2 Lec 7 (Exam2): Benign Soft Tissue Tumors
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
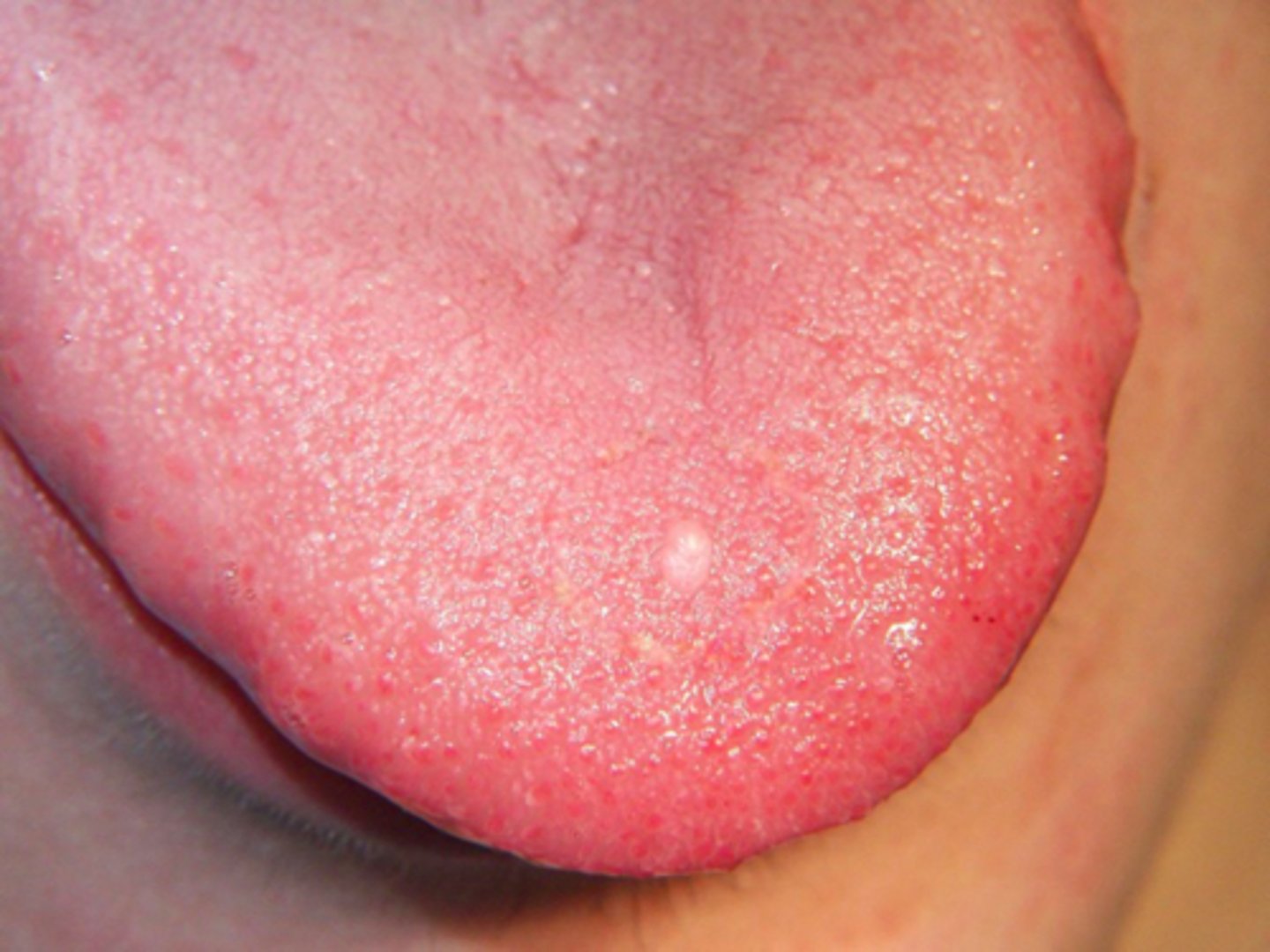
Fibroma
what is the MOST common soft tissue tumor?
densely collagenized fibrous connective tissue
what is the histopathologic presentation of fibromas?
false
t/f: fibromas are true neoplasms
Fibroma
ID the pathology:
-Reactive hyperplasia of fibrous connective tissue
-Results from chronic low-grade irritation
chronic low-grade irritation
what is normally the cause of fibromas?
Fibroma
patient presents with a pink nodule on the buccal mucosa. Patient claims they have always bitten their cheek and started to notice a "bump" forming near the same area. What could this be?
conservative excision
treatment for fibromas:
neoplasia
what needs to be ruled out when diagnosing a fibroma?
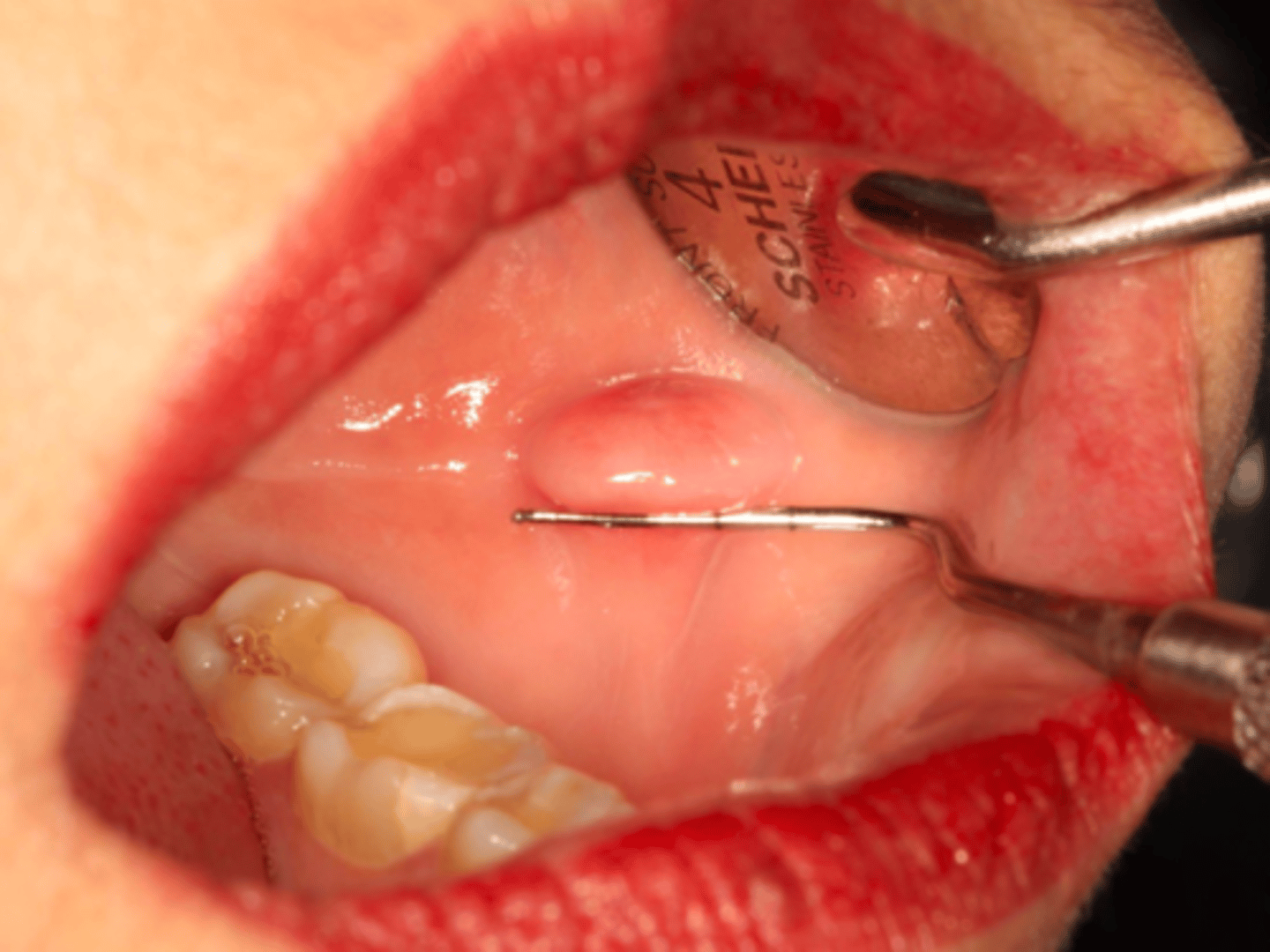
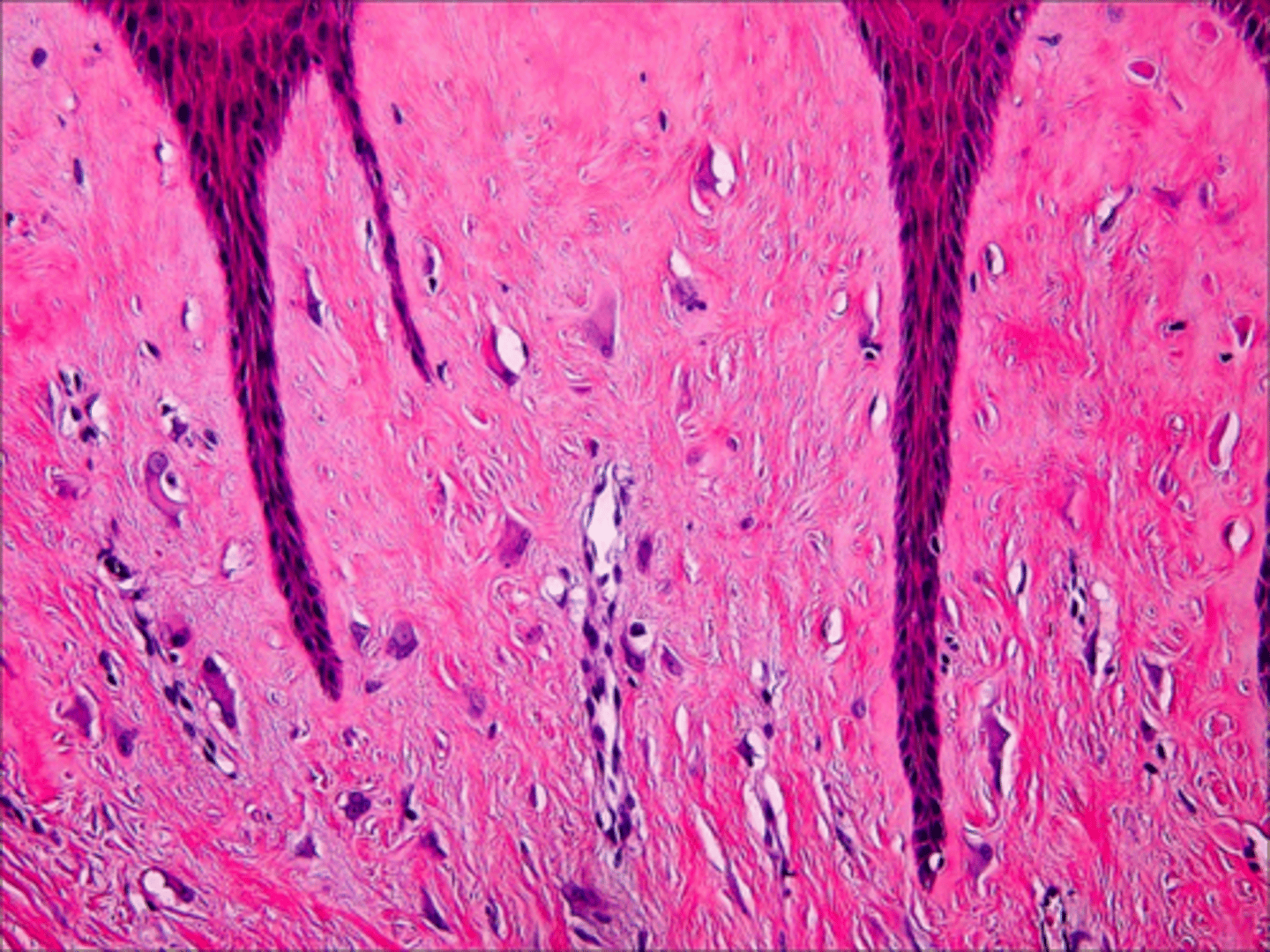
Giant Cell Fibroma
patient presents with an asymptomatic nodule with papillary surface on the anterior dorsal tongue. Histopathologic features show vascular fibrous connective tissue , numerous large stellate fibroblasts that contain several nuclei and rete ridges narrow and elongated. What do you suspect?
