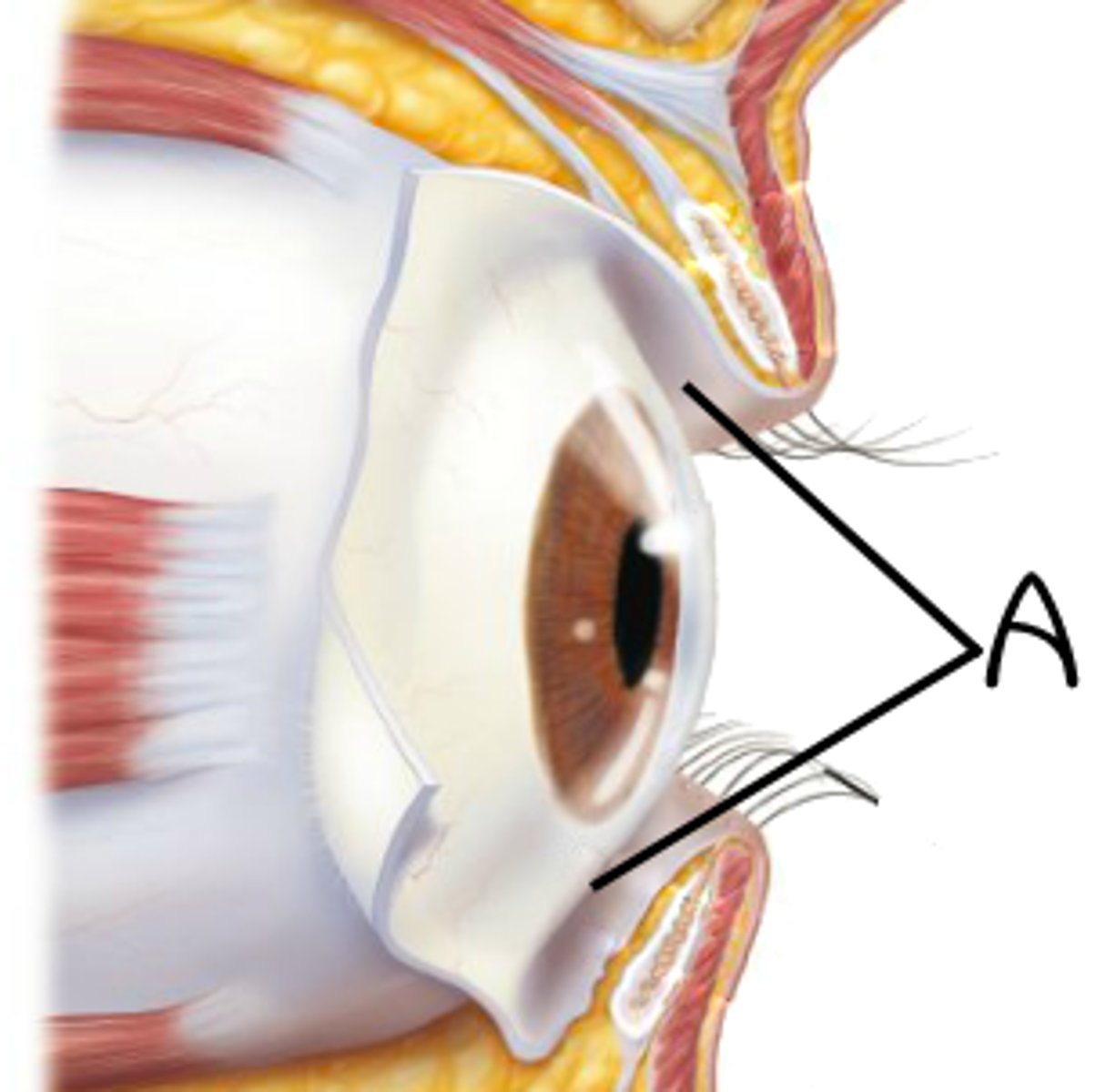
Eyelids (palpebrae)
protect the eyes and spread lacrimal fluid (tears) with blinking
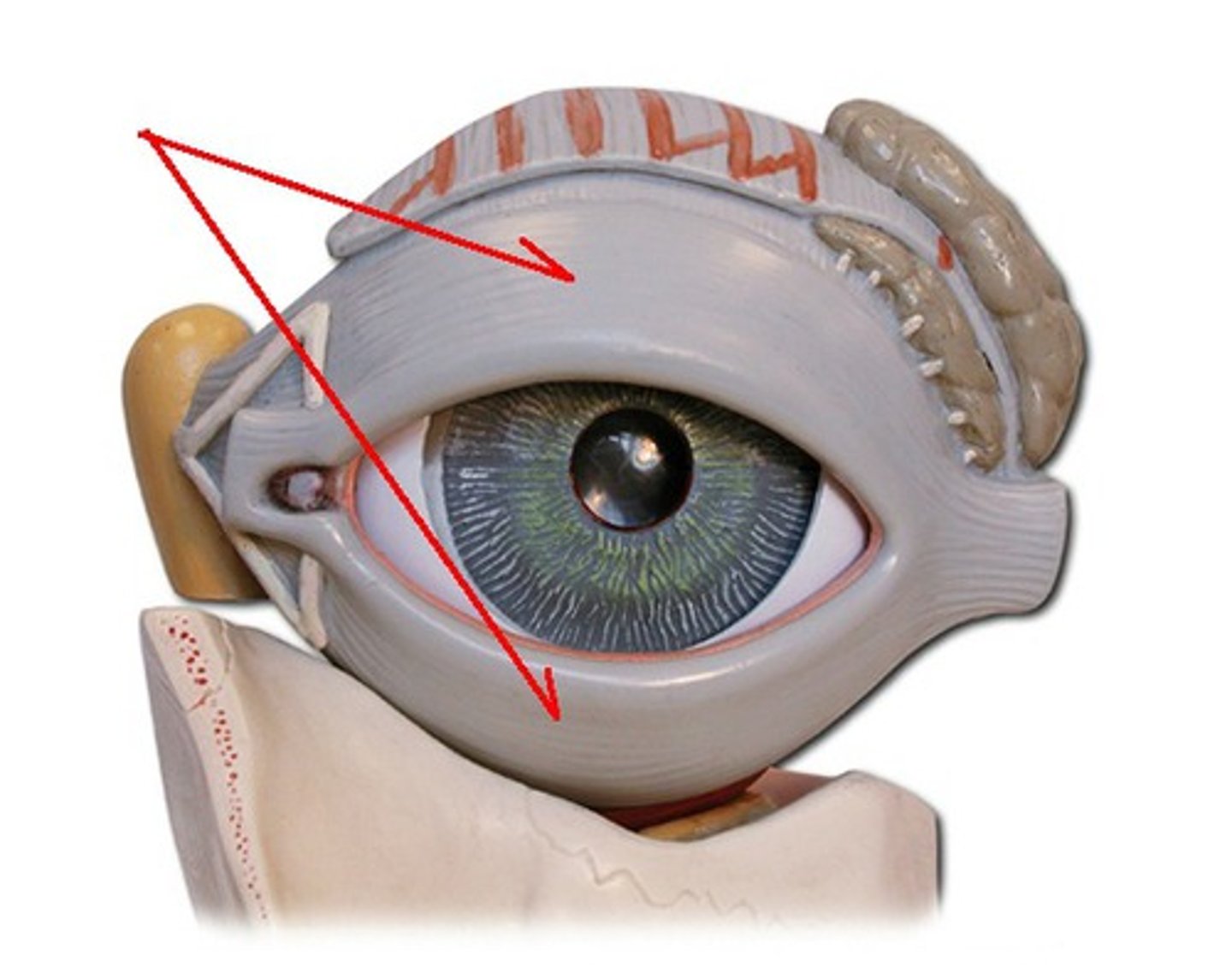
tarsal glands
secretors of an oily substance; located in the eyelids
