Sports Medicine Unit 4: Trauma
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/152
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
153 Terms
1
New cards
shock
inadequate tissue perfusion (tissues not getting enough nutrients+O2)
2
New cards
normal state / point of assault / compensatory / decompensated / irreversible
stages of shock
3
New cards
cardiogenic / obstructive / distributive
types of shock
4
New cards
cardiogenic shock
pump failure,
5
New cards
obstructive shock
pipe blockage (usually in or near heart),
6
New cards
distributive shock
not enough fluid, body can't get enough blood to your heart, brain and kidneys
7
New cards
Arrythmia / heart failure / pericardial tamponade / valve failure / heart attack
subtypes of cardiogenic shock
8
New cards
Arrythmia
arrythmic shock (bad rhythm)
9
New cards
heart failure
cardiac shock, congestive; occurs when the heart muscle doesn't pump blood as well as it should
10
New cards
pericardial tamponade
cardiac shock; Compression of the heart caused by fluid collecting in the sac surrounding the heart.
11
New cards
valve failure
cardio regression;
12
New cards
heart attack
heart stops, demi lovato song
13
New cards
aortic blockage / failure of venous return / catheterization failure
subtypes of obstructive shock
14
New cards
aortic blockage
aortic wall delamination/ dissection, atherosclerosis (clogged artery from fats, cholesterol, etc.), thrombosis/ embolism (blocked artery from air or blood clot)
