Histology q1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/148
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:32 PM on 11/18/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
1
New cards
What are the components of blood?
Plasma component & cellular/serum component
2
New cards
What does the Plasma component of blood include?
Albumin, globulins, & fibrinogen
3
New cards
What does the Cellular/serum component of blood include?
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, & platelets
4
New cards
What is Hematocrit?
Measures the volume of packed red blood cells per unit volume of total blood after centrifugation
5
New cards
Blood contains 55% ___ & 45% ___
Plasma; erythrocytes
6
New cards
What is the shape of a mature erythrocyte?
Biconcave disks
7
New cards
What is the life span of an Erythrocyte?
120 days
8
New cards
What are Reticulocytes?
Immature erythrocytes with small levels of rRNA
9
New cards
What is Hemoglobin composed of?
2 alpha chains, 2 beta chains, & 4 heme groups that bind to O2
10
New cards
What is Anemia?
Decreased concentration of hemoglobin in blood that can result from loss of blood, reduced prod. of RBCs, RBC that contain insufficient hemoglobin, & accelerated RBC destruction
11
New cards
What is Pernicious anemia?
Decreased secretion of intrinsic factor by cells of the intestinal mucosa, reduced level of vit. B12 = decreased erythrocyte production
12
New cards
What is Sickle cell anemia?
Point mutation of the beta globin gene, resulting in an AA substitution in the hemoglobulin molecule (HbS)
13
New cards
What is Thalassemia?
Deficient synthesis of the alpha & beta chain of hemoglobin
14
New cards
What can Thalassemia result in?
Asymptomatic anemia
15
New cards
What is Absolute polycythemia?
Excessive levels of erythrocytes caused by an overactive production of these cells within the bone marrow
16
New cards
What is Relative polycythemia?
Decreased plasma level without increased erythrocyte prod.
17
New cards
What are Leukocytes involved in?
Cellular & humoral (antibody mediated) defense against foreign material
18
New cards
Which cells are Granulocytes?
Neutrophils, eosinophils, & basophils
19
New cards
Which cells are Agranulocytes?
Monocytes
20
New cards
Which cells are Lymphocytes?
B cells, T cells, & NK cells
21
New cards
Which cell would be increased in an allergic reaction (phagocytosis of bacteria)
Neutrophils
22
New cards
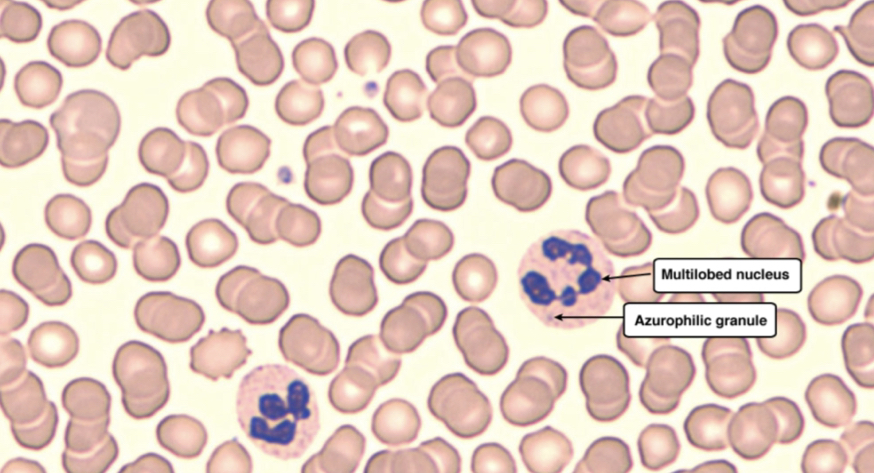
Which cell is this?
Neutrophil
23
New cards
What is the most abundant Granulocyte in the body?
Neutrophil
24
New cards
Which type of cell would increase in a parasitic infection?
Eosinophils
25
New cards
Which cell would be increased in an allergic reaction?
Basophils
26
New cards
What do the granules of Basophils contain?
Heparin & histamine
27
New cards
Which immunoglobulin is expressed on Basophil’s surface?