conjunctivae
secrete mucus to lubricate the eye
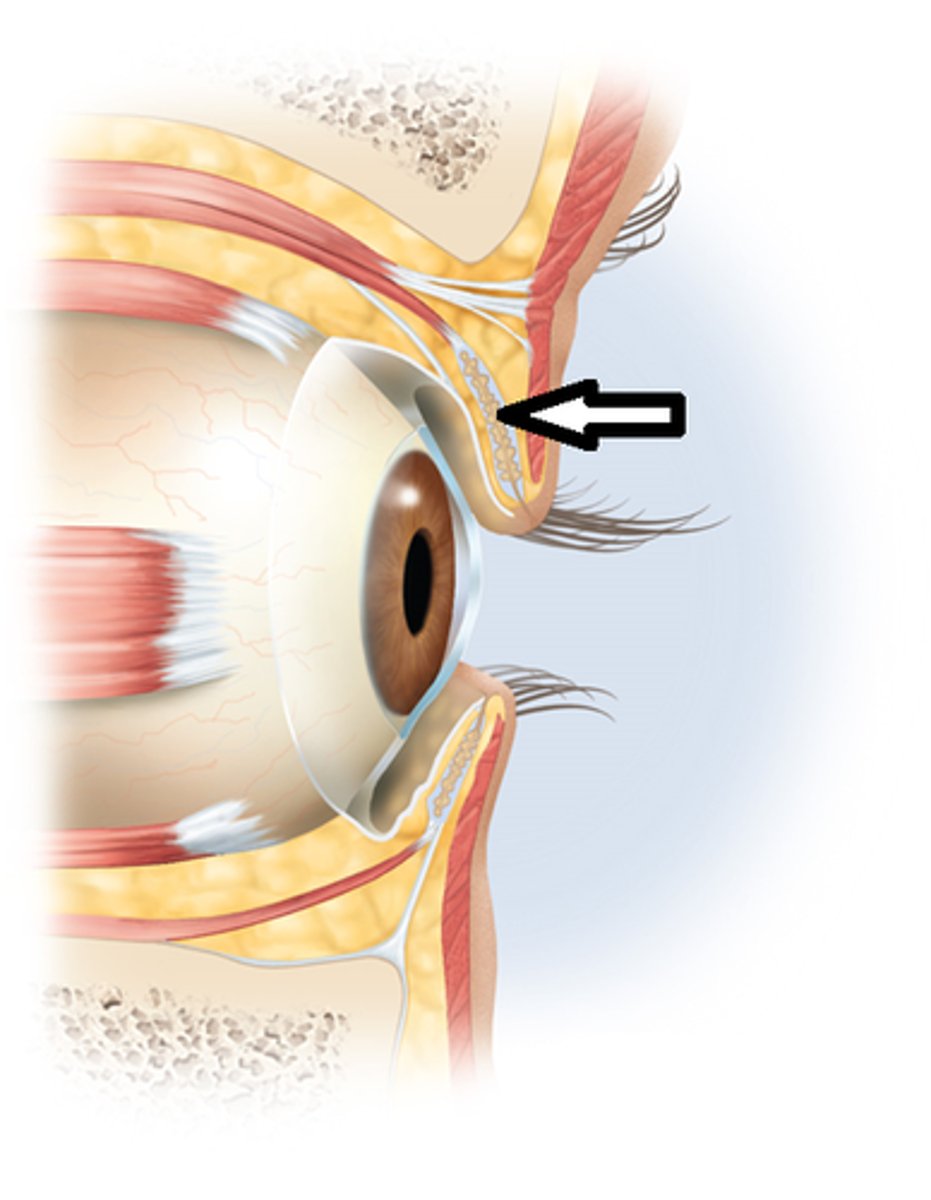
lacrimal sac
tear collector
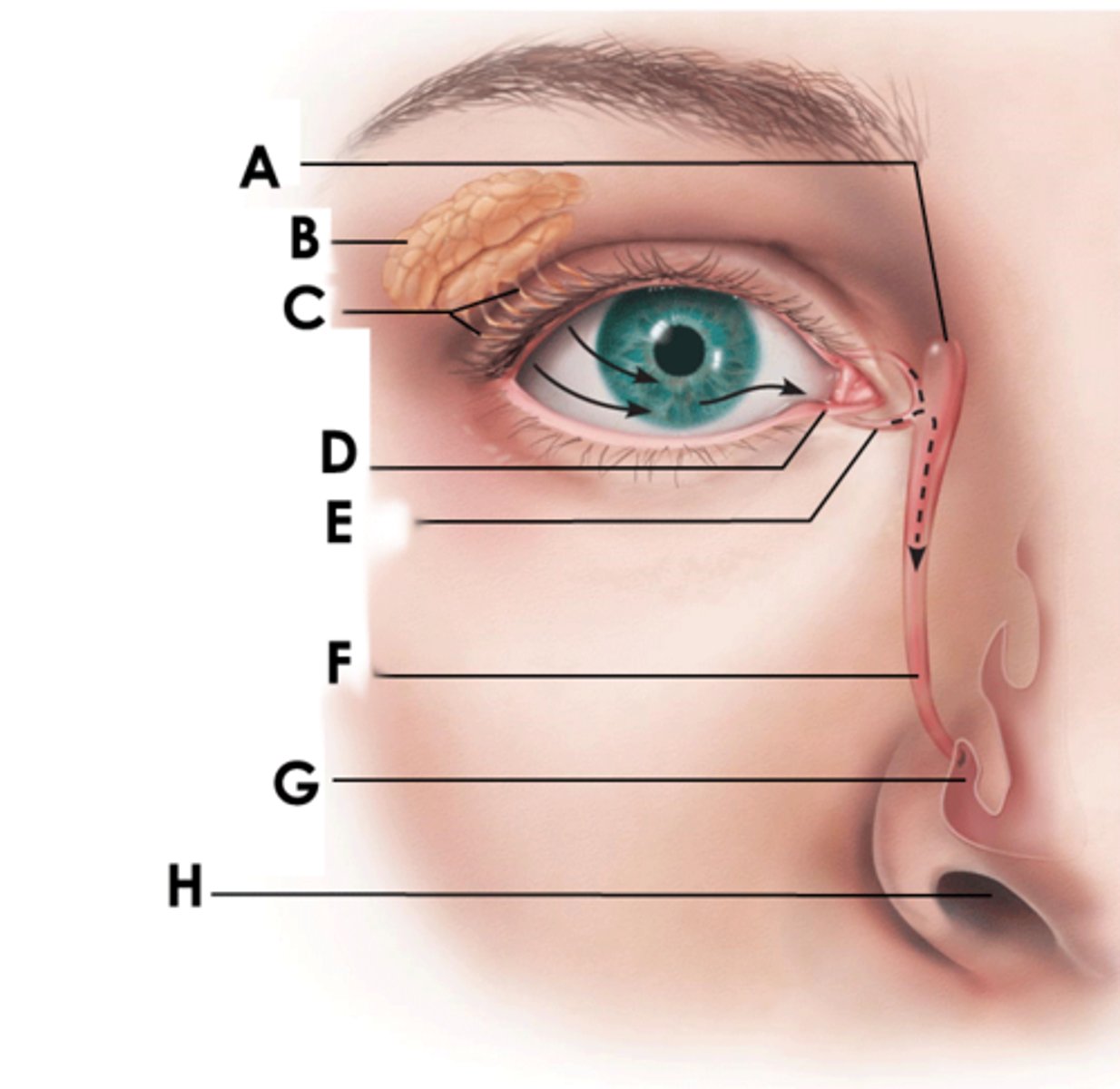
nasolacrimal duct
(F)