15
New cards
failure of venous return
venous pinching / dissection, embolism/thrombosis, disseminated intravascular coagulation (abnormal blood clotting), pulmonary embolism (blood clot in lung)
16
New cards
catheterization failure
central line failure, swan-ganz catheterization
17
New cards
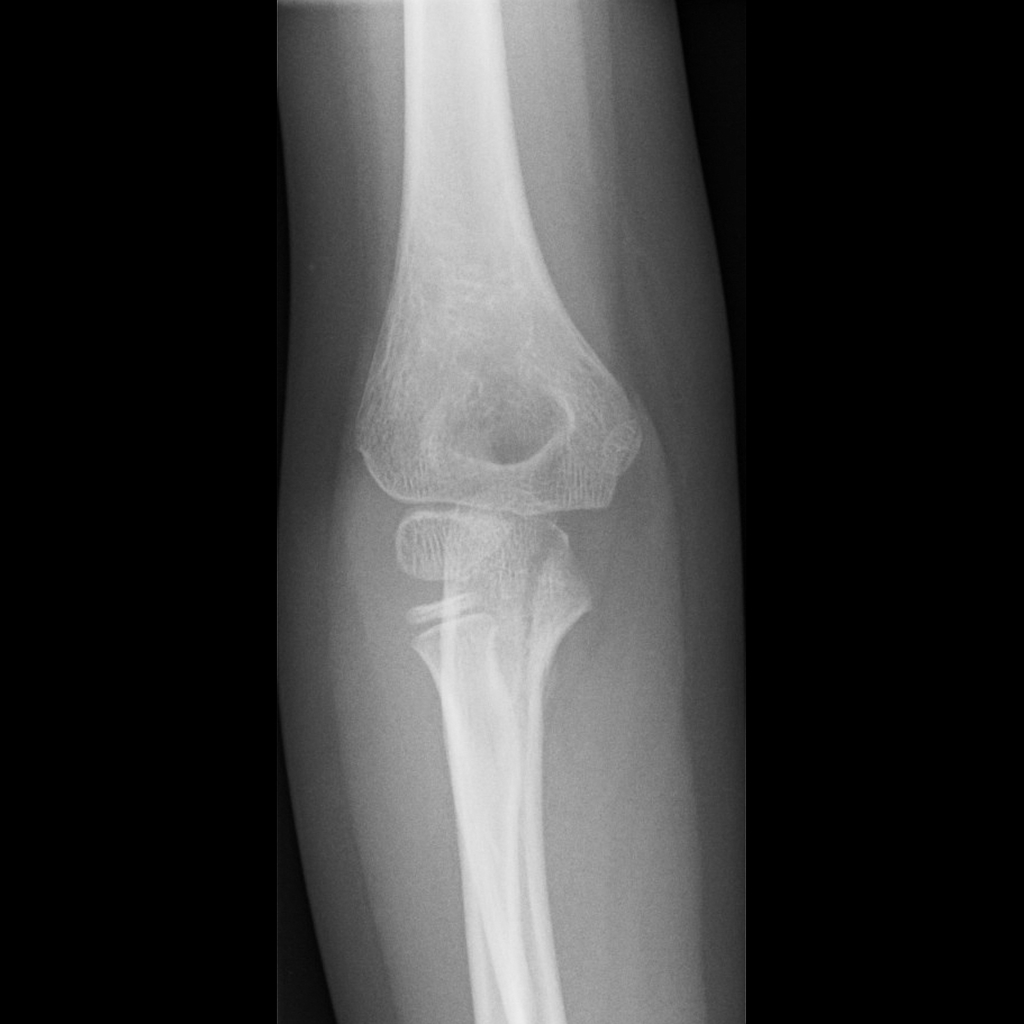
loss of peripheral vascular resistance / septic / anaphylactic / neurogenic / overwhelming burns / anemic / hypoxia
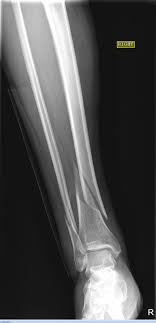
subtypes of distributive shock
18
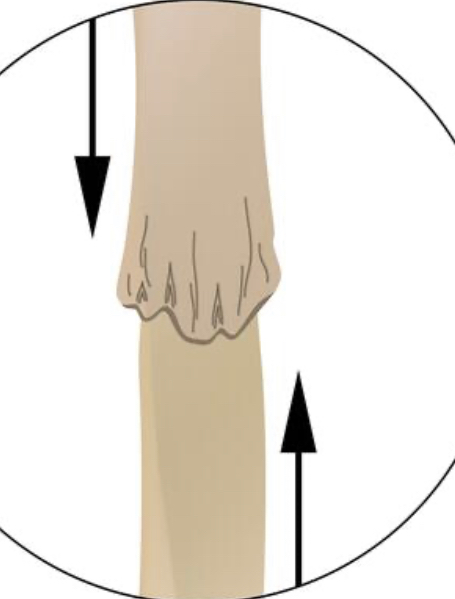
New cards
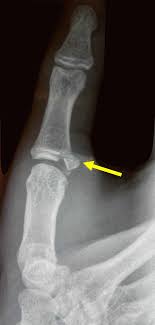
loss of peripheral vascular resistance
expansion of vascular tone
19
New cards
septic shock
overwhelming infection causing vasodilation (widening of blood vessels) & hypotension (low bp)
20
New cards
anaphylactic shock
overwhelming histamine mediated immune response
21
New cards
neurogenic shock
CNS fails causing loss of vascular tone, can also be cardiogenic if results in heart failure only
22
New cards
overwhelming burns
extreme loss of interstitial fluid resulting in hypotension, loss of thermal control resulting in vasodilation
23
New cards
anemic / hypoxia
not enough blood cells to distribute O2
24
New cards
hypovolemic shock
blood volume loss; special type of distributive shock
25
New cards
5 L
How much blood does the average adult have?
