AP REVIEW - Sleep & Genetic Psychology
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Nature Vs Nurture
Debate on whether genetics (nature) or environment and upbringing (nurture) have a greater influence on human behavior and traits.
Behavior geneticists
Study the role played by our genes and our environment in mental ability, emotional stability, temperament, personality, interests, and so forth; they look at the causes of our individual differences.
Identical twins
Two individuals who share all of the same genes/heredity because they develop from the same fertilized egg or zygote; they are monozygotic twins.
Fraternal twins
Siblings that share about half of the same genes because they develop from two different fertilized eggs or zygotes; they are dizygotic twins.
Heritability
The proportion of variation among individuals in a population that is due to genetic causes. It ranges from 0 (no genetic influence) to 1 (completely genetic).
Gene
A unit of heredity that is transferred from a parent to offspring and determines some characteristic of the offspring.
Chromosome
Carry genetic information to new cells during reproduction. Normal human body cells have 46 chromosomes, except for eggs and sperms that have 23 chromosomes.
Turner syndrome
Genetic disorder affecting females with missing or incomplete X chromosome, leading to short stature, heart defects, and infertility. (XO)
Klinefelter’s syndrome
Genetic condition where males have an extra X chromosome (XXY), causing infertility, reduced testosterone, and potential learning disabilities.
Down syndrome
Genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of chromosome 21. Associated with intellectual disability, characteristic facial features, and developmental delays.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism, representing the specific combination of alleles for a particular trait.
Phenotype
Refers to the observable physical characteristics of an organism resulting from the interaction of its genotype with the environment. (The expression of the genes).
Albinism
Genetic disorder characterized by a lack of melanin, resulting in pale skin, hair, and eyes. It can also cause vision problems and increased susceptibility to sun damage.
Huntington’s disease
Genetic disorder causing progressive breakdown of nerve cells in the brain. Symptoms include involuntary movements, cognitive decline, and psychiatric issues.
Alzheimer’s disease
A progressive brain disorder causing memory loss, cognitive decline, and behavioral changes. It impairs daily functioning and has no cure.
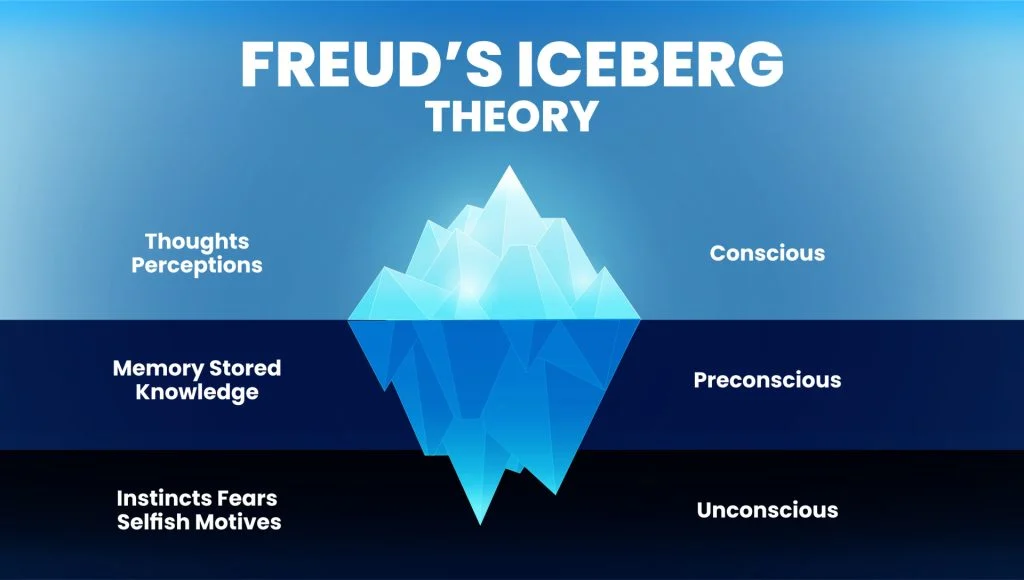
Preconscious
The level of consciousness that is outside of awareness but contains feelings and memories that you can easily bring into conscious awareness.
Nonconscious
The level of consciousness devoted to processes completely inaccessible to conscious awareness, such as blood flow, filtering of blood by kidneys, secretion of hormones, and lower-level processing of sensations, such as detecting edges, estimating size and distance of objects, recognizing patterns, and so forth.
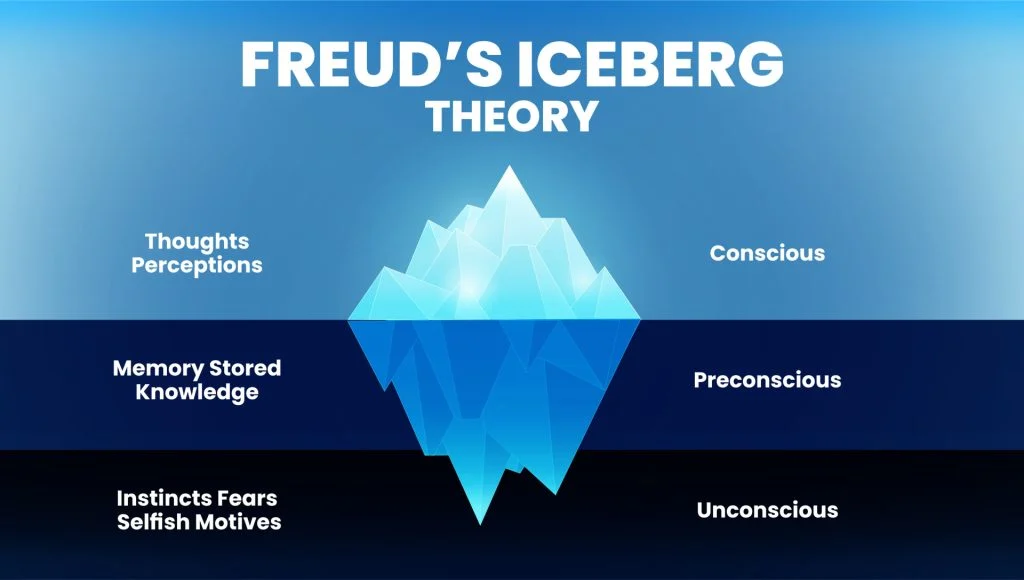
Unconscious
Sometimes called the subconscious, is the level of consciousness that includes often unacceptable feelings, wishes, and thoughts not directly available to conscious awareness.
