OIA1012 AMIDES & AMINES
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Definition of Amides
Organic compounds containing a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a nitrogen atom (-NH2, -NHR, -NR2).
Naming Amides
Replace "-oic acid" in carboxylic acids with "-amide" (e.g., ethanoic acid → ethanamide).
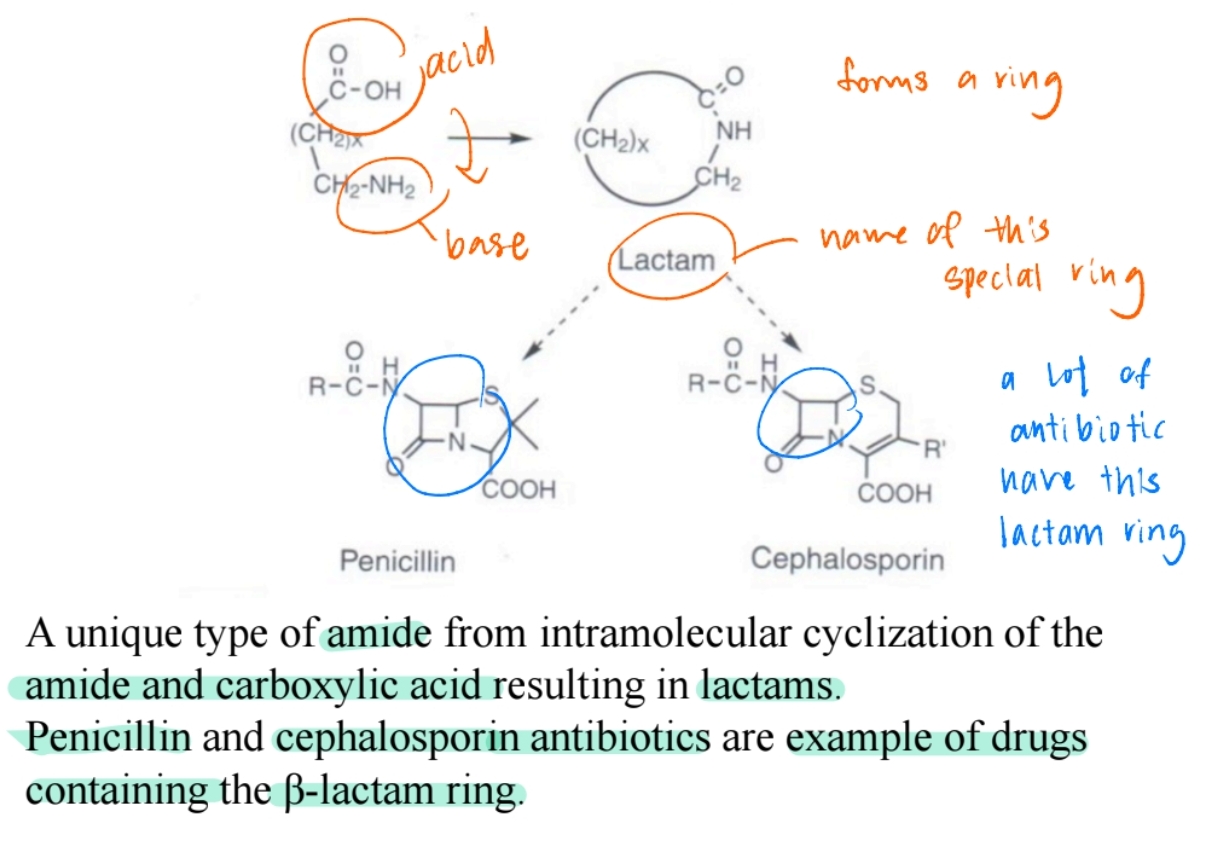
Lactams
Cyclic amides, found in antibiotics like penicillin and cephalosporins.
Physical Properties
- High boiling points due to hydrogen bonding.
- Lower amides are water-soluble; solubility decreases with size.
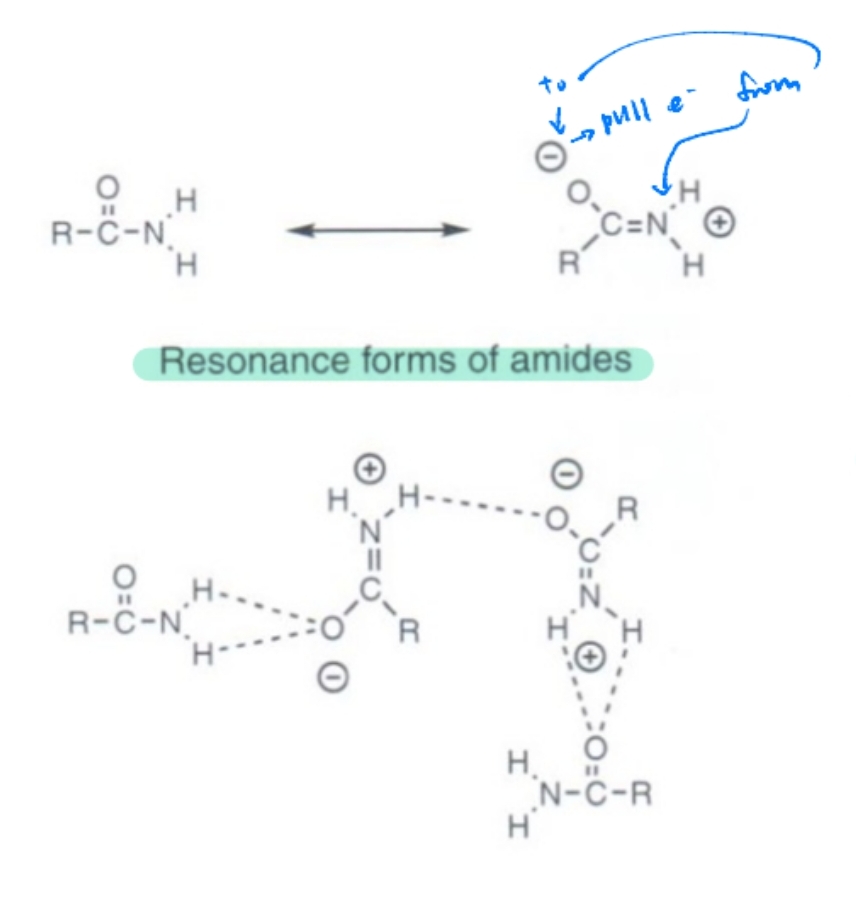
Resonance in Amides
Amides have partial double-bond character due to resonance, reducing basicity.