Giant Cell Fibroma
vascular fibrous connective tissue , numerous large stellate fibroblasts that contain several nuclei and rete ridges narrow and elongated. This is associated with what pathology?
conservative excision
treatment for Giant Cell Fibromas:
gingiva
what ONLY location do peripheral giant cell granuloma present on?
gingiva
what ONLY location do peripheral ossifying fibroma present on?
Lobular capillary hemangioma
pregnancy tumor
what are two other names for Pyogenic Granuloma?
neither pyogenic nor a granuloma
why is Pyogenic Granuloma a poor name for the entity?
Pyogenic Granuloma
male patient presents with red-pink ulcerated nodule on the facial aspect of the maxillary gingiva. Histopathology shows vascular proliferation of granulation tissue. What do you suspect?
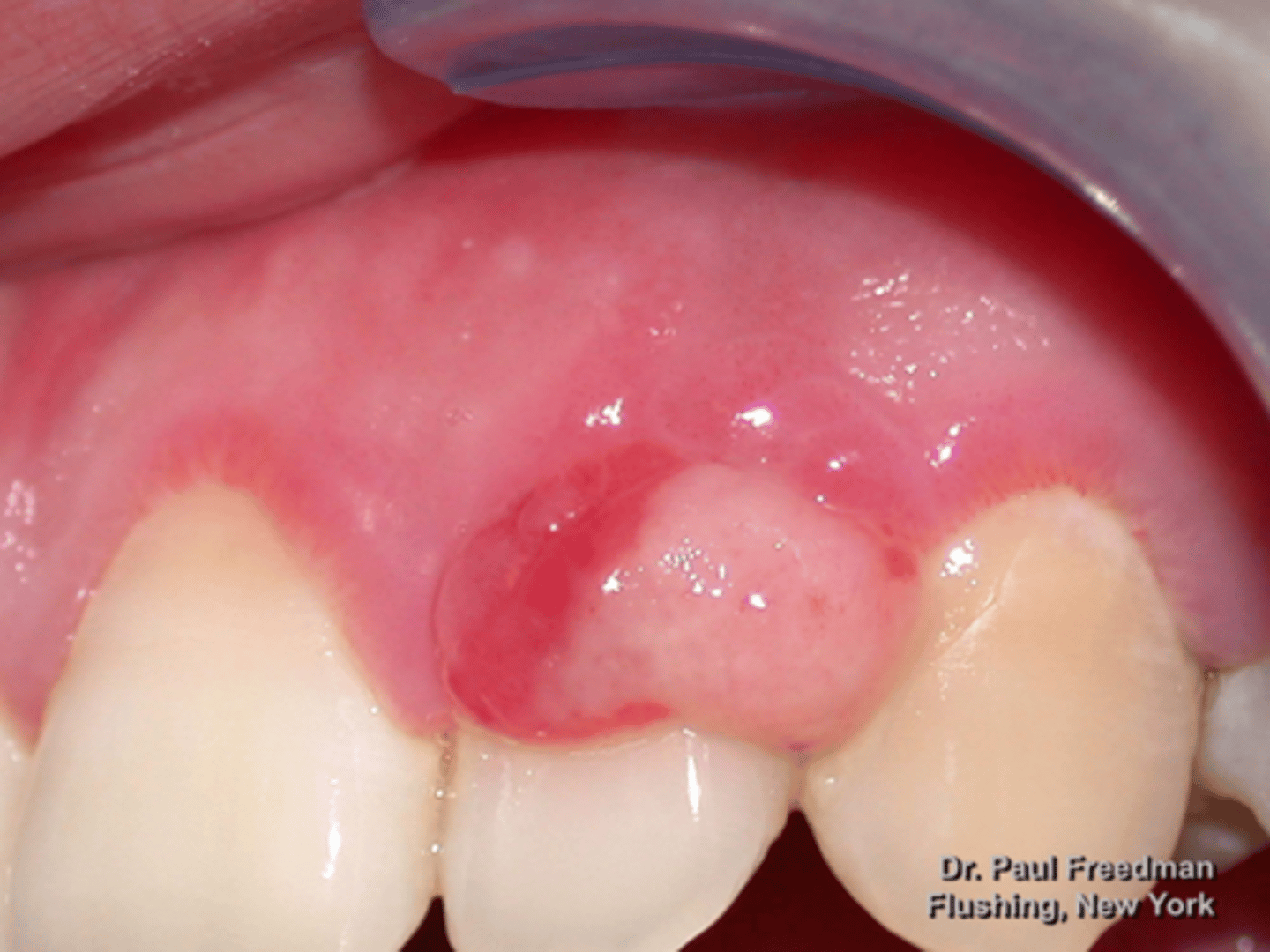
Pyogenic Granuloma
Vascular proliferation of granulation tissue is associated with what pathology?
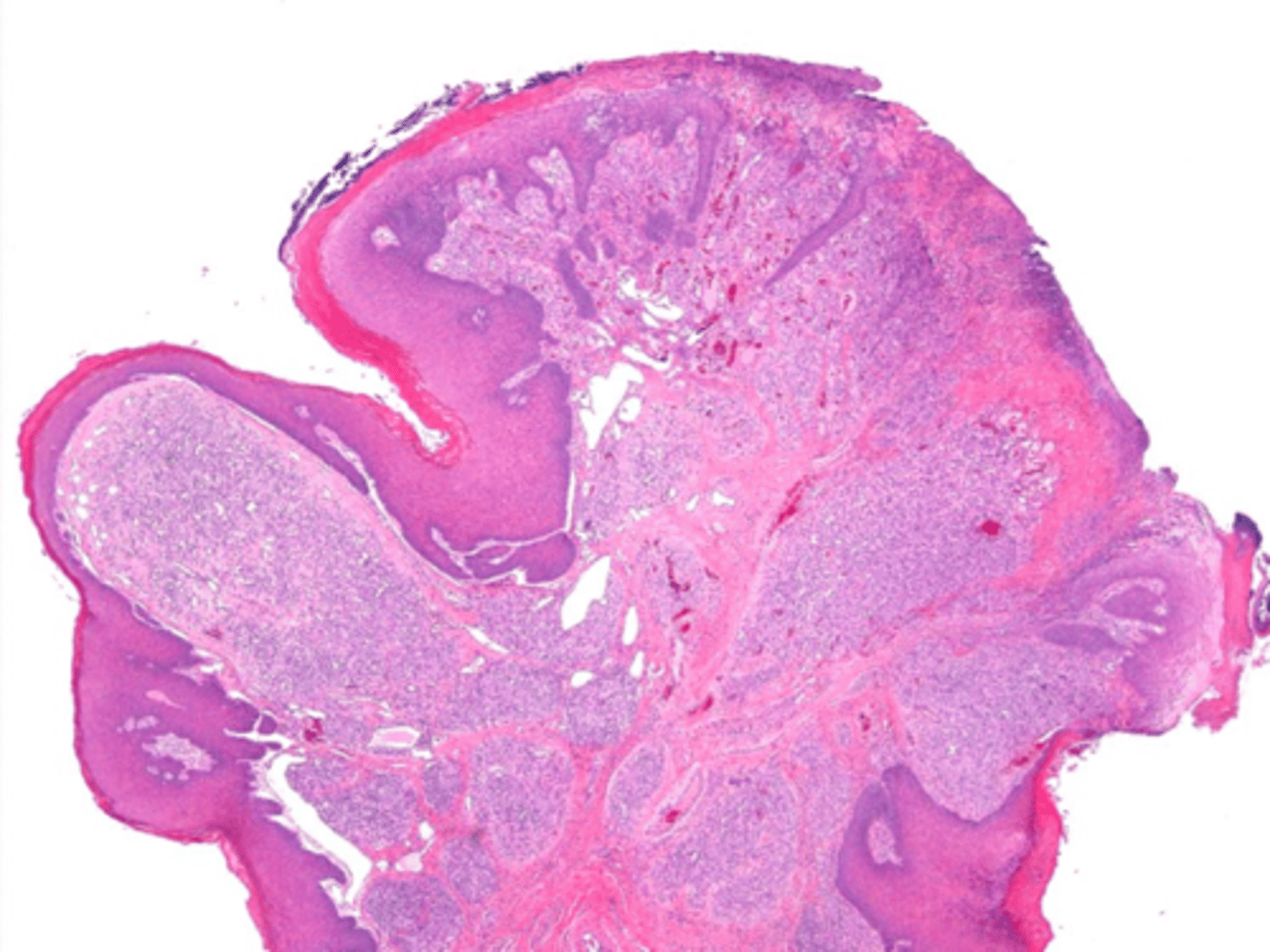
gingiva
75% of Pyogenic Granulomas present of what location?
conservative excision
eliminate irritants
what is the treatment for Pyogenic Granulomas?
Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma (PGCG)
patient presents with a purplish, slightly ulcerated nodule on the facial aspect of the maxillary gingiva. Histopathologic features show Multinucleated giant cells with up to several dozen nuclei, hemorrhage and hemosiderin. What do you suspect?