Dual processing
The brain's ability to process information using both conscious, deliberate thinking (explicit processing) and unconscious, automatic processing (implicit processing).
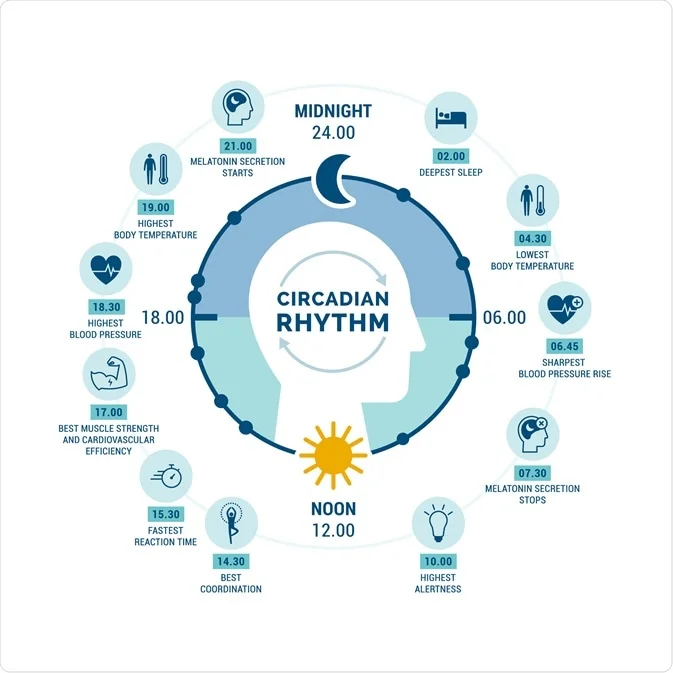
Circadian rhythm
A natural, internal process that regulates the sleep-wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It's also known as your body’s clock — it influences when you fall asleep and wake up. Mainly responds to light and darkness in your environment.
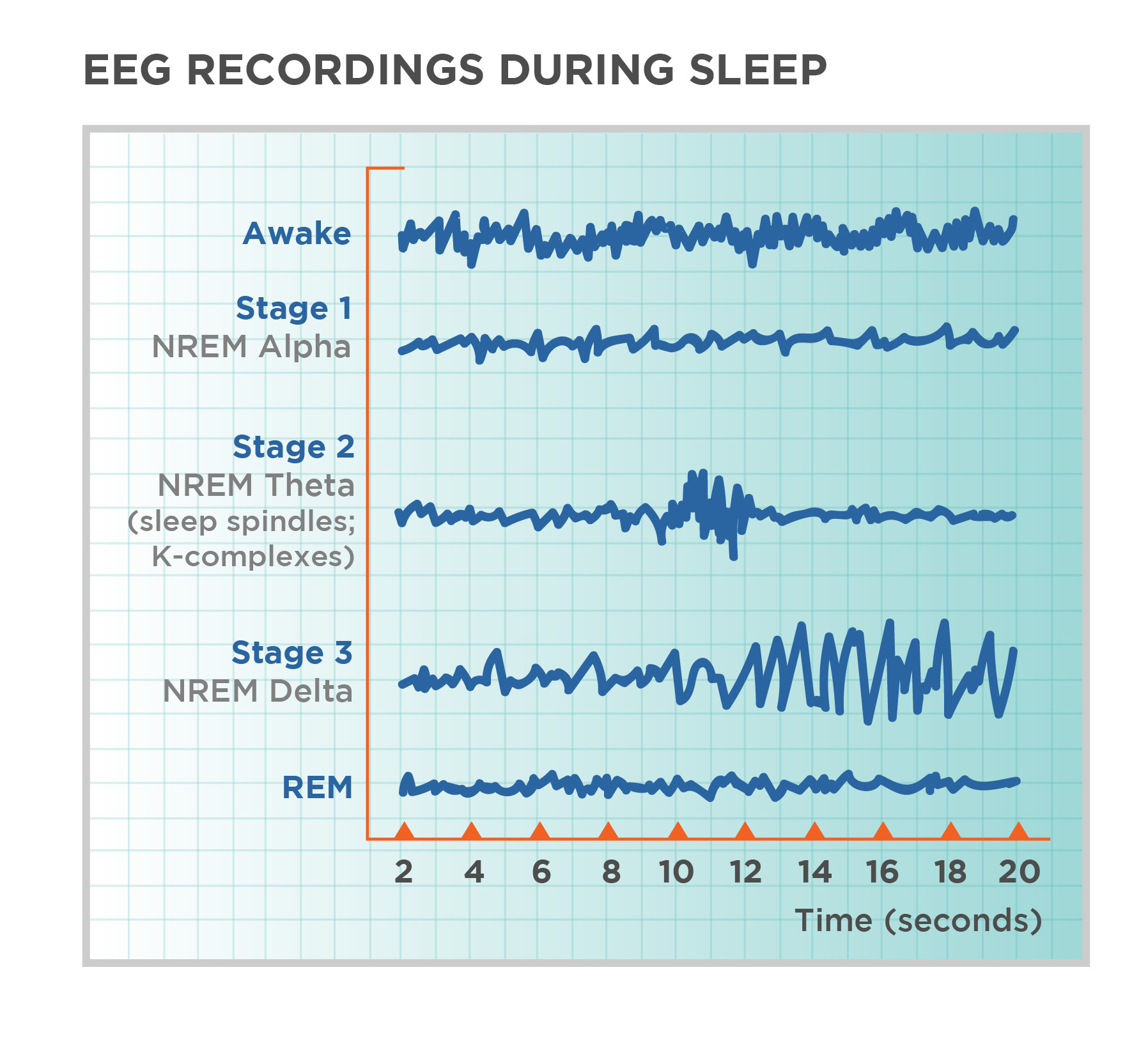
Stage one of sleep
A light sleep phase where you drift in and out of sleep, lasting around 5-10 minutes. It's easy to wake up during this stage. Dominated by theta waves, hypnic jerks, hypnagogic hallucinations, light sleep
Hypnic jerks
involuntary muscle twitches that occur as you are falling asleep. They are also known as sleep starts or hypnagogic jerks.
