Chapter 12
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
define a problem and know its key feature's ?
Well defined problem's, ill defined problem's
What is a problem?
when there is an obstacle between a present state and a goal
- needs to be identified before they can be solved
Well defined problem's
are easy to identify and solve ( mazes, crosswords, adding problem's, registering for classes)
ill- defined problems
are hard to identify and solve ( how to break up with someone, picking a careers, solving poverty, overpopulation, world hunger)

Know the gestalt approach solving and the processes that help and hinder finding solutions
problem representation, problem restructuring, insight, non insight, functional fixedness, and mental set.
Problem representation
the way a problem is translated (or represented ) in our mind. ( we may represent solving a puzzle differently in our mind like edges or in the middle )

Problem restructuring
the process of changing a problems representation. (ex: like those confusing brain twisters about who killed who but we never think of it properly till we structure it differently later)

Insight
a sudden realization of the solution to a problem. Like a lightbulb moment
Non-insight problem
it felt like they were gradually getting to the solution like a complex equation problem (ex; (1/5)x +10 = 25 )
Functional fixedness
tendency to focus on similar functions or uses of objects
- ex: Candle problem (functional fixedness): mount the candle to the wall so it will burn without dripping wax on the floor (tend to think the box as a container instead of using it ). Easier to overcome functional fixedness when the candles are presented outside the box. It is easier to overcome functional fixedness.
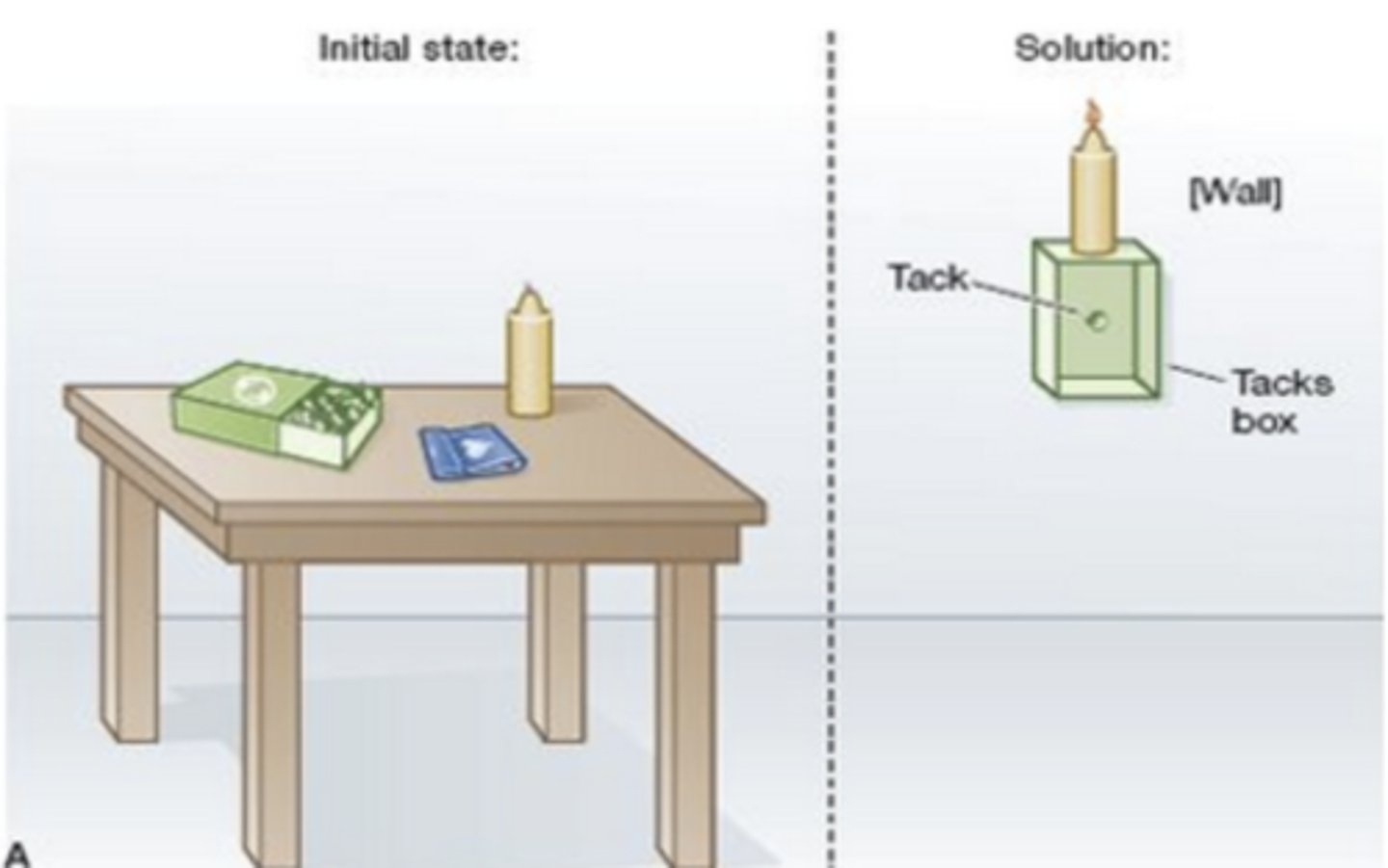
Mental set
A preconceived notion about how to approach a problem (functional fixedness arises from our mental set, which it means arise from our knowledge and our experience.
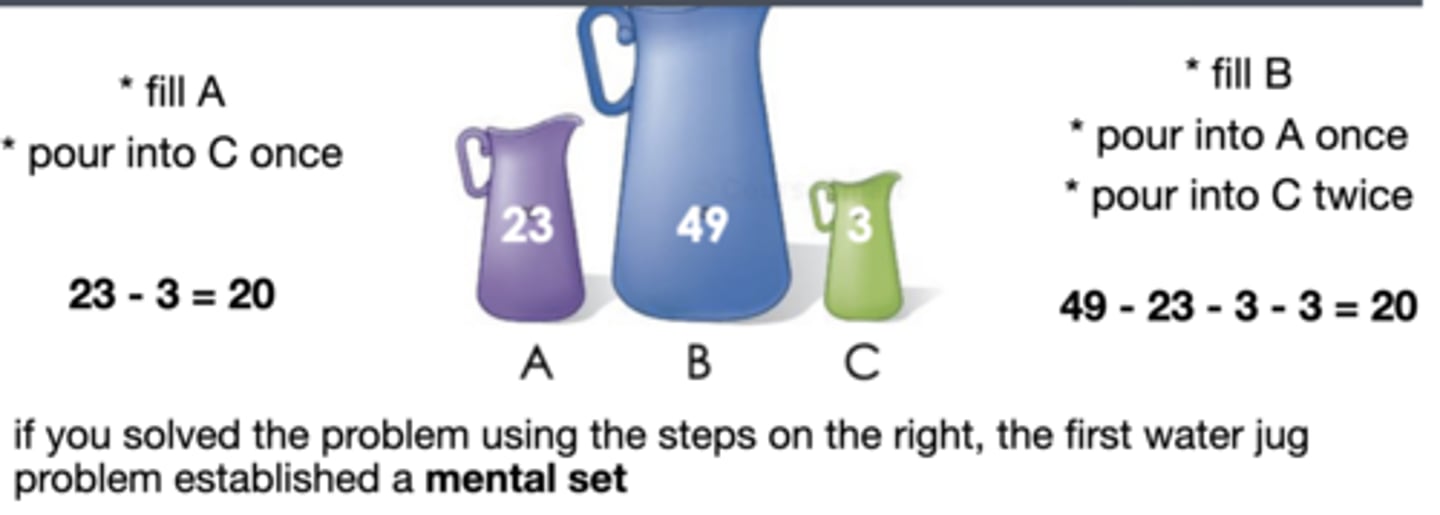
EX: water jug problem: measure a specific quantity of water from 3 empty jugs of varying capacities.
