CMIS 270: Exam 3
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
- create an interface that is easy to learn/use
- enhance user productivity
- provide feedback to user actions
- create an attractive layout/design
- enhance the interface
- focus on data entry screens
- covered in input/validation
- enhance user productivity
- provide feedback to user actions
- create an attractive layout/design
- enhance the interface
- focus on data entry screens
- covered in input/validation
screen design guidelines
2
New cards
- login
- navigation
- data input
- report generation
- navigation
- data input
- report generation
purpose of screen design
3
New cards
screen design
are the areas of the system where users can enter, update, and/or delete data
4
New cards
report design
are views of the data formatted for a specific use
5
New cards
- create a unique site identity and strive for consistency
- natural eye movement
- white space
- margins
- zones
- natural eye movement
- white space
- margins
- zones
layout guideline
6
New cards
- default values
- range control
- picture control
- null value control
- range control
- picture control
- null value control
data integrity control
7
New cards
default value
value a field assumes unless explicit value is entered
8
New cards
range control
allow limited set of permissible values
9
New cards
picture control
pattern of codes that restricts the width and possible values of each position in a field
10
New cards
null value control
Special value indicating that the value for a field is missing or unknown
11
New cards
- content
- repetition
- alignment
- proximity
- repetition
- alignment
- proximity
CRAP
12
New cards
content
should be meaningful
13
New cards
repetition
navigation
14
New cards
alignment
of text boxes and aligned to the business process
15
New cards
proximity
don't want users to move all around the screen to enter data, fields should be close to each other
16
New cards
data input
screens; putting data IN; used for inputting data to your database
17
New cards
data output
report; viewing/retrieving data FROM; used to retrieve data from your database
18
New cards
SDLC stage 1
deliverable
deliverable
Process Identification and selection
-List of projects to be undertaken
-List of projects to be undertaken
19
New cards
SDLC Stage 2
deliverable
deliverable
Process Initialization & Planning
-Scope Statement, Project Schedule plan
-Scope Statement, Project Schedule plan
20
New cards
SDLC Stage 3
deliverable
deliverable
Analysis
-Description of Solution (not detailed)
-Description of Solution (not detailed)
21
New cards
SDLC Stage 4
deliverable
deliverable
Logical Design
-Samples of Screen shots, reports, websites to be created
-Samples of Screen shots, reports, websites to be created
22
New cards
SDLC Stage 5
deliverable
deliverable
Physical Design
-Data dictionary
-Data dictionary
23
New cards
SDLC Stage 6
deliverable
deliverable
Implementation
-User manuals, actual code, test plans, user documentation, system documentation
-User manuals, actual code, test plans, user documentation, system documentation
24
New cards
SDLC Stage 7
deliverable
deliverable
Maintenance
-Documentation of fixes and troubleshooting
-Documentation of fixes and troubleshooting
25
New cards
Agile
Step 1
Step 1
Market: Talk to customers
26
New cards
Agile
Step 2
Step 2
Analysis: requirements, user stories
27
New cards
Agile
Step 3
Step 3
Prioritize: Product owner
28
New cards
Agile
Step 4
Step 4
Estimate and Plan: come up with a team of planners
29
New cards
Agile
Step 5
Step 5
DO: Create code: 8 days
30
New cards
Agile
Step 6
Step 6
Demo
31
New cards
Agile
Step 7
Step 7
Retrospective
32
New cards
- fixed costs
- fixed time
- fixed scope
- fixed time
- fixed scope
in SDLC the triple constraints are
33
New cards
- fixed costs
- fixed time
- est. scope
- fixed time
- est. scope
in Agile the triple constraints are
34
New cards
-In SDLC, quality is affected by time, budget, and scope
-In Agile, scope is affected by time, budget, and quality.
-In Agile, scope is affected by time, budget, and quality.
Between the triple constraints for SDLC model and the Agile Manifesto, which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
35
New cards
2-4 weeks
how long is a typical sprint?
36
New cards
less about a set way of doing things
Agile primary philosophy
37
New cards
SCRUM
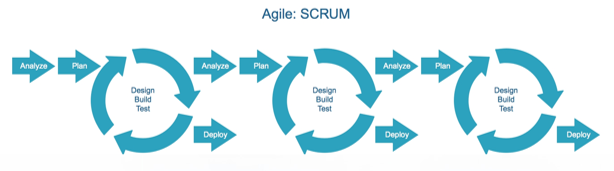
38
New cards
business value/impact
In an agile environment, which of the following is used to prioritize tasks?
39
New cards
Maintaining consistent standards, allowing shortcuts, and accelerator keys
Enhancing user productivity is the rationale for
40
New cards
false
Agile project teams are responsible for prioritizing which user stories will be completed in each sprint
41
New cards
noun phrases
How are data flow lines labeled?
42
New cards
true
A data flow diagram is referred to as an I-P-O model because every process inside of an information system requires data input and data output
43
New cards
card, conversation, confirmation
In relationship to user stories, what are the 3 Cs?
44
New cards
logical design
Functional, business related specifications of all system elements including how the system will look to the end user is developed in which stage of the SDLC?
45
New cards
User ID and passwords
What is the most common technique for managing user access to information systems?