Hypnagogic hallucinations
Vivid sensory experiences during the transition from wakefulness to sleep, often involving visual or auditory phenomena.
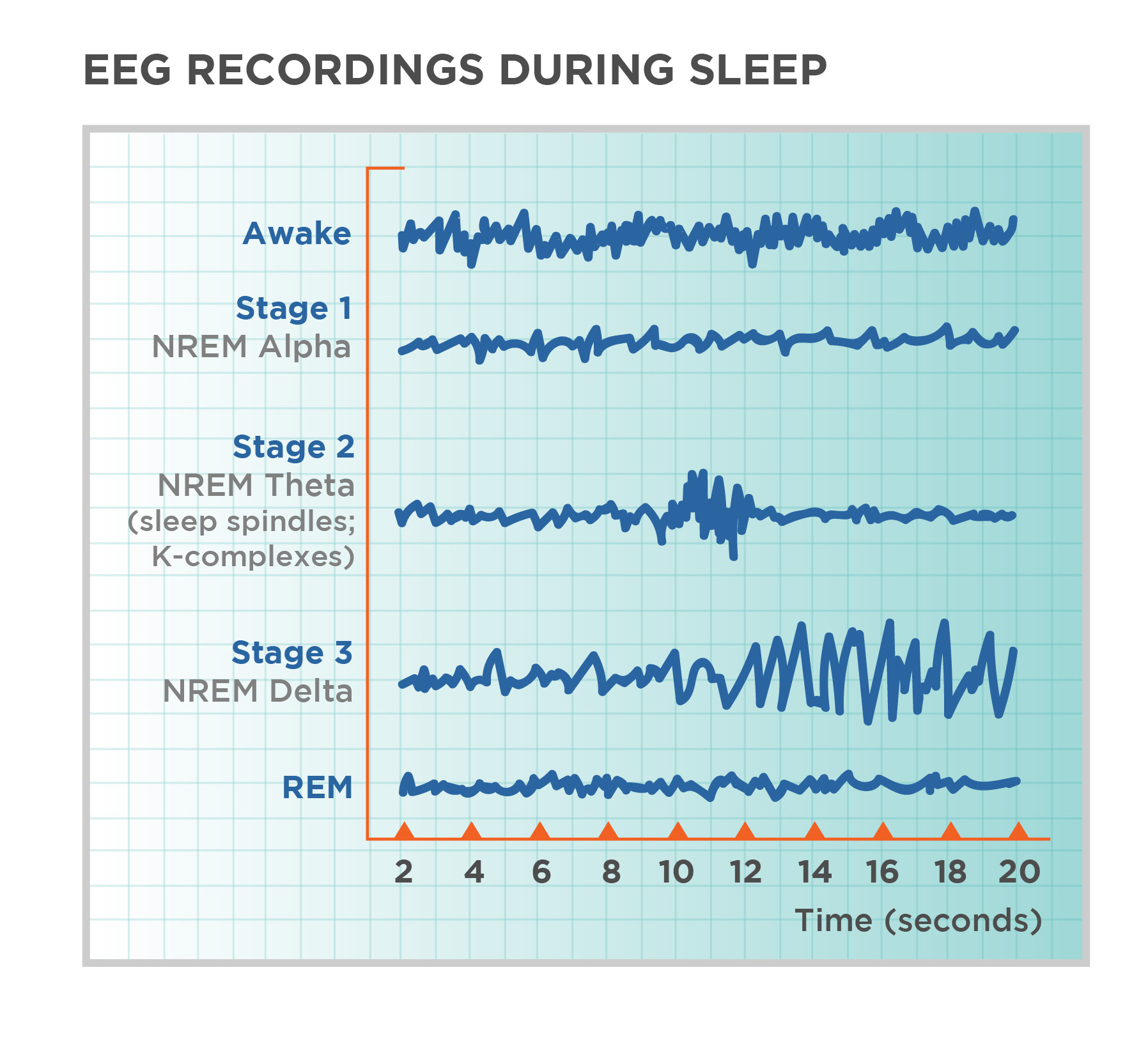
Stage two of sleep
Characterized by the presence of sleep spindles and K-complexes on an EEG, representing periods of light sleep before entering deeper sleep stages. More theta waves.