26
New cards
stage 1
this stage of hypovolemic shock has:
27
New cards
stage 2
this stage of hypovolemic shock has:
15-30% blood loss, 750-1500 cm3 blood loss, PT feels mildly anxious
15-30% blood loss, 750-1500 cm3 blood loss, PT feels mildly anxious
28
New cards
stage 3
this stage of hypovolemic shock has: 30-40% blood loss, 1500-2000 cm3 blood loss, PT feels confused+lethargic
29
New cards
stage 4
this stage of hypovolemic shock has: >40% blood loss, >2000 cm3 blood loss
30
New cards
profuse brain / keep PT warm / slightly raise legs / call ems
what should you do to treat shock? (4)
31
New cards
200-500 mL
blood loss into humeral that's bad
32
New cards
150-700mL
blood loss into cranial compartment that's bad
33
New cards
500 mL-2L
blood loss into femoral compartment that's bad
34
New cards
1 L-2.5 L
blood loss into thoracic compartment that's bad
35
New cards
500 mL <
blood loss into abdominopelvic compartment that's bad
36
New cards
heat index
a measure of risk that an athlete will experience a heat emergency, depends on humidity and temperature, Four levels
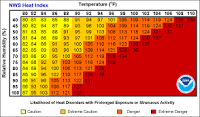
37
New cards
Caution / Extreme Caution / Danger / Extreme Danger
four levels of risk on the heat index
38
New cards
heat cramps
Earliest sign of heat risk, electrolyte imbalance, cramps of abdomen, back, and arms.
39
New cards
Heat Exhaustion
The heat risk with body's compensation mechanism failure, need to take immediate action to stop progression; includes faint or dizziness, excessive sweating, cool or clammy skin, nausea or vomiting, rapid, weak pulse, muscle cramps
40
New cards
Heat Stroke
the heat risk that's in the form of distributive shock, immediate life threat; includes throbbing headache, no sweating, red, hot, dry, skin, nausea or vomiting, rapid, strong pulse, possible loss of consciousness
41
New cards
remove from sunlight / remove pads / get wet and cold / hydrate with ice cold electrolytes
To treat heat, do this to the PT
42
New cards
wind chill
function of wind and temperature
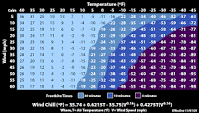
43
New cards
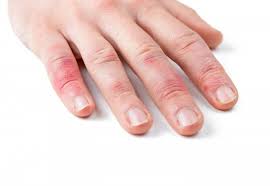
frostnip
First stage of cold injury, Only destroyed upper layers, No subdermal freezing, Incredibly Painful
44
New cards
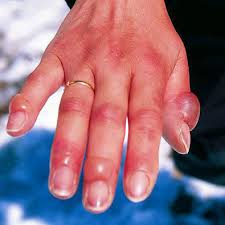
early frostbite
Subdermal freezing of tissues, Widespread cell death, Delineation of permanent damage, Similar to a burn, blistering
45
New cards
late frostbite
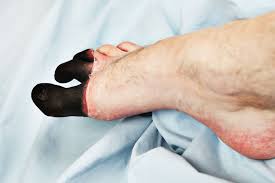
Clear delineation of living / death tissues, Dry gangrene, Autoamputation
46
New cards
Frostbite treatment
If possible, warm the affected part (Only if no possibility of refreezing!!!), Separate any affected digits, Wrap in sterile dry gauze, Transport to Trauma center, Minimize Friction, Do NOT pop blisters
47
New cards
hypothermia
Core temp, Esophageal or Rectal, Slowing of functions, Enzymatic Function Decay, Arrhythmias
48
New cards
mild hypothermia
Temp: 90-95F, cardiac: excitation response (HR, BP, RR), shivering and mild confusion
49
New cards
severe hypothermia
Temp:
50
New cards
moderate hypothermia