IgE
28
New cards
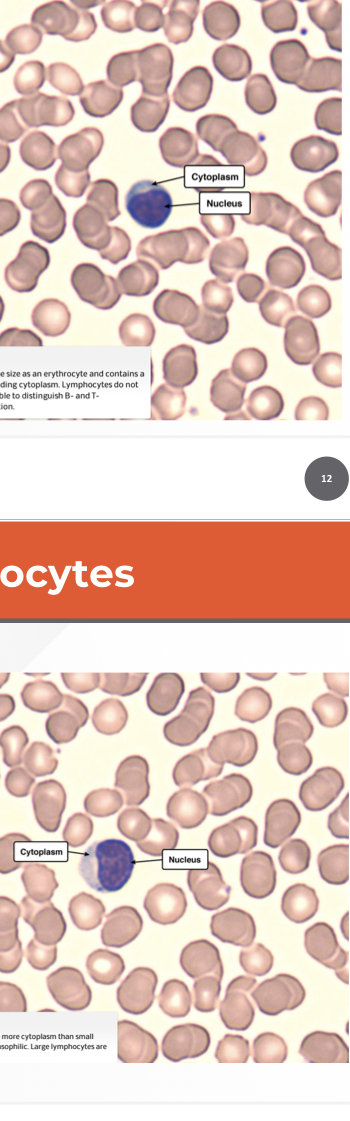
Which cell is this?
Small & large lymphocytes
29
New cards
Where do the precursor cells to lymphocytes originate in?
Bone marrow
30
New cards
Which cell is important for humoral immunity?
B cells
31
New cards
Which cell is important for cell-mediated immunity?
T cells
32
New cards
Antigen stimulated B cells differentiate into ___ that secrete antibodies
Plasma cells
33
New cards
Where do T cells differentiate into & how much of lymphocytes do they comprise?
Thymus & 80%
34
New cards
Which cells are Null cells?
NK cells & stem cells
35
New cards
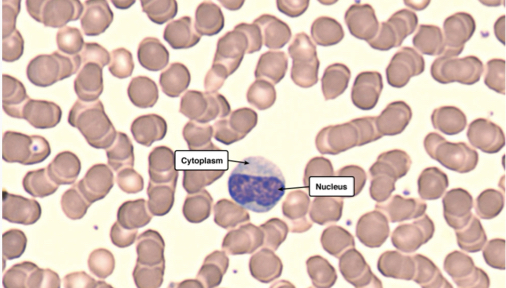
Which cell is this?
Monocyte
36
New cards
When do Monocytes differentiate into macrophages?
After migrating from bone marrow to CT like alveolar macrophages in the lung & Kupffer cells in the liver
37
New cards
What are Platelets/thrombocytes?
Specialized cells that bind to & coat damaged vessel walls, plug small defects in blood vessel walls & help activate the blood-clotting cascade
38
New cards
Where are Platelets formed in adults?
Bone marrow
39
New cards
What is Thombocytopenia?
A disorder marked by reduced level of circulating platelets
40
New cards
What is Thrombocytopenic purpura?
Chronic autoimmune disease where antibodies to platelets interfere with their blood-clotting function
41
New cards
Which illness is associated with low vit. B12 & cancer drugs?
Thrombocytopenias
42
New cards
What is Hemophilia A?
Clotting factor VIII is reduced
43
New cards
What is Hemophilia B?
Factor XI is a nonfunctional or deficient
44
New cards
What does Cartilage consist of?
Fibers, cellular elements, & amorphous ground substance
45
New cards
Is Cartilage vascular or avascular &how are things transported?
Avascular & materials are transported via passive diffusion
46
New cards
Appositional & interstitial cartilage grow together in early stages but which growth can also occur separately later?
Appositional
47
New cards
The matrix is ___ of Cartilage while the amorphous ground substance is ___
40%; 60%
48
New cards
What is the matrix made of?
Type II collagen & elastin
49
New cards
What does Ground substance consist of?
Glycosaminoglycans, chondroitin-6-sulfate & chondroitin-4-sulfate, hyaluronic acid, & keratin sulfate
50
New cards
What are Chondroblasts?
Cells found at the surface of cartilage derived from mesenchymal cells that are capable of elaborating a matrix
51
New cards
What are Chondrocytes?
Mature chondroblasts that are enclosed in the territorial matrix
52
New cards
Where do Chondrocytes reside?
Lacuna
53
New cards
What do proliferating Chondrocytes form?
Cartilaginous epiphyseal plates between the epiphysis & the shaft of a developing long bone
54
New cards
Which cells are large & responsible for absorption of cartilage?
Chondroblasts
55
New cards
What is the importance of the outer layer of the Perichondrium?
Encloses hyaline & elastic cartilage & consists of collagen fibers & fibroblasts
56
New cards
What is the importance of the inner layer of the Perichondrium?
Contains Collagen fibers, undifferentiated mesenchymal cells, & capillaries
57
New cards
Where does Appositional growth occurs?
Surface of cartilage or perichondrium
58
New cards
Where does Interstitial growth occur?
Between chondrocytes
59
New cards
When is Interstitial growth active?
