AP Human🧑🏻🦳 ✨Midterm✨
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:03 AM on 12/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
1
New cards
What is a physical map
A map that shows physical features
2
New cards
What is a relief map?
Map that dramatizes physical features
3
New cards
What is a political map?
* map that shows boundaries,labels,names,people etc
4
New cards
What is a world map?
Map that shows the entire world(landmasses and bodies of water)
5
New cards
Regional Map
* connections and similarities in a certain region
* Ex: South Florida
* Ex: South Florida
6
New cards
What is a national map?
* a map that only shows one country
7
New cards
What is a local map?
* a local map is a large-scale map that shows a small area in great detail
8
New cards
What is a reference map?
* its a map that one refers to a map to find a specific location
9
New cards
What is a mobility map?
A map that shows movement(roads,etc)
10
New cards
What is a chloropleth map?
Using colors to demonstrate the theme of the map
* often used for the climate map
* often used for the climate map
11
New cards
What is a dot map?
* uses a little or many dots with a theme
* Population map
* Population map
12
New cards
What is gradient map?
* uses size/different gradients of color to identify a theme
13
New cards
What is a thematic map?
* any map focused on any specific theme
14
New cards
What is topographic map?
* map that shows elevation(above and below sea level)
* Creates images with lines
* Creates images with lines
15
New cards
What is a contour map?
uses different elevations to create a visual such as a city
16
New cards
What is a homolosive map?
Cuts out a lot of the water and focuses on the land forms
17
New cards
What is a Robinson Projection Map?
* teaches students about the looks of the earth and relationships with the earth
* Often found in classrooms
* Map distorts distance and direction
* Often found in classrooms
* Map distorts distance and direction
18
New cards
What is Mercator Projection?
* distort size and shape
* Absolute in distance
* Care about how far away land is and how to get their(Vikings)
* Absolute in distance
* Care about how far away land is and how to get their(Vikings)
19
New cards
20
New cards
What is an Azimuthal Projection?
* see poles
* Everything past equater is distorted
* Everything past equater is distorted
21
New cards
What is a polar projection?
* only shows South Pole to equator
* Only one hemisphere
* Only one hemisphere
22
New cards
What is a Landsat?
* land photographed by a satellite
23
New cards
What is cartograph?
Takes a map and inflates a certain area based on a topic
24
New cards
What are the different types of scale?
* Fractional Scale: ratio representing the map measurements: real life measurements (1 inch:24,000 miles)
* Verbal Scale: geographical scope used to analyze and understand the phenomenon (local,national,and globa)
* Verbal Scale: geographical scope used to analyze and understand the phenomenon (local,national,and globa)
25
New cards
What does the term “Why of Where” describe
The term describes how the primary methodology behind geography is spatial analysis and that two questions make up this methodology.
* Where are things located?
* Why are they located where they are?
* Where are things located?
* Why are they located where they are?
26
New cards
Describe the geographical concept of Location.
\
* Refers to the geographical position of people/things on the earth(absolute;latitude,longitude)
* Understanding where something is/should be located and why it is there: Location Theory
* Refers to the geographical position of people/things on the earth(absolute;latitude,longitude)
* Understanding where something is/should be located and why it is there: Location Theory
27
New cards
What are the two different types of location?
1) absolute location: precise coordinates/ (latitude,longitude)
2) relative location: location of a place or attribute relative to another place or attribute
2) relative location: location of a place or attribute relative to another place or attribute
28
New cards
Describe the geographical concept of Human-Enviornment Interactions.
* relationship between humans and the physical world and how they mutually affect each other
* How people adapt and alter a new place and vice versa
* How people adapt and alter a new place and vice versa
29
New cards
What is culture ecology?
* concerned with culture as a system of adaptation to and alteration of the enviornment
30
New cards
What is enviornmental determinism?
* what you can do is limited by your physical enviornment
31
New cards
What is environmental possibilism?
As humans became more advanced through tecnology and ideas, people overcame what the enviorment determined a certain place to be
32
New cards
Describe the geographical concept of regions.
* similarities between places
* Examples:Human phenomenon(language,religion), Physical Phenomenon(tornadoes and earthquakes)
* Examples:Human phenomenon(language,religion), Physical Phenomenon(tornadoes and earthquakes)
33
New cards
What is a formal region?