allows lacrimal fluid to flow into the nasal cavity
sclera
(K)
white of the eye; maintains the shape of the eye and protects the delicate inner layers of tissue
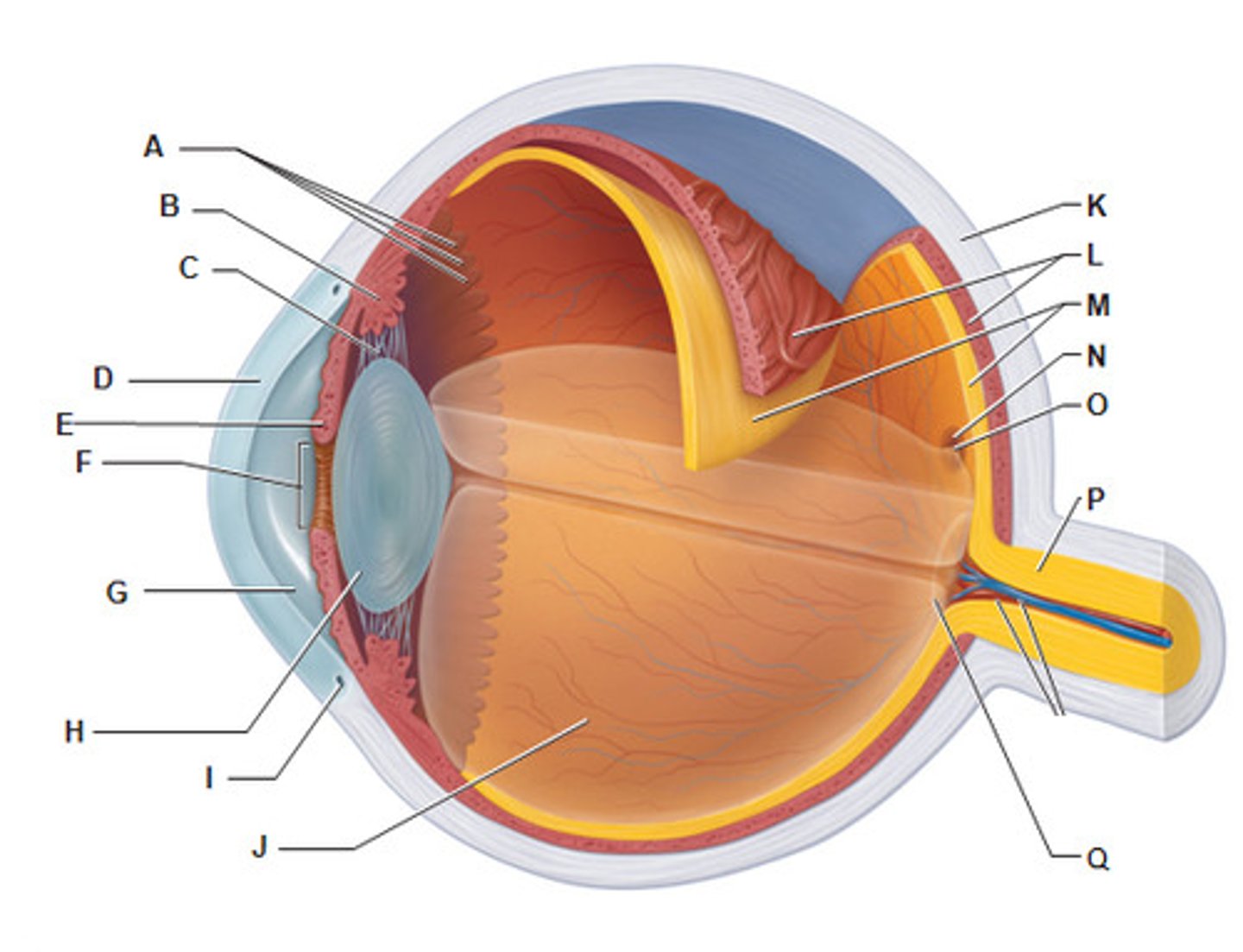
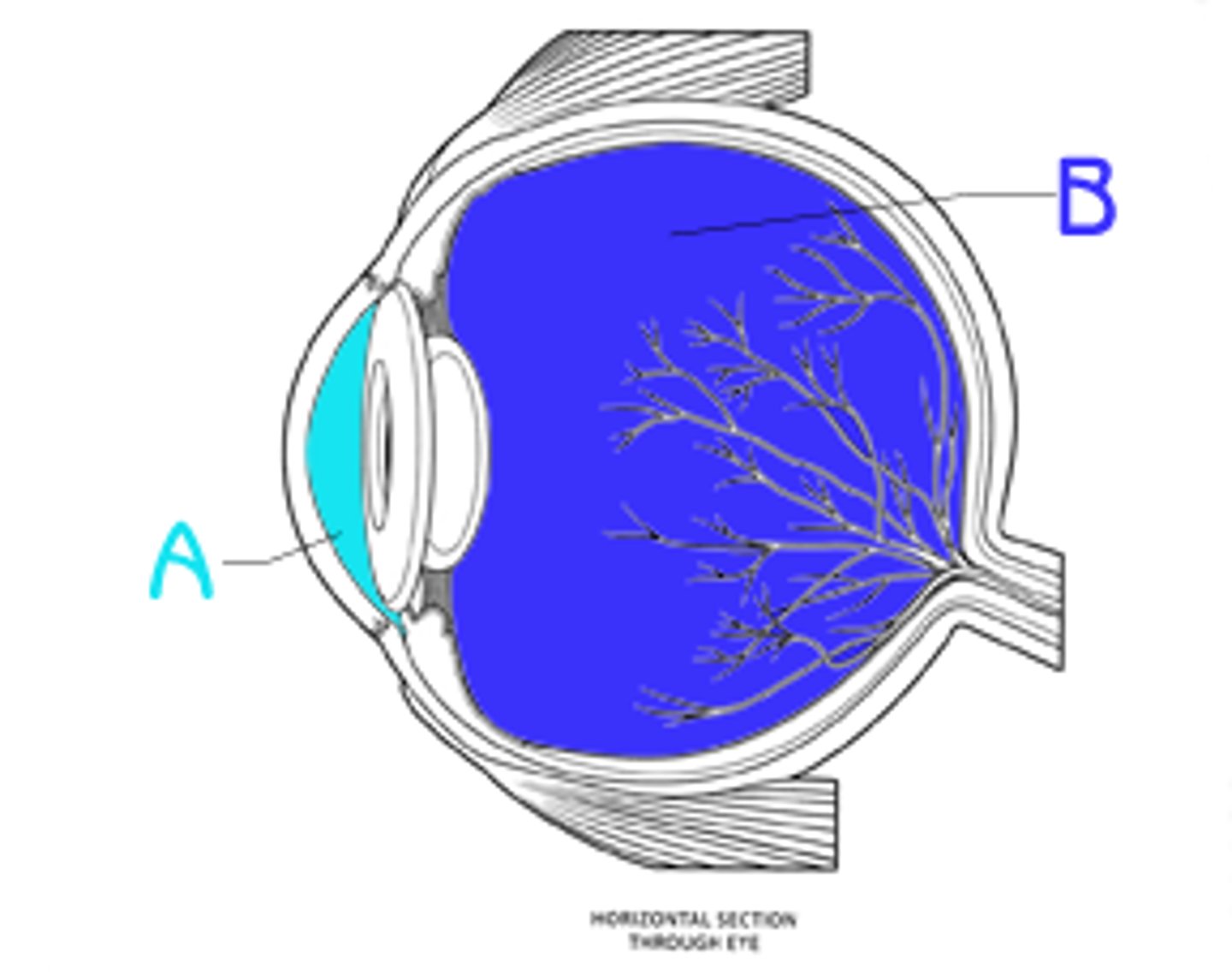