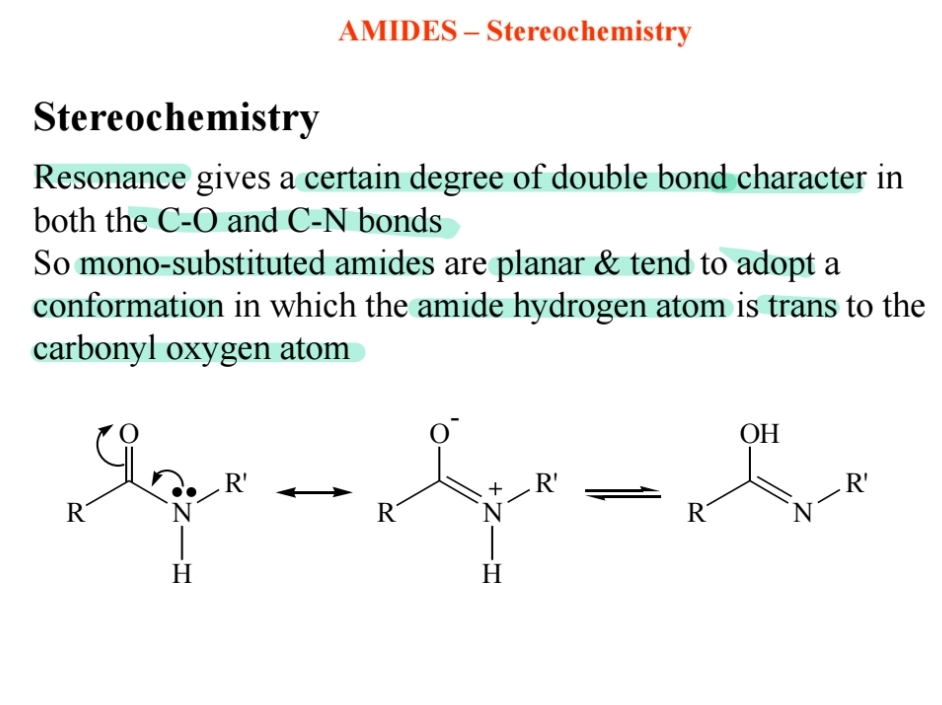
Stereochemistry of Amides
Planar structure due to resonance, with the amide hydrogen trans to the carbonyl oxygen.
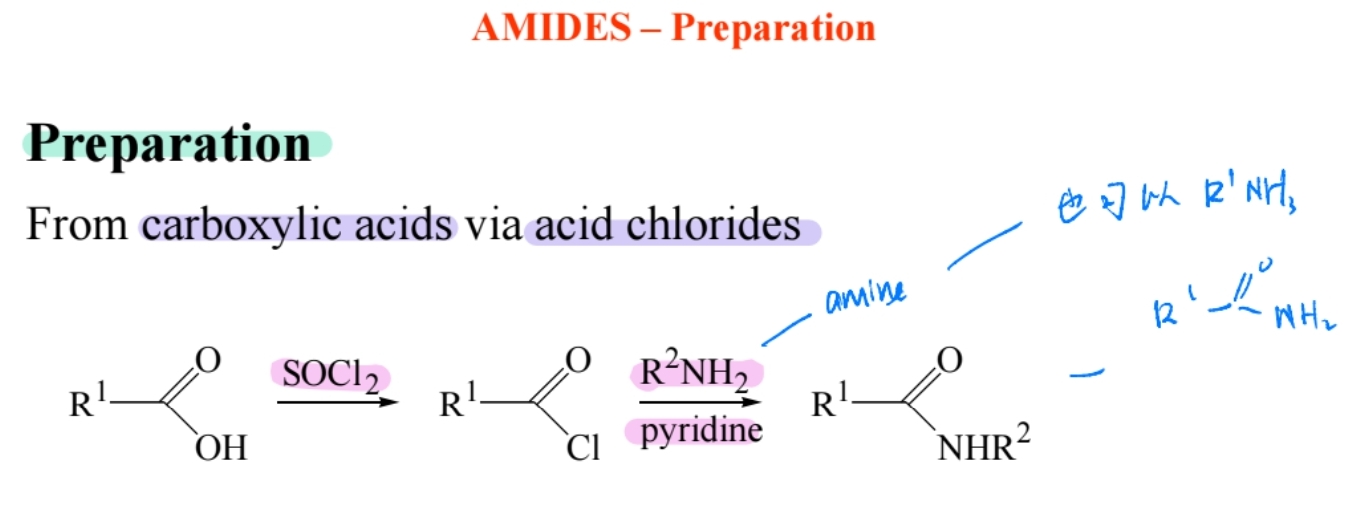
Preparation from Acid Chlorides
Reaction of acid chlorides with amines forms amides.
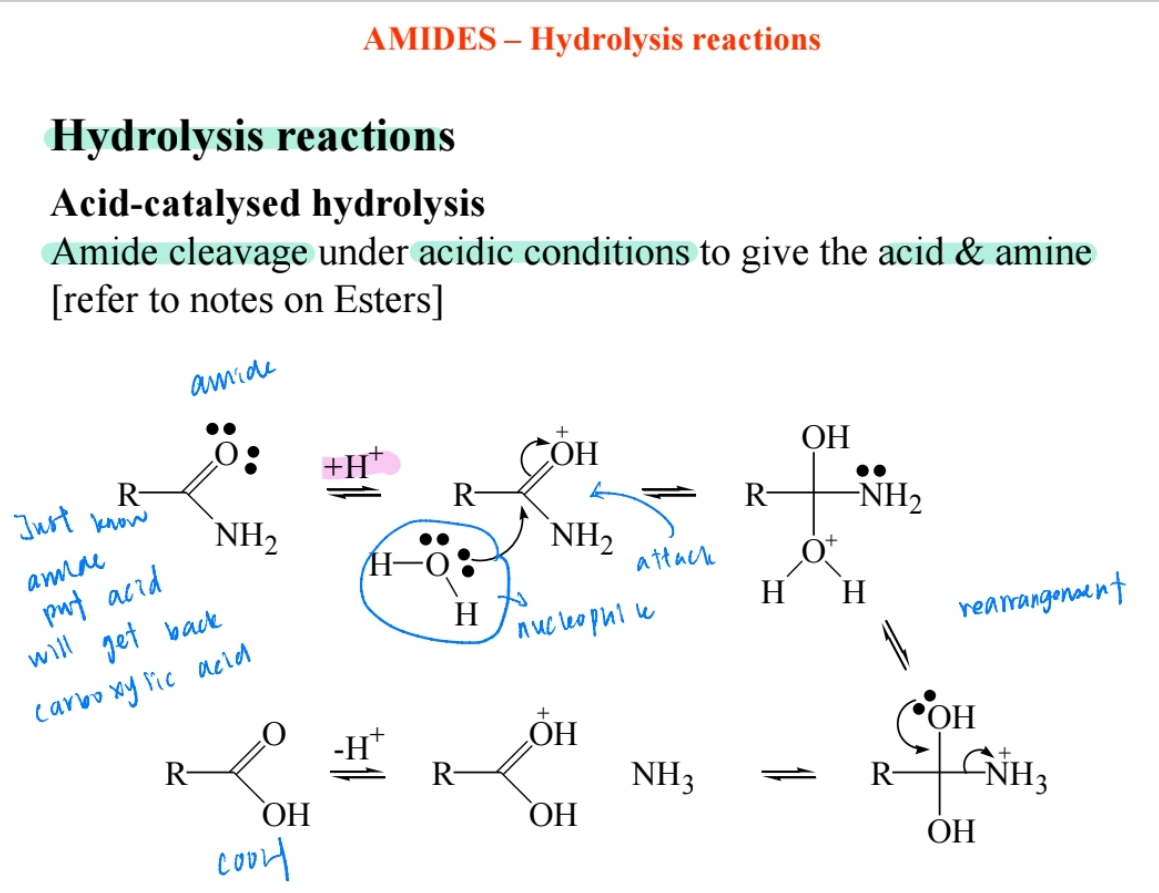
Hydrolysis in Acidic Conditions
Produces carboxylic acid and ammonium ion (NH4+).