Temp: 86-90F, cardiac: slowing of all physiologic functions, negative inotropic effect, cessation of shivering, worsening ataxia (poor muscle movement), and loss of papillary reflex, EKG: changes (osborn waves)
51
New cards
green flag
this flag means no restrictions, low humidity heat from 65-90F
52
New cards
Yellow flag
this flag means Moderate Restrictions, Heat from 50-68 F or 85-95 F, limit extreme activity to 120 min, Caution or Extreme Caution on Heat Index, Rain, Over 1 hour to frostbite on exposed skin
53
New cards
red flag
this flag means Significant Restrictions, Elevated caution for injury, Check in 20 min, Limit extreme activity to 90 minutes for heat, Limit exposure activity to 30 minutes for cold, For heat, make sure more electrolytes are available, Heat from 85-105F, Danger on Heat Index, AQI 50-150, Rain, cold under 60F, or sleet, At least 30 min to frostbite on exposed skin
54
New cards
black flag
This flag means Heavily Restricted, Extreme monitoring for injury, Check in 5 min, Limit extreme activity to 20 minutes heat, Limit exposure activity to 15 minutes cold, For heat: Make sure more electrolytes are available, Make sure active cooling available, Heat from 105F+, Extreme Danger on Heat Index, AQI 150 to 200, Rain with cold under 45F; Sleet; or Snow, At least 10 min to frostbite on exposed skin
55
New cards
white flag
this flag means NO outdoor practice, Only activities in air conditioned / heated spaces, AQI above 200, Heat index beyond mark, Less than 5 min to frostbite, Wind Chill less than 25 F
56
New cards
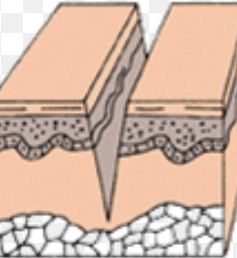
primary intention
wound ends come together, leaves scar tissue; includes acute inflammation then wound closure
57
New cards
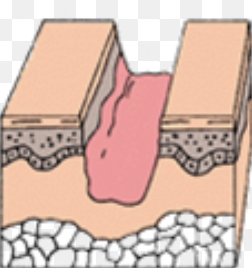
secondary intention
wound ends can't communicate, scab has to form, scar tissue is left; includes acute inflammation then reconstructing phase, then maturation phase
58
New cards
interruptions to wound healing
wounds in joints, high friction areas, thin areas, concurrent drug use, diff kind of med conditions and diseases
59
New cards
high risk wounds
dog/cat/human bites, foreign bodies, wounds requiring significant debridement, immunocompromised PTs, poor peripheral circulation, no health insurance, wounds in areas of social stigma, compounded mechanism injuries
60
New cards
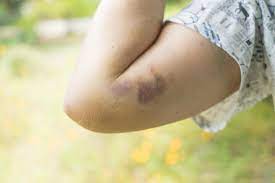
contusion
bruise, blood and serum (?) breaking down
61
New cards
hematoma
pocket of blood built up under skin, in arteriols
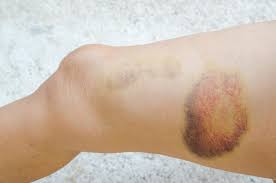
62
New cards
abrasion
scrapes, needs debridement (removal of damaged tissue or foreign objects from a wound)
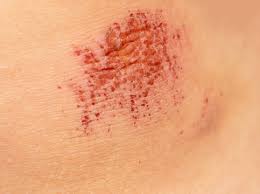
63
New cards
laceration
cuts that have 2ndary intention, jagged
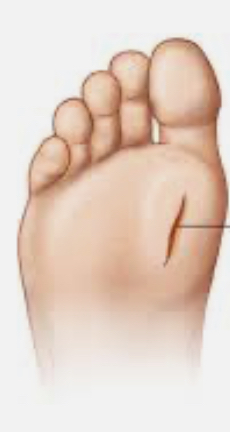
64
New cards
incision
cuts that'll be primary intention, clean cut
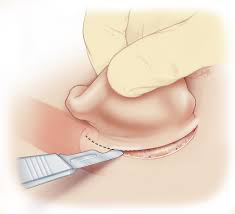
65
New cards
avulsion
flap of flesh created from a cut
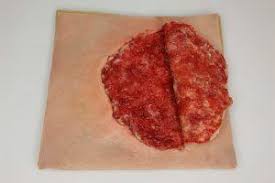
66
New cards
degloving injury
something constricts and skin comes off like a glove, to prevent, take off bracelets ,rings, etc.
67
New cards
puncture
A wound when something was poked and removed
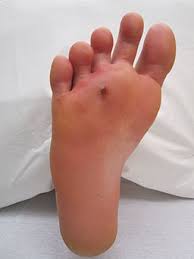
68
New cards
no
are all punctures penetrations?