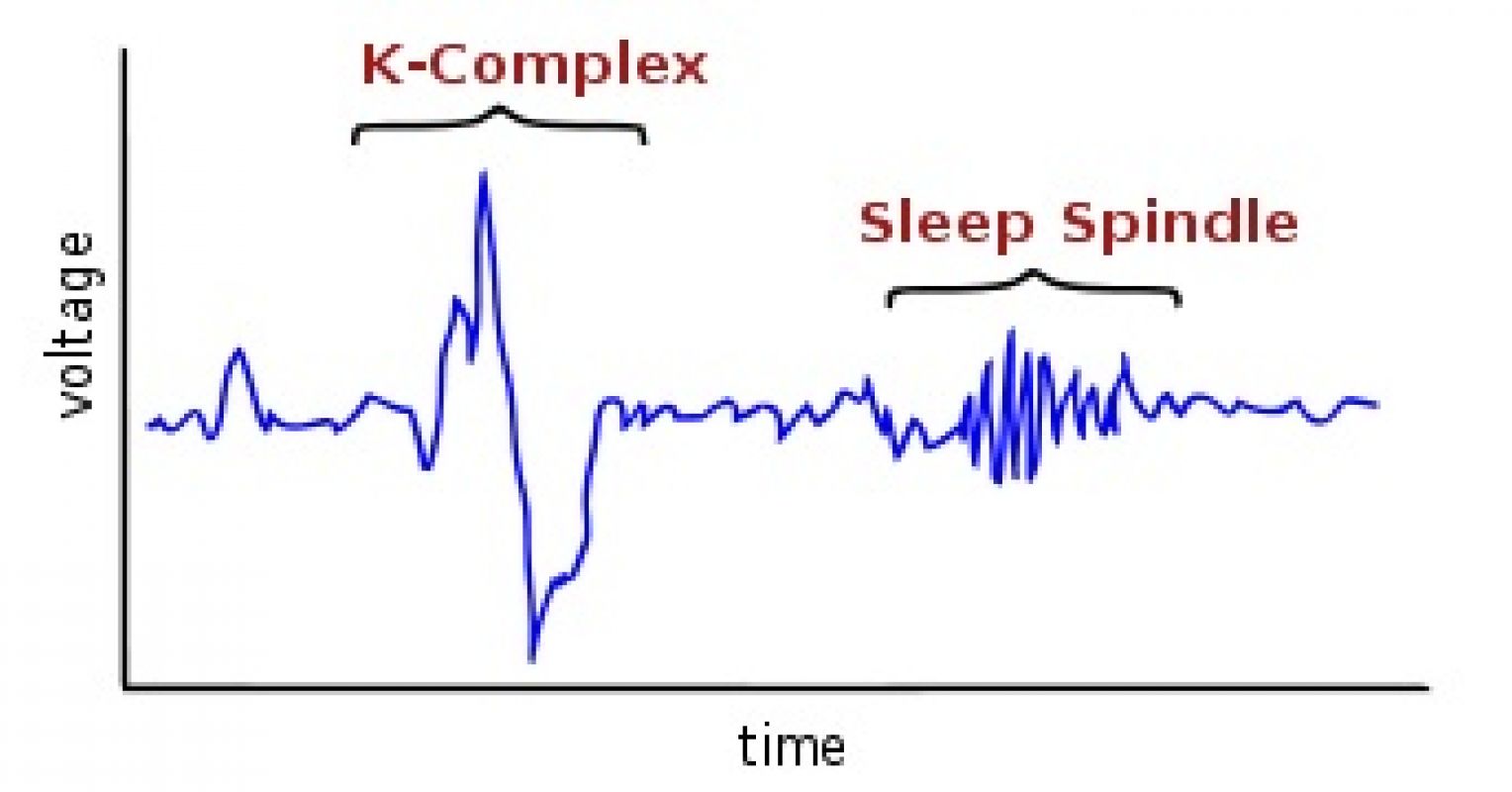
Sleep spindles
Bursts of brain activity visible on EEG during stage 2 NREM sleep, involved in memory consolidation and learning.
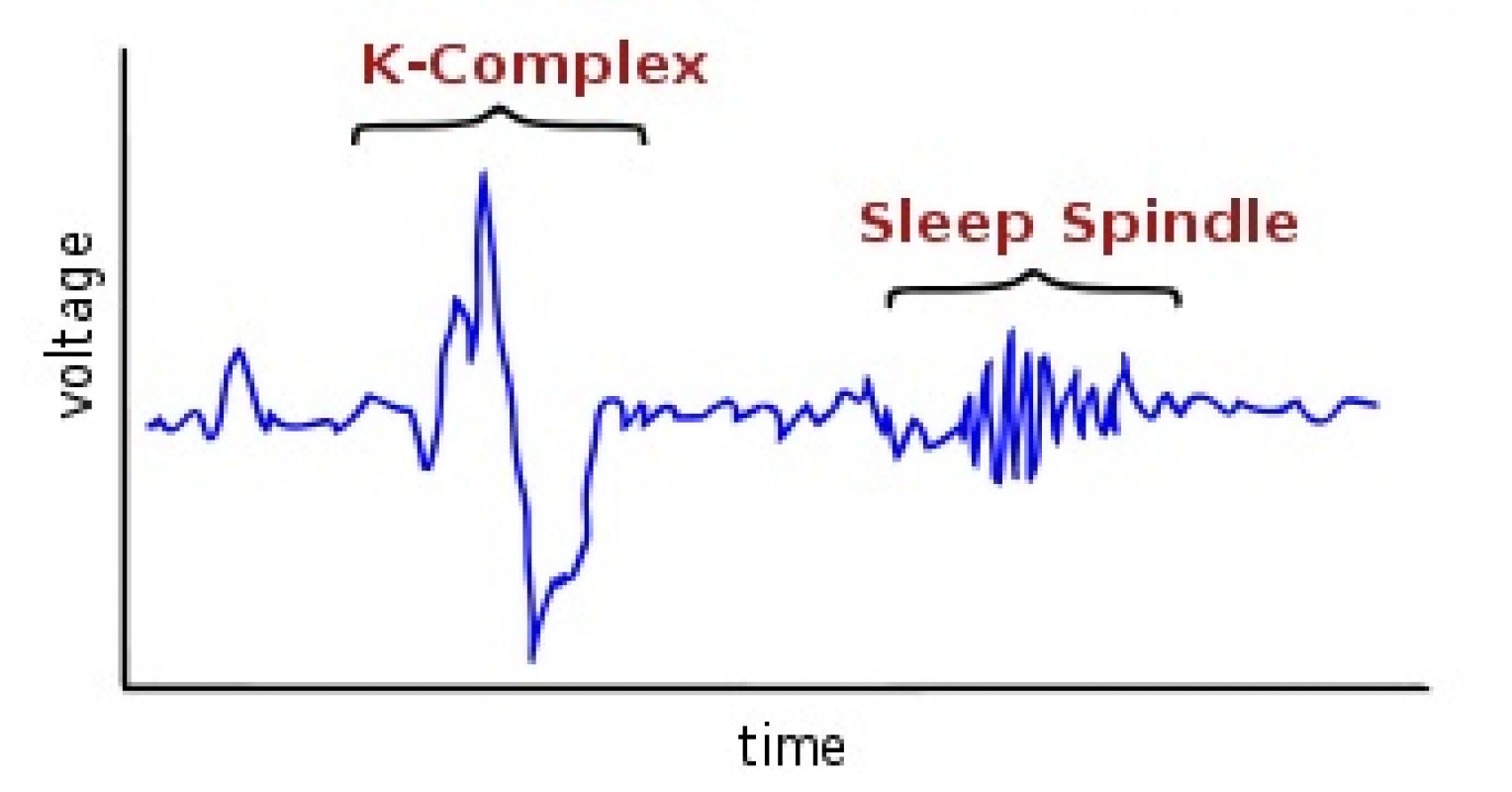
K-complexes
High-amplitude brain waves often seen during stage 2 of non-REM sleep. They help protect sleep by suppressing cortical arousal in response to external stimuli.