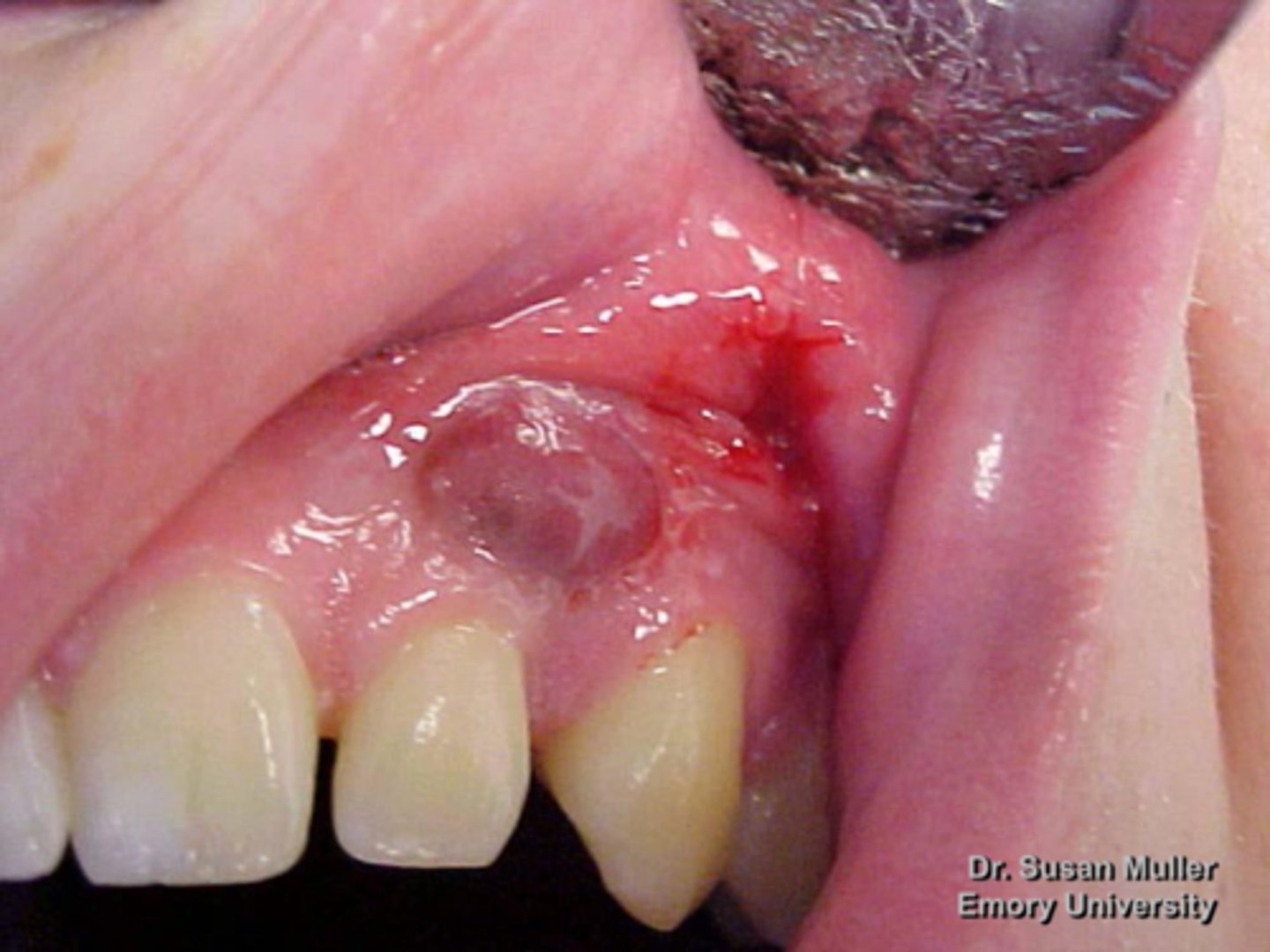
Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma (PGCG)
Multinucleated giant cells with up to several dozen nuclei, hemorrhage and hemosiderin is associated with what pathology?
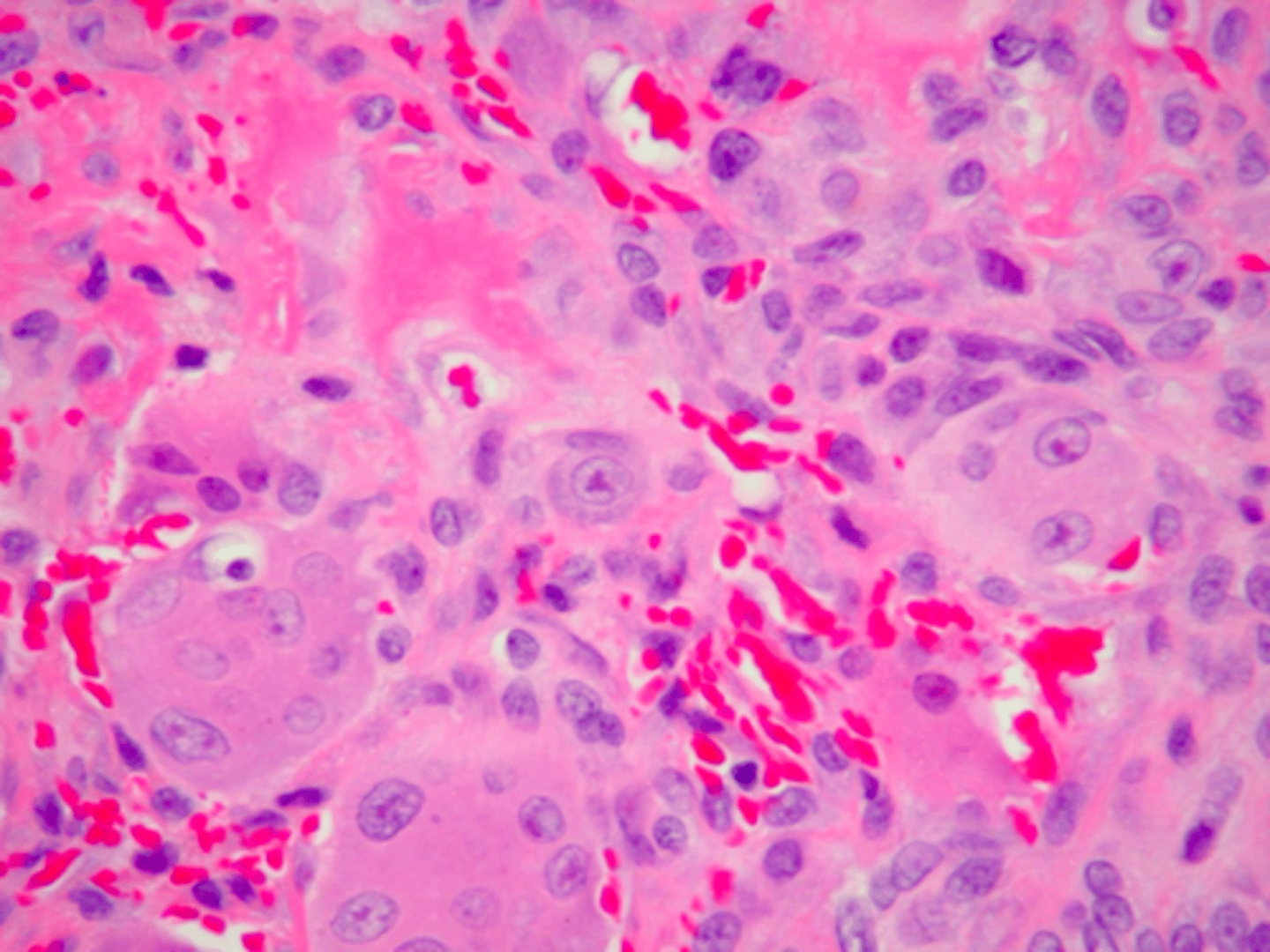
local excision down to bone
what is the treatment for Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma (PGCG)?
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma
patient presents with pink nodule on the facial aspect of the mandibular gingiva. Histopathology shows fibrous proliferation with formation of mineralized (osseous) product. What do you suspect?
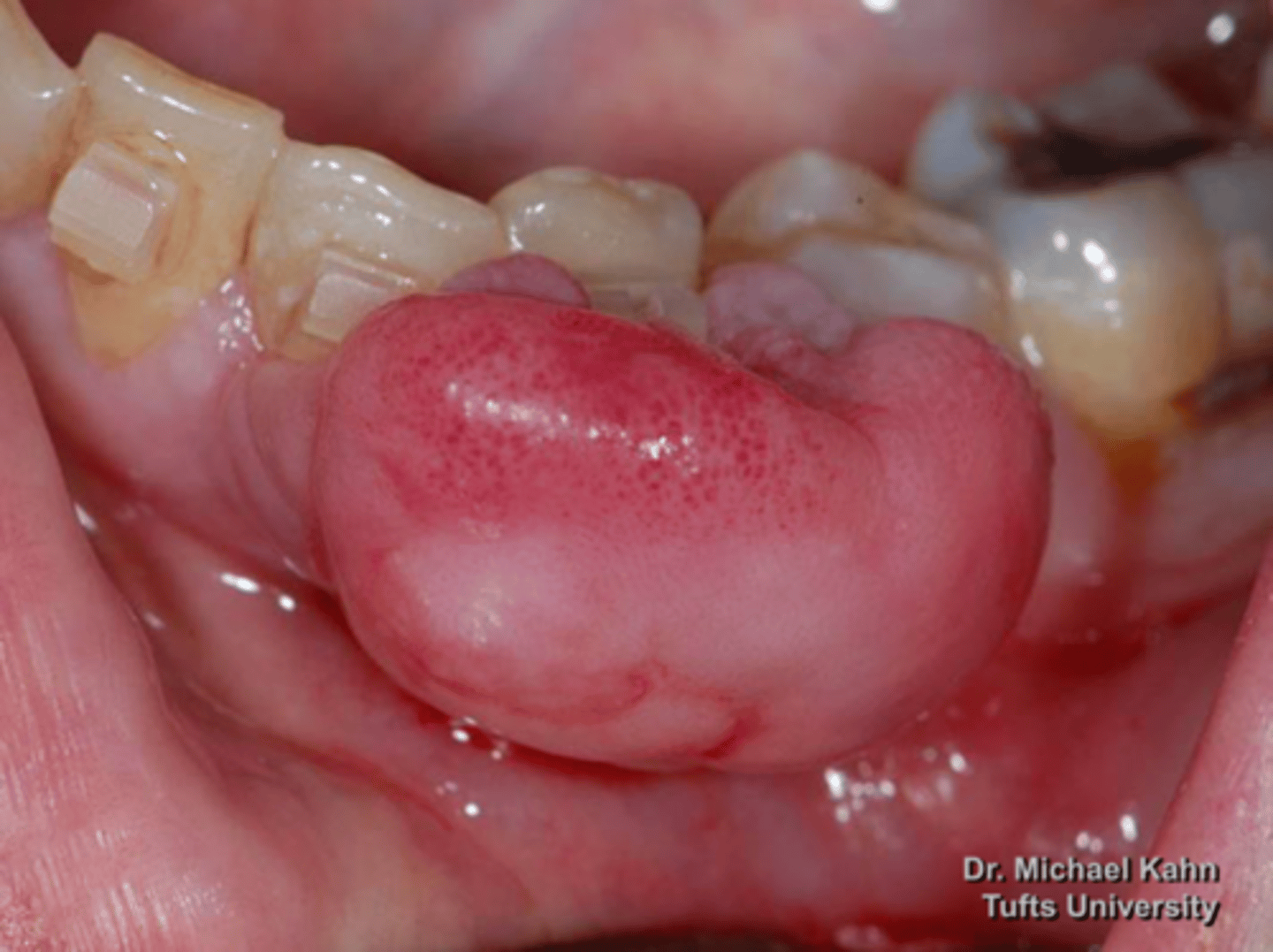
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma
fibrous proliferation with formation of mineralized (osseous) product is associated with what pathology?