Prior examples can establish a mental set that inhibits participants from using simpler solutions later on
know the information processing approach to problem solving vis the means end analysis'
Information processing approach (three stages), problem space, operators, means end analysis,
Information processing approach
problem solving in a search between the posing of a problem and its solution. It has three stages:
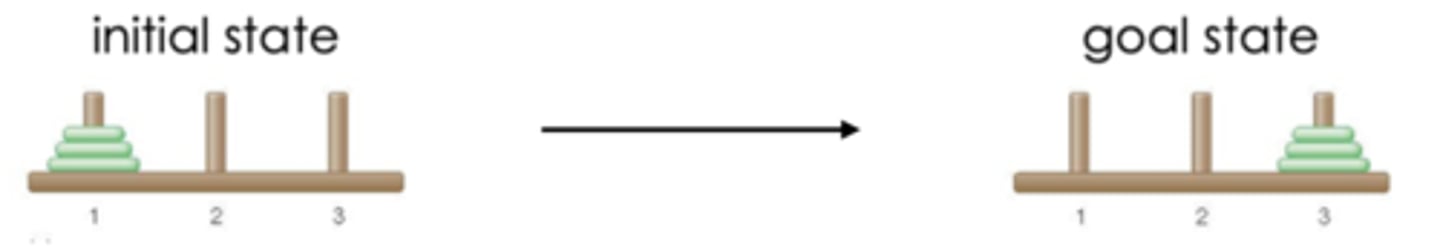
Initial state
conditions at the beginning of a problem