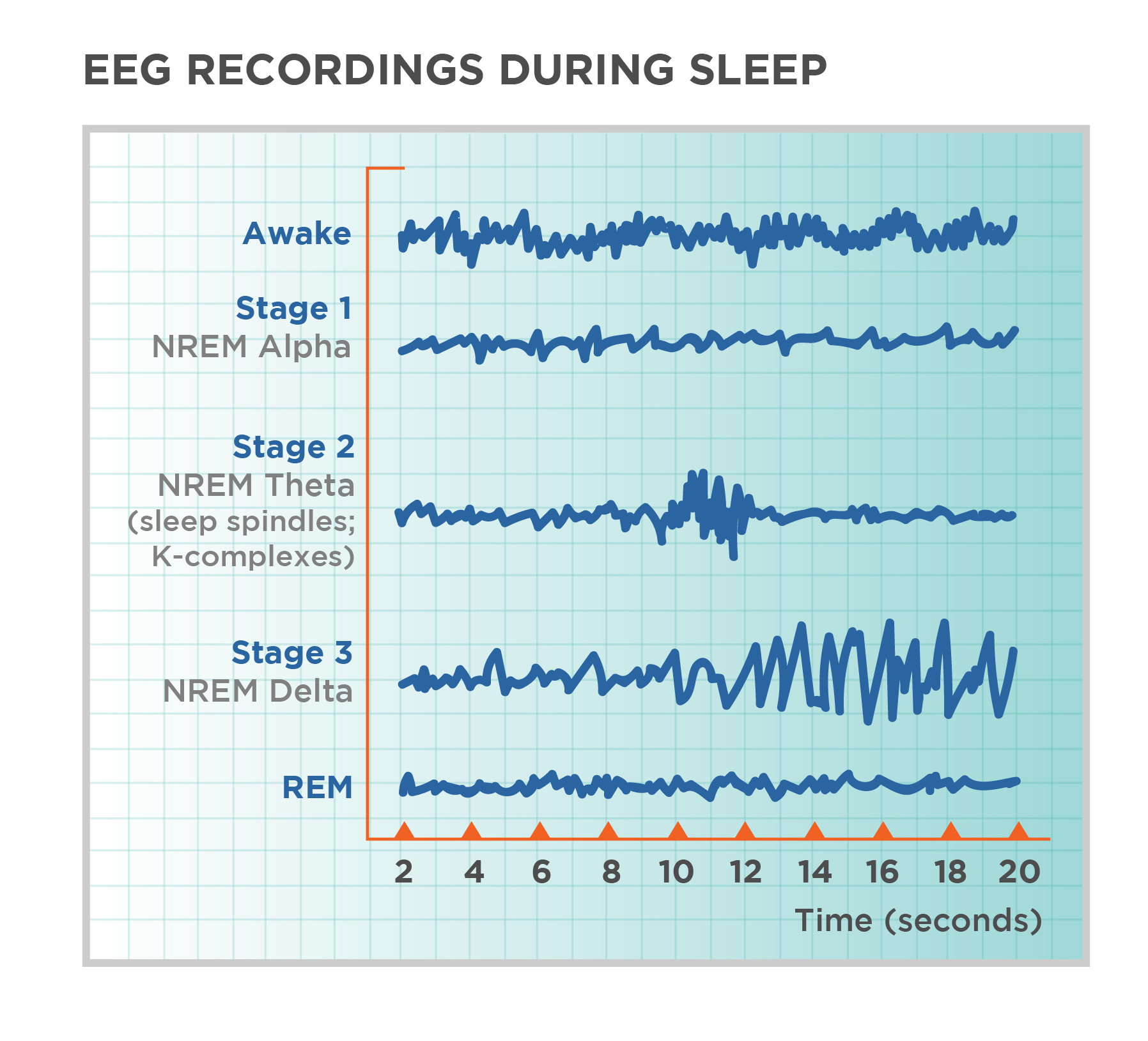
Stage three and four of sleep
Known as slow-wave sleep, characterized by deep, restorative sleep with slow brain waves. These stages are crucial for physical and mental restoration. Involve delta waves.