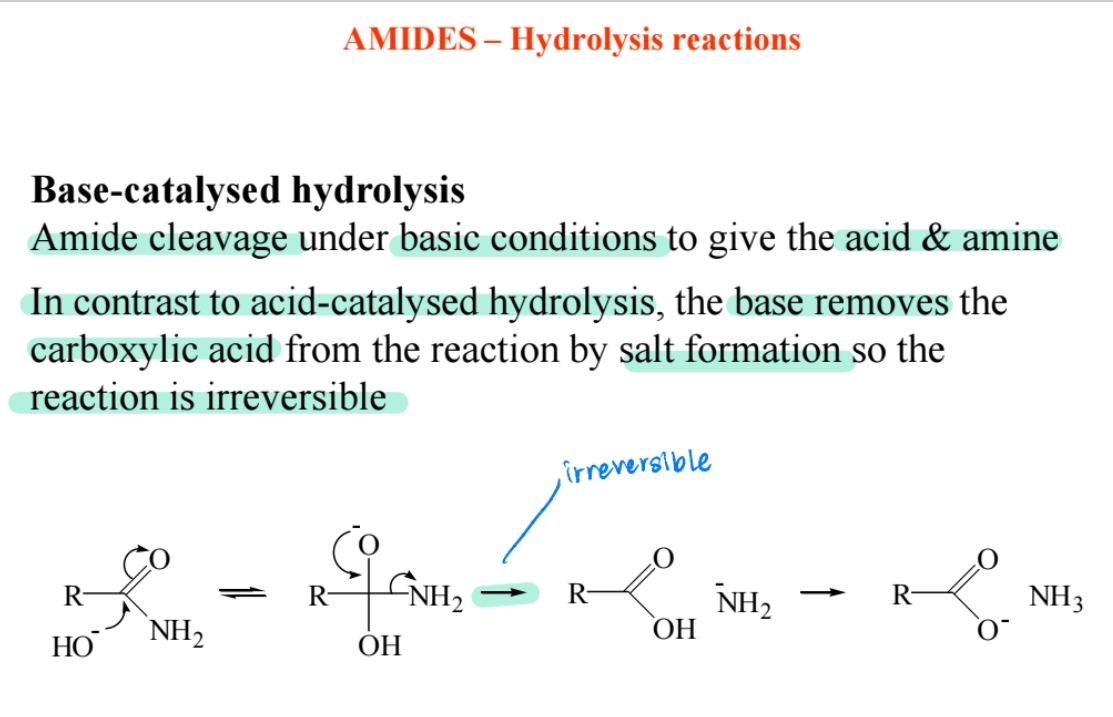
Hydrolysis in Basic Conditions
Produces carboxylate salt and amine; irreversible.
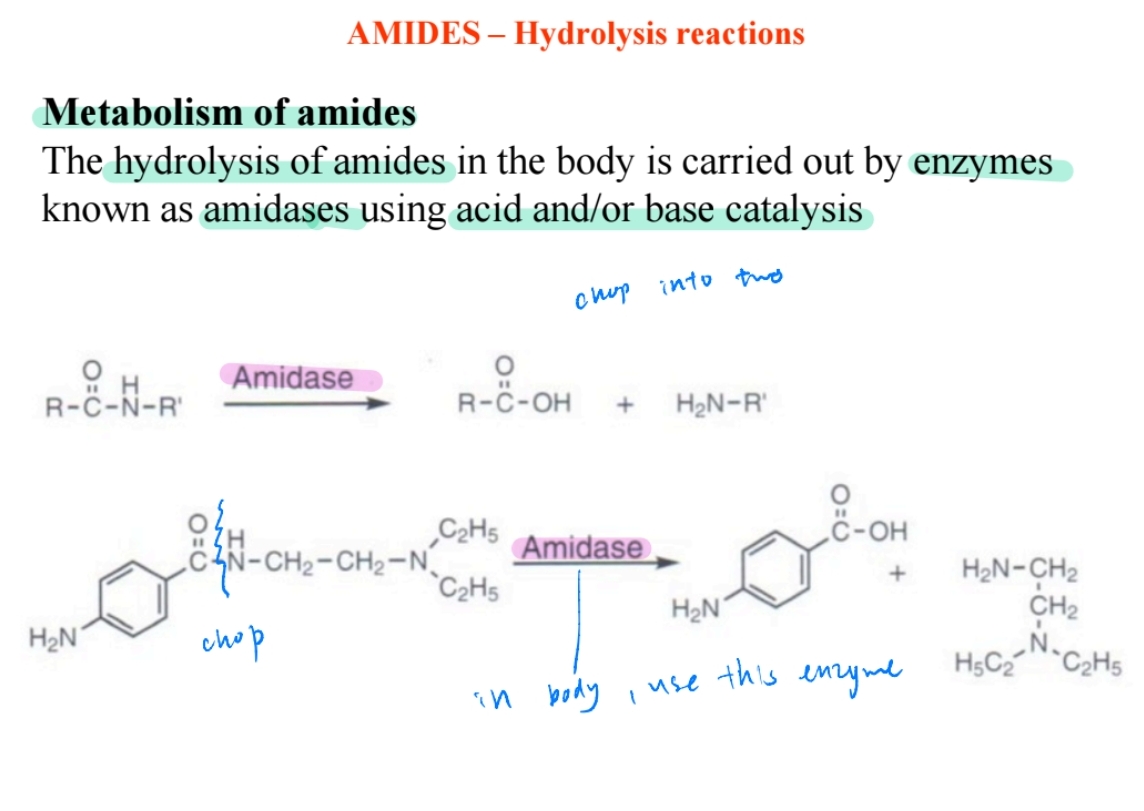
Amidase Enzymes in Metabolism
Enzymes hydrolyze amides in the body into acids and amines.