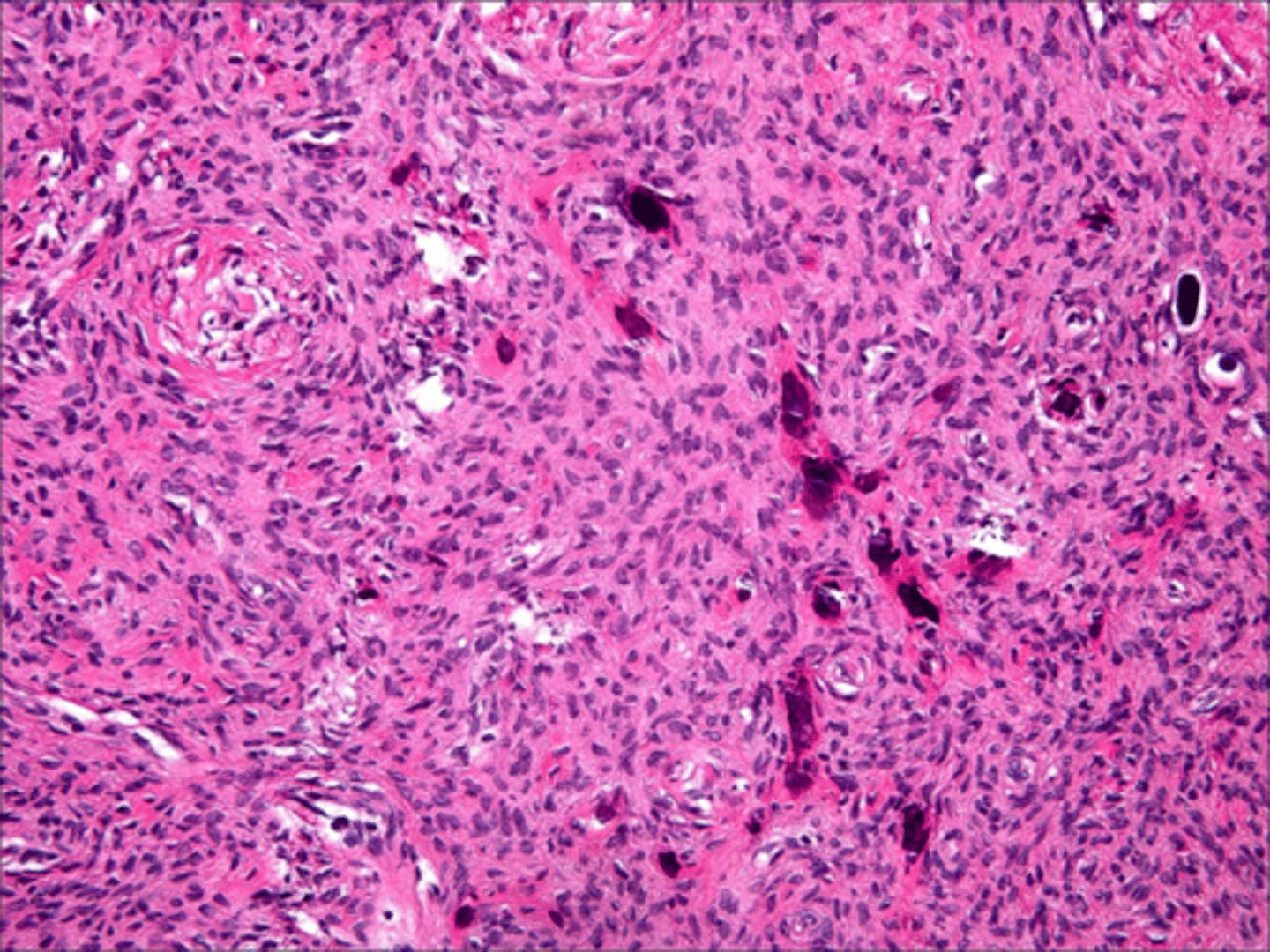
Lipoma
what is the most common mesenchymal neoplasm?
Lipoma
-Benign tumor of adipose tissue
-Most common mesenchymal neoplasm
-Pink or yellow in color
Lipomatous
Neural
Vascular*
Myofibroblastic
Muscular
name 5 types of benign soft tissue neoplastic tumors:
Lipoma
patient presents with nodule on the floor of the mouth that is and slight yellowish tint. Histopathology showed Well-circumscribed mature adipose tissue. What do you suspect?
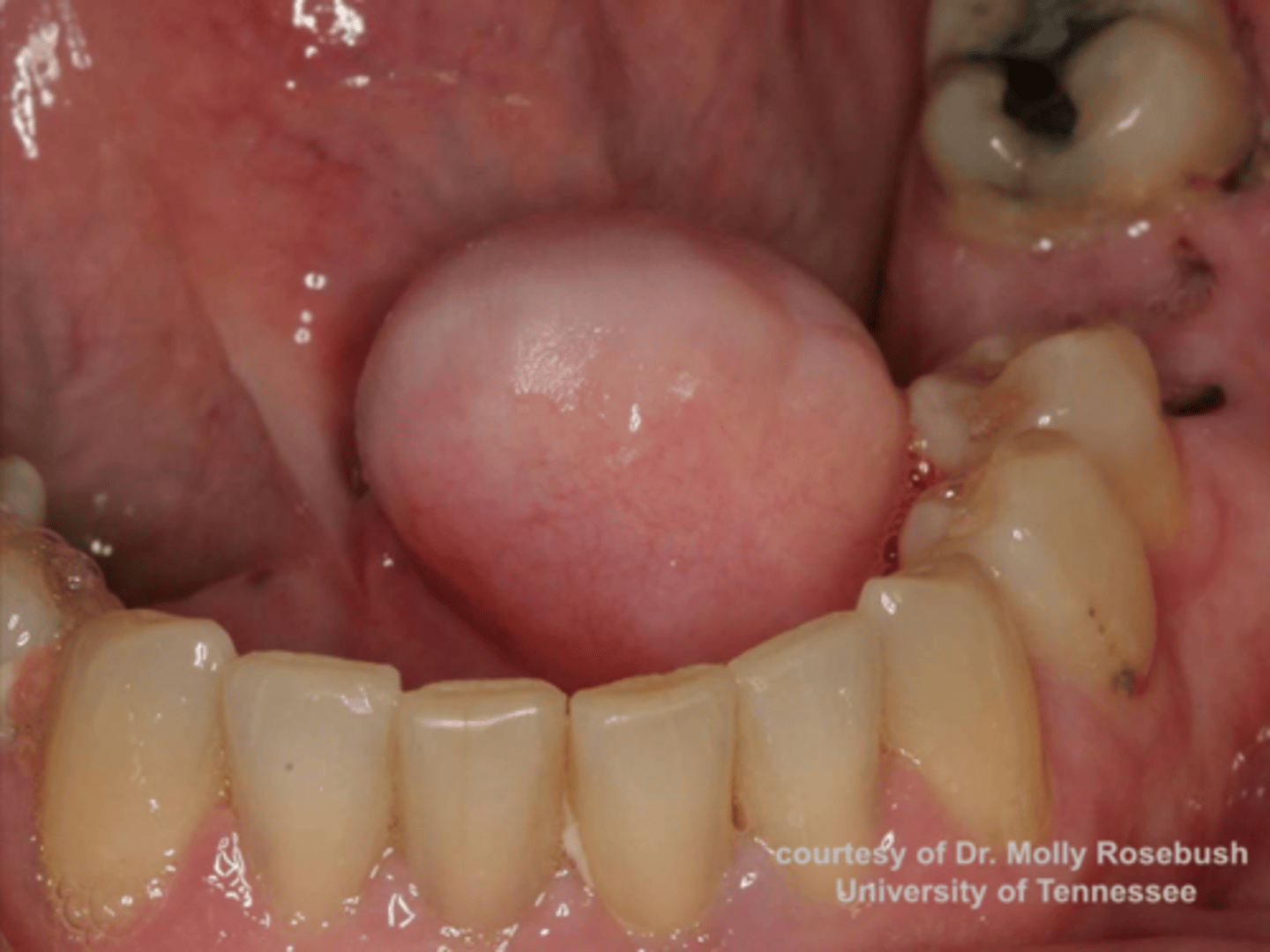
Lipoma
ID the pathology:
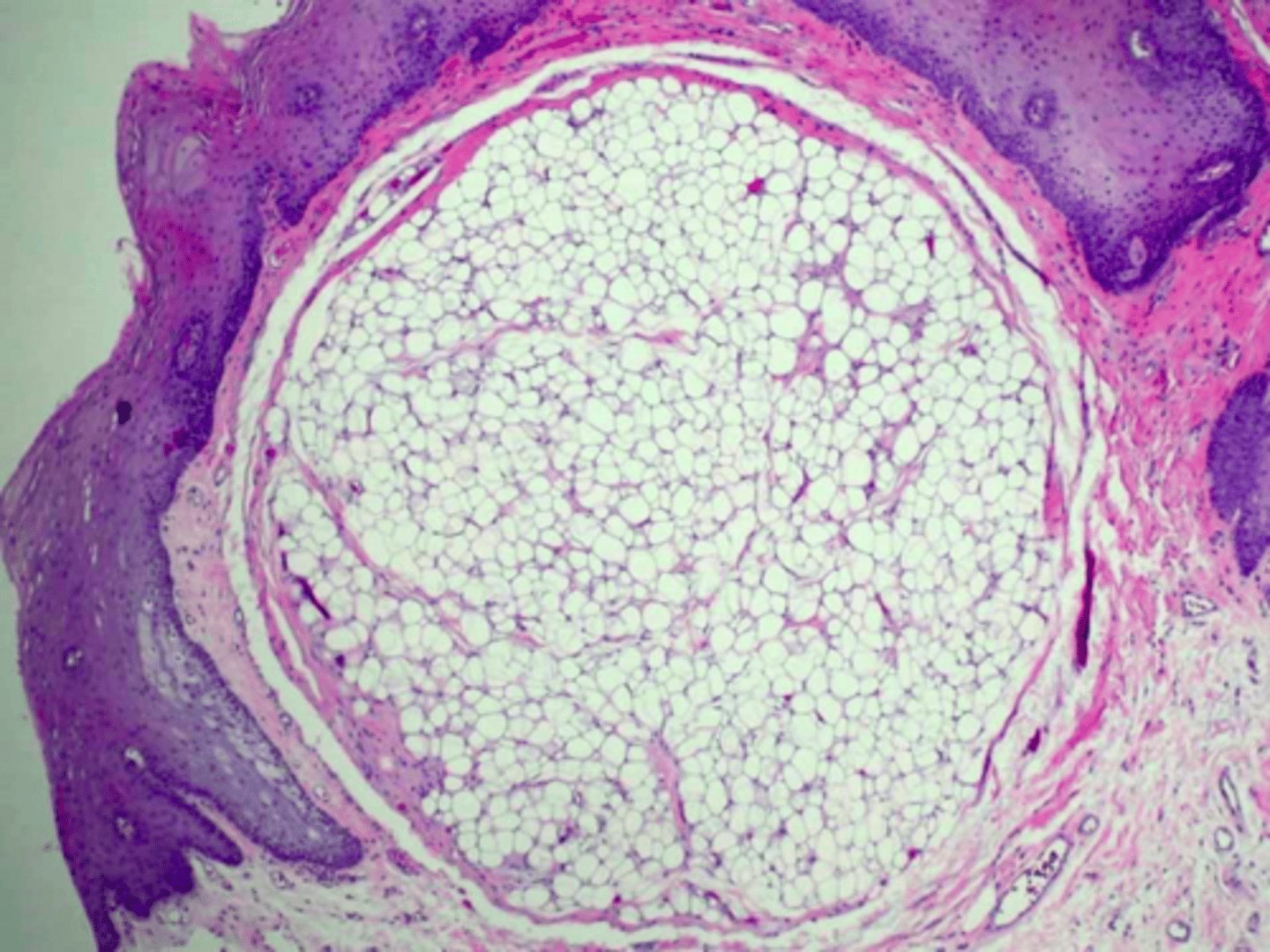
conservative excision
what is the treatment for a Lipoma?
dorsal tongue
what is the most common site presentation for a Granular Cell Tumor?