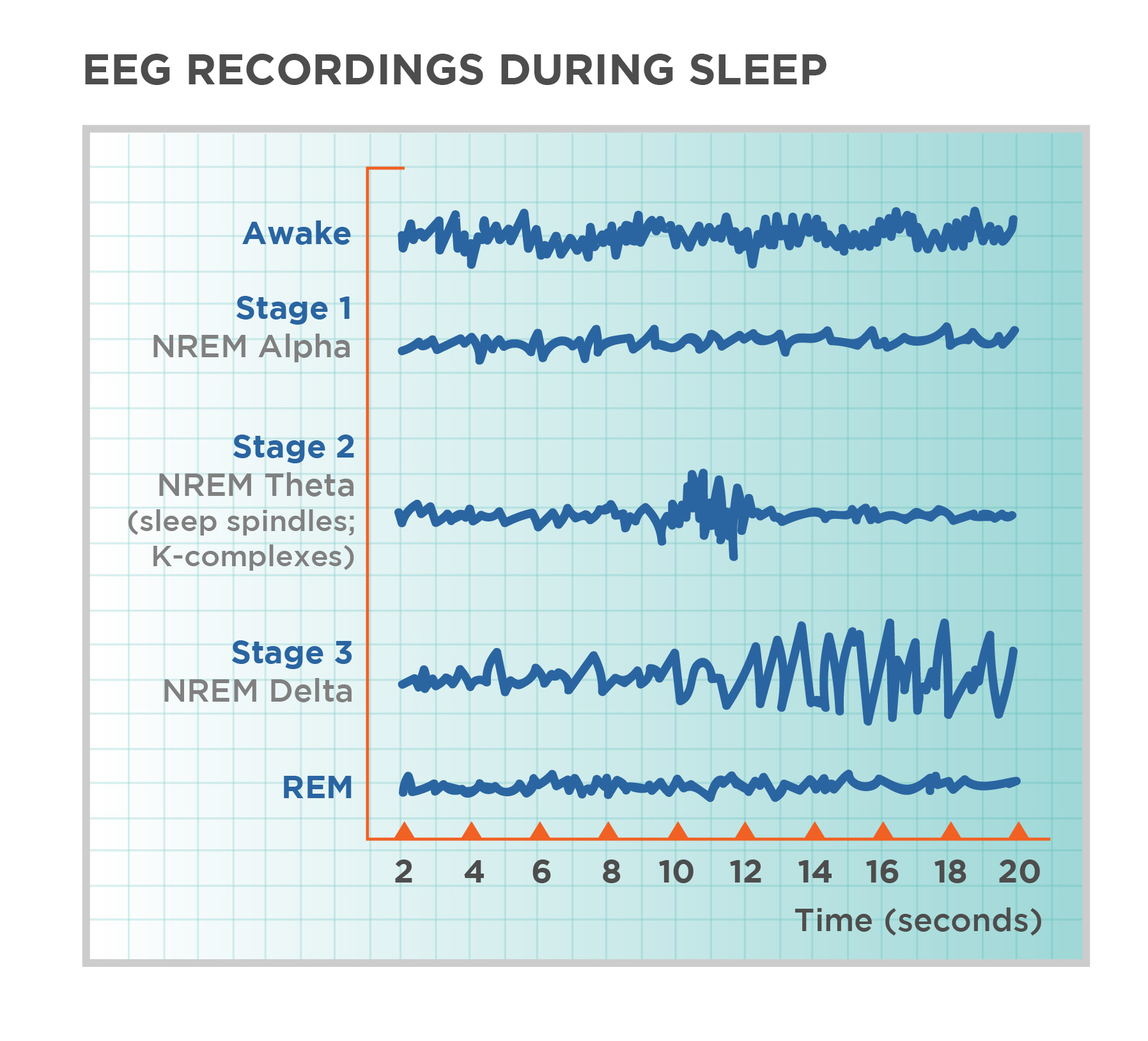
REM sleep
Stage of sleep characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreams. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because the muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches) but other body systems are active.
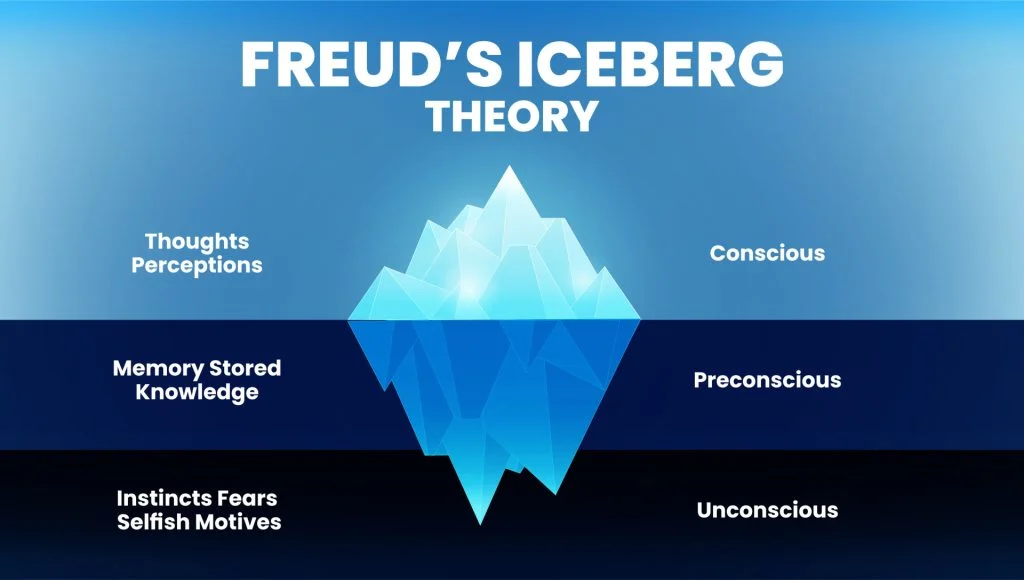
Consciousness
Awareness of ourselves and our environment; includes thoughts, sensations, and feelings.
Sleep apnea
A sleep disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, leading to poor sleep quality and daytime fatigue.
Insomnia
Difficulty falling or staying asleep, leading to tiredness, mood disturbances, and difficulty concentrating during the day. It can be short-term or chronic.
Narcolepsy
A rare sleep disorder in which a person suddenly falls into REM sleep, regardless of what they are doing
Somnambulism
A sleep disorder characterized by walking or performing complex actions while asleep, also known as sleepwalking.
REM sleep disorder
A sleep disorder where individuals physically act out their dreams due to the lack of muscle paralysis during REM sleep.
Night terrors
A sleep disorder characterized by high arousal and an appearance of being terrified; occur during Stage 4 sleep, within two or three hours of falling asleep, and are seldom remembered
Nightmares
Vivid and distressing dreams that occur during REM sleep, often causing fear, anxiety, or terror. They can disrupt sleep and lead to feelings of unease upon waking. Are remembered.
Information processing theory
A cognitive theory that explains how our brains process, store, and retrieve information like a computer. It involves encoding, storage, and retrieval processes. It basically says that dreams help us sort out the day's events and consolidate our memories
Activation-synthesis theory
A dream theory suggesting dreams are the brain's attempt to make sense of random neural activity during sleep. Says that dreams reflect inputs from brain activation originating in the pons, which the forebrain then attempts to weave into a story.
Freud’s dream theory
Dreams are a window to the unconscious mind, revealing repressed desires and emotions through manifest and latent content analysis. Dreams are carefully constructed and always contain a concealed meaning
Manifest content
The literal content of a dream as recalled by the dreamer. It is the surface-level storyline of the dream without deeper interpretation.
