pale lesions in retinal diseases differentiation
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
what is the posterior pole
the central part of retina, includes: optic disc, macula and around it
what does ischaemic mean
a lack of blood supply(oxygen) to tissue- causes retinal nerve fibres to malfunction or die
what does retinovitreal mean
attachment between retina and vitreous body
examples of retinovitreal degenerations
snail track
lattice
snowflake( early stage /variant of snail track)
cobblestone
retinoschosis
how does normal retinovitreal connection look
even, healthy peripheral retina with smooth reflectivity and no localized whitening or thinning.
early degeneration is
snowflake- small discrete white spots usually benign
what is moderate degeneration
snail track- glistening, frosting ,long snail slime like appearance
its a peripheral retina degeneration of neural layers, often superior or inferior temporal
how would snail track appear in fungus exam
flat and reflective
what is snail tracks clinical importance
high risk or retinal tear of detachment due to thin retina and stuck to vitreous
lattice degeneration- high degeneration
thin elongated, with criss cross white patches and pigmented borders
what is the cause
retinal thinning and liquified vitreous and firm vitro retinal adhesion at edges
high risk for retinal tear/degeneration
white with/without pressure
Translucent gray-white patches,
with pressure - needs indentation of sclerato be seen
due to retinovitreal interface irregularity
retinoschisis
smooth dome shaped transparent elevation of retina- symptomless
intraretinal degeneration - splitting of retinal layers
mimics degeneration
another intraretinal degeneration
microcystoid- peripheral greyish vesicles
doesn’t predispose to retinal detachment
