Option C - Ecology & Conservation
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Taken from Quizlet, made by davidfaure
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Define limiting factor
An environmental factor that limits the distribution or numbers in a population
Define limits of tolerance
They are the highest/lowest values of abiotic factors that an organism can survive
Define an ecological niche
The mode of living of a species; its use of biotic and abiotic resources.
There are two types: fundamental niche and realised niche
Define symbiosis
An interaction between two species where both benefit.
Five types of interaction between species
mutualism, parasitism, competition, predation, herbivory
Define a keystone species
a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its environment relative to its abundance
Define food conversion ratio
the percentage of ingested energy converted to biomass
Name two types of ecosystems
closed (e.g. aquarium) and open
Define biome
a geographical area that has a particular climate and sustains a specific community of plants and animals
Two main abiotic factors in biomes
rainfall and temperature
Gersmehl diagram
a diagram that shows the differences in nutrient flow and storage between different types of ecosystems
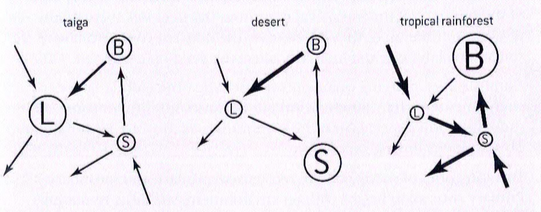
Three stores of nutrients in ecosystems
In biomass, litter, or soil.
Define Primary succession
ecological succession on entirely new lands without any established soil (due to events such as volcanic eruptions)
Define ecological succession
the process by which a sequence of increasingly complex communities develop over time
Define secondary succession
occurs when succession starts on existing soil following a natural artificial disturbance
Define endemic species
species that are native to a defined geographic region
Define alien species
species that have been transferred from their natural habitat to a new ecosystem
Define invasive species
plants and animals that have migrated to places where they have a tendency to spread causing damage to the environment, human economy and or human health
Define competitive exclusion
The idea that two species cannot occupy identical niches within a community, one will exclude the other
Examples of invasive species
Cane Toad
European Rabbit
European Rabbit
24 European rabbits exploded in number and are regarded as Australia's worst vertebrate pest
they thrived due to abundance of food and lack of natural predators (as well as a rapid reproduction cycle)
Define biomagnification
the process in which chemical substances become more concentrated each trophic level
Define microplastic
small plastic debris <1mm in size
Define indicator species
an organism used to assess a specific environmental condition; usually has a limited range of tolerance to that condition
Example of an indicator species
Lichens are composite organisms made up of fungi and algae in a mutualistic relationship.
They act as indicators of air pollution, especially sulfur dioxide, a waste product of the burning of sulfur-containing fossil fuels.
Depending on the species of lichen, various levels of sulfur dioxide are tolerated.
The bushy beard lichen is unable to tolerate even low levels of sulfur dioxide within the atmosphere. Therefore, if this lichen is absent it may indicate high levels of sulphur dioxide.