cornea
(B)
forms a clear window that us the major light-bending medium of the eye
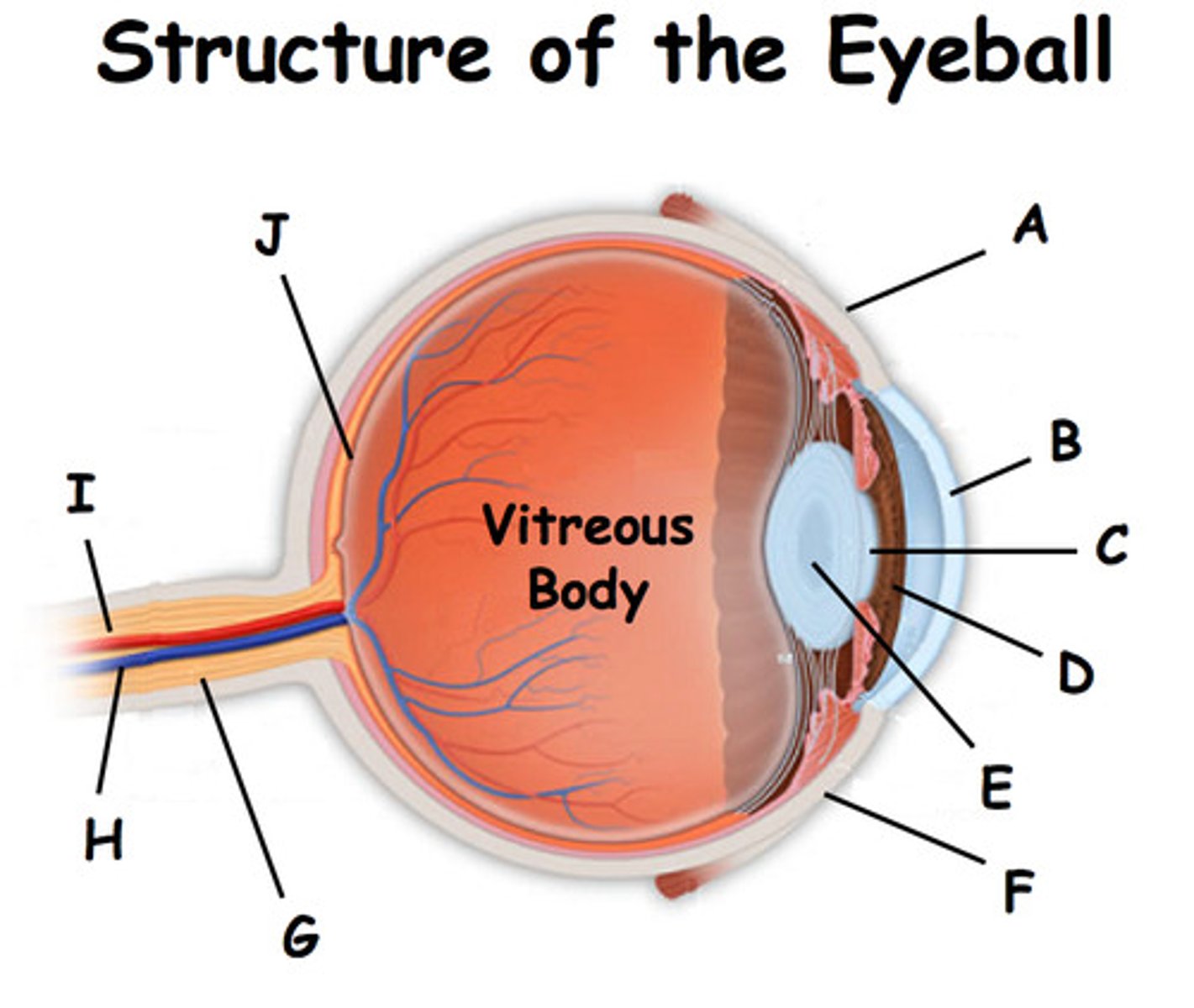
iris
(E)
- pigmented
- controls the amount of light entering the eye by