Biology Unit 2 (McGraw Hill)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
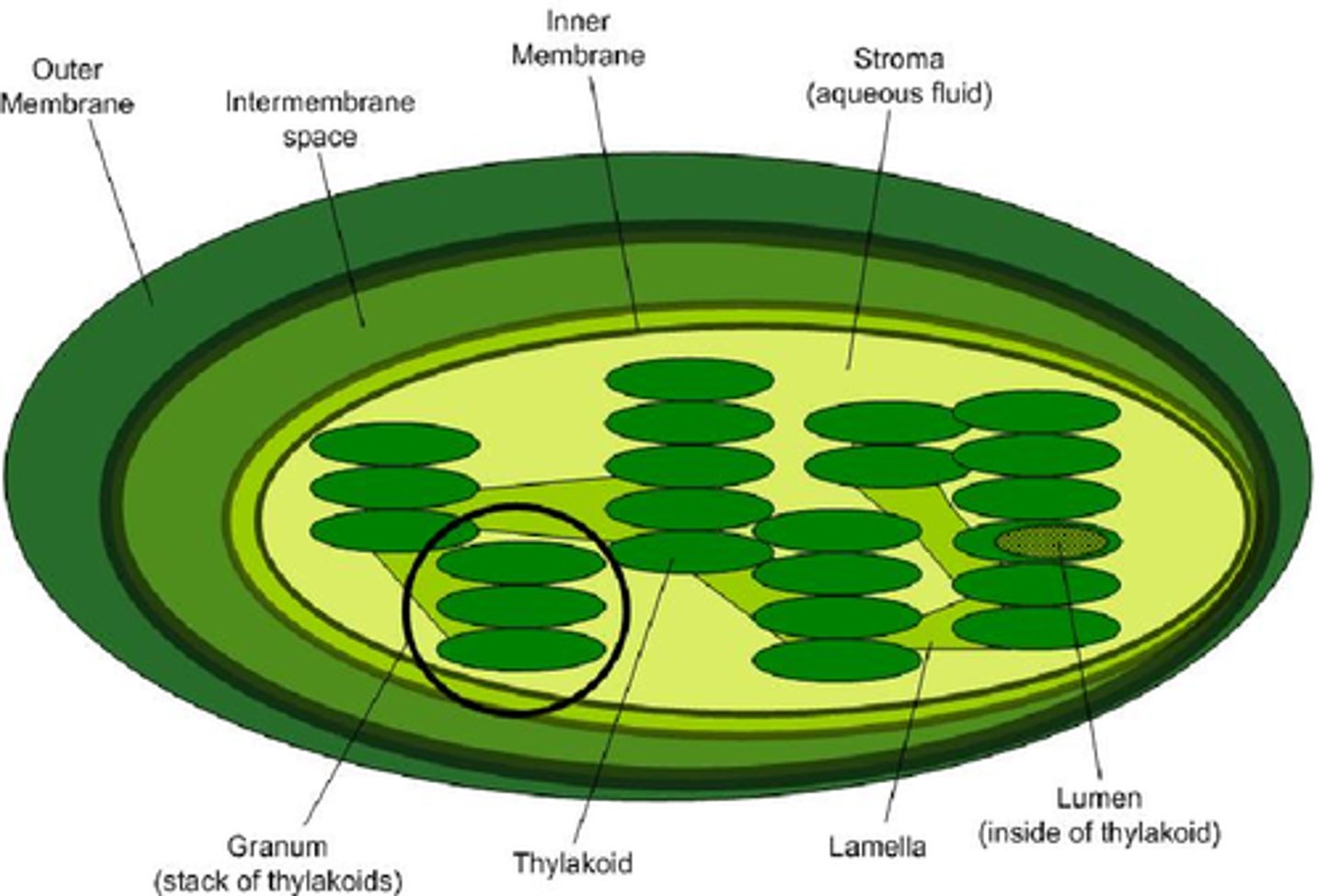
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
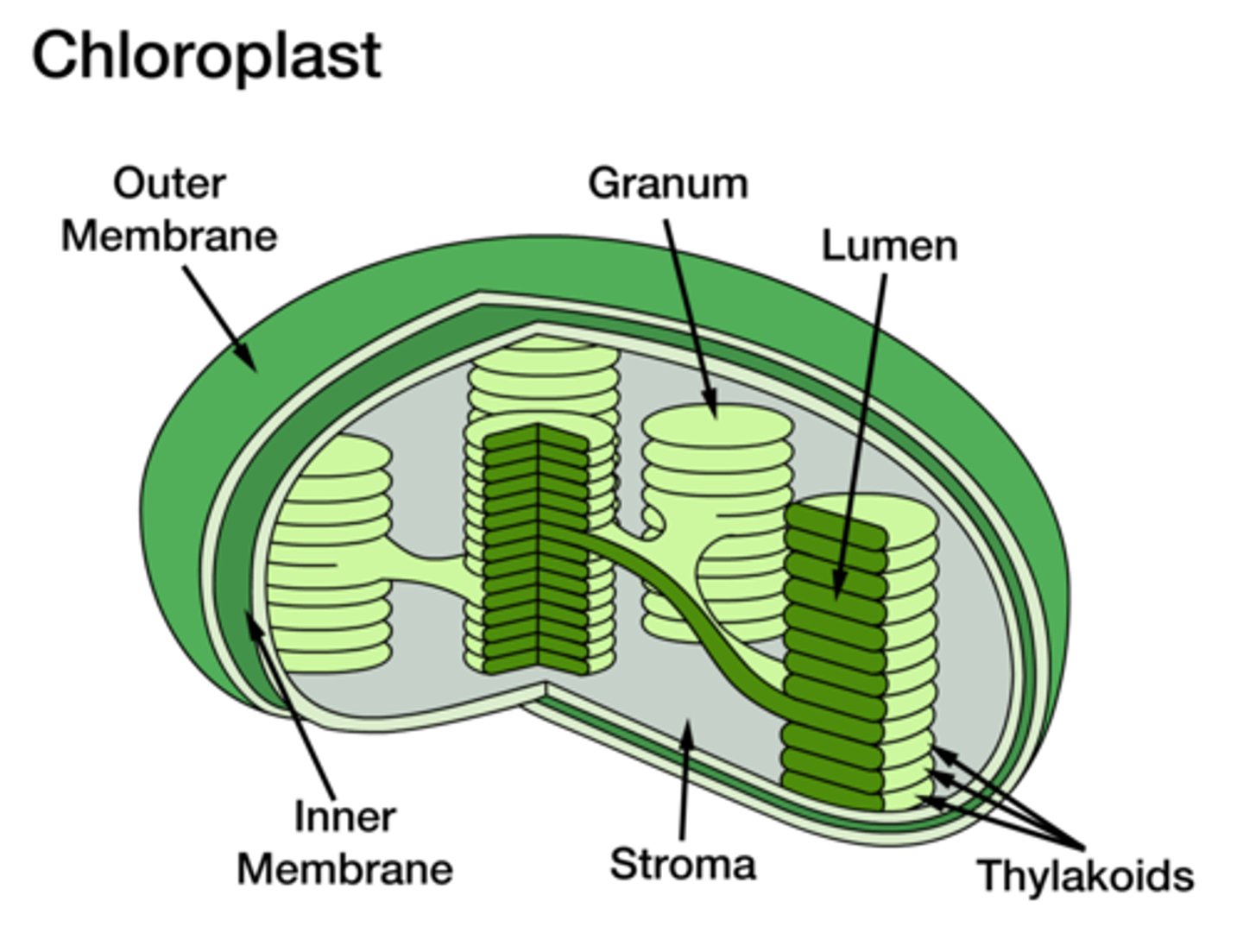
Thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
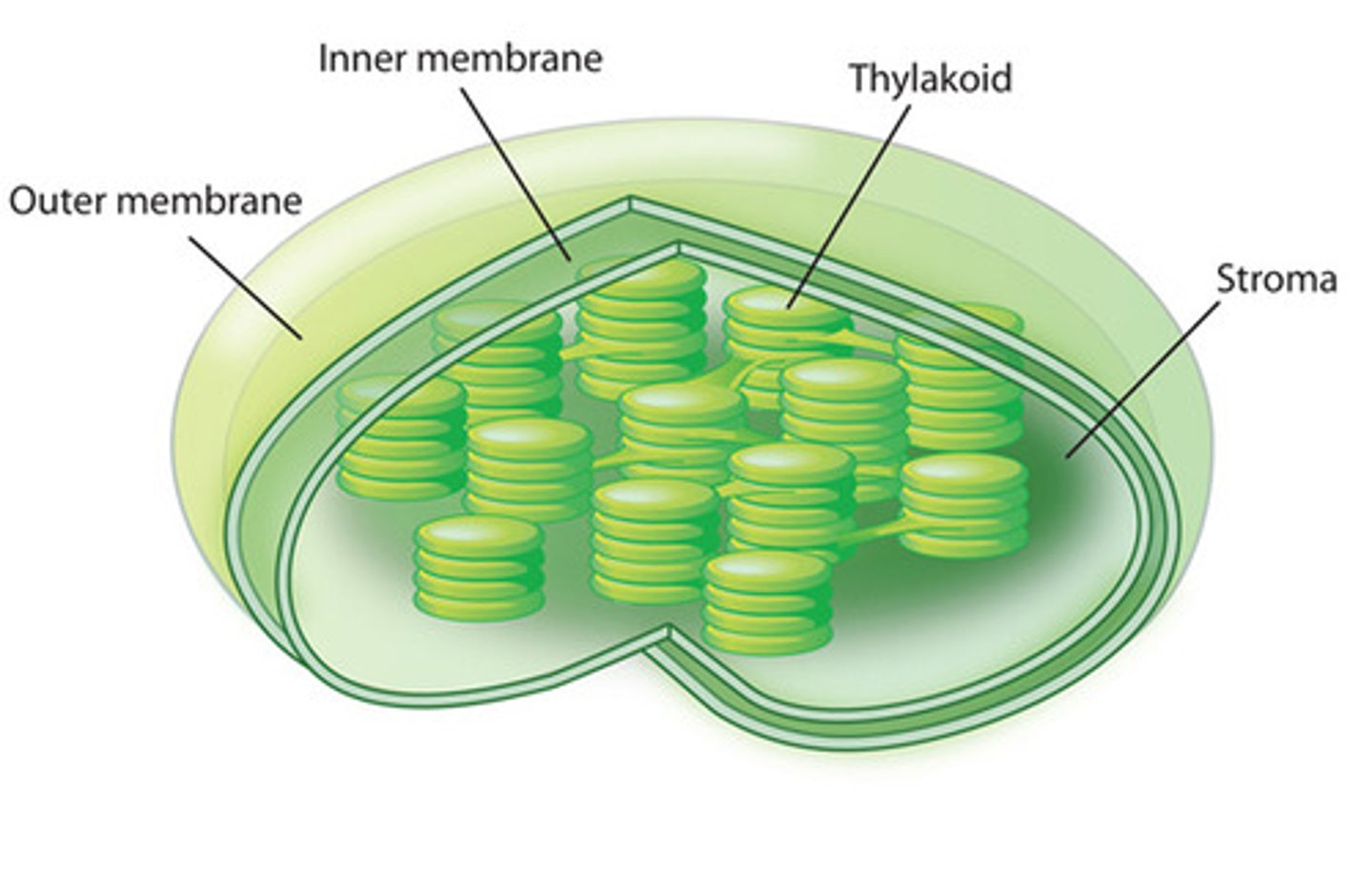
Grana
A stacked portion of the thylakoid membrane in the chloroplast. Grana function in the light reactions of photosynthesis
Chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O ------> C6H12O6 + 6O2
chemical equation for cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
