Linkage Mapping BSCI222
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
recombinant gametes
gametes with new combinations of alleles from crossing over
in meiosis what percent of gametes will be recombinant and parental?
50/50
complete linkage genes
crossing over never happens between alleles, always inherited together
incomplete linkage genes
crossing over sometimes happens between alleles, sometimes inherited together
unlinked genes
crossing over always occurs between alleles, never inherited together
OR two genes are on different chromosomes and independently assort during meiosis I
linked in repulsion
Ab/aB
- dominant alleles on different chromosomes
linked in coupling
AB/ab
- dominant alleles on one chromosome
what type of cross is preformed to test recombinant frequency?
test cross (heterozygous x homo. recessive)
if alleles are incompletely linked what percent of gametes will be recombinant?
<50%
how to calculate recombination frequency (RF)?
# recombinants / # progeny
recombination frequency
the percentage of recombinant offspring among the total
how to convert recombination frequency into centiMorgans (cM)?
0.__ -> % -> cM
example:
RF = 0.05 = 5% = 5cM
how to tell if a gene is linked using cM?
<50 cM apart
linkage group
represents all genes which may be linked in a part of or all of a chromosome
>50 cM
how to calculate recombination frequency when given cM
cM -> % -> 0.__ proportion
- even if genes are linked, still do this since there is a small change they won't be inherited together
genetic map
uses cM in linkage group to map chromosomes
cytogenetic map
uses chromosome banding pattern to map chromosomes
physical map
uses units of nucleotide base pairs to map chromosomes
wildtype vs non-wildtype
wildtype (+) = most common phenotype
non-wildtype (-) = less common phenotype
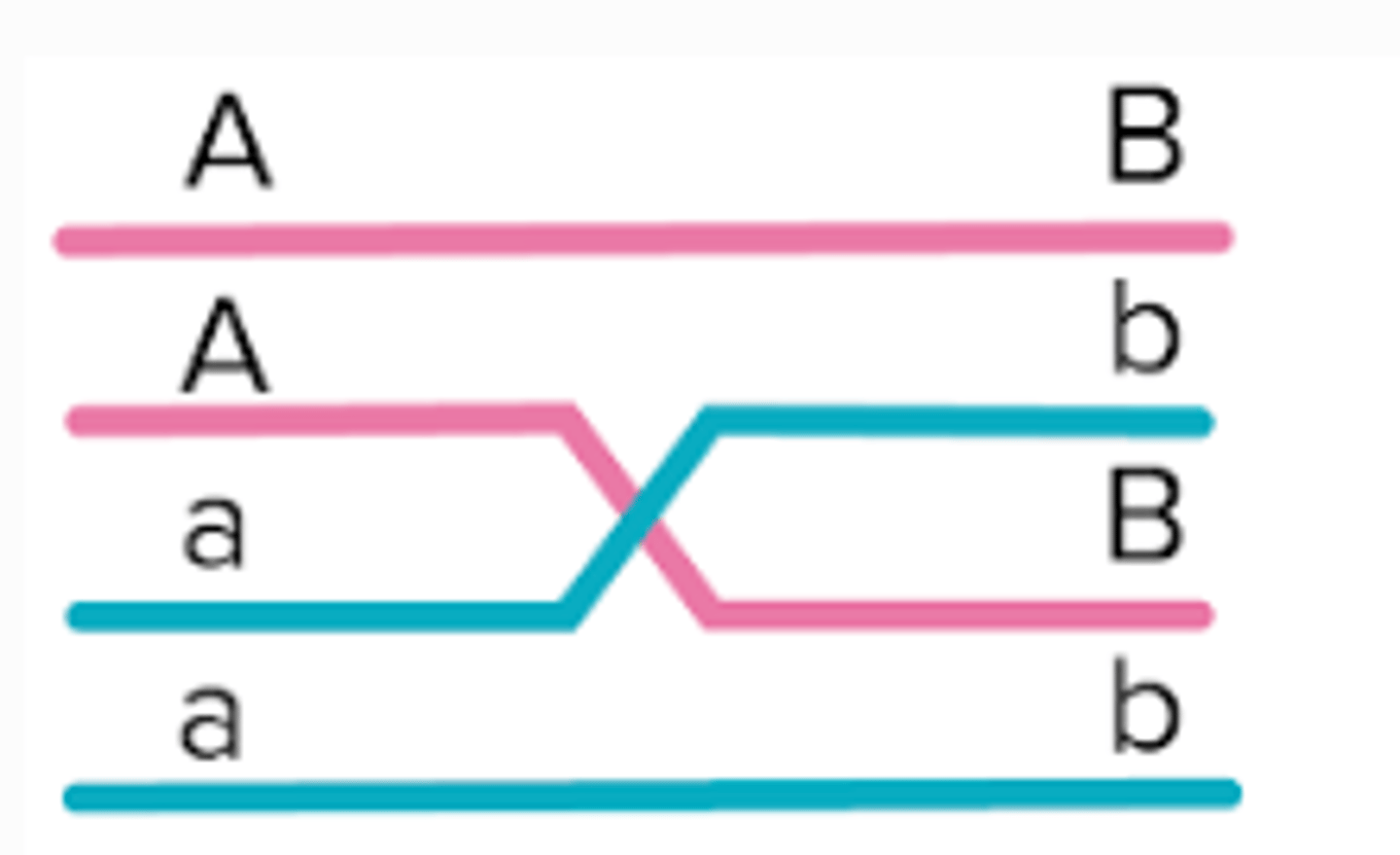
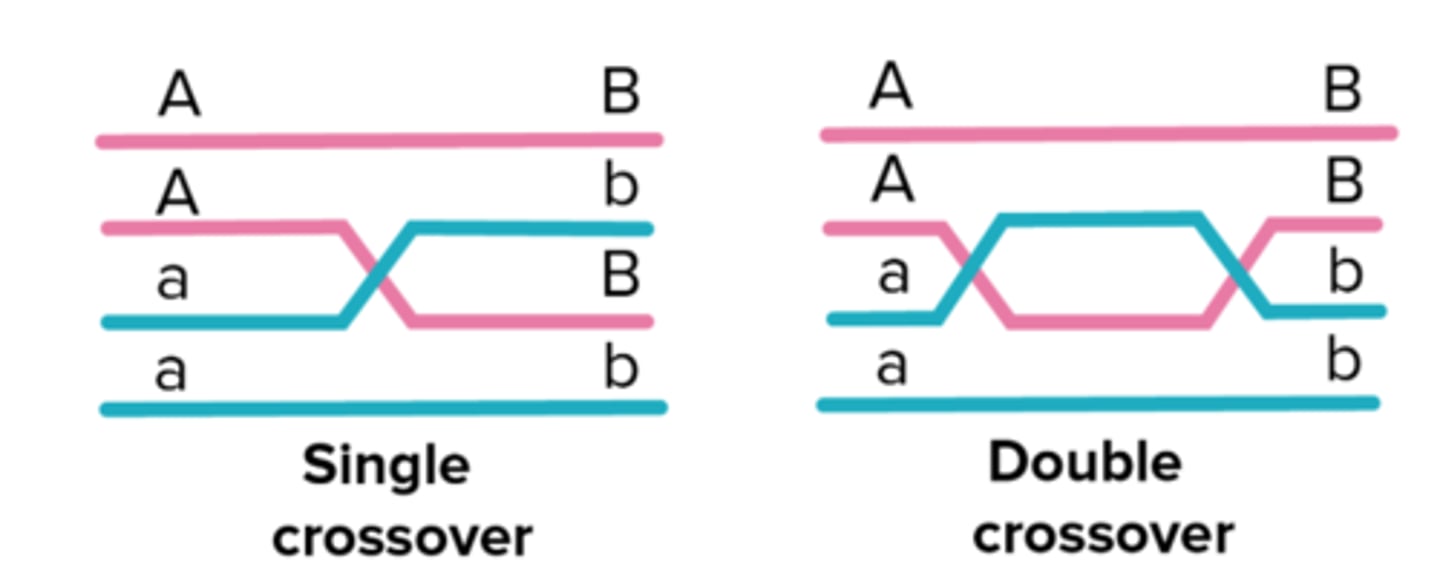
single cross over
single cross over between 3 alleles
double cross over
double cross over between 3 alleles
how to identify parental genotypes in a 3 point cross?
2 highest numbers of genotypes produced
how to identify double cross over recombinants in a 3 point cross?
2 lowest numbers of genotypes produced
how to identify which allele is in the middle in a 3 point cross?
compare parental and double cross over individuals genotypes, one different allele is the one in the middle
formula for recombination frequency in a 3 point cross
sum of (DR + genotypes from that point cross) / total progeny = probability which can be converted to centimorgans
interference
when one recombination event affects another
formula for interference
1 - (Observed DR / (total progeny P(cross over at point) P(cross over at other point))