Physics review
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
resistivity
J
J=nqvd=
σE=E/ρ
Ohm’s law
E/ρ
ρ
resistivity of conducting materials
TF ρ is a universal law
False
Unit of resistivity
Ωm (read ohm-meter) Where V/A = Ω = ohm
Conductivity
Conductivity = σ = 1/ρ [mho/m or Siemens/m]
R=
ρL/A
V=
RI (Ohm’s Law)
Resistors
Devices made with a specific value of electrical resistance (R).
The value allows us to estimate how much current a device/circuit will draw from a voltage supply.
allow us to control the current drawn from a voltage supply.
Unit: Ω (ohm)
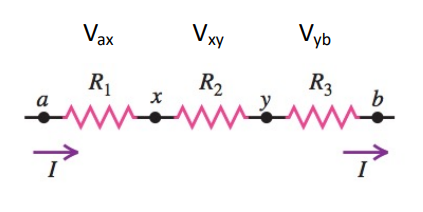
Resistors in Series
Resistors share the same current (I) § Resistors have distinct potential differences (V)
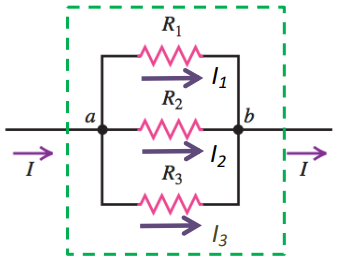
Resistors in Parallel
Resistors share the same potential difference (Vab) § Resistors have distinct currents
What makes a process safe?
Type safety
Memory safety
Control-flow safety
Program control flow
Unconditional jumps
Conditional jumps
Loops
Subroutines
Unconditional halt
Fundamen
CFI
Control-flow integrity (CFI)
Enforces integrity of a program’s execution flow path
Detects an undefined change in the path of execution by an adversary
CFI Method
build CFG statically (compile time)
Instrument (rewrite) binary, e.g., at install time
-add Ids and Id checks; maintain Id uniqueness
perform ID checks at run time
-indirect jumps have matching Ids
Control-Flow Integrity
Execution must follow a path of a Control-Flow Graph (CFG)
CFG can be pre-computed from:
source-code analysis
binary analysis
execution profiling
How can we enforce extracted control-flow?
Behavior-based Detection(A)
Challenges to defining the expected program behavior
Define “expected behavior”
Detect deviations from expectation efficiently
Avoid compromise of the detector
Basic Block
A consecutive sequence of instructions, control is “straight”(no jump targets except at beginning or end)
TF
CFG can be derived from a call graph
T
How CFI works
Define “expected behavior” (CFG)
Detect deviations from expectation efficiently (IRM)
Avoid compromise of detector (Sufficient randomization)
How does in-line Monitor work?
Implement the monitor in-line as a program transformation (instrumentation)
Insert a label just before the target address of an indirect transfer
Insert binary code that when run, checks whether the label of the target instruction matches the label of the possible destination
Ways we can’t defeat CFI
Inject code that has a legal label (we assume non-executable data)
Modify code labels (code is immutable)
main components of Java security architecture
class loaders
byte code verification
the Security Manager
Power=
dU/dt=dW/dt=VI
Unit of Power
Joules/s = Watts
Current(I)
I=V/R
Kirchhoff’s (Rule #1) Current Law
The algebraic sum of the currents into a circuit junction is zero.
Kirchhoff’s (Rule #2) Voltage Law
The algebraic sum of the potential differences in a circuit loop must equal zero.
TF
It has been observed that certain naturally-occurring rocks (magnetite) can attract or repel each other depending on the position with respect to each other.
T
TF
Magnetic poles can exist in isolation
F
Ampere’s Law
The magnetic field integrated around a closed loop is proportional to the electric current passing through the loop.
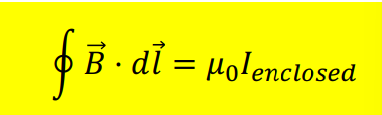
Solenoid
A coil wound into a close-packed helix
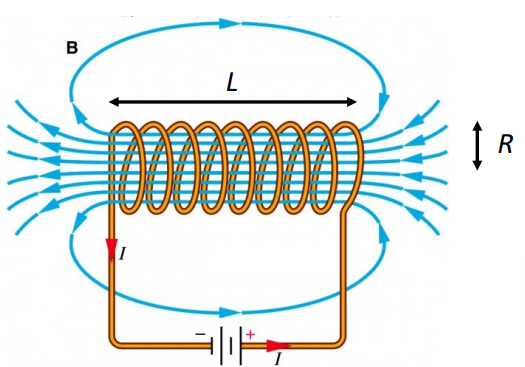
toroid
Ring-shaped type of solenoid