changing the size of the pupil diameter
(smooth muscle tissue, epithelial tissue)
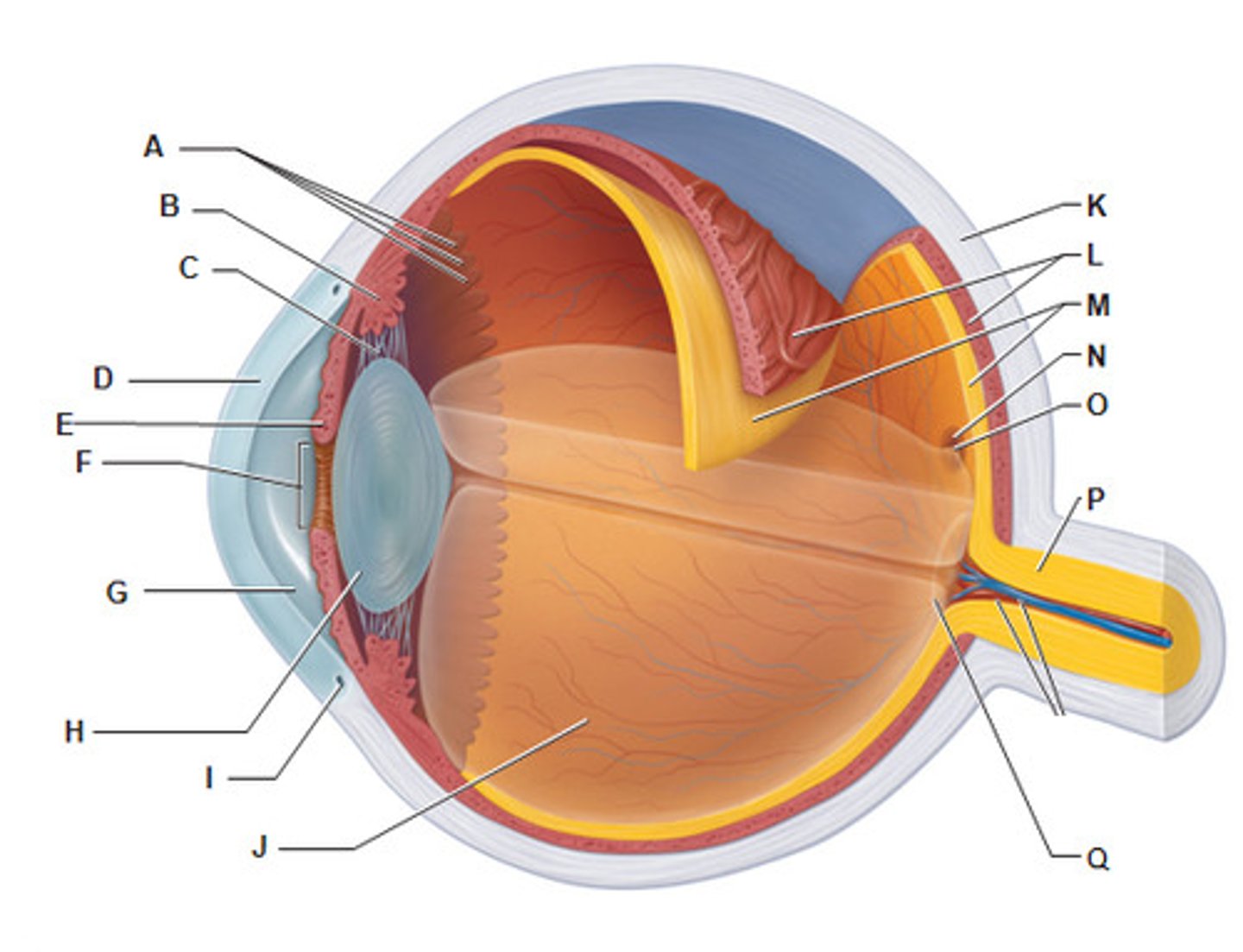
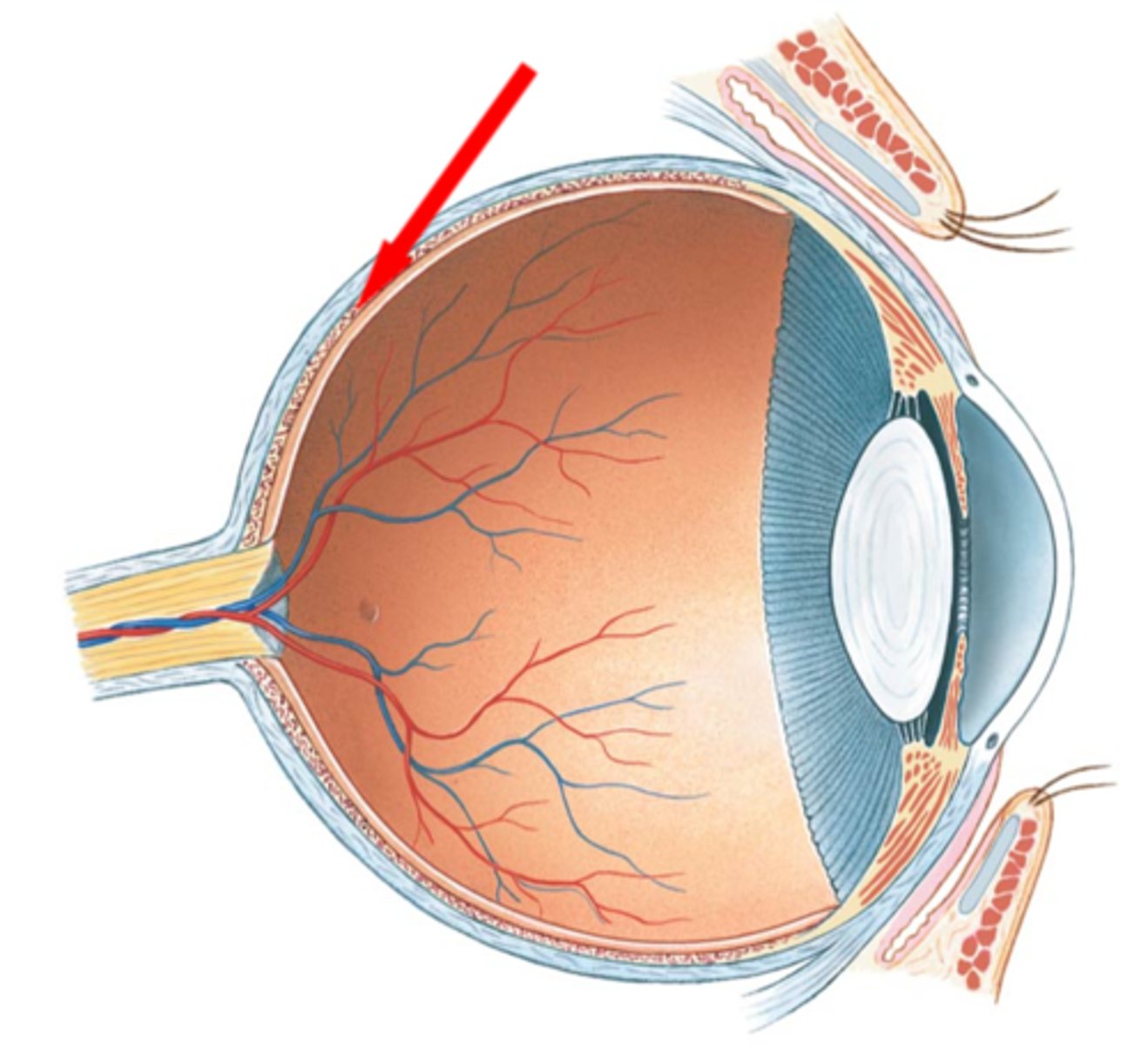
Choroiod
- rich with blood vessels
