CLINICAL CHEM EXAM NA ATA ITO (LEC)
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Centrifugation
Consist of head/rotor (attached to the shaft of the motor), carrier and shields.
Revolutions per minute and Relative Centrifugal force
The speed/centrifugal force is expresses by
Balanced, Vibration
Centrifuged must be properly ———- and free from excess ———-
Filtration
Paper, cellulose, polyester fibers and column materials
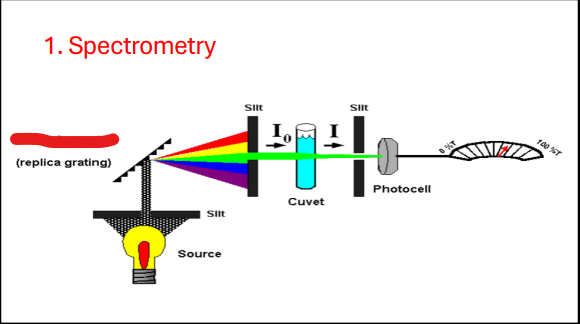
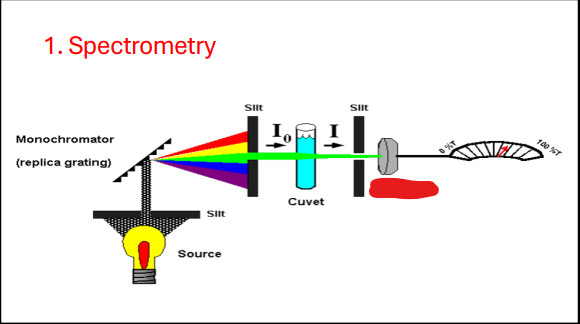
Spectrometry
I - Instruments that measure light energy
II - Based on the property of colored solutions to absorb light of specific wavelength.
Light
is a form of electromagnetic energy
̶ Transmitted via electromagnetic waves
̶ Waves is measured in nanometer (wavelength).
Monochromator
Slit
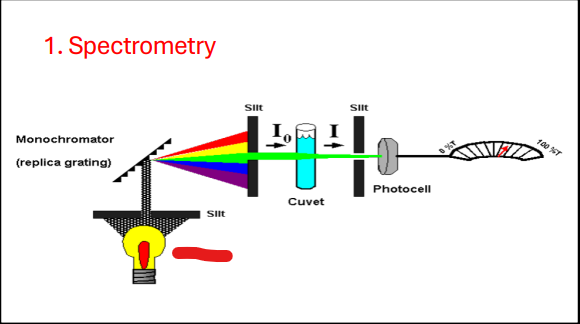
Source
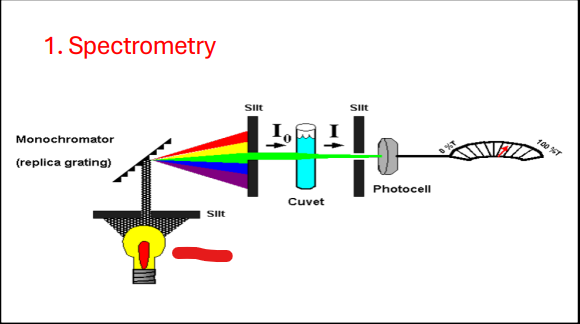
Slit
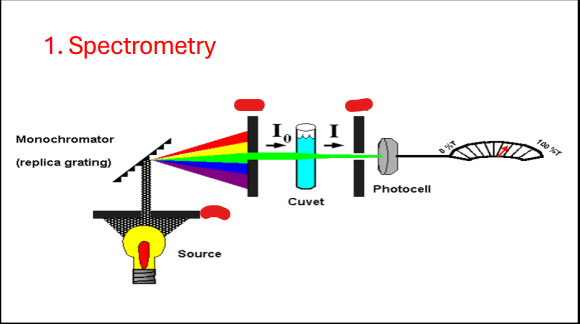
Cuvette
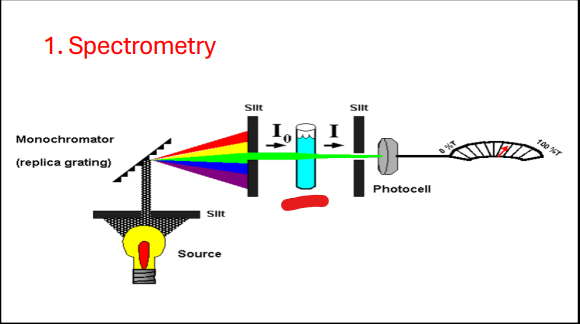
Photocell
Beer’s Law
The concentration of a substance is: Directly proportional to the amount of light absorbed, Inversely proportional to the amt. of transmitted light
2 – Log %T
A=
Spectrophotometry
Measures the light transmitted by a solution to determine the concentration of the substance in the solution
Light Source
? → Entrance Slit → Monochromator → Exit Slit → Sample cell → Photodetector
Entrance Slit
