chapter 6 cog
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
what is working memory?
memory system for storing and manipulating small amounts of information for a brief period of time
understanding speech
requires storing and manipulating small amounts of information for a brief period of time
Calculations
require storing and manipulating small amounts of information for a brief period of time ( so like adding and multiplying as an example)
Manipulations
require storing and manipulating small amounts of information for a brief period of time (ex: like spelling a word backwards)
Following direction's
requires storing and manipulating small amounts of information for a brief period of time (ex: following directions for a recipe )
Solving problem's
requires storing and manipulating small amounts of information for a brief period of time (ex: like solving sudoku, scramble, word)
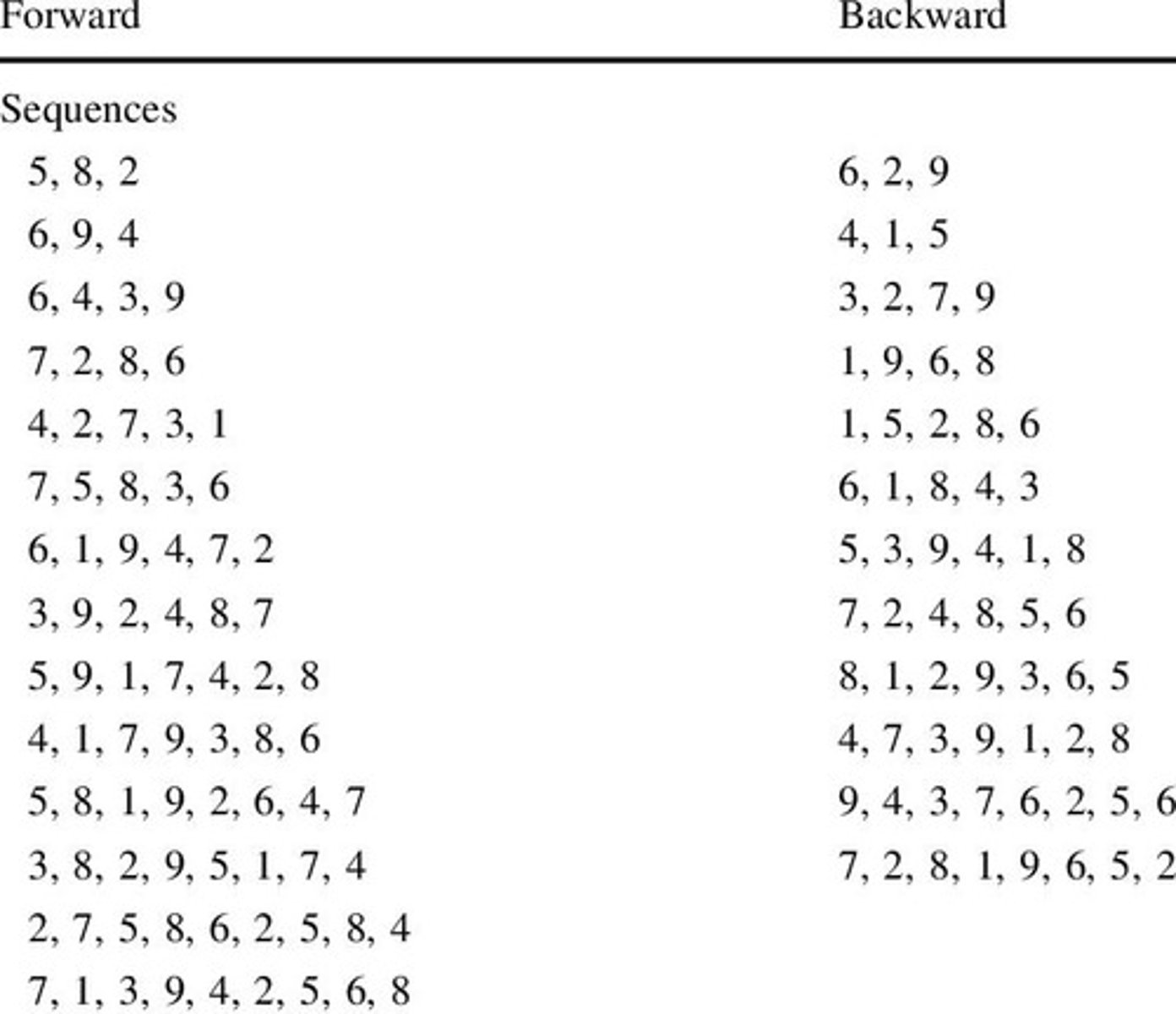
Digit span forward task
repeat a string of digits; the number of digits increases on each trial
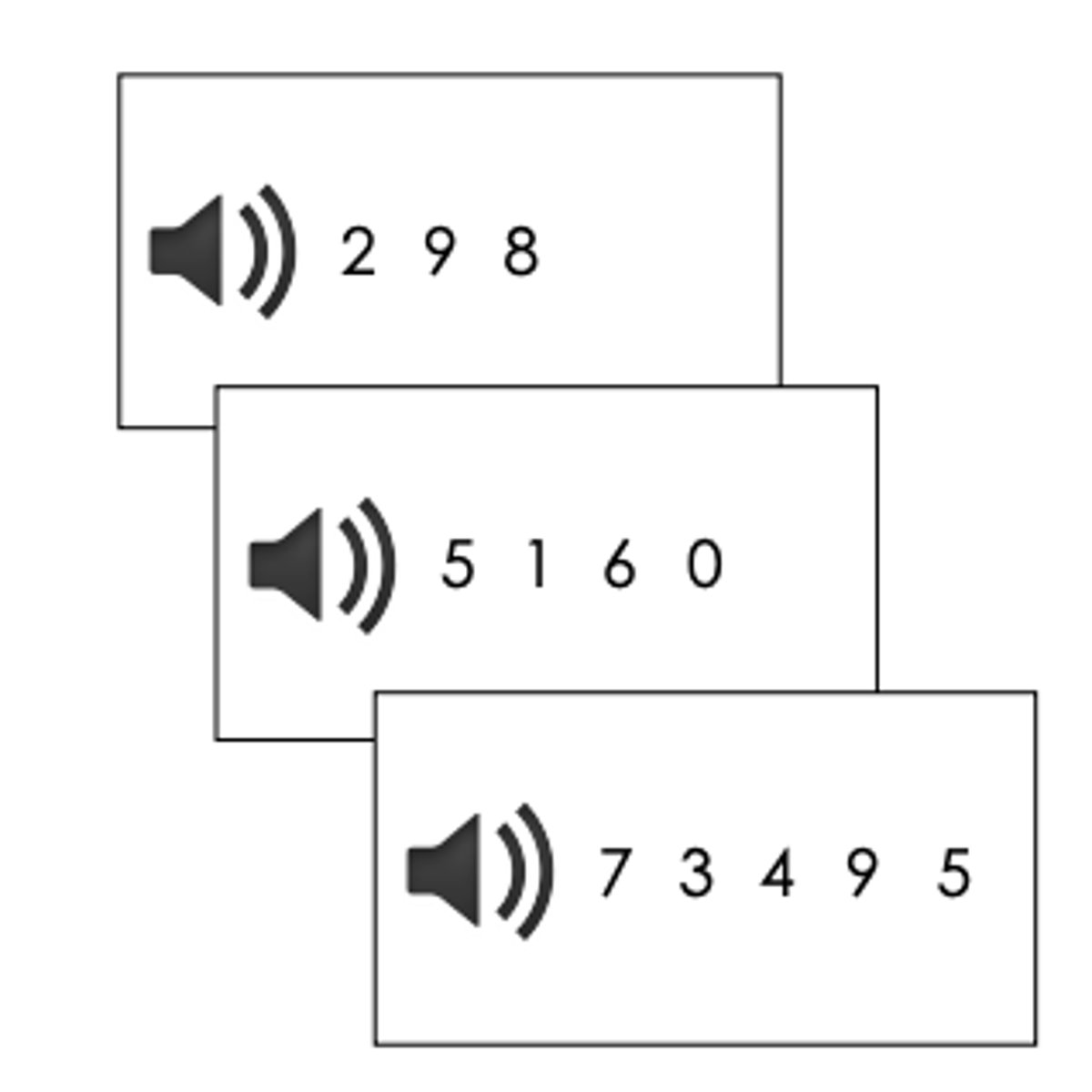
Digit span backward task
repeat a string of digits backward ; the number of digits increases on each trial
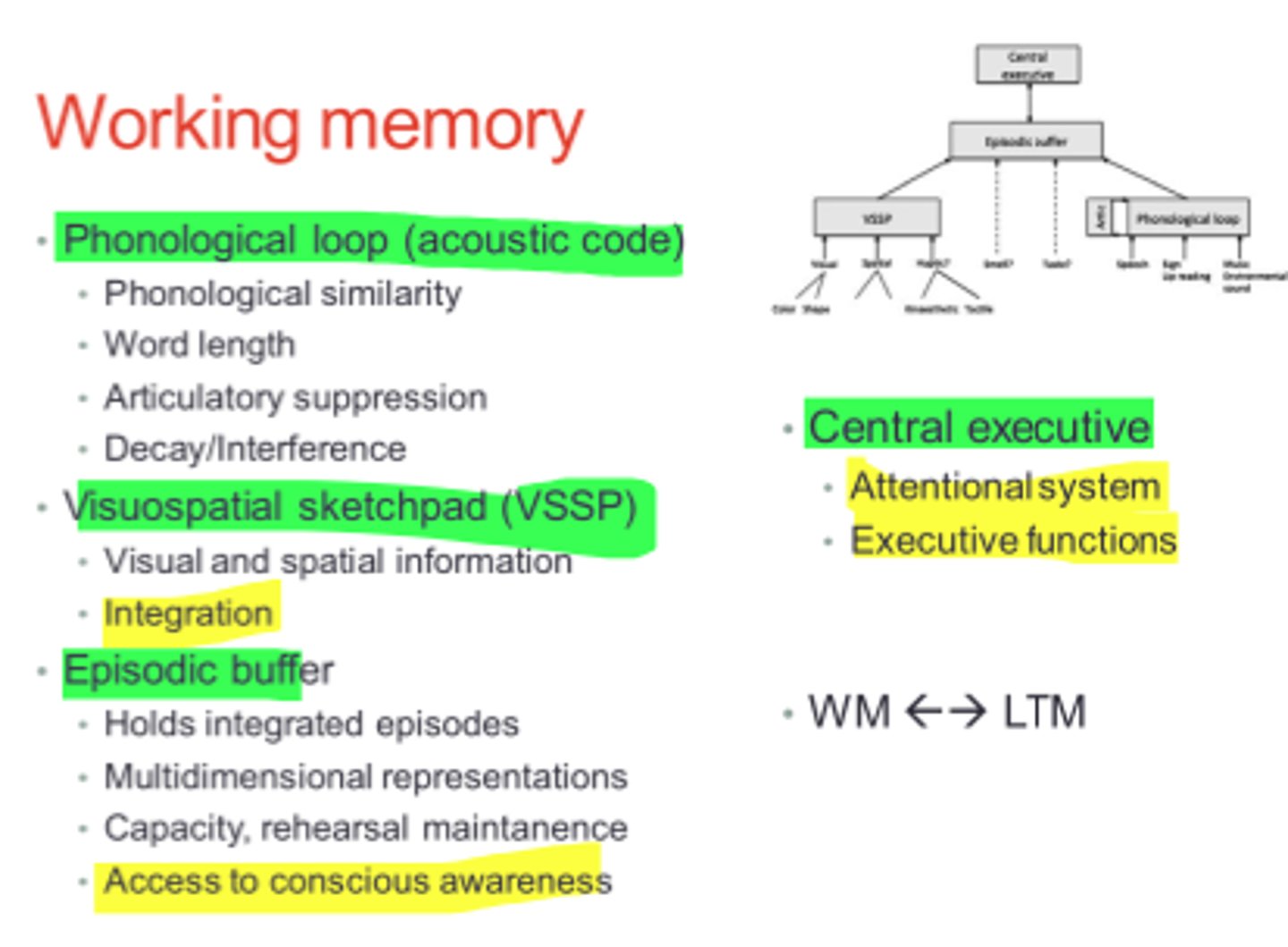
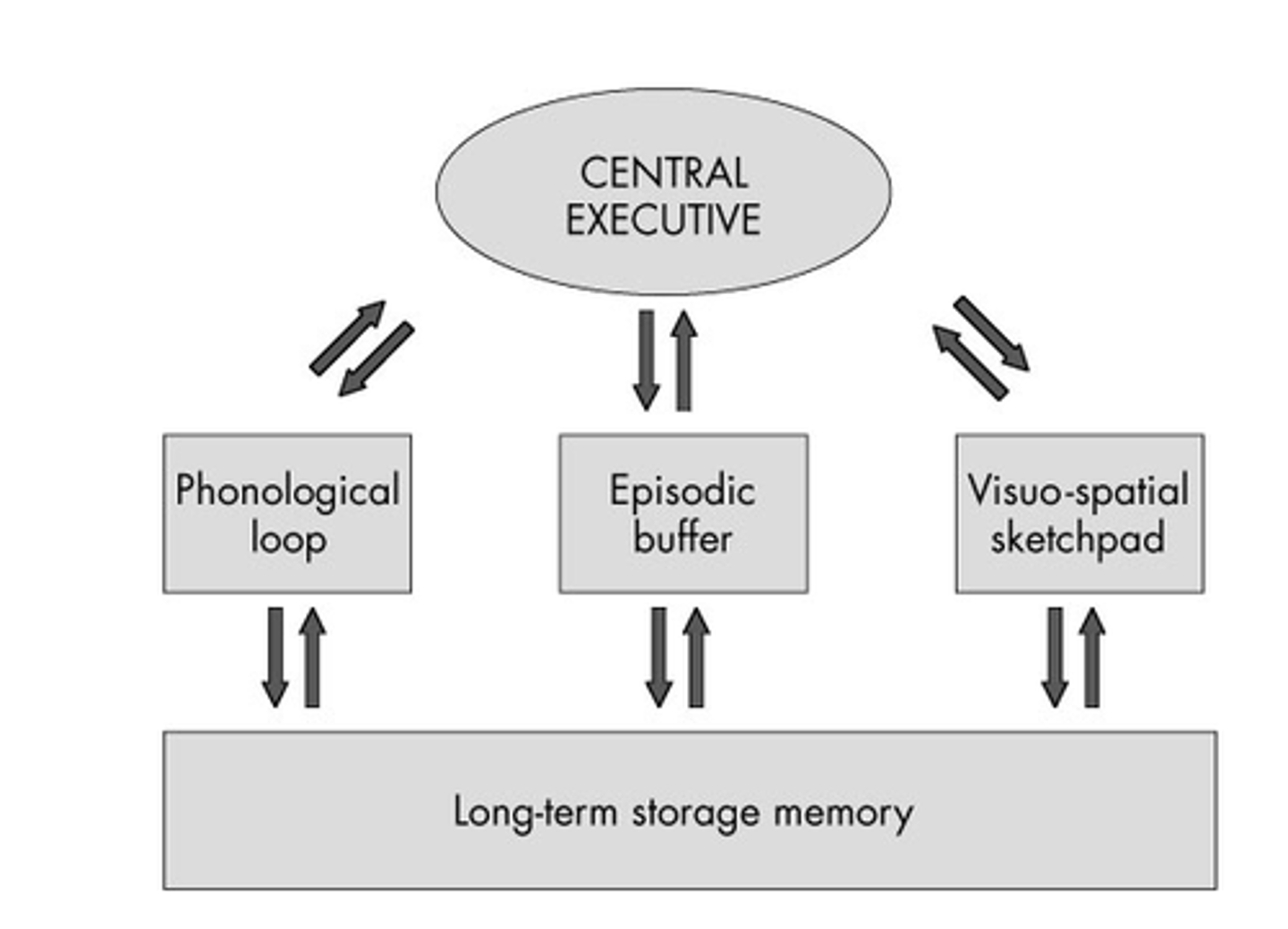
What are four components of Baddeley's working memory model?