what type of degeneration is cobblestone
chorioretinal
cobblestone/paving
well defined white patches with pigmented rim and visible choroid
benign and no tear risk
due to outer retina and retinal pigmented epithelium loss
is cobblestone normal?
appears in 25% normal eyes
Lets See Shiny White Retina Properly
L- lattice-(risky!)
S- snail track(risky!)
S-snowflake(benign- may progress)
W-white with/without pressure(benign)
R-retinoschosis-(usually benign)
P-paving stone-(benign)
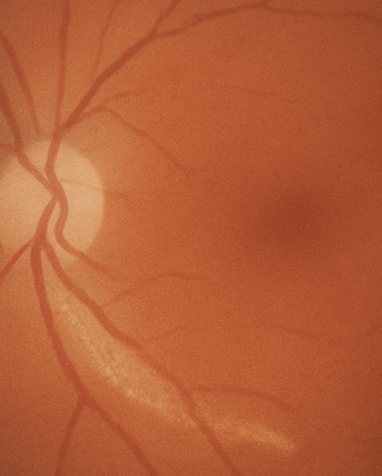
what is this
lattice degenation
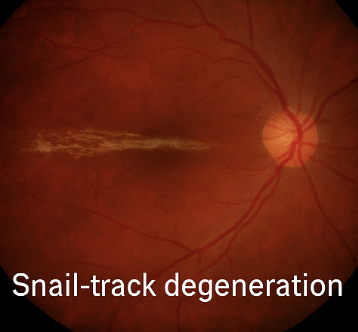
what is this
snail track
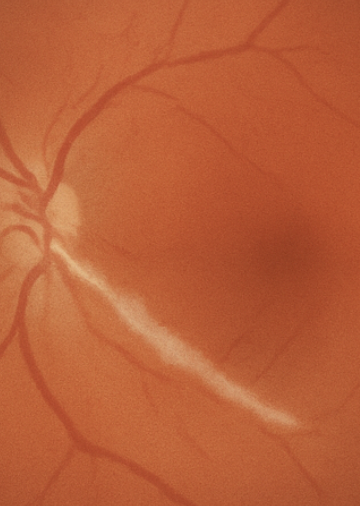
what is this
snail track
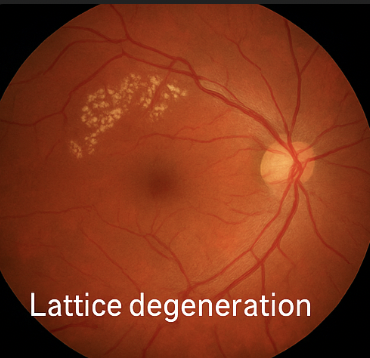
what is this
lattice degeneration
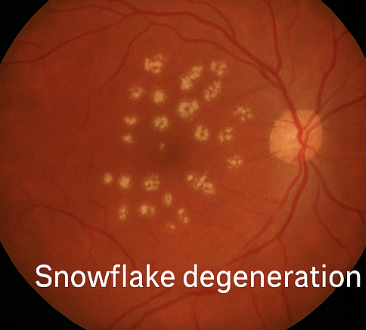
what is this
snowflake
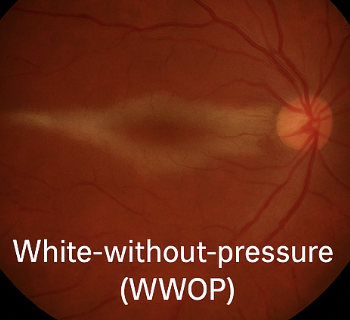
what is this