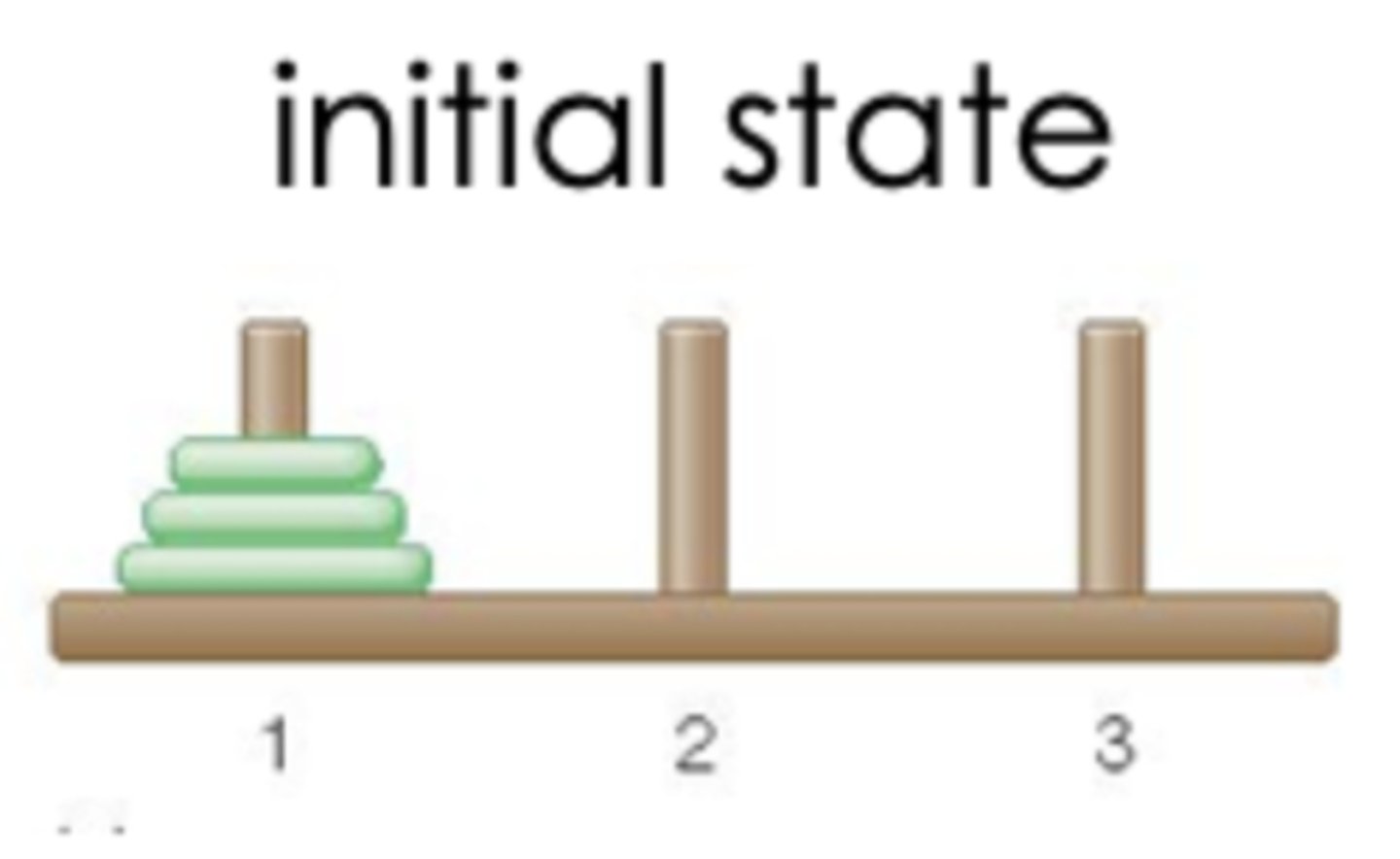
Intermediate state
conditions after each step is made toward solving a problem
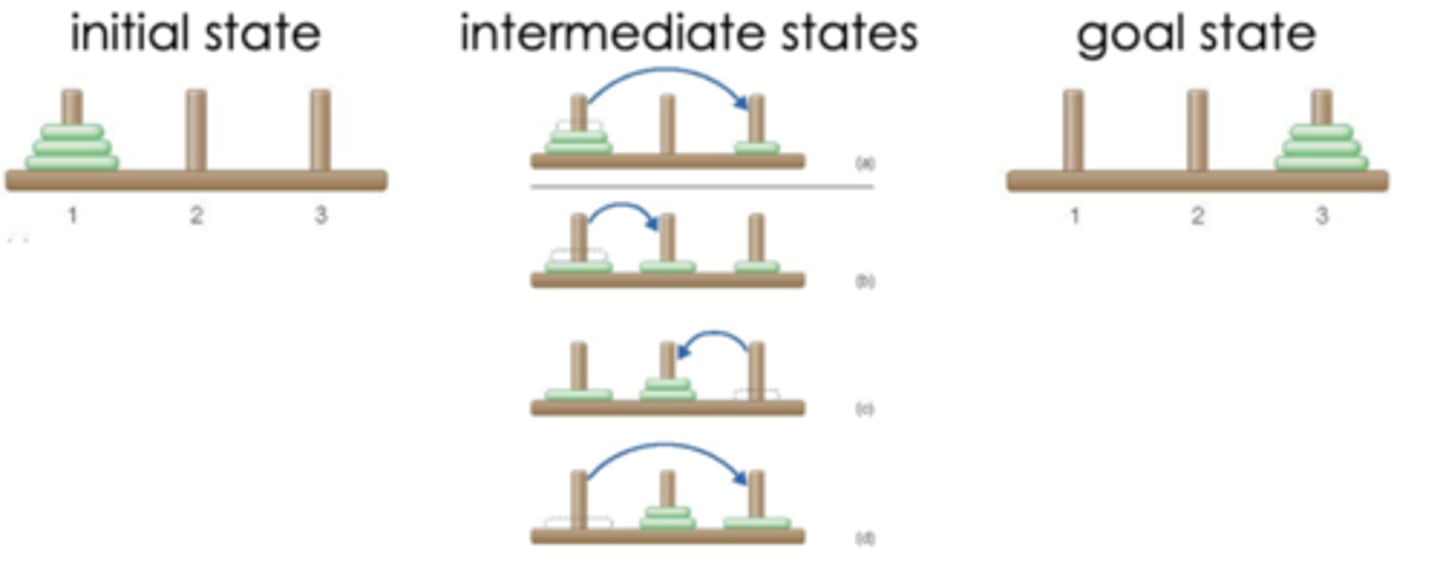
goal state
solution to the problem
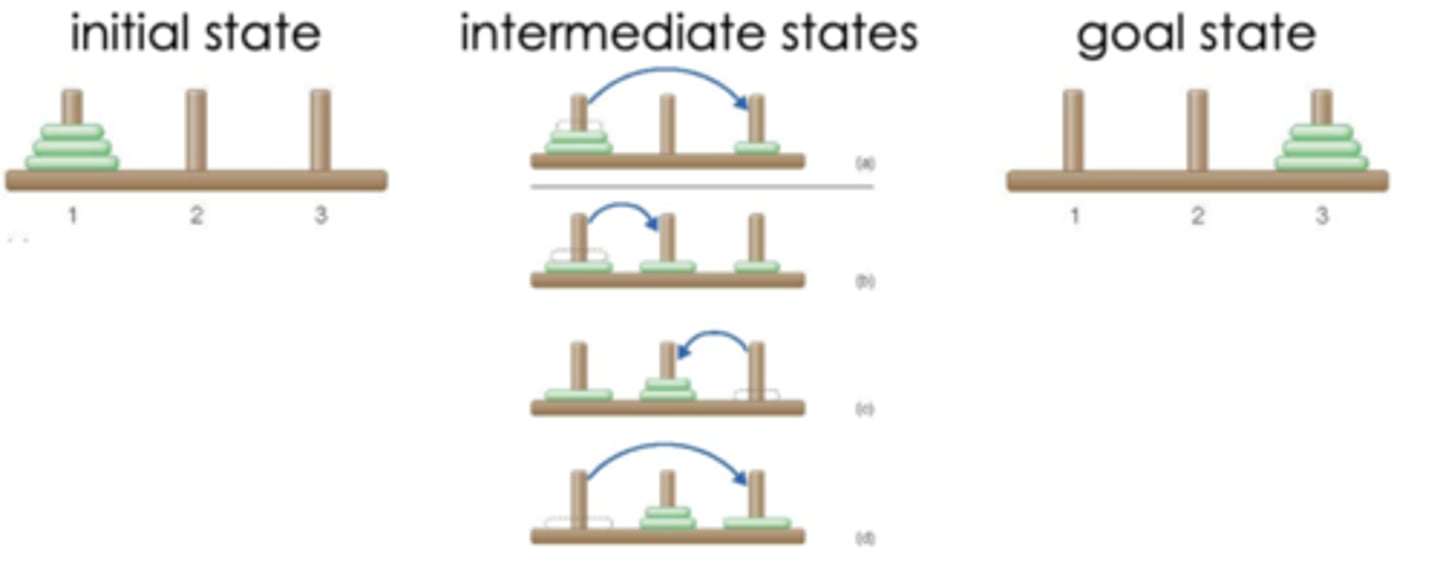
Problem space
all possible states that can occur when solving a problem (including all the states)
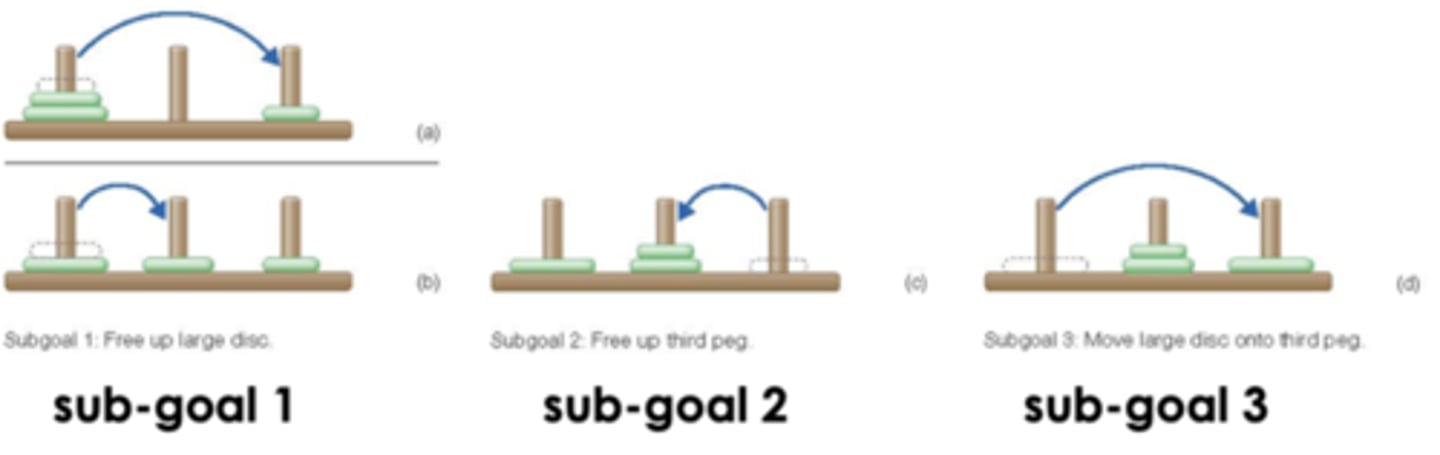
operators
actions that take the problem from one state to another (tend to be governed by rules) (example traveling somewhere)