Define biotic index
A calculated measure used to compare the relative health of two or more locations
Define biodiversity
A measure of the number and variety of organisms found within a specified ecosystem
Simpson's reciprocal index
measures the relative biodiversity
D = diversity index
N = total number of organisms of all species
n = number of individuals of a particular species
∑ = sum the values for each species
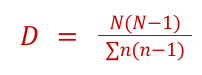
Four biogeographic factors, affecting biodiversity
Size of the conservation area (large is best)
Edge effect (less edge is best)
Isolation (close to other nature reserves is better)
Corridors (provide habitat to connect areas)
Define in situ conservation
the preservation of species within their natural habitat
Define ex situ conservation
the preservation of plant and animal species outside their natural habitat, in zoos or reserves
Advantages of ex situ conservation
allows for greater control of essential conditions (eg: climate control, dietary intake)
increases chances of breeding successfully by utilising artificial methods (eg : IVF)
Disadvantages for ex situ conservation
increases interbreeding by restricting the gene pool and restricts the evolution of the species
does not prevent potential destruction of their natural habitat
less likely to be successful reintroduced into the wild which results in the loss of autonomous survival
Define population
all the individuals of a given species living in the same area at the same time
Method used to estimate the population of a mobile species
capture-mark-release-recapture
Two types of population growth
Exponential Growth - impossible as there will always be factors affecting the growth rate of a population
Logistic Growth
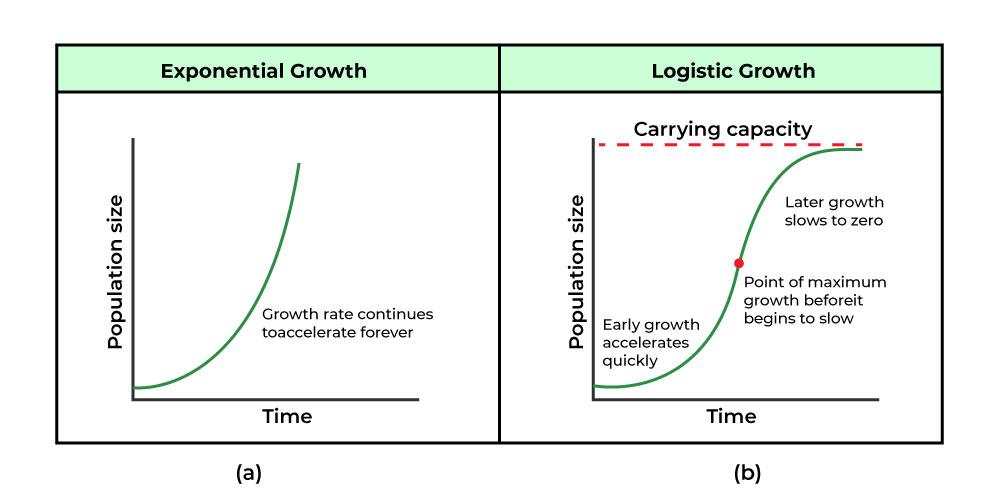
Phases of the Sigmoid growth curve
Lag phase
Exponential growth phase
Transitional phase
Plateau
Describe lag phase
population growth will be slow as there are few reproductive individuals that are likely widely spread
Describe exponential phase
As number increases, there is a rapid increase in population size as natality exceeds mortality
Mortality is low because there are abundant resources and minimal environmental resistance
Describe transitional phase
As population increases, resources become limited which results in increase competition for survival
As natality decreases and mortality increases, the population growth becomes slower
Describe plateau phase
mortality rates = natality rates and population growth becomes static
Population has reached the carrying capacity (k) of the environment, with limiting factors keeping the population stable
Population at this point will not be constant, but will oscillate around the carrying capacity to remain even.
Name two classifications of limiting factors
Top down control
Bottom up
Define top down control
population growth pressures applied by other organisms at higher trophic levels
Define bottom up control
factors that limit population growth by affecting resources or lower trophic levels
Define sustainable yield
the amount of natural resources that can be taken from an ecosystem without reducing the base stock
Define maximum sustainable yield (MSY) in fishing
The maximum sustainable yield is the largest amount of fish that can be caught without causing the population to fail.
List three methods to estimate commercial fish stock
capture-mark-release-recapture
Echo location
Analysis of fish data
Name three factors that need to be taken in for sustainable fishing practices
population size
reproductive status
age
Name bacteria involved in the nitrogen cycle
Rhizobium + Azotobacter →nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Nitrosomonas + Nitrobacter → nitrifying bacteria
Pseudomonas →denitrifying bacteria
Nitrogen Cycle
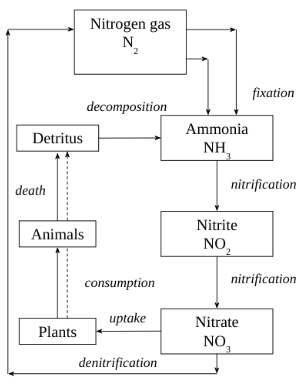
Outline the effects of water-logged soil on the nitrogen cycle
The anaerobic environment promotes denitrification by Pseudomonas denitrificans.
This depletes nitrates in the soil, which significantly reduces plant growth, as the fertility of the soil decreases.
Areas that are waterlogged for long periods of time have nitrogen-deficient soils.