the phonological loop, the visuospatial sketchpad, the central executive, and the episodic buffer
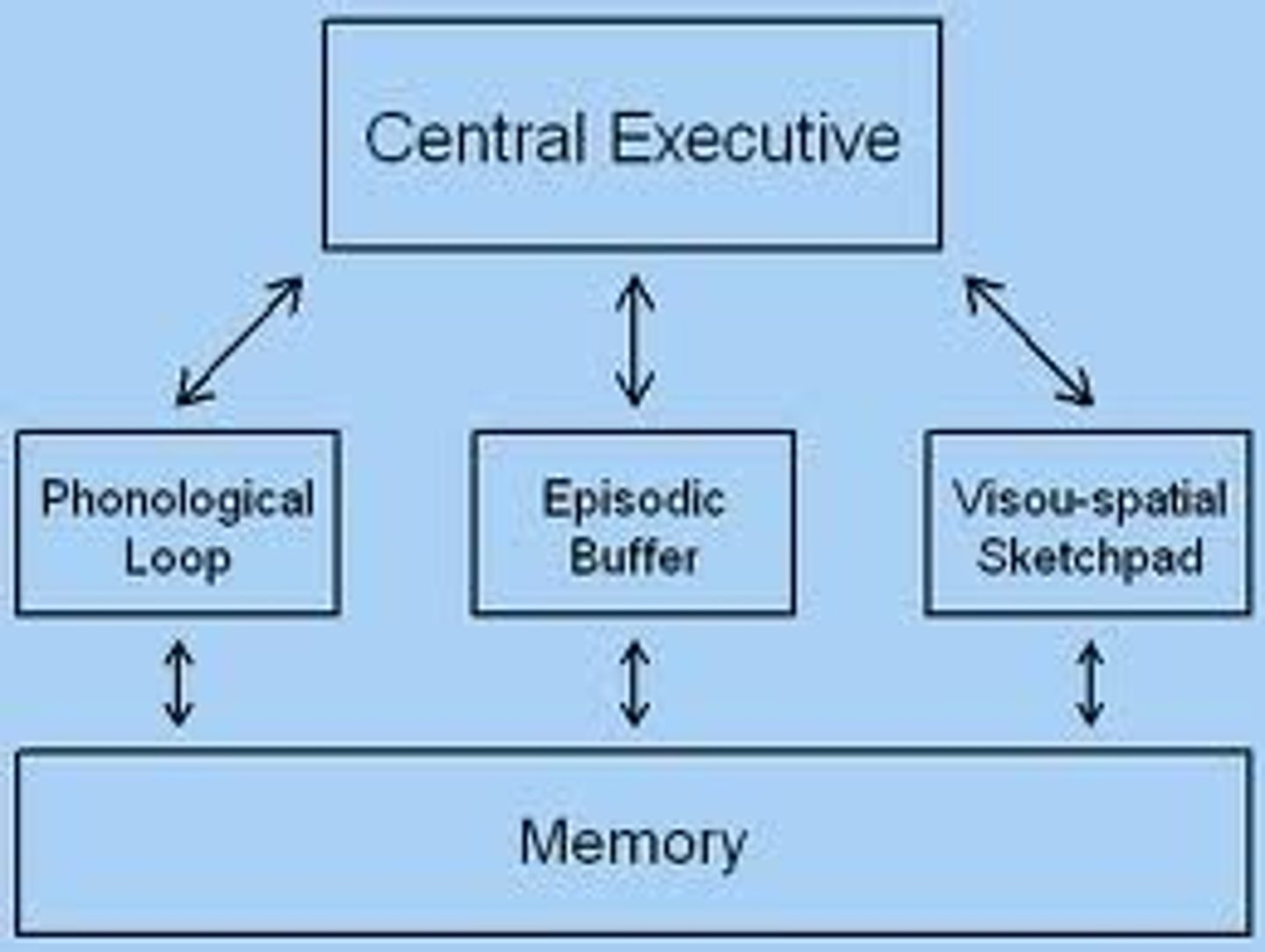
Phonological loop
holds verbal and auditory information (ex: following a phone conversation)
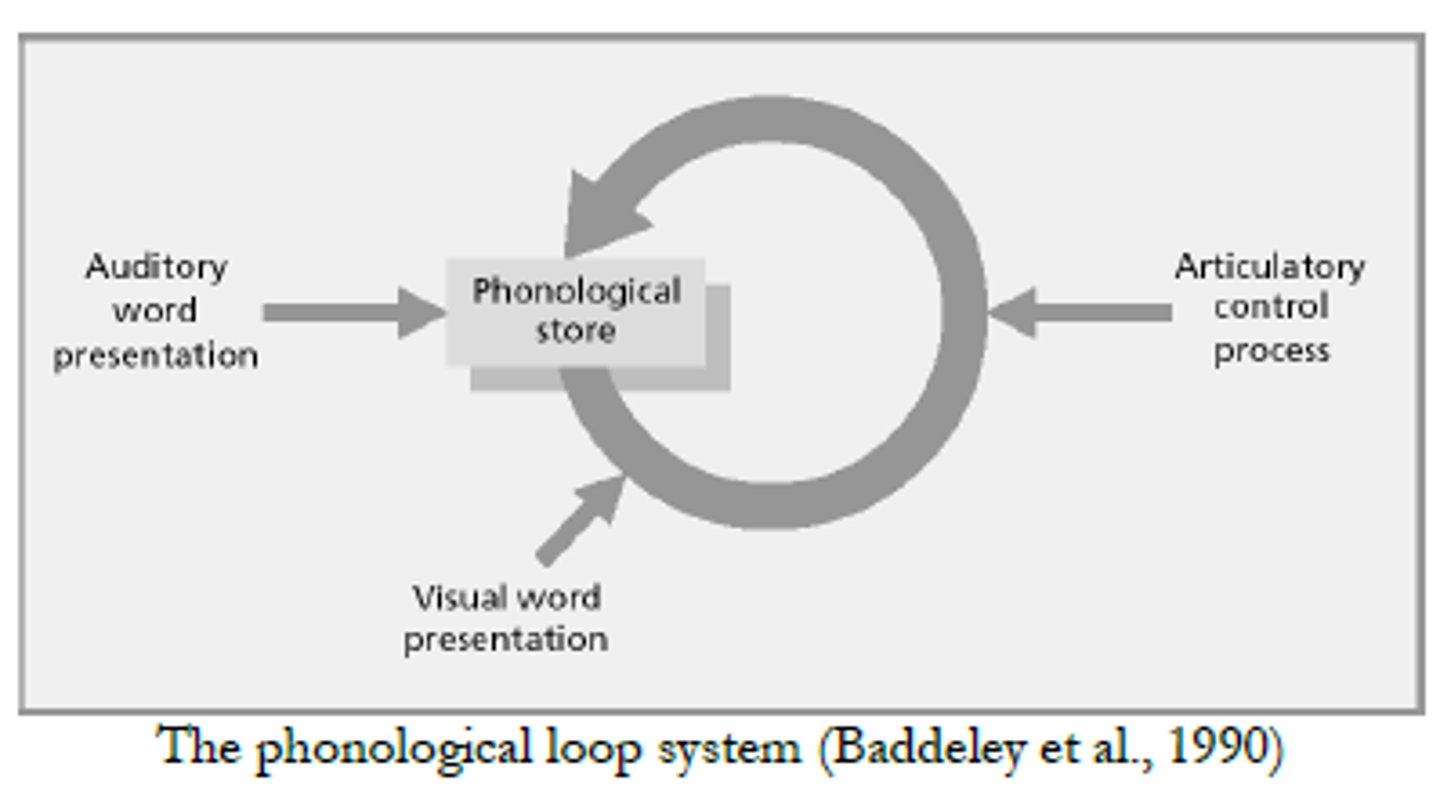
Phonological store:
holds a limited amount of verbal and auditory information for a few seconds

Phonological similarity effect:
letters or words that sound similar are confused

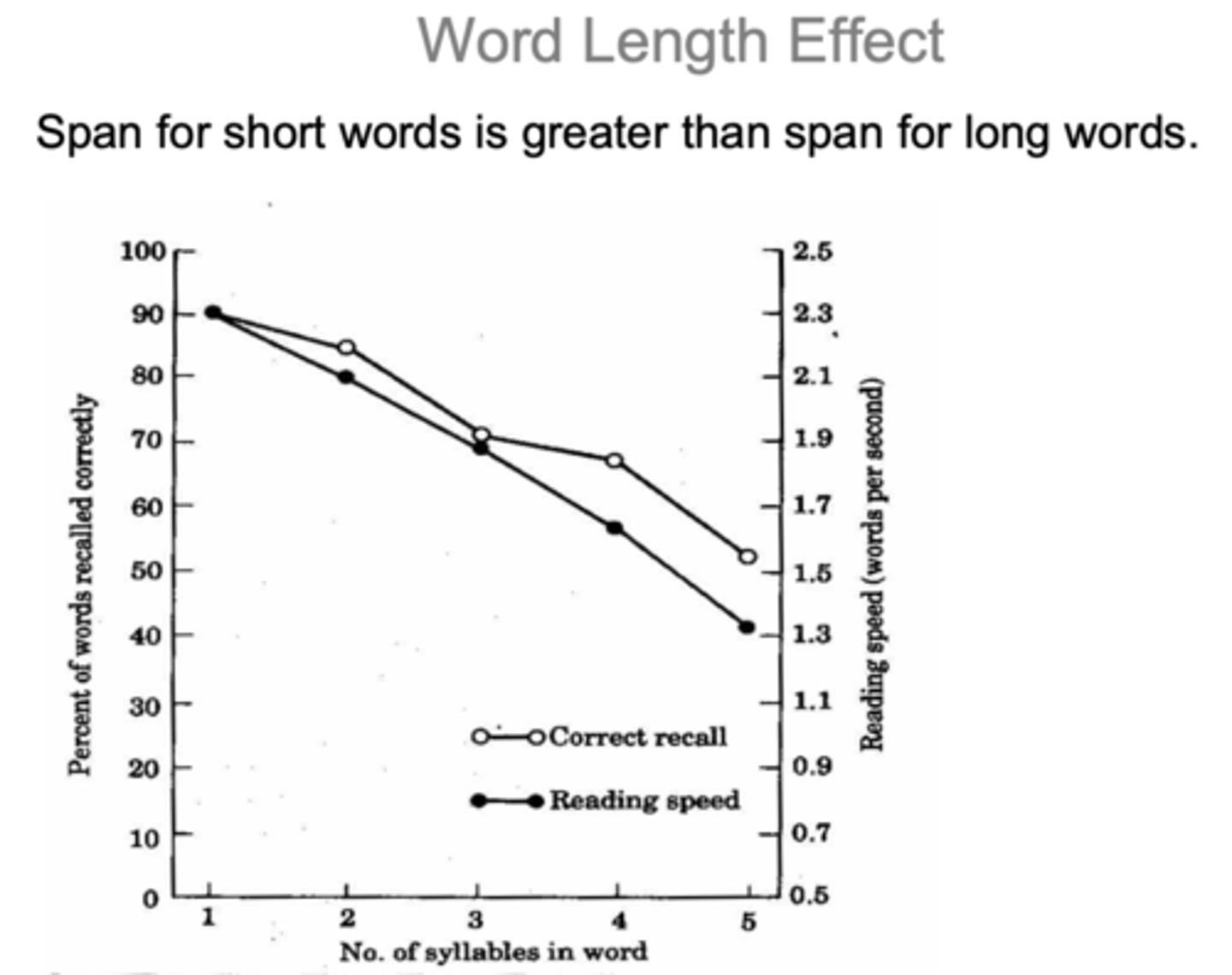
Word length effect
memory is better for shorter than for longer words
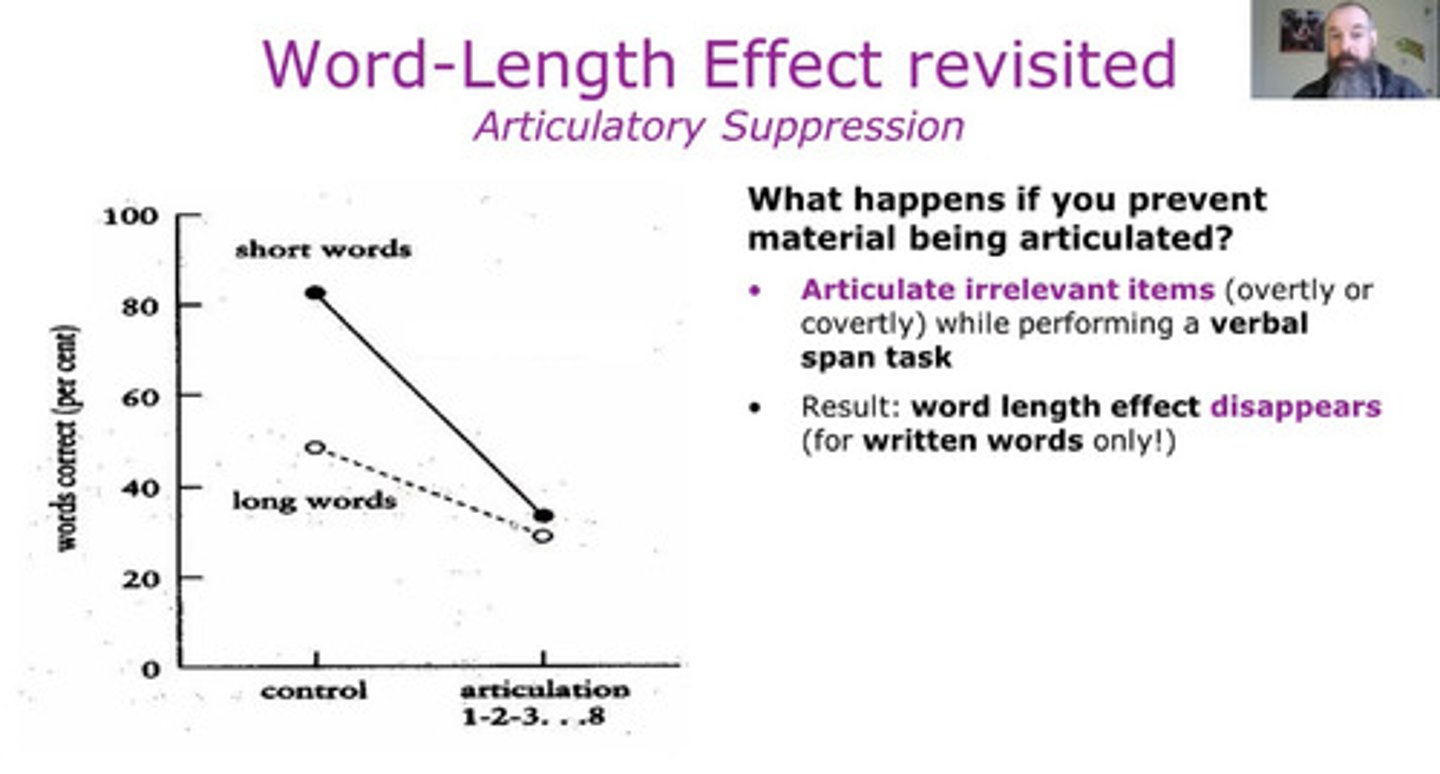
Articulatory suppression:
memory is worse when speaking interferes with rehearsal
Visuospatial sketch pad
holds visual and spatial information (ex: tracking cars, people, and roads; navigating the route )
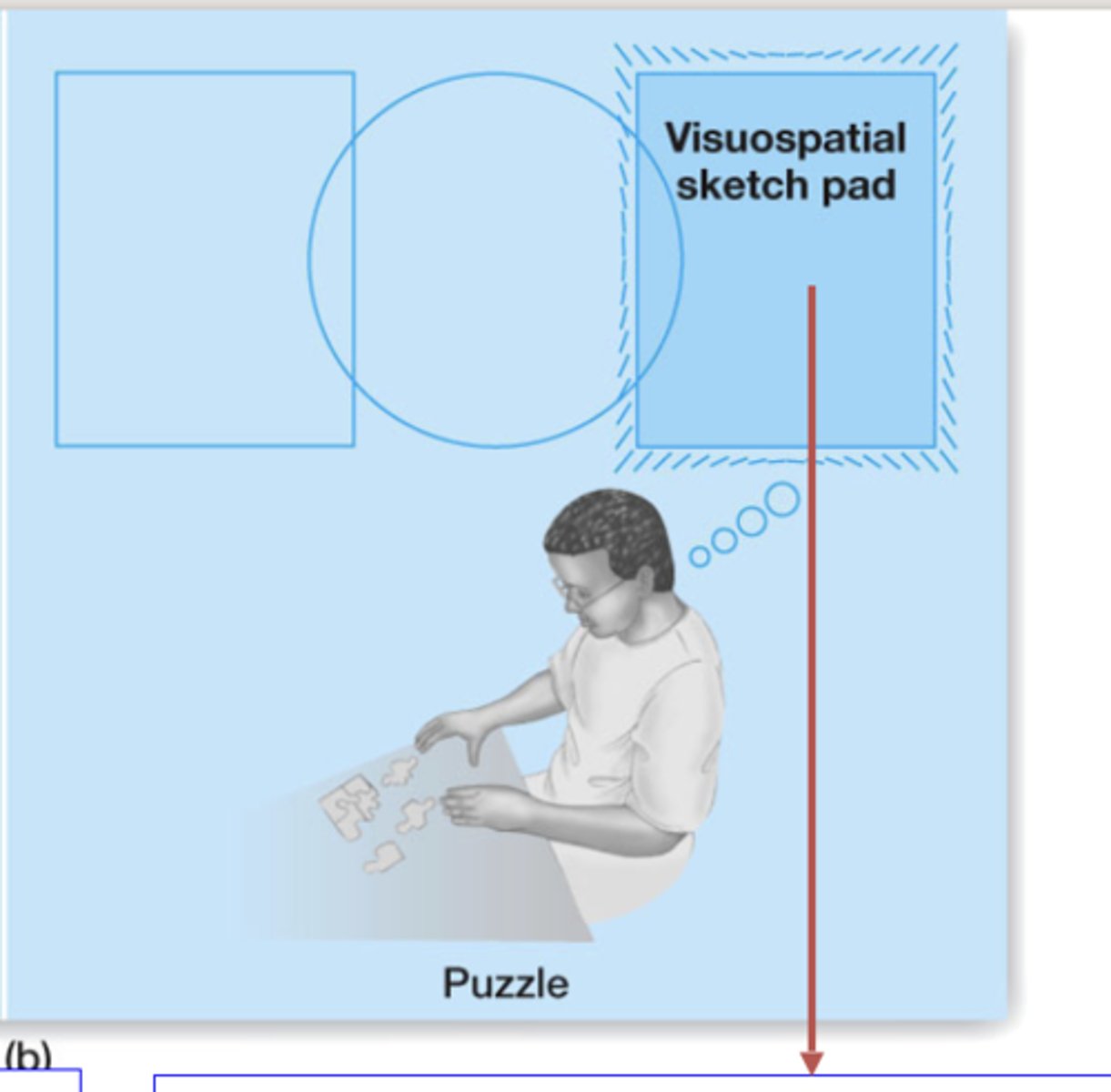
Visual imagery
creating visual images in the mind in the absence of visual input