Endochondrial ossification
60
New cards
Step 1 of Interstitial growth:
Chondrocyte's in lacuna exhibit mitotic activity
61
New cards
Step 2 of Interstitial growth:
Two chondroblasts are produced by mitosis from one chondrocyte & occupy one lacuna
62
New cards
Step 3 of Interstitial growth:
Each cell produces new matrix & begins to separate. The separated cell is a Chondrocyte
63
New cards
Step 4 of Interstitial growth:
Cartilage continues to grow
64
New cards
Step 1 of Appositional growth:
Mitotic activity occurs in stem cells within the Perichondrium
65
New cards
Step 2 of Appositional growth:
New undifferentiated stem cells & committed cells that differentiate into Chondroblasts are formed. They produce new matrix at the periphery
66
New cards
Step 3 of Appositional growth:
Bc of the new matrix, Chondroblasts push apart & become Chondrocytes which continue to produce more matrix at the periphery
67
New cards
What are the 3 types of Cartilage?
Hyaline, elastic, & fibrous
68
New cards
Where is Hyaline cartilage found?
Nasal septum, larynx, trachea, sternal ends of the ribs, articular cartilage at joints & tracheal ring
69
New cards
What type of collagen is in Hyaline cartilage?
Type II Collagen
70
New cards
What is a Chondroma?
Benign tumor of hyaline cartilage that develops within the substance of/at the periphery of cartilage
71
New cards
What is Chondromalacia?
Softening of articular cartilage such as the ant. surface of the patella & epiphyseal cartilage of still born fetuses
72
New cards
What can Chondromalacia cause?
Inflammation & bursitis
73
New cards
Where is Elastic cartilage found?
Pinna of ear, auditory/eustachian tube, epiglottis, & corniculate & cuneiform cartilages of the larynx
74
New cards
What type of collagen is found in Elastic cartilage?
Type II Collagen
75
New cards
Where is Fibrocartilage found?
Intervertebral discs, cartilage at the pubic symphysis, & insertions of tendons & ligaments
76
New cards
Which type of collagen is found in Fibrocartilage?
Type 1 Collagen
77
New cards
Which cartilage gives firm support & tensile strength?
Fibrocartilage
78
New cards
What are Chondroblastomas?
Benign tumors that are derived from immature cartilage cells
79
New cards
What are Chondrosarcomas?
Malignant tumors of cartilage cells or immediate precursor cells & occur in bones of the pelvic & shoulder of older individuals
80
New cards
Where do Chondroblastomas favor?
Epiphysis in the skeletally immature patient
81
New cards
Where do round cell lesions favor?
Diaphysis
82
New cards
Which CT tissues are CT proper?
Loose CT (areolar) & Dense regular & irregular CT
83
New cards
Which CT tissues are specialized CT?
Cartilage, bone, adipose tissue, blood, hemopoietic tissue, lymphatic tissue, reticular
84
New cards
What are Reticular tissues?
Made up of Type III collagen & serves as the Stroma for hemopoietic tissue, liver, spleen, & lymph nodes
85
New cards
What is the Stroma?
Cells & tissues that support & give structure to organs, glands, or other tissues in the body. Made up mostly of CT, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, & nerves. Provides nutrients to the tissues or organ & removes waste & extra fluid
86
New cards
What is the Parenchyma?
The functional tissue of an organ as distinguished from the connective/supporting tissue
87
New cards
Where is Loose CT found?
Surrounds small blood vessels, beneath the epithelia that covers body surfaces & line the internal surfaces of the body, & associated with epithelium of glands
88
New cards
Where is Dense irregular CT found?
Skin: thick deep layer of the dermis. Hollow organs: intestinal tract & submucosa which allows the organ to resist excessive stretching & distention
89
New cards
Where is Dense regular CT?
Tendons, ligaments, & aponeurosis
90
New cards
Loose CT has more ____ than ____
Ground substance; collagen
91
New cards
What are the functions of CT?
Physical support & connection to form the organs of the body. Mechanical strength (tendons & ligaments). Space filling (sculpting body shape). Metabolic support (interstitial fluid = medium for diffusion of nutrients & waste products). Body defense. Healing.
92
New cards
What are the components of CT?
Ground substance, protein fibers, & cells
93
New cards
What are the components of the ground substance of CT?
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), Proteoglycans, & multiadhesive glycoproteins (fibronectin & laminin)
94
New cards
What are the components of the protein fibers of CT?
Elastic fibers, collagen fibers, & reticular fibers
95
New cards
Which cells are components of CT?
Resident = fibroblasts & adult mesenchymal cells. Wandering = immune cells
96
New cards
What are the functions of GAGs?
Resist compression & absorb shock
97
New cards
What are the functions of Proteoglycans?
Regulate molecular trafficking in the ECM
98
New cards
What are the functions of Multiadhesive glycoproteins?
Promote binding sites for cell membranes ... cell migration & positioning
99
New cards
What is a Proteoglycan made of?
A core protein & glycosaminoglycans
100
New cards
Chondroitin sulfate & keratin sulfate are examples of?
GAGs