Light Source → ? → Monochromator → Exit Slit → Sample cell → Photodetector
Monochromator
Light Source → Entrance Slit → ? → Exit Slit → Sample cell → Photodetector
Exit Slit
Light Source → Entrance Slit → Monochromator → ?→ Sample cell → Photodetector
Sample cell
Light Source → Entrance Slit → Monochromator → Exit Slit → ? → Photodetector
Photodetector
Light Source → Entrance Slit → Monochromator → Exit Slit → Sample cell → ?
Light Source
Provide incident light for the system
Incandescent Tungsten or Tungsten iodide lamp
For visible and near infrared spectrum
Deuterium-discharge lamp and Mercury arc lamp
For UV spectrum
Silicone carbide
For infrared spectrum
Monochromator
Isolates specific wavelength from the light source
Interference Filter
Based on constructive interference of waves
Prism
Separates white light into a continuous spectrum.
Diffraction grating
Separates light into component wavelengths
Entrance Slit
Exclude unwanted or “stray light
Exit Slit
Controls the width of the light beam
Sample Cell
Cuvette or analytical cell
Holds the solution of which the absorption is to be measured
Glass cuvette
for visible range
Quartz or fused silica
for UV range
Photodetector
Converts transmitted radiant energy into an equivalent amount of electrical energy.
Photocell (Barrier layer cell, selenide cell)
Generates electromotive force (no external voltage) Output is not amplified