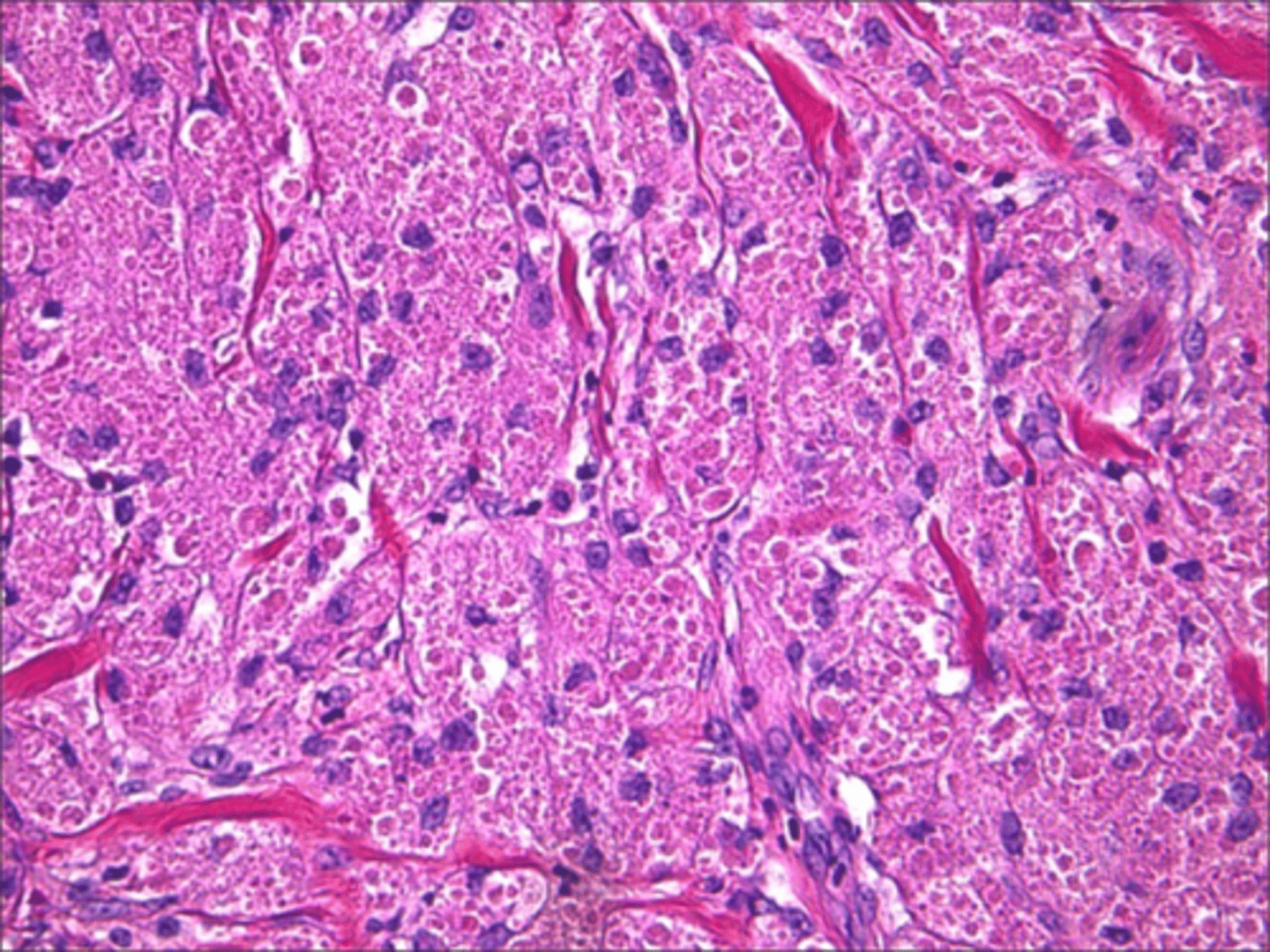
Granular Cell Tumor
Patient presents with a yellowish growth on the dorsolateral tongue surface. Histopathology showed Abundant pale, eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. What do you suspect?
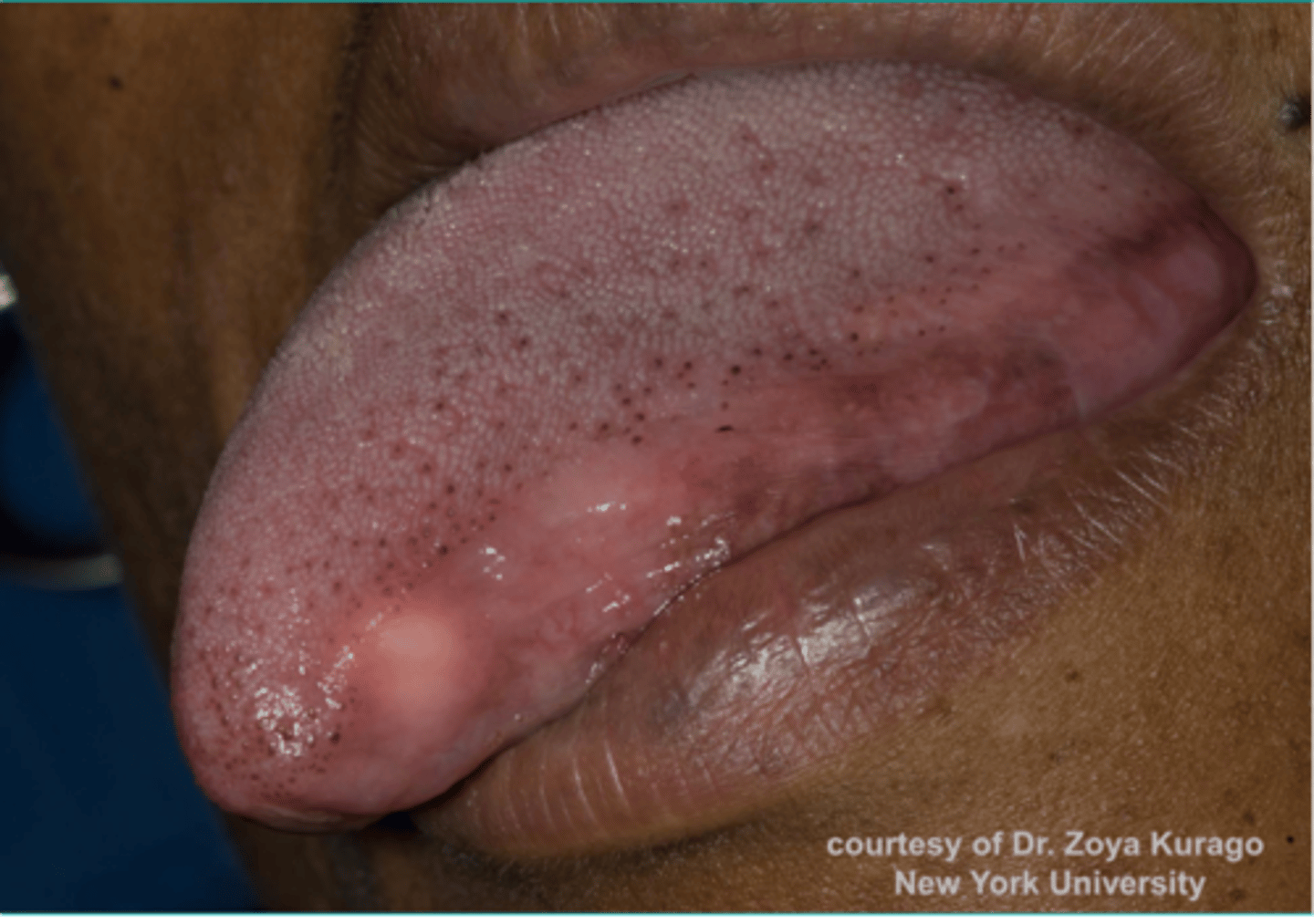
Granular Cell Tumor
Abundant pale, eosinophilic granular cytoplasm and pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is associated with what pathology?
Giant Cell Fibroma
which of the following is NOT associated with presenting yellow?
-Granular cell tumor
-Neurofibroma
-Giant Cell Fibroma
-Schwannoma
-Palisaded encapsulated neuroma
-Traumatic neuroma
-Lipoma
Congenital Epulis
3 week old female patient presents with a nodular formation on the maxillary gingiva lateral to the midline. Histopathology showed cells with granular cytoplasm resemble granular cell tumors. NO pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia were present. What do you suspect?
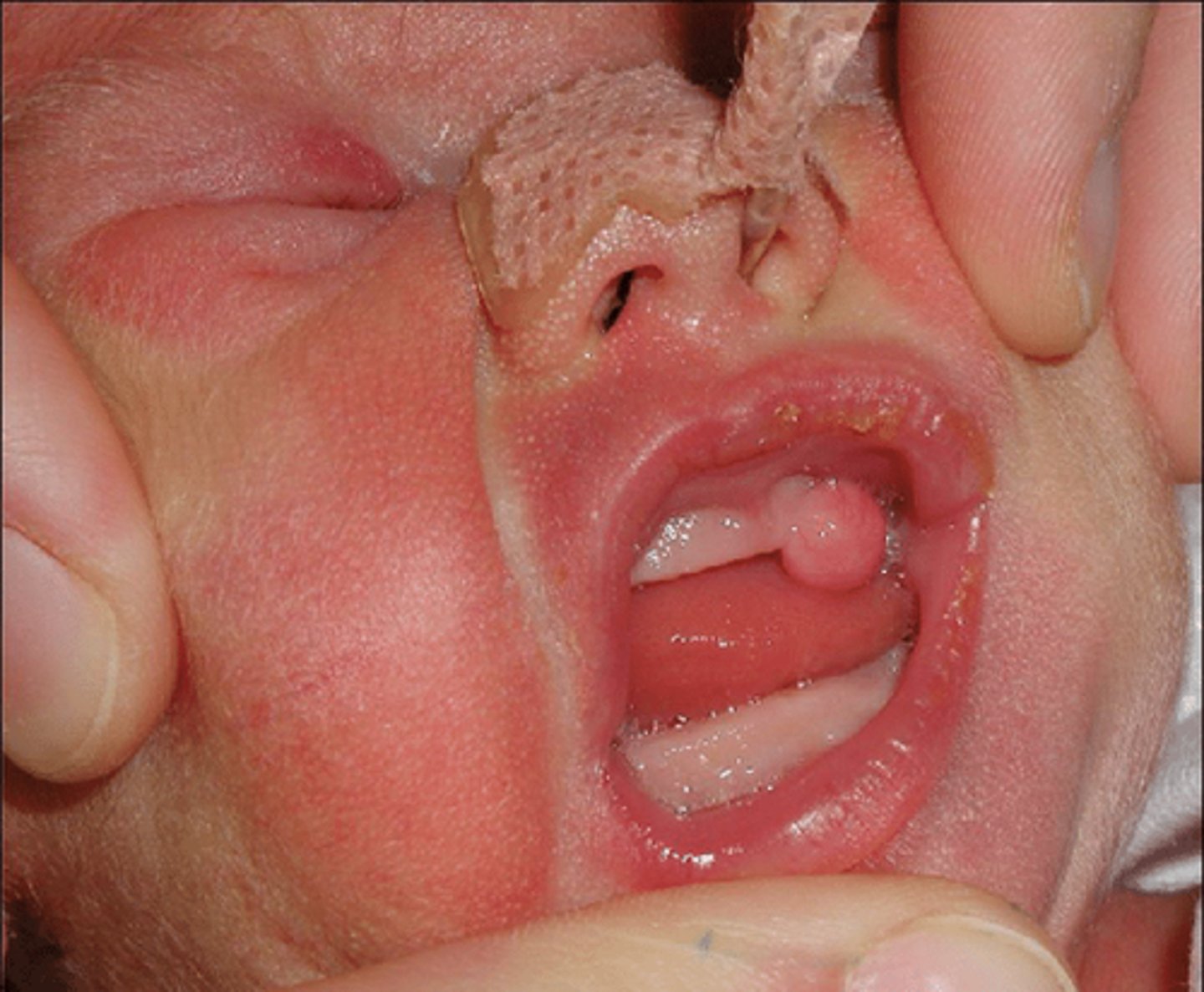
Congenital Epulis
granular cytoplasm with NO pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is associated with what pathology?