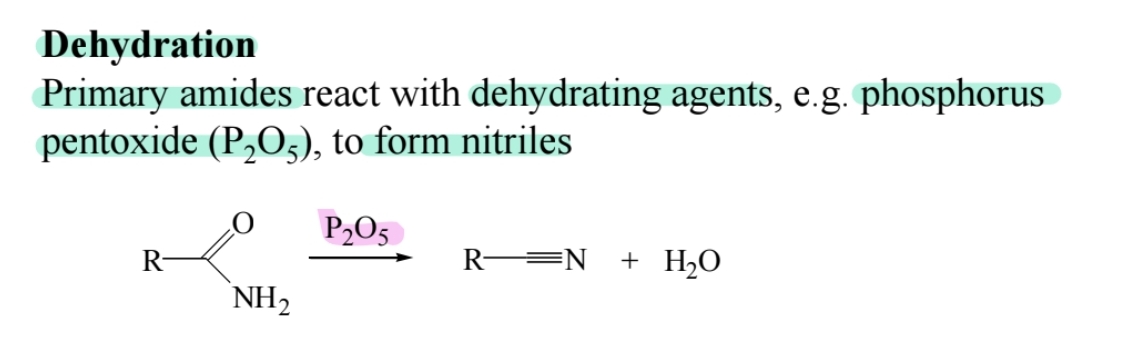
Dehydration to Nitriles
Treating primary amides with (P2O5) forms nitriles.
Hofmann Rearrangement
Primary amides react with bromine in alkaline solution to form amines with one fewer carbon.
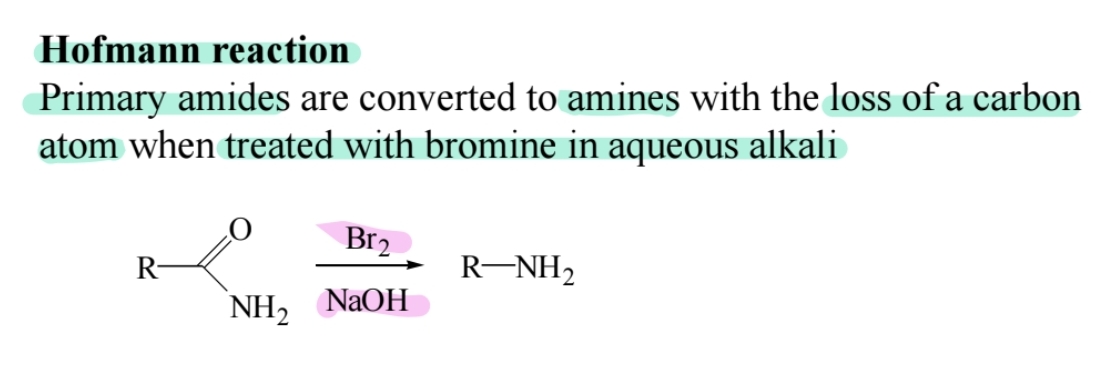
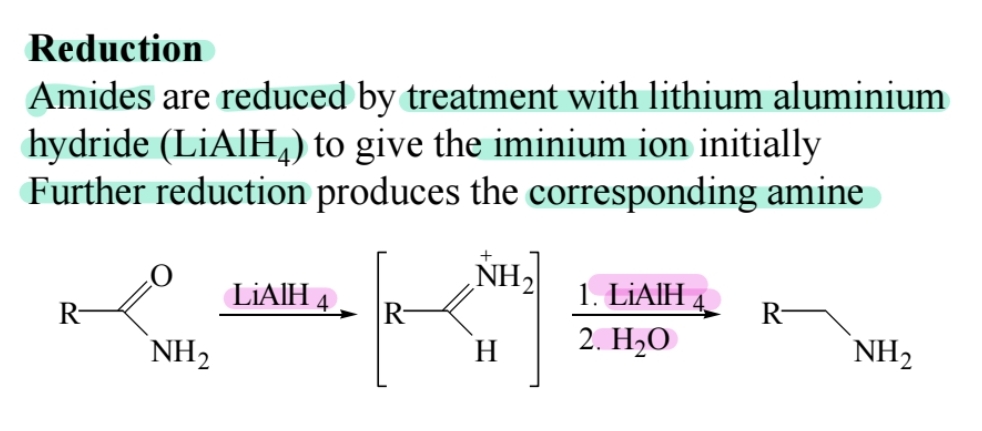
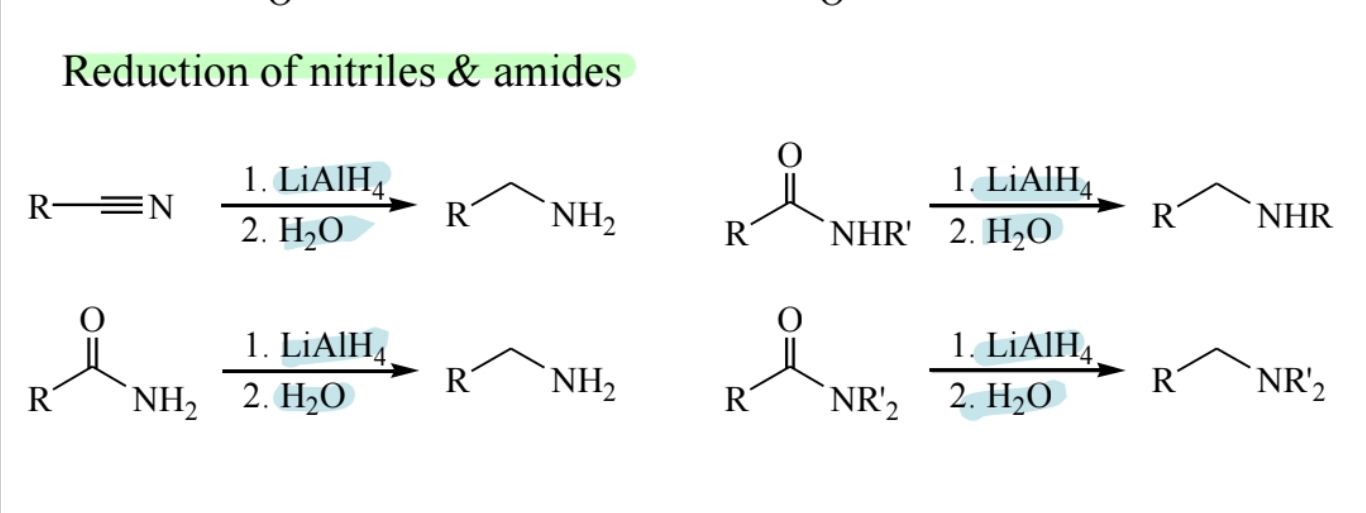
Reduction to Amines
Lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) reduces amides to amines.