white with/without pressure
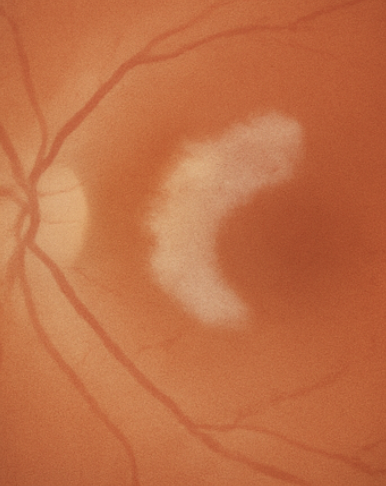
what is this
white with/without pressure
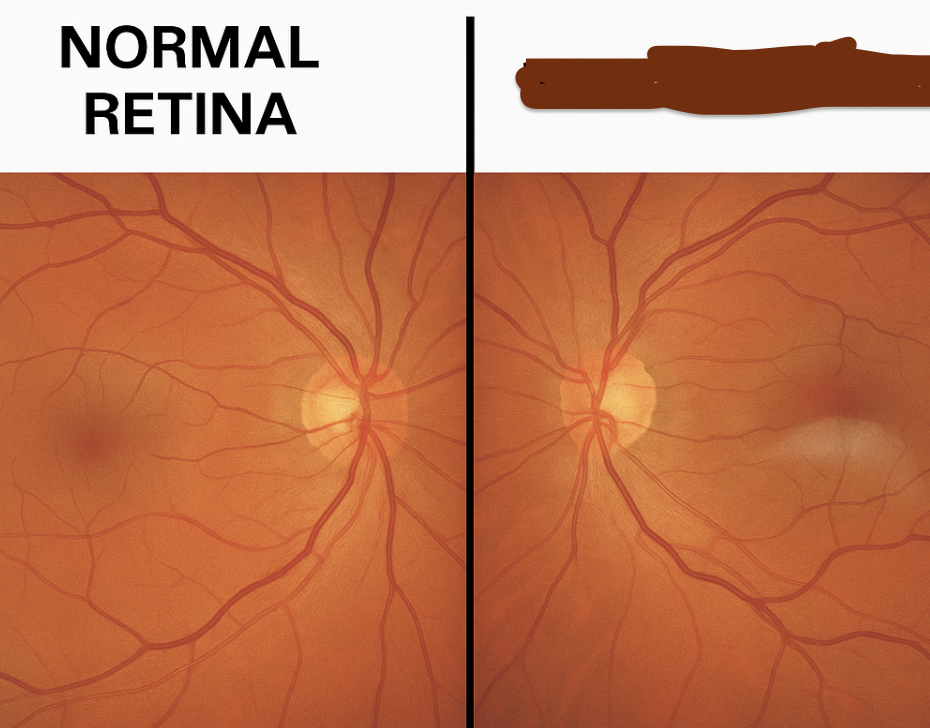
what is this
retinoschosis
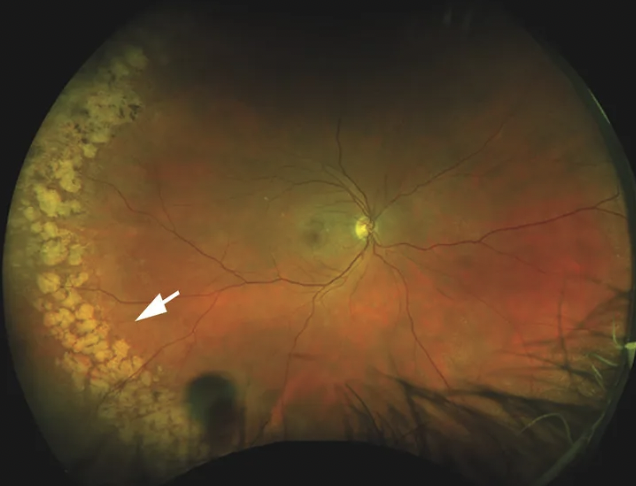
what is this
cobble stone
what is honeycomb degeneration
a peripheral retinal degeneration
honeycomb pattern of atrophy and pigmentation- benign so doesn’t predispose to retinal tears of degeneration
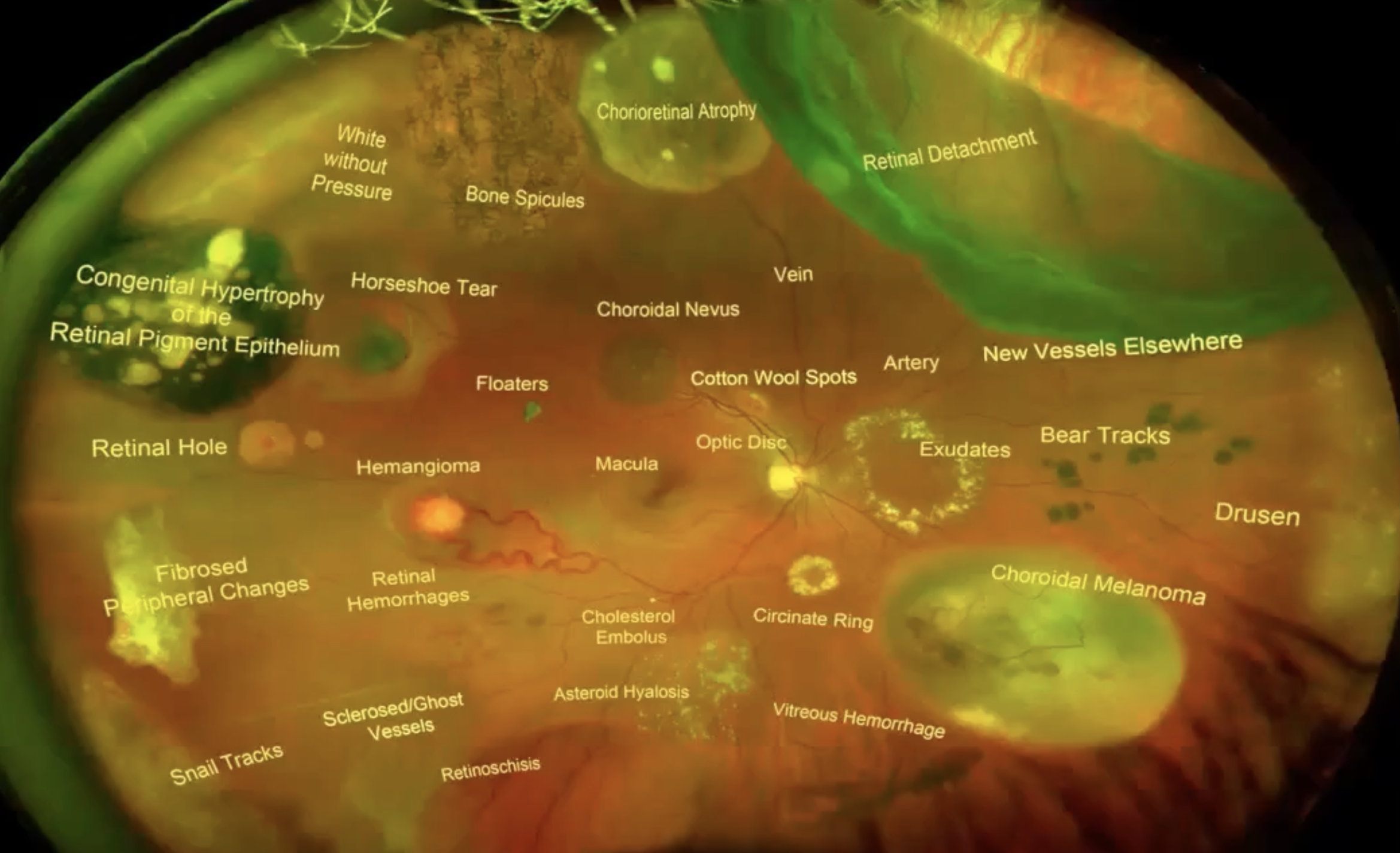
pigemtory lesions ( tumours)
CHRPE- congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium
Choroidal naevus
choroidal melanoma
retinitis pigmentosa
CHRPE
bear track
flat
dark grey/black
1-3 disc diamters
unilateral
benign
location CHRPE
peripheral or mid peripheral
what are multiple CHRPEs called
bear track
what should you do if bear track identified
not a bad condition for eye, but refer to GP as its related to colon cancer
choroidal naevus