1. Shortest travel time
2. Cost within budget

means end analysis
There are many ways to get from the initial state to the goal state
Most people unaware they are searching for the solutions like a problem diagram
Know the analogical approach to problem solving
analogical problem solving, analogical transfer, analogical paradox,
analogical problem solving
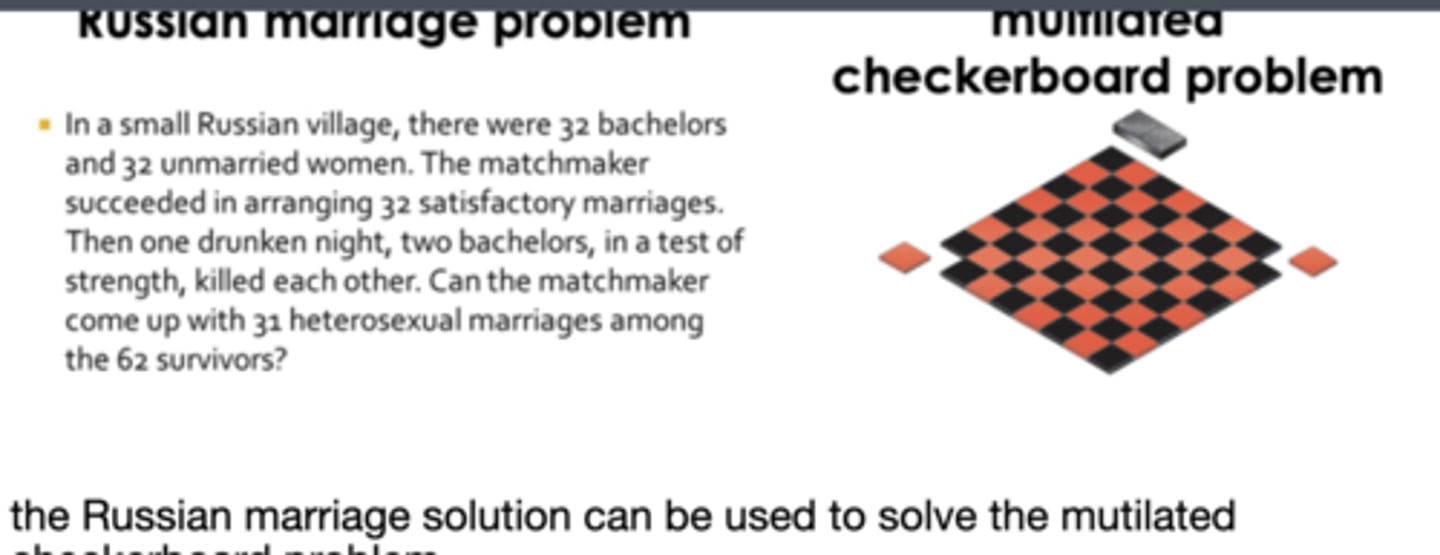
attempting to solve a problem using the solution to a similar problem. like using the Russian marriage solution for the mutilated checkerboard problem

analogical transfer
experience solving one problem is transferred to another problem
1. Target problem: the problem you are trying to solve
2. Source problem: another problem that is similar to and many illustrate a way to solve the target problem
- Analogical transfer requires that you notice, map, and apply the analogy
Analogical paradox
it can be difficult to apply analogies in the laboratory, but we routinely use analogies in real world settings.

