Simple harmonic motion
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything needed for AQA A-level simple harmonic motion A2. From basics to resonance so far. Have a look at the thing in resonance with being in/out of phase.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is simple harmonic motion?
Motion in which the acceleration of an object is directed towards a fixed point and is directly proportional to the negative displacement of the object.
What does w refer to in SHM?
The angular frequency: rate of change of angle (angle changes by how much in one second)
What happens to the time period in each oscillation of SHM?
The time period remains constant for each oscillation.
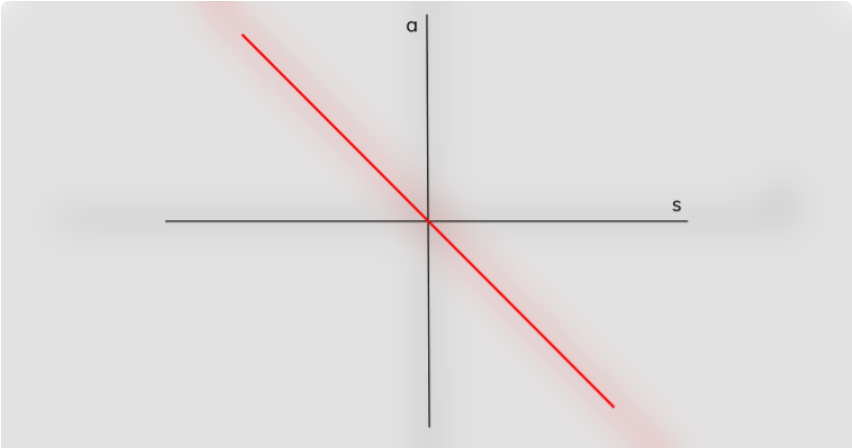
What does the acceleration-displacement graph look like?
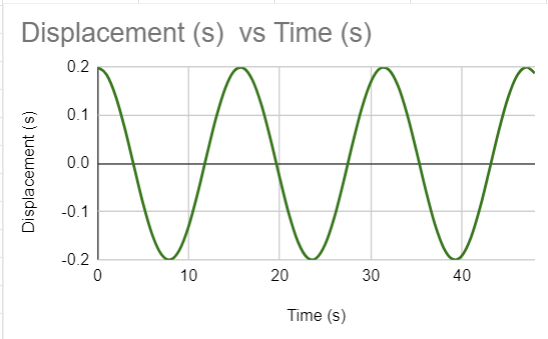
What does the displacement-time graph look like?
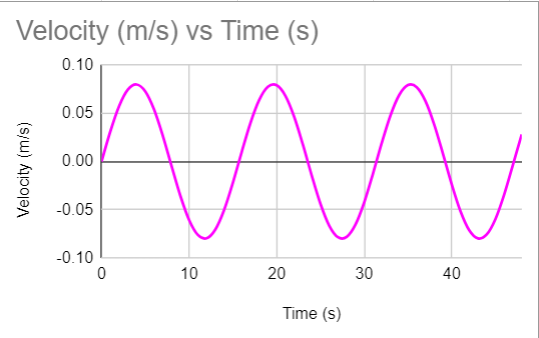
What does the velocity-time graph look like?
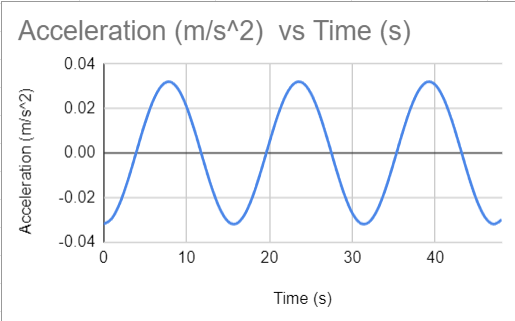
What does the acceleration-time graph look like?
What energies occur in simple harmonic motion of a pendulum (lead ball attached to the end of a string)?
Kinetic and gravitational potential energy
What energies occur in simple harmonic motion of a mass-spring system?
Kinetic, gravitational potential and elastic potential energy.
Which energies do we need to consider in SHM?
Kinetic energy and potential energies.
What is amplitude?
The maximum displacement of an object from the equilibrium position.
For a pendulum: when is kinetic energy at its maximum? And its minimum?