slight elevation
slate grey/brownish
may have drusen on surface
Indistinct edges
naevus location
mid peripheral or posterior pole
what is procedure once naevus found
monitor for changes in elevation, orange pigment or broth- may develop to melanoma
melanoma
significant elevation
white/greenish grey
more than 10DD
cause serious retinal detachment
melanoma location
posterior pole- near macula
asymptomatic unless detachment occurs
requires urgent referral
retinitis pigmentosa
inherited retinal dystrophy
breakdown of RPE and photoreceptors - pigment distributes( appears like black branches- not always visible)- spicules
retinal arteries become very thin(attenuated)- due to photoreceptor loss
optic disc appears pale
how are the spicules formed
RPE cells migrate to inner retina along blood vessels- carry pigment with them
what does retinitis pigmentosa cause
low vision at night due to loss of rods
peripheral vision lost first- tunnel vision
cones lost later on - cause eventual vision reduction
big difference between nevaus and. melanoma
naevus won’t grow melanoma will with time, so record keeping is important
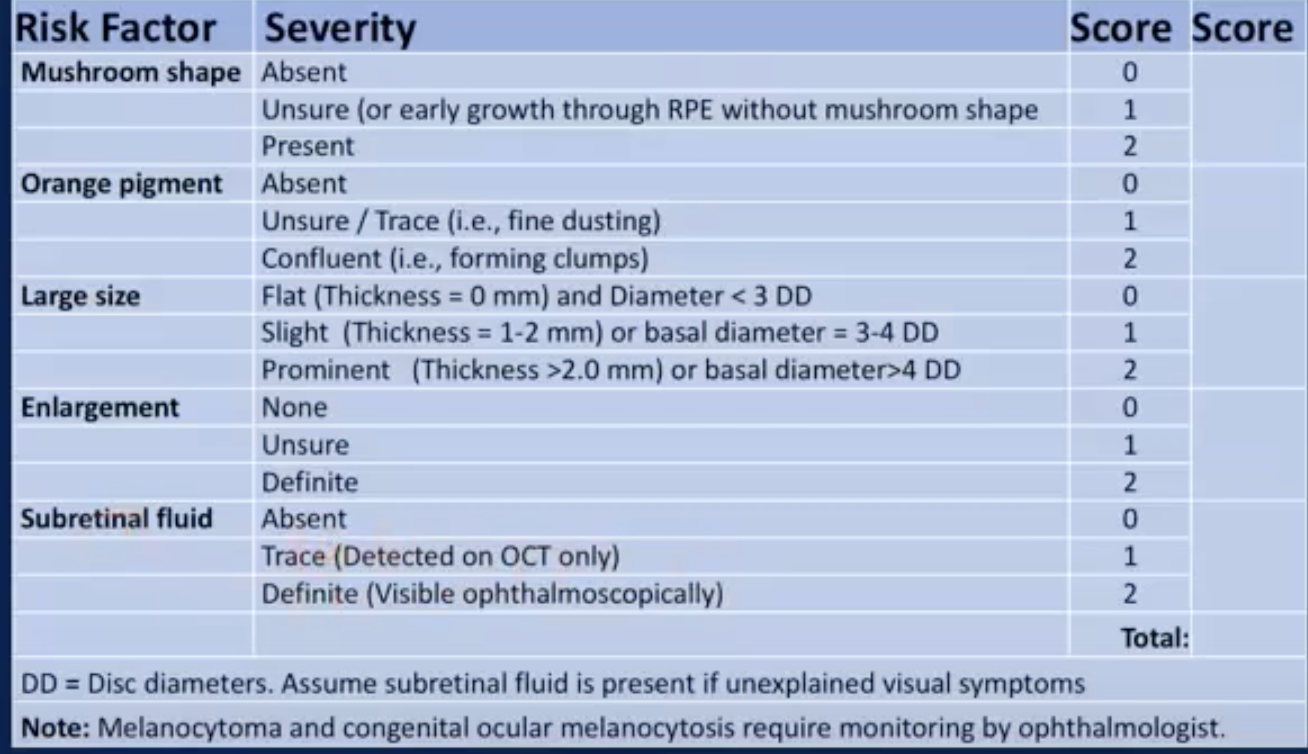
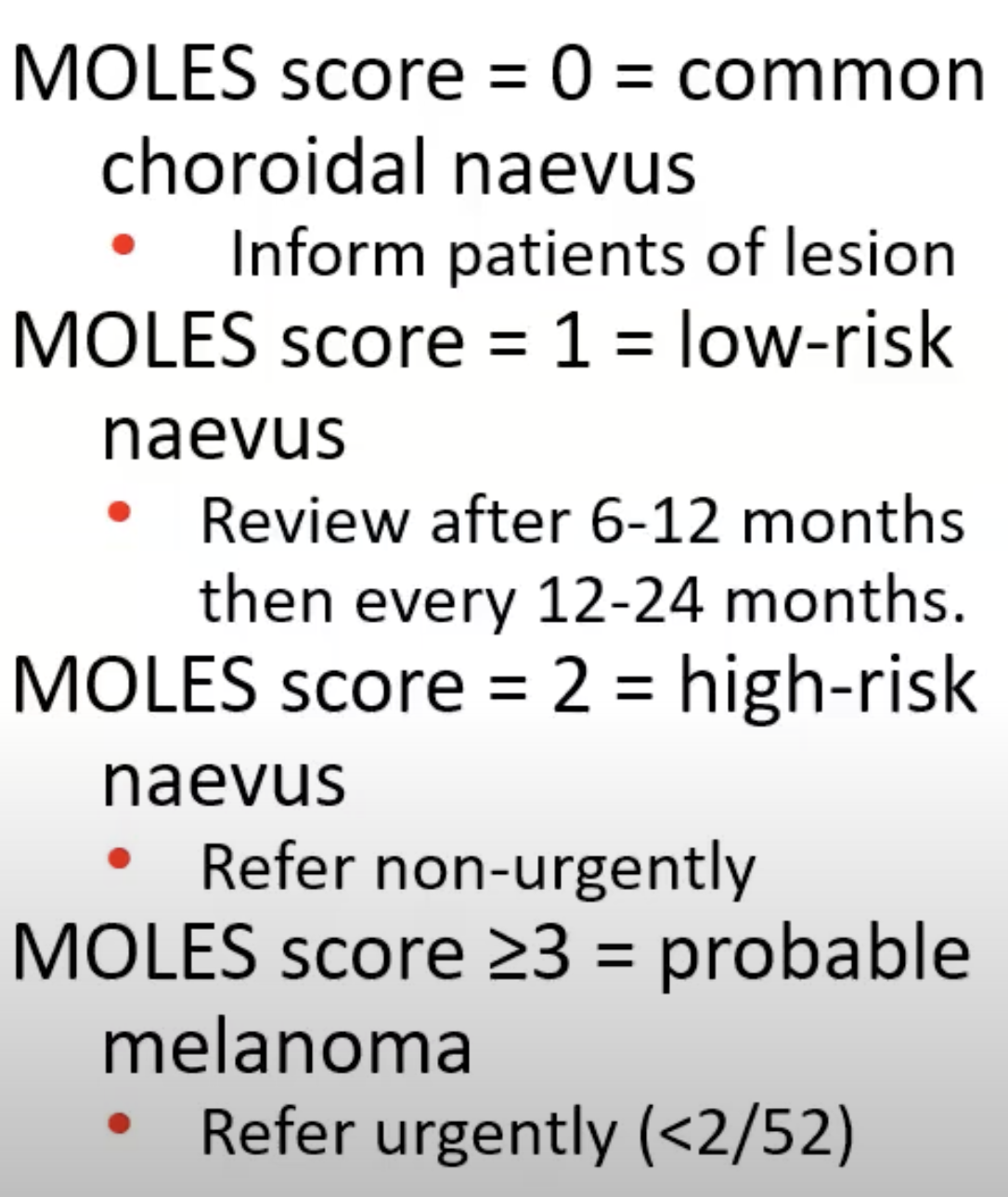
albinism
lack of pigment
view of all choroidal vessels
poor VA - less than 6/60
nystagmus
Risk of High myopia
higher risk of:
glaucoma
retinal detachment
posterior sub capsular or early onset nuclear sclerosis
optic disc anomalies- peripapillary atrophy
the thinning or loss of tissue around disc
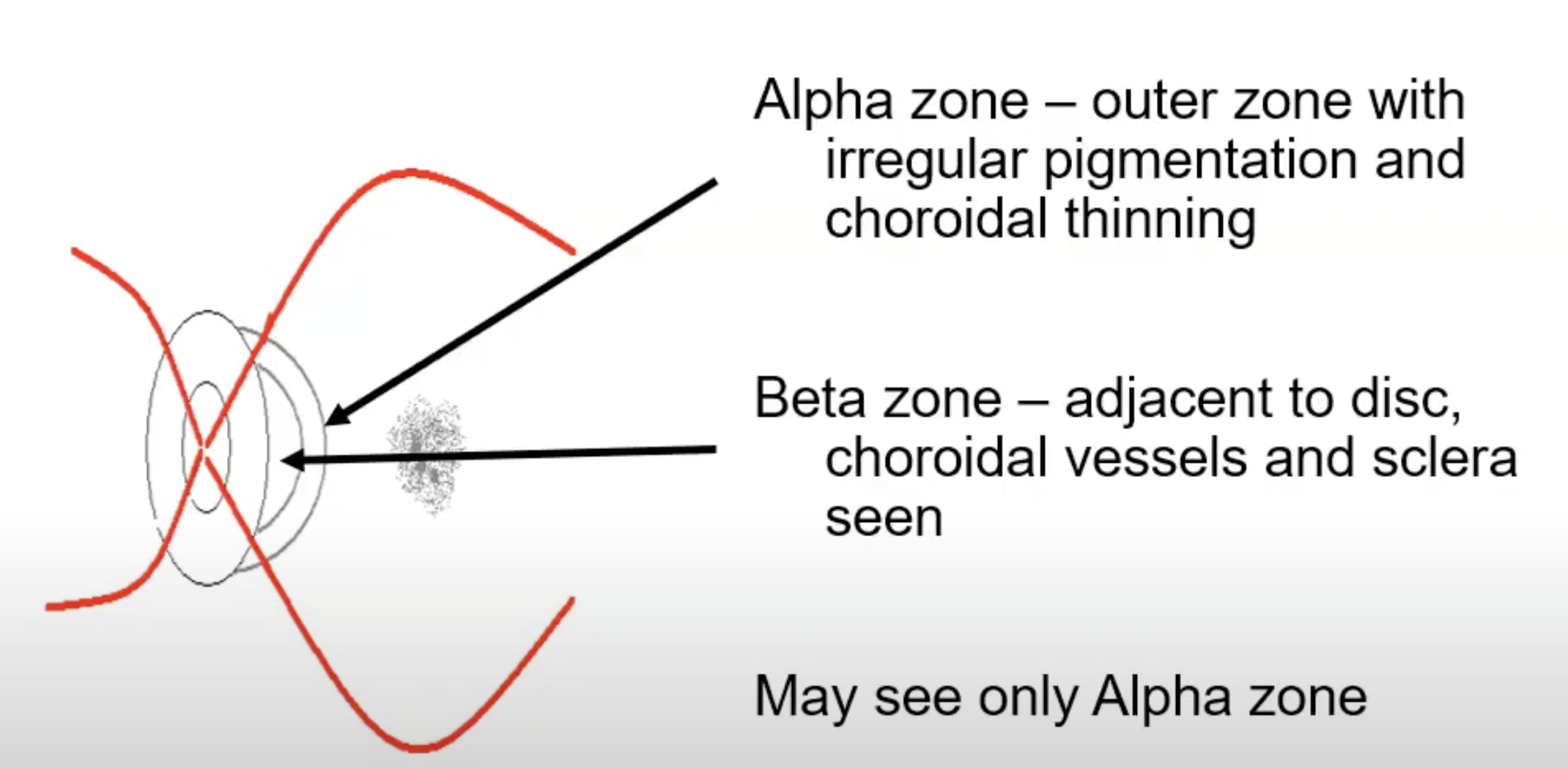
scleral or choral cresecent:
if RPE stretched- choridal- alpha
chord stretched- scleral- beta
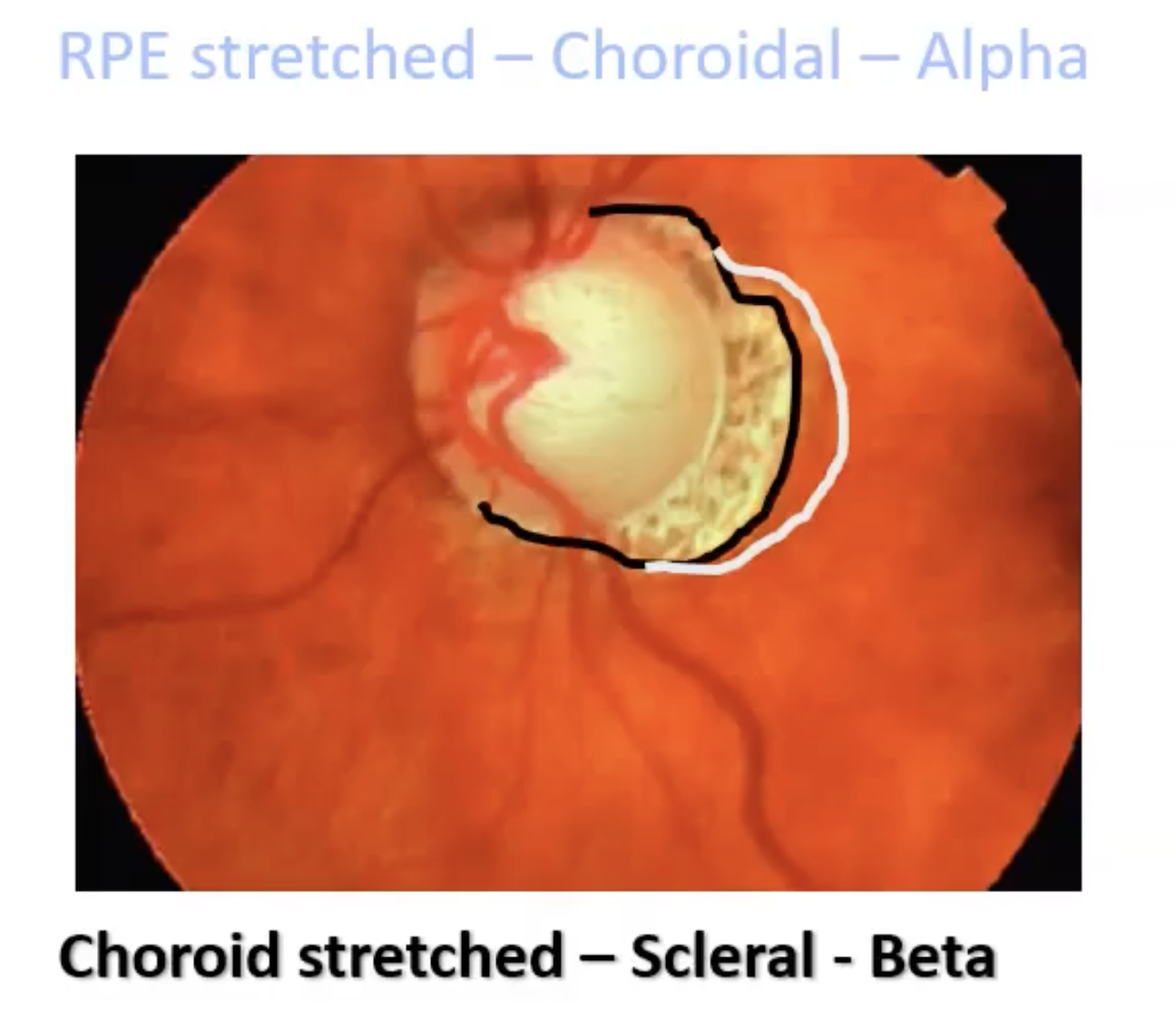
what’s this
zones of peripapillary atrophy
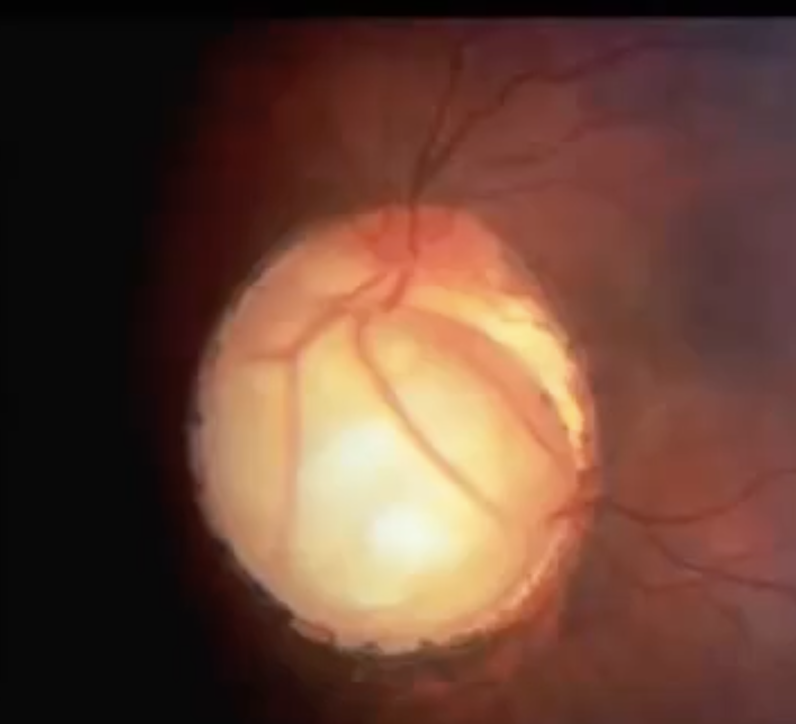
Bergmeister’s papilla