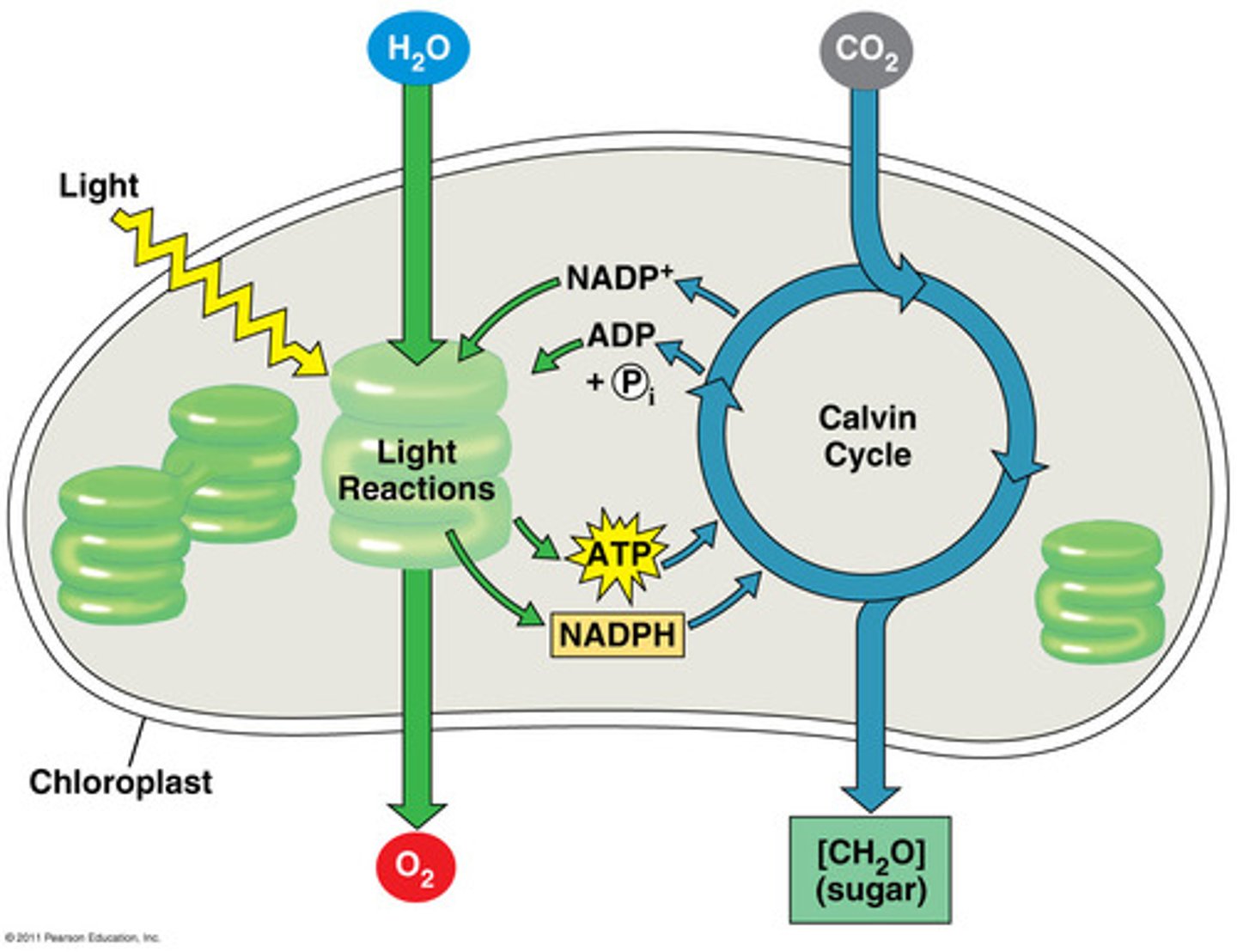
Describe light reactions
Occurs in thylakoids; convert solar energy to chemical energy; Light absorbed by chlorophyll drives a transfer of e- from H2O to an acceptor celled NADP+, which temporarily stored the e-. H2O is split and gives off O2. The solar power reduces NADP+ to NADPH by adding H+. ATP is also generated using chemiosmosis to power addition of a Phosphate group ADP (phosphorylation). This light energy is converted to chemical energy in the compounds: NADPH (source of energized e-) and ATP (energy currency of the cell). No sugar is produced.