69
New cards
penetration
impaled object left in skin, can come out if blocking airway
70
New cards
amputation
what was once connected to a body part is no longer connected
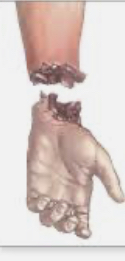
71
New cards
sprain
injury to a ligament, grade 1: microtear, grade 2: tear goes thru ligament, some laxity, endpoint
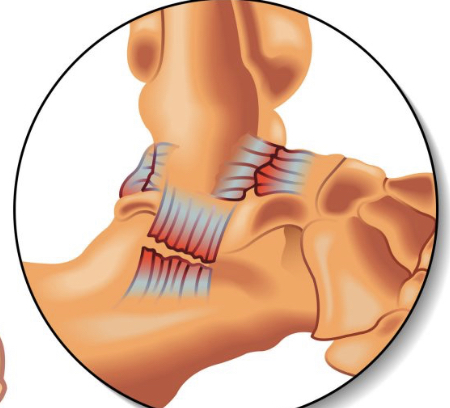
72
New cards
strain
injuries in tendons or muscles
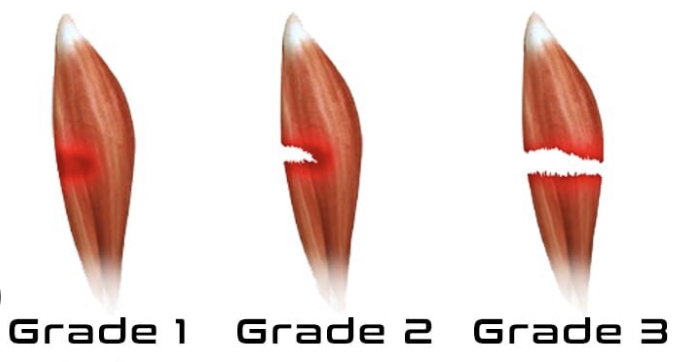
73
New cards
fracture
broken bone
74
New cards
transverse fracture
a break that occurs straight across the bone
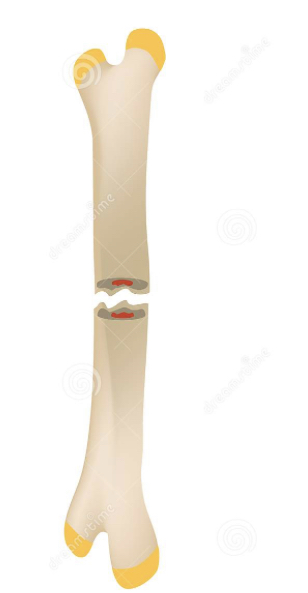
75
New cards
oblique fracture with offset
occurs at an angle across the bone, ends are SHARP
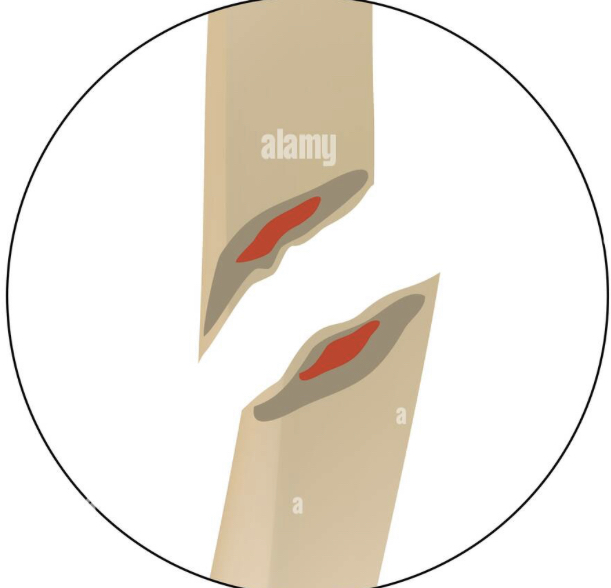
76
New cards
oblique fracture
occurs at an angle across the bone
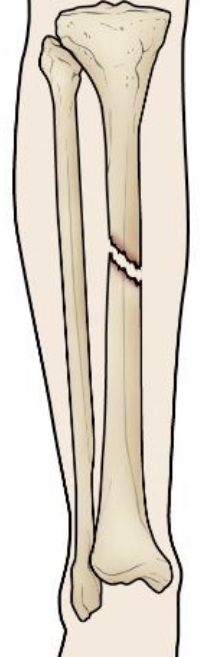
77
New cards
longitudinal fracture
a fracture that runs parallel to the long axis of the bone
78
New cards
spiral fracture
a fracture in which the bone has been twisted apart
79
New cards
impacted fracture
broken bone ends are forced into each other
80
New cards
avulsion fracture
fragment of bone chipped away from the main bone
81
New cards
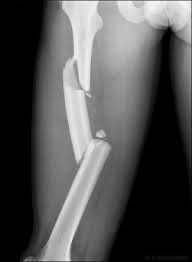
segmental fracture
free floating piece of bone between well-defined fracture lines
