unit 3 economics
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
12th grade ap microeconomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
explicit cost
a cost that involves spending money
implicit cost
- opportunity cost
- cost of resources already owned by the firm that could have been put to some other use
accounting profit
total revenue - explicit cost
economic profit
total revenue - (explicit + implicit costs)
economic profit
- anything above normal profit
- called normal profit if the profit equals zero
normal profit
minimum level of profit needed for a company to remain competitive in the market and cover their explicit and implicit costs
economic cost
always lower because they add the accounting cost/opportunity cost
short run production
- some cost(s) is/are fixed (ex: more workers but no more resources)
- change in variable costs shifts market supply
- changes in fixed costs will not change firm or market output or pricing (only shifts ATC upwards)
- no entry or exit of new firms or tech
- firm is constrained in regard to what production decisions it can make
long run production
- all costs are variable (ex: company can have infinite number of resources)
- market supply shifts with firm entry/exit
- tech can be developed to improve production
- firm chooses from all possible production techniques
law of diminishing marginal product/returns
- only exist in the short run
- averages aren't a good reflection bc it doesn't tell the whole story
- ex: too many workers in the short run will diminish productivity
law of diminishing marginal product/returns stages
- increasing marginal returns
- diminishing returns: begins where MC is minimized (bc next unit of output will be produced at a higher cost) and MP is maximized
- negative returns: begins where MP = 0
law of diminish marginal product/returns relationships
- MP & MC: inverse
- AP & AC = inverse
- highest point of AP = MP
- lowest point of AC = MC
total variable cost (TVC)
costs that can change over time and depend on production
total fixed cost (TFC)
- costs that cannot change in the short run
- not related to the amount of production
- found between TVC and TC
total costs (explicit & implicit costs)
total variable cost + total fixed cost
average fixed cost (AFC)
TFC/Q
average variable cost (AVC)
TVC/Q
average total cost (ATC)
AFC + AVC
marginal cost (MC)
additional cost to produce one additional output
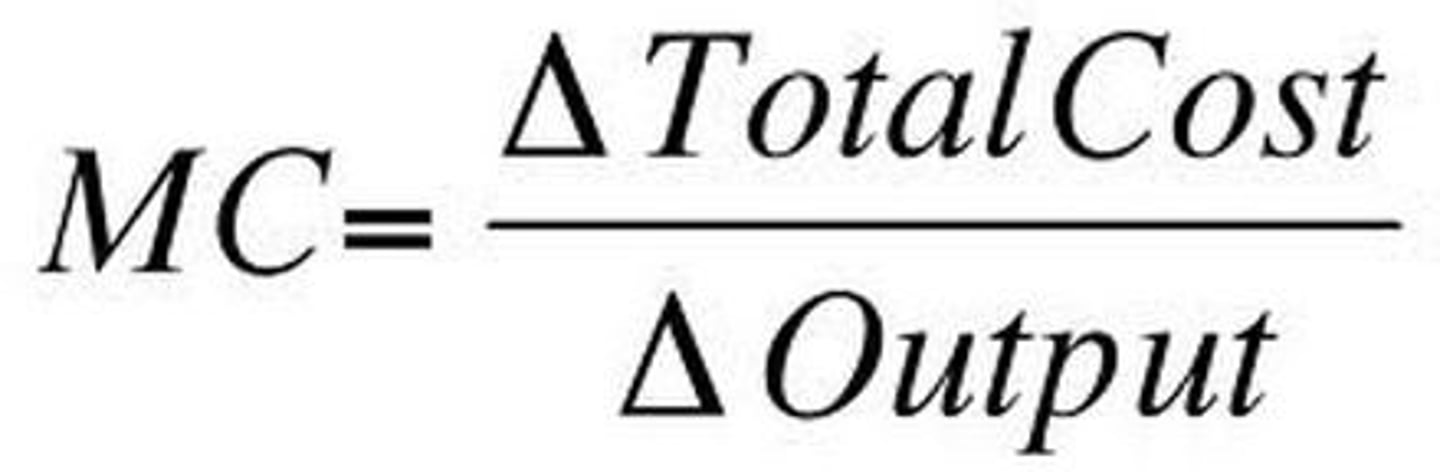
AVC and ATC
distance between the curves must shrink as the company produces more output
lump sum taxes
- one time tax that only impact the firm's fixed costs
- quantity will not change
- ATC will shift upwards
lump sum subsidies
- one time payment that only impact the firm's fixed costs
- quantity will not change
- ATC will shift downward
per unit tax
- taxes charged to each unit that only impact the firm's variable costs
- quantity will change
- ATC, MC, & AVC will shift upward
per unit subsidies
- payments provided for each unit that only impact the firm's variable costs
- quantity will change
- ATC, MC, & AVC will shift downward
economies of scale
- LRATC decreases as output increases
- long run concept
constant returns to scale
- LRATC is constant as output increases
- minimum efficient scale occurs at lowest point in LRATC
- long run concept
diseconomies of scale
- LRATC increases as output increases
- long run concept
LRATC
long run average total costs increase as firms exhaust all forms of production methods and resources become scarce
profit maximization rule
MR = MC
shut down rule
- firms should shut down when they cannot cover any portion of their variable expense/ the price falls below the minimum AVC
- occurs in the short run
- AVC is above MRDARP
perfect competition
- price is determined by the market
- many firms (each being a price taker)
- identical products
- easy entry and exit
- long run: returns to normal profits
price takers
- they take the price they are given and can't change the price
- no market power
market power
ability to set one's own prices
short run (perfect competition)
- profits and loss
- marginal revenue looks like a horizontal line
long run (perfect competition)
- profits always return to normal profit/ zero economic profit
- no profits or loss
- minimum point of ATC hits MR
- lump sum tax increases fixed costs -> ATC increase -> firms exit
- per unit tax increases variable costs -> ATC & MC increase -> firms exit
productive efficiency
- production = lowest ATC
- perfectively competitive firms will always return to this point in the long run
allocative efficiency
- price = MC
- no deadweight loss
- quantity of output produced achieves the greatest level of total welfare possible
market
- sets the price
- consists of many different ranges of elasticities
firm
- takes price from market
- costs do not change when there is entry/exit
- faces a perfectly elastic demand
- too small to take advantage of economies of scale
- in long run, will produce at productively efficient and allocatively efficient point
marginal cost changes
only when variable costs changes
marginal product = 0
total product is maximized bc the change in total product is 0