Decision Maths - Edexcel
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:35 AM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
Activity
A job or process that forms part of an overall project.
2
New cards
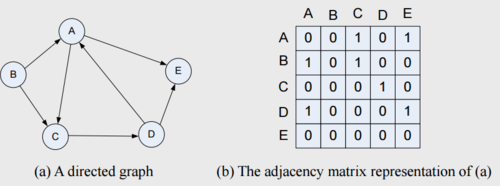
Adjacency Matrix
A way of representing a graph on a matrix. Rows and columns respond to vertices, and the entries in the matrix correspond to the number of edges from one vertex to another.
3
New cards
Algorithm
A sequence of precise instructions to solve a problem.
4
New cards
Complete graph
A simple graph in which every pair of vertices is connected by an edge.
5
New cards
Connected graph
A graph is connected if a path exists between every pair of vertices.
6
New cards
Critical activity
An activity with no float - any delay to a critical activity will result in a delay for the whole project. A critical activity must lie on a critical path.
7
New cards
Critical path
A route through a precedence network on which all of the activities are critical activities.
8
New cards
Cycle
A closed path (the end of the last edge is the start of the first edge and no vertices are repeated except that the final vertex is the same as the first).
9
New cards
Degree / Order / Valency of a vertex
The number of edges connecting to it.
10
New cards
Digraph
A graph in which at least one edge has direction associated with it.
11
New cards
Distance table
A tabular representation of a network, in which each element represents the weight of the arc between two nodes on the network.
12
New cards
Edge
A line connecting two vertices (nodes) on a graph.
13
New cards
Eulerian graph
A graph in which it is possible to traverse each edge once, starting and finishing at the same vertex (all vertices have even valency).
14
New cards
Eulerian cycle
A cycle that includes each edge of a graph exactly once.
15
New cards
Even vertex
A vertex where an even number of edges meet
16
New cards
Event
An event occurs when an activity can start, or when a whole project is complete (represented by nodes on an activity network).
17
New cards
Feasible region
A region on a graph where all the constraints in a linear programming problem are satisfied.
18
New cards
Float
The amount of time by which an activity can be delayed without affecting the completion time of the project.
19
New cards
Flowchart
A diagrammatic representation of the sequence of steps in an algorithm (in a clear and economical way).
20
New cards
Graph
A set of vertices, linked with a set of edges.
21
New cards
Isomorphic
Two graphs are isomorphic if one can be stretched, twisted or otherwise distorted into the other.
22
New cards
Loop
An edge whose beginning and end both link into the same vertex.
23
New cards
Minimum spanning tree
A tree that connects all the nodes of a network together using the minimum total arc length.
24
New cards
Network
A weighted graph (has a weight associated with each arc).
25
New cards
Objective function
The value of the quantity you wish to maximise or minimise in a linear programming problem.
26
New cards
Objective line method
The optimal solution in a linear programming problem with the objective function ax+b may be solved from its graph by drawing the line ax+b=c, which lies within the feasible region, and then moving the line parallel to this line as far (upwards if maximising, downwards if minimising) as possible within the feasible region.
27
New cards
Odd vertex
A vertex where an odd number of edges meet
28
New cards
Optimal solution
The set of values of the variables that maximise or minimise the value of the objective function while satisfying all the constraints (it will always lie in the feasible region).
29
New cards
Path
A finite sequence of edges, so that the end of one edge is the start of the next, and in which no vertex is repeated.
30
New cards
Precedence network
A network drawn to show how the activities in a project are dependent upon each other. Activities are represented by arcs.
31
New cards
Precedence table
A table listing the activities involved in a project, showing all the dependencies of activities on other activities.
32
New cards
Project
This is the overall task to be analysed using critical path analysis, A project is made up of a number of different activities.
33
New cards
Semi-eulerian
A graph is semi-eulerian if it is possible to find a route in which each edge is traversed once only, starting and finishing at different vertices. This is only the case if all the vertices are even vertices except for the start and finish vertices, which are odd.
34
New cards
Simple graph
A graph in which there are no loops and in which there is no more than one edge connecting any pair of vertices.
35
New cards
Solution to a linear programming problem
Any set of values for the decision variables that satisfies all the constraints.
36
New cards
Sorting algorithm
Sorts a list into order.
37
New cards
Source node
This is the event node that represents the event that occurs at the beginning of a whole project. The earliest event time and latest event time for the source node is zero.
38
New cards
Spanning tree
A tree which includes all the vertices of the graph.
39
New cards
Subgraph
A subset of the vertices of a graph, together with a subset of edges.
40
New cards
Traversable
A network where all the nodes can be connected and the same edge cannot be traced twice (if it has zero or two odd vertices, the network is traversable - it is therefore either eulerian or semi-eulerian).
41
New cards
Tree
A simple connected graph with no cycles.
42
New cards
Vertex
A point on a graph that is connected to other vertices by edges.
43
New cards
Vertex set
The set of all the vertices of a graph
44
New cards
Walk
A sequence of edges in which the end of each edge, is the beginning of the next.
45
New cards
Weight
A numerical value associated with an arc on a network.