Phototube
Similar to photocell but requires external voltage
Photomultiplier tube
Amplifies radiant energy (200x sensitive)
Phototransistors and Photo iodide
Uses a photosensitive positive-negative junction diode to produce a photocurrent.
Read-out Device
A moving needle on a dial or a digital display which indicates the amount of light passing through a sample.
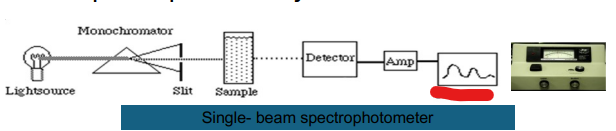
Single- beam
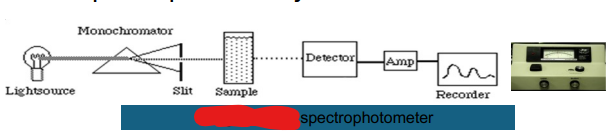
Light Source
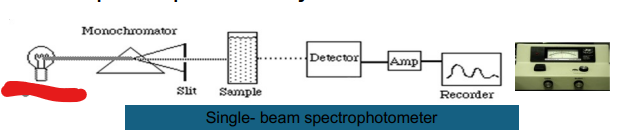
Monochromator
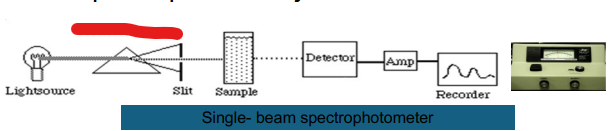
Slit
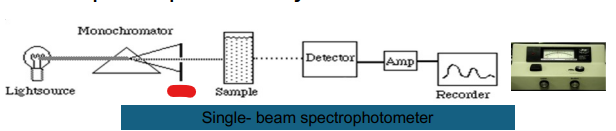
Sample
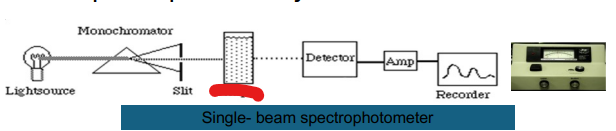
Detector
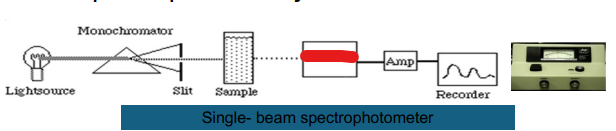
Amp
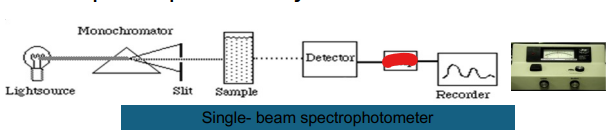
Recorder
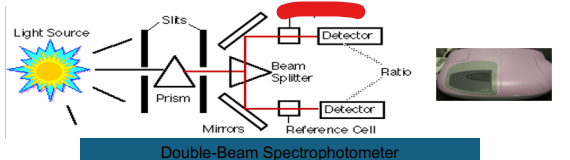
Double Beam
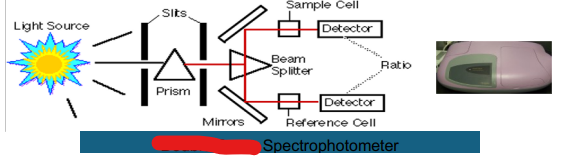
Prism
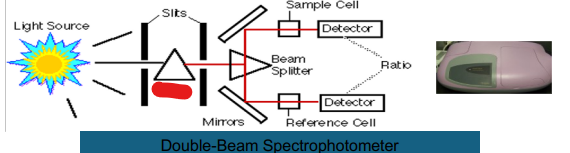
Slits
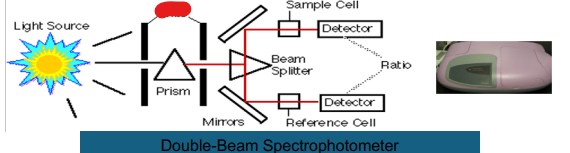
Light Source
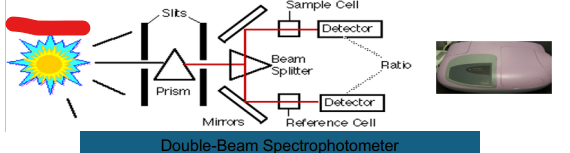
Beam Splitter
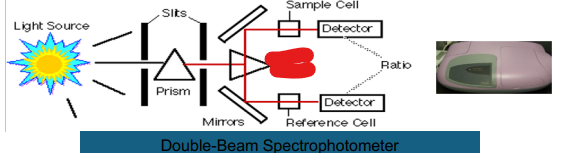
Mirror
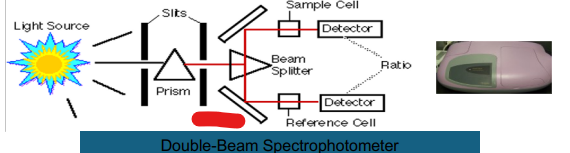
Reference Cell
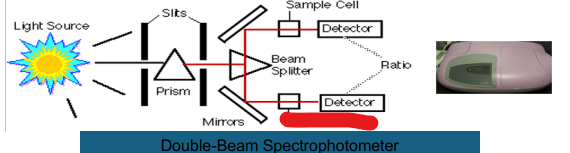
Ratio
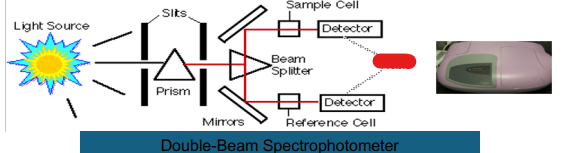
Detector
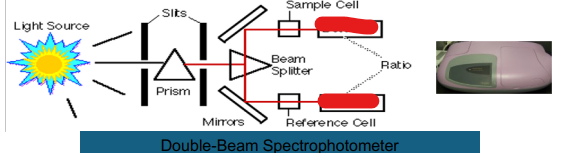
Sample Cell
Flame Emission
Measures light emitted by excited atoms
̶ Measure sodium and potassium because they are easy to excite.