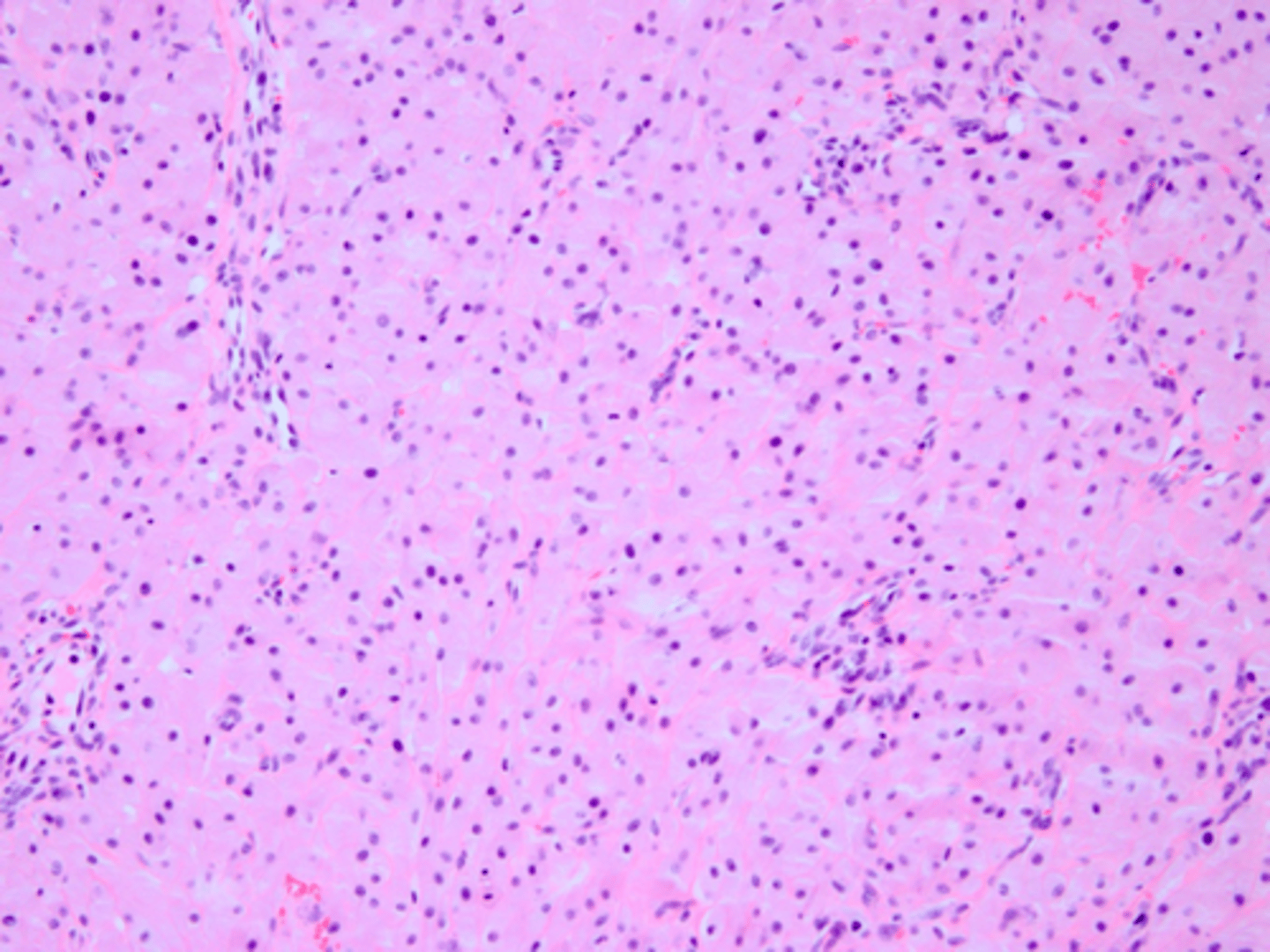
Congenital Epulis
-Rare non-neural soft tissue tumor occurring on alveolar ridge of newborns:
Congenital Epulis
This oral pathology resembles granular cell tumor microscopically:
female
Congenital Epulis as a 90% predilection for what gender?
Surgical excision or
Complete regression over time
treatment for Congenital Epulis?
Granular cell tumor
Congenital Epulis
What two oral pathologies histologically will present with eosinophilic granular cytoplasm?
Neurofibroma
What is the most common peripheral nerve tumor?
Neurofibromatosis
Patients that present with multiple neurofibromas must be investigated for what condition?
Neurofibroma
Patient presents with yellowish nodule on the dorsal tongue and gingiva. Histopathology shows interlacing bundles of spindle-cells with wavy nuclei. Patient also has several nodules all over the body that vary in size. What do you suspect the oral presentations to be?
Neurofibroma
interlacing bundles of spindle-cells with wavy nuclei is associated with what pathology?
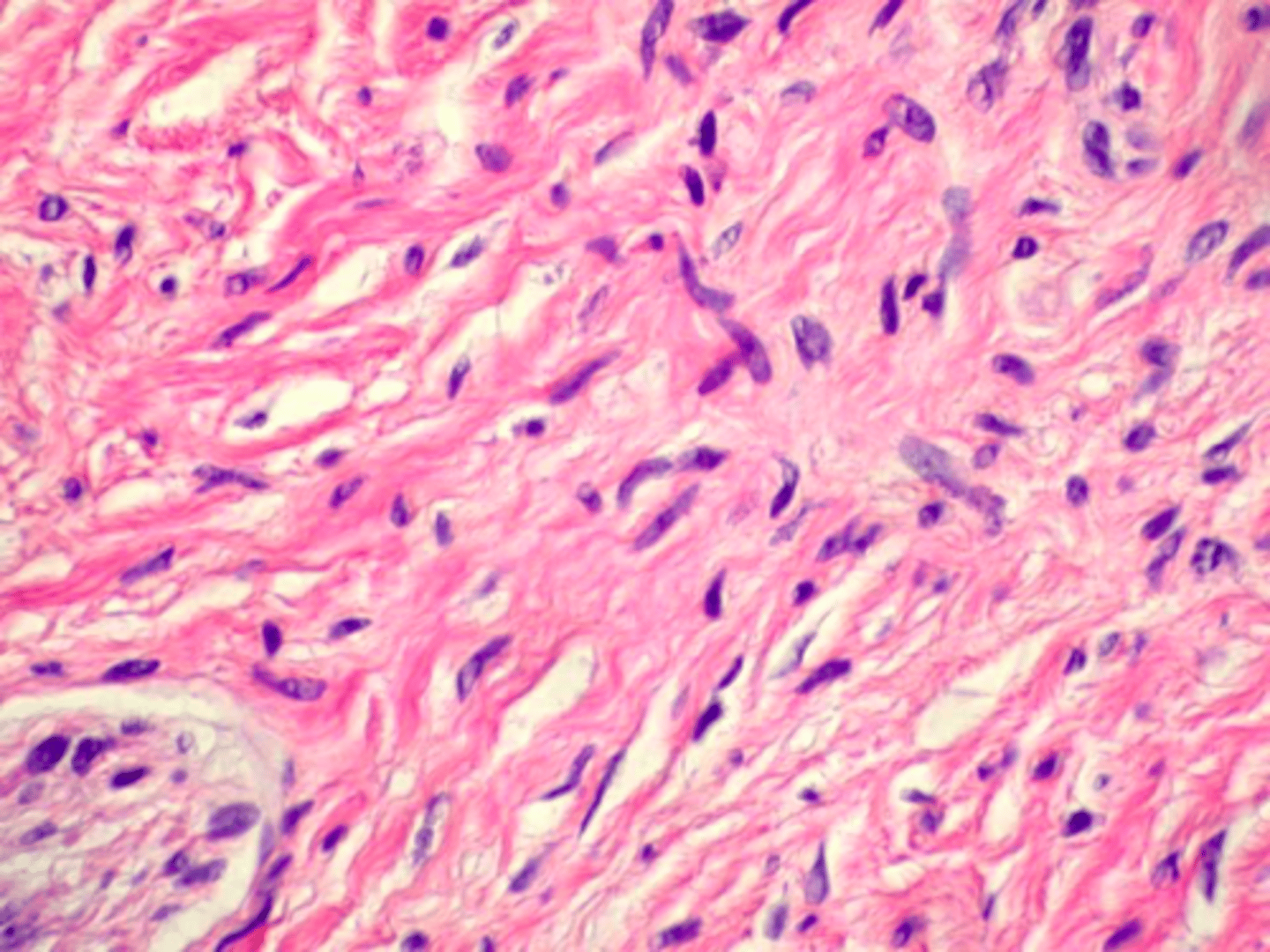
local surgical excision
treatment for Neurofibroma:
Type I/von Recklinghausen Disease
of the 8 forms of neurofibromatosis, what type is the most common?