normal fetal developmental remnant of hyaloid artery
like a tat at optic disc
mittendorfs dots
small white spot on interior lens capsule
optic disc anomalie- colobloma
incomplete closure of sclera
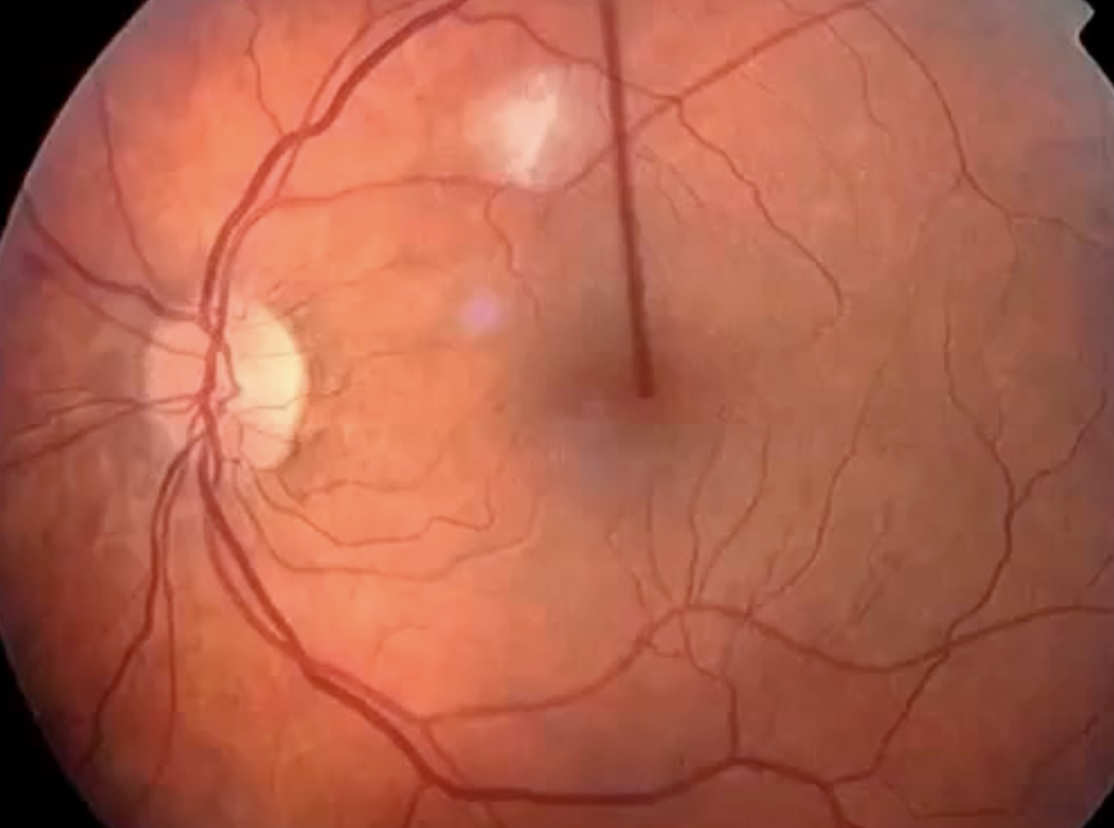
what’s this
coloboma
what is sx/signs
uni or bilateral
reduced VA
superior field defects
optic disc pit
atypical colobloma
enlarged blind spot
disc drusen
calcified deposits
edge of disc is lumpy
70% bilateral
what it may be confused with
papillodema
hypertension on retina (hypertensive retinopathy) signs
papillodema(severe)
cotton wool spots(moderate)
flame haemorrage(moderate)
hard exudates(moderate)
arteriovenous nipping (mild)
cotton wool spots
white spots to remember
disruptions to axoplasmic flow in RNFL
seen in diabetic and hypertensive retinopathy
hard to differentiate with hard exudates
cotton wool spots
arteriosclerosis