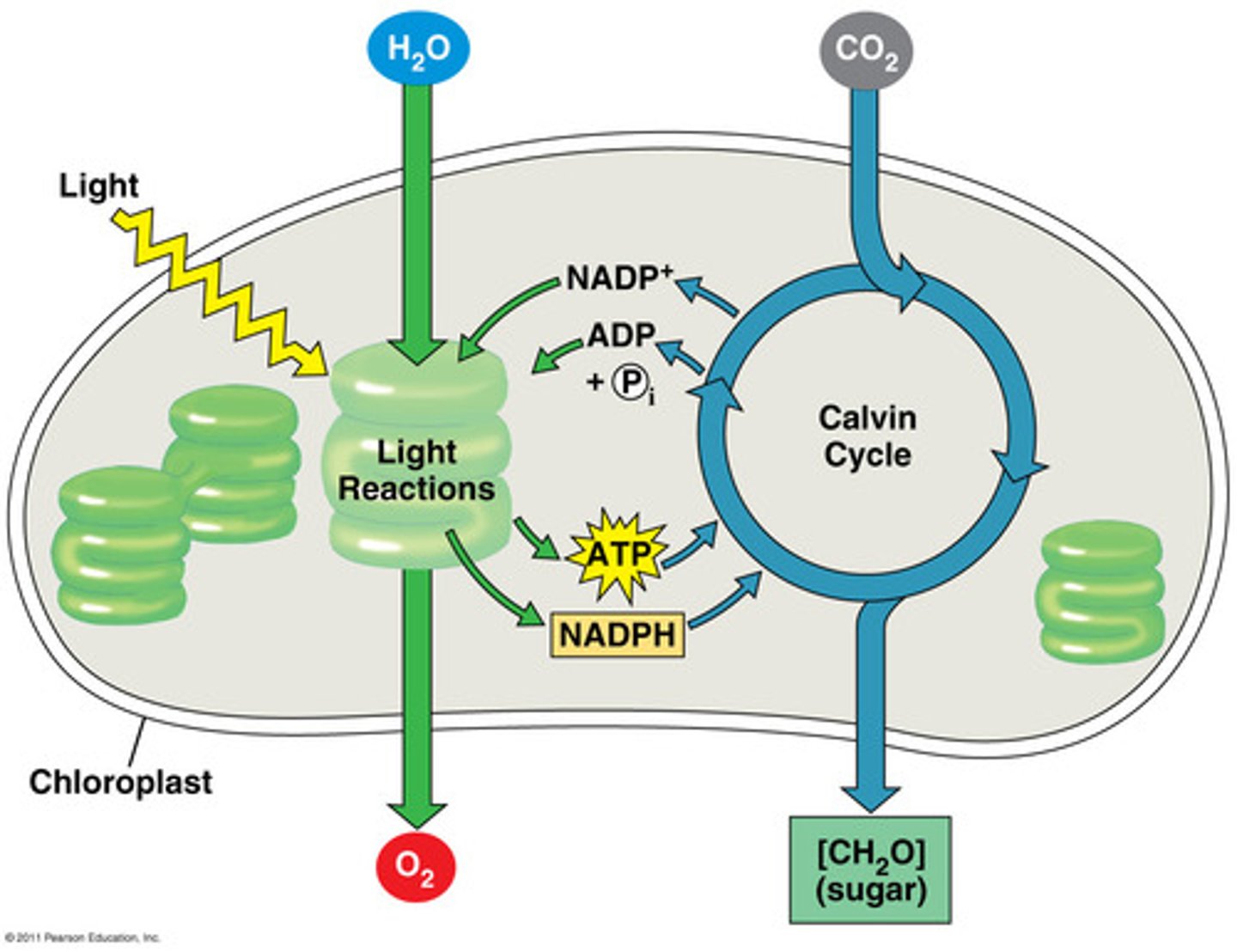
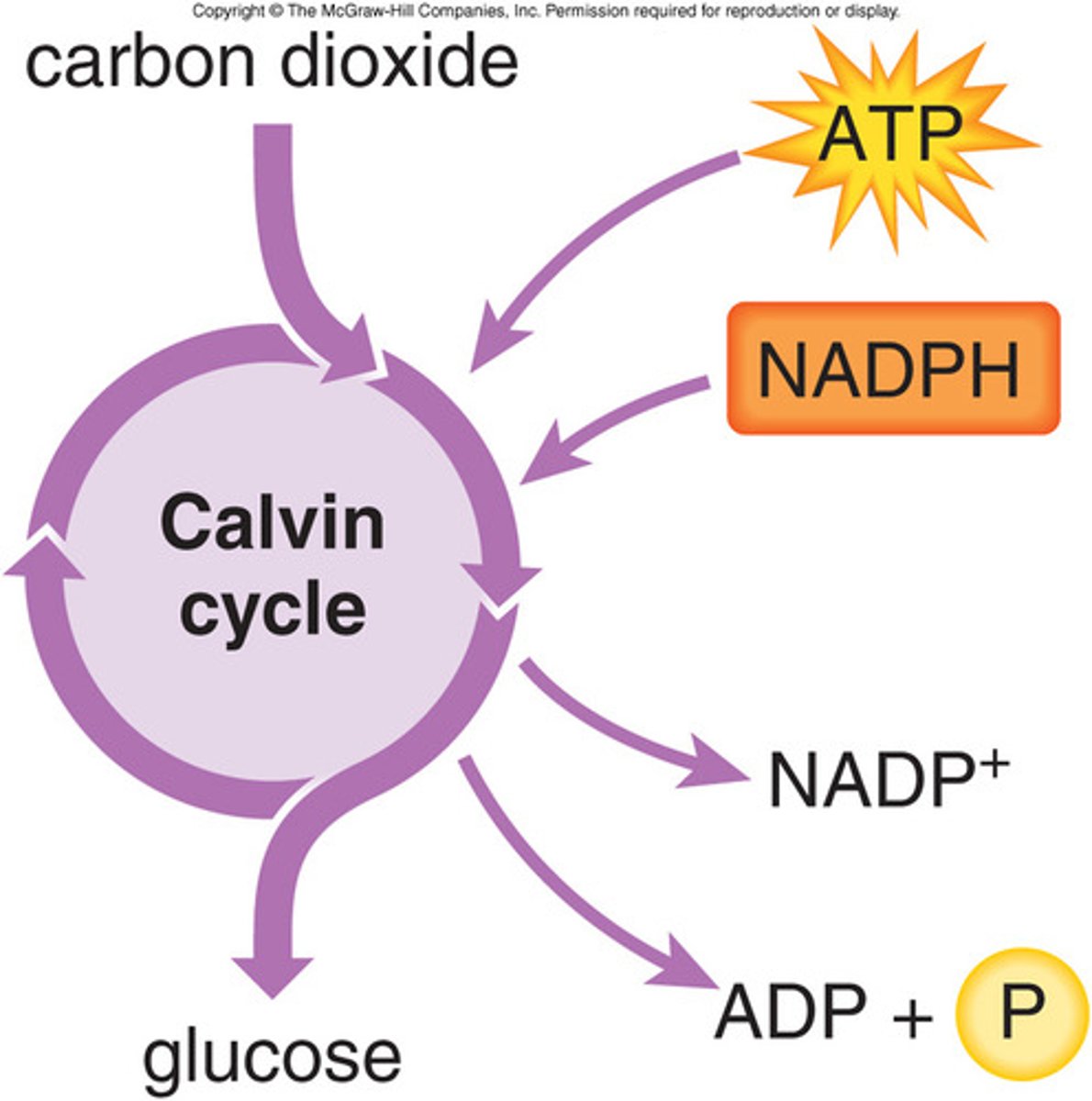
Describe the Calvin Cycle
Occurs in stroma; Incorporates CO2 from air into organic molecules already present in the chloroplast (carbon fixation). The fixed carbon is then reduced to carbohydrate by the addition of e-. The reducing power is provided by NADPH (source of energized e). The ATP (chemical energy) converts CO2 to carbohydrates. Sugar is made with help of NADPH and ATP produced by light reactions. Mostly occus during daylight because it is waiting on the NADPH and ATP from light reactions.
Steps of cellular respiration
glycolysis, preparatory reaction, Calvin cycle, electron transport chain
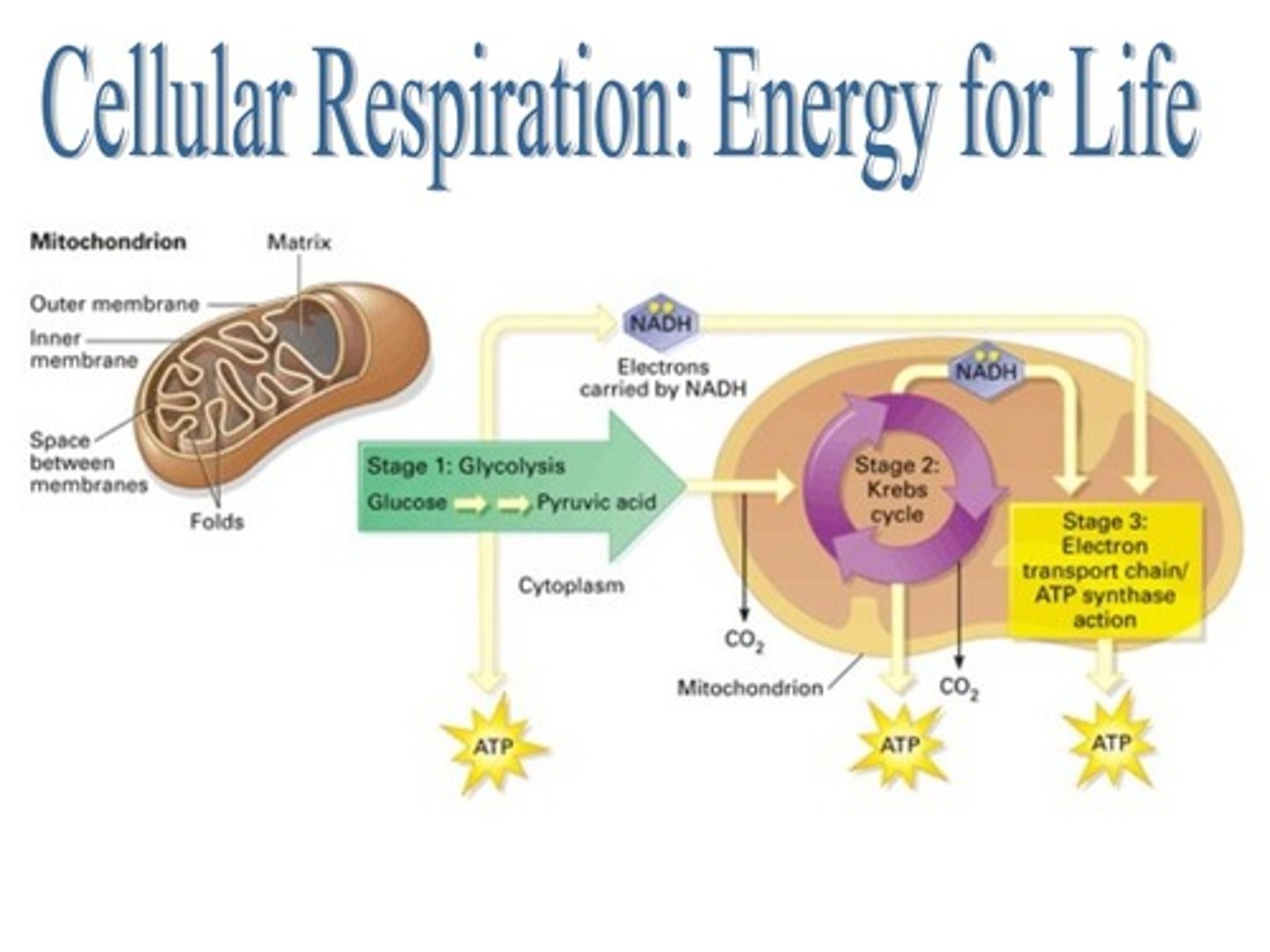
Glycolysis
the breakdown of glucose by enzymes, releasing energy and pyruvic acid.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
series of electron carrier proteins that shuttle high-energy electrons during ATP-generating reactions
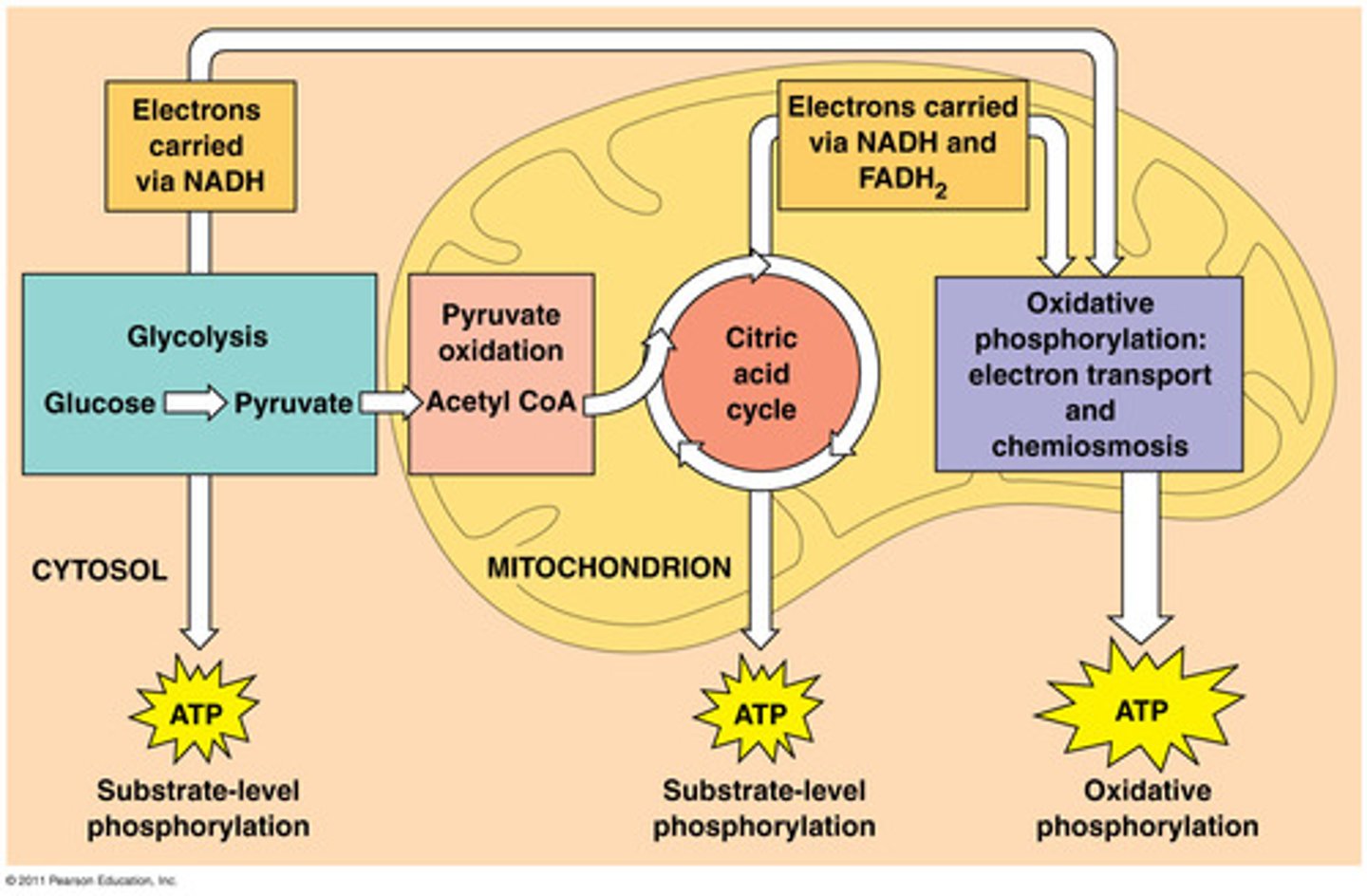
preparatory reaction