Expert
someone knowledgeable or skilled in a particular
-Expert solve problems in their field more quickly and more often than beginners
-Experts posses more knowledge about their field
-Experts organize their knowledge differently than novices

Understand the relationship between creativity and problem solving
creativity, divergent thinking, creative cognition, daydreaming, solitude, mindfulness
creativity
the use of imagination or original ideas

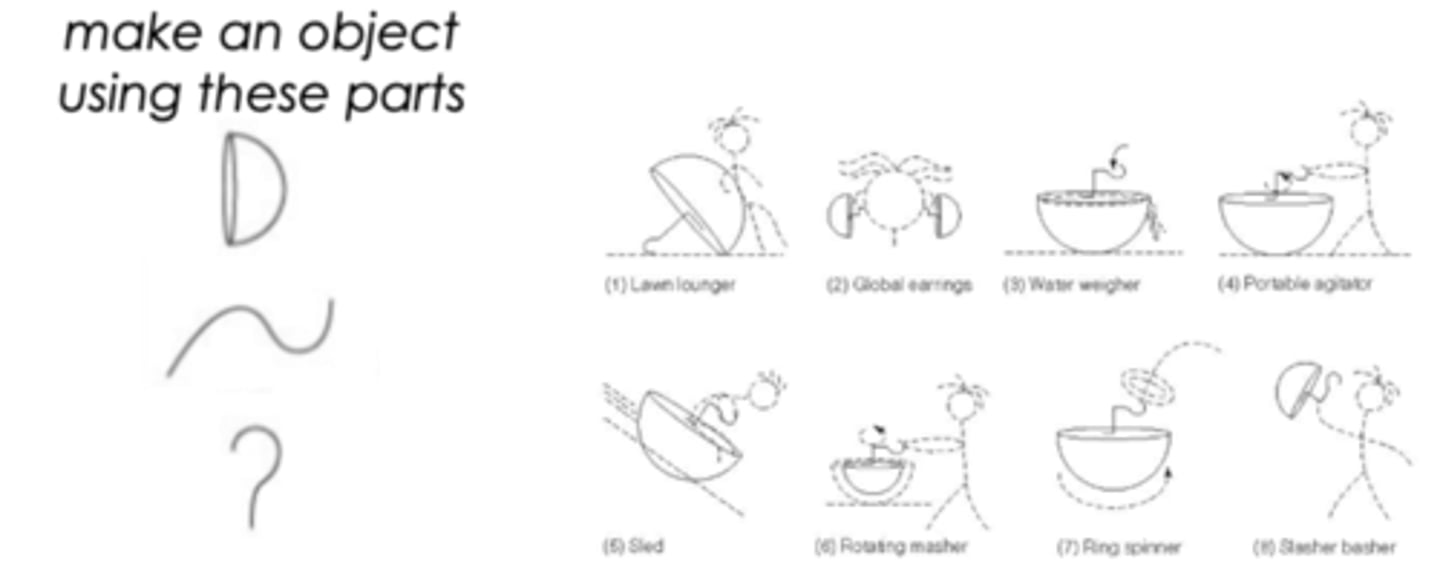
divergent thinking
thinking that is open-ended and involves a large number of potential "solutions"
Example: how could you use this paper clip?
-Holds paper together
-Cufflinks
-Earring
-Imitation mini-trombone
-Thing you use to push restart button on router
-Keep headphones from getting tangled
-Bookmark
-Pick a lock

creative cognition
technique to train people to think creatively
- creative problem is a process
Daydreaming
purposeful mind wandering
Solitude
avoiding distractions; giving the mind space and time to make new connections and find meaning
Mindfulness
pay attention to what is happening in our mind and in the environment