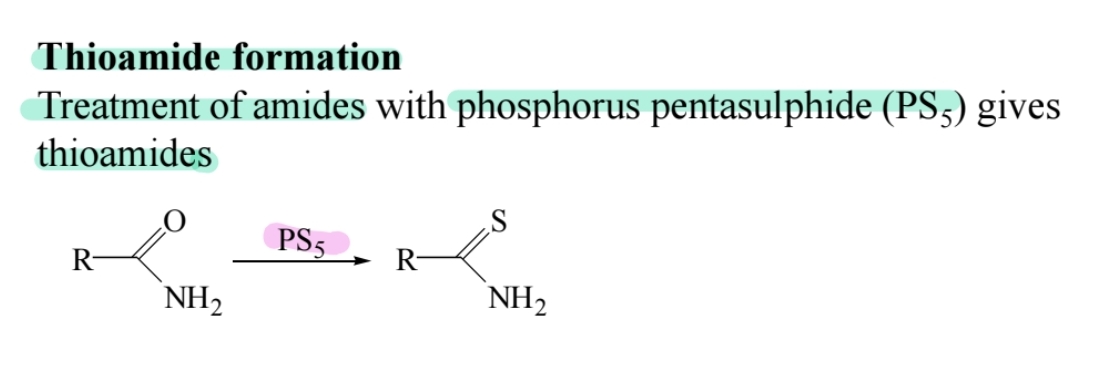
Thioamide Formation
Amides react with (P2S5) to form thioamides (-C=S).
Definition of Amines
Organic derivatives of ammonia (NH3), classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
Naming Amines
- Replace "-e" in alkanes with "-amine" (e.g., ethane → ethylamine).
- For multiple functional groups, use "amino-" as a prefix.
Physical Properties
- Low molecular weight amines are gases or liquids with a fishy odor.
- Higher amines and aromatic amines have higher boiling points and lower solubility.
Basicity of Amines
- Due to the lone pair on nitrogen, amines act as proton acceptors.
- Strength increases with alkyl substitution due to electron donation.
Aliphatic vs. Aromatic Amines
- Aliphatic amines are stronger bases than ammonia.
- Aromatic amines are weaker due to delocalization of the nitrogen lone pair.
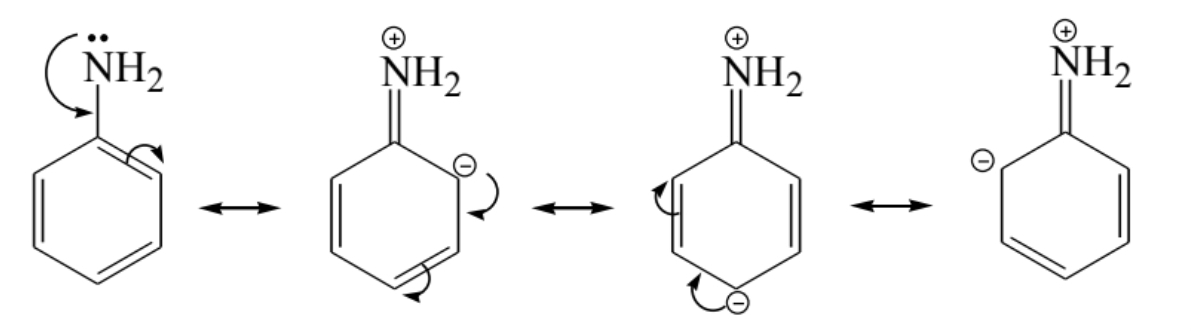
Amides vs. Amines in Basicity
- Amides are weaker bases than amines because of resonance stabilization.
Salt Formation in Pharmaceuticals
- Amines react with acids to form stable, water-soluble salts used in drugs.
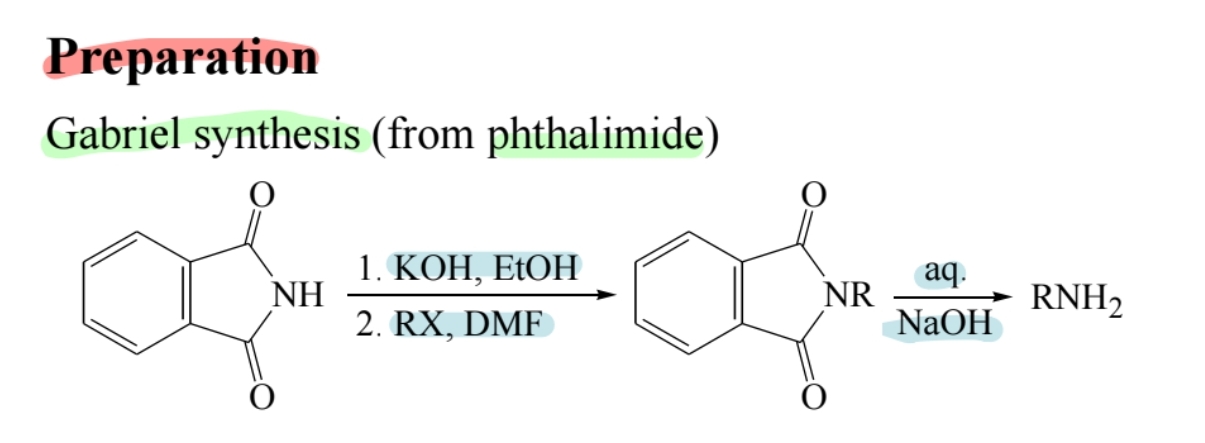
Gabriel Synthesis
Produces primary amines from phthalimide.
Reduction of Nitriles and Amides
(LiAlH4) reduces nitriles and amides to amines.