Reaction that oxidizes pyruvate with the release of carbon dioxide; results in acetyl CoA and connects glycolysis to the citric acid cycle.
Compare fermentation and cellular respiration.
Fermentation(anaerobic-without oxygen) and cellular respiration(aerobic-oxygen) are alike in that they both begin with a series of reactions known as glycolysis, which breaks glucose molecules into smaller pyruvate molecules. They are also similar in that during both processes, ATP is produced for the cell to use.
Where does fermentation occur?
cytoplasm
Where does cellular respiration occur?
mitochondria
Where does photosynthesis occur?
Chloroplast
Compare asexual and sexual reproduction
The production of genetically identical offspring from a single parent is known as asexual reproduction. Offspring produced by sexual reproduction inherit some of their genetic information from each parent.
phases of eukaryotic cell cycle
Interphase (G1, S, G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis)
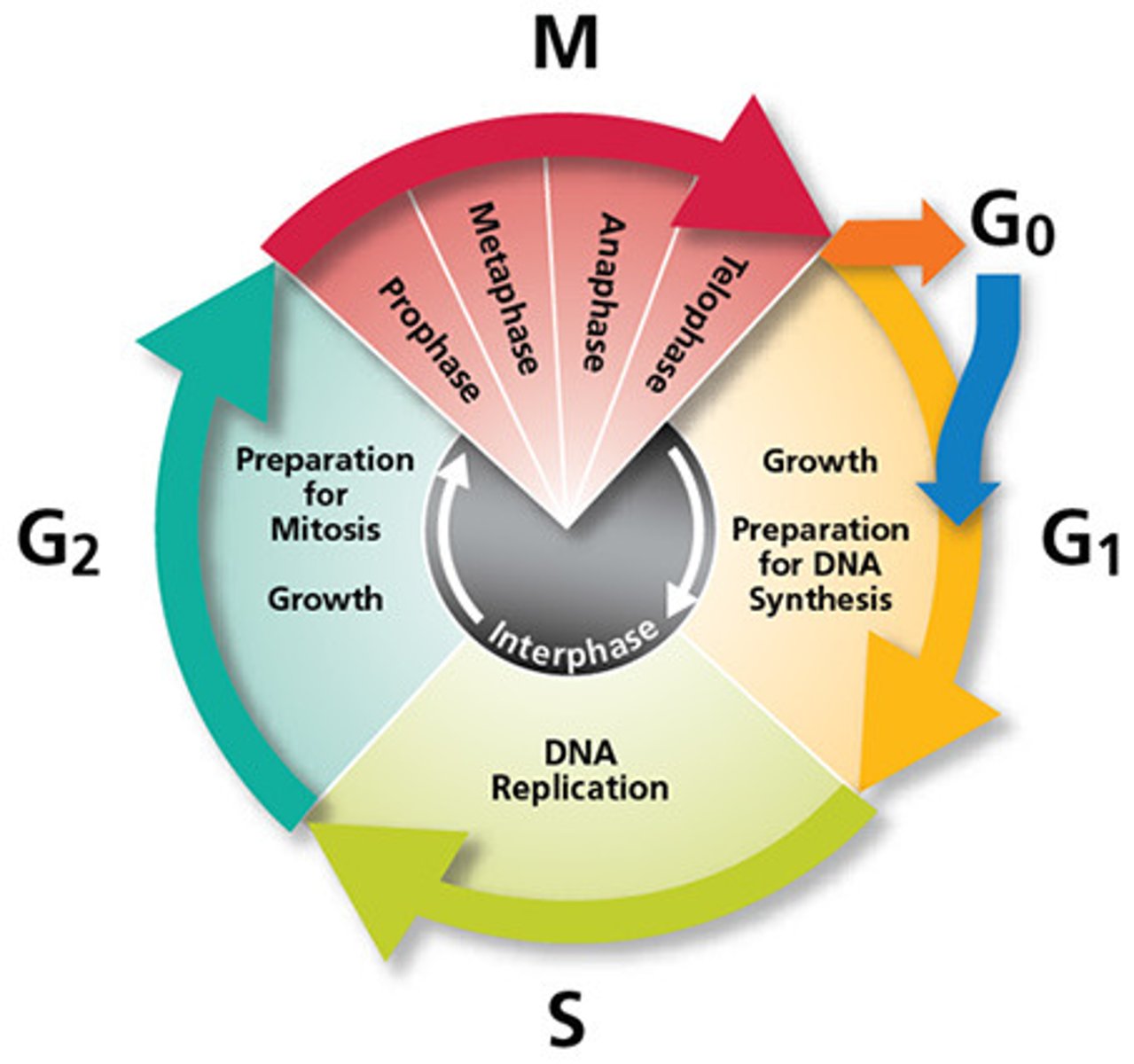
G1 of interphase (mitosis)
the cell doubles its organelles and accumulates materials that will be used for DNA replication.