- blood vessels nourish the other layers of the eye
lens
(H)
- flexible (changes shape depends on light)
- elastic/ flexible
- function: focus the light by changing shape then project it into the retina
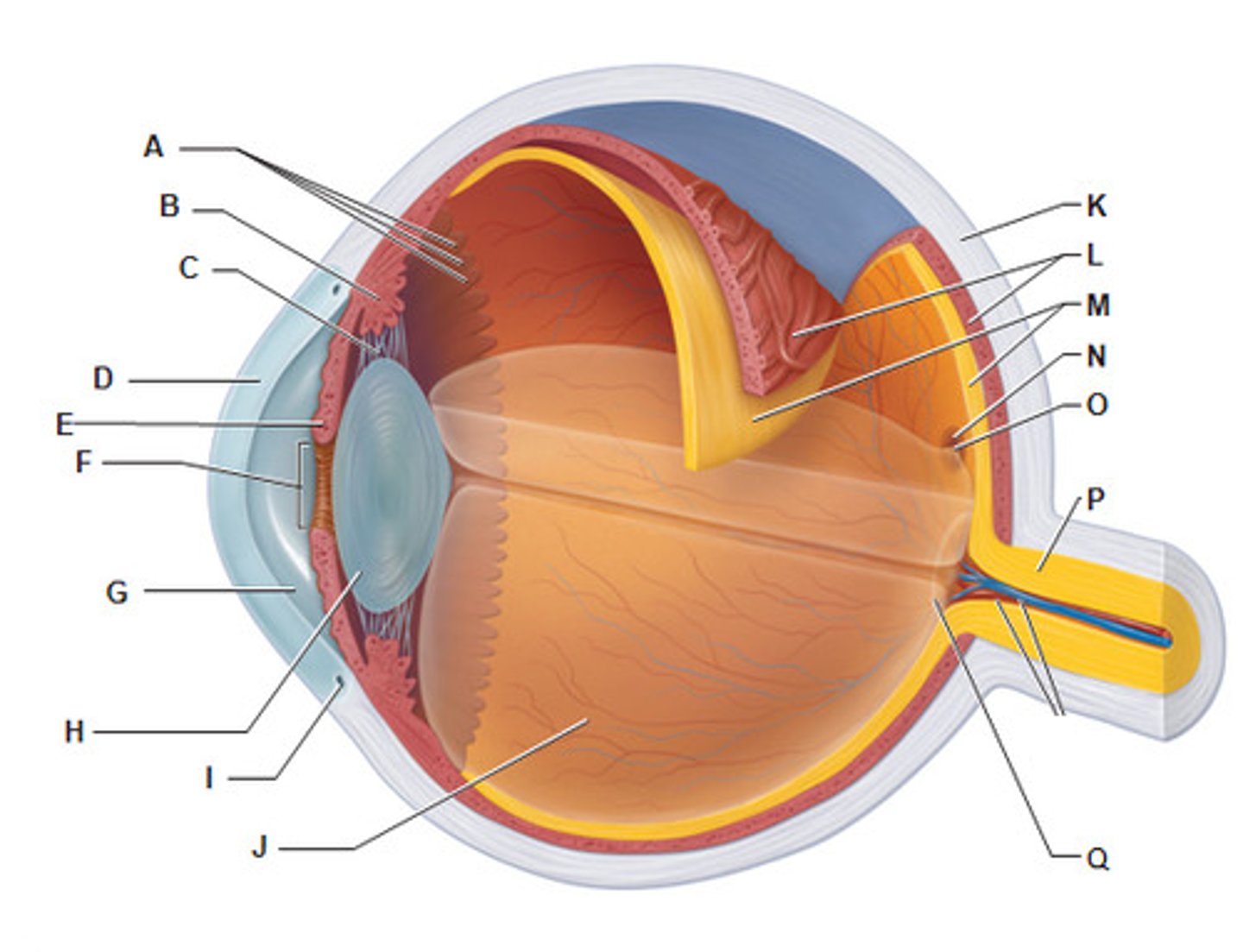