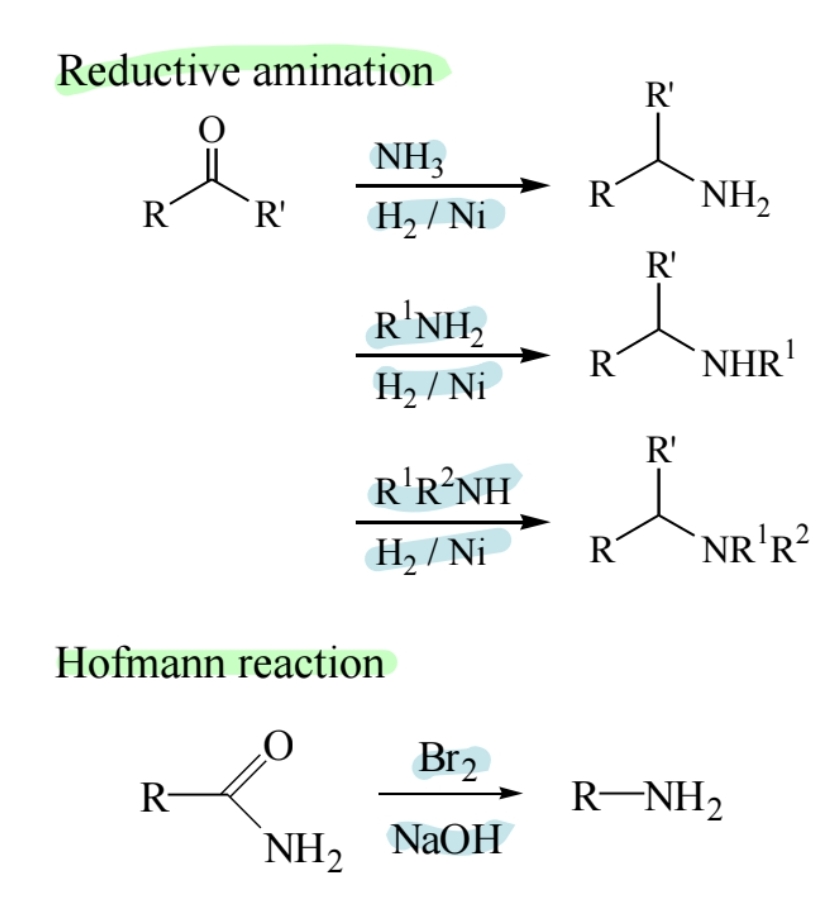
Reductive Amination
Aldehydes or ketones react with ammonia or amines in the presence of reducing agents to form amines.
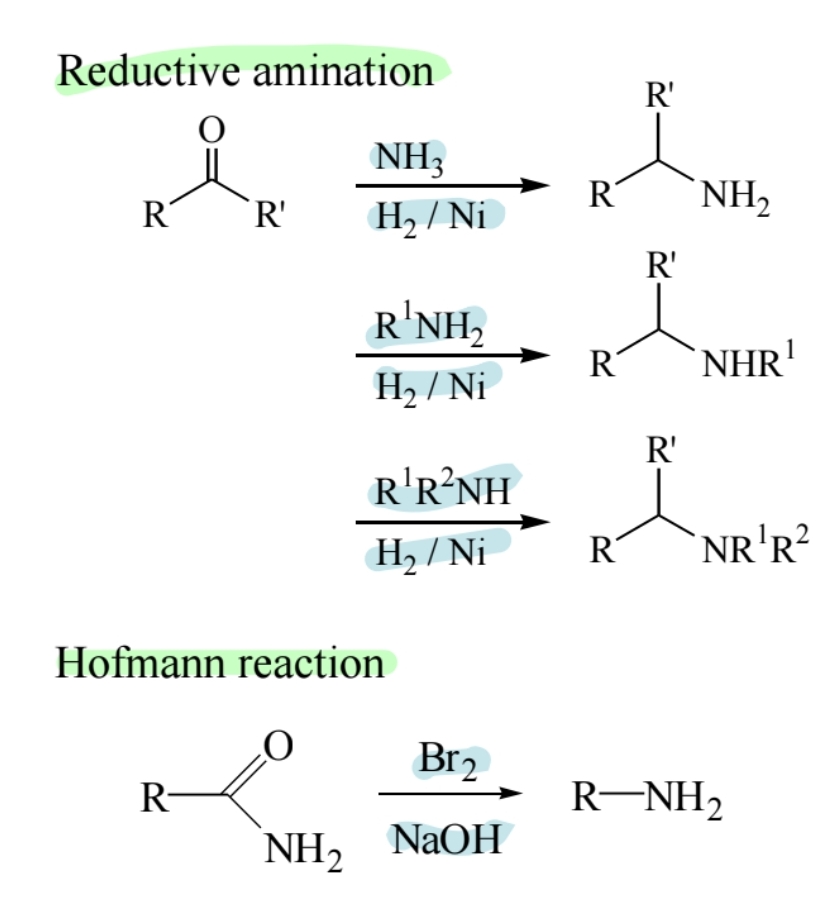
Hofmann Rearrangement of Amides
Converts amides to amines with loss of one carbon atom.
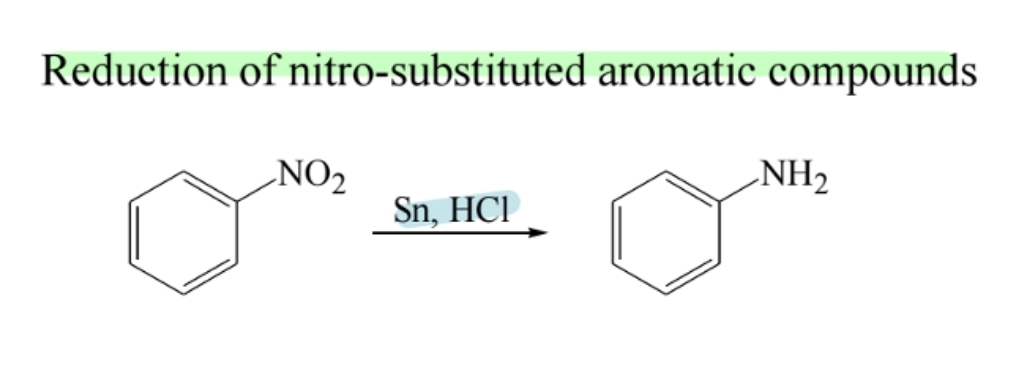
Reduction of Nitro Compounds
Nitrobenzenes reduce to anilines using Sn/HCl or catalytic hydrogenation.