S phase of interphase
DNA replication
G2 phase of interphase
the cell synthesizes those proteins needed for cell division
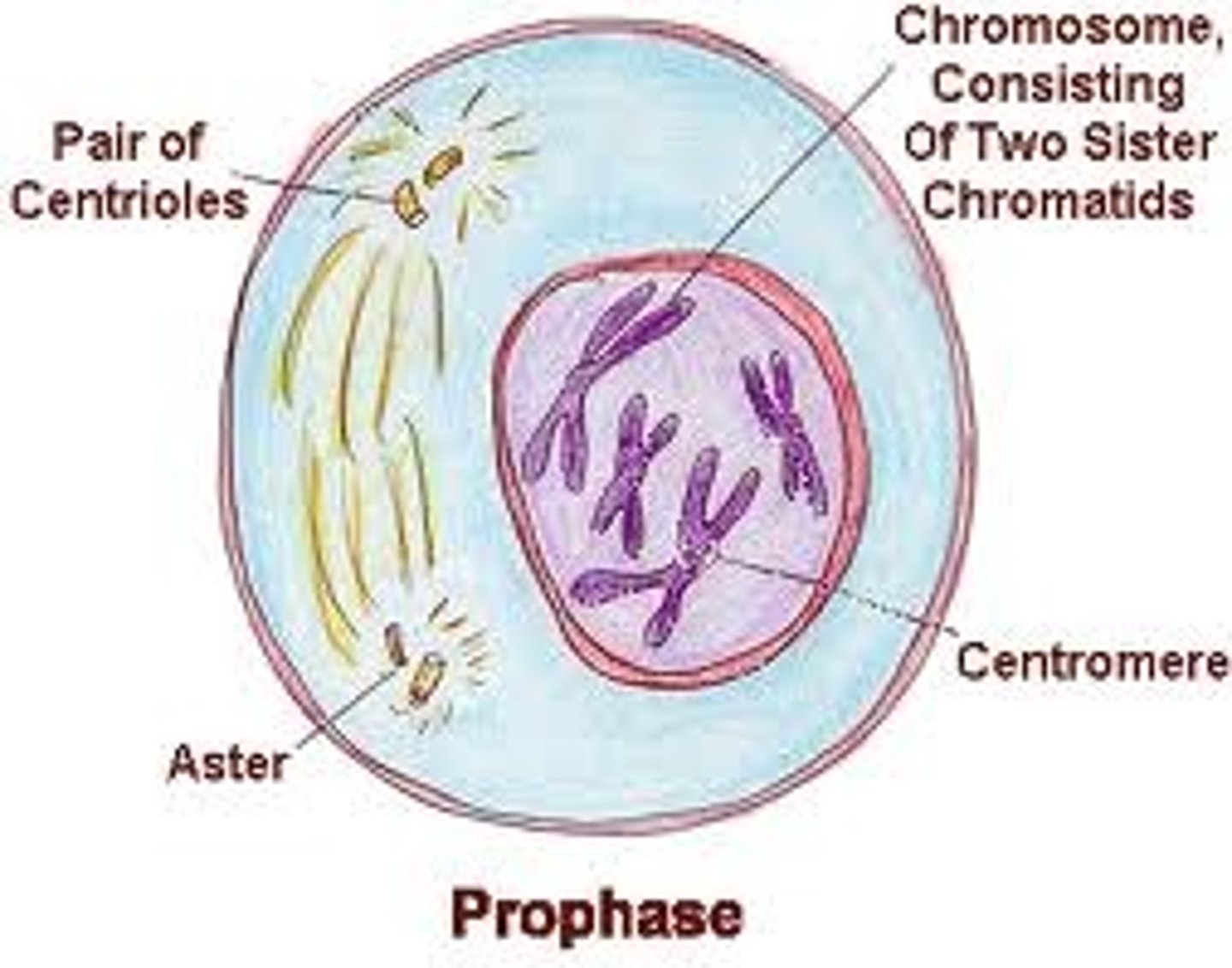
Prophase (mitosis)
chromosomes condense and spindle apparatus begins to form
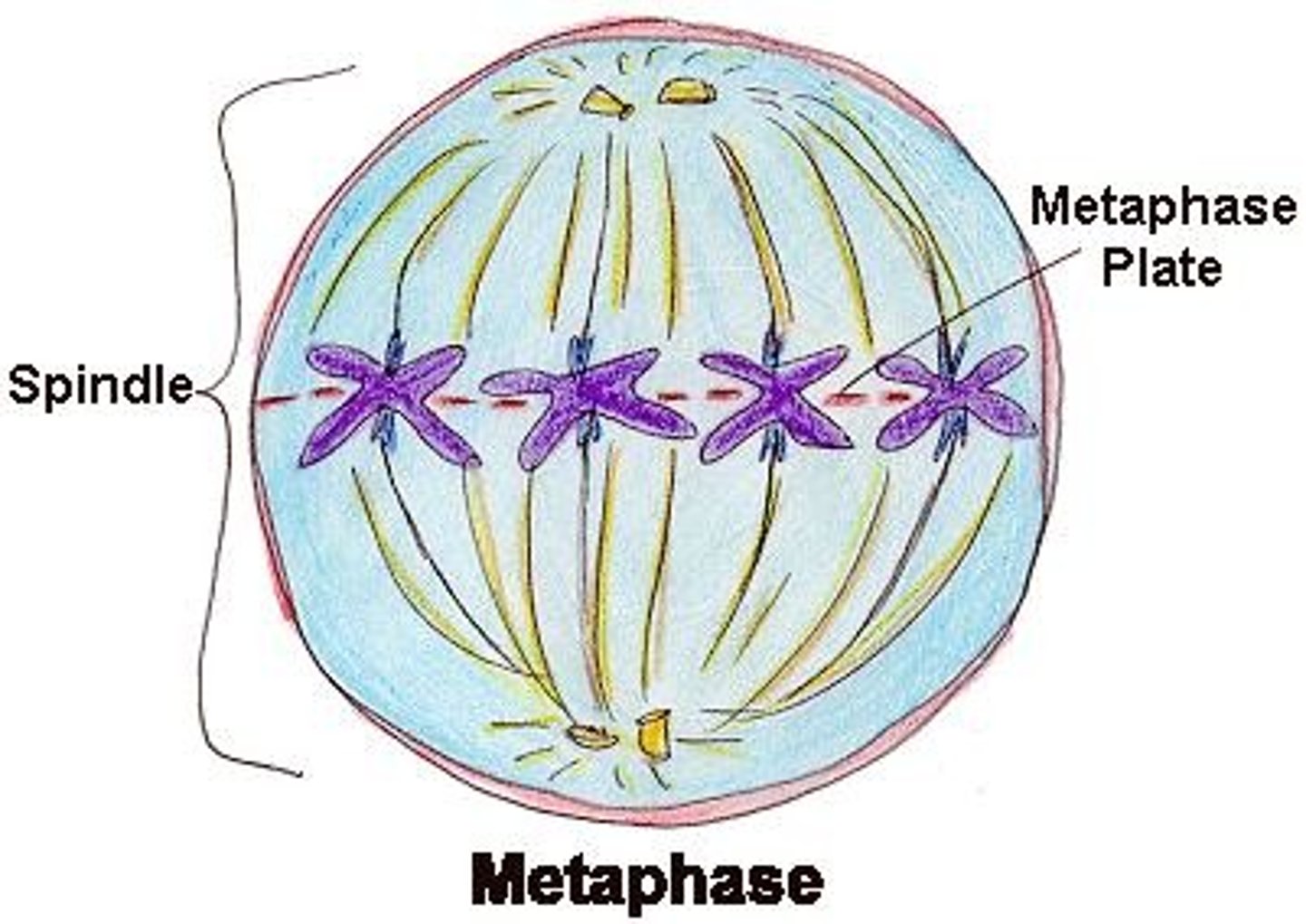
Metaphase (mitosis)
chromosomes align at spindle equator midway between spindle poles
Anaphase (Mitosis)
sister chromatids separate and become daughter chromosomes
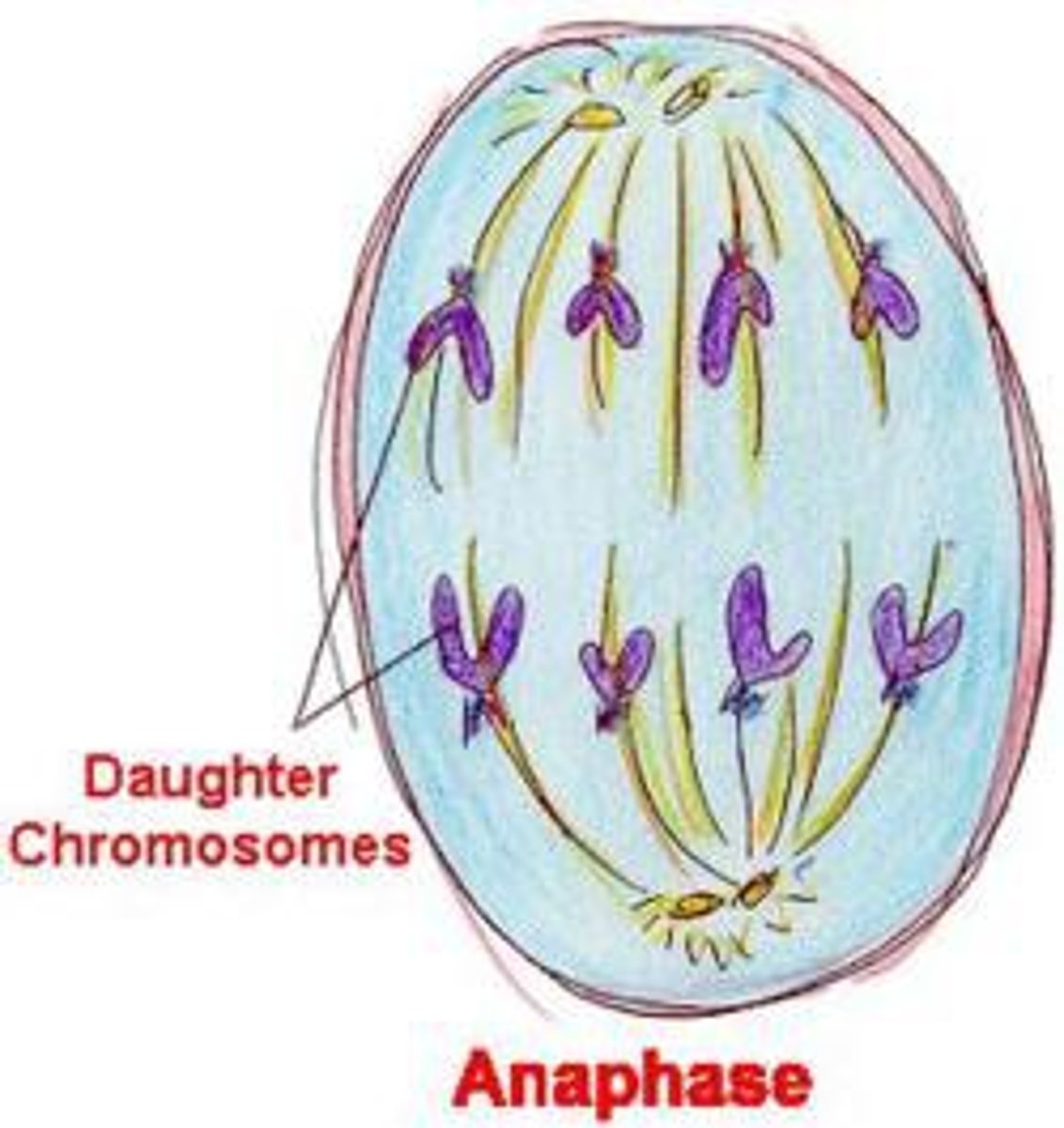
Telophase (mitosis)
spindle apparatus disappears; nuclear membrane forms around each set of newly formed chromosomes