82
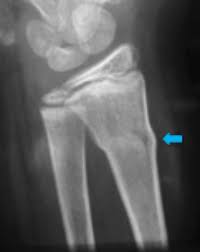
New cards
Torus fracture
cortex buckles but does not break
83
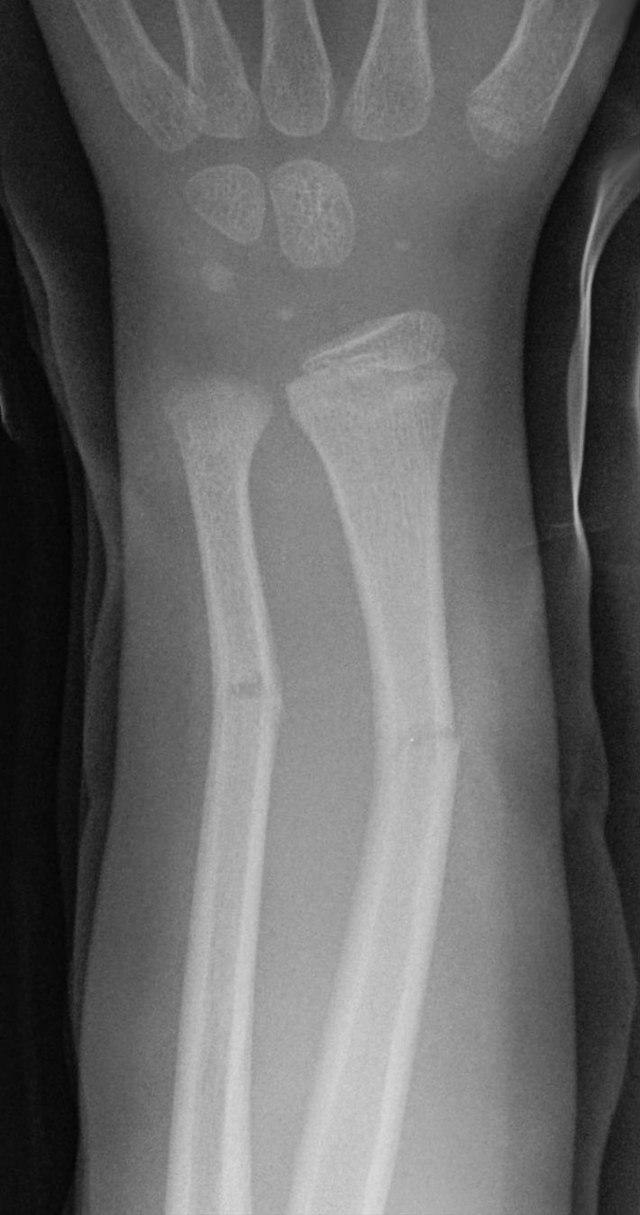
New cards
greenstick fracture
bone breaks incompletely
84
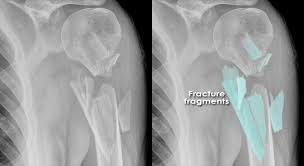
New cards
comminuted fracture
bone breaks into many fragments
85
New cards
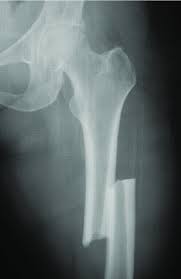
displaced fracture
bone ends are out of normal alignment
86
New cards
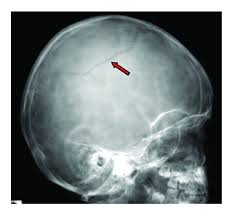
linear fracture
usually in flat bones, a break in the bone, but it does not move the bone
87
New cards
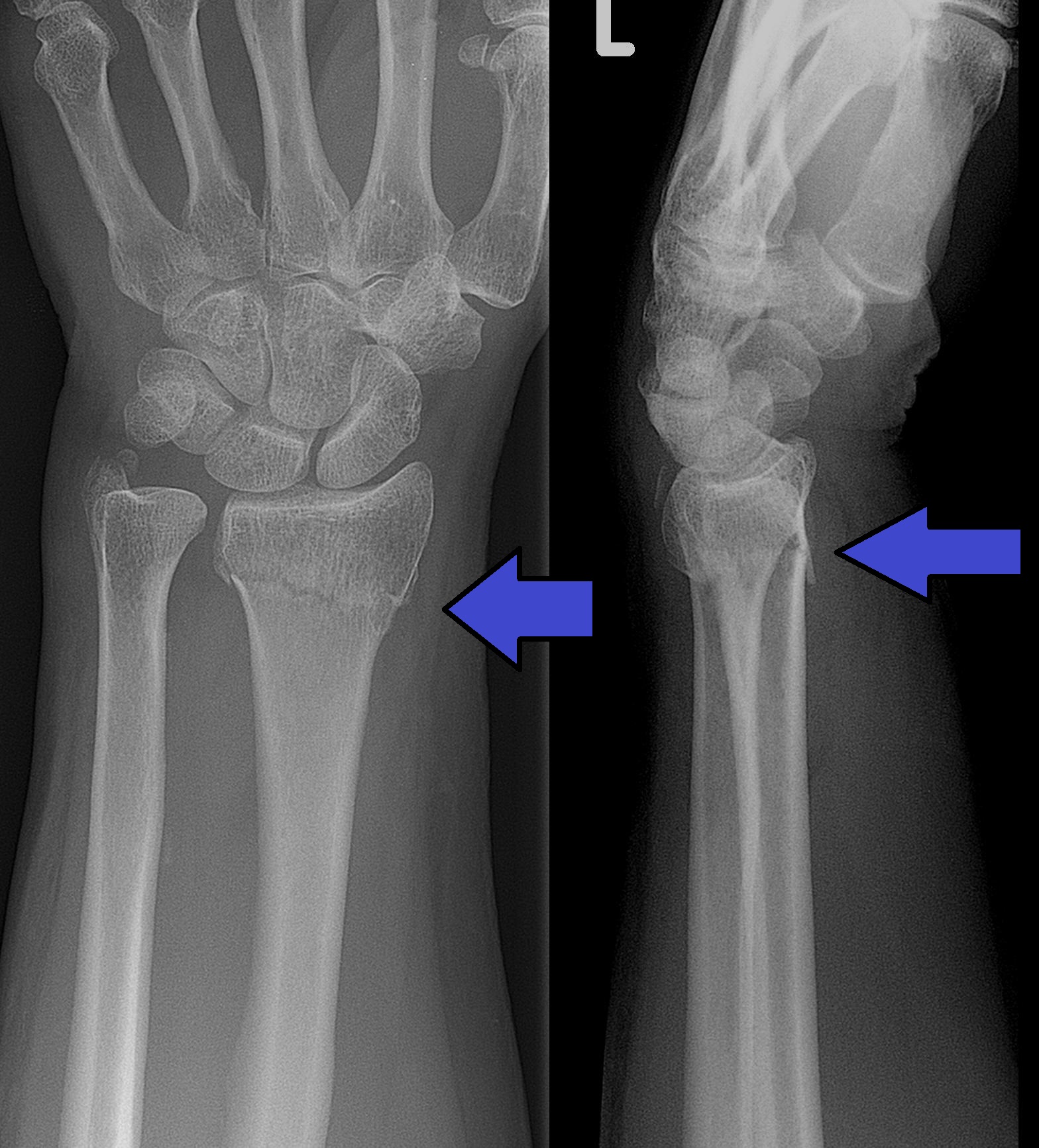
Colles fracture
fracture of the distal radius at the wrist
88
New cards
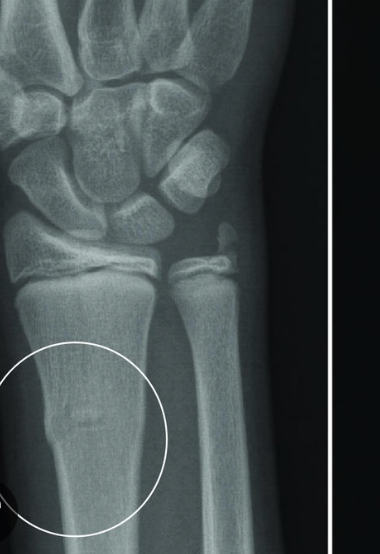
buckled fracture
ends are driven into each other a little bit
89
New cards
Fibrin
An insoluble protein which is produced in response to bleeding, formed from fibrinogen which is a soluble protein found in the liver and in blood plasma, essential for blood clot contraction, or spontaneous shrinkage of the clot. Ex: when an injury occurs, this is the protein which allows for clotting to occur, which ensures healing of the wound and a stop to the flow of blood seen.
90
New cards
Histamine