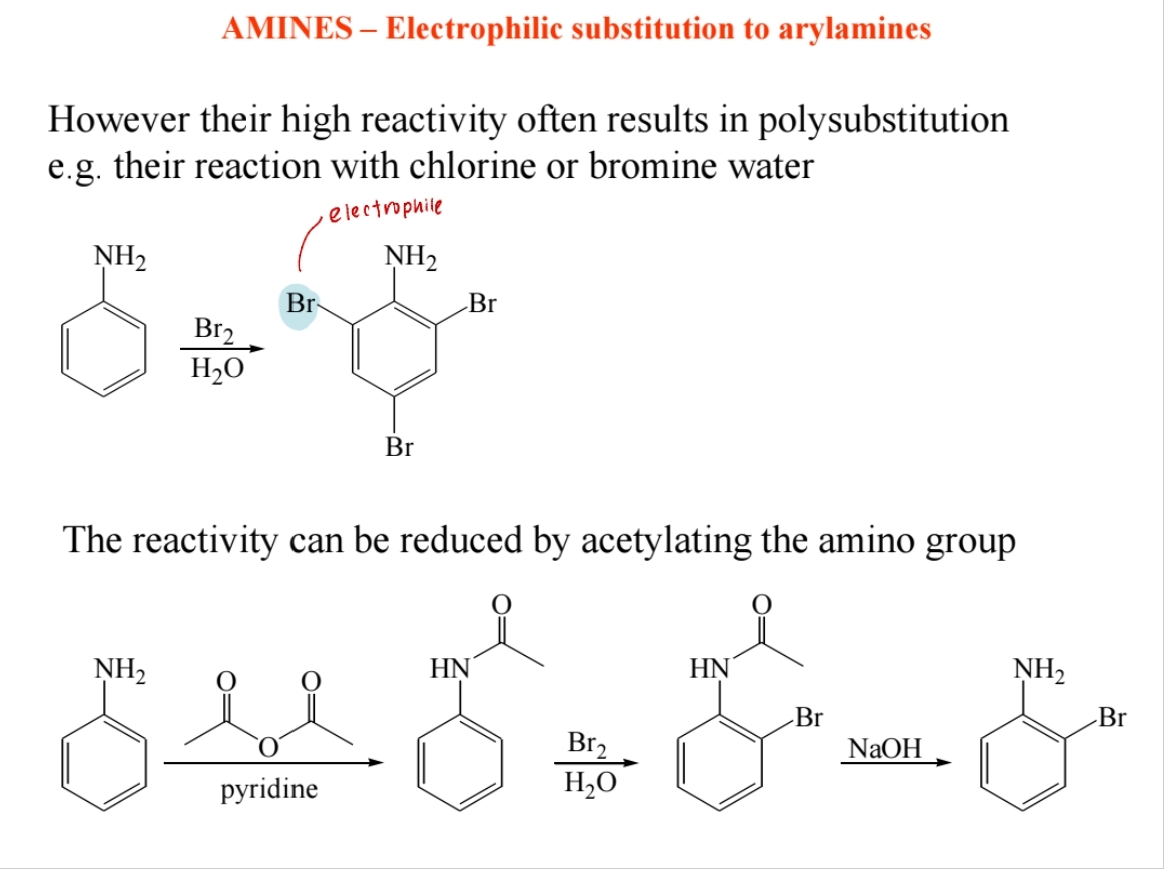
Nucleophilic Alkylation
Amines react with alkyl halides, forming secondary and tertiary amines.
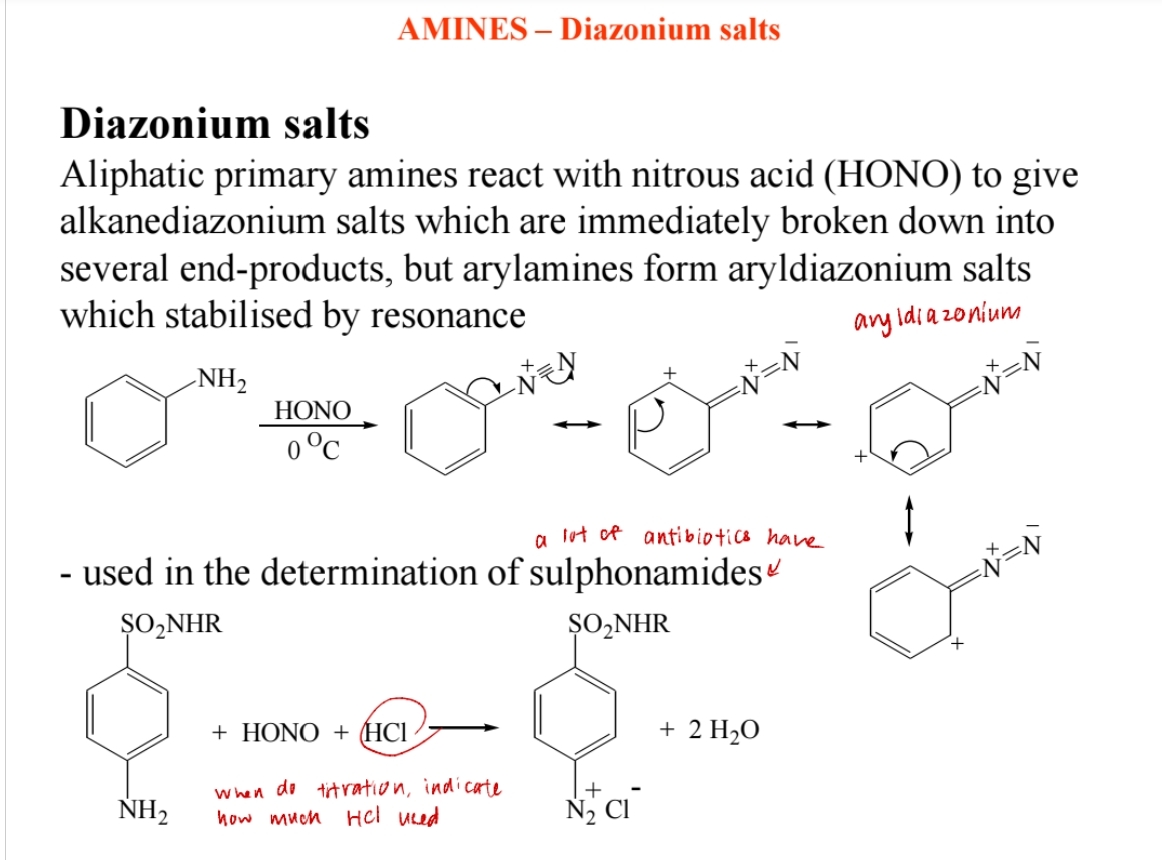
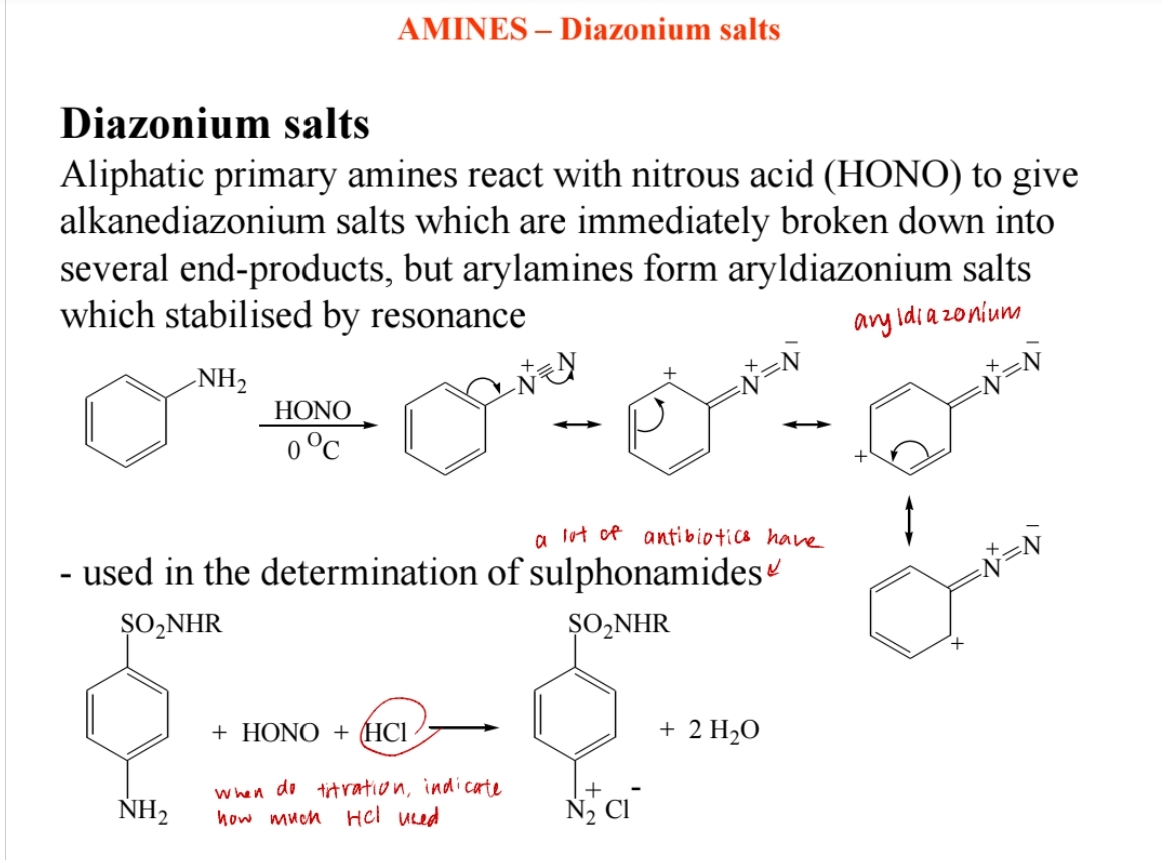
Diazonium Salt Formation
Aromatic primary amines react with nitrous acid (HNO2) to form diazonium salts.