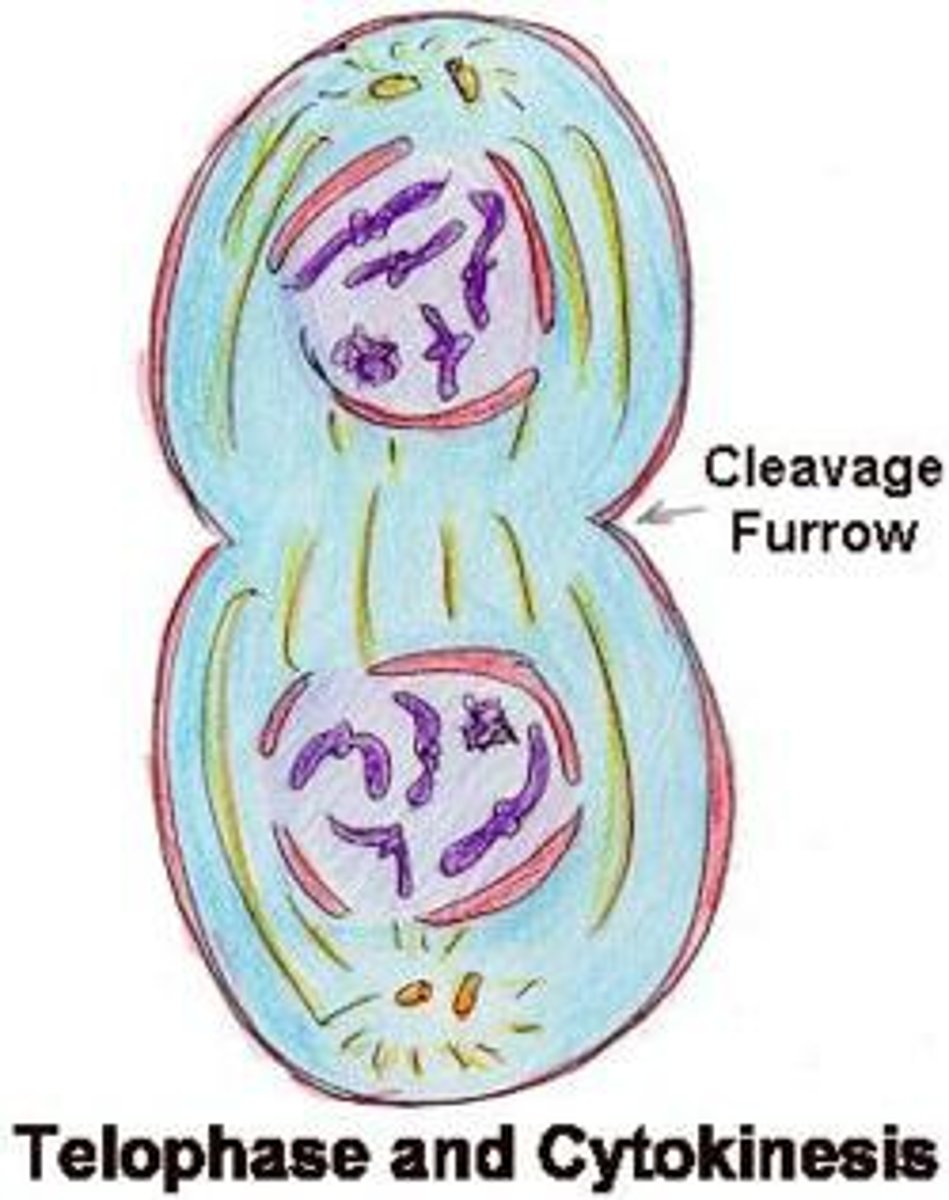
Cytokinesis in animal cells
cleavage furrow
cytokinesis in plant cells
cell plate forms
Why is meiosis important?
because the chromosome number stays constant between the generations of individuals and because the daughter cells, and therefore the gametes are genetically different.
How many divisions occur in meiosis?
2 divisions
how many divisions occur in mitosis?
1 division
Meiosis results in four____ daughter cells, different from each other genetically and from the parent cell.
haploid
Mitosis results in two_____ daughter cells, genetically identical to the parent cell.