* shared physical/cultural traits(one or more)
* Shares a specific geographical feature Ex: l’arts of China
* Shares a specific geographical feature Ex: l’arts of China
34
New cards
What is a functional region?
* area with a shared common purposes such as trade
* Shared economical,political,social purpose
* Defined by the fact of how people within a certain region function together politically socially or economically
* Shared economical,political,social purpose
* Defined by the fact of how people within a certain region function together politically socially or economically
35
New cards
What is a perceptual region?
* images people carry in their minds of certain people,places,and things
* Can include people and their cultural traits,places and physical traits, and build enviornments
* Involves pictures while vernacular region involves words
* Can include people and their cultural traits,places and physical traits, and build enviornments
* Involves pictures while vernacular region involves words
36
New cards
What is the “sense of place”?
* The emotions and feeling associated with a certain place
37
New cards
What is perception of a place?
* one develops a perception of a place that they have never been to by reading books,seeing pictures,watching movies,hearing stories,etc
38
New cards
Describe the geographical concept of movement
* mobility of people,goods and ideas
* Migration
* Expresses how people are interconnected
* Migration
* Expresses how people are interconnected
39
New cards
What is diffusion?
* spread of idea,innovation from its hearth(origin) to other people/places
40
New cards
What is spatial interaction?
* degree of connectedness or contact among certain people/places
* Another term for distance-decay
* Dépends on distance between places, accessibility of other places and the transportation/communication connectivity among certain places
* Another term for distance-decay
* Dépends on distance between places, accessibility of other places and the transportation/communication connectivity among certain places
41
New cards
What is expansion diffusion?
Innovation or idea that develops in a hearth and remains strong while spreading outward
42
New cards
What is cultural landscape?
* visible imprint of human activity on the land
43
New cards
How does Carl Sauer explain cultural landscape?
* composed of the « forms superimposed on the physical landscape » by human activity
44
New cards
What is sequential occupancy?
* People living in a certain area leave behind some of their culture when they locate
45
New cards
What is GIS?
* Geographical information system
* combine computers hardware and software to analyse And solve geographical problem by layering maps
* combine computers hardware and software to analyse And solve geographical problem by layering maps
46
New cards
What is GPS?
* geographical positioning system
* Enables us to find features on Earth accurately
* Location
* Often satellite based
* Enables us to find features on Earth accurately
* Location
* Often satellite based
47
New cards
What is remote sensing?
* method that collects data through instruments that are far away from the area being studied
* Examples:satellite,aircrafts, and drones
* Examples:satellite,aircrafts, and drones
48
New cards
What is an activity space?
Space we move through routinely
49
New cards
What is a mental map?
* map made from our own personal experiences differs between indivisuals
50
New cards
Describe geographical concept of place
Relationship with the things around you
51
New cards
What is population density?
Measure of total population relative to land area
52
New cards
What is arithmetic population density
Amount of people per square mile of land in a country
53
New cards
What is physiologic population density?
* amount of people per square land of arable land
* More people per square mile
* More accurate than arithmetic population density
* More people per square mile
* More accurate than arithmetic population density
54
New cards
What are the four largest population clusters and describe them?
1) East Asia: China,Korea,Japan
2) South Asia: India,Pakistani,Bangladesh
3) Europe
4) North America
2) South Asia: India,Pakistani,Bangladesh
3) Europe
4) North America
55
New cards
What does the term megalopolis mean?
Refer to a huge urban agglomeration such as the one that stretches along the areas of the East coast in the United States and Canada
56
New cards
Who was Thomas Malthus?
* British economist
* He warned the world that about ow the world’s population was increasing faster than the food supplies needed to sustain it
* Reasoned that food growled linearly and that population grows exponentially
* He warned the world that about ow the world’s population was increasing faster than the food supplies needed to sustain it
* Reasoned that food growled linearly and that population grows exponentially
57
New cards
58
New cards
What are problems with Malthus’ theory?
He did not foresee how goods would be spread through globalization and the advancements of new agricultural methods
59
New cards
What are neo-malthusians?