A type of substance which has many effects in the body depending on its reason for existing in that moment. Ex: released from some types of white blood cells during allergic reactions (anti\___ is a drug which treats numerous types of allergies).
91
New cards
Granulocytes
A common white blood cell capable of secretion in its cytoplasm. It is an immune cell that releases enzymes through granules during infection. Ex: neutrophil, basophil, eosinophil
92
New cards
Phagocyte
An immune cell that engulfs materials such as small cells, particles, and bacteria using its plasma membrane (pinching off), ingests foreign materials, kills microorganisms, and removes dead cells. Ex: when phagocytosis occurs & pinocytosis with liquids
93
New cards
Macrophages
A big phagocytic cell in tissues found at sites of infection responsible for killing harmful organisms (bacteria). Ex: A mobile white blood cell
94
New cards
Endothelial Cells
These types of cells are the main cells found inside the lining of the blood vessels, lymph vessels, and heart, regulate the exchanges between the surrounding tissues and the bloodstream that interacts with them, Organizes the connective tissue cells' growth and development surrounding the blood vessel wall
95
New cards
Neovascularization
The process in which new blood vessels are formed from existing blood vessels. EX: Many diseases of the eyes, including macular degeneration and uveitis, allow this process to take place often.
96
New cards
Epithelialization
process of epithelial cells migrating up to heal and repair wounded skin, occurs during proliferative phase of wound healing, allows the epidermis to regenerate over the surface of a wound. EX: The lighter pink tissue that surrounds a wound
97
New cards
Fibroblasts
Located inside of connective tissue, this type of cell secretes collagen, which is a structural protein found in skin, as well as other fibers, and allows the structural framework of tissues to be stable.
Ex: Injury to tissue stimulates the formation of this, as they help to stabilize the structure of the tissue.
Ex: Injury to tissue stimulates the formation of this, as they help to stabilize the structure of the tissue.
98
New cards
Hydroxylysine
This amino acid is found only within collagens, and usually within animal proteins. They serve as sites of attachment for carbohydrates, and stabilize molecular crosslinks.
99
New cards
crush injury
mechanism any time the body or a part of it is compressed beyond the structural or physiological limit of the organism
100
New cards
compartment syndrome
a part of the body, a compartment, swells to the point that the pressure w/in the compartment increases