progressive hardening and narrowing of arteries- thickened tunic media and loss of elasticity
blood vessel signs for arteriosclerosis
salus sign -cross at 90degrees
bonnet sign- bulging vein
gunn sign- tapering of veins
Atherosclerosis
deposition of fatty material in walls- plaque formed
platelets bind
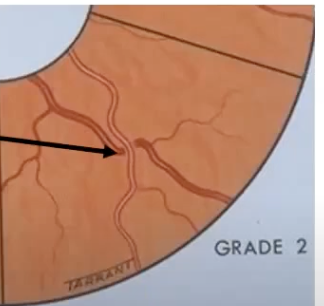
salus sign
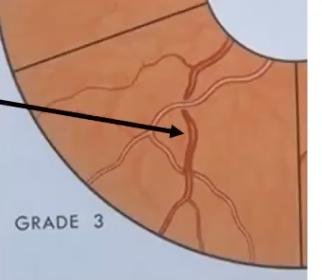
bonnet sign
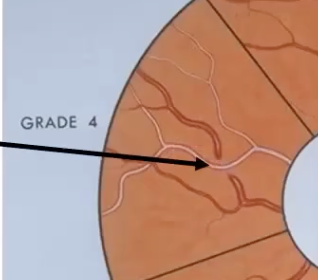
tapering
retinal vascular diseases
retinal artery occlusoon- more serious due to oxygen stopped from reaching tissue
retinal vein occlusion
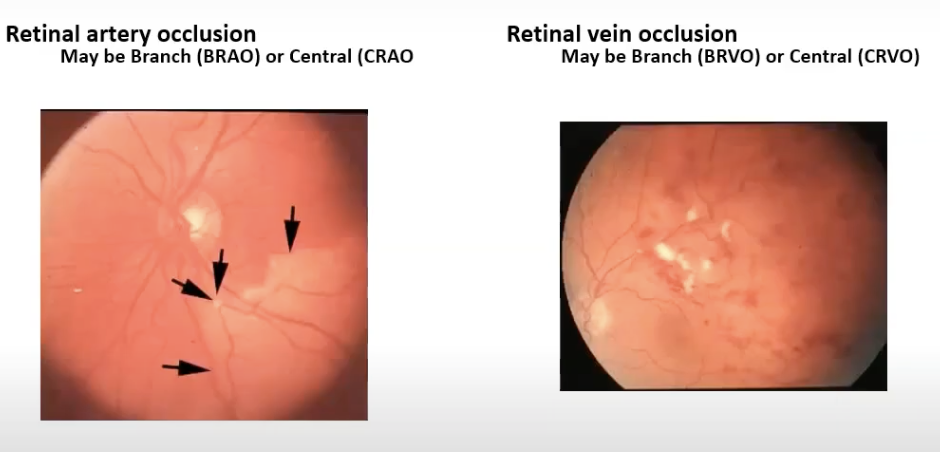
central retina artery occlusion (CRAO)
painless loss of vision
whitening of retina
red spot at macula
(CRVO)
reduced vision
cotton wool spots
exudates
neovascularisation
haemorrhage in 4 quadrants
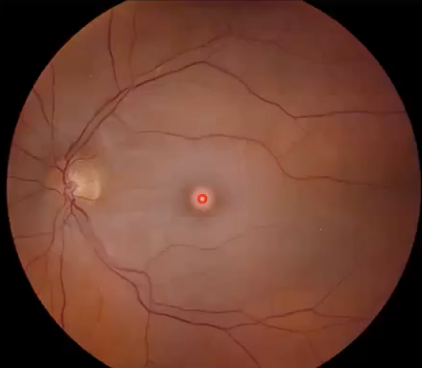
CRAO
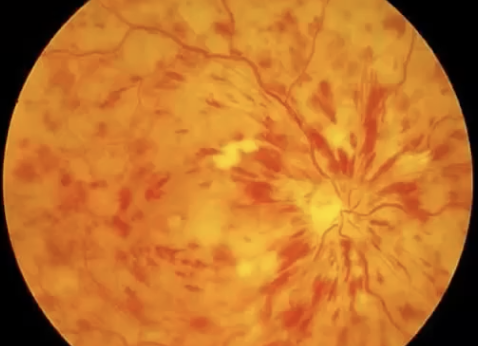
CRVO