Neurofibromatosis
"Café au lait" pigmentation (smooth-edged cutaneous macules) are associated with ______
Neurofibromatosis
Crowe sign (axillary freckling) is associated with ______
Neurofibromatosis
Lisch Nodules (brown pigmentation on iris) are associated with ______
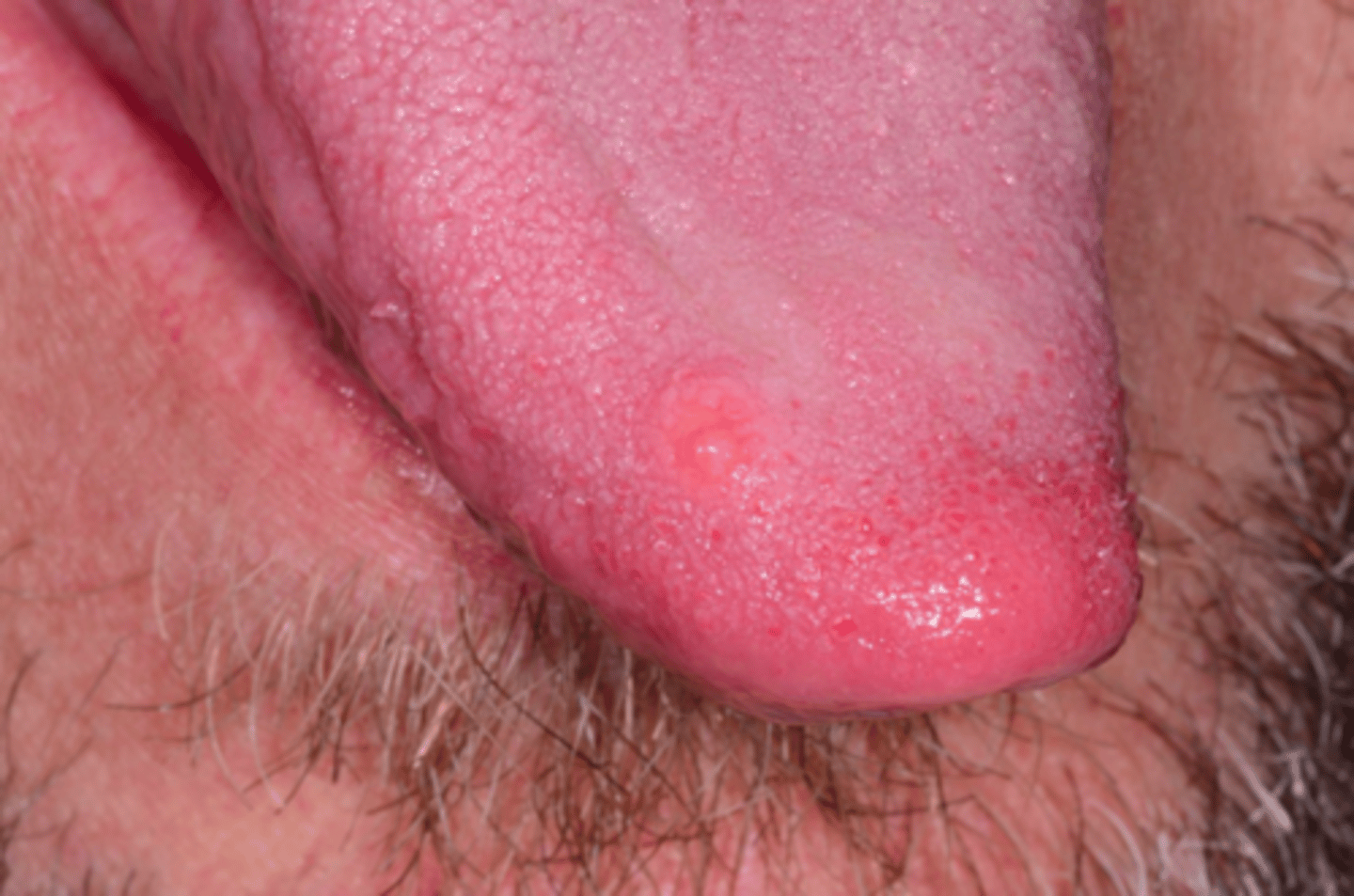
Schwannoma
Patient presents with small yellow papule on dorsal tongue. Histopathology shows microscopic circumscription and Antoni A and Antoni B histopathologic patterns. What do you suspect the oral presentation to be?
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
Patient presents with large nodule on the roof of the mouth. Patient recalls accidentally biting hard onto a fish bone that perforated the palatal mucosa. Biopsy reveals it to a neuroma. Patient returns to office after 7 months and a 2nd similar nodule has developed. What must the patient be worked up for?
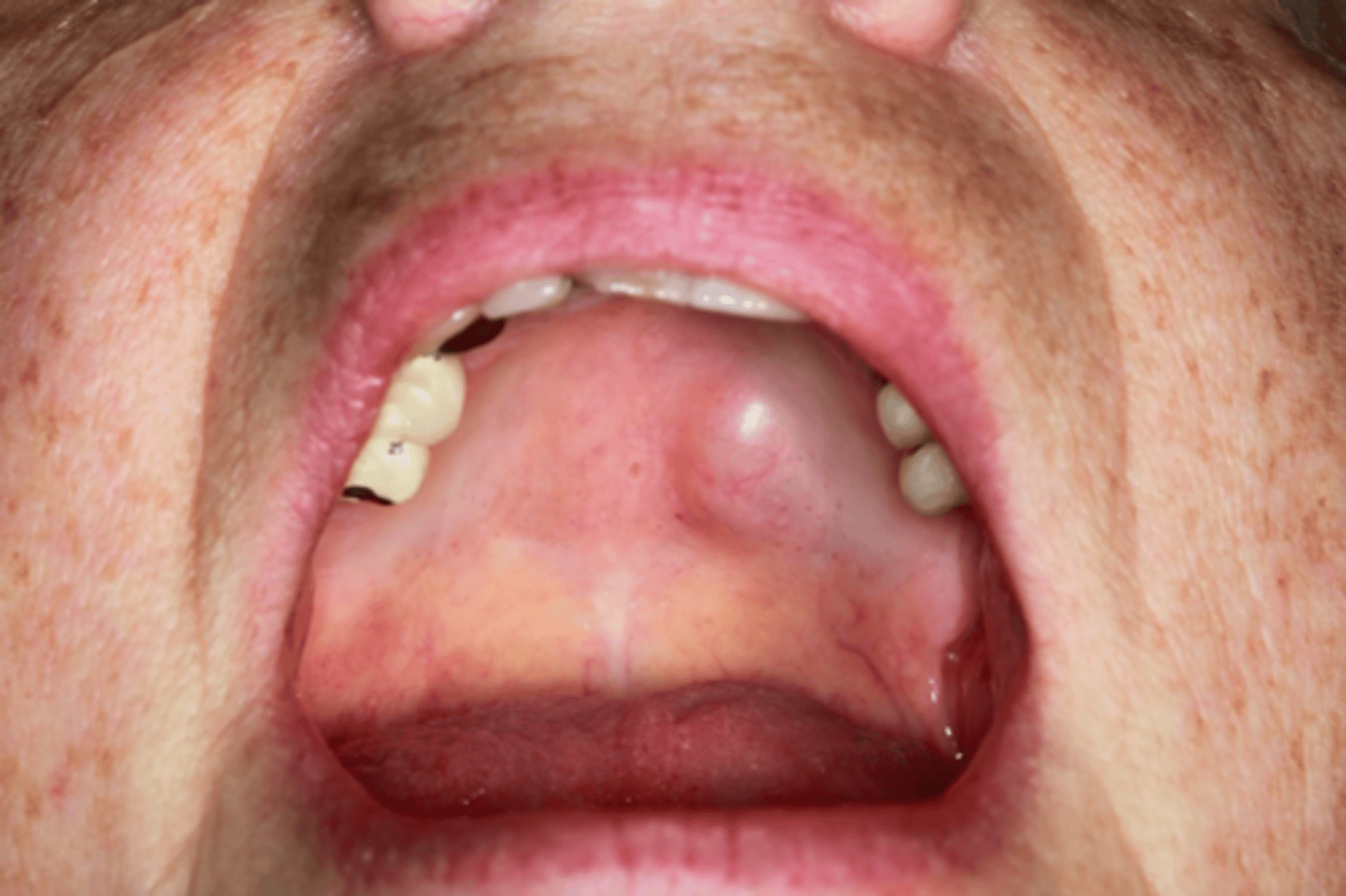
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) Type 2B
Patient presents with multiple nodules on the surface of the tongue (later found to be neuromas). Patient was recently diagnosed with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid (MTC), pheochromocytomas of adrenal medulla, and parathyroid hyperplasia. Mucosal neuromas on eyelid are also present. What is the diagnosis?
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) Type 2B
mutation of RET protooncogene is associated with _______
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2 (A/B)
Familial medullary thyroid carcinoma syndrome is associated with _______
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2 (A/B)
Pheochromocytomas is associated with _____
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) Type 2A
Patient was recently diagnosed with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid (MTC), pheochromocytomas of adrenal medulla, and parathyroid hyperplasia. No oral neuromas are present. What is the diagnosis?
Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid
elevated serum or urinary levels of calcitonin is associated with what condition?
Pheochromocytomas
urinary vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and increased epinephrine:norepinephrine is associated with what condition?
Early recognition of oral features
Prophylactic removal of thyroid gland
Monitor for pheochromocytomas
treatment for Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) Type 2B:
Arteriovenous
All of the following are Vascular neoplasms EXCPET one:
•Hemangioma of infancy
•Congenital hemangioma
•Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma
•Tufted angioma
•Arteriovenous
Tufted angioma
All of the following are Vascular developmental malformations EXCPET one:
•Capillary
•Tufted angioma
•Venous
•Lymphatic
•Arteriovenous
Vascular neoplasms
Hemangioma of infancy is what type of vascular anomaly?
Vascular neoplasms
Congenital hemangioma is what type of vascular anomaly?
Vascular neoplasms
Kaposiform hemangioendothelioma is what type of vascular anomaly?
Vascular neoplasms
Tufted angioma is what type of vascular anomaly?
Vascular developmental malformations
Capillary type is what type of vascular anomaly?
Vascular developmental malformations
Venous type is what type of vascular anomaly?
Vascular developmental malformations
Lymphatics type is what type of vascular anomaly?
Vascular developmental malformations
Arteriovenous type is what type of vascular anomaly?
Hemangioma of Infancy
What is the most common tumor of children?
Hemangioma of Infancy
1 year old female patient presents with purple nodule on the surface of the skin lateral to the nose. Her parents noted that it came out of nowhere when she was about 4 weeks old and grew very fast, but has since started to shrink. What is the diagnosis?