diploid
Phases of meiosis
Prophase 1, Metaphase 1, Anaphase 1, Telophase 1, Prophase 2, Metaphase 2, Anaphase 2, Telophase 2
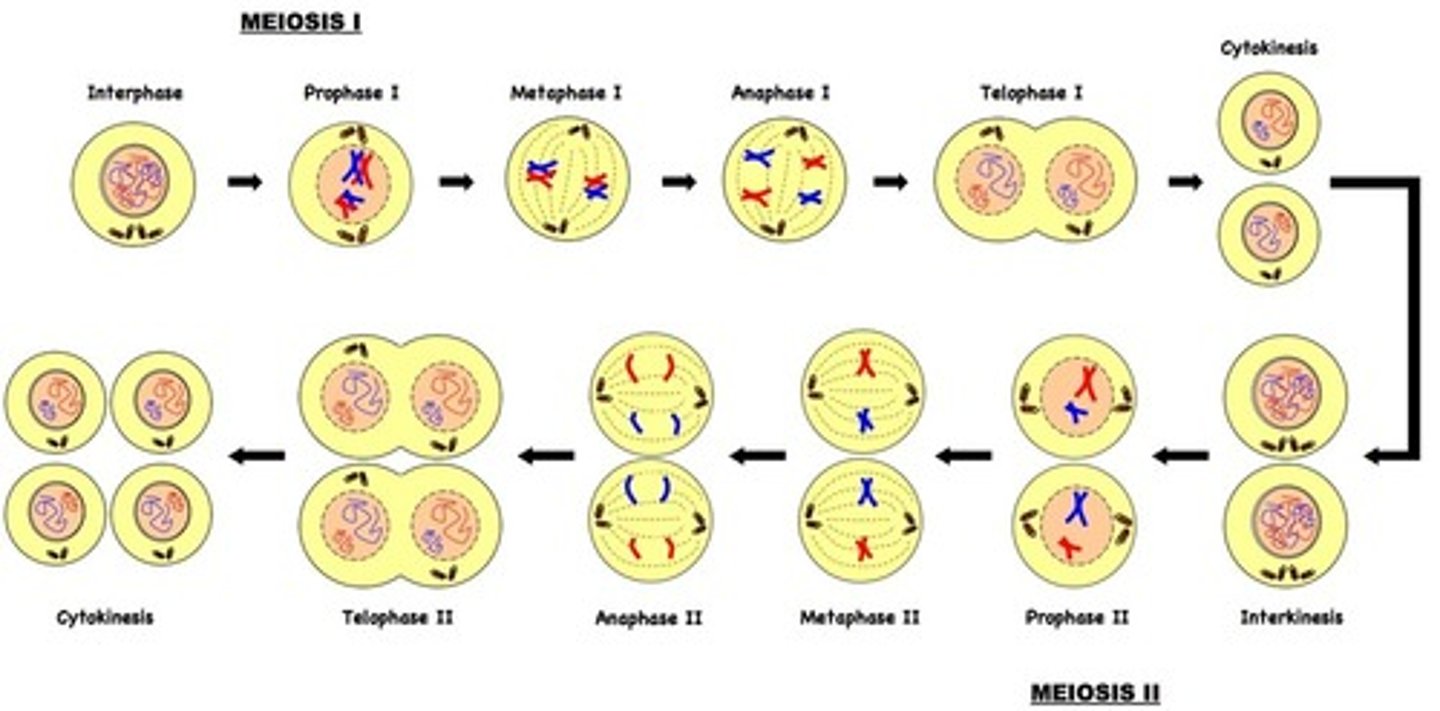
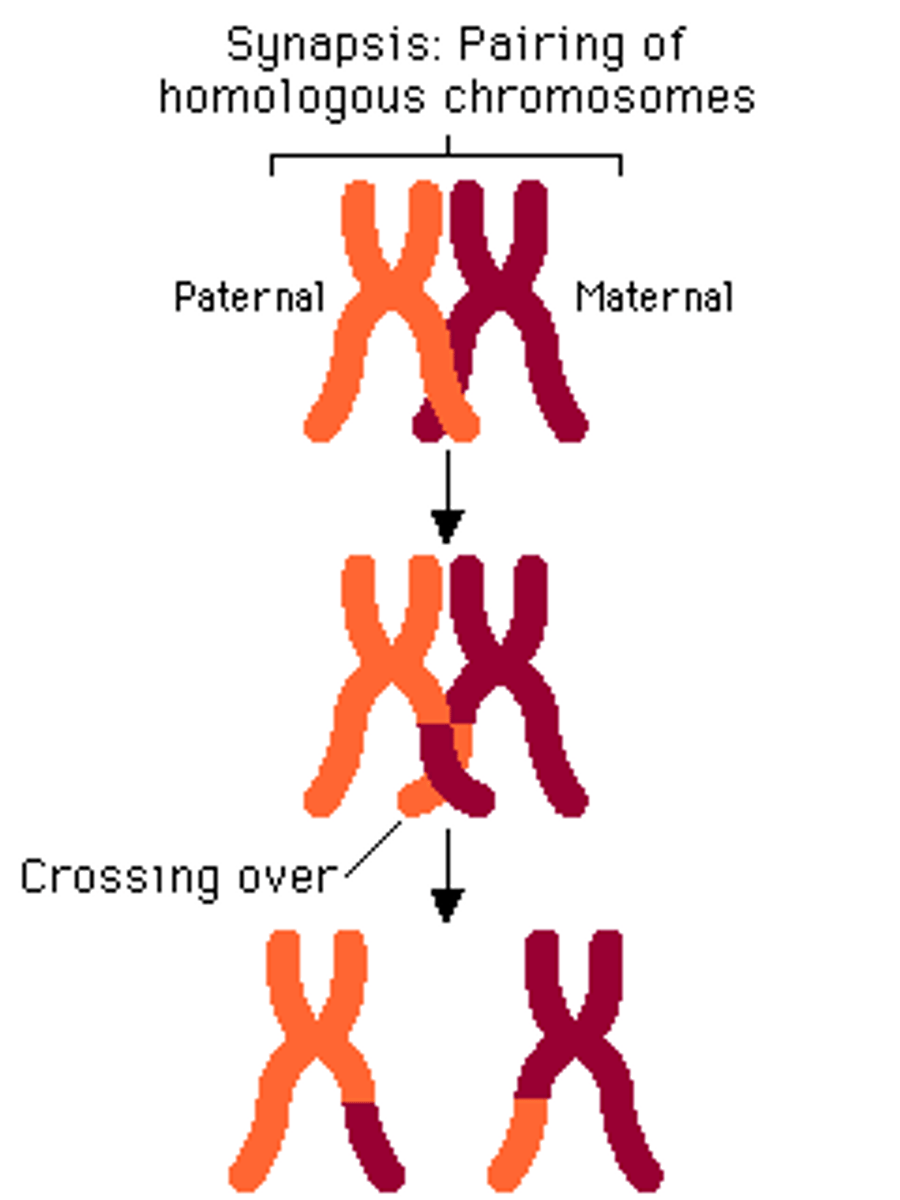
Meiosis Prophase 1
pairing of homologous chromosomes; crossing over
Meiosis Metaphase 1
homologous chromosome pairs align independently at spindle equator.
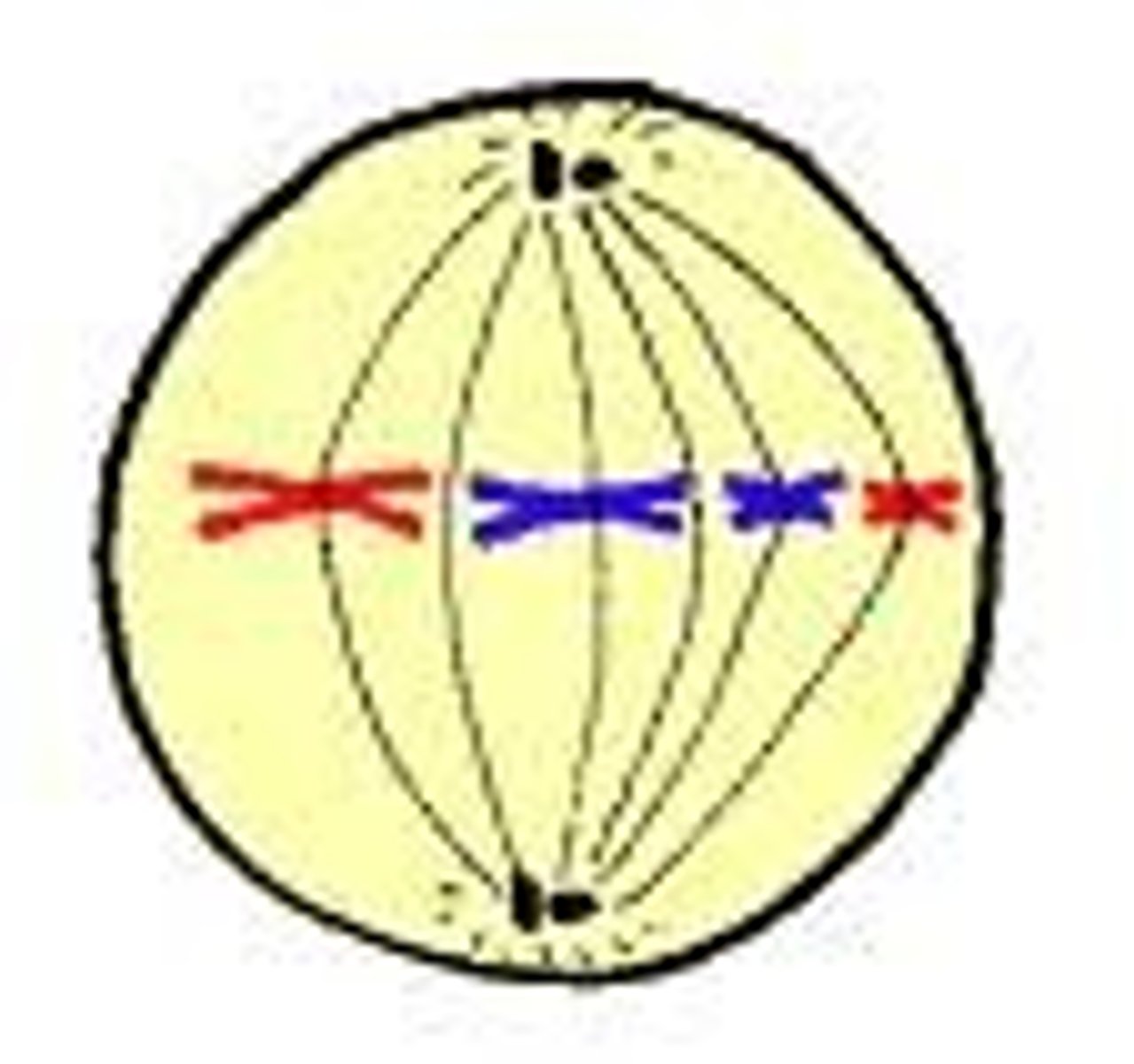
Meiosis Anaphase 1
homologous pairs separate and are pulled to opposite poles of cell; this is called disjunction when they are pulled apart; daughter cells get a mixture of mom and dads chromosomes
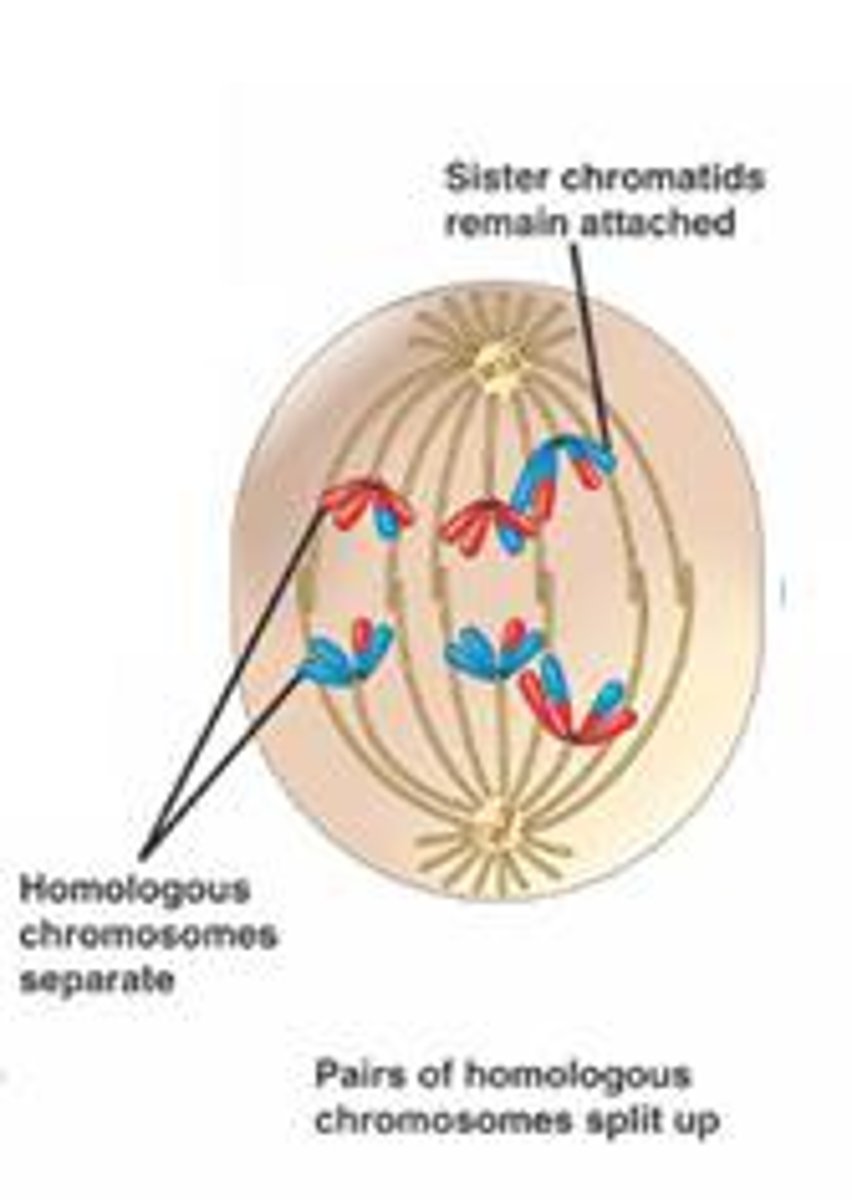
Meiosis Telophase 1
two haploid daughter cells, not identical to the parent
Meiosis Prophase 2
No pairing of chromosomes
Meiosis Metaphase 2
Haploid number of chromosomes at spindle equator
Meiosis Anaphase 2
sister chromatids separate becoming daughter chromosomes that move to the poles
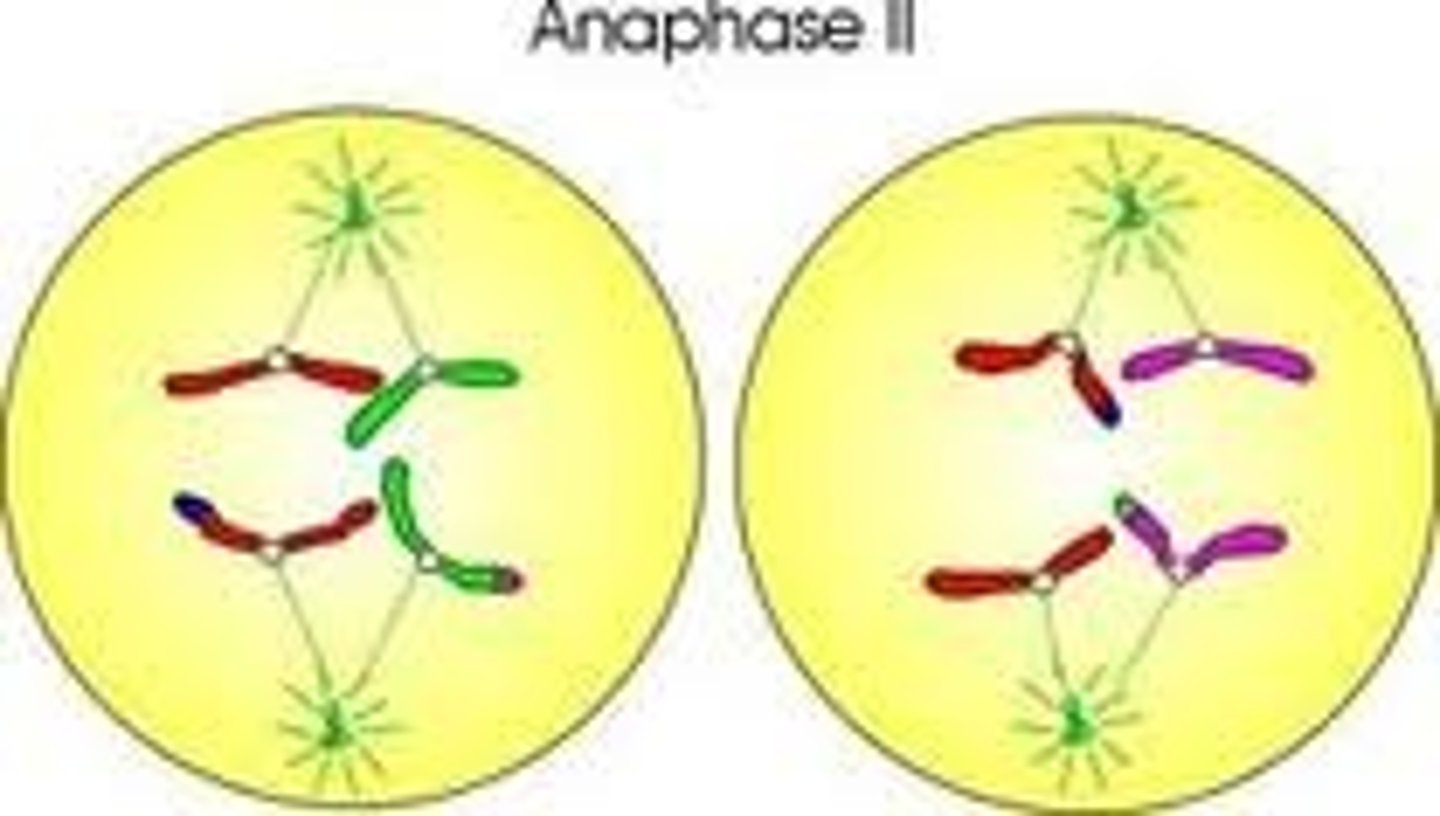
Meiosis Telophase 2
Four haploid daughter cells, different from each other genetically and from the parent cell
Define producers
plants/makes their own food
define consumers
animals/have to eat producers
In what organelle does photosynthesis occur?
Chloroplast
what are the names of the 2 sets of reactions involved in photosynthesis?
light reactions and Calvin cycle reactions
what part of chloroplasts do the light reactions occur?
thylakoid membrane
what part of chloroplasts does the Calvin cycle occur?
stroma
what is the energy source that chloroplasts use to generate atp?
solar engergy
The law of segregation states that
an individual has two alleles, but the gametes have only one allele for every trait.
The law of independent assortment states that
the gametes have all possible combinations of alleles
Genotype
refers to the alleles an individual receives at fertilization (AA, Aa, aa)
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
Homozygous
having two identical alleles for a trait
Heterozygous
having two different alleles for a trait
incomplete dominance
heterozygous phenotype that is a blend of the two homozygous phenotypes
Codominance
A condition in which neither of two alleles of a gene is dominant or recessive.
Pleiotropy
when a single gene affects multiple traits
Polygenetic inheritance
several genes that affect 1 characteristic
Cellular Respiration
the aerobic harvesting of chemical energy from organic fuel molecules