* support Malthus
* Say that overpopulation will cause disaster on earth
* Say that overpopulation will cause disaster on earth
60
New cards
What is natrual increase?
* Difference between number of births and deaths in a year. Positive if births exceed deaths and negative if deaths exceed births. Does not include emigration and immigration.
61
New cards
What is the crude birth rate?
Number of live births per year per thousand people
62
New cards
What is crude death rate?
* number of deaths per year per thousand people
63
New cards
What is a dot map?
* used to repersent population distribution
* Each dot on the map represents a certain number of people
* Each dot on the map represents a certain number of people
64
New cards
What is a doubling time?
The time required for a population to double in size
65
New cards
What is carrying capacity?
The amount of people/animals that a certain area of land can hold
66
New cards
What is total fertility rate?
* the average number of children born to women of childbearing age(15-49)
67
New cards
What replacement level does a country need to keep their stable population?
TFR 2.1
68
New cards
What is the DTM model?
Model suggesting that a country’s birth and death rate change in predictable ways over stages of economic development
69
New cards
Describe the first stage of the DTM model.
* fluctuating birth and death rates
* Low population growth
* Pre agricultural stage to agricultural revolution stage
* Marked by high birth and death rates(plagues and epidemics)
* Low population growth
* Pre agricultural stage to agricultural revolution stage
* Marked by high birth and death rates(plagues and epidemics)
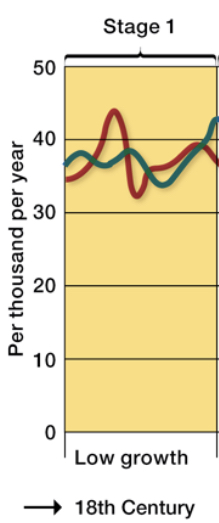
70
New cards
Specific example of DTM first stage
* Europe was hit by bubonic plague and several people died causing low population growth despite high birth rates
* 18th century
* 18th century
71
New cards
What is the third stage of the DTM model?
* **high** birth rates and **rapidly declining** death rates and very **high** natrual increase rates
* “Population explosion” in Europe
* Improvements in medical technology,food,sanitation,healthcare
* Increased life span
* 20th century
* “Population explosion” in Europe
* Improvements in medical technology,food,sanitation,healthcare
* Increased life span
* 20th century
72
New cards
Describe stage two of the DTM.
* increasing population growth
* Gradually decreasing deaths and slightly increasing births
* From agriculture to industry
* Machines make work easier
* Second agricultural revolution
* 19th century
* Gradually decreasing deaths and slightly increasing births
* From agriculture to industry
* Machines make work easier
* Second agricultural revolution
* 19th century
73
New cards
Describe the 4th stage of the DTM.
* 21st century
* Low birth rates,low death rates, stable/slowing rates of natural increase
* Happened due to modern contraceptives and more women in the workforce
* Include higher income countries
* Low birth rates,low death rates, stable/slowing rates of natural increase
* Happened due to modern contraceptives and more women in the workforce
* Include higher income countries
74
New cards
What do population pyramids repersent?
* Represent certain structures of the population such as age and sex
75
New cards
What are the different types of population pyramids?
1) Chimney/Peripheral
* poor country
* Workforce starts young at age 10
* Short life span/only live till late 40s
* Need a lot of children to take care of the few adults by working
2) Inverted Pyramid
* Japan
* Elderly is the biggest portion as the population isn’t having many children
* Issue as there is no future workforce
3) Normal/Perfect
4)round vase
* rural/farming
* Dependent on agriculture
* Central America/Asian countries
5) Vase
* dependent on industry
* Wealthy countries
* Big workforce and smaller youth
* poor country
* Workforce starts young at age 10
* Short life span/only live till late 40s
* Need a lot of children to take care of the few adults by working
2) Inverted Pyramid
* Japan
* Elderly is the biggest portion as the population isn’t having many children
* Issue as there is no future workforce
3) Normal/Perfect
4)round vase
* rural/farming
* Dependent on agriculture
* Central America/Asian countries
5) Vase
* dependent on industry
* Wealthy countries
* Big workforce and smaller youth
76
New cards
What is infant mortality rate?
Probability that a child will die before the age of 1
77
New cards
What is child mortality rate?
probability a child will die when between the ages of 1-5
78
New cards
What is life expectancy?
