Ap US History period 3, ap US history period 3, Ap US History period 3 (Paeth)
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
The French and Indian War
1754-1763 War between French and British in American colonies part of 7 years

federalism
A system of government in which power is distributed among certain geographical territories rather than concentrated within a central government.
republican government
System of government in which power is held by the voters and is exercised by elected representatives responsible for promoting the common welfare.
Common Sense
A pamphlet written by Thomas Paine that claimed the colonies had a right to be an independent nation
legislative branch
Branch of government that makes the laws
French and Indian War
Inspired many colonists to see themselves as different from the British and gave them military confidence to (eventually) challenge England
loyalist
American colonists who opposed the war for independence.
natural rights
the idea that all humans are born with rights, which include the right to life, liberty, and property
Declaration of Independence
1776 statement, issued by the Second Continental Congress, explaining why the colonies wanted independence from Britain.
The Constitution
New format of government focuses more on a central national power and less on states 3 branch government that limit each other

Bill of Rights
the first ten amendments to the Constitution, which guaranteed the civil rights of American citizens.
Federalism
A system in which power is divided between the national and state governments
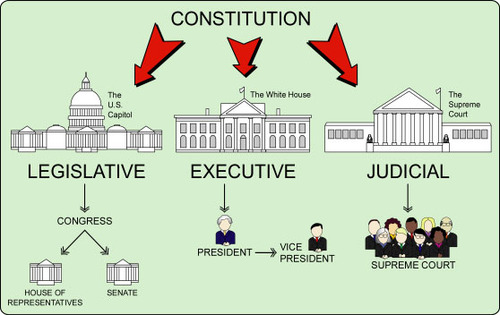
Northwest Ordinance
Enacted in 1787, it is considered one of the most significant achievements of the Articles of Confederation. It established a system for setting up governments in the western territories so they could eventually join the Union on an equal footing with the original 13 states
Albany Congress
A conference called by Franklin in 17454 that proposed unified, colonial action with regards to Indian policy. Rejected by colonies, but seeds of independence were planted
Paris Peace, 1763
ended the French and Indian War, France gave up all its territories in mainland North America, effectively ending any foreign military threat to the British colonies there
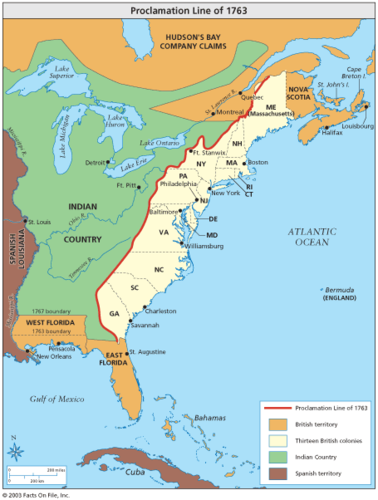
Proclamation of 1763
British government forbade British colonists from settling west of the Appalachian Mountains, and which required any settlers already living west of the mountains to move back east. It was ignored
George Washington's presidency
1st president formed the cabinets 2nd term strictly followed constitution left office to tell everyone they needed to be unified established framework of Supreme Court and how they will be decided judiciary