Latent content
Hidden, symbolic meaning within a dream, often representing unconscious thoughts and desires.
Psychoactive drugs
Chemicals that can pass through the blood-brain barrier into the brain to alter perception, thinking, behavior, and mood, producing a wide range of effects from mild relaxation or increased alertness to vivid hallucinations.
Tolerance
Increased responsivity to a drug
Withdrawal symptoms
Unpleasant physical or psychological effects that occur when a person stops using a substance they have become dependent on.
Depressants
Class of drugs that slow down the central nervous system, leading to relaxation, sedation, and reduced brain activity. Examples include alcohol, benzodiazepines, and opioids.
Narcotics
Drugs that induce sleep or dull the senses, often used for pain relief or recreationally. They can be addictive and have sedative effects.
Stimulants
Drugs that increase activity in the brain and body, leading to heightened alertness, attention, and energy levels. Examples include caffeine, nicotine, and amphetamines.
Hallucinogens
Drugs that alter perception, thoughts, and feelings. They can cause hallucinations, intense emotions, and changes in time perception.
Gamma Waves
Brain waves with the highest frequency, associated with higher mental processes like problem-solving, learning, and memory consolidation.
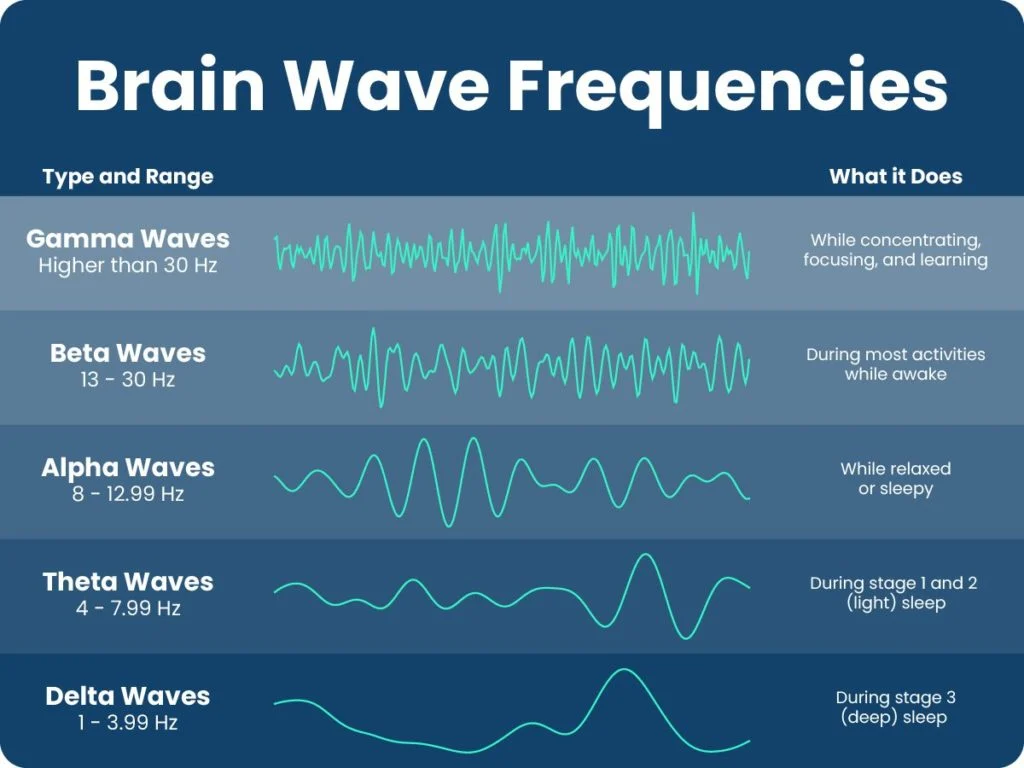
Beta Waves
High-frequency brain waves associated with alertness, active thinking, and concentration. Typically present during waking hours and periods of focused mental activity.
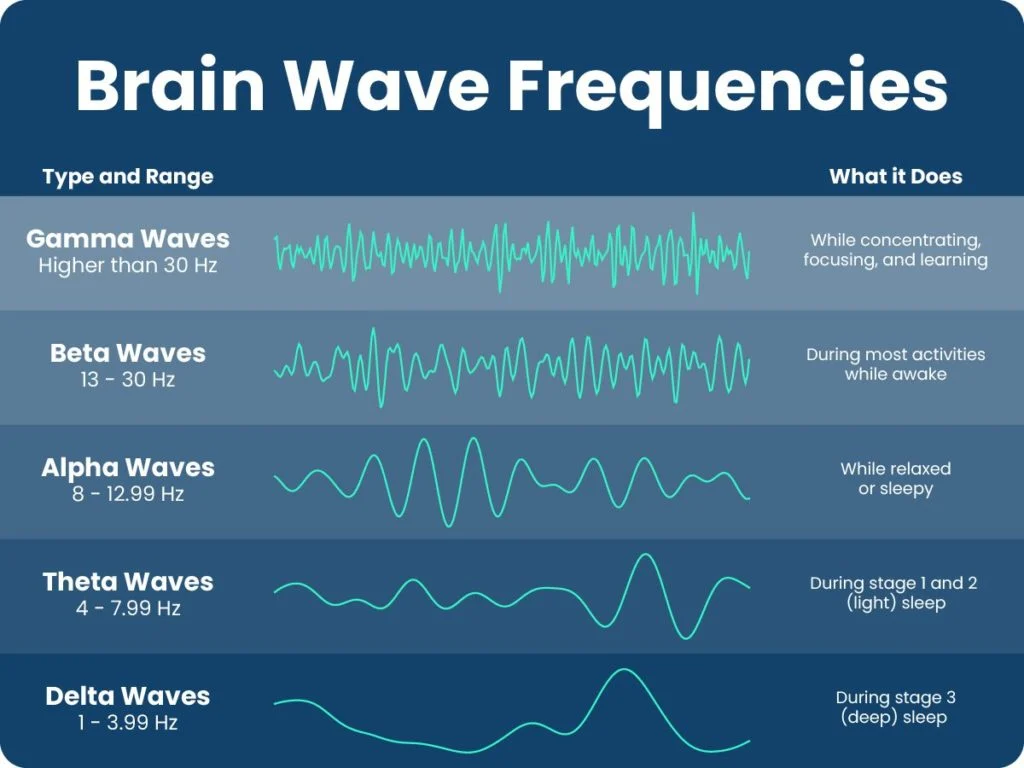
Alpha Waves
Neural oscillations in the frequency range of 8-12 Hz, associated with a relaxed and calm mental state during wakefulness.