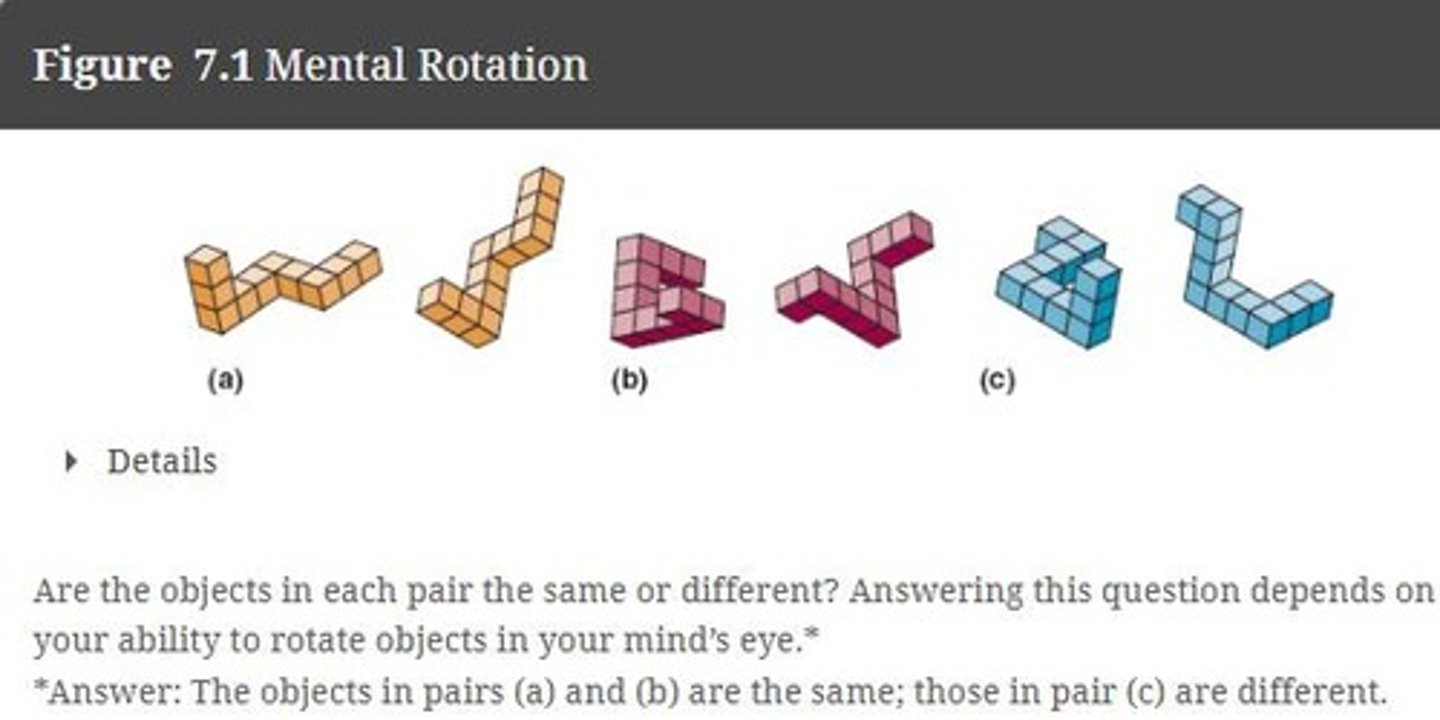
Mental rotation
rotating visual images in the mind
Central executive
coordinates the information in the phonological loop and visuospatial sketch pad to direct attention (ex: directing attention between the tasks)

Perseveration
repeatedly perform the same action or thought

Episodic buffer
integrates information across modalities (visual, verbal) to form units
- Not meaningful: explain not but successful a difficult the was to concept students to professor the tried
- Meaningful: the professor tried to explain a difficult concept to the students, but was not successful