mercantilism
Economic policy where the colonies were to provide raw materials for England and a place to sell finished British goods
Sugar Act, 1764
The first act that Parliament passed that raised taxes on the colonies. Indirect tax on imported foods from the West Indies. Colonists became so angry that Parliament lowered the duties.
Quartering Act, 1765
Was an act enforced by the British on their North American colonies. It required colonist to provide adequate housing and basic necessities like food and drink to British soldiers.
Stamp Act, 1765
Direct tax imposed on the colonists by Parliament which increased the money colonists paid on printed goods. Purpose was to pay for British soldiers stationed in North America after the French and Indian War.
Sons/Daughter of Liberty
A radical political organization for colonial independence which formed in 1765 after the passage of the Stamp Act. leaders included Samuel Adams and Paul Revere.
Townshend Act
A tax that the British Parliament passed in 1767 that was placed on leads, glass, paint and tea
Boston Massacre
The first bloodshed of the American Revolution (1770), as British guards at the Boston Customs House opened fire on a crowd killing five Americans
Committee Correspondence
Colonial organizations created to share information about actions of the British prior to the revolution.
Intolerable Acts
in response to Boston Tea Party, 4 acts passed in 1774, Port of Boston closed, reduced power of assemblies in colonies, permitted royal officers to be tried elsewhere, provided for quartering of troop's in barns and empty houses
First Continental Congress
In 1774, this was the first attempt to create official colonial unity (and kind of a government) against the British. Formed in response to the Intolerable Acts and voted to boycott British good.
Hessians
German soldiers hired by George III to smash Colonial rebellion. Caused some undecided colonists to turn against England
Second Continental Congress
Convened in May 1775, this colonial group was created to officially protest the crack-down of Intolerable Acts. Sent the Olive Branch Petition to King as last ditch effort to stop war. Ultimately, this group was the "government" that organized and fought the war.
Declaratory Act
Act passed in 1766 after the repeal of the stamp act; stated that Parliament had authority over the the colonies and the right to tax and pass legislation "in all cases whatsoever."
Lexington and Concord
First battle of the Revolutionary War. Later referred to as "The Shot Heard 'Round the World"
Valley Forge
Place where Washington's army spent the winter of 1777-1778, a 4th of troops died here from disease and malnutrition, Steuben comes and trains troops
Saratoga
A battle that took place in New York where the Continental Army defeated the British. It proved to be the turning point of the war. This battle ultimately had France to openly support the colonies with military forces in addition to the supplies and money already being sent.
Treaty of Paris, 1783
agreement signed by British and American leaders that stated the United States of America was a free and independent country
Shays' Rebellion
Rebellion of of farmers in western Massachusetts in 1786-1787, protesting mortgage foreclosures. It highlighted the need for a strong national government just as the call for the Constitutional Convention went out.
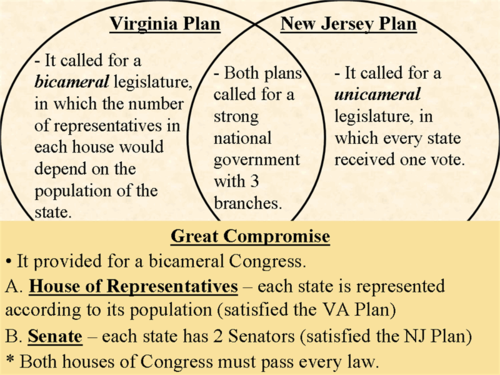
Virginia Plan
"Large state" proposal for the new constitution, calling for proportional representation in both houses of a bicameral Congress. The plan favored larger states and thus prompted smaller states to come back with their own plan for apportioning representation.
New Jersey Plan
"Small state" proposal for the new constitution, in which states got an equal number of representatives in Congress
Connecticut Compromise
1787; This compromise was between the large and small states of the colonies. The Great Compromise resolved that there would be representation by population in the House of Representatives, and equal representation would exist in the Senate.
Three-fifths Compromise
Agreement that each slave counted as three-fifths of a person in determining representation in the House for representation and taxation purposes (negated by the 13th amendment)
Electoral College
Process for electing the President. Seen as a compromise between direct popular vote and having Congress pick the President.
"Thanks Electoral College!" -Love and kisses: Donald Trump
Judiciary Act of 1789
Act which created the federal-court system.
LIMITED GOVERNMENT
In this type of government everyone, including all authority figures, must obey laws. Constitutions, statements of rights, or other laws define the limits of those in power so they cannot take advantage of the elected, appointed, or inherited positions
Bank of the United States
Proposed by Alexander Hamilton as the basis of his economic plan. Wold serve as the storehouse for government revenue and establish fiscal policy for the nation
Whiskey Rebellion
In 1794, farmers in Pennsylvania rebelled against Hamilton's excise tax on alcohol. In October, 1794, the army, led by Washington, put down the rebellion. The incident showed that the new government under the Constitution could react swiftly and effectively
Legislative Branch
-function: to pass laws, gotta pass both chambers by majority vote before it can become a law; can declare war
Farewell Address, 1796
1796 speech by Washington urging US to maintain neutrality and avoid permanent alliances with European nations
Executive Branch
The president and his cabinet. The president cannot legislate but can pass executive orders under certain defined circumstances.
Alien & Sedition Acts
Acts passed by federalists giving the government power to imprison critics of the government
Judicial Branch
A branch of government that interprets Congressional laws
Democratic-Republicans
Political party that wanted more power to the states and rose in direct opposition to the Federalist party
House of Representatives
the lower legislative house of the United States Congress. The number of people per state is determined by population of the state
Federalist Party
Political party of Alexander Hamilton and John Adams. Supported a strong central government and "urbanization"
The Proclamation of 1763
Line drawn by British Parliament, colonists not allowed to settle past Appalachian mountains
Stamp Act
1765 direct tax on a stamp that must be put on paper, office documents, etc.