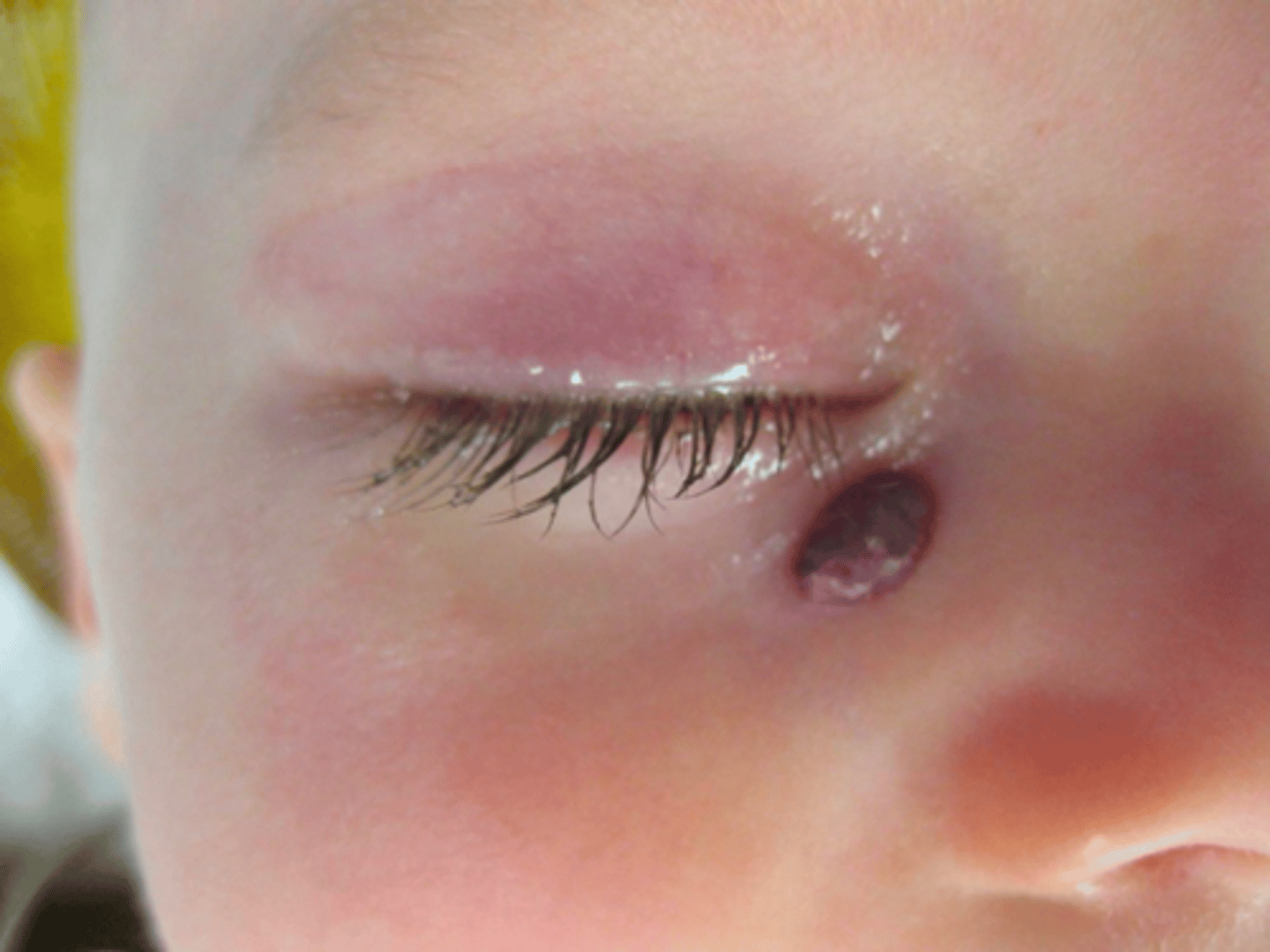
true
t/f: Hemangioma of Infancy is a type of neoplasm
false
t/f: Vascular malformations are a type of neoplasm
Vascular developmental malformations
Patient presents with a dark purple, port-wine stain macule on the buccal mucosa. Patient claims that is has been there all his life, it was present when he was born. What is the diagnosis?
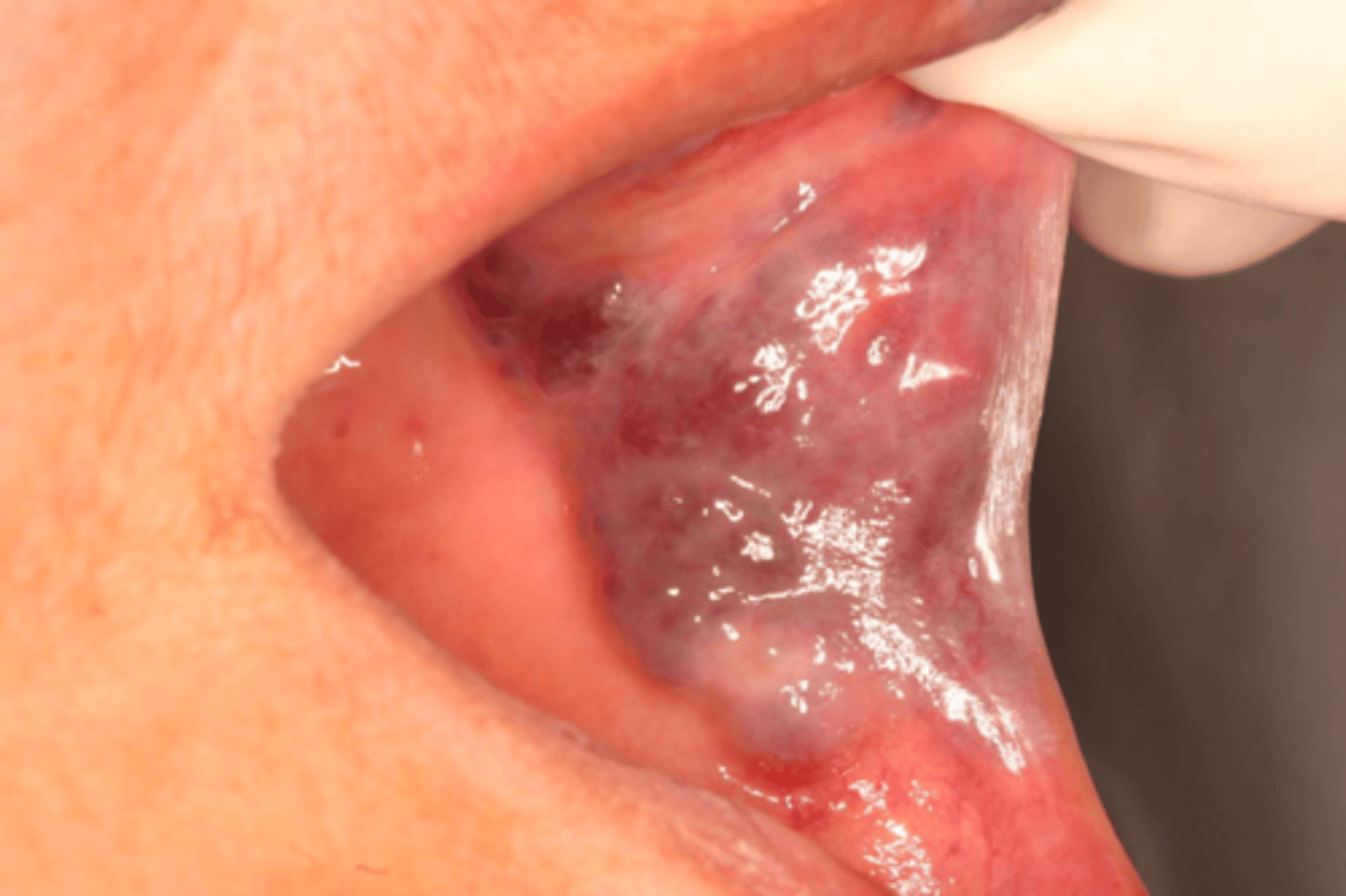
Vascular developmental malformations
this type of vascular condition that affects infants is present at birth:
Myofibroma
•Rare myofibroblastic neoplasm
•Most common in mandible, but peripheral lesions often develop
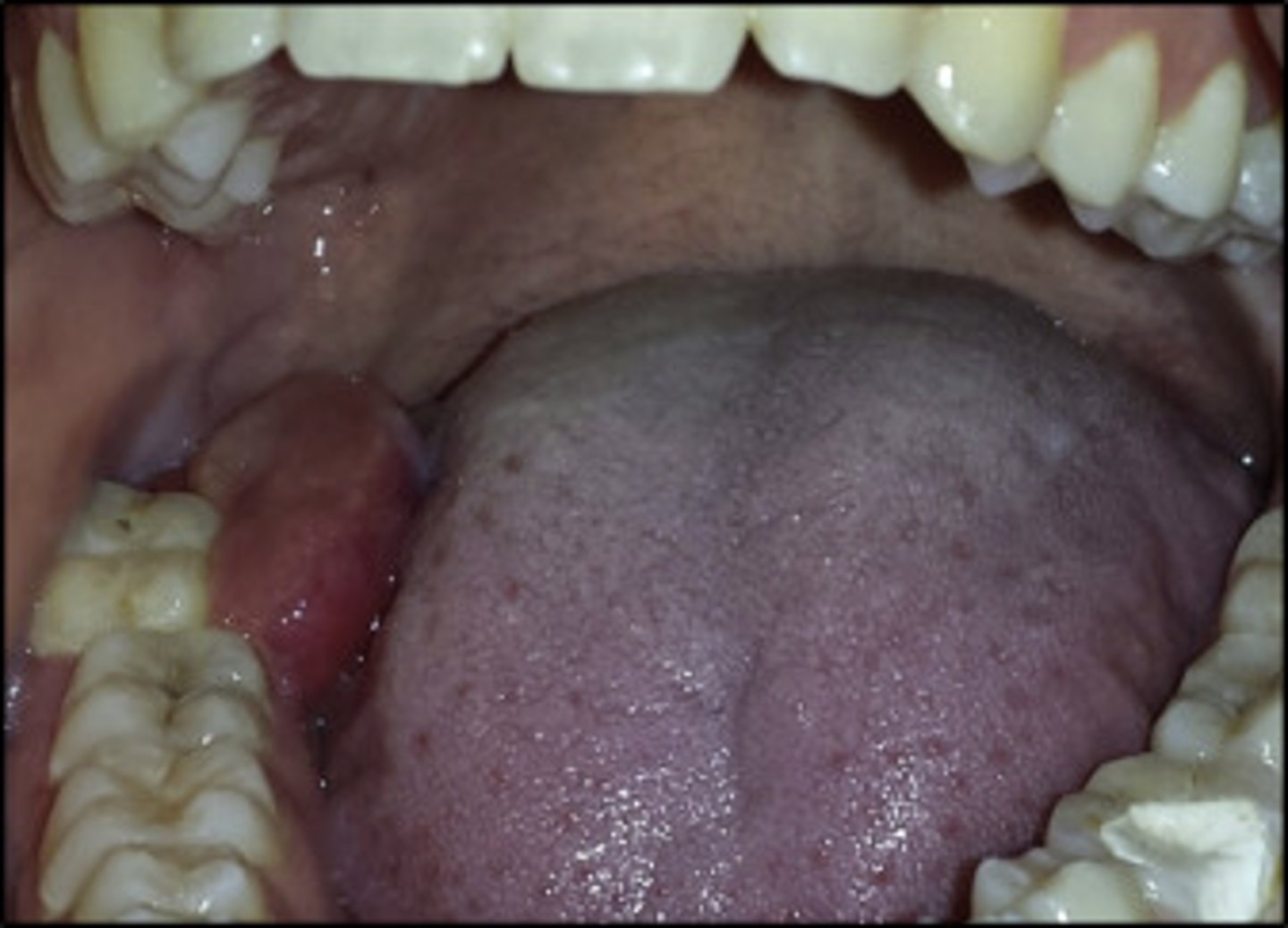
conservative excision
treatment for Myofibroma:
Hemangioma of Infancy
this type of vascular condition that affects infants is rarely present at birth:
muscular
Leiomyoma (Vascular leiomyoma) and Rhabdomyoma in the oral cavity are rare types of ______ neoplasms