Plant adaptions to waterlogged soil
Some plants have adapted to obtaining nitrogen by digesting animals.
For example, some plants use pitfall traps to lure insects with nectar. Their inner lining is slippery, so insects fall in and are broken down by digestive enzymes.
Phosphorus Cycle
the movement of phosphorus atoms from rocks through the biosphere and hydrosphere and back to rocks via the process of chemical weathering
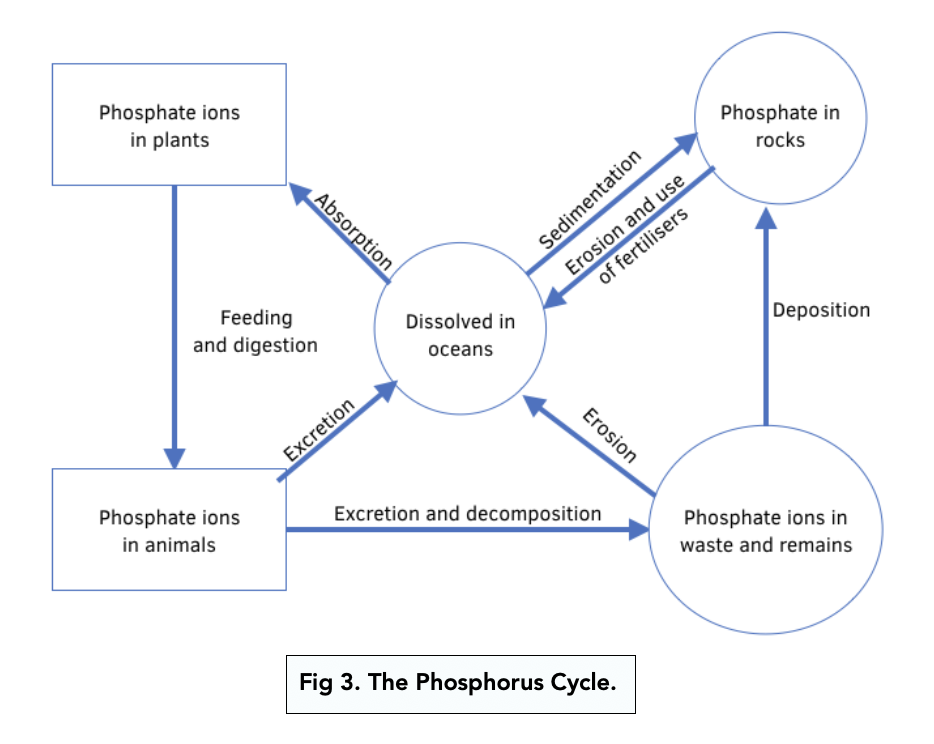
Steps of the Phosphorus Cycle
The weathering of phosphorite, sedimentary rock containing large quantities of phosphorus in the ocean, releases the phosphate ions and other minerals into the soil and water.
The phosphate ions and associated minerals are readily taken up by plants, which are consumed by animals. The phosphate is incorporated into organic molecules such as ATP or DNA.
After the plants and animals die, the phosphate is released back into the soil and water.
After the phosphate has been released back into the soil or water, it may be recycled and taken up by new plants.
Phosphorus in the soil can be washed into the waterways and ends up in the oceans through a process called leaching. Once the phosphate finds its way into the oceans, it can be thousands of years before it returns to the land as it is recycled within the ocean food webs or held within the sediments on the ocean floor.
Define eutrophication
The nutrient-enrichment of waterways and streams caused by leaching and/or the release of untreated sewage
Ecological consequences of eutrophication
Nutrients encourage the growth of algae on the water surface
Algal blooms black light to water plants below them
If the algae and plants die, bacteria feed on them and use up oxygen, causing a higher BOD
The reduced levels of oxygen lead to the death of sensitive organisms, such as invertebrates and fish
Density-dependent Factors
competition for limited resources available within an area such as the availability of food, habitats or fending off/hiding from predators
Most vulnerable = young, old, weak
Density-independent Factors
the environment in which the animal lives and such things as a harsh and cold winter or a dry summer, which can impact numbers as the population struggles to survive
Most vulnerable = everyone is affected (though weaker organisms will die first)