The Coercive Acts
1774 intolerable acts

The Declaration Of Independence
1776 document written by colonist elites to British King and Parliament stating independence and what all was wrong with British rule and the King

Battle of Saratoga
Head to head battle between the British and Americans in country side, Americans win by a lot and show they have a chance. The French joined the war effort
Treaty of Paris
1783 ended the American Revolutionary War Granted the land British gave Indians as American land now American colonies recognized as their own independent country

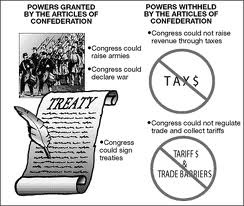
Articles of confederation
First form of government A lot of weaknesses No strong central government Strong state governments Causes economical problems and failure
Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise)
New Jersey and Virginia plans together and create the senate and House of Representatives senate equal vote house of rep by population
The Three-Fifths compromise
Slaves count as population for vote in congress 3 slaves for every 5 white were counted

Hamilton
Tackle debt- grant money back to people, national bank create national government, manufacturing establish tax revenue

Enlightenment
A movement in the 18th century that advocated the use of reason in the reappraisal of accepted ideas and social institutions.
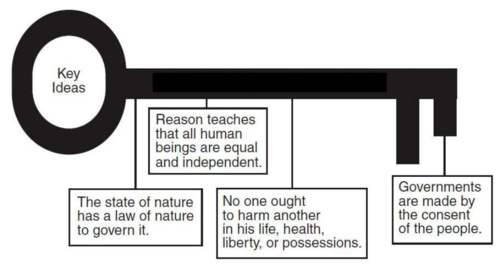
John Locke
English philosopher who advocated the idea of a "social contract" in which government powers are derived from the consent of the governed and in which the government serves the people; also said people have natural rights to life, liberty and property.
Ben Franklin
A delegate from Pennsylvania and proposed the "Albany Plan of the Union" as a way to strengthen colonies.

Sugar Act of 1764
An act that raised tax revenue in the colonies for the crown. It also increased the duty on foreign sugar imported from the West Indies.

Quartering Act of 1765
Act forcing colonists to house and supply British forces in the colonies; created more resentment; seen as assault on liberties.

Townshend Acts
A tax that the British Parliament passed in 1767 that was placed on leads, glass, paint and tea

Popular Sovereignty
A belief that ultimate power resides in the people.

Thomas Jefferson
Wrote the Declaration of Independence, Leader of the Democratic-Republican Party

Second Continental Congress (1775)
Managed the colonial war effort, and moved incrementally towards independence - finally adopting the Declaration of Independence in 1776.

Sons of Liberty
A radical political organization for colonial independence which formed in 1765 after the passage of the Stamp Act. They incited riots and burned the customs houses where the stamped British paper was kept. After the repeal of the Stamp Act, many of the local chapters formed the Committees of Correspondence which continued to promote opposition to British policies towards the colonies. The Sons leaders included Samuel Adams and Paul Revere.

Patriots
(also known as Revolutionaries, Continentals, Rebels, or American Whigs) were those colonists of the Thirteen Colonies who rejected British rule during the American Revolution and declared the United States of America as an independent nation in July 1776.

Tories/Loyalists
Colonists who favored remaining under British control

Constitutional Convention
A meeting in Philadelphia in 1787 that produced a new constitution

Articles of Confederation
(1777) the document that created the first central government for the United States; was repealed by the Constitution in 1789
POPULAR SOVEREIGNTY
Constitutional principle stating that the people hold the power in our government. People hold this power with the ability to vote
whiskey rebellion
In 1794, farmers in Pennsylvania rebelled against Hamilton's excise tax on whiskey, and several federal officers were killed in the riots caused by their attempts to serve arrest warrants on the offenders. In October, 1794, the army, led by Washington, put down the rebellion. The incident showed that the new government under the Constitution could react swiftly and effectively to such a problem, in contrast to the inability of the government under the Articles of Confederation to deal with Shay's Rebellion.
Jay's treaty
1794- British and US agreed- British trade w/ Americans and the British leave northwest territory
Washington's Farewell Address, 1796
Urged Americans to avoid excessive political party spirit and geographical distinctions. In foreign affairs, warned against long-term alliances with other nations -
XYZ Affair (1797)
Diplomatic conflict between France and the United States when American envoys to France were asked to pay a hefty bribe for the privilege of meeting with the French foreign minister. Many in the U.S. called for war against France, while American sailors and privateers waged an undeclared war against French merchants in the Caribbean.
Alien and Sedition Acts
Series of four laws enacted in 1798 to reduce the political power of recent immigrants
Republican Motherhood
suggested that women would be responsible for raising their children to be virtuous citizens of the new American republic.
Federalist Papers
A collection of 85 articles written by Alexander Hamilton, John Jay, and James Madison under the name "Publius" to defend the Constitution in detail.
Federalist vs Democratic-Republican
A supporter of a strong national government. Vs. A supporter of state liberties