Principle:
A. Flame using propane is used to excite the atoms (higher energy state)
B. Excited atoms return to the ground state by emitting light energy.
Nebulizer (atomizer)
o Deliver a fine spray of sample containing the metallic ion to the burner.
Burner
A fuel gas (propane) with an oxidizing agent (compressed air) burned to produce the flame
Monochromator system
Allow only emitted line spectrum of specific element to strike the PMT.
Atomic Absorption
i. Measures light absorbed by ground state atoms
ii. Used to measure concentration of calcium atom
iii. 100 times more sensitive than FES
Light Source
Provide incident light for the system
Hallow cathode lamp
Evacuated gas tight chamber filled with inert gas
Electrodeless discharge lamp
Bulb filled with argon and the analyte Radiofrequency generator excites the element
Beam Chopper
Modulates the hollow cathode light beam.
Nebulizer
Deliver a fine spray of sample
Burner
▪ Long narrow slit (permits absorption of incident light)
▪ A fuel gas (acetylene) is burned to produce the flame.
Light Source
Components of AAS
1. ?
2. Beam Chopper
3. Nebulizer
4. Burner
5. Monochromator
6. Photodetector
Beam Chopper
Components of AAS
1. Light Source
2. ?
3. Nebulizer
4. Burner
5. Monochromator
6. Photodetector
Nebulizer
Components of AAS
1. Light Source
2. Beam Chopper
3. ?
4. Burner
5. Monochromator
6. Photodetector
Burner
Components of AAS
1. Light Source
2. Beam Chopper
3. Nebulizer
4. ?
5. Monochromator
6. Photodetector
Monochromator
Components of AAS
1. Light Source
2. Beam Chopper
3. Nebulizer
4. Burner
5. ?
6. Photodetector
Photodetector
Components of AAS
1. Light Source
2. Beam Chopper
3. Nebulizer
4. Burner
5. Monochromator
6. ?
Nebulizer (atomizer)
Components of FES
1. ?
2. Burner
3. Monochromator system
4. Photosensitive detector (photomultiplier tube)
Burner
Components of FES
1. Nebulizer (atomizer)
2. ?
3. Monochromator system
4. Photosensitive detector (photomultiplier tube)
Monochromator system
Components of FES
1. Nebulizer (atomizer)
2. Burner
3. ?
4. Photosensitive detector (photomultiplier tube)
Photosensitive detector (photomultiplier tube)
Components of FES
1. Nebulizer (atomizer)
2. Burner
3. Monochromator system
4. ?
Electrophoresis
̶ The process of separating the charged constituents of a sample by means of an electrical current.
Iontophoresis
o Migration of small ions
Zone electrophoresis
o Migration of charged macromolecules in a porous support
Driving force (power supply)
Electrophoresis Components:
i. ?
ii. Buffer
ii. Support medium
iv. Sample
v. Detecting System
Buffer
Electrophoresis Components:
i. Driving force (power supply)
ii. ?
ii. Support medium
iv. Sample
v. Detecting System
Support medium
Electrophoresis Components:
i. Driving force (power supply)
ii. Buffer
ii. ?
iv. Sample
v. Detecting System
Sample
Electrophoresis Components:
i. Driving force (power supply)
ii. Buffer
ii. Support medium
iv. ?
v. Detecting System
Detecting System
Electrophoresis Components:
i. Driving force (power supply)
ii. Buffer
ii. Support medium
iv. Sample
v. ?
Cellulose acetate
Separates serum proteins into 5 bands
Agarose Gel
10 -15 bands
Polyacrylamide gel
>20 bands
Electrophoretogram
̶ Result of electrophoresis consisting of separated strands of a macromolecule
Electroendosmosis
Movement of buffer and solvent relative to their fixed support.
Isoelectric focusing
Movement of buffer and solvent relative to their fixed support
Capillary electrophoresis
Separation is performed in narrow-bore fuse silica capillaries
Chromatography
Separate complex mixtures between mobile and stationary phase
Mobile Phase
carries the complex mixture
Stationary phase
through which mobile phase flows
Column
holds the stationary phase
Eluate
separated components
Body fluids
Blood, CSF, urine, sweat, gastric juices, etc.