At the bottom of the swing, in the equilibrium position
At the top of the swing, at the maximum displacement from equilibrium (amplitude)
For a pendulum: when is GPE at its maximum? And its minimum?
At the top of the swing, at the maximum displacement from equilibrium (amplitude)
At the bottom of the swing, in the equilibrium position
For a mass-spring system: when is EPE at its maximum? And its minimum?
When the spring is fully compressed or fully stretched out
?
For a mass-spring system: when is GPE at its maximum? And its minimum?
xyz
What is the total energy?
The sum of the kinetic and potential energies of the system.
What happens to the total energy of the system throughout oscillations?
It remains constant (conservation of energy)
What does the kinetic energy graph look like?
parabola (against displacement)
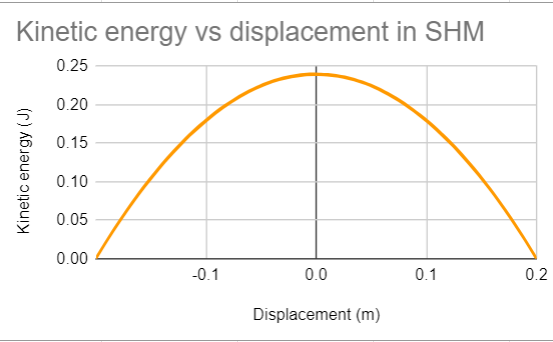
What does the potential energy graph look like?
parabola (against displacement), inverse of the kinetic energy graph (both against time and displacement)
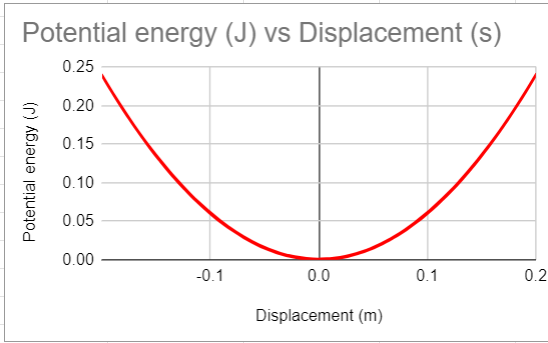
What is damping?
When an oscillation is dampened, the frequency, amplitude and time period of the wave decrease.
What is a damping/dampening force?
any force which opposes the movement of an object (in SHM)
What is under-damping?
When the damping force is very small. It takes the object a long time to reach equilibrium. The frequency and time period of oscillations remain constant throughout the damping, only the amplitude decreases.
light damping = under-damping
What is over damping?
When there is too much damping. No oscillations occur, the object goes to the maximum height then slowly returns to equilibrium.
over damping = heavy damping
What is critical damping?
When the object returns to equilibrium with no further oscillations as quickly as possible.
What are some uses of critical damping?
car suspension, it reduces oscillations quickly and avoids damage
What is natural frequency?
The natural frequency an object oscillates at without the application of a periodic force.
What is driving frequency?
The frequency an object oscillates at while a periodic force is applied.
What is a periodic force?
A force that is applied at a specific interval.
What is resonance?
When the driving frequency is equal to the natural frequency of the object. Or when the periodic force is exactly in phase with the velocity of the oscillating system.
Example: child on a swing.
What is the resonant frequency?
The frequency at the maximum amplitude of oscillation.
How does a child reach the maximum amplitude on a swing?
When the periodic force applied by the child leaning forwards/backwards is exactly in phase with the velocity of the oscillating system.
What happens if the damping is lighter. E.g. light damping versus medium damping
The lighter the damping:
the larger the maximum amplitude becomes at resonance
the closer the resonant frequency is to the natural frequency of the system
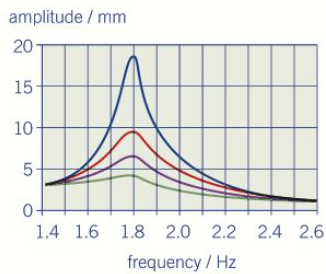
What happens when the frequency becomes increasingly larger than the resonant frequency of system?
the amplitudes of the oscillations decrease
the phase difference between the displacement and the periodic force increases from ½ pi until the displacement is pi rad out pf phase with the periodic force
What happens when an oscillating system has little or no damping at resonance
The applied frequency of the periodic force = the natural frequency of the system
What is the phase difference between the variation of displacement with time and the variation of acceleration with time for a body performing SHM?
pi rad/180 degrees