pupil
(F)
allows light to enter the eye
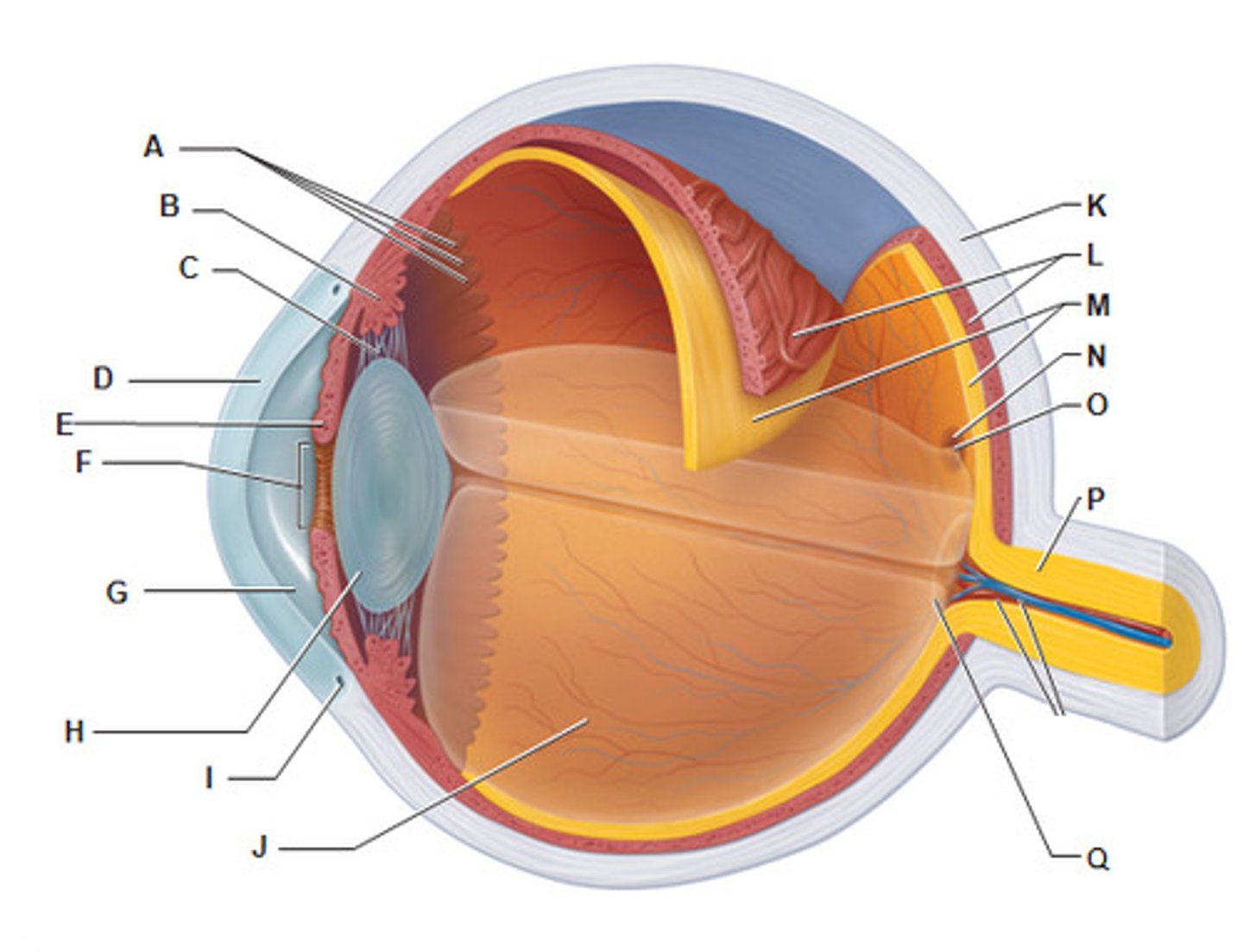
Mecula lutea
- majority of photoreceptors in macula lutea is cones
- center of macula lutea fovea centralis (cones only)