* Average number of years a person is supposed to live for
* Differs between men and women
* Differs between men and women
79
New cards
What is HIV/AIDS impact in Africa?
* many people are dieing due to this
* Shortened people’s life span in Africa
* Affected Africa’s economy and the amount of people that are able to work
* Began to spread to other countries
* Shortened people’s life span in Africa
* Affected Africa’s economy and the amount of people that are able to work
* Began to spread to other countries
80
New cards
What causes infectious diseases?
* resulting from an invasion of parasites and their multiplication in the body
* infects youths weak immune system
* infects youths weak immune system
81
New cards
What is an endemic?
A disease that prevails over a very small area
82
New cards
What is a epidemic?
A disease that spreads throughout one country
83
New cards
What is a pandemic?
A disease that has spread to more than one country
84
New cards
What is a vectored infectious disease?
* A disease transmitted by a carrier with disease from person to person
* Ex: Example:
1) a mosquito stings a person that is infected with malaria
2)The mosquito sucks up some of that blood along with parasities that reach the bug’s saliva
3)These mosquitos’s then sting someone else and the disease is injected into someone’s blood stream
4)Now that person develops malaria as the parasites grow in the infected person’s body
* Ex: Example:
1) a mosquito stings a person that is infected with malaria
2)The mosquito sucks up some of that blood along with parasities that reach the bug’s saliva
3)These mosquitos’s then sting someone else and the disease is injected into someone’s blood stream
4)Now that person develops malaria as the parasites grow in the infected person’s body
85
New cards
What is an expansive population policy?
Policy that encourages large families and raises the rate of natrual increase
86
New cards
Expansive Policies in Europe
* Ulyanovsk Provice held a national day of conception(Russia)
* More companies such as France and widen began promoting gender equality and boosting fertility rates by adopting family friendly policies
* Offered tas incentives,job leaves,etc to parents
* More women were in the work force meaning less kids meaning less future workers leading to these policies
* More companies such as France and widen began promoting gender equality and boosting fertility rates by adopting family friendly policies
* Offered tas incentives,job leaves,etc to parents
* More women were in the work force meaning less kids meaning less future workers leading to these policies
87
New cards
What is a eugenic policy and give an example.
* Policies designed to discourage/ostracize different groups of people from having children
* In the Holocast the Nazi’s targeted the Jewish population from reproducing as they wanted to get rid of them
* In the Holocast the Nazi’s targeted the Jewish population from reproducing as they wanted to get rid of them
88
New cards
What is a restrictive policy and give an example.
* policies designed to restrict a population’s birth/fertility rate
* Example: China’s one-child policy restricts how many children the citizens of China were able to have by penalizing them
* Example: China’s one-child policy restricts how many children the citizens of China were able to have by penalizing them
89
New cards
What is cyclic movement?
Describes a regular journey that begins at a certain place and returns to the same place in a short period of time
90
New cards
Cyclic movement examples
* going from home to school and going back home again
91
New cards
What is periodic movement?
a longer period of time away from the home base than cyclic movement but still coming home eventually
92
New cards
Periodic movement example
Going home to college for a long period of time then going home to spring break
93
New cards
What is nomadism?
* way of life of peoples who do not live continually in the same place but move cyclically or periodically
* Move around based on trade and carry goods to places to trade
* Move around based on trade and carry goods to places to trade
94
New cards
What is transhumance?
* a specialized form of pastoralism that is practiced on a mountain when ranchers move livestock to move up and down the mountain during summer months and winter months
95
New cards
What is migration?
Intent to make a permanent move to a destination different from starting point
96
New cards
What is international migration?
* Intent to cross some country border to permanently reside somewhere else outside of the country’s borders
97
New cards
What is internal migration?
* leave one place with internet to permantley reside somewhere else within the same country
98
New cards
What is immigration?
Crossing a border and entering a country
99
New cards
What is emmigration
Crossing a countries’ borders to leave that country
100
New cards
What is forced migration?
* Migration imposed on a group of people from one place to another
* Jewish people in Germany were forced to flee during the holocaust as their lives were in danger
* Jewish people in Germany were forced to flee during the holocaust as their lives were in danger