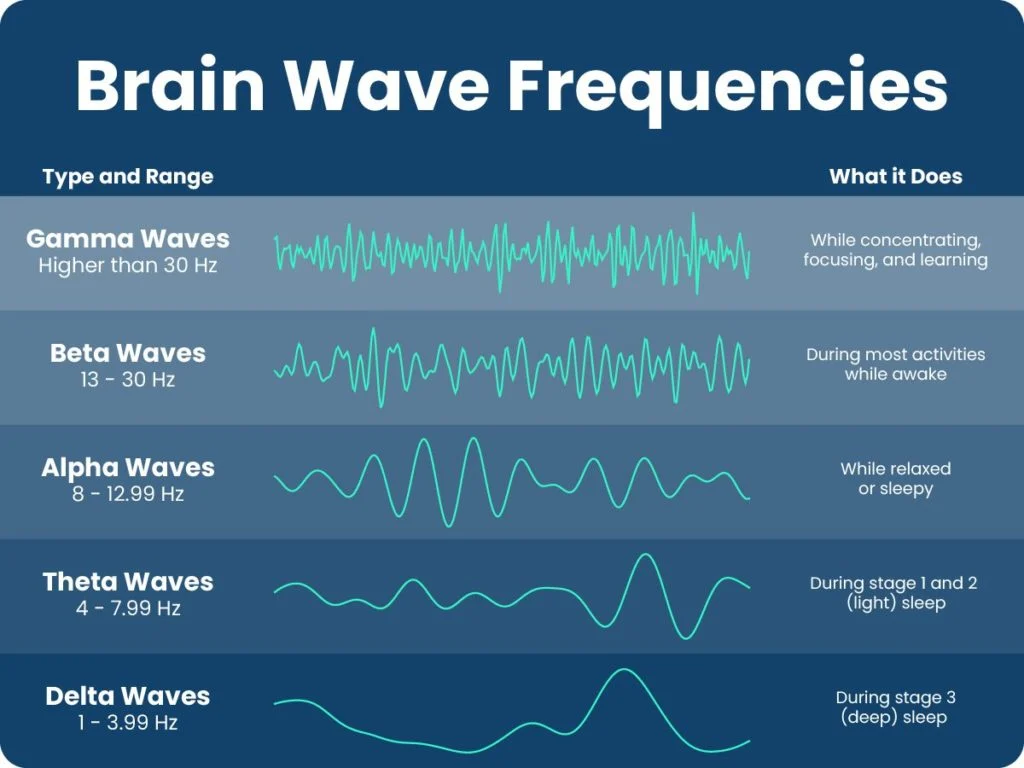
Theta Waves
Brain waves with a frequency of 4-7 Hz, occurring during deep relaxation or light sleep. Associated with creativity, problem-solving, and memory consolidation.
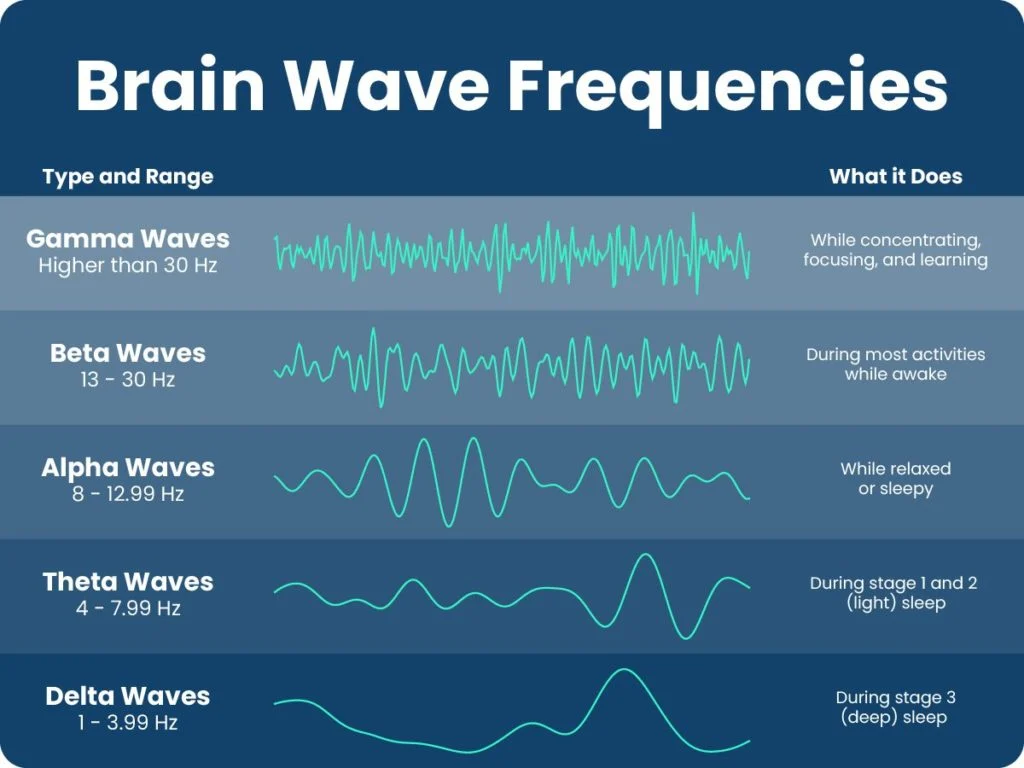
Delta Waves
Type of brain wave associated with deep sleep, characterized by high amplitude and slow frequency. Predominant in stages 3 and 4 of non-REM sleep.