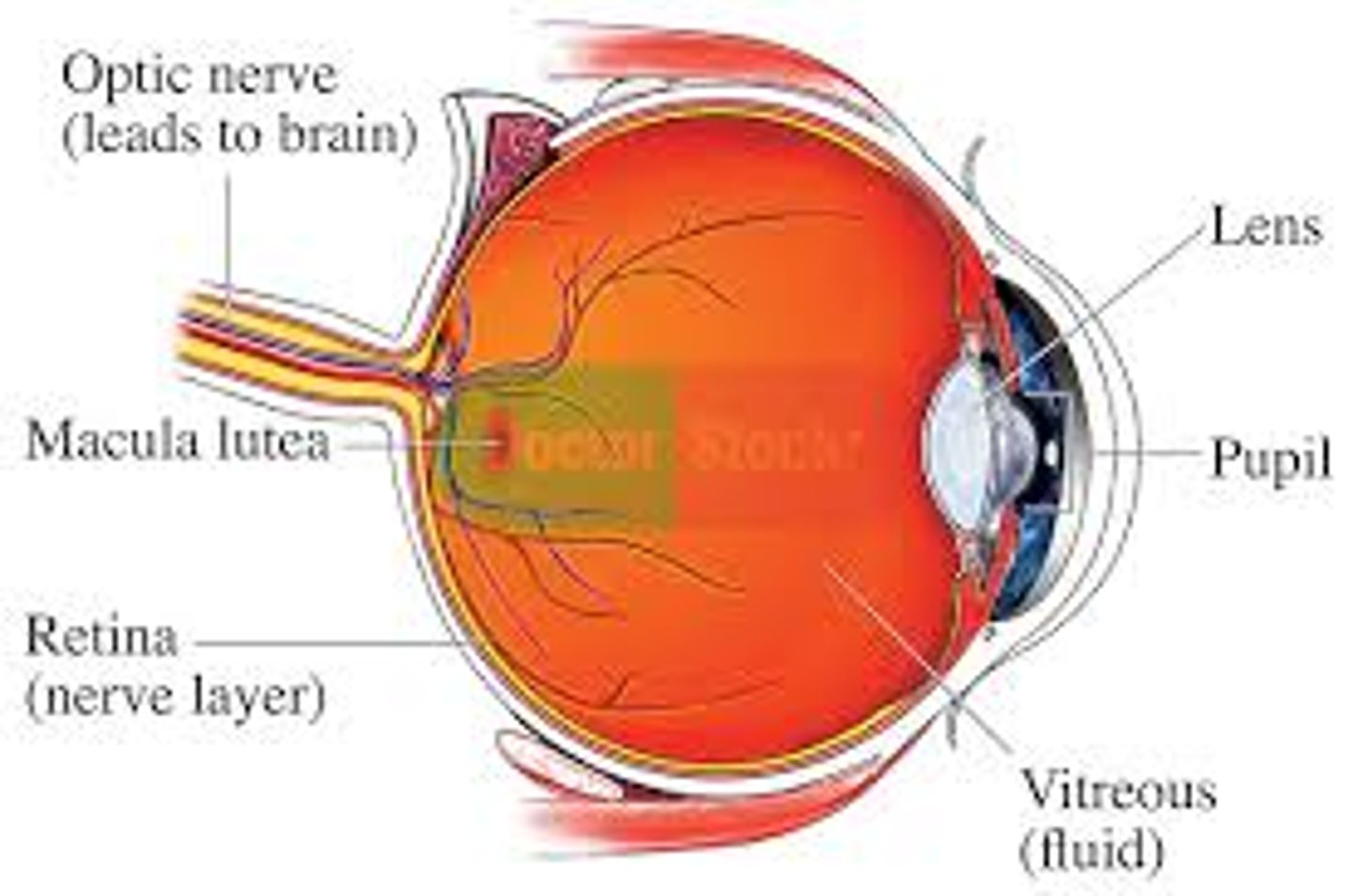
posterior segment of eye
(B)
contains vitreous humor
optic disc (blind spot)
(Q)
- where the cranial nerve leaves the eyeball (2nd cranial nerve)
- not enough photoreceptors