Diazo Coupling Reactions
Aryldiazonium salts react with phenols or aromatic amines to form azo dyes.
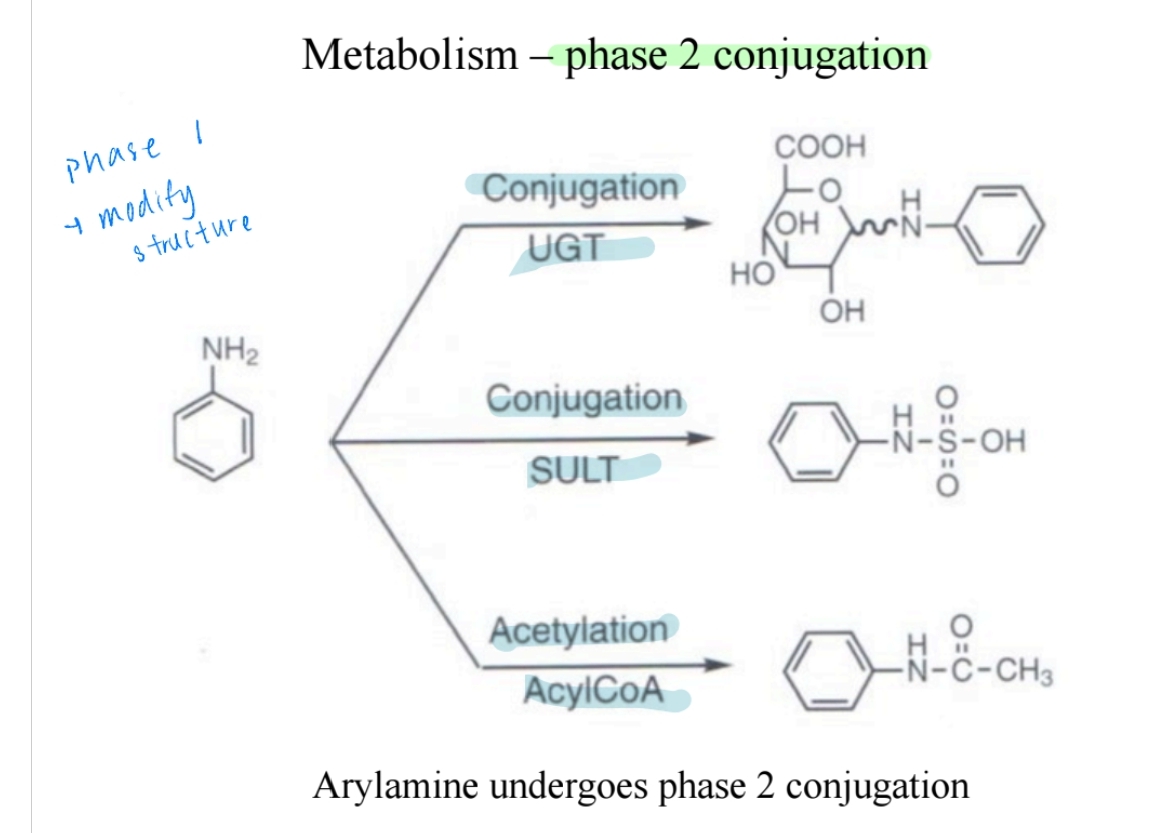
Metabolism: Dealkylation and Oxidation
- Secondary and tertiary amines undergo dealkylation in metabolism.
- Oxidation converts amines into N-oxides or nitroso compounds.